Hyperspectral Imaging from a Multipurpose Floating Platform to Estimate Chlorophyll-a Concentrations in Irrigation Pond Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
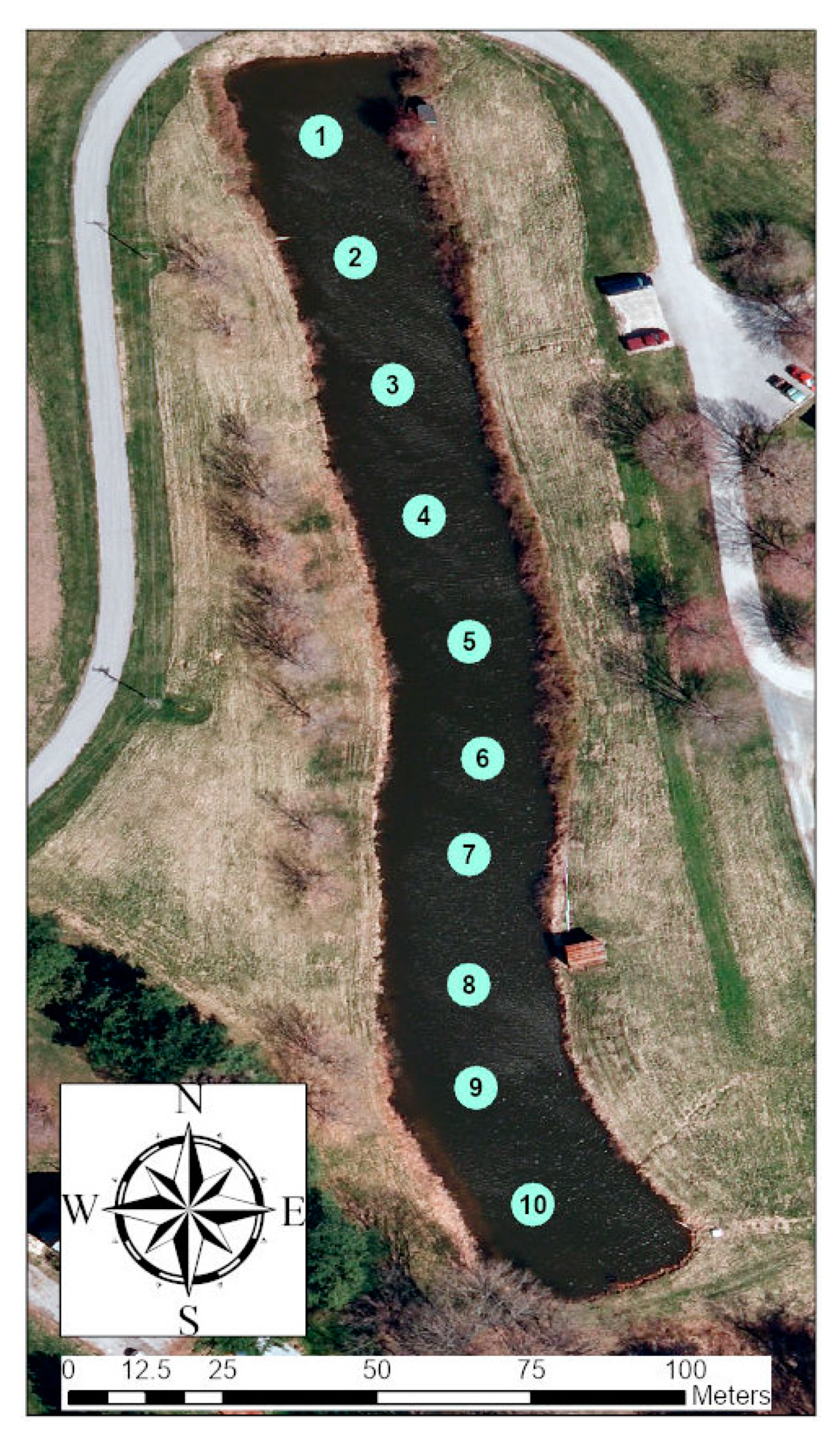
