Phaseless Radar Coincidence Imaging with a MIMO SAR Platform
Abstract
1. Introduction
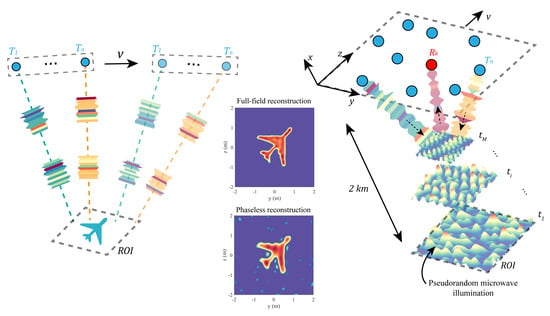
2. Results
2.1. Imaging Configuration
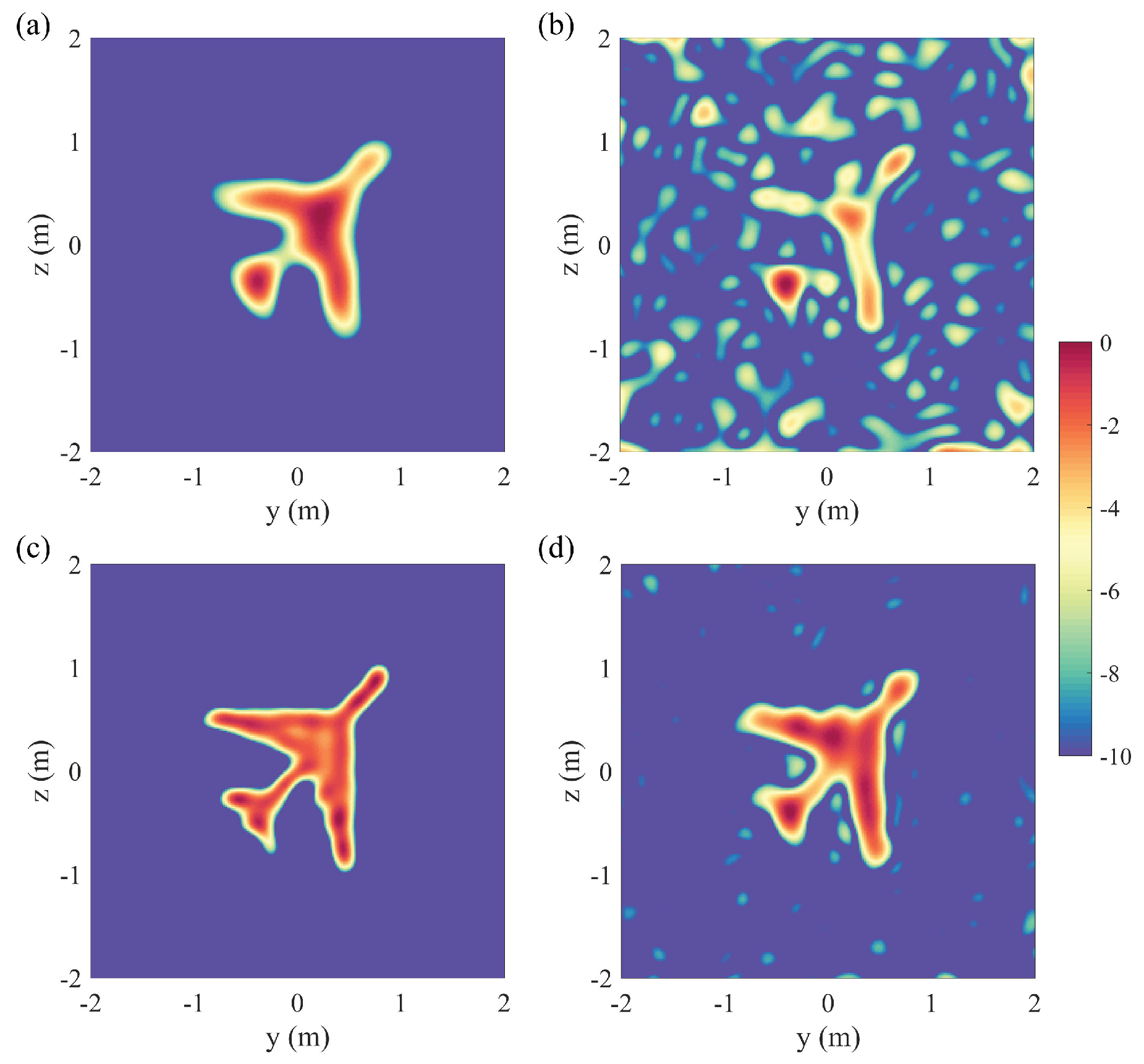
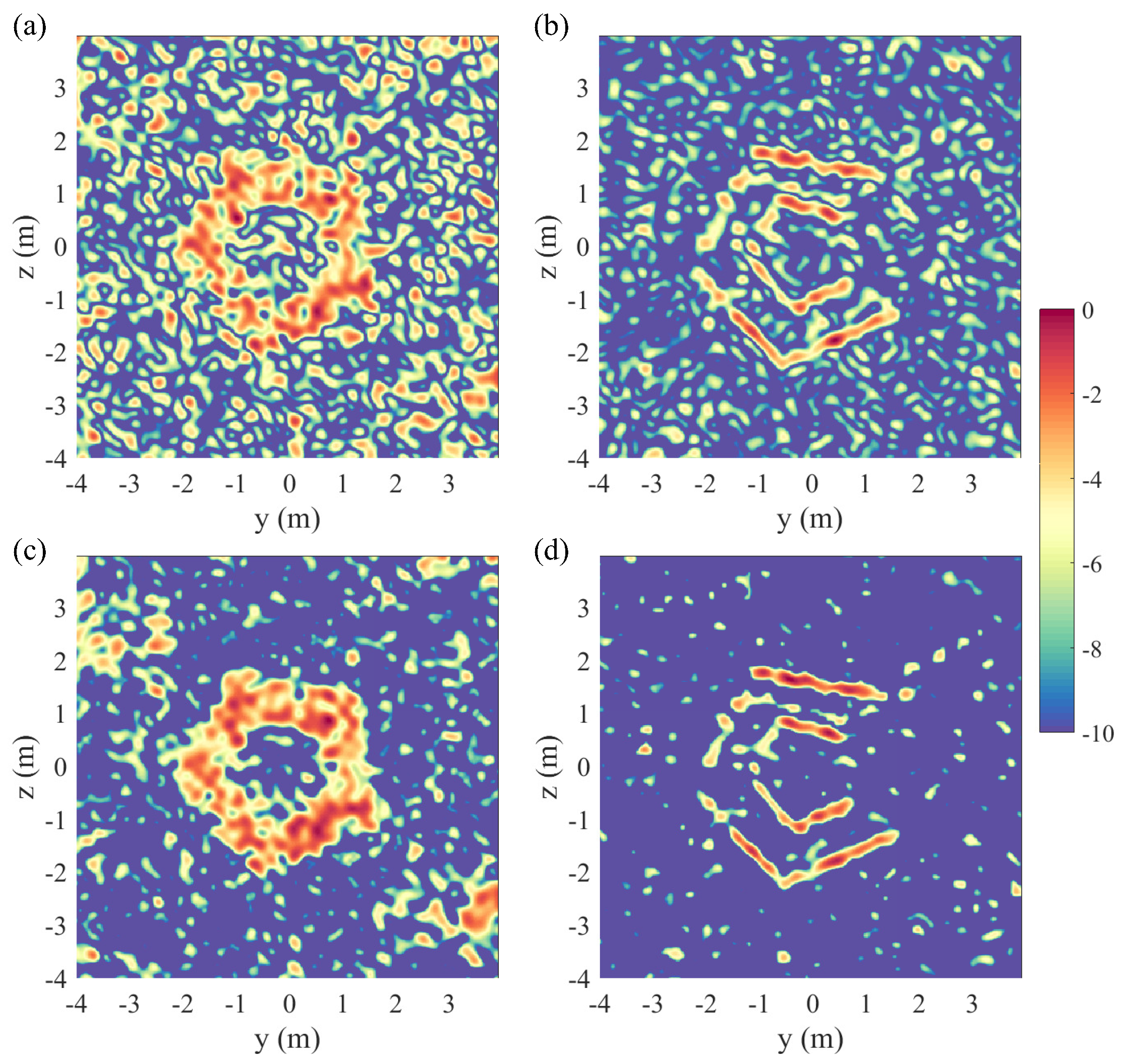
2.2. Reconstruction
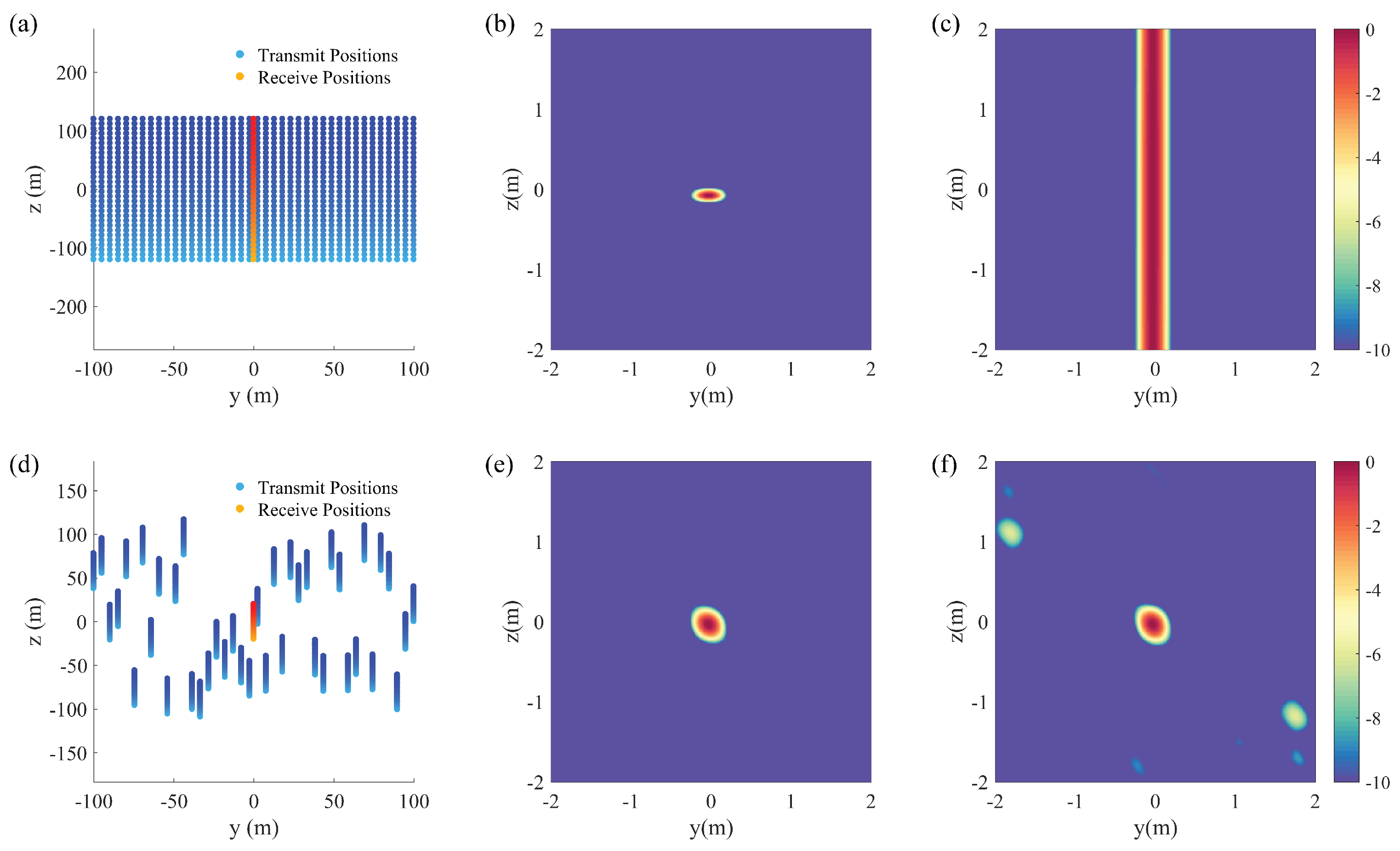
2.2.1. Single Receiver
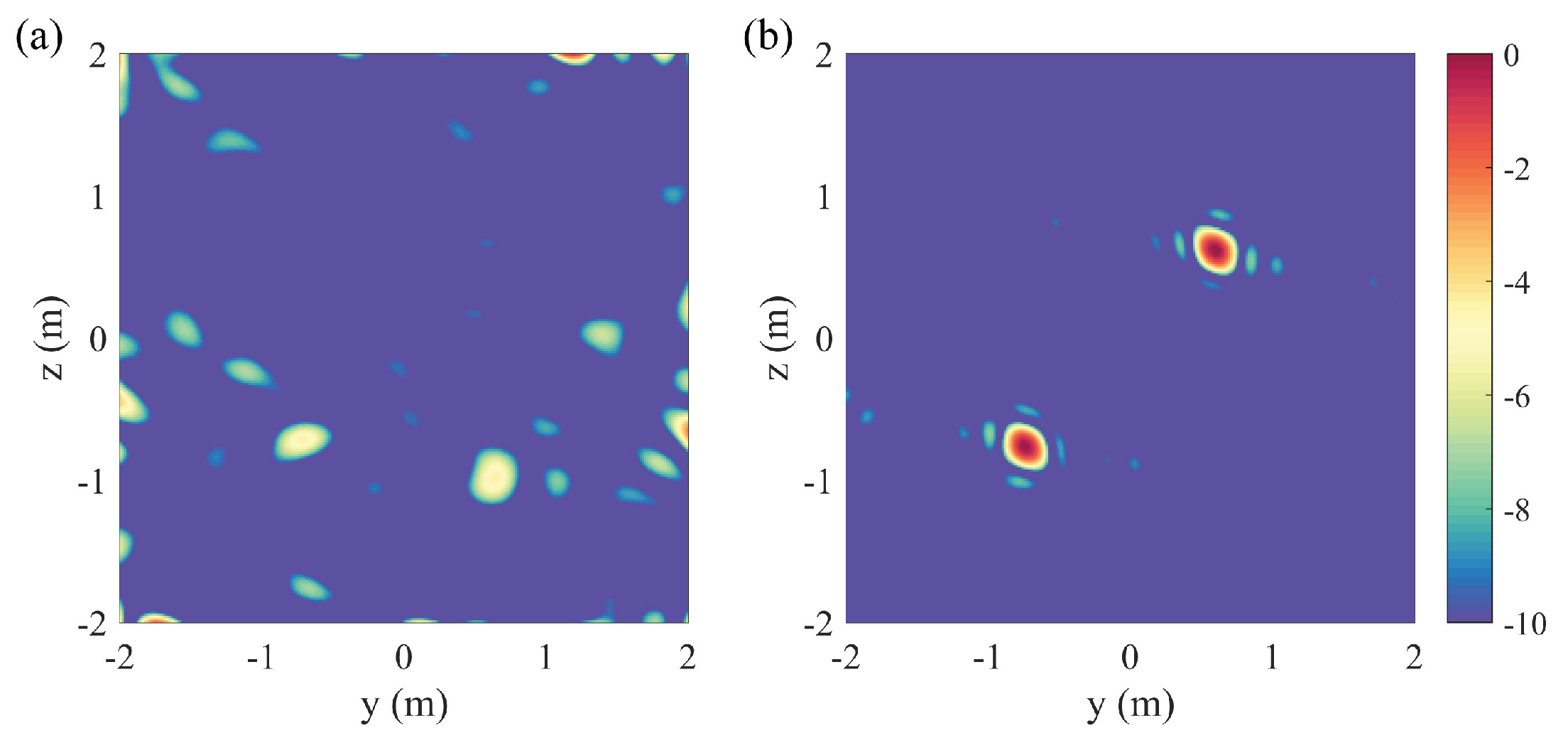
2.2.2. Multiple Receivers
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RCI | Radar Coincidence Imaging |
| MIMO | Multiple-Input Multiple-Output |
| MISO | Multiple-Input Single-Output |
| SIMO | Single-Input Multiple-Output |
| SAR | Synthetic Aperture Radar |
| UAV | Unmanned Aerial Vehicle |
| SVD | Singular Value Decomposition |
| GGI | Gradient Ghost Imaging |
References
- Li, D.; Li, X.; Qin, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, H. Radar coincidence imaging: An instantaneous imaging technique with stochastic signals. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 2261–2277. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Zhang, A.; Xu, Z.; Dong, X. Radar coincidence imaging with random microwave source. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2015, 14, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, X.; Cheng, Y.; Qin, Y.L.; Wang, H. Three dimensional radar coincidence imaging. Prog. Electromagn. Res. M 2013, 33, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Xu, X.; Qin, Y.; Wang, H. Radar coincidence imaging with stochastic frequency modulated array. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2017, 11, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Dong, X.; Zhang, M.; Lu, R.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, A. A Super-Resolution Computational Coincidence Imaging Method Based on SIMO Radar System. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 2265–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soumekh, M. Synthetic Aperture Radar Signal Processing; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1999; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Bliss, D.; Forsythe, K. Multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) radar and imaging: Degrees of freedom and resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE Thirty-Seventh Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 9–12 November 2003; Volume 1, pp. 