Sinking Tide Gauge Revealed by Space-borne InSAR: Implications for Sea Level Acceleration at Pohang, South Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
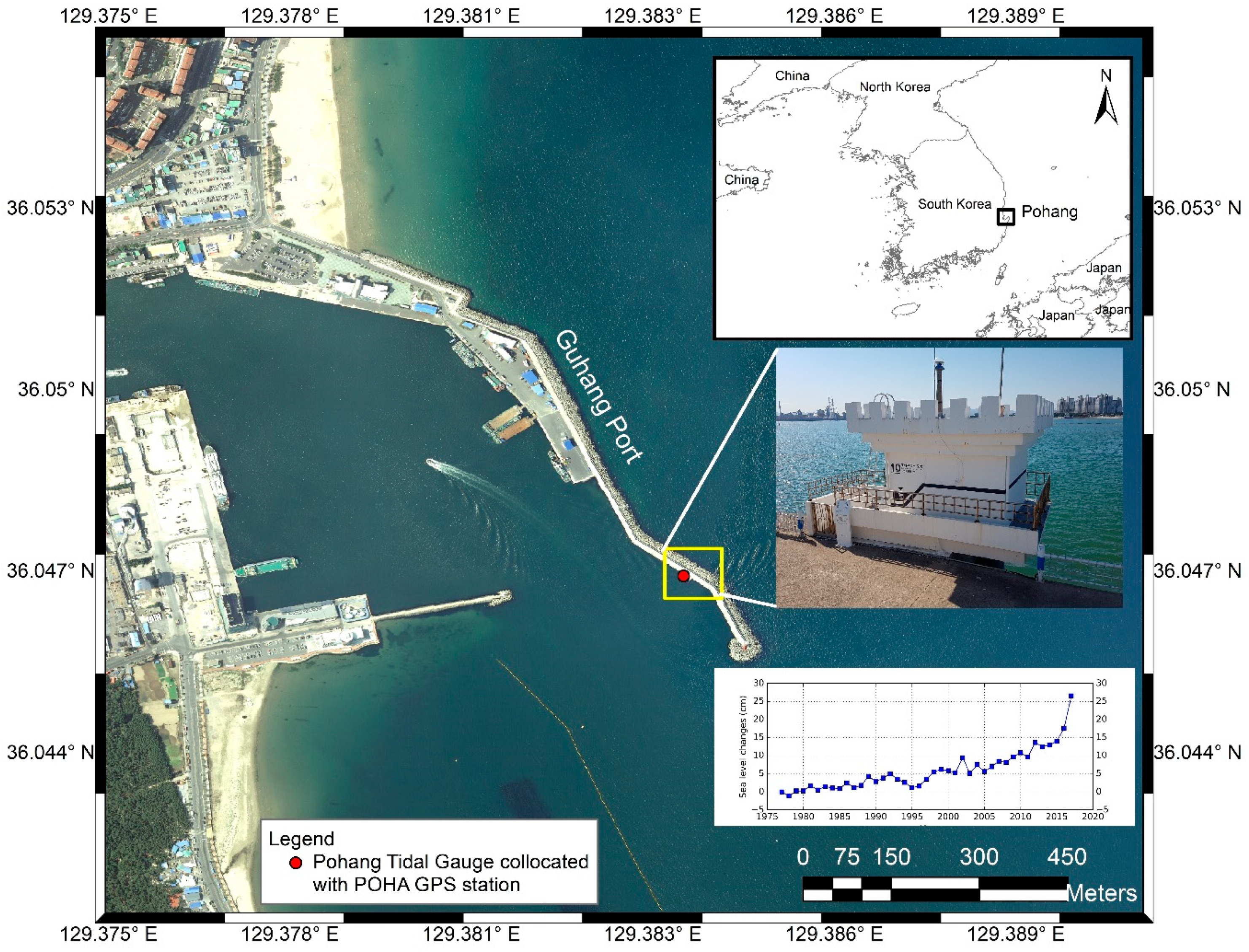
2. Study Area
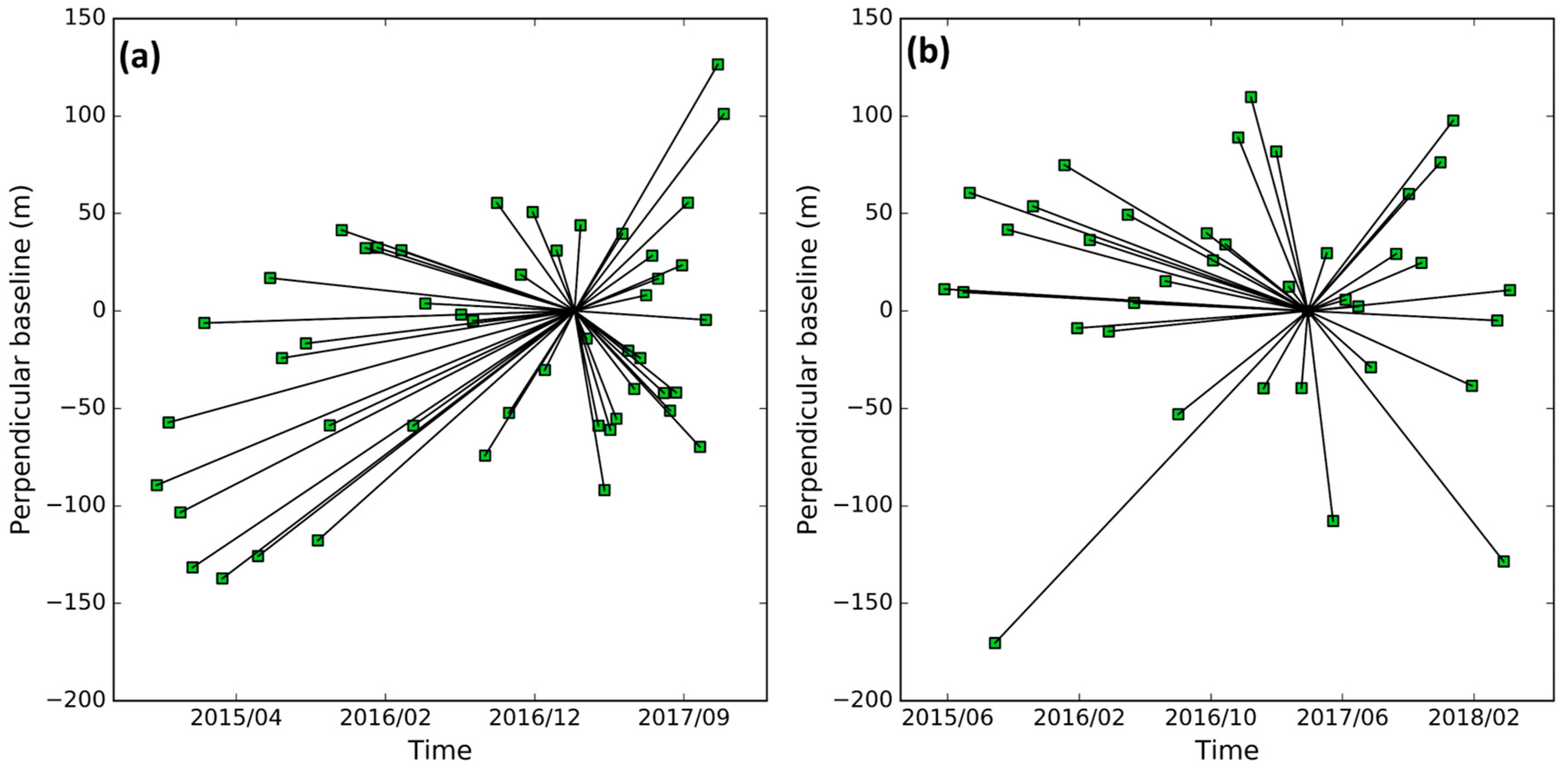
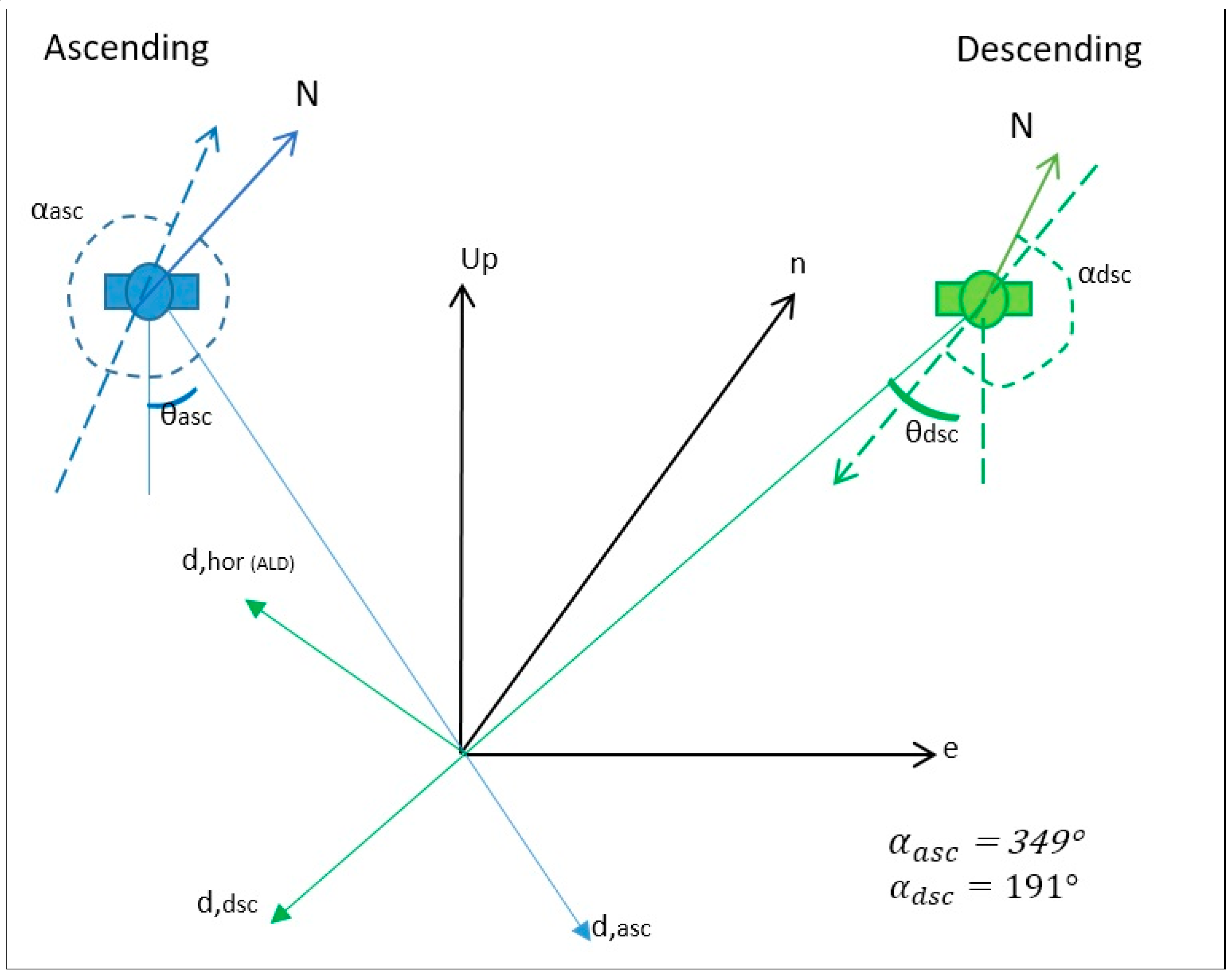
3. Methodology: SAR Data Collection and Time-Series PS-InSAR
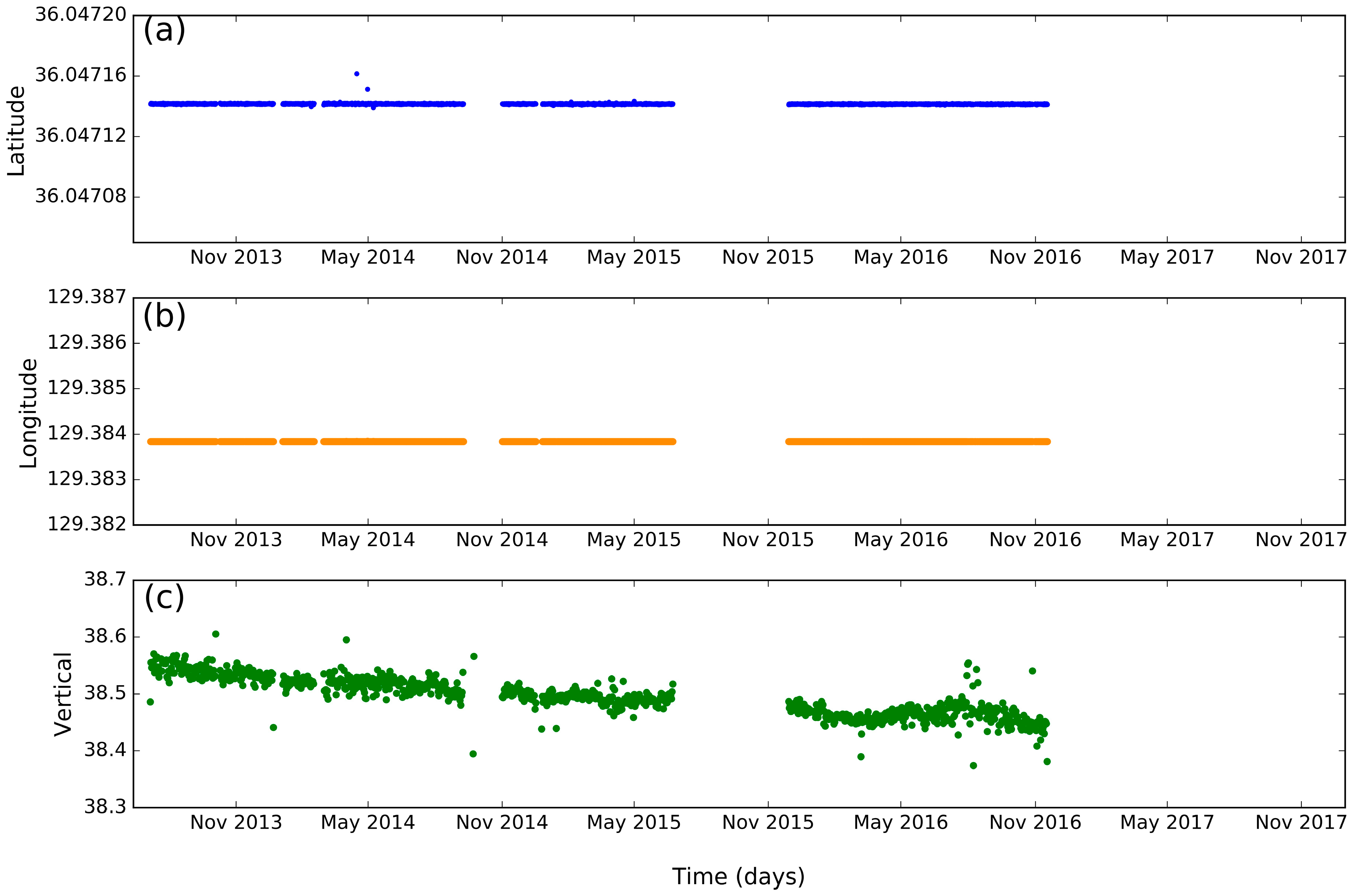
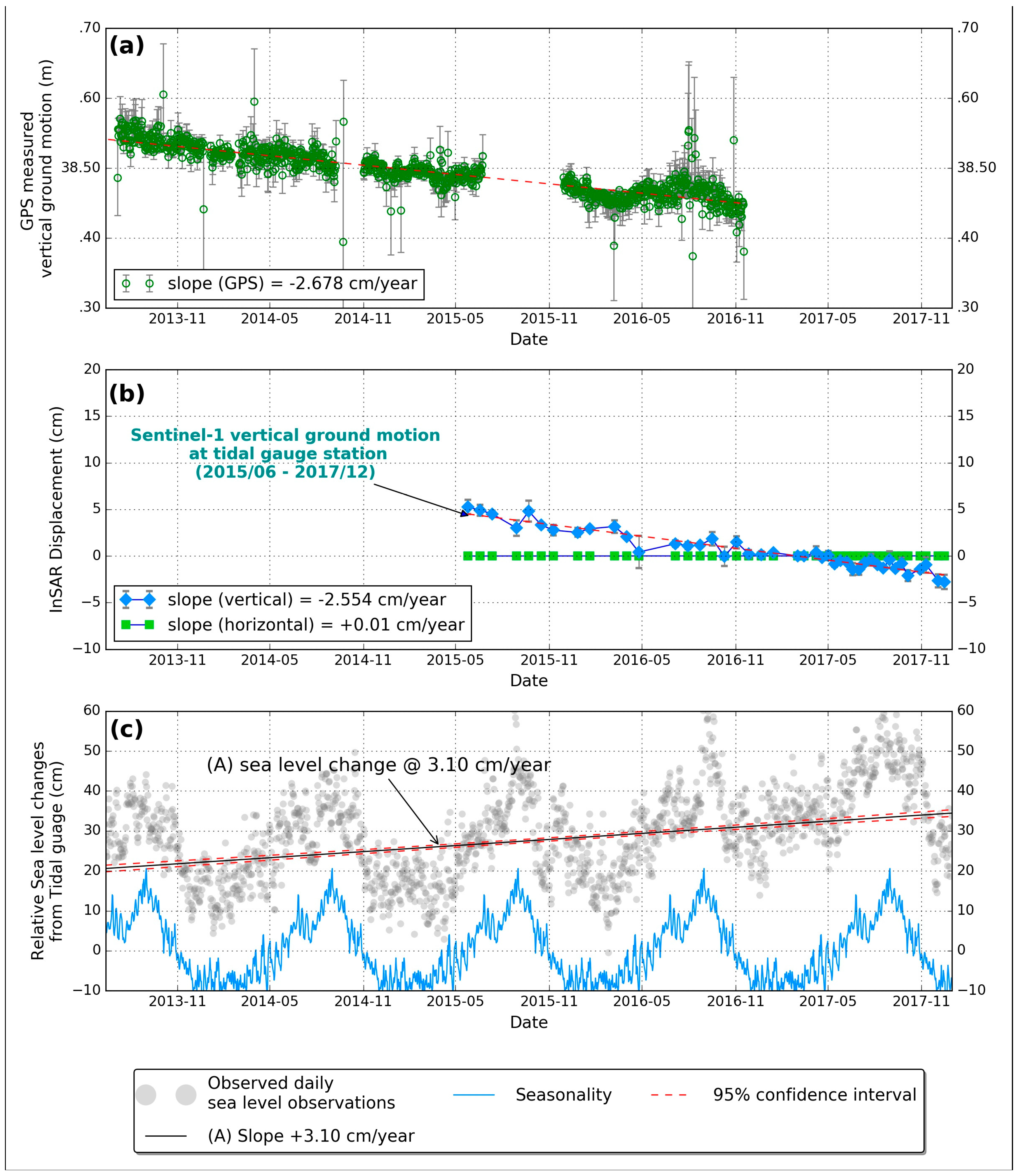
4. Vertical Ground Motion at Pohang Tide Gauge Station
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clark, P.U.; Shakun, J.D.; Marcott, S.A.; Mix, A.C.; Eby, M.; Kulp, S.; Levermann, A.; Milne, G.A.; Pfister, P.L.; Santer, B.D.; et al. Consequences of twenty-first-century policy for multi-millennial climate and sea-level change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, C.C.; Morrow, E.; Kopp, R.E.; Mitrovica, J.X. Probabilistic reanalysis of twentieth-century sea-level rise. Nature 2015, 517, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Church, J.A.; Clark, P.U.; Cazenave, A.; Gregory, J.M.; Jevrejeva, S.; Levermann, A.; Merrifield, M.A.; Milne, G.A.; Nerem, R.S.; Nunn, P.D.; et al. Sea-level rise by 2100. Science 2013, 342, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodworth, P.L.; White, N.J.; Jevrejeva, S.; Holgate, S.J.; Church, J.A.; Gehrels, W.R. Evidence for the accelerations of sea level on multi-decade and century timescales. Int. J. Climatol. 2009, 29, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wöppelmann, G.; Pouvreau, N.; Coulomb, A.; Simon, B.; Woodworth, P.L. Tide gauge datum continuity at brest since 1711: France’s longest sea-level record. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez, M.; Woodworth, P.L. Changes in extreme high water levels based on a quasi-global tide-gauge data set. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyssignac, B.; Becker, M.; Llovel, W.; Cazenave, A. An assessment of two-dimensional past sea level reconstructions over 1950–2009 based on tide-gauge data and different input sea level grids. Surv. Geophys. 2012, 33, 945–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyssignac, B.; Calafat, F.M.; Somot, S.; Rupolo, V.; Stocchi, P.; Llovel, W.; Cazenave, A. Two-dimensional reconstruction of the Mediterranean sea level over 1970–2006 from tide gage data and regional ocean circulation model outputs. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2011, 77, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ablain, M.; Cazenave, A.; Valladeau, G.; Guinehut, S. A new assessment of the error budget of global mean sea level rate estimated by satellite altimetry over 1993–2008. Ocean Sci. 2009, 5, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchum, G.T. An improved calibration of satellite altimetric heights using tide gauge sea levels with adjustment for land motion. Mar. Geod. 2000, 23, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.-L.; Haines, B.J. The challenges in long-term altimetry calibration for addressing the problem of global sea level change. Adv. Space Res. 2013, 51, 1284–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, C.S.; White, N.J.; Church, J.A.; King, M.A.; Burgette, R.J.; Legresy, B. Unabated global mean sea-level rise over the satellite altimeter era. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazenave, A.; Palanisamy, H.; Ablain, M. Contemporary Sea Level Changes from Satellite Altimetry: What Have We Learned? What are the New Challenges? Adv. Space Res. 2018, 62, 1639–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekaert, D.P.S.; Hamlington, B.D.; Buzzanga, B.; Jones, C.E. Spaceborne synthetic aperture radar survey of subsidence in Hampton Roads, Virginia (USA). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goddard, P.B.; Yin, J.; Griffies, S.M.; Zhang, S. An extreme event of sea-level rise along the northeast coast of North America in 2009–2010. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, W.-C.; Hwang, C.; Chen, Y.-A.; Zhang, L.; Chen, K.-H.; Wei, S.-H.; Huang, D.-R.; Lin, S.-H. Land Subsidence in Chiayi, Taiwan, from Compaction Well, Leveling and ALOS/PALSAR: Aquaculture-Induced Relative Sea Level Rise. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karegar, M.A.; Dixon, T.H.; Engelhart, S.E. Subsidence along the atlantic coast of North America: Insights from gps and late holocene relative sea level data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 3126–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Cozannet, G.; Raucoules, D.; Wöppelmann, G.; Garcin, M.; Da Sylva, S.; Meyssignac, B.; Gravelle, M.; Lavigne, F. Vertical ground motion and historical sea-level records in Dakar (Denegal). Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 084016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.Y.; Shum, C.K.; Braun, A.; Mitrovica, J.X. Vertical crustal motion determined by satellite altimetry and tide gauge data in Fennoscandia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wöppelmann, G.; Marcos, M. Vertical land motion as a key to understanding sea level change and variability. Rev. Geophys. 2016, 54, 64–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos, A.G.; Hamlington, B.D.; Thompson, P.R.; Ray, R.D. Future nuisance flooding in Norfolk, VA, from astronomical tides and annual to decadal internal climate variability. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazenave, A.; Nerem, R.S. Present-day sea level change: Observations and causes. Rev. Geophys. 2004, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raucoules, D.; Le Cozannet, G.; Wöppelmann, G.; de Michele, M.; Gravelle, M.; Daag, A.; Marcos, M. High nonlinear urban ground motion in Manila (Philippines) from 1993 to 2010 observed by dinsar: Implications for sea-level measurement. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 139, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltier, W.R.; Tushingham, A.M. Influence of glacial isostatic adjustment on tide gauge measurements of secular sea level change. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1991, 96, 6779–6796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrovica, J.X.; Tamisiea, M.E.; Davis, J.L.; Milne, G.A. Recent mass balance of polar ice sheets inferred from patterns of global sea-level change. Nature 2001, 409, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadil, A.; Denys, P.; Tenzer, R.; Grenfell, H.R.; Willis, P. New zealand 20th century sea level rise: Resolving the vertical land motion using space geodetic and geological data. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2013, 118, 6076–6091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Ma, Z.; Chen, N.; Yang, J.; Chen, N. Coastal sea level projections with improved accounting for vertical land motion. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.; Park, S.-H.; Kim, D.-Y.; Woo, S.-B.; Jeong, K.-Y. Influence of steric effect on the rapid sea level rise at Jeju Island, Korea. J. Coast. Res. 2017, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Cho, K. Sea level rise around Korea: Analysis of tide gauge station data with the ensemble empirical mode decomposition method. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2016, 11, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wöppelmann, G.; Martin Miguez, B.; Bouin, M.N.; Altamimi, Z. Geocentric sea-level trend estimates from gps analyses at relevant tide gauges world-wide. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2007, 57, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wöppelmann, G.; Marcos, M. Coastal sea level rise in Southern Europe and the nonclimate contribution of vertical land motion. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massonnet, D.; Rossi, M.; Carmona, C.; Adragna, F.; Peltzer, G.; Feigl, K.; Rabaute, T. The displacement field of the Landers earthquake mapped by radar interferometry. Nature 1993, 364, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Zebker, H.; Segall, P.; Kampes, B. A new method for measuring deformation on volcanoes and other natural terrains using InSAR persistent scatterers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wöppelmann, G.; Cozannet, G.L.; Michele, M.; Raucoules, D.; Cazenave, A.; Garcin, M.; Hanson, S.; Marcos, M.; Santamaría-Gómez, A. Is land subsidence increasing the exposure to sea level rise in Alexandria, Egypt? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 2953–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S. Spatial Variability in long-term changes of climate and oceanographic conditions in Korea. J. Environ. Biol. 2008, 29, 519–529. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Kang, H.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, M. Changes in the extreme daily rainfall in South Korea. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 2290–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, P.A.; Gurrola, E.; Sacco, G.F.; Zebker, H. The InSAR scientific computing environment. In Proceedings of the 9th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Nürnberg, Germany, 23–26 April 2012; pp. 730–733. [Google Scholar]