2.1. Irrigation Pond
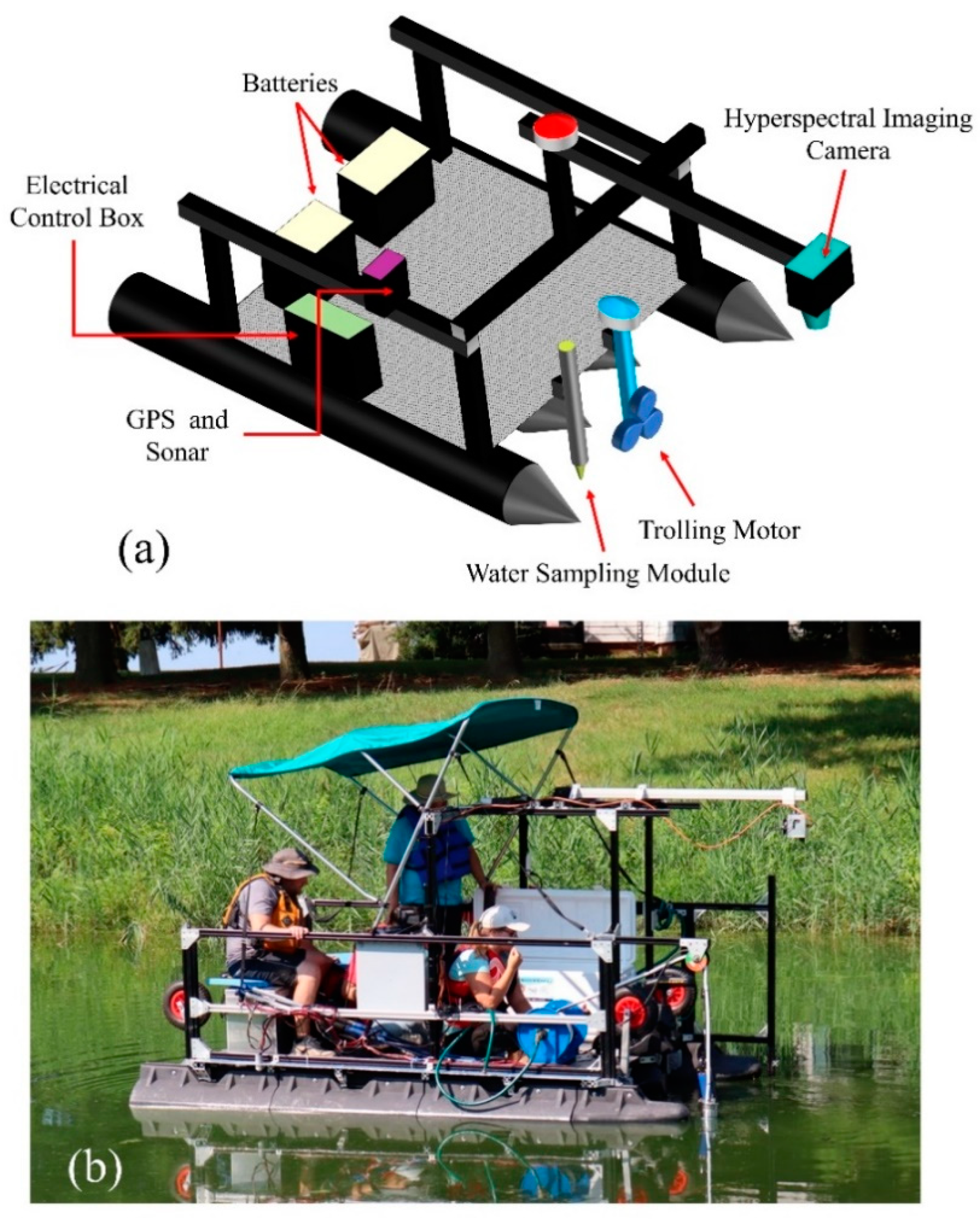
2.2. MFP Design and Components
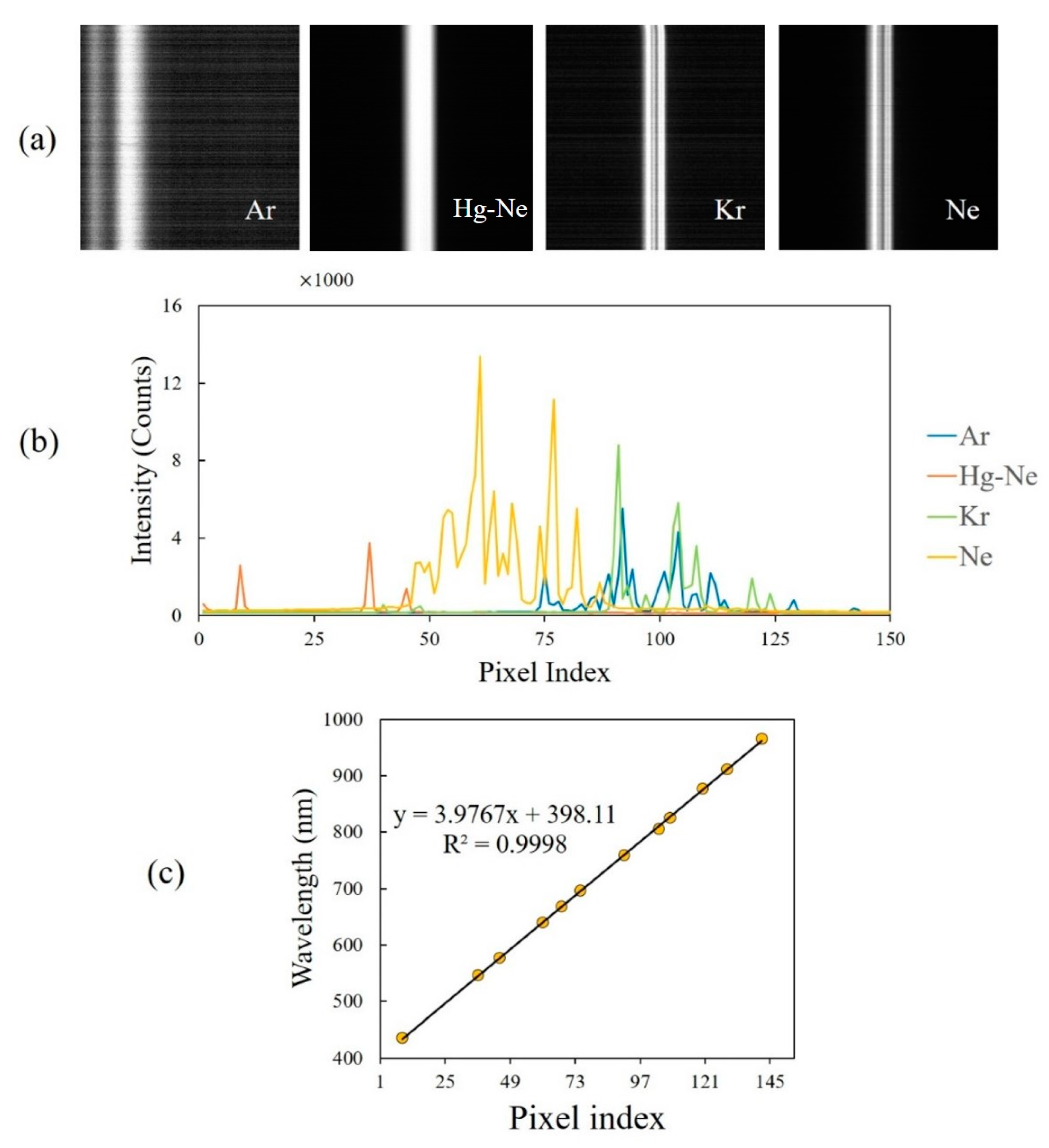
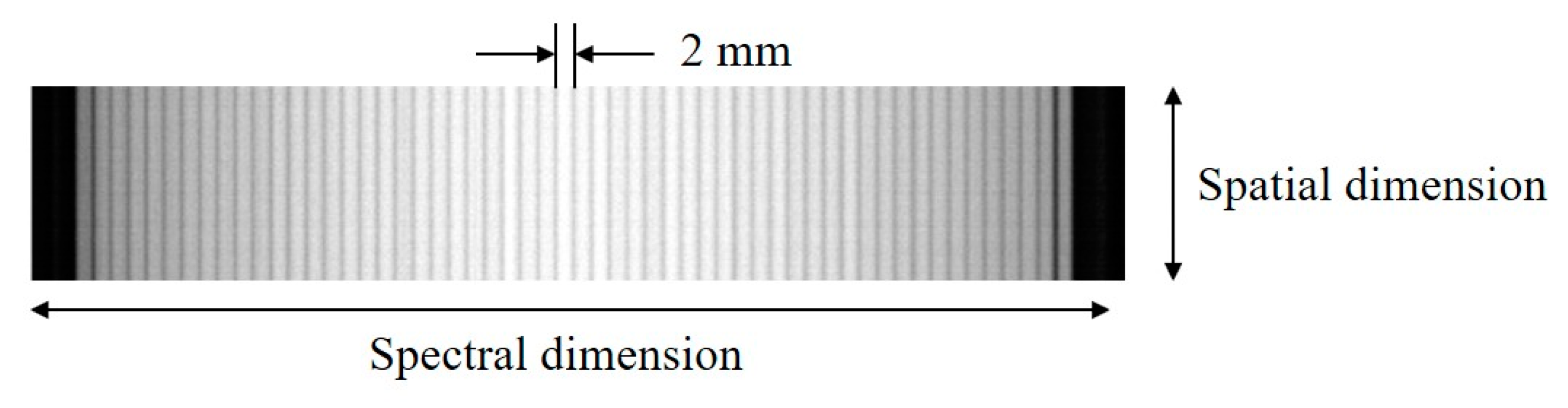
2.3. System Calibration
