Survey of Hyperspectral Earth Observation Applications from Space in the Sentinel-2 Context
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Review of Hyperspectral Sensors
2.2. Review of the Applications
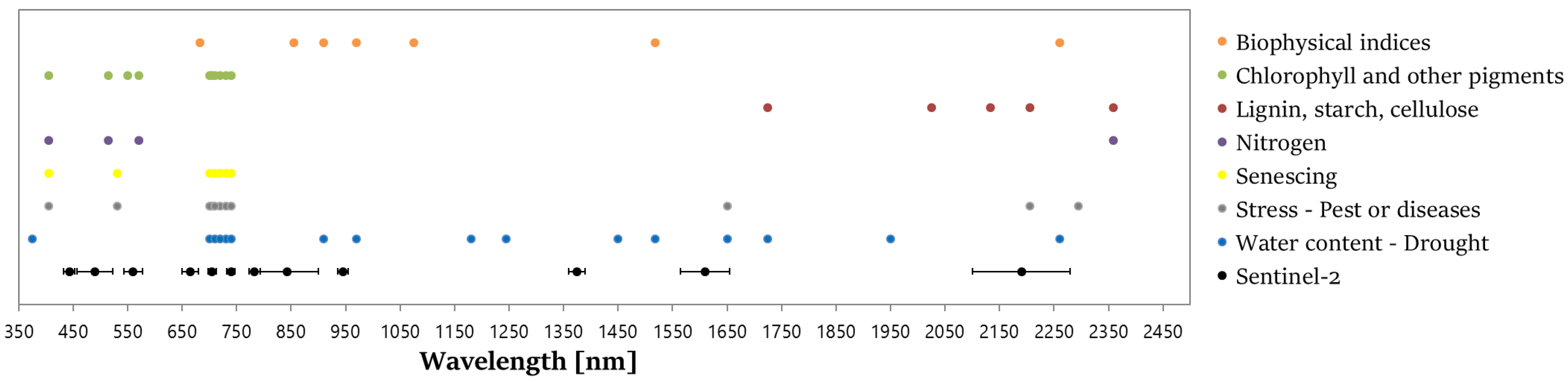
2.3. Inventory of the Useful Wavelengths
3. Results
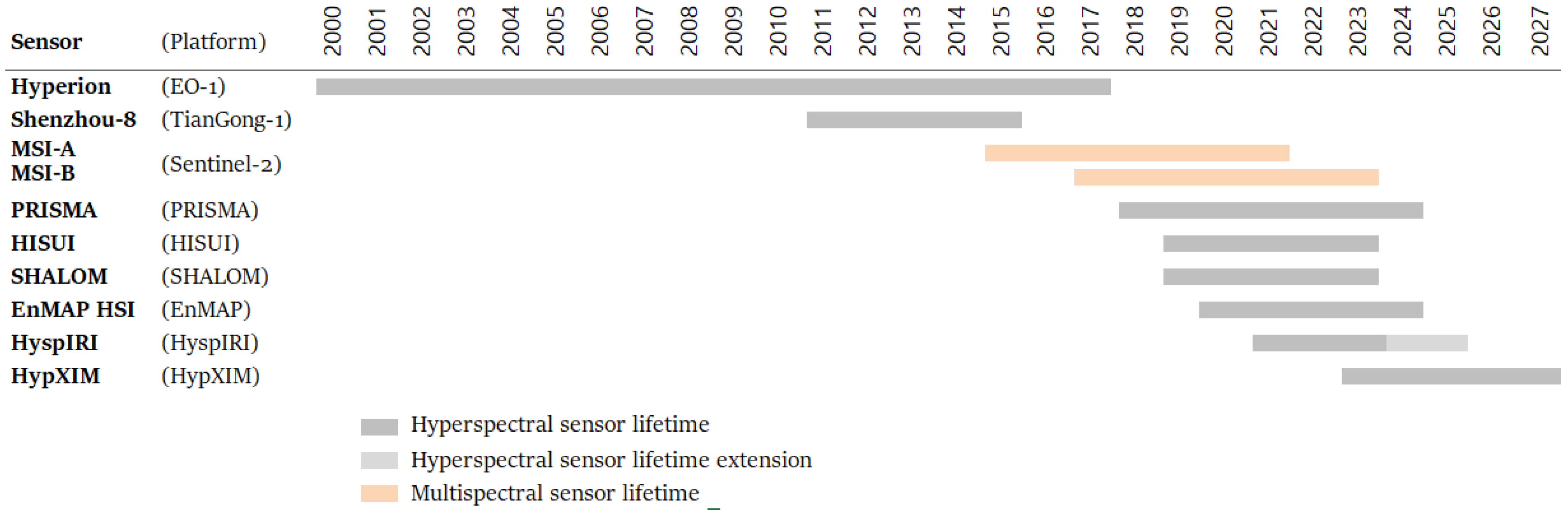
3.1. Review of the Hyperspectral Sensors
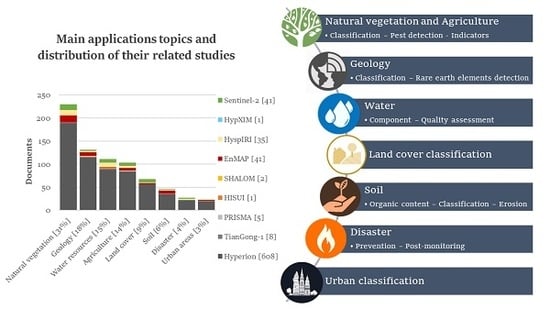
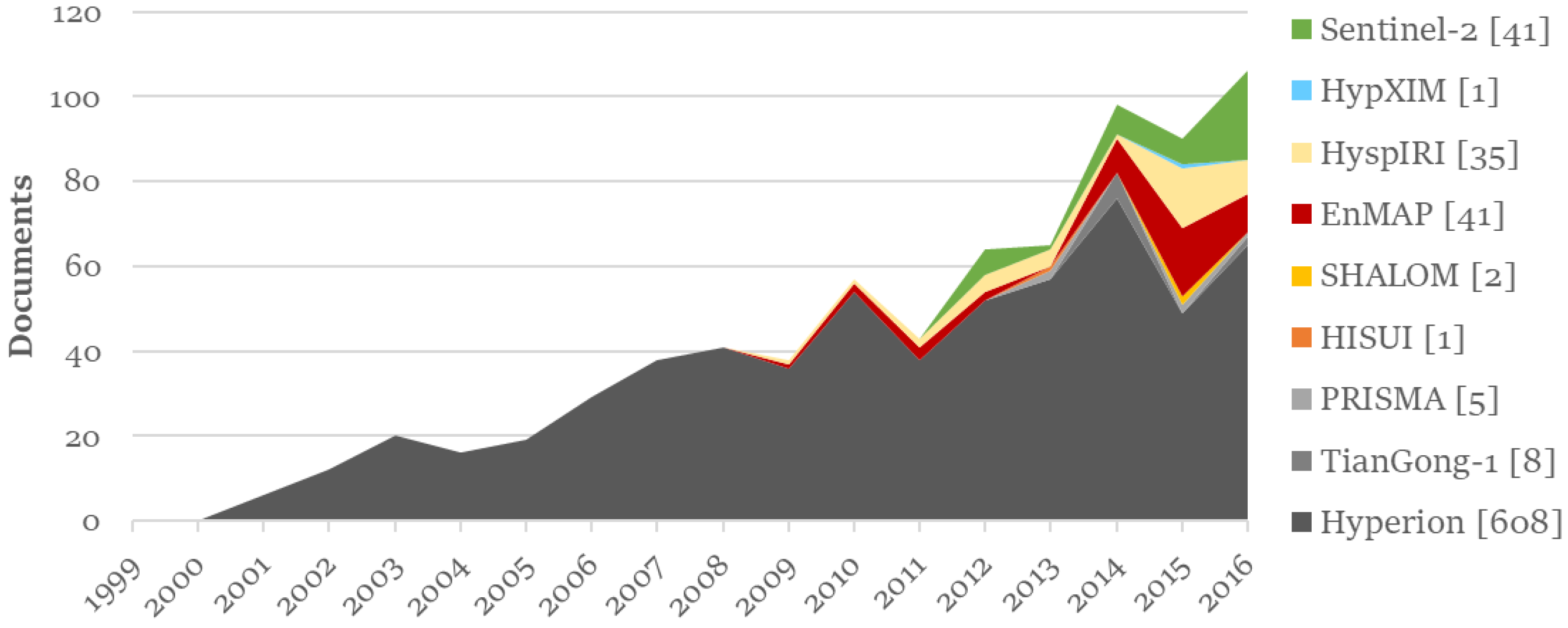
3.2. Preliminary Analysis of the Literature Database
3.3. Hyperspectral and Sentinel-2 Application Analysis
3.3.1. Natural and Agricultural Vegetation Applications
3.3.2. Geology Applications
3.3.3. Soil Applications
3.3.4. Land Cover Applications
3.3.5. Urban Applications
3.3.6. Water Resource Applications
3.3.7. Disaster Applications
4. Discussion
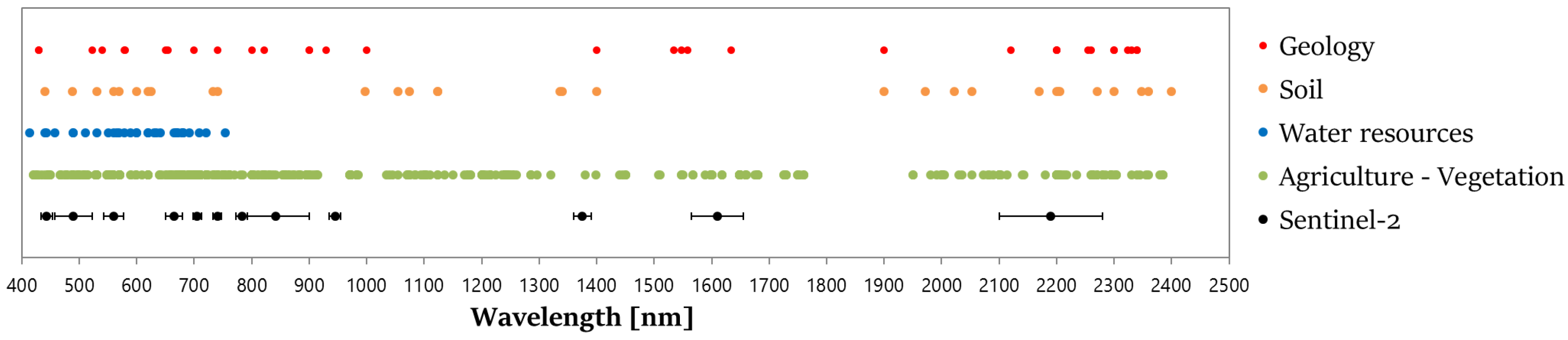
4.1. Inventory of the Useful Wavelengths
4.2. Limitations of the Hyperspectral Sensors Specifications
4.2.1. Spatial Resolution
4.2.2. Revisit Time
4.2.3. Signal-To-Noise Ratios in the SWIR for Hyperion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Sensors Excluded from This Application Review
| Instrument | CHRIS | HSI | HSI | HSA | DESIS | GISAT | HYSI | FLORIS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mission | PROBA-1 | HJ-1 | HICO | Resurs-P | MUSES | GISAT | CartoSat-3 | FLEX |
| Platform | PROBA-1 | HJ-1 | ISS | Resurs-P1 | ISS | CartoSat-3 | TAS Proteus 150 | |
| Swath width (km) | 14 | 50 | 42 | 30 | 30 | <500 | 5 | 150 |
| Spectral range (nm) | 415–1050 | 450–950 | 400–900 | 400–1000 | 400–1000 | 350–2500 | 400–2400 | 500–780 |
| Spectral bands | 19–63 | 115 | 128 | 130 | 235 | 210 | 200 | |
| Resolution | ||||||||
| Spatial (m) | 17-36 | 100 | 90 | 30 | 30 | 500 | 12 | 300 |
| Temporal (day) | 8 | 4–31 | 3 | 3–6 | 3–5 | 10–30 | 19 | |
| Spectral (nm) | 1.3–12 | 2–8 | 5.7 | 4.5–6.5 | 2.55 | <10 | 0.3 | |