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- Haimovich, A.M.; Blum, R.S.; Cimini, L.J. MIMO radar with widely separated antennas. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2008, 25, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, G. MIMO-SAR: Opportunities and pitfalls. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 2628–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin, J.M. Phased array radars in France: Present and future. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Phased Array Systems and Technology, Boston, MA, USA, 15–18 October 1996; pp. 458–462. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.Q. MIMO SAR OFDM chirp waveform diversity design with random matrix modulation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Younis, M.; Moreira, A.; Wiesbeck, W. Spaceborne MIMO synthetic aperture radar for multimodal operation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 2453–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Q. Large time-bandwidth product MIMO radar waveform design based on chirp rate diversity. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Blum, R.S. Phase synchronization for coherent MIMO radar: Algorithms and their analysis. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2011, 59, 5538–5557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godrich, H.; Haimovich, A.M.; Poor, H.V. An analysis of phase synchronization mismatch sensitivity for coherent MIMO radar systems. In Proceedings of the 3rd IEEE International Workshop on Computational Advances in Multi-Sensor Adaptive Processing (CAMSAP), Aruba, Dutch Antilles, The Netherlands, 13–16 December 2009; pp. 153–156. [Google Scholar]
- Akçakaya, M.; Nehorai, A. MIMO radar detection and adaptive design under a phase synchronization mismatch. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2010, 58, 4994–5005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Dekker, P.; Mallorquí, J.J.; Serra-Morales, P.; Sanz-Marcos, J. Phase synchronization and Doppler centroid estimation in fixed receiver bistatic SAR systems. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 3459–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollub, J.; Yurduseven, O.; Trofatter, K.; Arnitz, D.; Imani, M.; Sleasman, T.; Boyarsky, M.; Rose, A.; Pedross-Engel, A.; Odabasi, H.; et al. Large metasurface aperture for millimeter wave computational imaging at the human-scale. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatti, A.; Bache, M.; Magatti, D.; Brambilla, E.; Ferri, F.; Lugiato, L. Coherent imaging with pseudo-thermal incoherent light. J. Mod. Opt. 2006, 53, 739–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, J.H. Computational ghost imaging. Phys. Rev. A 2008, 78, 061802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromberg, Y.; Katz, O.; Silberberg, Y. Ghost imaging with a single detector. Phys. Rev. A 2009, 79, 053840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, J.W. Statistical Optics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hardy, N.D.; Shapiro, J.H. Computational ghost imaging versus imaging laser radar for three-dimensional imaging. Phys. Rev. A 2013, 87, 023820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, N.D.; Shapiro, J.H. Reflective ghost imaging through turbulence. Phys. Rev. A 2011, 84, 063824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkmen, B.I. Computational ghost imaging for remote sensing. JOSA A 2012, 29, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maci, S.; Minatti, G.; Casaletti, M.; Bosiljevac, M. Metasurfing: Addressing waves on impenetrable metasurfaces. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2011, 10, 1499–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Ovejero, D.; Chahat, N.; Sauleau, R.; Chattopadhyay, G.; Maci, S.; Ettorre, M. Additive Manufactured Metal-Only Modulated Metasurface Antennas. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 6106–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleasman, T.; Imani, M.F.; Gollub, J.N.; Smith, D.R. Dynamic metamaterial aperture for microwave imaging. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 204104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyarsky, M.; Sleasman, T.; Pulido-Mancera, L.; Fromenteze, T.; Pedross-Engel, A.; Watts, C.M.; Imani, M.F.; Reynolds, M.S.; Smith, D.R. Synthetic aperture radar with dynamic metasurface antennas: A conceptual development. JOSA A 2017, 34, A22–A36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, C.M.; Pedross-Engel, A.; Smith, D.R.; Reynolds, M.S. X-band SAR imaging with a liquid-crystal-based dynamic metasurface antenna. JOSA B 2017, 34, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleasman, T.; Boyarsky, M.; Pulido-Mancera, L.; Fromenteze, T.; Imani, M.F.; Reynolds, M.S.; Smith, D.R. Experimental Synthetic Aperture Radar with Dynamic Metasurfaces. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 6864–6877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.R.; Yurduseven, O.; Mancera, L.P.; Bowen, P.; Kundtz, N.B. Analysis of a waveguide-fed metasurface antenna. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2017, 8, 054048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skolnik, M.I. Introduction to Radar Systems; McGraw Hill Book Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Diebold, A.V.; Imani, M.F.; Sleasman, T.; Smith, D.R. Phaseless computational ghost imaging at microwave frequencies using a dynamic metasurface aperture. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 2142–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J. Transfer functions in lensless ghost-imaging systems. Phys. Rev. A 2008, 78, 043823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diebold, A.V.; Imani, M.F.; Sleasman, T.; Smith, D.R. Phaseless coherent and incoherent microwave ghost imaging with dynamic metasurface apertures. Optica 2018, 5, 