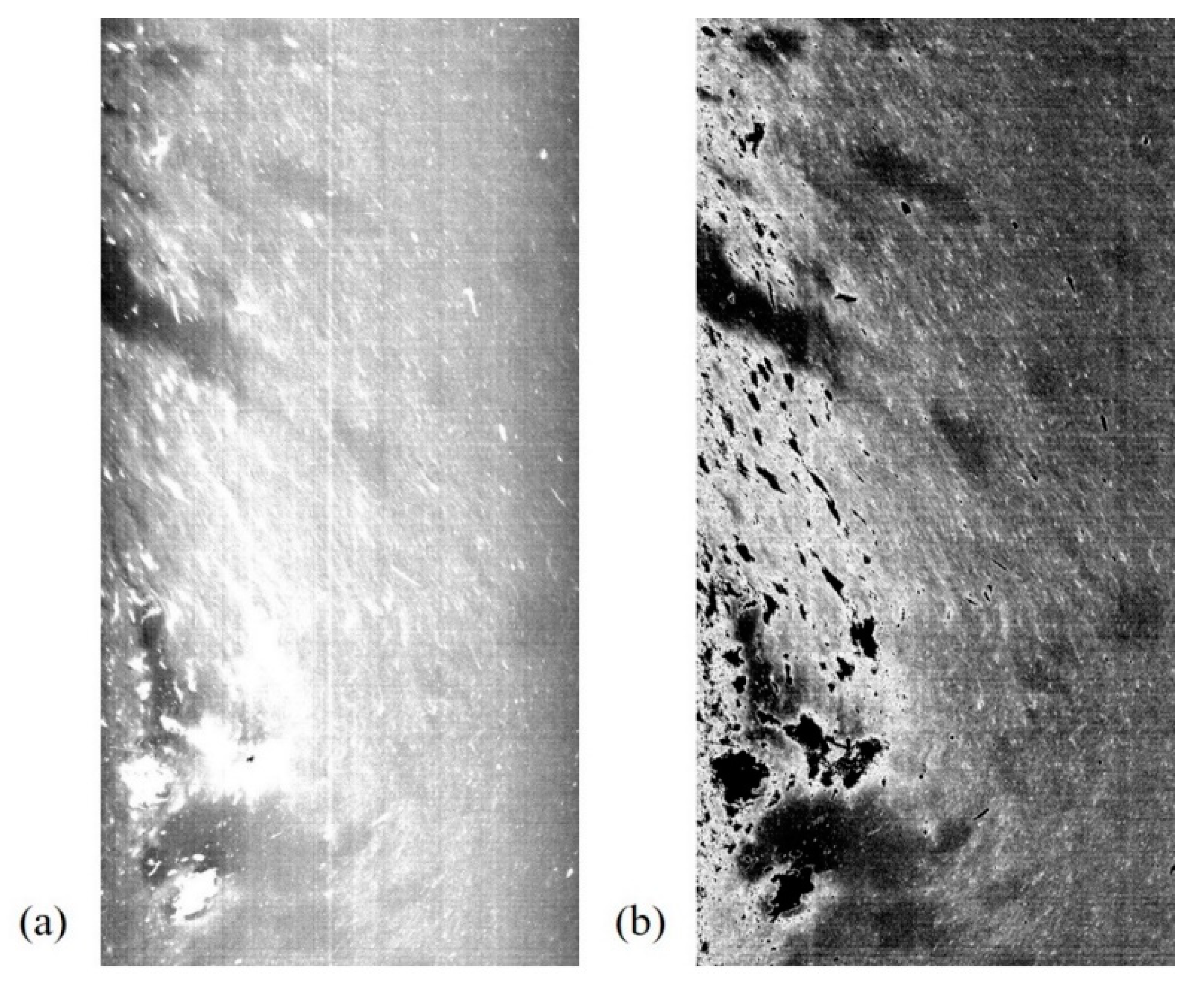
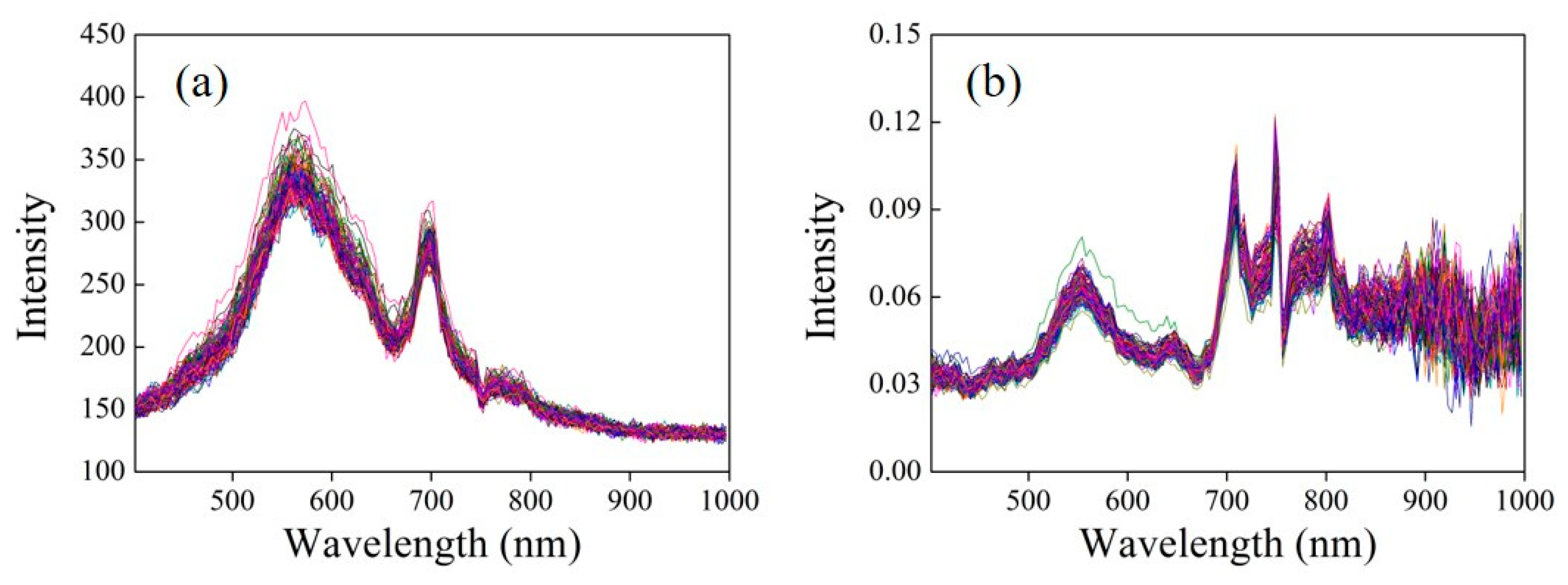
2.4. Hyperspectral Image Acquisition
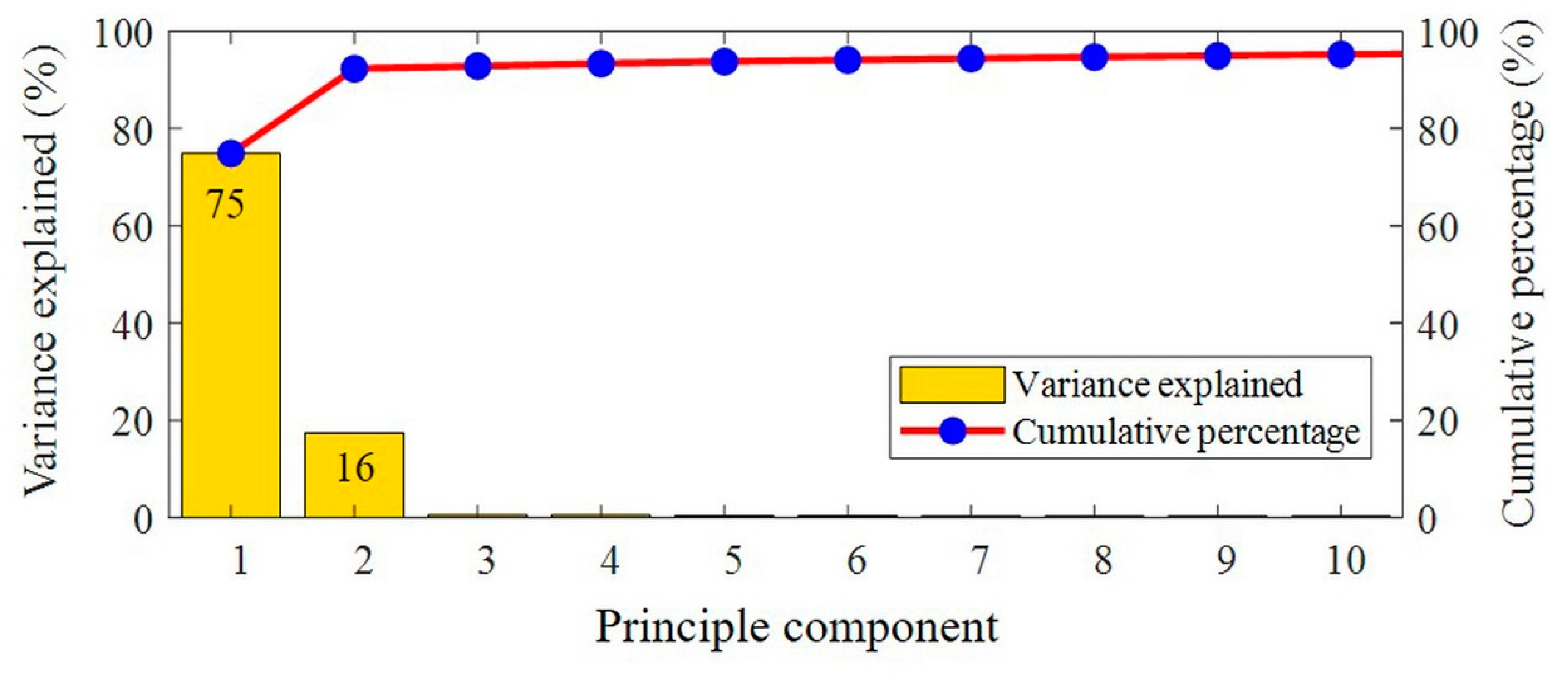
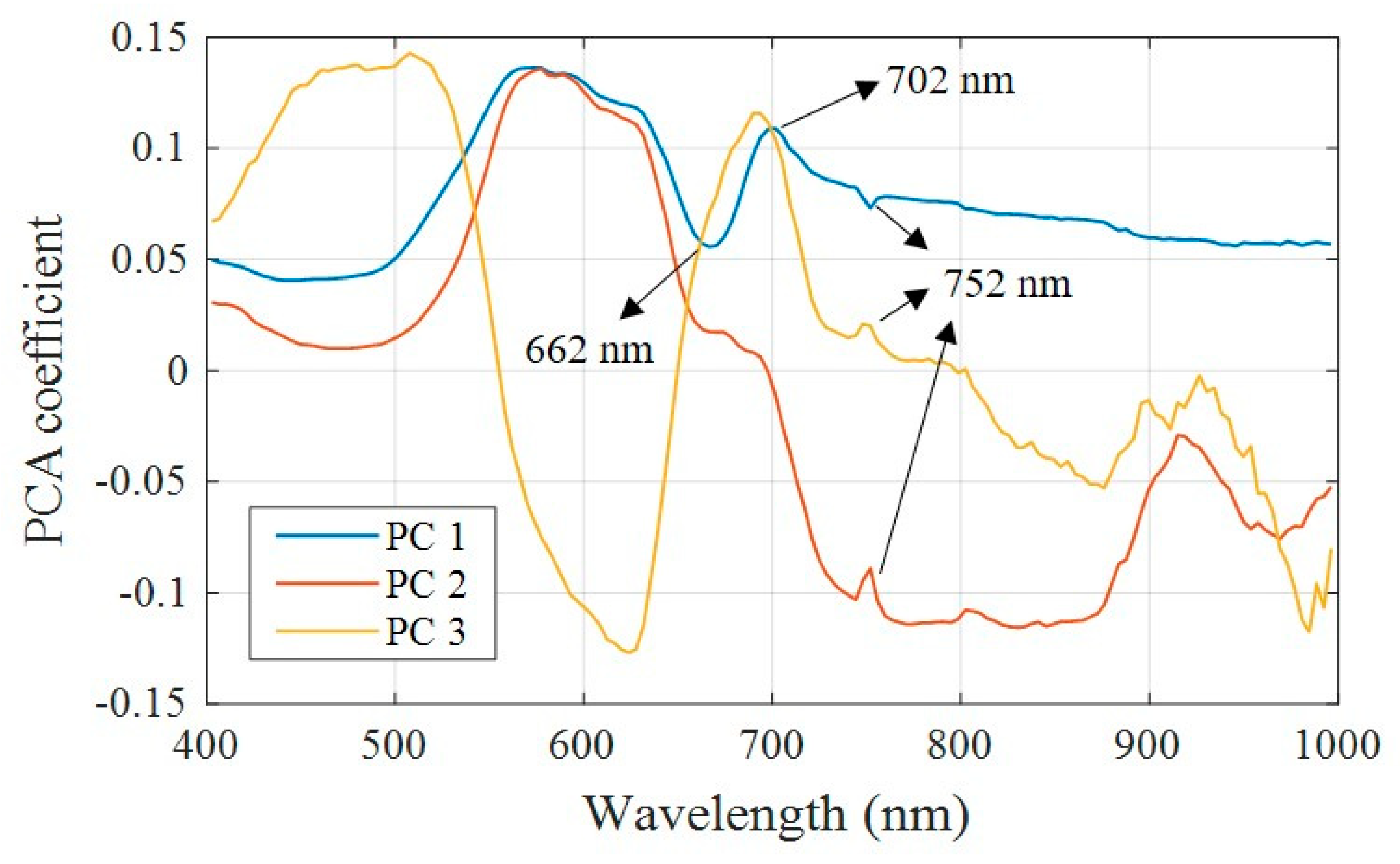
