Estimating Dynamics of Terminal Lakes in the Second Largest Endorheic River Basin of Northwestern China from 2000 to 2017 with Landsat Imagery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Lake Area Determination
2.3. Water Consumption Calculation
2.4. Data Sources
3. Results
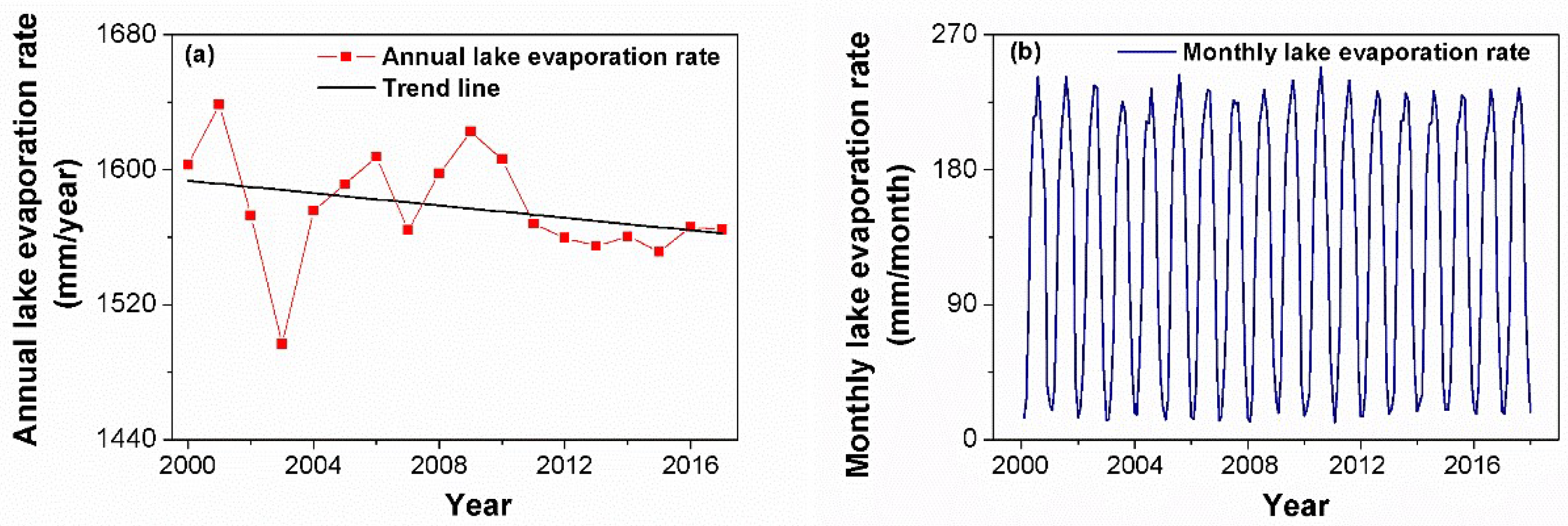
3.1. Changes in Lake Evaporation Rate
3.2. Lake Area Variation
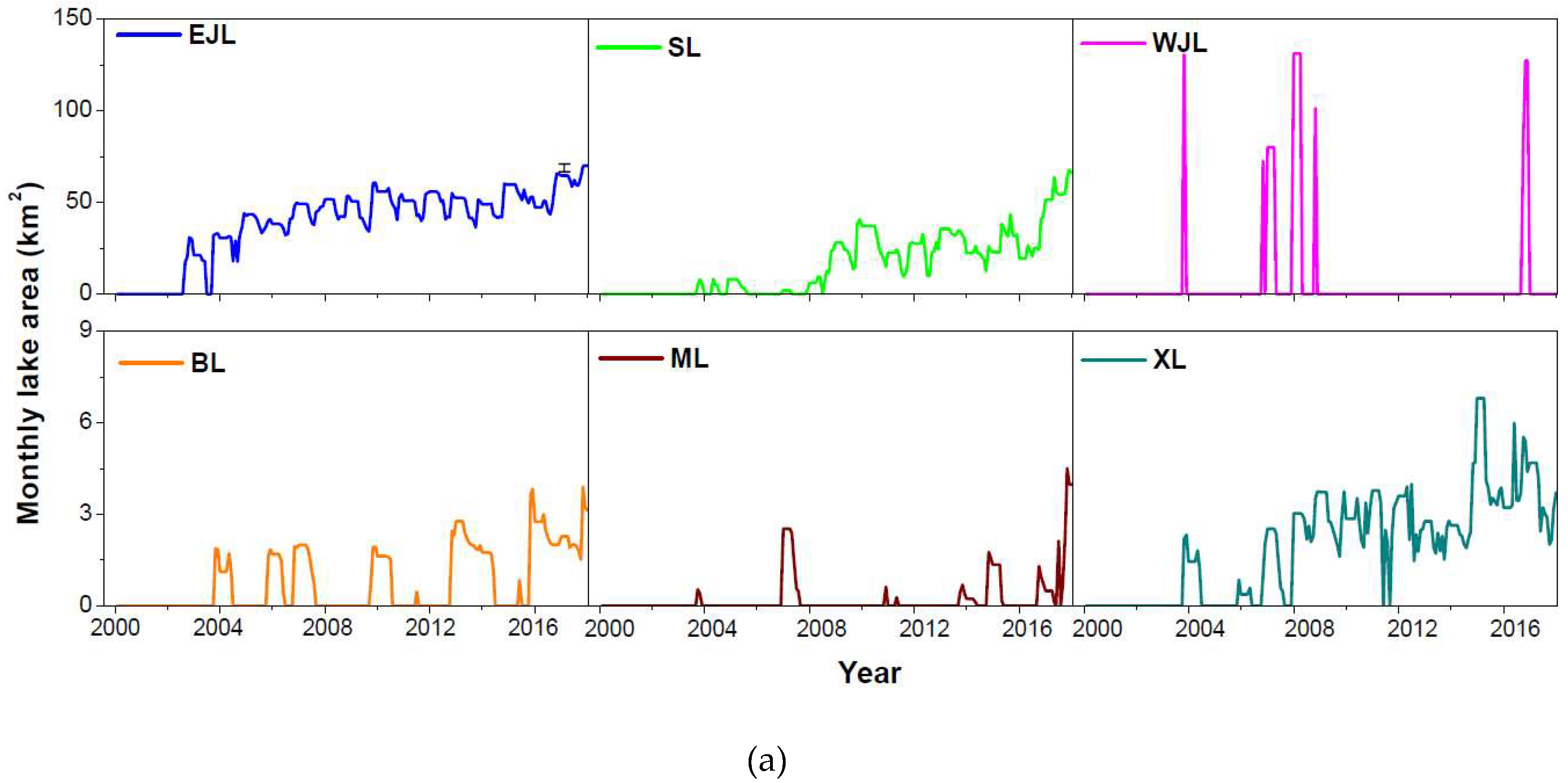
3.2.1. Temporal Dynamics in Lake Area
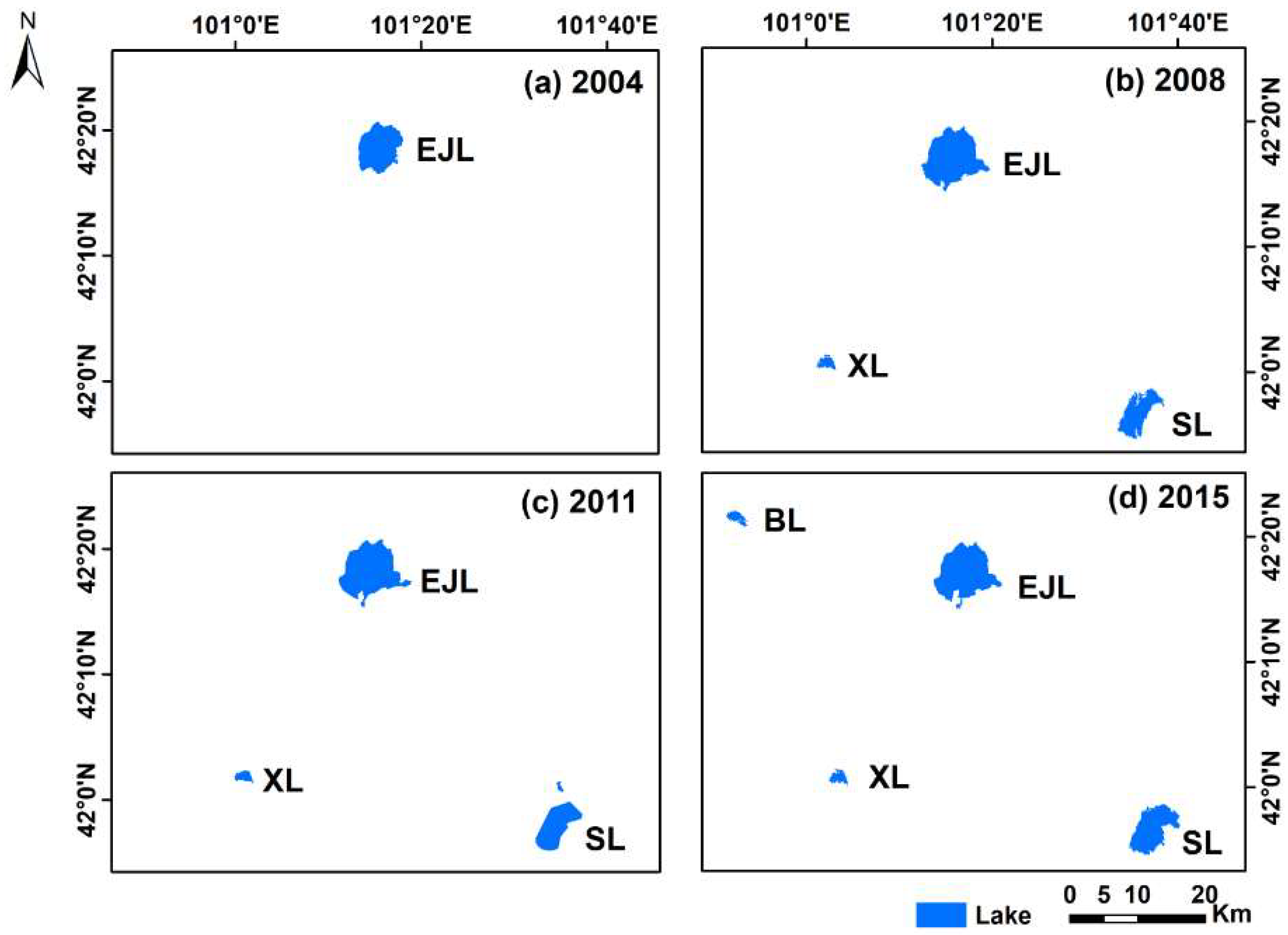
3.2.2. Spatial Patterns of Lake Changes
3.3. Variation in Lake Water Consumption
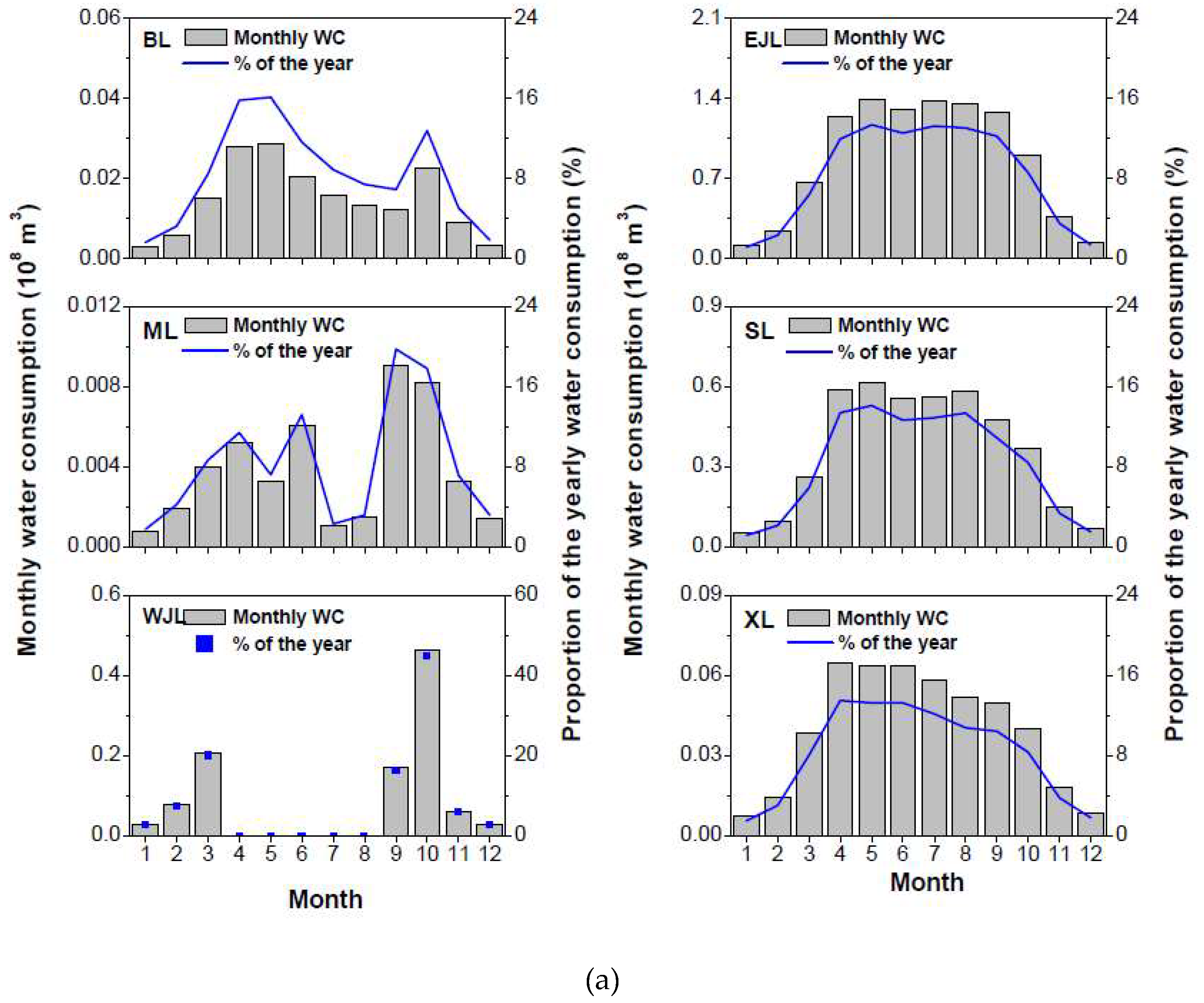
3.3.1. Seasonal Patterns of Water Consumption
3.3.2. Inter-Annual Changes in Water Consumption
3.4. Sources of Uncertainty
4. Discussion
4.1. Ecological Effects of the EWDP on Terminal-Lake Ecosystems
4.2. Implications for Sustainable Water Management
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lehner, B.; Grill, G. Global river hydrography and network routing: Baseline data and new approaches to study the world’s large river systems. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 2171–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, K.; Zhou, J. Assessing the impacts of an ecological water diversion project on water consumption through high-resolution estimations of actual evapotranspiration in the downstream regions of the Heihe River Basin, China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 249, 210–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Li, X.; Zhao, W.; Xu, Z.; Feng, Q.; Xiao, S.; Xiao, H. Integrated study of the water-ecosystem-economy in the Heihe River Basin. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2014, 1, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, G.D.; Ge, Y.C.; Li, H.Y.; Han, F.; Hu, X.L.; Tian, W.; Tian, Y.; Pan, X.D.; Nian, Y.Y.; et al. Hydrological Cycle in the Heihe River Basin and Its Implication for Water Resource Management in Endorheic Basins. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 890–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabi Haghighi, A.; Fazel, N.; Hekmatzadeh, A.A.; Klöve, B. Analysis of Effective Environmental Flow Release Strategies for Lake Urmia Restoration. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 32, 3595–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, P.A.; Hartmann, J.; Lauerwald, R.; Sobek, S.; McDonald, C.; Hoover, M.; Butman, D.; Striegl, R.; Mayorga, E.; Humborg, C.; et al. Global carbon dioxide emissions from inland waters. Nature 2013, 503, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, C.; Reager, J.T.; Yao, F.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Sheng, Y.; MacDonald, G.M.; Brun, F.; Schmied, H.M.; Marston, R.A.; et al. Recent global decline in endorheic basin water storages. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Miller, C.; Null, S.E.; DeRose, R.J.; Wilcock, P.; Hahnenberger, M.; Howe, F.; Moore, J. Decline of the world’s saline lakes. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.P.; Jiang, B.; Bohn, T.J.; Lee, K.N.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Ma, D.; Ouyang, Z. Lake and wetland ecosystem services measuring water storage and local climate regulation. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 3197–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin-Ming, Y.; Li-Gang, M.; Cheng-Zhi, L.; Yang, L.; Jian-li, D.; Sheng-Tian, Y. Temporal-spatial variations and influencing factors of Lakes in inland arid areas from 2000 to 2017: A case study in Xinjiang. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2019, 10, 519–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, V.; Hermoso, V.; Hamilton, S.K.; Ward, D.; Fluet-Chouinard, E.; Lehner, B.; Linke, S. A Global Assessment of Inland Wetland Conservation Status. BioScience 2017, 67, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McJannet, D.; Hawdon, A.; Van Niel, T.; Boadle, D.; Baker, B.; Trefry, M.; Rea, I. Measurements of evaporation from a mine void lake and testing of modelling approaches. J. Hydrol. 