Assessment of the Representativeness of MODIS Aerosol Optical Depth Products at Different Temporal Scales Using Global AERONET Measurements
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Polar orbiters acquire images at a fixed time of a day (for example, the local overpass times for MODIS Aqua and Terra are 1:30 pm and 10:30 am, respectively), but atmospheric aerosol loading and its associated properties could vary substantially over a very short time scale due to various emission sources, small scale meteorology effects as well as complex aerosol compositions and atmospheric processing [15,52]. Therefore, the satellite AOD retrievals and associated products may not well represent the daily aerosol conditions in theory. To address this issue, Kaufman [53] used AERONET observations to compare the daily means and mean values averaged over the MODIS Aqua/Terra time windows (i.e., synthetic MODIS data using AERONET), and they concluded that the AOD measurements at the satellite overpass time could represent daily AOD averages within an error level of 5%. While this former effort was conducted before the launch of the two MODIS instruments when real satellite data were not available, the results were only based on simulations with AERONET data. As such, the expected errors (i.e., 5%) could be different from the real satellite observations since the uncertainties in the satellite AOD retrieval algorithms were not considered. Additionally, data gaps may also exist in the AERONET AOD measurement within a day due to unfavorable weather conditions, instrument malfunctions, and many other factors [51]. However, the associated uncertainties to the daily mean AERONET AODs were not quantified [53].
- (2)
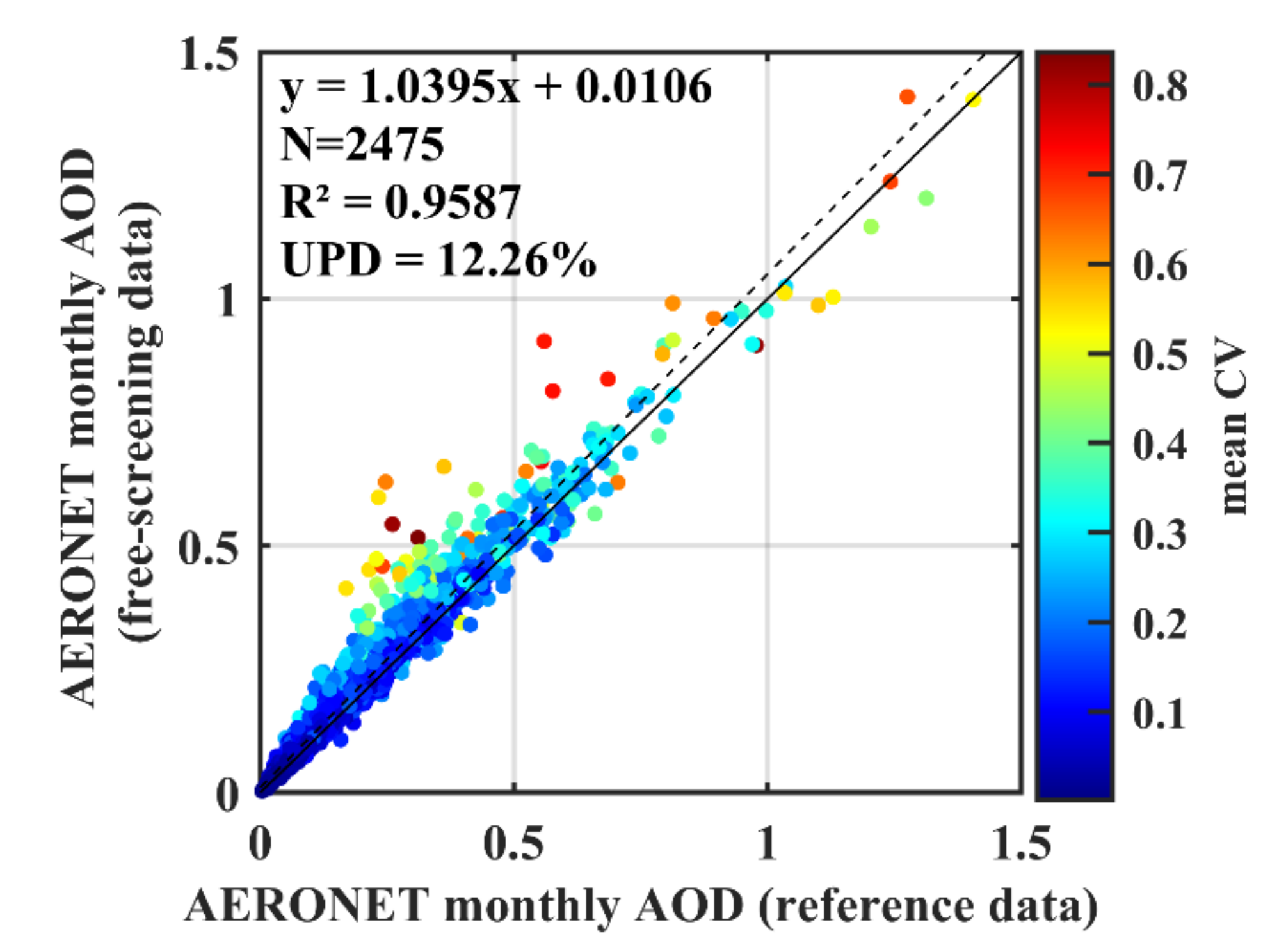
- Optical remote sensing suffers from cloud contamination, which results in a rather limited number of available high-quality data and remarkable observation gaps in the dataset. Indeed, a global cloud cover statistic using MODIS cloud mask products revealed that the global mean cloud coverage was 67% [54] and could vary substantially over different seasons and locations, which could significantly reduce the number of valid AOD retrievals. Moreover, this problem could be further exacerbated due to the associated issues of sub-pixel clouds, thin clouds, and their adjacency effects [55] as well as biases in retrievals [50]. Additionally, high AODs (e.g., smoke plumes, dust storms, biomass burning days) scenarios are often misinterpreted as clouds, where the signals tend to be saturated, leading to upper limitation of satellite retrievals [56,57]. This kind of misclassification could not only decrease the frequency of valid instantaneous remote sensed retrievals, especially for large values, but also further underestimate long-term satellite composites. That is, often only a few days of daily satellite AOD images with relatively lower observations were used to compose monthly (or other temporal binning) products. It remains unclear whether and to what extent these composed monthly, seasonal, or annual aerosol products could represent actual global or regional levels of aerosol concentrations. Although a recent attempt by Fan et al. (2018) was performed to examine whether the AOD trends of 53 sites detected by monthly AERONET observations could be reproduced through MODIS AOD data, the fundamental question of how satellite observation gaps could impact the reliability of monthly satellite products has never been analyzed. Similarly, Yoon et al. (2011) realized the uncertainty caused by data gaps and discarded monthly AOD data when less than five observations per month were available. However, how the uncertainties could be impacted by the changing numbers of valid data within a month has never been investigated.
