Modeling the Stereoscopic Features of Mountainous Forest Landscapes for the Extraction of Forest Heights from Stereo Imagery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Descriptions of the LandStereo Model
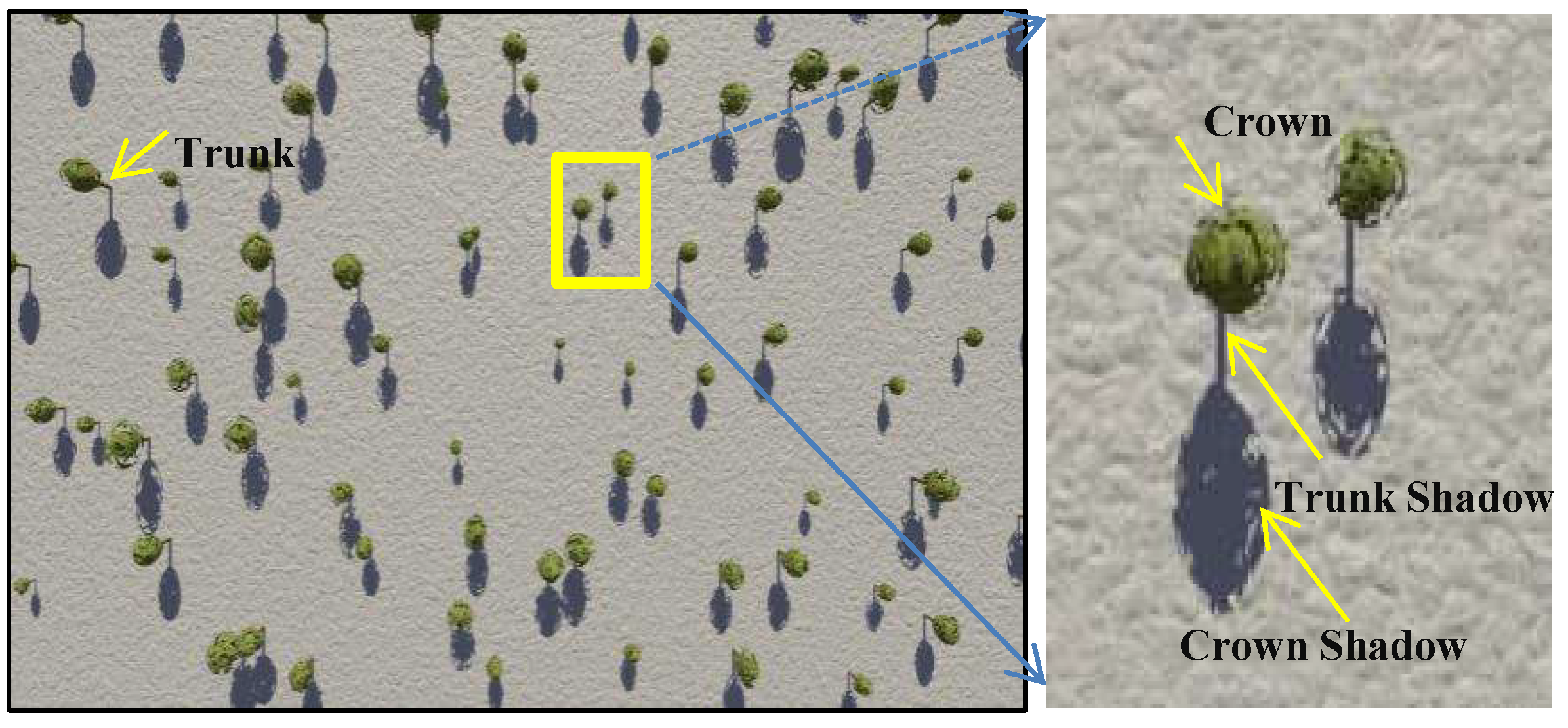
2.1. Features of the Mountainous Forest Landscapes
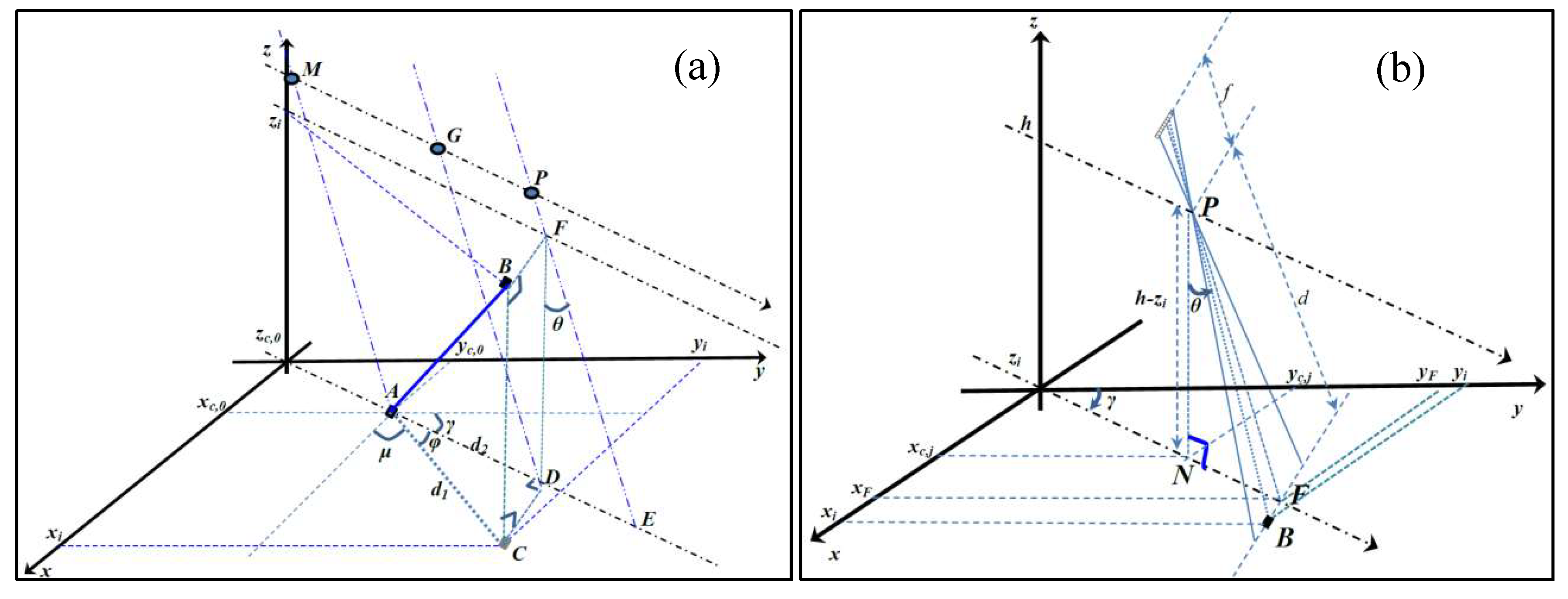
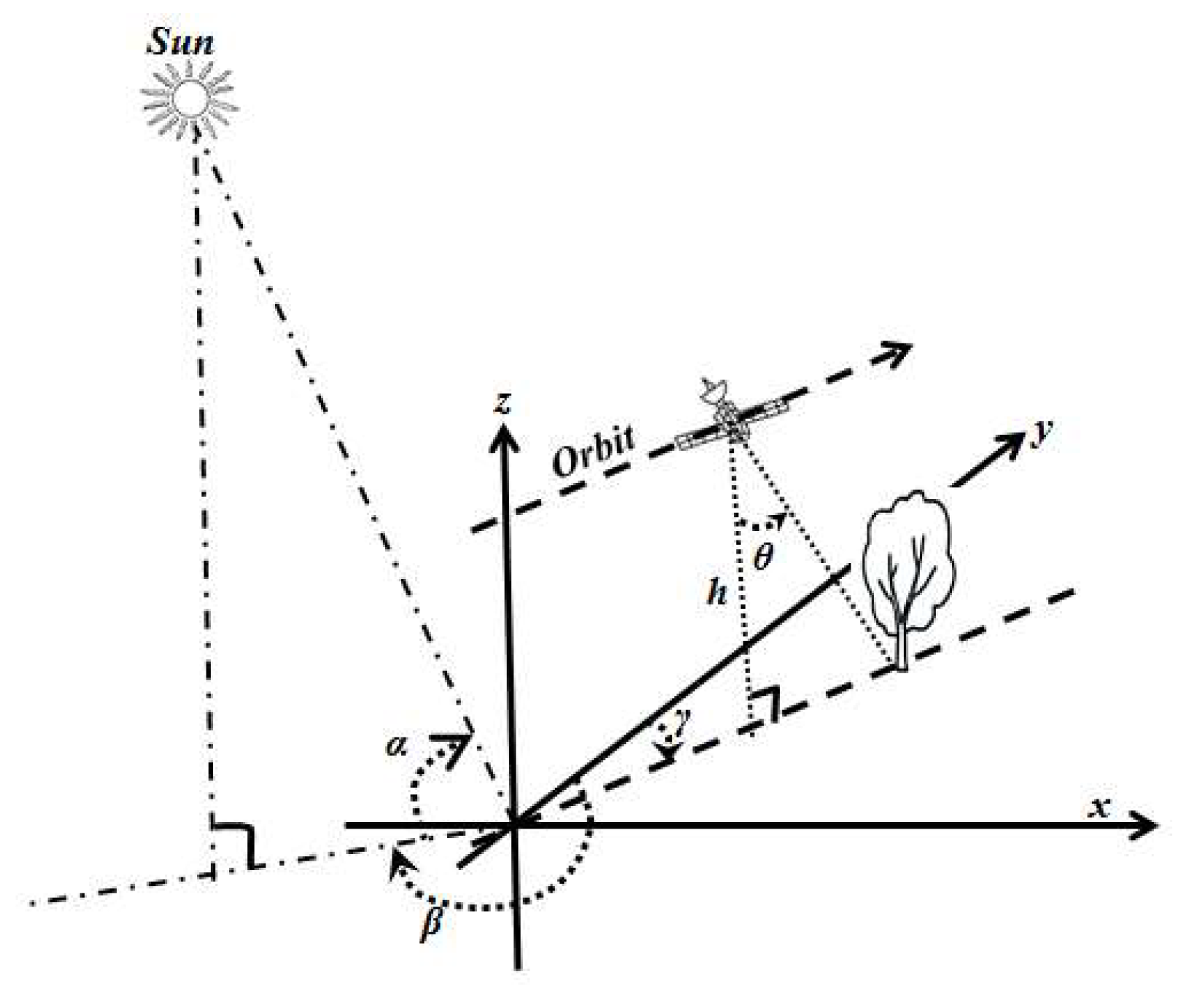
2.2. Settings of the Observation Geometry
3. Building the Geometric Sensor Model
3.1. Description of the Geometric Sensor Model
3.2. Generation of the Ground Control Points
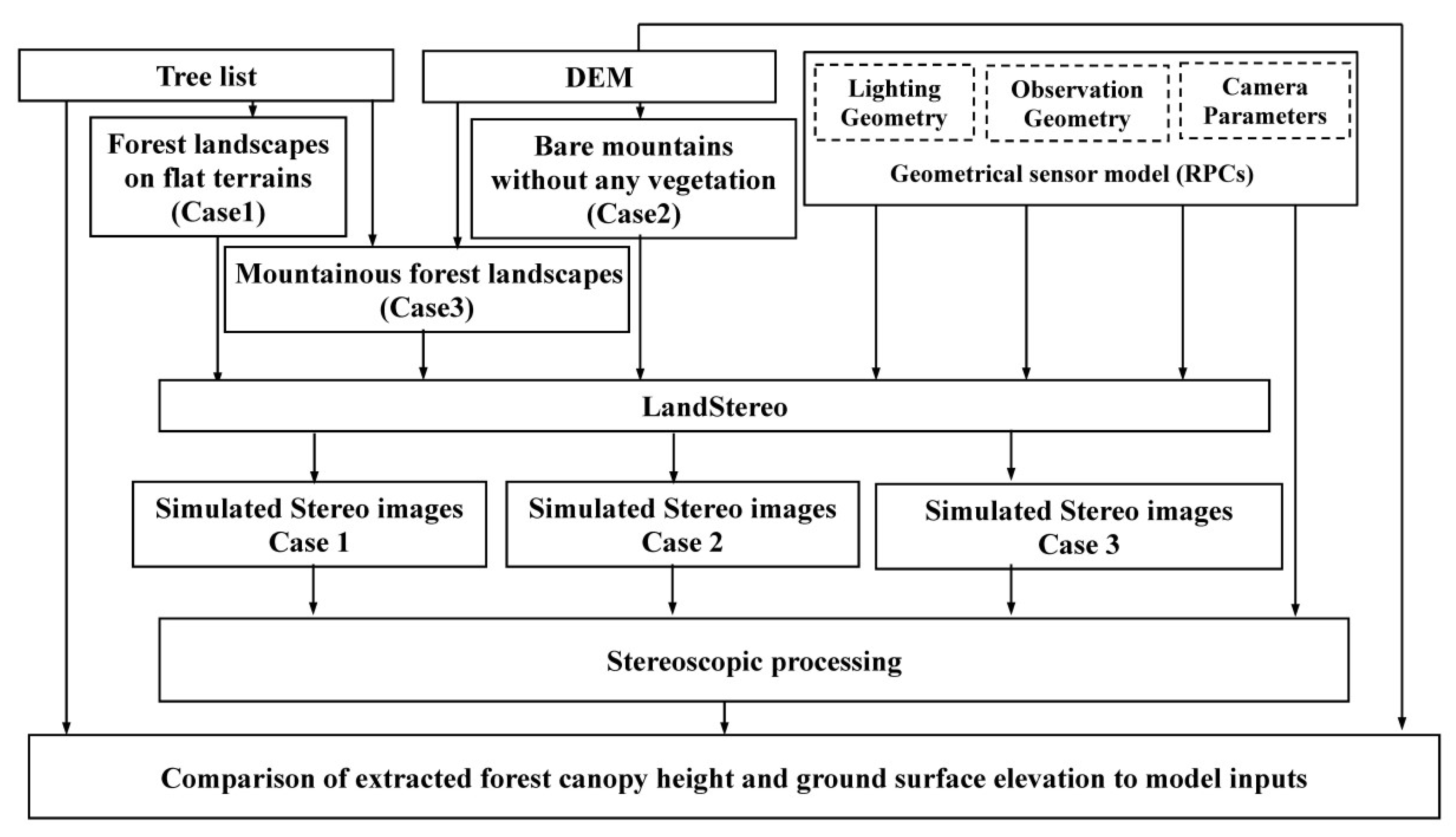
4. Validation Settings of the LandStereo Model
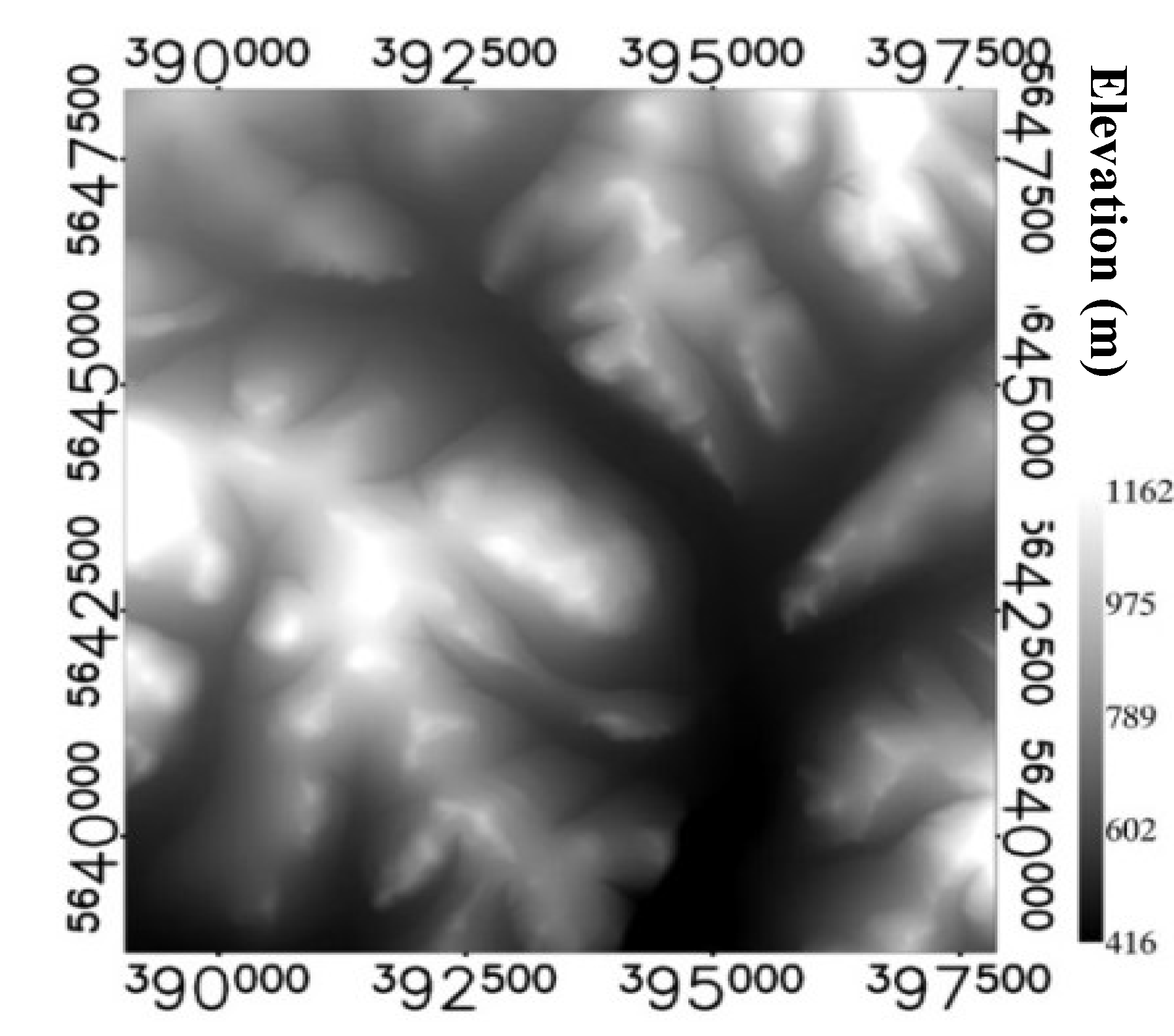
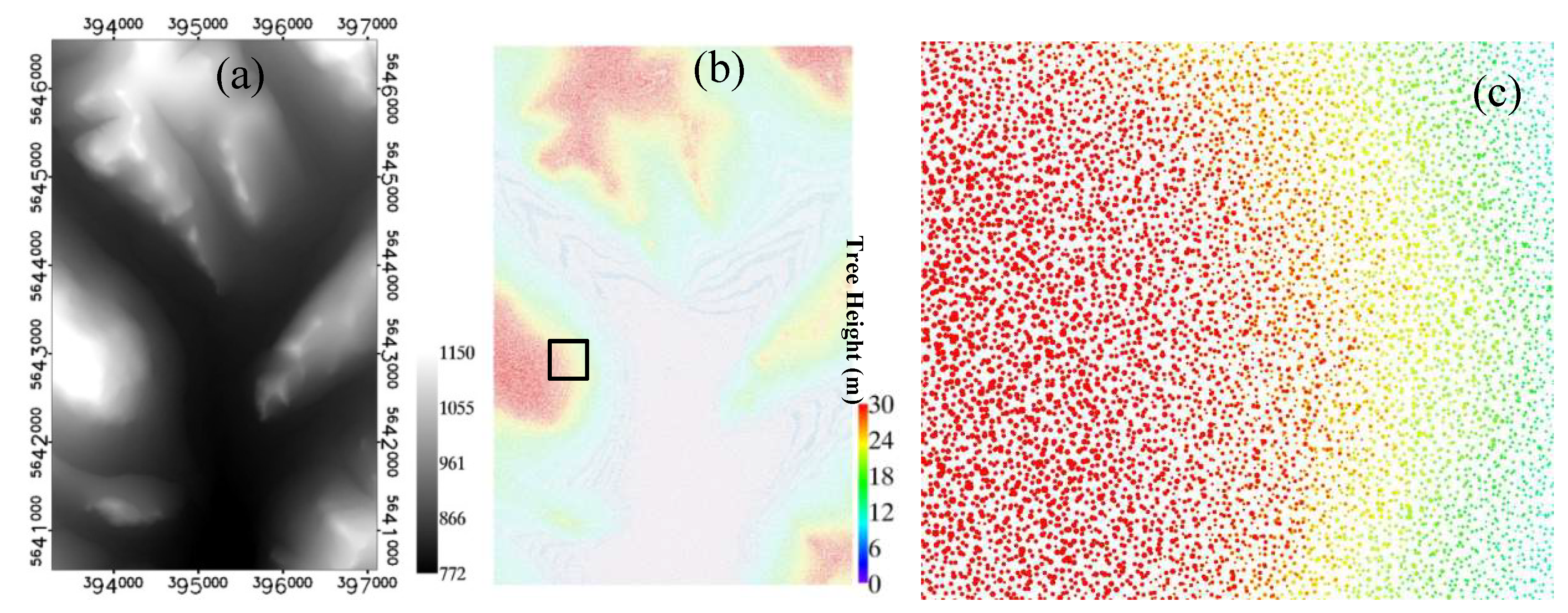
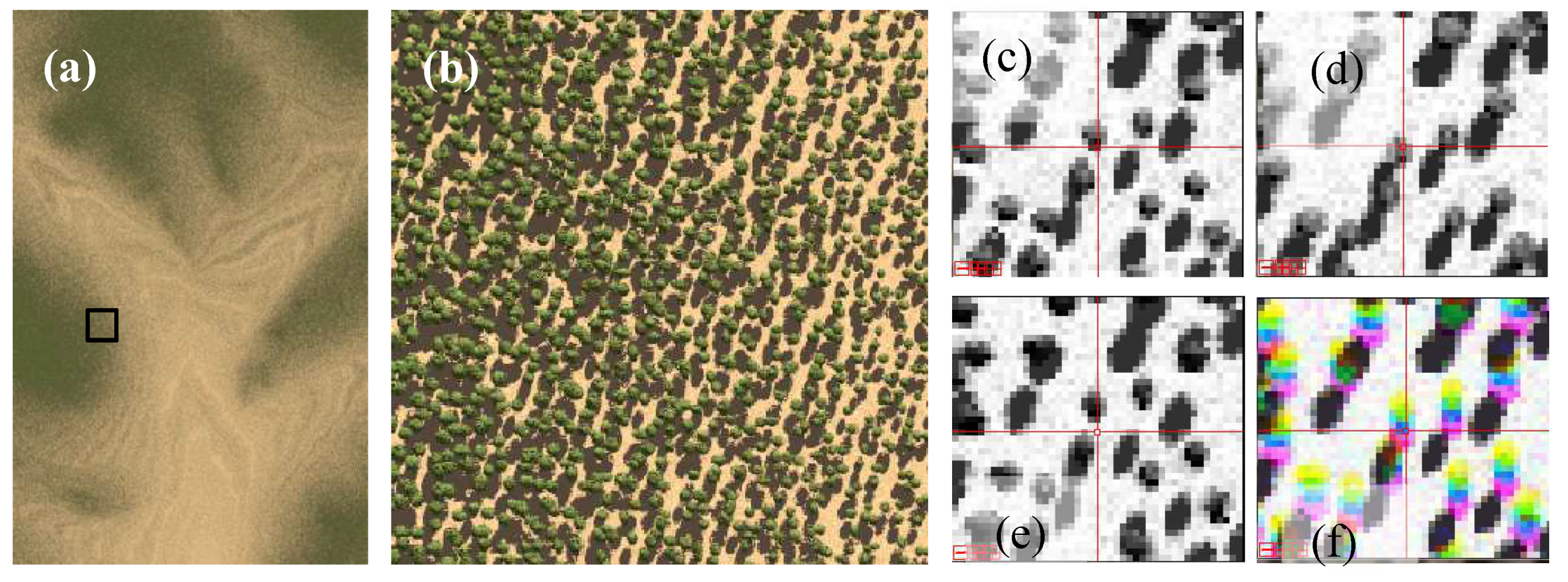
4.1. Simulated Landscapes
4.2. Simulation Parameters
5. Validation Results of the LandStereo Model
5.1. Accuracy of the Sensor Model
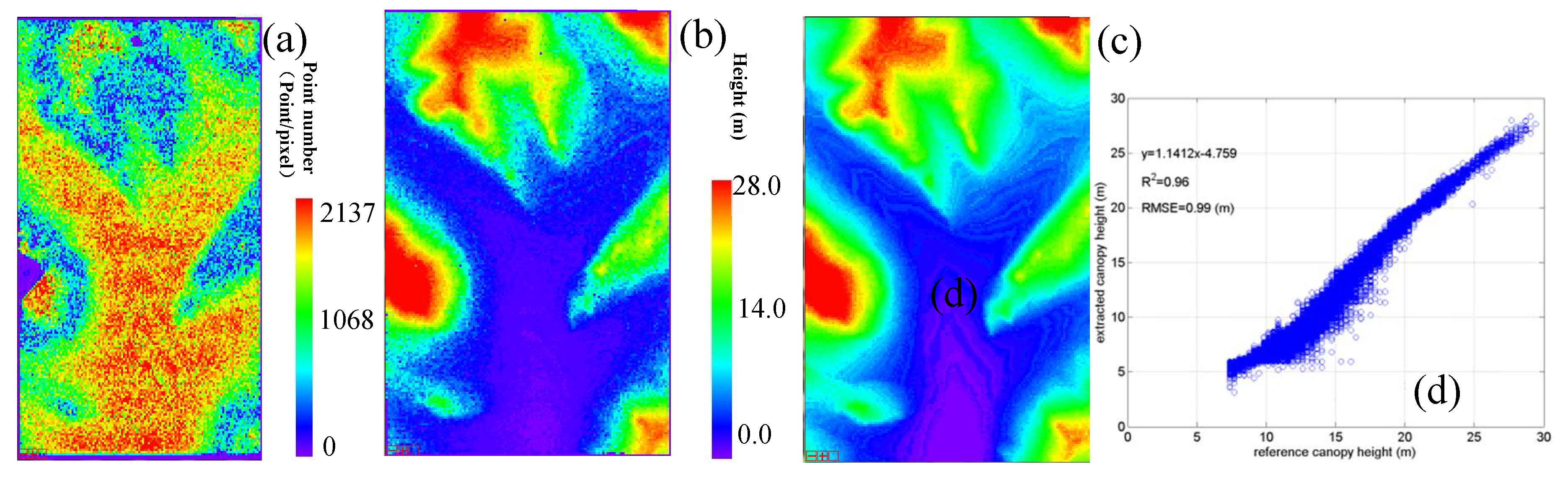
5.2. Accuracy of the Flat Forest Landscapes
5.3. Accuracy of the Bare Mountainous Landscapes
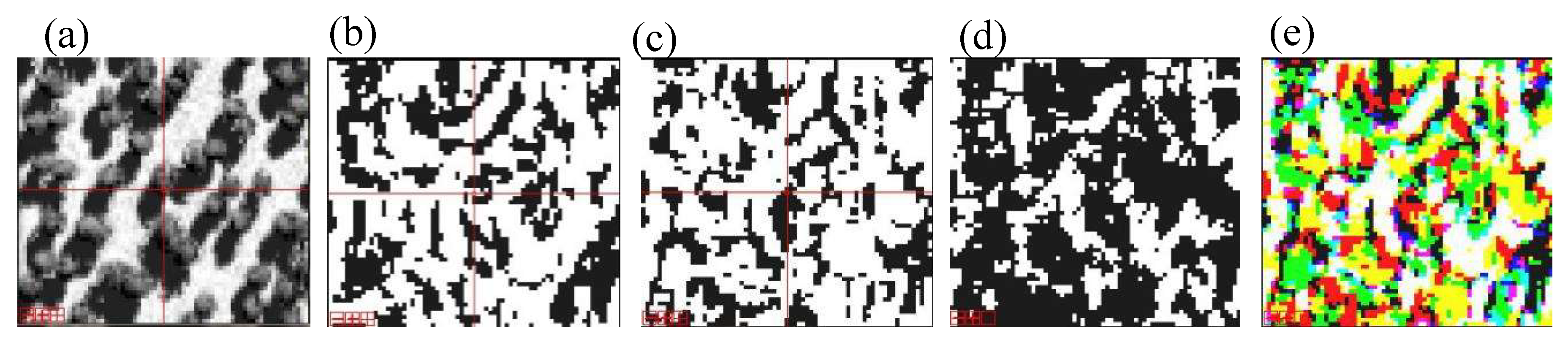
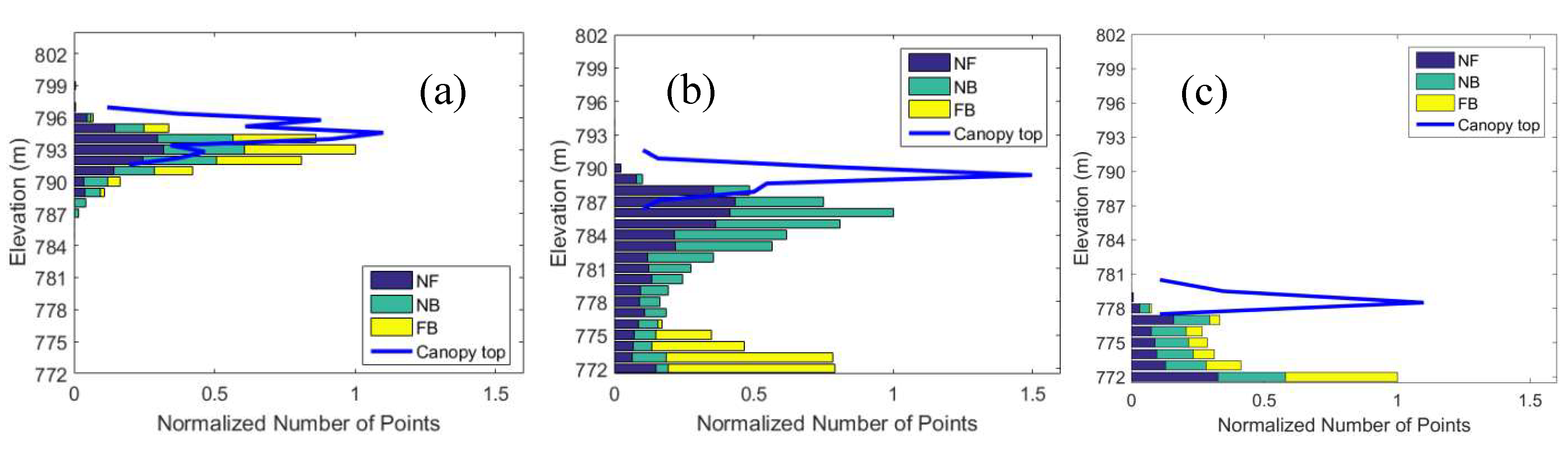
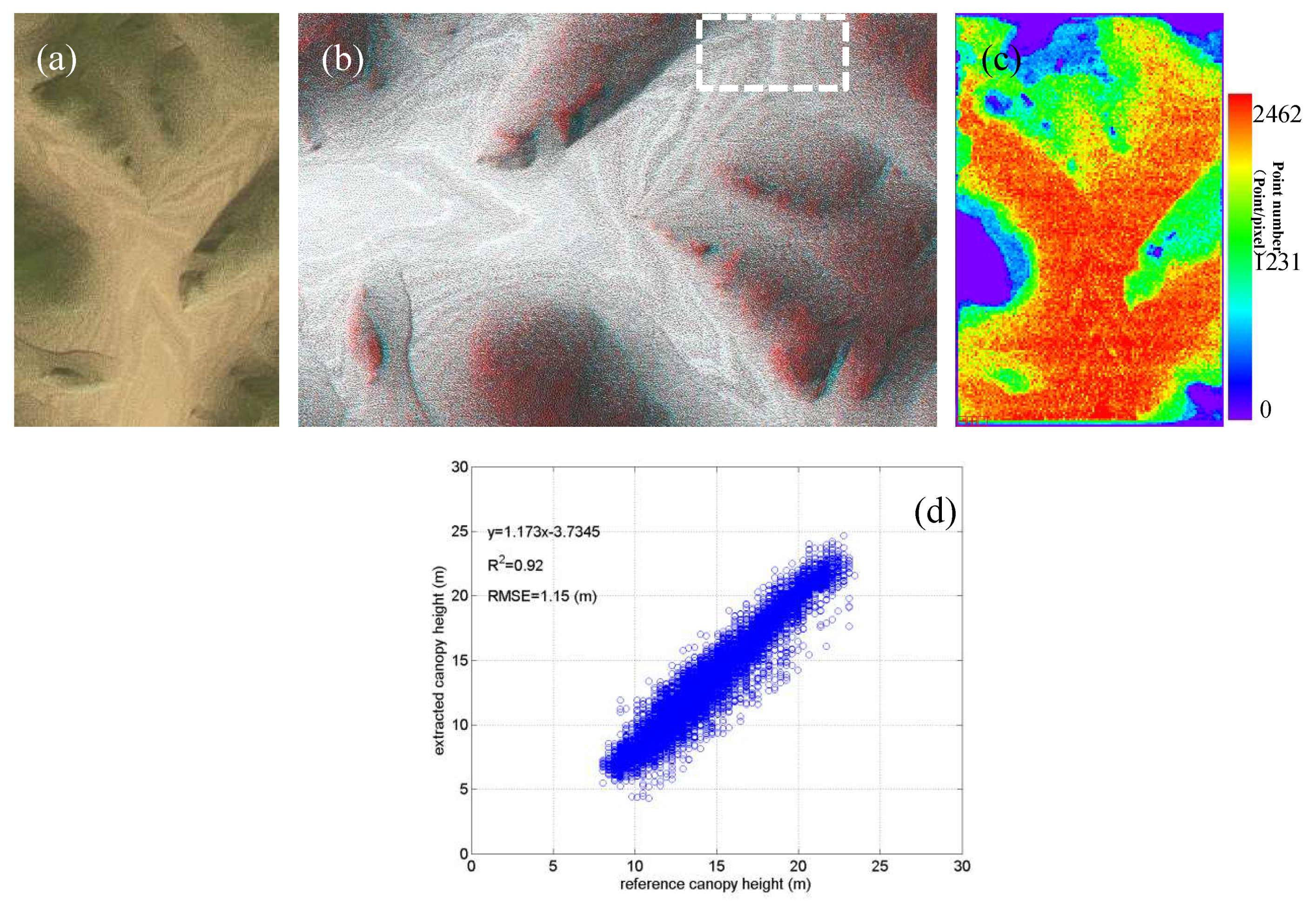
5.4. Accuracy of the Mountainous Forest Landscapes