2.5. Key Wavelength Selection and NIR-red Models
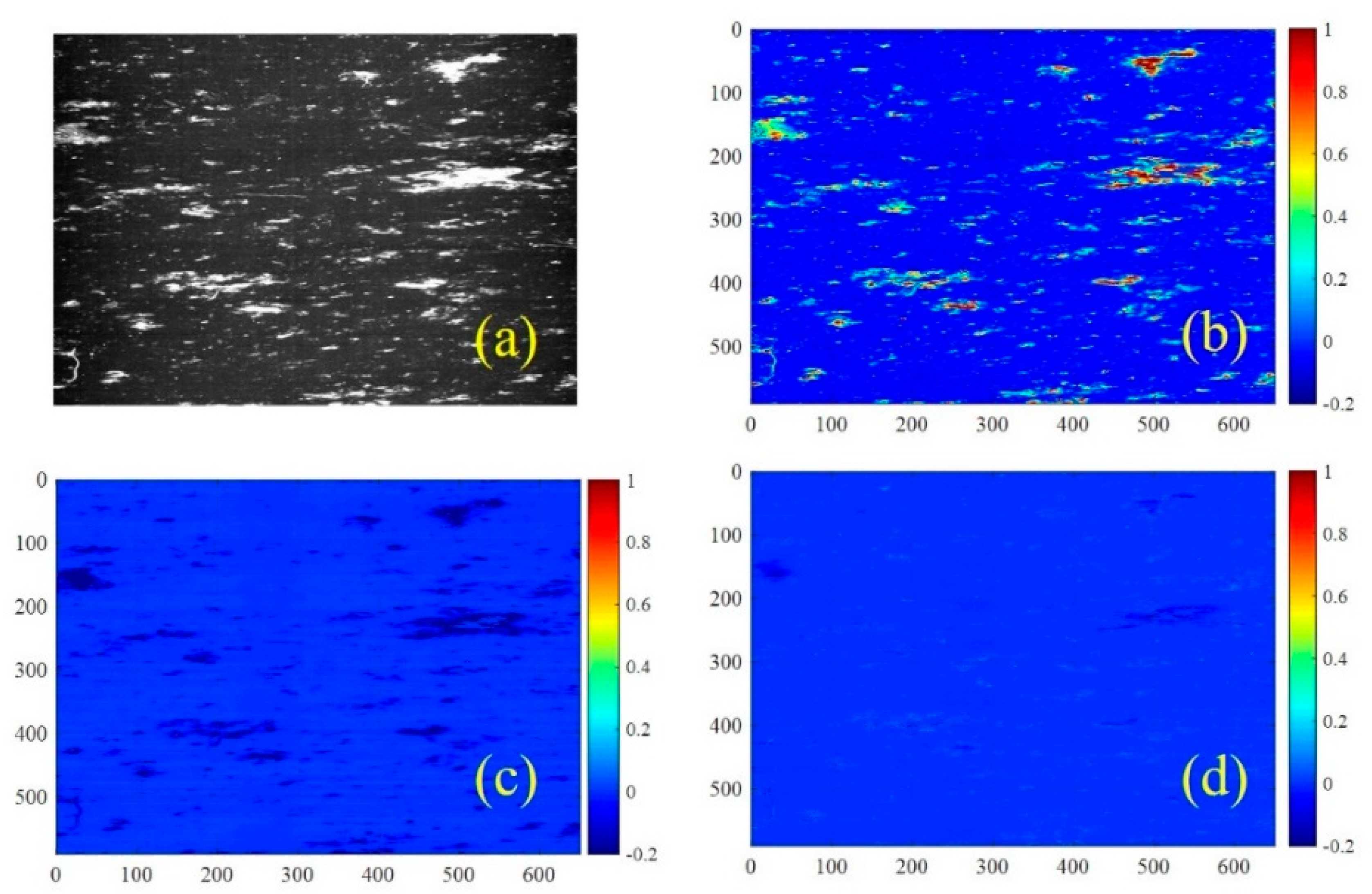
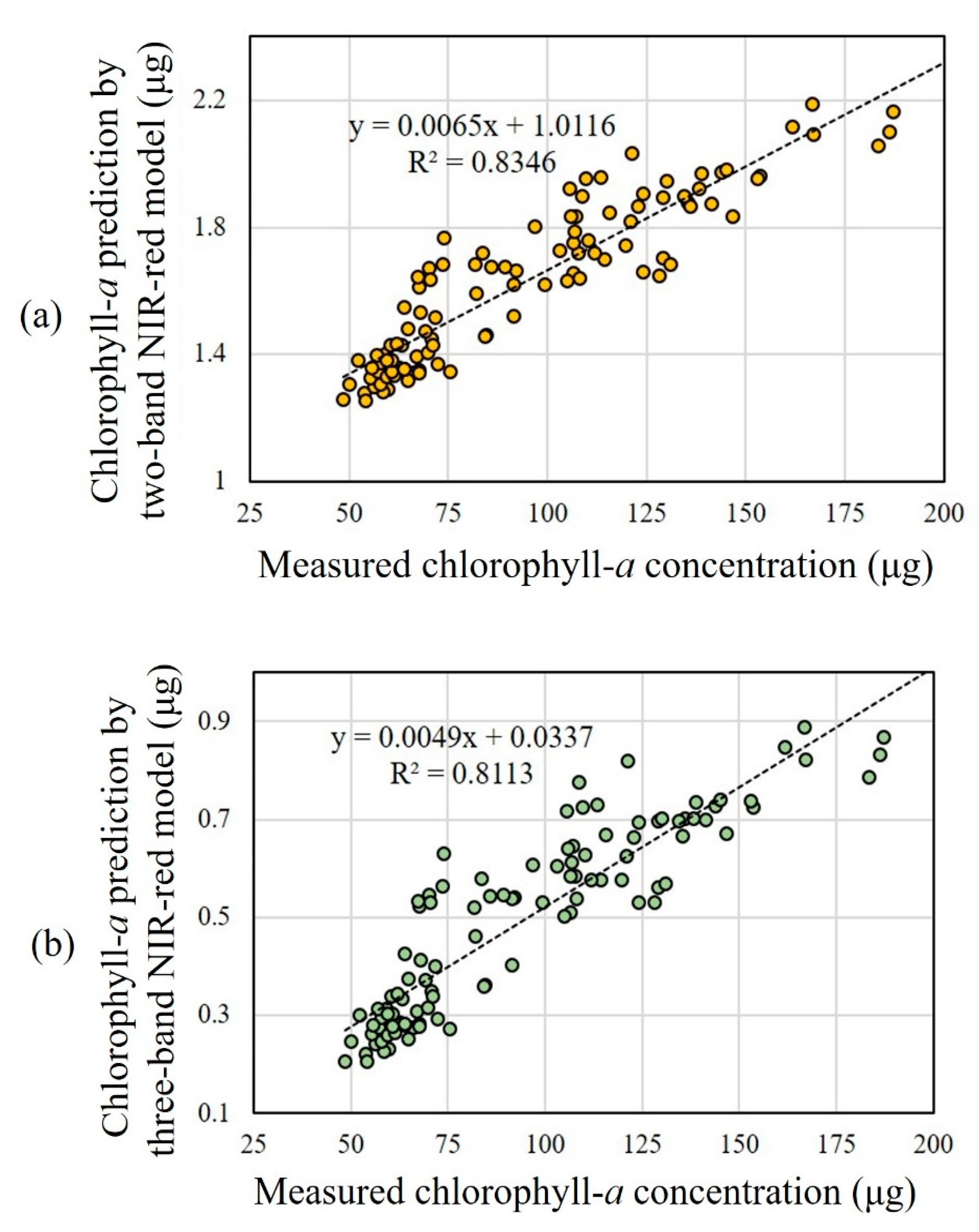
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Irrigation Water Use. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/special-topic/water-science-school/science/irrigation-water-use?qt-science_center_objects=0#qt-science_center_objects (accessed on 20 June 2020).
- Dieter, C.A.; Maupin, M.A.; Caldwell, R.R.; Harris, M.A.; Ivahnenko, T.I.; Lovelace, J.K.; Barber, N.L.; Linsey, K.S. Estimated Use of Water in the United States in 2015; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2018.