- (1)
- Quantify the uncertainty levels of satellite AOD products in various temporal domains based on global long-term concurrent measurements between the MODIS and AERONET observations; and
- (2)
- Understand the potential factors that could affect the temporal representativeness of the satellite AOD products, and discuss the future efforts that could be used to improve the validity of AOD temporal binning products and their derived long-term trends.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. MODIS AOD Data
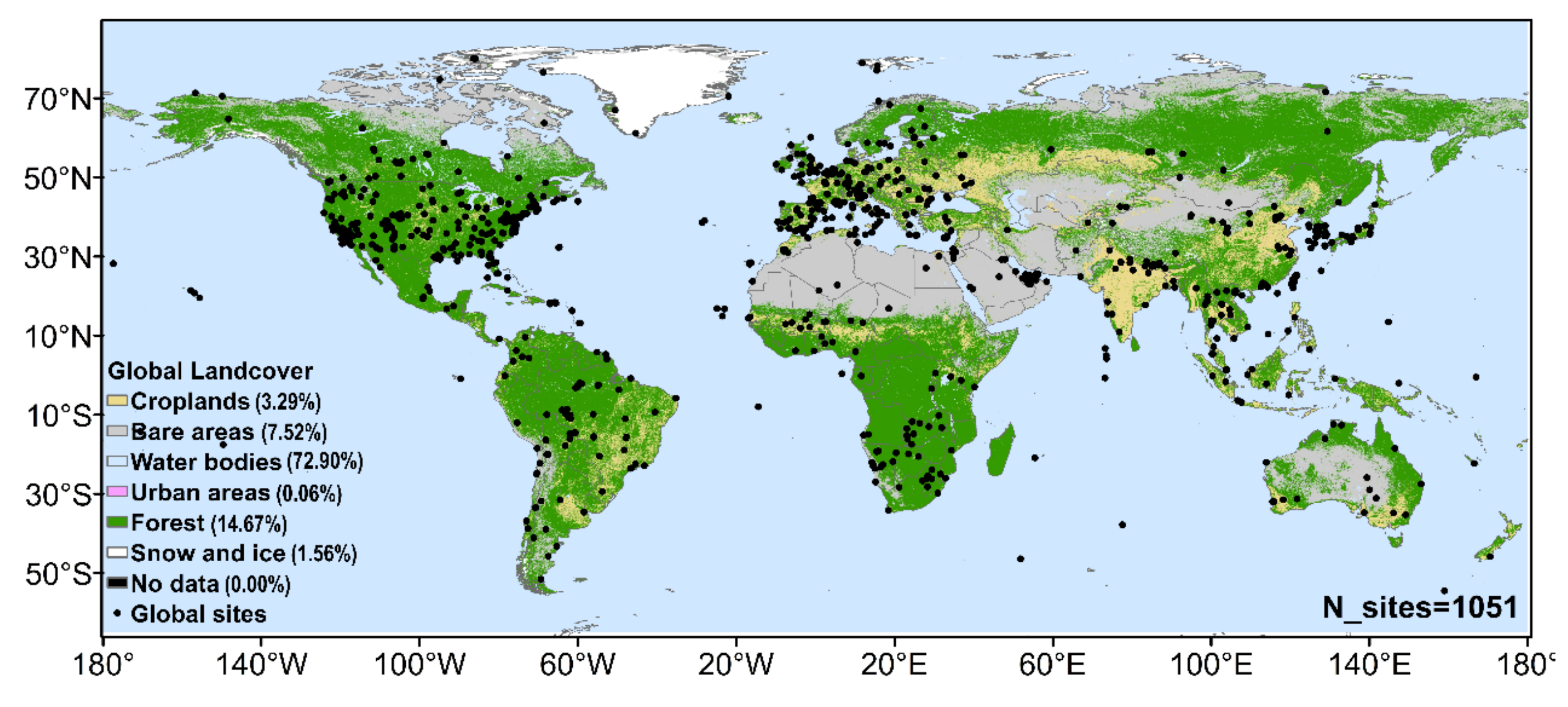
2.2. AERONET AOD Data
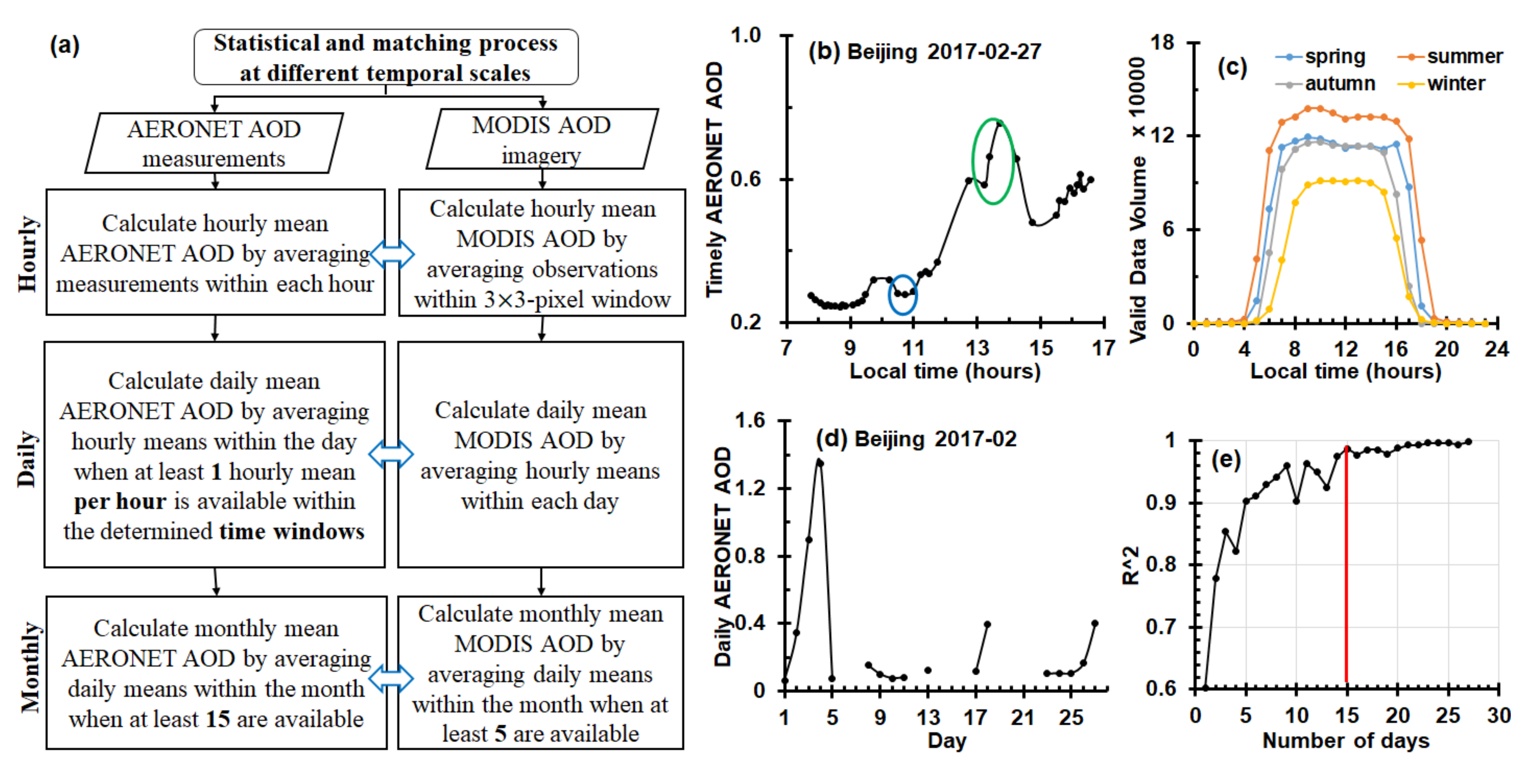
2.3. Determination of the Satellite and AERONET Match-Ups
2.4. Statistical Measures for the Representativeness Analysis
3. Results
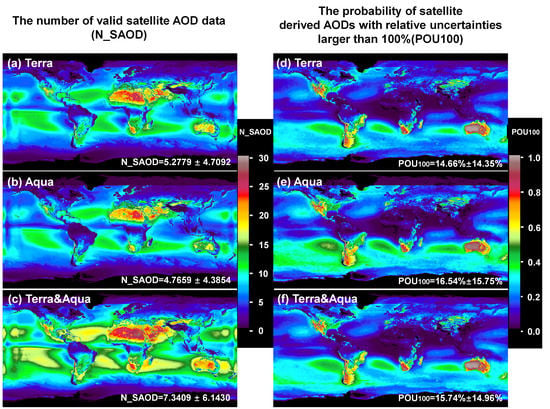
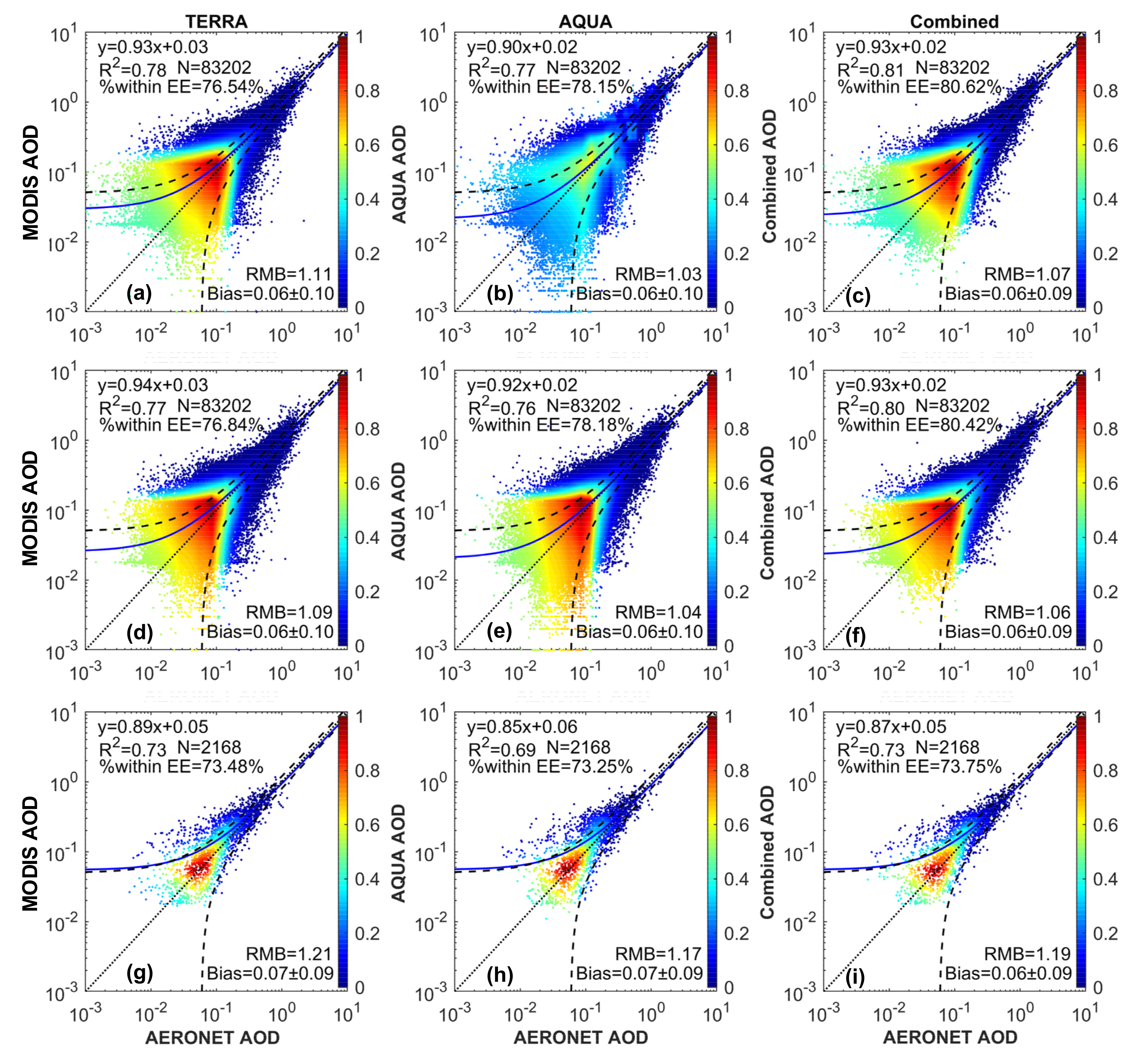
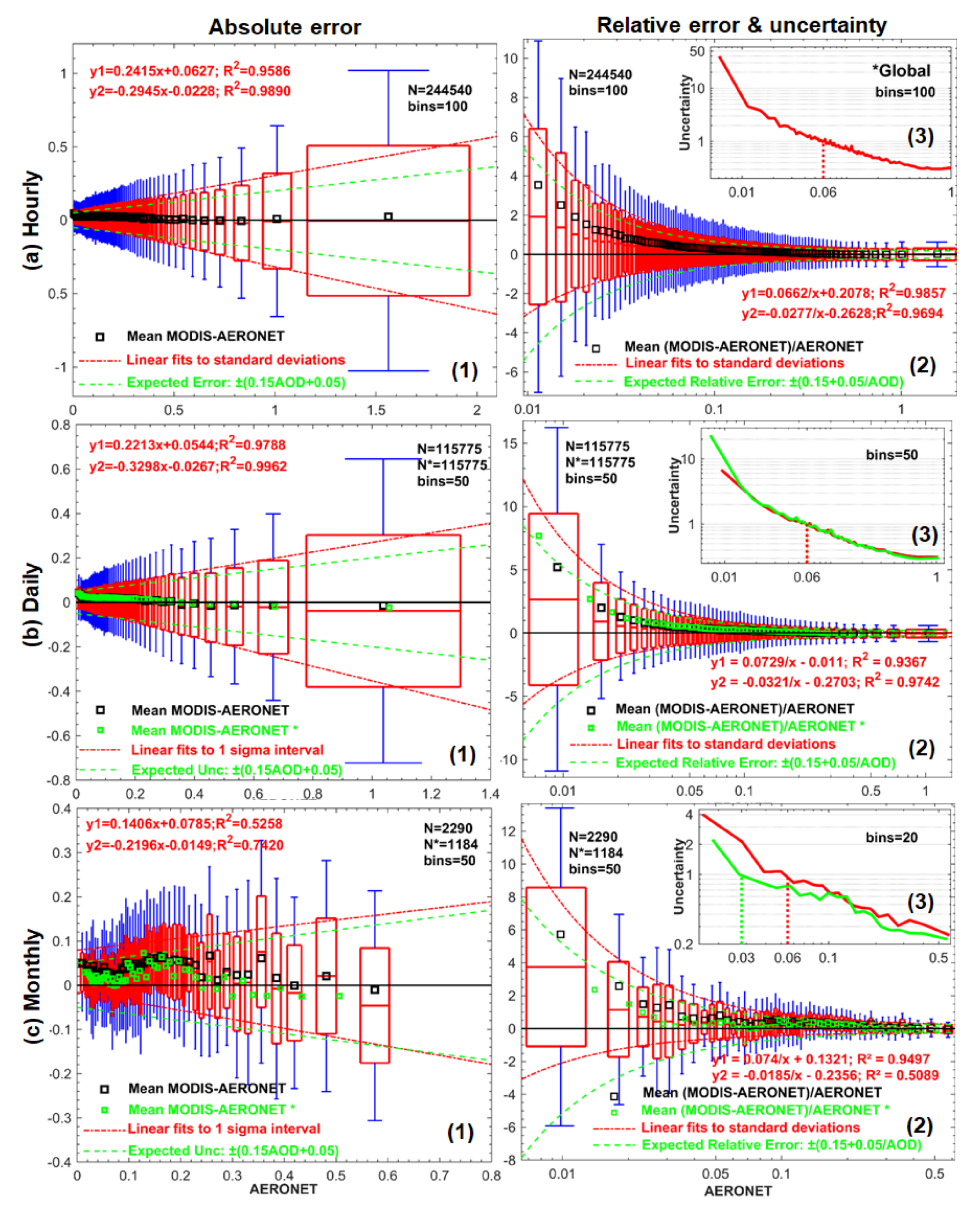
3.1. Overall Global Statistics
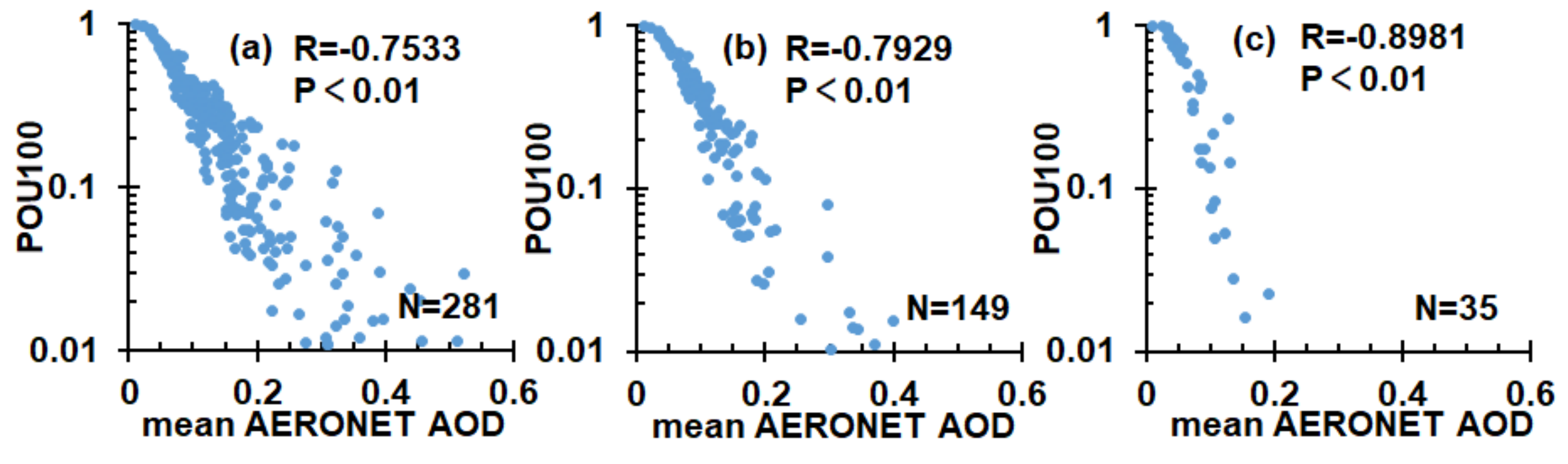
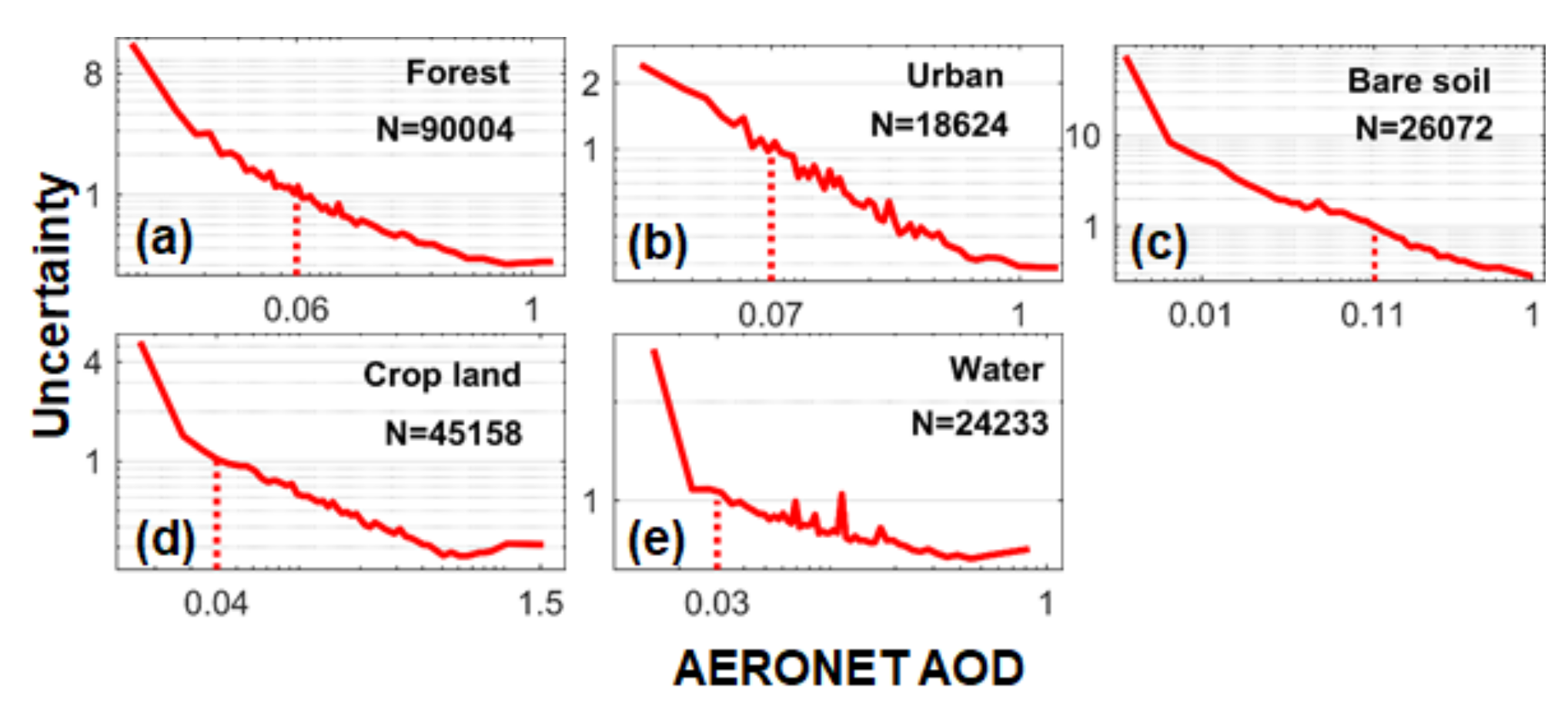
3.2. Site-Specific Assessments
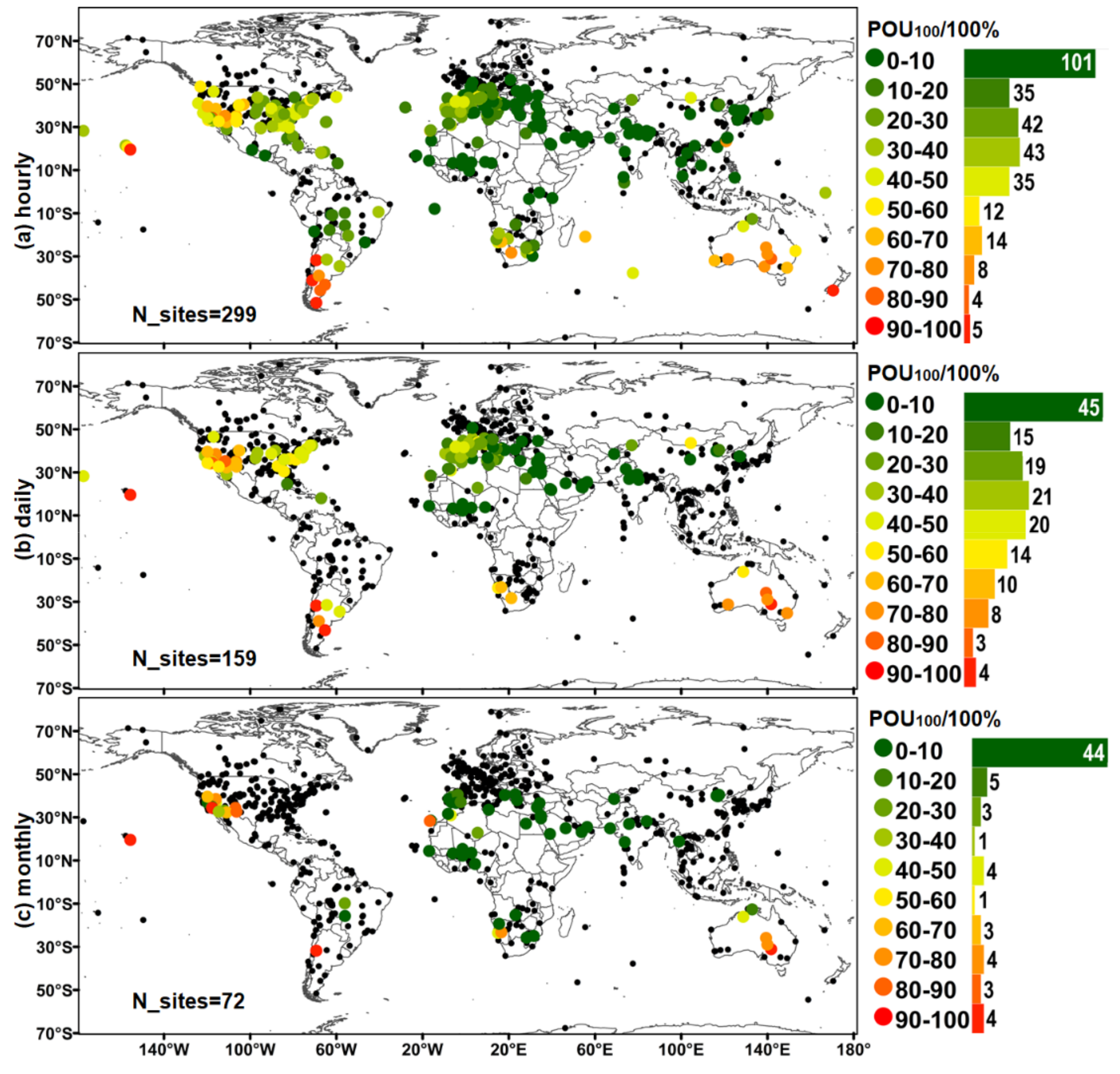
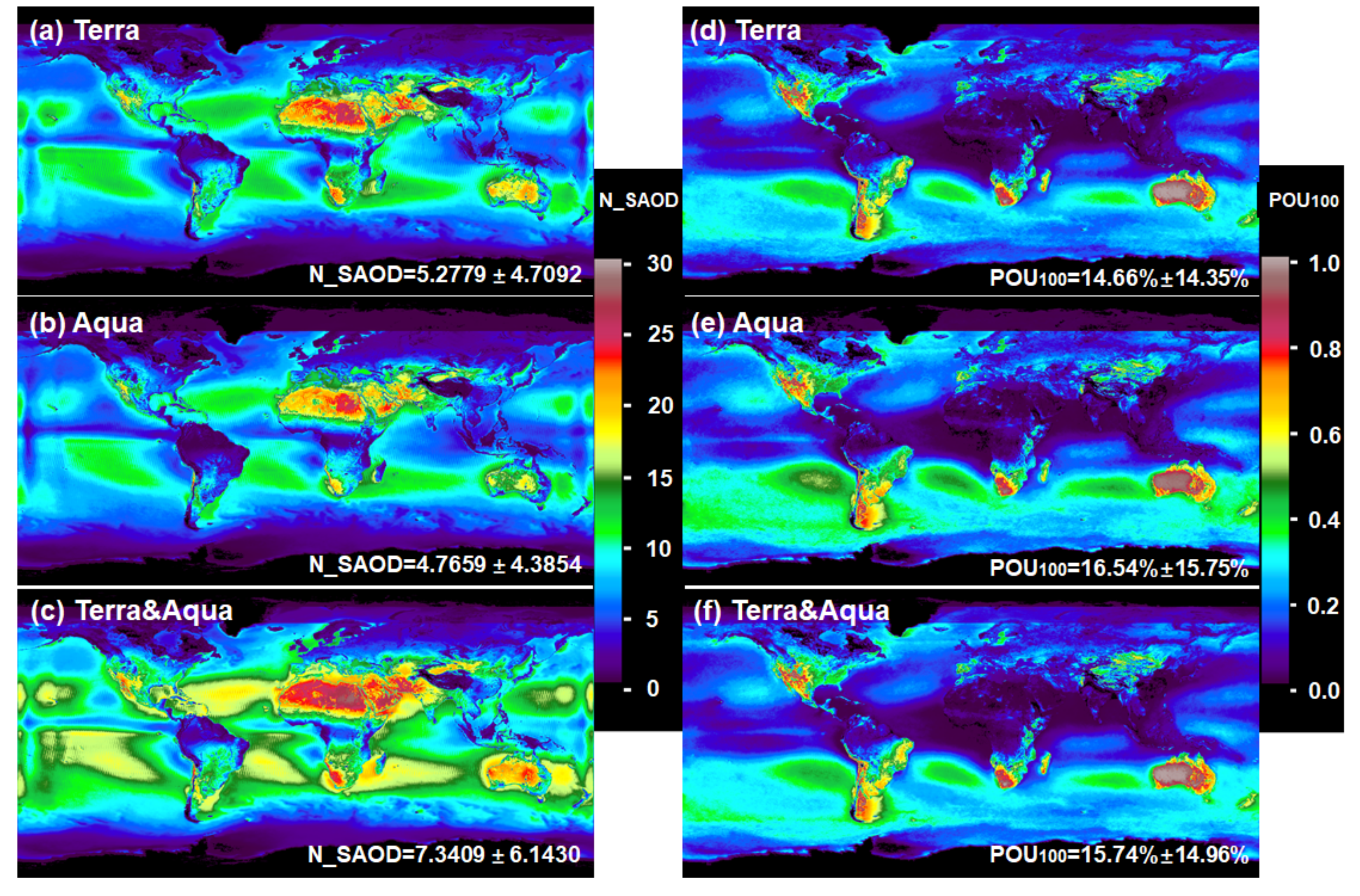
3.3. Global Distributions of the POU100
4. Discussion
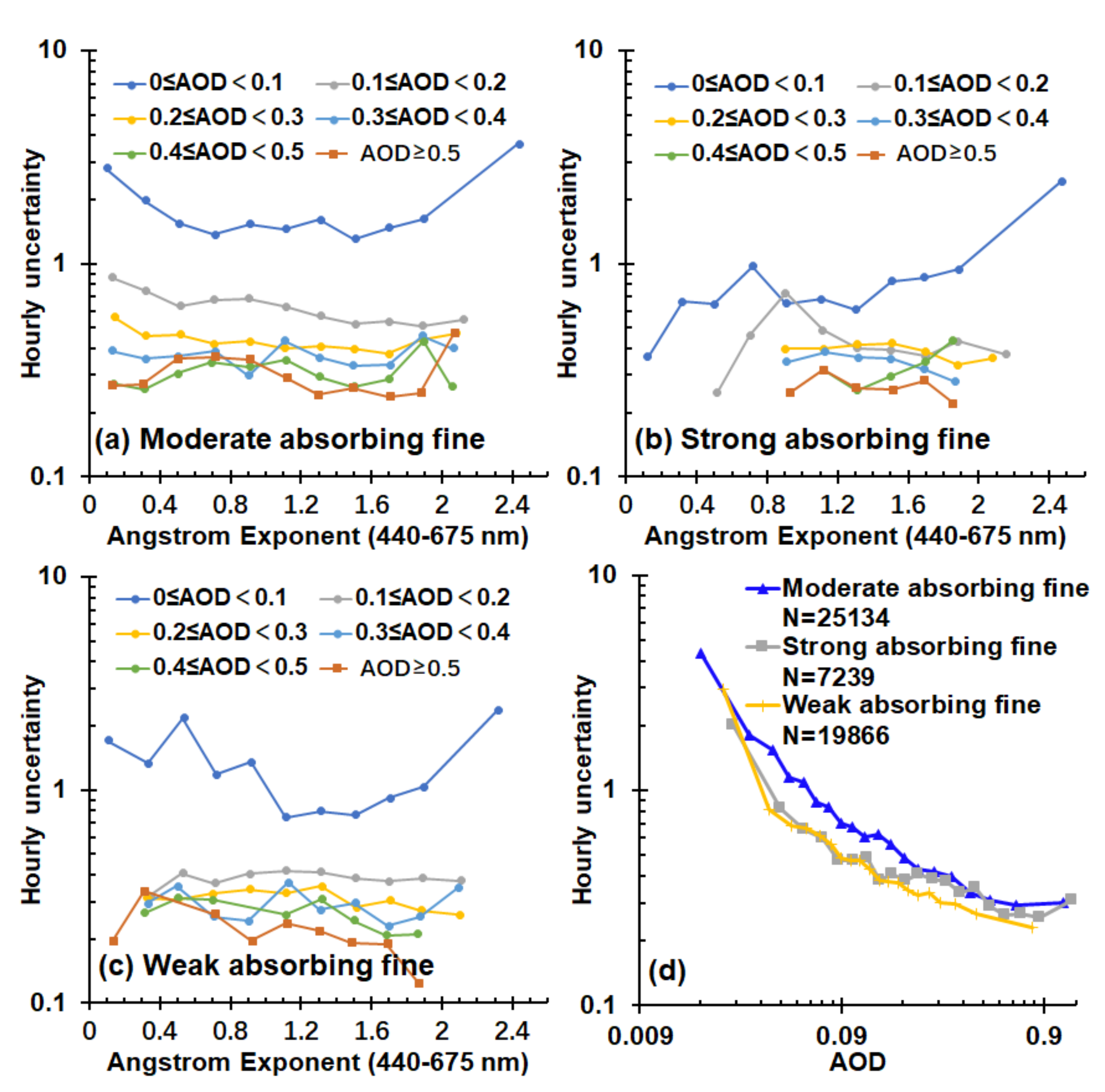
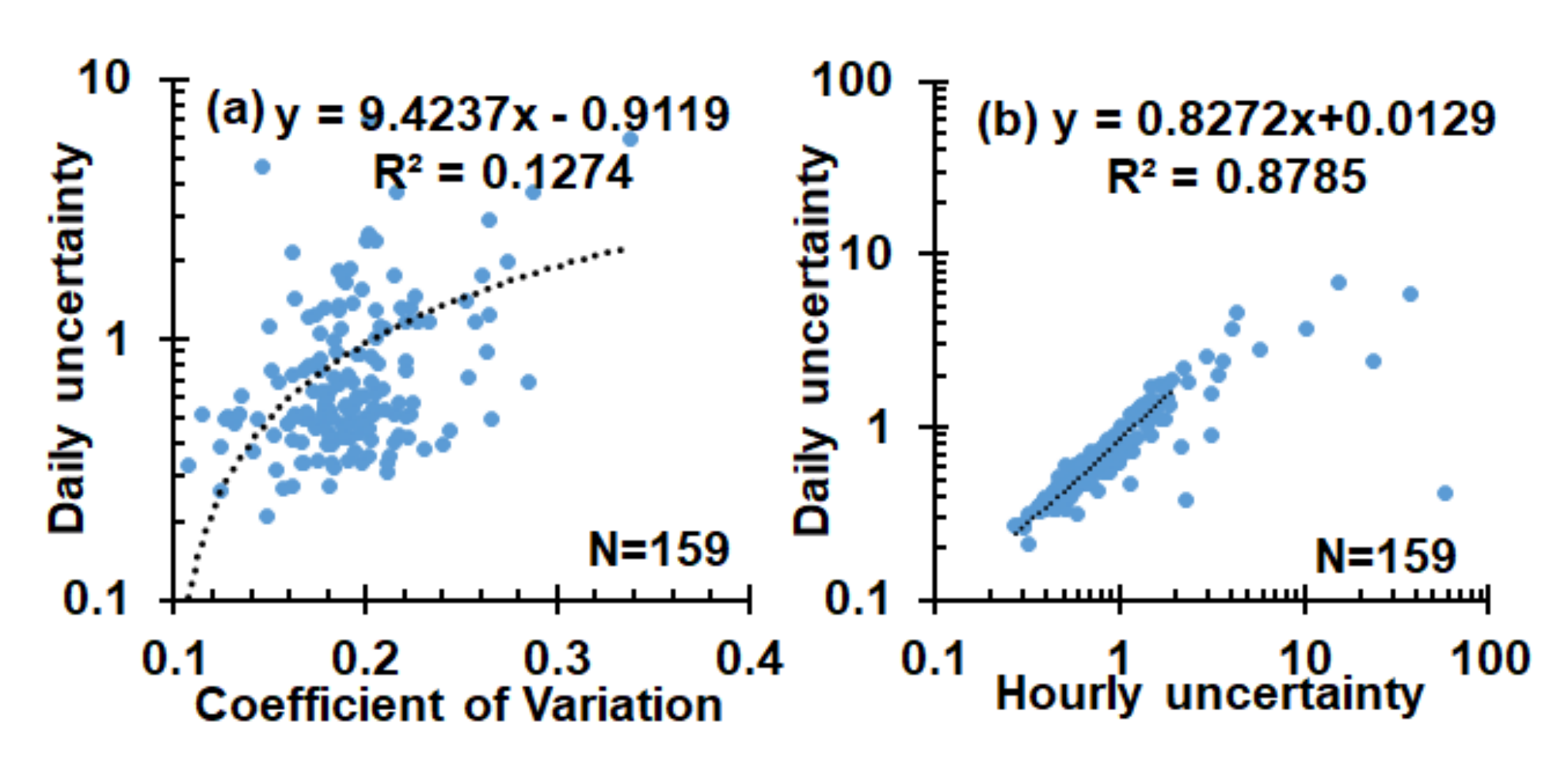
4.1. Factors Influencing the Representativeness of Satellite AOD Products
4.2. Implications and Future Efforts
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Notations
| AERONET | Aerosol Robotic Network |
| MODIS | Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer |
| AOD | Aerosol optical depth |
| PHOTONS | PHOtométrie pour le Traitement Opérationnel de Normalisation Satellitaire |
| DB | Deep Blue |
| DT | Dark Target |
| AVHRR | Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer |
| TOMS | Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer |
| SeaWiFS | Sea-Viewing Wide Field-of-View Sensor |
| MISR | Multiangle Imaging Spectroradiometer |
| VIIRS | Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite |
| GOCI | Geostationary Ocean Color Imager |
| NASA | U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration |
| GSFC | Goddard Space Flight Center |
| NDVI | Normalized Difference Vegetation Index |
| α | Angström exponent |
| N_SAOD | Number of valid satellite AOD data |
| RMB | relative mean bias |
| EE | error envelope |
| POU100 | Probabilities of satellite-derived AODs with uncertainties larger than 100% |
References
- Charlson, R.J. Climate forcing by anthropogenic aerosols. Science 1992, 255, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IPCC. Climate Change and Land: An IPCC Special Report on Climate Change, Desertification, Land Degradation, Sustainable land Management, Food Security, and Greenhouse Gas Fluxes in Terrestrial Ecosystems. Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bellouin, N.; Quaas, J.; Gryspeerdt, E.; Kinne, S.; Stier, P.; Watson-Parris, D.; Boucher, O.; Carslaw, K.S.; Christensen, M.; Daniau, A.L.; et al. Bounding Global Aerosol Radiative Forcing of Climate Change. Rev. Geophys. 2020, 58, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carslaw, K.S.; Lee, L.A.; Reddington, C.L.; Pringle, K.J.; Rap, A.; Forster, P.M.; Mann, G.W.; Spracklen, D.V.; Woodhouse, M.T.; Regayre, L.A.; et al. Large contribution of natural aerosols to uncertainty in indirect forcing. Nature 2013, 503, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Carlson, B.E.; Dubovik, O.; Lacis, A.A. Recent trends in aerosol optical properties derived from AERONET measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 12271–12289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, X.; Kahn, R.; Mishchenko, M.; Remer, L.; Lee, K.H.; Wang, M.; Laszlo, I.; Nakajima, T.; Maring, H. Uncertainties in satellite remote sensing of aerosols and impact on monitoring its long-term trend: A review and perspective. Ann. Geophys. 