6. Discussions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Spectral Features of Mountainous Forest Landscapes
Appendix B. The Rational Function Model
Appendix C. Geometry for the Generation of GCP
Appendix D. Detailed Workflow of the LandStereo Validation
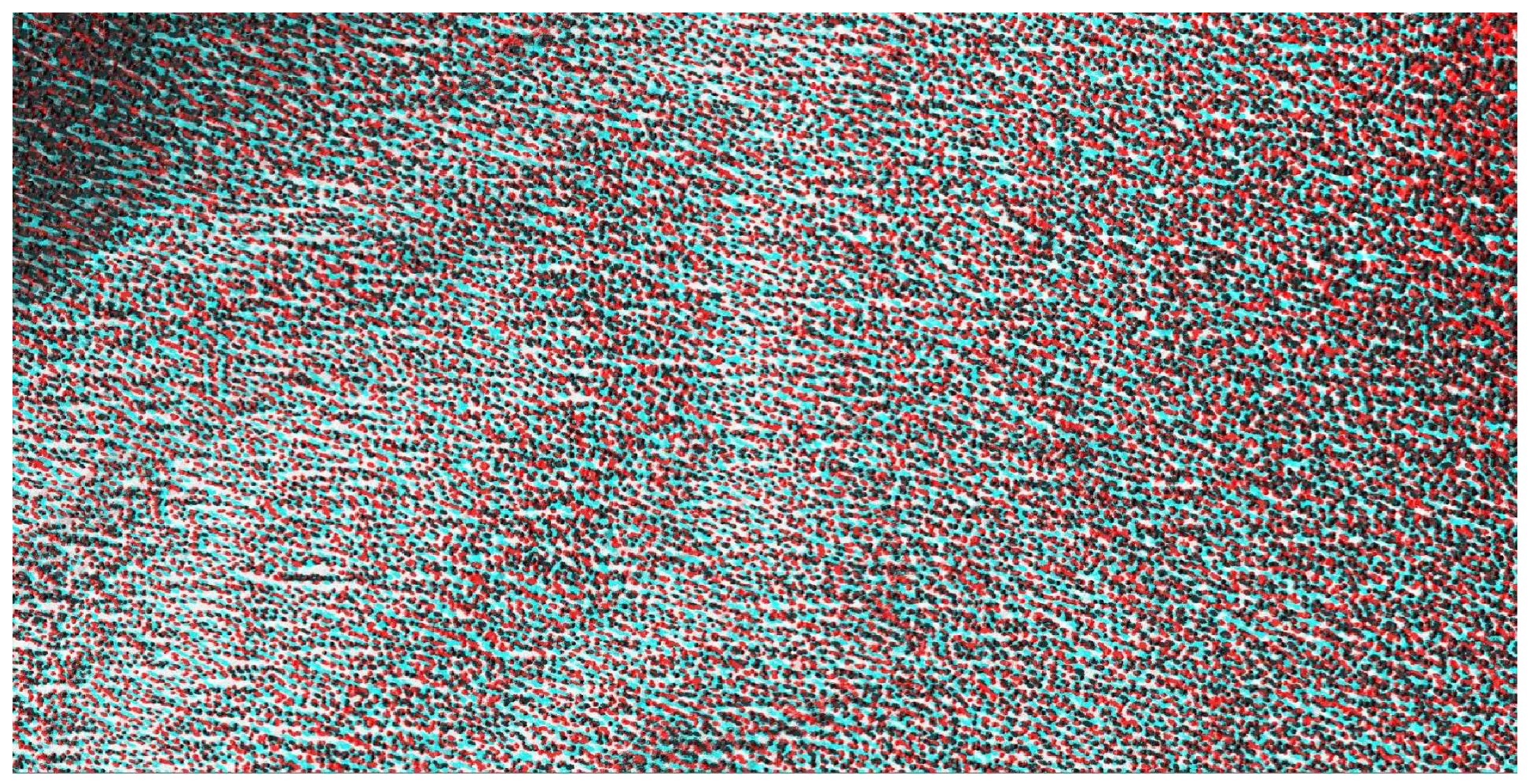
Appendix E. Subset of an Anaglyph Stereoscopic Image
References
- Dunn, R.E.; Stromberg, C.A.E.; Madden, R.H.; Kohn, M.J.; Carlini, A.A. Linked canopy, climate, and faunal change in the cenozoic of patagonia. Science 2015, 347, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purves, D.; Pacala, S. Predictive models of forest dynamics. Science 2008, 320, 1452–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, F.G.; Bergen, K.; Blair, J.B.; Dubayah, R.; Houghton, R.; Hurtt, G.; Kellndorfer, J.; Lefsky, M.; Ranson, J.; Saatchi, S.; et al. Characterizing 3d vegetation structure from space: Mission requirements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2753–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.L.; Dubayah, R.O. Combining tandem-x insar and simulated gedi lidar observations for forest structure mapping. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 187, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Toan, T.; Quegan, S.; Davidson, M.W.J.; Balzter, H.; Paillou, P.; Papathanassiou, K.; Plummer, S.; Rocca, F.; Saatchi, S.; Shugart, H.; et al. The biomass mission: Mapping global forest biomass to better understand the terrestrial carbon cycle. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2850–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreiras, J.M.B.; Shaun, Q.G.; Toan, T.L.; Minh, D.H.T.; Saatchi, S.S.; Carvalhais, N.; Reichstein, M.; Scipal, K. Coverage of high biomass forests by the esa biomass mission under defense restrictions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 196, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, J.A.; Heady, B.; Kroenung, G.; Curtis, W.; Haase, J.; Hoegemann, D.; Shockley, C.; Tracy, K. Evaluation of the New Aster Global Digital Elevation Model; National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency: Virginia, VA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Berthier, E.; Toutin, T. Spot5-hrs digital elevation models and the monitoring of glacier elevation changes in north-west canada and south-east alaska. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 2443–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadono, T.; Shimada, M.; Murakami, H.; Takaku, J. Calibration of prism and avnir-2 onboard alos “daichi”. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 4042–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.J.; Sun, G.Q.; Ranson, K.J. Characterization of aster gdem elevation data over vegetated area compared with lidar data. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2015, 8, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Onge, B.; Hu, Y.; Vega, C. Mapping the height and above-ground biomass of a mixed forest using lidar and stereo ikonos images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 1277–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neigh, C.S.R.; Masek, J.G.; Bourget, P.; Cook, B.; Huang, C.Q.; Rishmawi, K.; Zhao, F. Deciphering the precision of stereo ikonos canopy height models for us forests with g-liht airborne lidar. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1762–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesano, P.M.; Neigh, C.; Sun, G.Q.; Duncanson, L.; Van Den Hoek, J.; Ranson, K.J. The use of sun elevation angle for stereogrammetric boreal forest height in open canopies. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 196, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.; Ranson, K.J.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, G. Features of point clouds synthesized from multi-view alos/prism data and comparisons with lidar data in forested areas. Remote Sens.Environ. 2014, 149, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandois, J.; Olano, M.; Ellis, E. Optimal altitude, overlap, and weather conditions for computer vision uav estimates of forest structure. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 13895–13920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisada, H.; Urai, M.; Iwasaki, A. Technical methodology for aster global dem. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3725–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallerman, J.; Fransson, J.E.S.; Bohlin, J.; Reese, H.; Olsson, H. Forest mapping using 3d data from spot-5 hrs and z/i dmc. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 July 2010; pp. 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Kocaman, S.; Gruen, A. Orientation and self-calibration of alos prism imagery. Photogramm. Rec. 2008, 23, 323–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, H.; Katayama, H.; Sagisaka, M.; Hatooka, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Osawa, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Tadono, T. A conceptual design of prism-2 for advanced land observing satellite-3(alos-3). SPIE Remote Sens. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, J.A.; Heady, B.; Kroenung, G.; Curtis, W.; Haase, J.; Hoegemann, D.; Shockley, C.; Tracy, K. Global assessment of the new aster global digital elevation model. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2011, 77, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.W.; Strahler, A.H. Geometric-optical bidirectional reflectance modeling of a conifer forest canopy. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1986, 24, 906–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.M.; Leblanc, S.G. A four-scale bidirectional reflectance model based on canopy architecture. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 1316–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.H.; Gerstl, S.A.W. 3-d scene modeling of semidesert vegetation cover and its radiation regime. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 74, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.G.; Li, X.W.; Woodcock, C.E.; Caetano, M.R.; Strahler, A.H. An analytical hybrid gort model for bidirectional reflectance over discontinuous plant canopies. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 987–999. [Google Scholar]
- Gastellu-Etchegorry, J.P.; Martin, E.; Gascon, F. Dart: A 3d model for simulating satellite images and studying surface radiation budget. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 73–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.G.; Qin, W.H.; Liu, Q.H. Rapid: A radiosity applicable to porous individual objects for directional reflectance over complex vegetated scenes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 132, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.B.; Xie, D.H.; Yin, T.G.; Yan, G.J.; Gastellu-Etchegorry, J.P.; Li, L.Y.; Zhang, W.M.; Mu, X.H.; Norford, L.K. Less: Large-scale remote sensing data and image simulation framework over heterogeneous 3d scenes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, D. Ray-tracing and pov-ray. Dr Dobbs J. 1994, 19, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Mackay, D. Generating Synthetic Stereo Pairs and a Depth Map with Povray. 2006. Available online: http://cradpdf.drdc-rddc.gc.ca/PDFS/unc57/p527215.pdf (accessed on 22 May 2019).
