Investigation of C-Band SAR Polarimetry for Mapping a High-Tidal Coastal Environment in Northern Canada
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Overview of SAR Compact Polarimetry
3. Study Site and Data Processing
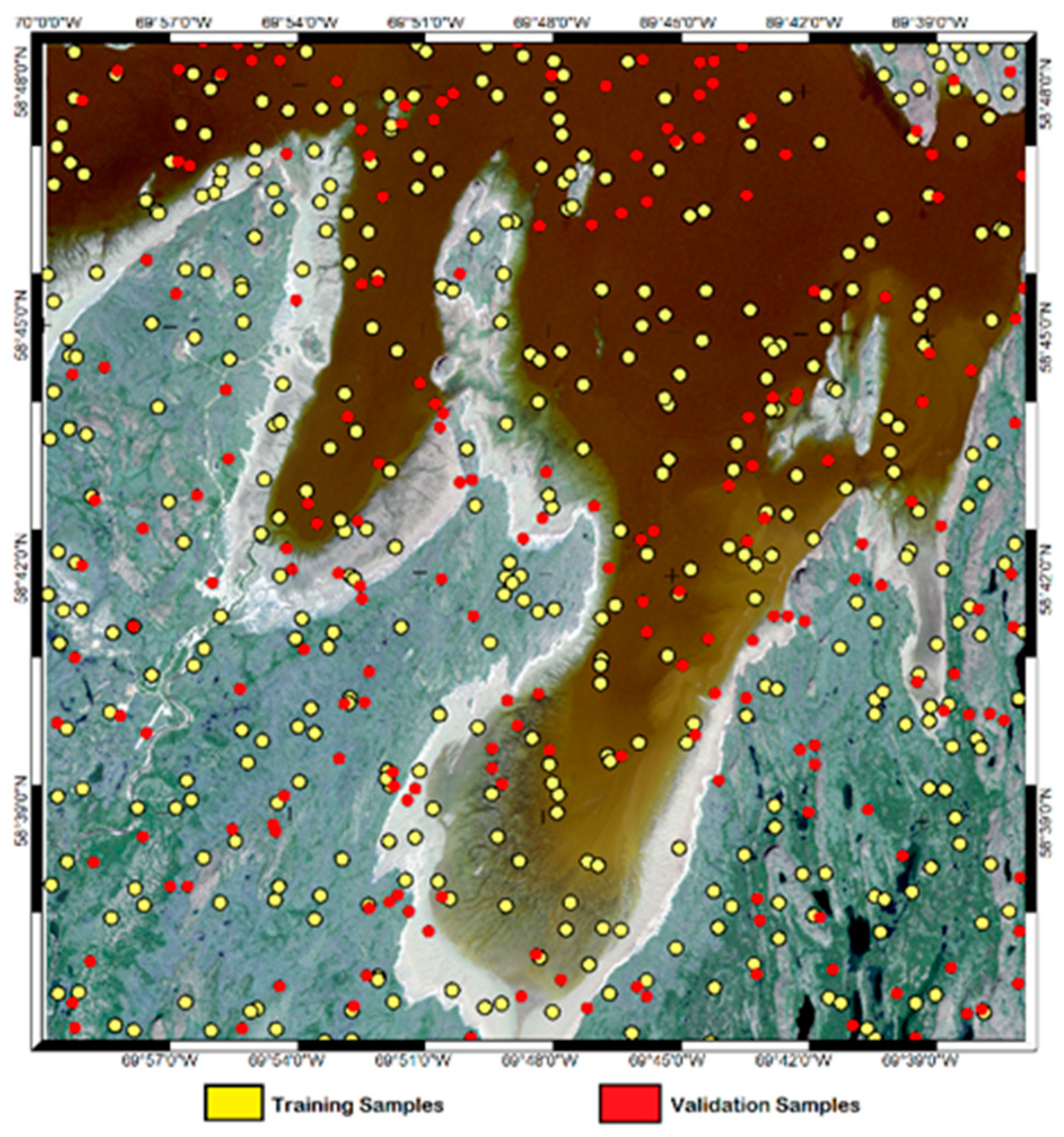
3.1. Study Site
3.2. RADARSAT-2 Collection and Processing
3.3. Random Forest
4. Results and Discussion
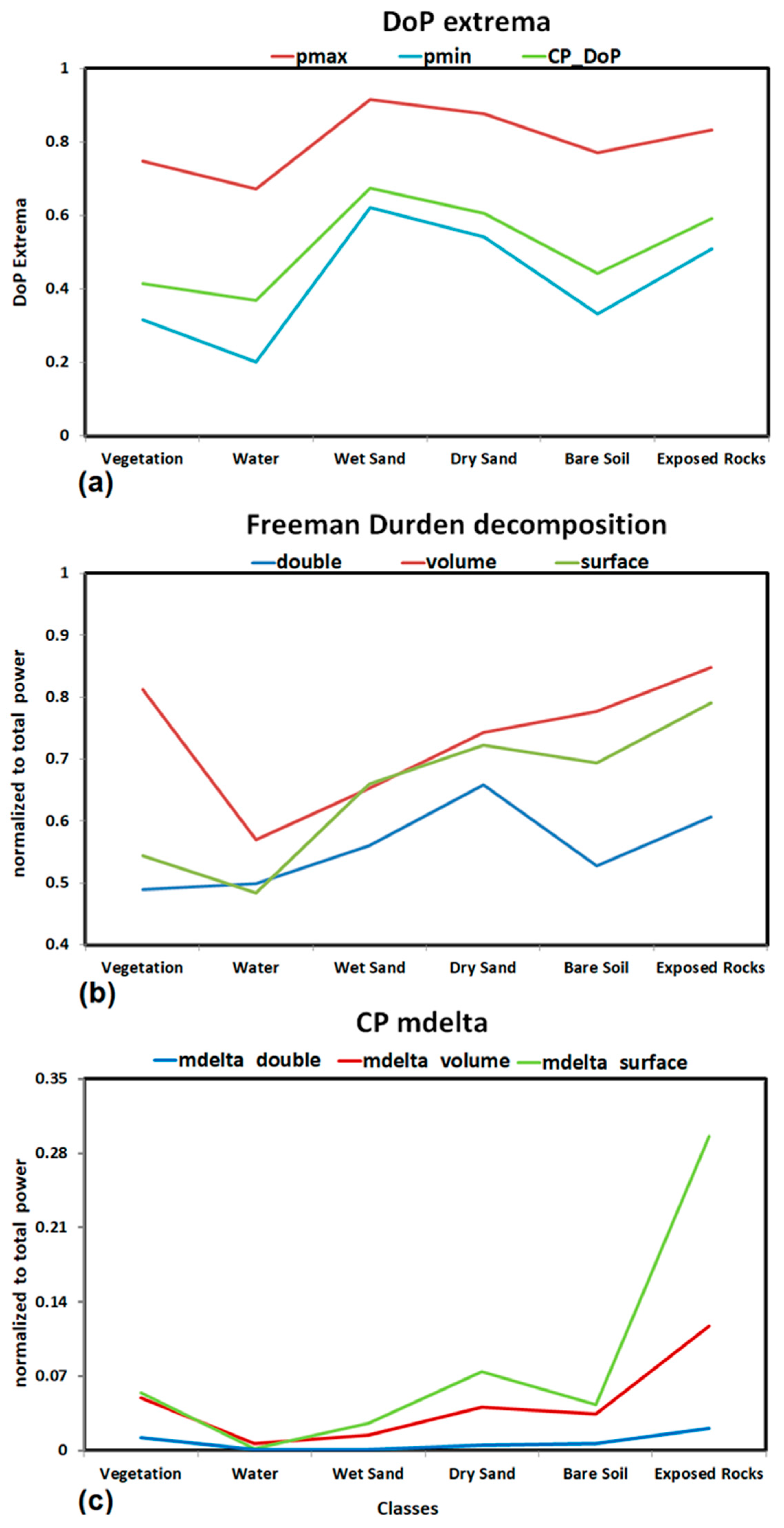
4.1. Separability Analysis
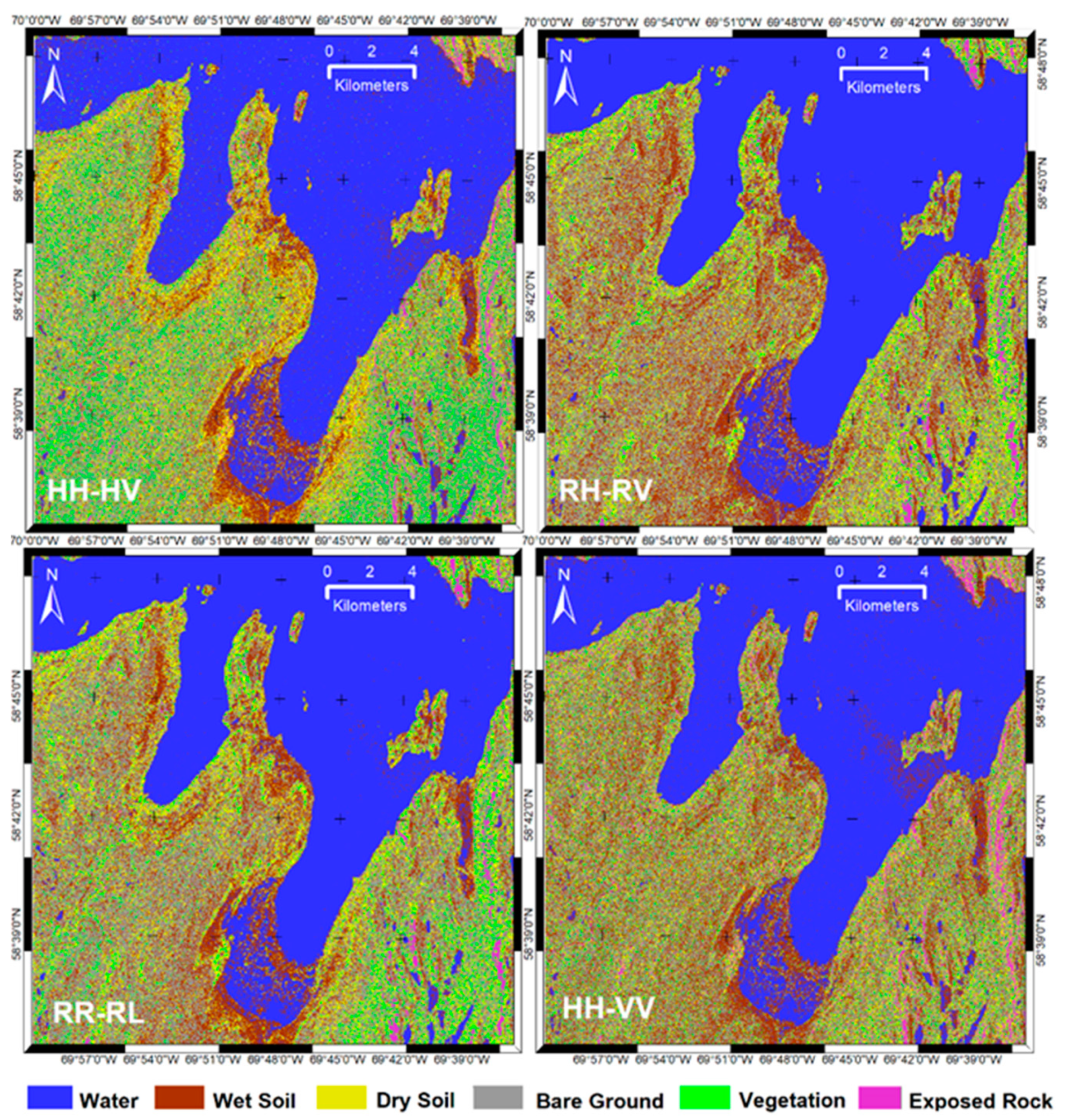
4.2. Classification
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Airoldi, L.; Beck, M.W. Loss, Status and Trends for Coastal Marine Habitats of Europe. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. 2007, 45, 345–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, M.; Tian, B.; Zhou, Y.; Li, B.; Ma, Z. Land claim and loss of tidal flats in the Yangtze estuary. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, R.S.; Clemens, S.R.; Phinn, H.P.; Possingham, R.A. Fuller Tracking the rapid loss of tidal wetlands in the Yellow Sea Front. Ecol. Environ. 2014, 12, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Short, A.D. Handbook of Beach and Shoreface Morphodynamics; John Wiley and Sons: Chichester, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Collin, A.; Long, B.; Archambault, P. Merging land-marine realms: Spatial patterns of seamless coastal habitats using a multispectral LiDAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.H.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, Y.K.; Won, J.S.; Chun, S.S.; Lee, S. Detecting the intertidal morphologic change using satellite data. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 78, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, D.C.; Scott, T.R.; Dance, S.L. Remote sensing of intertidal morphological change in Morecambe Bay, U.K., between 1991 and 2007. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 87, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olliver, E.A.; Edmonds, D.A. Defining the ecogeomorphic succession of land building for freshwater, intertidal wetlands in Wax Lake Delta, Louisiana. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 196, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, S.; Roberts, D.; Bala, B.; Lymburner, L. Extracting the intertidal extent and topography of the Australian coastline from a 28 year time series of Landsat observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 195, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.H.; Na, Y.H.; Won, J.S.; Doerffer, R. A critical grain size for Landsat ETM+ investigations into intertidal sediments: A case study of the Gomso intertidal flats, Korea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 60, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, N.; Phinn, S.; Clemens, R.; Roelfsema, C.; Fuller, R. Continental scale mapping of tidal flats across East Asia using the Landsat archive. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 3417–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brockmann, C.; Stelzer, K. Optical remote sensing of intertidal flats. In Remote Sensing of the European Seas; Barale, V., Gade, M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gade, M.; Alpers, W.; Melsheimer, C.; Tanck, G. Classification of sediments on exposed tidal flats in the German Bight using multi-frequency radar data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1603–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, B.-H.; Kim, D.-J.; Hwang, J.-H.; Oh, Y.; Moon, W. Detection of oyster habitat in tidal flats using multi-frequency polarimetric SAR data. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 97, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-E.; Moon, W.M.; Kim, D.-J. Estimation of surface roughness parameter in intertidal mudflat using airborne polarimetric SAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 1022–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza-Filho, P.W.M.; Paradella, W.R.; Rodrigues, S.W.P.; Costa, F.R.; Mura, J.C.; Gonçalves, F.D. Discrimination of coastal wetland environments in the Amazon region based on multi-polarized L-band airborne synthetic aperture radar imagery. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 95, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-K.; Park, J.-W.; Choi, J.-K.; Oh, Y.; Won, J.-S. Potential uses of TerraSAR-X for mapping herbaceous halophytes over salt marsh and tidal flats. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 115, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.M.; Li, X.M.; Velotto, D.; Chen, K.S. Study of the polarimetric characteristics of mud flats in an intertidal zone using C–and X–band spaceborne SAR data. Remote Sens Environ. 2016, 176, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gade, M.; Wang, W.; Kemme, L. On the imaging of exposed intertidal flats by single- and dual-co-polarization Synthetic Aperture Radar. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 205, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerner, W.M.; Mott, H.; Luneburg, E.; Livigstone, C.; Brisco, B.; Brown, R.J.; Paterson, J.S. Polarimetry in radar remote sensing: Basic and applied concepts in “Principles and Applications of Imaging Radar”. In Manual of Remote Sensing, 3rd ed.; Ryerson, R.A., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998; Volume 2, pp. 271–358. [Google Scholar]