2009, 27, 2755–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; von Hoyningen-Huene, W.; Kokhanovsky, A.A.; Vountas, M.; Burrows, J.P. Trend analysis of aerosol optical thickness and Angstrom exponent derived from the global AERONET spectral observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 1271–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boys, B.L.; Martin, R.V.; van Donkelaar, A.; MacDonell, R.J.; Hsu, N.C.; Cooper, M.J.; Yantosca, R.M.; Lu, Z.; Streets, D.G.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Fifteen-Year Global Time Series of Satellite-Derived Fine Particulate Matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 11109–11118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Si, M.L.; Li, W.F.; Wu, J.S. A multidimensional comparison between MODIS and VIIRS AOD in estimating ground-level PM2.5 concentrations over a heavily polluted region in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McComiskey, A.; Schwartz, S.E.; Schmid, B.; Guan, H.; Lewis, E.R.; Ricchiazzi, P.; Ogren, J.A. Direct aerosol forcing: Calculation from observables and sensitivities to inputs. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persad, G.G.; Caldeira, K. Divergent global-scale temperature effects from identical aerosols emitted in different regions. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddington, C.L.; Butt, E.W.; Ridley, D.A.; Artaxo, P.; Morgan, W.T.; Coe, H.; Spracklen, D.V. Air quality and human health improvements from reductions in deforestation-related fire in Brazil. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanre, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T.; et al. AERONET—A federated instrument network and data archive for aerosol characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Reid, J.S.; Dubovik, O.; Smirnov, A.; O’Neill, N.T.; Slutsker, I.; Kinne, S. Wavelength dependence of the optical depth of biomass burning, urban, and desert dust aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 31333–31349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Peng, Y.R.; Mahmood, R.; Sun, L.; Guo, J.P. Intercomparison in spatial distributions and temporal trends derived from multi-source satellite aerosol products. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 7183–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.L.; Chang, N.B.; Bai, K.X.; Gao, W. Satellite remote sensing of aerosol optical depth: Advances, challenges, and perspectives. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.C.; Jeong, M.J.; Bettenhausen, C.; Sayer, A.M.; Hansell, R.; Seftor, C.S.; Huang, J.; Tsay, S.C. Enhanced Deep Blue aerosol retrieval algorithm: The second generation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 9296–9315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A.; Sayer, A.M.; Patadia, F.; Hsu, N.C. The Collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Korkin, S.; Huang, D. MODIS Collection 6 MAIAC algorithm. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 5741–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popp, T.; De Leeuw, G.; Bingen, C.; Brühl, C.; Capelle, V.; Chedin, A.; Clarisse, L.; Dubovik, O.; Grainger, R.; Griesfeller, J.J.R.S. Development, production and evaluation of aerosol climate data records from European satellite observations (Aerosol_cci). Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Higurashi, A. A use of two-channel radiances for an aerosol characterization from space. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 3815–3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatov, A.; Sapper, J.; Cox, S.; Laszlo, I.; Nalli, N.R.; Kidwell, K.B. Operational aerosol observations (AEROBS) from AVHRR/3 on board NOAA-KLM satellites. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2004, 21, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishchenko, M.I.; Liu, L.; Geogdzhayev, I.V.; Li, J.; Carlson, B.E.; Lacis, A.A.; Cairns, B.; Travis, L.D. Aerosol retrievals from channel-1 and -2 AVHRR radiances: Long-term trends updated and revisited. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2012, 113, 1974–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Y.H.; Xue, Y.; Guang, J.; She, L.; Guo, J.P. Evaluation of the AVHRR DeepBlue aerosol optical depth dataset over mainland China. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 146, 74–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, O.; Bhartia, P.K.; Herman, J.R.; Sinyuk, A.; Ginoux, P.; Holben, B. A long-term record of aerosol optical depth from TOMS observations and comparison to AERONET measurements. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 398–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.C.; Tsay, S.C.; King, M.D.; Herman, J.R. Aerosol properties over bright-reflecting source regions. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.H.; Knobelspiesse, K.D.; McClain, C.R. Study of the Sea-Viewing Wide Field-of-View Sensor (SeaWiFS) aerosol optical property data over ocean in combination with the ocean color products. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, R.A.; Gaitley, B.J.; Martonchik, J.V.; Diner, D.J.; Crean, K.A.; Holben, B. Multiangle Imaging Spectroradiometer (MISR) global aerosol optical depth validation based on 2 years of coincident Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remer, L.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D.; Mattoo, S.; Chu, D.A.; Martins, J.V.; Li, R.R.; Ichoku, C.; Levy, R.C.; Kleidman, R.G.; et al. The MODIS Aerosol Algorithm, Products, and Validation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 62, 947–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Kleidman, R.G.; Mattoo, S.; Ichoku, C.; Kahn, R.; Eck, T.F. Global evaluation of the Collection 5 MODIS dark-target aerosol products over land. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 10399–10420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Nichol, J.E.; Bleiweiss, M.P.; Dubois, D. A Simplified high resolution MODIS Aerosol Retrieval Algorithm (SARA) for use over mixed surfaces. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 136, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.M.; Liu, H.Q.; Laszlo, I.; Kondragunta, S.; Remer, L.A.; Huang, J.F.; Huang, H.C. Suomi-NPP VIIRS aerosol algorithms and data products. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 12673–12689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Wu, J.S.; Li, W.F.; Peng, J. A spatially structured adaptive two-stage model for retrieving ground-level PM2.5 concentrations from VIIRS AOD in China. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 151, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Chen, X.L. Spatio-temporal distribution of localized aerosol loading in China: A satellite view. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 163, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Brauer, M.; Kahn, R.; Levy, R.; Verduzco, C.; Villeneuve, P.J. Global Estimates of Ambient Fine Particulate Matter Concentrations from Satellite-Based Aerosol Optical Depth: Development and Application. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Brauer, M.; Hsu, N.C.; Kahn, R.A.; Levy, R.C.; Lyapustin, A.; Sayer, A.M.; Winker, D.M. Global Estimates of Fine Particulate Matter using a Combined Geophysical-Statistical Method with Information from Satellites, Models, and Monitors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3762–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myhre, G. Consistency Between Satellite-Derived and Modeled Estimates of the Direct Aerosol Effect. Science 2009, 325, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercado, L.M.; Bellouin, N.; Sitch, S.; Boucher, O.; Huntingford, C.; Wild, M.; Cox, P.M. Impact of changes in diffuse radiation on the global land carbon sink. Nature 2009, 458, U1014–U1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalsky, J.J.; Anderson, G.P.; Barnard, J.; Delamere, J.; Gueymard, C.; Kato, S.; Kiedron, P.; McComiskey, A.; Ricchiazzi, P. Shortwave radiative closure studies for clear skies during the atmospheric radiation measurement 2003 aerosol intensive observation period. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Lyu, R.; Xie, X.; Meng, Z.; Huang, M.J.; Wu, J.S.; Mu, H.Z.; Yu, Q.R.; He, Q.S.; Cheng, T.T. Retrieval of Gridded Aerosol Direct Radiative Forcing Based on Multiplatform Datasets. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 575–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Dubovik, O. Global aerosol optical properties and application to Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer aerosol retrieval over land. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.Q.; Peng, Y.R.; Sun, L. MODIS Collection 6.1 aerosol optical depth products over land and ocean: Validation and comparison. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 201, 428–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.D.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanre, D.; Nakajima, T. Remote sensing of tropospheric aerosols from space: Past, present, and future. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 80, 2229–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Ichoku, C.; Remer, L.A.; Tanre, D.; Holben, B.N. Validation of MODIS aerosol optical depth retrieval over land. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, M.J.; Li, Z.Q. Quality, compatibility, and synergy analyses of global aerosol products derived from the advanced very high resolution radiometer and Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Remer, L.A.; Tanre, D.; Li, R.R.; Kleidman, R.; Mattoo, S.; Levy, R.C.; Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Ichoku, C.; et al. A critical examination of the residual cloud contamination and diurnal sampling effects on MODIS estimates of aerosol over ocean. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 2886–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, A.M.; Hsu, N.C.; Bettenhausen, C.; Jeong, M.J.; Holben, B.N.; Zhang, J. Global and regional evaluation of over-land spectral aerosol optical depth retrievals from SeaWiFS. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 1761–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Q.; Niu, F.; Lee, K.H.; Xin, J.Y.; Hao, W.M.; Nordgren, B.; Wang, Y.S.; Wang, P.C. Validation and understanding of moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer aerosol products (C5) using ground-based measurements from the handheld Sun photometer network in China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remer, L.A.; Mattoo, S.; Levy, R.C.; Munchak, L.A. MODIS 3 km aerosol product: Algorithm and global perspective. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, H.; Alam, K.; Chishtie, F.; Bibi, S.; Shahid, I.; Blaschke, T. Intercomparison of MOD’S, MISR, OMI, and CALIPSO aerosol optical depth retrievals for four locations on the Indo-Gangetic plains and validation against AERONET data. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 111, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Remer, L.A.; Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S. Validation of MODIS 3 km land aerosol optical depth from NASA’s EOS Terra and Aqua missions. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 3145–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, R.A. Reducing the Uncertainties in Direct Aerosol Radiative Forcing. Surv. Geophys. 2012, 33, 701–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Holben, B.N.; Tanre, D.; Slutsker, I.; Smirnov, A.; Eck, T.F. Will aerosol measurements from Terra and Aqua polar orbiting satellites represent the daily aerosol abundance and properties? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 3861–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.D.; Platnick, S.; Menzel, W.P.; Ackerman, S.A.; Hubanks, P.A. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Clouds Observed by MODIS Onboard the Terra and Aqua Satellites. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 3826–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshak, A.; Wen, G.; Coakley, J.A.; Remer, L.A.; Loeb, N.G.; Cahalan, R.F. A simple model for the cloud adjacency effect and the apparent bluing of aerosols near clouds. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Giles, D.M.; Slutsker, I.; Sinyuk, A.; Schafer, J.S.; Smirnov, A.; Sorokin, M.; Reid, J.S.; Sayer, A.M.; et al. AERONET Remotely Sensed Measurements and Retrievals of Biomass Burning Aerosol Optical Properties During the 2015 Indonesian Burning Season. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 4722–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.R.; Levy, R.C.; Eck, T.F.; Fisher, B.; Mattoo, S.; Remer, L.A.; Slutsker, I.; Zhang, J. Characterizing the 2015 Indonesia fire event using modified MODIS aerosol retrievals. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Chen, X.L.; Wang, J.L.; Zhang, T.H.; Zhu, Z.M. Investigation of air quality over the largest city in central China using high resolution satellite derived aerosol optical depth data. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2018, 9, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.F.; Zhang, J.H.; Meng, X.; Fang, Y.; Ge, Y.; Wang, J.F.; Wang, C.Y.; Wu, J.; Kan, H.D. Estimation of PM2.5 concentrations at a high spatiotemporal resolution using constrained mixed-effect bagging models with MAIAC aerosol optical depth. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 217, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Remer, L.A.; Munchak, L.A. A surface reflectance scheme for retrieving aerosol optical depth over urban surfaces in MODIS Dark Target retrieval algorithm. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 3293–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.C.; Lee, J.; Sayer, A.M.; Kim, W.; Bettenhausen, C.; Tsay, S.C. VIIRS Deep Blue Aerosol Products Over Land: Extending the EOS Long-Term Aerosol Data Records. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 4026–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, A.M.; Hsu, N.C.; Lee, J.; Kim, W.V.; Dutcher, S.T. Validation, Stability, and Consistency of MODIS Collection 6.1 and VIIRS Version 1 Deep Blue Aerosol Data Over Land. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 4658–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Tanre, D.; Smirnov, A.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Abuhassan, N.; Newcomb, W.W.; Schafer, J.S.; Chatenet, B.; Lavenu, F.; et al. An emerging ground-based aerosol climatology: Aerosol optical depth from AERONET. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 12067–12097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wei, J.; Wang, J.; Mi, X.T.; Guo, Y.M.; Lv, Y.; Yang, Y.K.; Gan, P.; Zhou, X.Y.; Jia, C.; et al. A Universal Dynamic Threshold Cloud Detection Algorithm (UDTCDA) supported by a prior surface reflectance database. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 7172–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, X.C.; Carlson, B.E.; Kahn, R.A.; Lacis, A.A.; Dubovik, O.; Nakajima, T. Reducing multisensor satellite monthly mean aerosol optical depth uncertainty: 1. Objective assessment of current AERONET locations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 13609–13627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, D.M.; Sinyuk, A.; Sorokin, M.G.; Schafer, J.S.; Smirnov, A.; Slutsker, I.; Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Lewis, J.R.; Campbell, J.R.; et al. Advancements in the Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) Version 3 database – automated near-real-time quality control algorithm with improved cloud screening for Sun photometer aerosol optical depth (AOD) measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.Q.; Sun, L.; Peng, Y.R.; Wang, L.C. Improved merge schemes for MODIS Collection 6.1 Dark Target and Deep Blue combined aerosol products. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 202, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, A.M.; Hsu, N.C.; Bettenhausen, C.; Jeong, M.J. Validation and uncertainty estimates for MODIS Collection 6 “Deep Blue” aerosol data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 7864–7872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichoku, C.; Chu, D.A.; Mattoo, S.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Remer, L.A.; Tanre, D.; Slutsker, I.; Holben, B.N. A spatio-temporal approach for global validation and analysis of MODIS aerosol products. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Xia, X.; Chen, H. Can MODIS detect trends in aerosol optical depth over land? Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 35, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; von Hoyningen-Huene, W.; Vountas, M.; Burrows, J.P. Analysis of linear long-term trend of aerosol optical thickness derived from SeaWiFS using BAER over Europe and South China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 12149–12167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Nichol, J.E. Evaluation of MODIS aerosol retrieval algorithms over the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region during low to very high pollution events. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 7941–7957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Carlson, B.E.; Lacis, A. Application of spectral analysis techniques to the intercomparison of aerosol data - Part 4: Synthesized analysis of multisensor satellite and ground-based AOD measurements using combined maximum covariance analysis. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 2531–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, A.M.; Hsu, N.C.; Lee, J.; Kim, W.V.; Dubovik, O.; Dutcher, S.; Huang, D.; Litvinov, P.; Lyapustin, A.; Tackett, J.L.; et al. Validation of SOAR VIIRS Over-Water Aerosol Retrievals and Context Within the Global Satellite Aerosol Data Record. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 13496–13526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Kambezidis, H.D.; Hatzianastassiou, N.; Kosmopoulos, P.G.; Badarinath, K.V.S. Aerosol climatology: Dependence of the Angstrom exponent on wavelength over four AERONET sites. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2007, 2007, 7347–7397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meloni, D.; di Sarra, A.; Pace, G.; Monteleone, F. Aerosol optical properties at Lampedusa (Central Mediterranean). 2. Determination of single scattering albedo at two wavelengths for different aerosol types. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Reid, J.S.; Sinyuk, A.; Dubovik, O.; Smirnov, A.; Giles, D.; O’Neill, N.T.; Tsay, S.C.; Ji, Q.; et al. Spatial and temporal variability of column-integrated aerosol optical properties in the southern Arabian Gulf and United Arab Emirates in summer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacagnina, C.; Hasekamp, O.P.; Bian, H.S.; Curci, G.; Myhre, G.; van Noije, T.; Schulz, M.; Skeie, R.B.; Takemura, T.; Zhang, K. Aerosol single-scattering albedo over the global oceans: Comparing PARASOL retrievals with AERONET, OMI, and AeroCom models estimates. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 9814–9836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.L.; Ge, J.M.; Huang, J.P. Spatial and temporal distribution of MODIS and MISR aerosol optical depth over northern China and comparison with AERONET. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 2497–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Nazeer, M.; Qiu, Z.; Ding, X.; Wei, J. Global Validation of MODIS C6 and C6.1 Merged Aerosol Products over Diverse Vegetated Surfaces. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutgens, N.; Tsyro, S.; Gryspeerdt, E.; Goto, D.; Weigum, N.; Schulz, M.; Stier, P. On the spatio-temporal representativeness of observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 9761–9780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Reid, J.S.; Arola, A.; Ferrare, R.A.; Hostetler, C.A.; Crumeyrolle, S.N.; Berkoff, T.A.; Welton, E.J.; Lolli, S.; et al. Observations of rapid aerosol optical depth enhancements in the vicinity of polluted cumulus clouds. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 11633–11656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtanen, T.H.; Kolmonen, P.; Sogacheva, L.; Rodriguez, E.; Saponaro, G.; de Leeuw, G. Collocation mismatch uncertainties in satellite aerosol retrieval validation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutgens, N.A. Site representativity of AERONET and GAW remotely sensed AOT and AAOT observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 20, 7473–7488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.C.; Gautam, R.; Sayer, A.M.; Bettenhausen, C.; Li, C.; Jeong, M.J.; Tsay, S.C.; Holben, B.N. Global and regional trends of aerosol optical depth over land and ocean using SeaWiFS measurements from 1997 to 2010. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 8037–8053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Leptoukh, G.G.; Kahn, R.; Zubko, V.; Gopalan, A.; Remer, L.A. A Critical Look at Deriving Monthly Aerosol Optical Depth from Satellite Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 2942–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Choi, M.; Li, S.; Kondragunta, S.; Kim, J.; Holben, B.; Levy, R.C.; Liu, Y. Evaluation of VIIRS, GOCI, and MODIS Collection 6AOD retrievals against ground sunphotometer observations over East Asia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 1255–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpert, P.; Shvainshtein, O.; Kishcha, P. AOD Trends over Megacities Based on Space Monitoring Using MODIS and MISR. Am. J. Clim. Chang. 2012, 1, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, M.; Singh, R.; Singh, A.; Singh, N.; Anshumali. Recent global aerosol optical depth variations and trends—A comparative study using MODIS and MISR level 3 datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 181, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tong, Y.; Feng, L.; Sun, K.; Tang, J. Assessment of the Representativeness of MODIS Aerosol Optical Depth Products at Different Temporal Scales Using Global AERONET Measurements. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2330. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12142330
Tong Y, Feng L, Sun K, Tang J. Assessment of the Representativeness of MODIS Aerosol Optical Depth Products at Different Temporal Scales Using Global AERONET Measurements. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(14):2330. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12142330
Chicago/Turabian StyleTong, Yan, Lian Feng, Kun Sun, and Jing Tang. 2020. "Assessment of the Representativeness of MODIS Aerosol Optical Depth Products at Different Temporal Scales Using Global AERONET Measurements" Remote Sensing 12, no. 14: 2330. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12142330
APA StyleTong, Y., Feng, L., Sun, K., & Tang, J. (2020). Assessment of the Representativeness of MODIS Aerosol Optical Depth Products at Different Temporal Scales Using Global AERONET Measurements. Remote Sensing, 12(14), 2330. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12142330