2017, 555, 631–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilo, E.; Ziv, B.; Shamir, E.; Rimmer, A. Evaporation from Lake Kinneret, Israel, during hot summer days. J. Hydrol. 2015, 528, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerschman, J.P.; Van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Mattersdorf, G.; Beringer, J.; Hutley, L.B.; Leuning, R.; Pipunic, R.C.; Sherman, B.S. Scaling of potential evapotranspiration with MODIS data reproduces flux observations and catchment water balance observations across Australia. J. Hydrol. 2009, 369, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Liu, J.; Shao, Q.; Liu, R. Changing inland lakes responding to climate warming in Northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Clim. Chang. 2011, 109, 479–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekel, J.-F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes. Nature 2016, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jingjie Yu, P.W. Relationship between Water and Vegetation in the Ejina Delta. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2012, 26, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C. Groundwater recharge and hydrogeochemical evolution in the Ejina Basin, northwest China. J. Hydrol. 2013, 476, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, N.; Ma, Y.; Jiang, X.; Fu, B. Determining spatio-temporal variations of ecological water consumption by natural oases for sustainable water resources allocation in a hyper-arid endorheic basin. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 185, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yu, J.; Du, C.; Wang, P. Research on wetland restoration process of the East Juyan Lake. Geogr. Res. 2017, 36, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Peng, X.; Tian, Q. Climatic and human drivers of recent lake-level change in East Juyan Lake, China. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2015, 16, 1063–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, G. Water use efficiency and evapotranspiration partitioning for three typical ecosystems in the Heihe River Basin, northwestern China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 253–254, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Sun, F.; Yu, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y. New interpretation of the role of water balance in an extended Budyko hypothesis in arid regions. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, J.; Kinzelbach, W.; Cheng, G.D.; Li, X.; Zhao, W.Z. Coupling a SVAT heat and water flow model, a stomatal-photosynthesis model and a crop growth model to simulate energy, water and carbon fluxes in an irrigated maize ecosystem. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 176, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yu, J.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Du, C. Lake Evaporation in a Hyper-Arid Environment, Northwest of China—Measurement and Estimation. Water 2016, 8, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Song, C.; Wang, J.; Lyons, E.A.; Knox, B.R.; Cox, J.S.; Gao, F. Representative lake water extent mapping at continental scales using multi-temporal Landsat-8 imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frohn, R.C.; Hinkel, K.M.; Eisner, W.R. Satellite remote sensing classification of thaw lakes and drained thaw lake basins on the North Slope of Alaska. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 97, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, N.; Lewis, A.; Roberts, D.; Ring, S.; Melrose, R.; Sixsmith, J.; Lymburner, L.; McIntyre, A.; Tan, P.; Curnow, S.; et al. Water observations from space: Mapping surface water from 25years of Landsat imagery across Australia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 174, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yu, J.; Pozdniakov, S.P.; Grinevsky, S.O.; Liu, C. Shallow groundwater dynamics and its driving forces in extremely arid areas: A case study of the lower Heihe River in northwestern China. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 1539–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Fu, G.; Ao, F. Vegetation dynamics induced by groundwater fluctuations in the lower Heihe River Basin, northwestern China. J. Plant Ecol. 2011, 4, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, P.; Fu, G. Vegetation responses to integrated water management in the Ejina basin, northwest China. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 3448–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, E.M.; Gorelick, S.M. Drying drives decline in muskrat population in the Peace-Athabasca Delta, Canada. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 124026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Wu, B.F.; Yan, N.N.; Zeng, H.W. Satellite-Based Water Consumption Dynamics Monitoring in an Extremely Arid Area. Remote Sens. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Pan, Y.; Kang, S.; Song, Y.; Tian, C. Comparison of the ref erence crop evapotranspiration estimated by the Penman-Monteith and Penman methods in Tarim River Basin. Trans. Csae 2005, 21, 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Zheng, C.; Tian, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, J. Eco-hydrological effects associated with environmental flow management: A case study from the arid desert region of China. Ecohydrology 2018, 11, e1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, J.; Feng, Q.; Yu, T.; Zhao, C. Inland river terminal lake preservation: Determining basin scale and the ecological water requirement. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 3327–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Gao, G.; Lu, Y.; Wang, S.; Jiang, X.; Fu, B. River flow is critical for vegetation dynamics: Lessons from multi-scale analysis in a hyper-arid endorheic basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 603–604, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Liu, P.; Su, S.; Jiang, G.; Shi, T.; Shi, F.; Wang, J. Inland desert lake in recent years, Juyanhai change course and water after fish invesigation and protection measures. J. Inner. Mongolia. Agric. Univ. 2013, 34, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Fu, B.; Gao, G.; Shen, Q. Ecological