| Objective | EO | Disaster, environment monitoring and prediction | Coastal ocean applications | EO | Land use, forestry and aquaculture | EO | Snow cover and vegetation | Vegetation observation |
| Country | UK | China | USA | Russia | Germany-USA | India | India | UK |
| Organization | ESA | CAST | NASA-ONR | Roscosmos | DLR-Teledyne | ISRO | ISRO | ESA |
| Launching date | 2001 | 2008 | 2009 | 2013 | mid 2017 | 2017 | >2018 | 2022 |
References
- European Space Agency (ESA). Earth Observation History on Technology Introduction; Technical Report; ESA: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann, H.; Segl, K.; Guanter, L.; Chabrillat, S.; Hofer, S.; Bach, H.; Hostert, P.; Mueller, A.; Chlebek, C. Review of EnMAP Scientific Potential and Preparation Phase. In Proceedings of the 6th EARSeL SIG IS Workshop, Tel Aviv, Israel, 16–19 March 2009; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, P.; Wang, L.; Niu, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, W. Prediction of Soil Properties Using Laboratory VIS-NIR Spectroscopy and Hyperion Imagery. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 132, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; He, T.; Lv, C.; Chen, Y.; Jian, W. Mapping Soil Organic Matter Based on Land Degradation Spectral Response Units Using Hyperion Images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinform. 2010, 12, S171–S180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, C.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; McBratney, A.B. Soil Organic Carbon Prediction by Hyperspectral Remote Sensing and Field VIS-NIR Spectroscopy: An Australian Case Study. Geoderma 2008, 146, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, A.; Chabrillat, S.; Stevens, A.; Segl, K.; Foerster, S. Prediction of Common Surface Soil Properties Based on Vis-NIR Airborne and Simulated EnMAP Imaging Spectroscopy Data: Prediction Accuracy and Influence of Spatial Resolution. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, F.A.; Boardman, J.W.; Huntington, J.F. Comparison of Airborne Hyperspectral Data and EO-1 Hyperion for Mineral Mapping. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1388–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, F.A. Comparison of AVIRIS and Hyperion for hyperspectral mineral mapping. In Proceedings of the 11th JPL Airborne Geoscience Workshop, Pasadena, CA, USA, 4–8 March 2002; pp. 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Guanter, L.; Kaufmann, H.; Foerster, S.; Brosinsky, A.; Wulf, H.; Bochow, M.; Boesche, N.; Brell, M.; Buddenbaum, H.; Chabrillat, S.; et al. EnMAP Science Plan—Environmental Mapping and Analysis Program; Technical Report; GFZ Data Services: Potsdam, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Govender, M.; Chetty, K.; Bulcock, H. A Review of Hyperspectral Remote Sensing and its Application in Vegetation and Water Resource Studies. Water SA 2007, 33, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Meer, F.D.; van der Werff, H.M.A.; van Ruitenbeek, F.J.A.; Hecker, C.A.; Bakker, W.H.; Noomen, M.F.; van der Meijde, M.; Carranza, E.J.M.; de Smeth, J.B.; Woldai, T. Multi- and Hyperspectral Geologic Remote Sensing: A Review. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinform. 2012, 14, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.C.M. Hyperspectral imagery for mapping yield for precision agriculture. In Hyperspectral Imaging Technology in Food and Agriculture, 1st ed.; Park, B., Lu, R., Eds.; Springer Science & Business Media: London, UK, 2015; Chapter 12; pp. 289–292. [Google Scholar]
- Folkman, M.; Pearlman, J.; Lushalan, L.; Jarecke, P. EO-1/Hyperion hyperspectral imager design, development, characterization, and calibration. Proc. SPIE 2001, 4151, 40–51. [Google Scholar]