1529–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, D.J. Optical Imaging and Spectroscopy; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Marks, D.L.; Gollub, J.; Smith, D.R. Spatially resolving antenna arrays using frequency diversity. JOSA A 2016, 33, 899–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lustig, M.; Donoho, D.; Pauly, J.M. Sparse MRI: The application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2007, 58, 1182–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohmann, A.W.; Dorsch, R.G.; Mendlovic, D.; Zalevsky, Z.; Ferreira, C. Space—Bandwidth product of optical signals and systems. JOSA A 1996, 13, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Blum, R.S. Cramer-Rao bound for MIMO radar target localization with phase errors. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2010, 17, 83–86. [Google Scholar]
- Krieger, G.; Moreira, A. Spaceborne bi-and multistatic SAR: Potential and challenges. IEE Proc.-Radar Sonar Navig. 2006, 153, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.S. Electronic Microwave Imaging with Planar Multistatic Arrays; Logos Verlag Berlin GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, J.W. Introduction to Fourier Optics; Roberts and Company Publishers: Englewood, CO, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Guo, S.; Cao, J.; Guan, J.; Gao, F. Object reconstitution using pseudo-inverse for ghost imaging. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 30063–30073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.F.; Yao, X.R.; Lan, R.M.; Wang, C.; Zhai, G.J. Edge detection based on gradient ghost imaging. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 33802–33811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gureyev, T.; Paganin, D.; Kozlov, A.; Nesterets, Y.I.; Quiney, H. Complementary aspects of spatial resolution and signal-to-noise ratio in computational imaging. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 97, 053819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, O.; Bromberg, Y.; Silberberg, Y. Compressive ghost imaging. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 131110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldar, Y.C.; Kutyniok, G. Compressed Sensing: Theory and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Potter, L.C.; Ertin, E.; Parker, J.T.; Cetin, M. Sparsity and compressed sensing in radar imaging. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 1006–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, M.; Stojanovic, I.; Onhon, O.; Varshney, K.; Samadi, S.; Karl, W.C.; Willsky, A.S. Sparsity-driven synthetic aperture radar imaging: Reconstruction, autofocusing, moving targets, and compressed sensing. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2014, 31, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Figueiredo, M.A. A new TwIST: Two-step iterative shrinkage/thresholding algorithms for image restoration. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2007, 16, 2992–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehm, M.E.; McCain, S.T.; Pitsianis, N.P.; Brady, D.J.; Potuluri, P.; Sullivan, M.E. Static two-dimensional aperture coding for multimodal, multiplex spectroscopy. Appl. Opt. 2006, 45, 2965–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diebold, A.V.; Imani, M.F.; Smith, D.R. Phaseless Radar Coincidence Imaging with a MIMO SAR Platform. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11050533
Diebold AV, Imani MF, Smith DR. Phaseless Radar Coincidence Imaging with a MIMO SAR Platform. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(5):533. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11050533
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiebold, Aaron V., Mohammadreza F. Imani, and David R. Smith. 2019. "Phaseless Radar Coincidence Imaging with a MIMO SAR Platform" Remote Sensing 11, no. 5: 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11050533
APA StyleDiebold, A. V., Imani, M. F., & Smith, D. R. (2019). Phaseless Radar Coincidence Imaging with a MIMO SAR Platform. Remote Sensing, 11(5), 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11050533