effects and potential risks of the water diversion project in the Heihe River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 794–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ren, L.; Lü, H.; Zhao, W.; Yuan, F.; Xu, M. Ecosystem restoration and conservation in the arid inland river basins of Northwest China: Problems and strategies. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 94, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.C.; Xiao, H.L.; Peng, X.M.; Song, X. Hydroclimate-driven changes in the landscape structure of the terminal lakes and wetlands of the China’s Heihe River Basin. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Tian, Y.; Andrews, C.; Li, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, C. Role of Groundwater in the Dryland Ecohydrological System: A Case Study of the Heihe River Basin. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 6760–6776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Feng, Q.; Si, J.; Xi, H.; O’Grady, A.P.; Pinkard, E.A. Responses of riparian forests to flood irrigation in the hyper-arid zone of NW China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Data types | Band ratio | Threshold |
|---|---|---|
| Landsat-5/TM | TM1/TM4 | 3.0 |
| Landsat-7/ETM | ETM1/ETM4 | 3.0 |
| Landsat-8/OLI | OLI2/OLI5 | 1.1 |
| Data types | Detailed description | Periods | Data sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Meteorological data | Daily mean air temperature, wind speed, humidity | April 1 to September 30, 2000–2017 | Ejina weather station |
| Monthly observed pan evaporation rate | October to March, 2000–2017 | ||
| Remote sensing data | Landsat-5/TM Landsat-7/ETM Landsat-8/OLI | 2000–2017 | United States Geological Survey (https://glovis.usgs.gov/) |
| Hydrological observation | Runoff at the LXS hydrological station | 2000–2017 | Wuhai water bureau |
| River | Lake | Largest area(km2) | Recovery time | Perennial periods | Storage time (months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| East river | EJL | 70.1 | 7/2002 | 9/2003–12/2017 | 182 |