- Barber, N.L. Summary of estimated Water Use in the United States in 2005: U.S. Geological Survey Fact Sheet 2009-3098; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2018.
- Ouyang, Y.; Feng, G.; Read, J.J.; Leininger, T.D.; Jenkins, J.N. Estimating the ratio of pond size to irrigated soybean land in Mississippi: A case study. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2016, 16, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettygrove, G.S.; Dennis, W.W.; Robert, S.A. Irrigation Water Quality Criteria. Irrig. Reclaimed Munic. Wastewater–A Guid. Man. 2019, 3-1–3-35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.K.; Dutta, S.K.; Pramanik, S.; Kole, R.K. Assessment of river water quality for agricultural irrigation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavurmaci, M.; Apaydin, A. Assessment of irrigation water quality by a Geographic Information System–Multicriteria Decision Analysis-based model: A case study from Ankara, Turkey. Water Environ. Res. 2019, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmanson, L.G.; Brezonik, P.L.; Bauer, M.E. Airborne hyperspectral remote sensing to assess spatial distribution of water quality characteristics in large rivers: The Mississippi River and its tributaries in Minnesota. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 130, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zovko, M.; Žibrat, U.; Knapič, M.; Bubalo, M.; Romić, M.; Romić, D. Hyperspectral imagery as a supporting tool in precision irrigation of karst landscapes. Adv. Anim. Biosci. 2017, 8, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brando, V.E.; Dekker, A.G. Satellite hyperspectral remote sensing for estimating estuarine and coastal water quality. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1378–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.K.; Tripathi, B.D. Microbial contamination in vegetables due to irrigation with partially treated municipal wastewater in a tropical city. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2007, 17, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, M.D.; Smith, J.E.; Hernandez, C.; Macarisin, D.; Pachepsky, Y. Seasonality of E. coli and Enterococci Concentrations in Creek Water, Sediment, and Periphyton. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allende, A.; Monaghan, J. Irrigation water quality for leafy crops: A perspective of risks and potential solutions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 7457–7477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Doyle, M.P.; Phatak, S.C.; Millner, P.; Jiang, X. Survival of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in soil and on carrots and onions grown in fields treated with contaminated manure composts or irrigation water. Food Microbiol. 2005, 22, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, M.D.; Pachepsky, Y.A.; Hill, R.L.; Sellner, K.G.; Macarisin, D.; Staver, K.W. Intraseasonal variation of E. coli and environmental covariates in two irrigation ponds in Maryland, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moses, W.J.; Gitelson, A.A.; Perk, R.L.; Gurlin, D.; Rundquist, D.C.; Leavitt, B.C.; Barrow, T.M.; Brakhage, P. Estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in turbid productive waters using airborne hyperspectral data. Water Res. 2012, 46, 993–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyo, J.C.; Pachepsky, Y.; Baek, S.S.; Kwon, Y.S.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, H.; Park, S.; Cha, Y.K.; Ha, R.; Nam, G.; et al. Optimizing semi-analytical algorithms for estimating chlorophyll-a and phycocyanin concentrations in inland waters in Korea. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, P.M.; Keller, S. Estimating chlorophyll a concentrations of several inland waters with hyperspectral data and machine learning models. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, 4, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaustein, R.A.; Pachepsky, Y.; Hill, R.L.; Shelton, D.R.; Whelan, G. Escherichia coli survival in waters: Temperature dependence. Water Res. 2013, 47, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachepsky, Y.; Shelton, D.R.; McLain, J.E.T.; Patel, J.; Mandrell, R.E. Irrigation Waters as a Source of Pathogenic Microorganisms in Produce: A Review. Adv. Agron. 2011, 113, 75–141. [Google Scholar]
- Havelaar, A.H.; Vazquez, K.M.; Topalcengiz, Z.; Muñoz-Carpena, R.; Danyluk, M.D. Evaluating the U.S. Food Safety Modernization Act Produce Safety Rule Standard for Microbial Quality of Agricultural Water for Growing Produce. J. Food Prot. 2017, 80, 1832–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Landgrebe, D. Information Extraction Principles and Methods for Multispectral and Hyperspectral Image Data. Inf. Process. Remote Sens. 1999, 3–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloutis, E.A. Review article hyperspectral geological remote sensing: Evaluation of analytical techniques. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 2215–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.J.; Khan, H.S.; Yousaf, A.; Khurshid, K.; Abbas, A. Modern Trends in Hyperspectral Image Analysis: A Review. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 14118–14129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adão, T.; Hruška, J.; Pádua, L.; Bessa, J.; Peres, E.; Morais, R.; Sousa, J.J. Hyperspectral imaging: A review on UAV-based sensors, data processing and applications for agriculture and forestry. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govender, M.; Chetty, K.; Bulcock, H. A review of hyperspectral remote sensing and its application in vegetation and water resource studies. Water SA 2007, 33, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, S.C.; Choo, C.K.; Lau, J.W.M.; Chan, W.S.; Dang, T.C. Monitoring water quality in Singapore reservoirs with hyperspectral remote sensing technology. Water Pract. Technol. 2019, 14, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Kawamura, K.; Sakuno, Y.; Fan, X.; Gong, Z.; Lim, J. Retrieval of chlorophyll-a and total suspended solids using iterative stepwise elimination partial least squares (ISE-PLS) regression based on field hyperspectral measurements in irrigation ponds in Higashihiroshima, Japan. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, E.M.; Mutanga, O.; Odindi, J.; Adam, E.; Odindo, A.; Ismail, R. Estimating Swiss chard foliar macro- and micronutrient concentrations under different irrigation water sources using ground-based hyperspectral data and four partial least squares (PLS)-based (PLS1, PLS2, SPLS1 and SPLS2) regression algorithms. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 132, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Dall’Olmo, G.; Moses, W.; Rundquist, D.C.; Barrow, T.; Fisher, T.R.; Gurlin, D.; Holz, J. A simple semi-analytical model for remote estimation of chlorophyll-a in turbid waters: Validation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3582–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Olmo, G.; Gitelson, A.A. Erratum: Effect of bio-optical parameter variability on the remote estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in turbid productive waters: Experimental results. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaustein, J. The peak near 700 nm on radiance spectra of algae and water: Relationships of its magnitude and position with chlorophyll. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1992, 13, 3367–3373. [Google Scholar]