- Touzi, R.; Gosselin, G.; Brook, R. Polarimetric L-band SAR for peatland mapping and monitoring. In ESA Book on Principles and Applications of Pol-InSAR; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.-S.; Pottier, E. Polarimetric Radar Imaging: From Basics to Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Banks, S.N.; King, D.J.; Merzouki, A.; Duffe, J. Characterizing scattering behaviour and assessing potential for classification of arctic shore and near-shore land covers with fine quad-pol RADARSAT-2 data. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 40, 291–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, A.; Durden, S. A three-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR data. IEEE Trans Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cloude, S.R.; Pottier, E. An Entropy Based Classification Scheme for Land Applications of Polarimetric SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yang, X.; Li, X. A Fully Polarimetric SAR Imagery Classification Scheme for Mud and Sand Flats in Intertidal Zones. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 1734–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhroy, V.; Charbonneau, F. RADARSAT: Science and applications. Phys. Can. 2014, 70, 212–217. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, A. Overview of the RADARSAT constellation mission. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 41, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raney, R.K. Hybrid-polarity SAR architecture. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 3397–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dabboor, M.; Geldsetzer, T. Towards sea ice classification using simulated RADARSAT Constellation Mission compact polarimetric SAR imagery. Remote Sens Environ. 2014, 140, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geldsetzer, T.; Charbonneau, F.; Arkett, M.; Zagon, T. Ocean Wind Study Using Simulated RCM Compact-Polarimetry SAR. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 41, 418–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, L.; Millard, K.; Banks, S.; Richardson, M.; Pasher, J.; Duffe, J. Moving to the RADARSAT Constellation Mission: Comparing Synthesized Compact Polarimetry and Dual Polarimetry Data with Fully Polarimetric RADARSAT-2 Data for Image Classification of Peatlands. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banks, S.; Millard, K.; Behnamian, A.; White, L.; Ullmann, T.; Charbonneau, F.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Pasher, J.; Duffe, J. Contributions of Actual and Simulated Satellite SAR Data for Substrate Type Differentiation and Shoreline Mapping in the Canadian Arctic. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Touzi, R.; Vachon, P.W. Vachon PWRCM polarimetric SAR for enhanced ship detection classification. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 41, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raney, R.K. Hybrid Dual-Polarization Synthetic Aperture Radar. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charbonneau, F.; Brisco, B.; Raney, K.; McNairn, H.; Liu, C.; Vachon, P.; Shang, J.; De Abreu, R.; Champagne, C.; Merzouki, A.; et al. Compact polarimetry overview and applications assessment. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 36 (Suppl. 2), S298–S315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzi, R. Hybrid Versus Matched Antenna for Dual- and Fully Polarimetric SAR; PolinSAR’13; Frascatti: Rome, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Touzi, R.; Hurley, J.; Vachon, P. Optimization of the Degree of Polarization for Enhanced Ship Detection Using Polarimetric RADARSAT-2. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 5403–5424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirvany, R.; Chabert, M.; Tourneret, J.-Y. Ship and oil-spill detection using the degree of polarization in linear and hybrid/compact dual-pol SAR. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marino, A. A notch filter for ship detection with polarimetric SAR images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 1219–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Souyris, J.-C.; Imbo, P.; Fjortoft, R.; Mingot, S.; Lee, J.-S. Compact polarimetry based on symmetry properties of geophysical media: The pi/4 mode. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raney, R.K.; Cahill, J.T.S.; Patterson, G.W.; Bussey, D.B.J. The M-Chi Decomposition of Hybrid Dual-Polarimetric Radar Data with Application to Lunar Craters. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, B.; Tian, S. Compact polarimetric SAR ship detection with m- decomposition using visual attention model. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, J.; Yang, J. Ship detection by using the M-Chi and M-Delta decompositions. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Quebec, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.J.; Denbina, M.; Atteia, G. On the reconstruction of quad-pol SAR data from compact polarimetry data for ocean target detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Perrie, W.; He, Y.J.; Lehner, S.; Brusch, S. Target detection on the ocean with the relative phase of compact polarimetry SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 3299–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Vicente-Guijalba, F.; Ballester-Berman, J.D.; Cloude, S.R. Polarimetric Response of Rice Fields at C-Band: Analysis and Phenology Retrieval. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 2977–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Li, K.; Liu, L.; Shao, Y.; Brisco, B.; Li, W.G. Rice growth monitoring using simulated compact polarimetric C band SAR. Radio Sci. 2014, 49, 1300–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, S.; Ressel, R. Arctic sea ice characterization using RISAT-1 compact-pol SAR imagery and feature evaluation: A case study over North-East Greenland. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 3504–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Espeseth, M.; Brekke, C.; Johansson, A. Assessment of RISAT-1 and RADARSAT-2 for Sea Ice Observations from a Hybrid-Polarity Perspective. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.Y.; Perrie, W. Sea Ice Characterization and Classification Using Hybrid Polarimetry SAR. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 4998–5010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabboor, M.; Iris, S.; Singhroy, V. The RADARSAT Constellation Mission in Support of Environmental Applications. Proceedings 2018, 2, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chenier, R.; Omari, K.; Ahola, R.; Sagram, M. Charting Dynamic Areas in the Mackenzie River with RADARSAT-2, Simulated RADARSAT Constellation Mission and Optical Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, T.; Zhang, G.; Perrie, W.; Zhang, B.; Guan, C.; Khurshid, S.; Warner, K.; Sun, J. Ocean Wind Retrieval Models for RADARSAT Constellation Mission Compact Polarimetry SAR. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, J.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Z.-S.; Song, J. The extended bragg scattering model-based method for ship and oil-spill observation using compact polarimetric SAR. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 3760–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasankar, T.; Srivastava, H.S.; Sharma, P.K.; Kumar, D.; Patel, P. Study of hybrid polarimetric parameters generated from risat-1 SAR data for various land cover targets. Int. J. Adv. Remote Sens. Gis Grogr. 2015, 3, 32–42. [Google Scholar]
- Allard, M.; Calmels, F.; Fortier, D.; Laurent, C.; L’Hérault, E.; Vinet, F. Cartographie des conditions de pergélisol dans les communautés du Nunavik en vue de l’adaptation au réchauffement climatique. In Réalisé Pour le Compte d’Ouranos, Ressources Naturelles Canada; Centre D’études Nordiques, Université Laval: Québec City, QC, Canada, 2007; 42p, Available online: https://www.ouranos.ca/publication-scientifique/RapportAllard2007_FR.pdf (accessed on 11 January 2020).
- Vinet, F. Géomorphologie, Stratigraphie et Évolution du Niveau Marin Holocène D’une Vallée Soumise à des Conditions Macrotidales en Régression Forcée, Région de Tasiujaq, Nunavik. Master’s Thesis, Université Laval, Département de Géographie, Québec City, QC, Canada, 2008. Unpublished. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11794/19578 (accessed on 12 January 2020).