| SL | 67.7 | 9/2003 | 7/2008–12/2017 | 140 | |
| ML | 4.5 | 9/2003 | \ | 41 | |
| XL | 6.8 | 10/2003 | 12/2007–4/2011, 9/2011–12/2017 | 143 | |
| West river | WJL | 131.4 | 10/2003 | \ | 15 |
| BL | 3.9 | 10/2003 | 10/2012–5/2014, 10/2015–12/2017 | 85 |
| Year | Total lake area (km2) | Total water consumption (108 m3) |
|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 0 | 0 |
| 2001 | 0 | 0 |
| 2002 | 30.7 | 0.13 |
| 2003 | 175.8 | 0.37 |
| 2004 | 52.4 | 0.50 |
| 2005 | 51.7 | 0.65 |
| 2006 | 138.5 | 0.73 |
| 2007 | 192.0 | 0.87 |
| 2008 | 192.0 | 1.23 |
| 2009 | 107.2 | 1.10 |
| 2010 | 100.0 | 1.36 |
| 2011 | 87.2 | 1.04 |
| 2012 | 93.5 | 1.13 |
| 2013 | 93.5 | 1.28 |
| 2014 | 92.9 | 1.09 |
| 2015 | 99.5 | 1.43 |
| 2016 | 243.1 | 1.66 |
| 2017 | 148.2 | 1.95 |
| Average (2002–2017) | 118.6 | 1.03 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Wang, P.; Du, C.-Y.; Yu, J.-J. Estimating Dynamics of Terminal Lakes in the Second Largest Endorheic River Basin of Northwestern China from 2000 to 2017 with Landsat Imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11101164
Li B, Zhang Y-C, Wang P, Du C-Y, Yu J-J. Estimating Dynamics of Terminal Lakes in the Second Largest Endorheic River Basin of Northwestern China from 2000 to 2017 with Landsat Imagery. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(10):1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11101164
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Bei, Yi-Chi Zhang, Ping Wang, Chao-Yang Du, and Jing-Jie Yu. 2019. "Estimating Dynamics of Terminal Lakes in the Second Largest Endorheic River Basin of Northwestern China from 2000 to 2017 with Landsat Imagery" Remote Sensing 11, no. 10: 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11101164
APA StyleLi, B., Zhang, Y.-C., Wang, P., Du, C.-Y., & Yu, J.-J. (2019). Estimating Dynamics of Terminal Lakes in the Second Largest Endorheic River Basin of Northwestern China from 2000 to 2017 with Landsat Imagery. Remote Sensing, 11(10), 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11101164