- Randolph, K.; Wilson, J.; Tedesco, L.; Li, L.; Pascual, D.L.; Soyeux, E. Hyperspectral remote sensing of cyanobacteria in turbid productive water using optically active pigments, chlorophyll a and phycocyanin. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 4009–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachepsky, Y.; Kierzewski, R.; Stocker, M.; Sellner, K.; Mulbry, W.; Lee, H.; Kim, M. Temporal stability of Escherichia coli concentrations in waters of two irrigation ponds in Maryland. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.S.; Chao, K.; Chan, D.E.; Jun, W.; Lefcourt, A.M.; Delwiche, S.R.; Kang, S.; Lee, K. Line-Scan Hyperspectral Imaging Platform for Agro-Food Safety and Quality Evaluation: System Enhancement and Characterization. Trans. ASABE 2011, 54, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Chao, K.; Kim, M.S.; Lu, R.; Burks, T.F. Hyperspectral and multispectral imaging for evaluating food safety and quality. J. Food Eng. 2013, 118, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Chen, Y.R.; Mehl, P.M. Hyperspectral reflectance and fluorescence imaging system for food quality and safety. Trans. Am. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2001, 44, 721–729. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, I.; Kim, M.S.; Cho, B.K.; Mo, C.; Barnaby, J.Y.; McClung, A.M.; Oh, M. Selection of optimal hyperspectral wavebands for detection of discolored, diseased rice seeds. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-de-Santiago, F.; Kovacs, J.M.; Flores-Verdugo, F. The influence of seasonality in estimating mangrove leaf chlorophyll-a content from hyperspectral data. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 21, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji-Yong, S.; Xiao-Bo, Z.; Jie-Wen, Z.; Kai-Liang, W.; Zheng-Wei, C.; Xiao-Wei, H.; De-Tao, Z.; Holmes, M. Nondestructive diagnostics of nitrogen deficiency by cucumber leaf chlorophyll distribution map based on near infrared hyperspectral imaging. Sci. Hortic. (Amsterdam). 2012, 138, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, L.F.; Hu, H.; Zheng, K.F.; Jin, Q.Y. Monitoring leaf chlorophyll fluorescence with spectral reflectance in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Procedia Eng. 2011, 15, 4403–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luoheng, H.; Rundquist, D.C. Comparison of NIR/RED ratio and first derivative of reflectance in estimating algal-chlorophyll concentration: A case study in a turbid reservoir. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 62, 253–261. [Google Scholar]
- Gons, H.J. Optical teledetection of chlorophyll a in turbid inland waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 1127–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.K.; Kim, M.S.; Baek, I.S.; Kim, D.Y.; Lee, W.H.; Kim, J.; Bae, H.; Kim, Y.S. Detection of cuticle defects on cherry tomatoes using hyperspectral fluorescence imagery. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2013, 76, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manley, M. Near-infrared spectroscopy and hyperspectral imaging: Non-destructive analysis of biological materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 8200–8214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Liu, H.; Beck, R.; Lekki, J.; Yang, B.; Shu, S.; Liu, Y.; Benko, T.; Anderson, R.; Tokars, R.; et al. Regionally and Locally Adaptive Models for Retrieving Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Inland Waters from Remotely Sensed Multispectral and Hyperspectral Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 4758–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardino, C.; Bresciani, M.; Valentini, E.; Gasperini, L.; Bolpagni, R.; Brando, V.E. Airborne hyperspectral data to assess suspended particulate matter and aquatic vegetation in a shallow and turbid lake. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 157, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Time | Condition | Water Temperature (°C) | Wind Speed (m/s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 29 July 2019 | 09:00–11:00 | Sunny | 27.5–28.3 | 2.2–2.7 |
| 15 Aug 2019 | 09:00–11:00 | Sunny | 26.9–27.2 | 3.1–5.3 |
| 22 Aug 2019 | 09:00–11:00 | Sunny | 28.5–29.8 | 3.1–3.6 |
| 30 Aug 2019 | 09:00–11:00 | Sunny | 28.2–30.6 | 0–2.7 |
| Spectral Range (nm) | Selected Key Wavelength (nm) |
|---|---|
| (660~670) | 662 |
| (700~730) | 702 |
| (740~760) | 752 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, G.; Baek, I.; Stocker, M.D.; Smith, J.E.; Van Tassell, A.L.; Qin, J.; Chan, D.E.; Pachepsky, Y.; Kim, M.S. Hyperspectral Imaging from a Multipurpose Floating Platform to Estimate Chlorophyll-a Concentrations in Irrigation Pond Water. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2070. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12132070
Kim G, Baek I, Stocker MD, Smith JE, Van Tassell AL, Qin J, Chan DE, Pachepsky Y, Kim MS. Hyperspectral Imaging from a Multipurpose Floating Platform to Estimate Chlorophyll-a Concentrations in Irrigation Pond Water. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(13):2070. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12132070
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Geonwoo, Insuck Baek, Matthew D. Stocker, Jaclyn E. Smith, Andrew L. Van Tassell, Jianwei Qin, Diane E. Chan, Yakov Pachepsky, and Moon S. Kim. 2020. "Hyperspectral Imaging from a Multipurpose Floating Platform to Estimate Chlorophyll-a Concentrations in Irrigation Pond Water" Remote Sensing 12, no. 13: 2070. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12132070
APA StyleKim, G., Baek, I., Stocker, M. D., Smith, J. E., Van Tassell, A. L., Qin, J., Chan, D. E., Pachepsky, Y., & Kim, M. S. (2020). Hyperspectral Imaging from a Multipurpose Floating Platform to Estimate Chlorophyll-a Concentrations in Irrigation Pond Water. Remote Sensing, 12(13), 2070. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12132070