- Prats-Iraola, P.; Scheiber, R.; Marotti, L.; Wollstadt, S.; Reigber, A. Tops interferometry with TerraSAR-X. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3179–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Segall, P.; Zebker, H. Persistent scatterer interferometric synthetic aperture radar for crustal deformation analysis, with application to Volcán Alcedo, Galápagos. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.W.; Zebker, H.A. Two-dimensional phase unwrapping with use of statistical models for cost functions in nonlinear optimization. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2001, 18, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motagh, M.; Shamshiri, R.; Haghshenas Haghighi, M.; Wetzel, H.U.; Akbari, B.; Nahavandchi, H.; Roessner, S.; Arabi, S. Quantifying groundwater exploitation induced subsidence in the Rafsanjan plain, southeastern Iran, using InSAR time-series and in situ measurements. Eng. Geol. 2017, 218, 134–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Lin, H. Integrated analysis of SAR interferometric and geological data for investigating long-term reclamation settlement of Chek Lap Kok Airport, Hong Kong. Eng. Geol. 2010, 110, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Min, S.-K.; Weller, E.; Lee, H.; Wang, X.L. Influence of climate variability on extreme ocean surface wave heights assessed from ERA-interim and ERA-20c. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 4031–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiruddin, A.M.; Haigh, I.D.; Tsimplis, M.N.; Calafat, F.M.; Dangendorf, S. The seasonal cycle and variability of sea level in the South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2015, 120, 5490–5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, J.A.; White, N.J. Sea-level rise from the late 19th to the early 21st century. Surv. Geophys. 