- Plachetka, T. Pov Ray: Persistence of Vision Parallel Raytracer. In Spring Conference on Computer Graphics; Comenius University: Bratislava, Slovakia, 1998; pp. 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- POV-Tam. Persistence of Vision Ray-Tracer Version 3.7 User’s Documentation. Available online: http://www.povray.org/documentation/3.7.0/ (accessed on 22 May 2019).
- Casa, R.; Jones, H.G. Lai retrieval from multiangular image classification and inversion of a ray tracing model. Remote Sens.Environ. 2005, 98, 414–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagouarde, J.P.; Dayau, S.; Moreau, P.; Guyon, D. Directional anisotropy of brightness surface temperature over vineyards: Case study over the medoc region (sw france). IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagouarde, J.P.; Henon, A.; Kurz, B.; Moreau, P.; Irvine, M.; Voogt, J.; Mestayer, P. Modelling daytime thermal infrared directional anisotropy over toulouse city centre. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hormann, C. landscape.pov, In Persistence Of Vision Ray Tracer; Persistence of Vision Raytracer Pty. Ltd., Place: Victoria, Australia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, R.; Hartley, R.I. Linear pushbroom cameras. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1997, 19, 963–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.V.; Hu, Y. A comprehensive study of the rational function model for photogrammetric processing. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2001, 67, 1347–1357. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, G.; Ranson, K.J. A three-dimensional radar backscatter model of forest canopies. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1995, 33, 372–382. [Google Scholar]
- Brazhnik, K.; Shugart, H.H. Sibbork: A new spatially-explicit gap model for boreal forest. Ecol. Model. 2016, 320, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, J.A.; Shugart, H.H.; Van Bloem, S.J.; Larocque, G.R. Gap model development, validation, and application to succession of secondary subtropical dry forests of puerto rico. Ecol. Model. 2012, 233, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, F.A. Mapping Biomass and Its Dynamic Changes Analysis in the Boreal Forest of Northeastern Asia From Multi-Sensor Synergy; Graduate University of Chinese Academy Sciences: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.P.; Yan, L.N. Local stereo matching algorithm with efficient matching cost and adaptive guided image filter. Vis. Comput. 2017, 33, 1087–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milledge, D.G.; Lane, S.N.; Warburton, J. Optimization of stereo-matching algorithms using existing dem data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2009, 75, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, D.R.; Tang, X.M.; Jiang, Y.H.; Pan, H.B.; Zhu, X.Y.; Fang, C. Geometric accuracy validation for zy-3 satellite imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 1168–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toutin, T. Dtm generation from ikonos in-track stereo images using a 3d physical model. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2004, 70, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Zheng, M.T.; Xiong, J.X.; Lu, Y.H.; Xiong, X.D. On-orbit geometric calibration of zy-3 three-line array imagery with multistrip data sets. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Line# | Parameters | Value | Parameters | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DTM samples () | 9559 | DTM lines () | 8813 |
| 2 | DTM resolution X () | 1.0 m | DTM resolution Y () | 1.0 m |
| 3 | Maximum elevation () | 1162 m | Minimum elevation () | 416 m |
| 4 | X of UL DTM () | 389052.0 m | Y of UL DTM () | 5648265.0 m |
| 5 | Sun elevation angle (φ) | 60° | Sun azimuth angle (β) | 160° |
| 6 | Focal length (f) | 1000 mm | Elements size () | 0.002 mm |
| 7 | Image samples () | 3840 | Image lines () | 6000 |
| 8 | Starting point X () | 395190.0 m | Starting point Y () | 5640550.0 m |
| 9 | Flying height (h) | 500 km | Heading angle (γ) | 0° |
| 10 | View angle (θ) | 0°, 20°, −20° | Image resolution () | 1.0 m |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ni, W.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, G.; Liu, Q. Modeling the Stereoscopic Features of Mountainous Forest Landscapes for the Extraction of Forest Heights from Stereo Imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11101222
Ni W, Zhang Z, Sun G, Liu Q. Modeling the Stereoscopic Features of Mountainous Forest Landscapes for the Extraction of Forest Heights from Stereo Imagery. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(10):1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11101222
Chicago/Turabian StyleNi, Wenjian, Zhiyu Zhang, Guoqing Sun, and Qinhuo Liu. 2019. "Modeling the Stereoscopic Features of Mountainous Forest Landscapes for the Extraction of Forest Heights from Stereo Imagery" Remote Sensing 11, no. 10: 1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11101222
APA StyleNi, W., Zhang, Z., Sun, G., & Liu, Q. (2019). Modeling the Stereoscopic Features of Mountainous Forest Landscapes for the Extraction of Forest Heights from Stereo Imagery. Remote Sensing, 11(10), 1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11101222