- Arbic, B.K.; St-Laurent, P.; Sutherland, G.; Garrett, C. On the resonance and influence of the tides in Ungava Bay and HudsonStrait. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dignard, N.; Michaud, A. La Flore Vasculaire de L’aire D’étude du Projet de Parc National de la Baie-Aux-Feuilles, Québec (58°45′N., 69°35′O.); Ministère des Ressources Naturelles, Direction de la Recherche Forestière: Québec City, QC, Canada, 2013; 218p. Available online: https://mffp.gouv.qc.ca/nos-publications/flore-vasculaire-baie-aux-feuilles/ (accessed on 12 January 2020).
- Touzi, R.; Charbonneau, F.J. PWS: A friendly and effective tool for polarimetric image analysis. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 30, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lawrence, R.L.; Wood, S.D.; Sheley, R.L. Mapping invasive plants using hyperspectral imagery and Breiman Cutler classifications (random forest). Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Galiano, V.F.; Ghimire, B.; Rogan, J.; Chica-Olmo, M.; Rigol-Sanchez, J.P. An assessment of the effectiveness of a random forest classifier for land-cover classification. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 67, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanBeijma, S.; Comber, A.; Lamb, A. Random forest classification of salt marsh vegetation habitats using quad-polarimetric airborne SAR, elevation and optical RS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 149, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, J.M.; Knight, J.F.; Gallant, A.L. Influence of Multi-Source and Multi-Temporal Remotely Sensed and Ancillary Data on the Accuracy of Random Forest Classification of Wetlands in Northern Minnesota. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3212–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Archer, A.W. World’s highest tides: Hypertidal coastal systems in North America, South America, and Europe. Sediment. Geol. 2013, 284–285, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Water | Wet Soil | Dry Soil | Bare Ground | Exposed Rocks | Vegetation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HH | 29.4 | 15.2 | 12.3 | 12.3 | 2.7 | 10.9 |
| HV | 34.6 | 26.5 | 23.9 | 22.1 | 14.1 | 18.5 |
| VV | 28.1 | 15.2 | 12.5 | 12.7 | 2.9 | 11.3 |
| RH | 23.4 | 14.9 | 10.2 | 12.8 | 5.4 | 12.1 |
| RV | 23.2 | 14.9 | 11.2 | 13.3 | 6.3 | 12.3 |
| RR | 23.5 | 18.2 | 14.2 | 16.6 | 10.7 | 13.1 |
| RL | 23.1 | 13 | 8.8 | 11.1 | 3.6 | 11.4 |