2011, 32, 585–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Description | Ascending | Descending |
|---|---|---|
| Acquisition Mode | Interferometric wide swath (IW) | |
| No. of scenes | 49 | 42 |
| Incidence angle | 40° | 39° |
| Temporal coverage | November 2014–December 2017 | May 2015–May 2018 |
| Azimuth heading angle | 349° | 191° |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palanisamy Vadivel, S.K.; Kim, D.-j.; Jung, J.; Cho, Y.-K.; Han, K.-J.; Jeong, K.-Y. Sinking Tide Gauge Revealed by Space-borne InSAR: Implications for Sea Level Acceleration at Pohang, South Korea. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11030277
Palanisamy Vadivel SK, Kim D-j, Jung J, Cho Y-K, Han K-J, Jeong K-Y. Sinking Tide Gauge Revealed by Space-borne InSAR: Implications for Sea Level Acceleration at Pohang, South Korea. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(3):277. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11030277
Chicago/Turabian StylePalanisamy Vadivel, Suresh Krishnan, Duk-jin Kim, Jungkyo Jung, Yang-Ki Cho, Ki-Jong Han, and Kwang-Young Jeong. 2019. "Sinking Tide Gauge Revealed by Space-borne InSAR: Implications for Sea Level Acceleration at Pohang, South Korea" Remote Sensing 11, no. 3: 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11030277
APA StylePalanisamy Vadivel, S. K., Kim, D.-j., Jung, J., Cho, Y.-K., Han, K.-J., & Jeong, K.-Y. (2019). Sinking Tide Gauge Revealed by Space-borne InSAR: Implications for Sea Level Acceleration at Pohang, South Korea. Remote Sensing, 11(3), 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11030277