| Parameters | Producer’s Accuracy (%) | User’s Accuracy (%) | Overall Accuracy (%) | Kappa Coef. | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Wet Soil | Dry Soil | Bare Ground | Veg. | Exposed Rocks | Water | Wet Soil | Dry Soil | Bare Ground | Veg. | Exposed Rocks | ||||
| Polar | FD | 97.31 | 42.72 | 41.01 | 57.19 | 47.29 | 36.74 | 93.53 | 65.67 | 37.01 | 66.09 | 50.41 | 17.14 | 67.08 | 0.564 |
| Touzi * | 94.84 | 42.72 | 58.99 | 72.75 | 64.00 | 42.86 | 87.50 | 94.44 | 76.92 | 20.00 | 77.78 | 10.00 | 71.08 | 0.611 | |
| m-delta | 97.31 | 55.34 | 28.78 | 53.29 | 20.16 | 20.00 | 93.94 | 31.32 | 27.40 | 54.27 | 41.94 | 50.00 | 62.08 | 0.493 | |
| Dual | HH/HV | 94.85 | 49.33 | 33.91 | 55.32 | 46.09 | 20.46 | 95.63 | 50.69 | 35.14 | 61.18 | 33.97 | 23.08 | 64.40 | 0.529 |
| RH/RV | 97.31 | 55.34 | 17.27 | 51.20 | 11.63 | 18.37 | 93.53 | 24.89 | 20.51 | 52.94 | 81.00 | 30.61 | 59.17 | 0.455 | |
| RR/RL | 97.31 | 55.34 | 20.86 | 53.29 | 21.71 | 14.29 | 93.53 | 28.64 | 24.58 | 53.45 | 40.00 | 43.75 | 61.08 | 0.479 | |
| HH/VV | 94.17 | 42.72 | 25.90 | 57.49 | 20.16 | 20.41 | 95.24 | 33.85 | 30.25 | 55.01 | 21.85 | 23.81 | 60.67 | 0.475 | |
| Single | DoD | 94.62 | 0.00 | 13.67 | 25.15 | 16.28 | 38.78 | 71.04 | 0.00 | 19.19 | 48.84 | 17.50 | 8.84 | 47.08 | 0.293 |
| Cor. coef. | 92.83 | 28.16 | 1.44 | 0.00 | 14.73 | 42.86 | 69.58 | 13.49 | 25.00 | 0.00 | 20.88 | 7.22 | 40.42 | 0.238 | |
| Cir. pol. rat. | 86.32 | 78.64 | 0.00 | 6.29 | 1.55 | 4.08 | 74.76 | 13.73 | 0.00 | 28.77 | 20.00 | 0.00 | 40.92 | 0.242 | |
| Conformity | 92.38 | 47.57 | 0.00 | 27.27 | 8.00 | 24.49 | 64.58 | 13.39 | 0.00 | 42.27 | 16.67 | 12.37 | 42.83 | 0.238 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Omari, K.; Chenier, R.; Touzi, R.; Sagram, M. Investigation of C-Band SAR Polarimetry for Mapping a High-Tidal Coastal Environment in Northern Canada. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1941. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12121941
Omari K, Chenier R, Touzi R, Sagram M. Investigation of C-Band SAR Polarimetry for Mapping a High-Tidal Coastal Environment in Northern Canada. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(12):1941. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12121941
Chicago/Turabian StyleOmari, Khalid, René Chenier, Ridha Touzi, and Mesha Sagram. 2020. "Investigation of C-Band SAR Polarimetry for Mapping a High-Tidal Coastal Environment in Northern Canada" Remote Sensing 12, no. 12: 1941. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12121941
APA StyleOmari, K., Chenier, R., Touzi, R., & Sagram, M. (2020). Investigation of C-Band SAR Polarimetry for Mapping a High-Tidal Coastal Environment in Northern Canada. Remote Sensing, 12(12), 1941. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12121941