- Labate, D.; Ceccherini, M.; Cisbani, A.; De Cosmo, V.; Galeazzi, C.; Giunti, L.; Melozzi, M.; Pieraccini, S.; Stagi, M. The PRISMA Payload Optomechanical Design, a High Performance Instrument for a New Hyperspectral Mission. Acta Astronaut. 2009, 65, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashimura, O.; Hirose, K.; Tachikawa, T.; Tanii, J. Hyperspectral Space-Borne Sensor HISUI and its Data Application. In Proceedings of the 34th Asian Conference on Remote Sensing, Bali, Indonesia, 20–24 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Thenkabail, P.S.; Gumma, M.K.; Teluguntla, P.; Mohammed, I.A. Hyperspectral remote sensing of vegetation and agricultural crops. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2014, 80, 697–709. [Google Scholar]
- Adam, E.; Mutanga, O.; Rugege, D. Multispectral and Hyperspectral Remote Sensing for Identification and Mapping of Wetland Vegetation: A Review. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 18, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, A.; Brando, V.; Anstee, J.; Pinnel, N.; Held, A. Preliminary assessment of the performance of Hyperion in coastal waters. Cal/Val activities in Moreton Bay, Queensland, Australia. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2001 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Sydney, Australia, 9–13 July 2001; Volume 6, pp. 2665–2667. [Google Scholar]
- Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Plaza, A.; Camps-valls, G.; Scheunders, P.; Nasrabadi, N.M.; Chanussot, J. Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Data Analysis and Future Challenges. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2013, 1, 6–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Cohen, W.B.; Kennedy, R.E.; Maiersperger, T.K.; Gower, S.T. Hyperspectral versus Multispectral Data for Estimating Leaf Area Index in Four Different Biomes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 91, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.; Hu, X.; Lu, D. Extracting Impervious Surfaces from Medium Spatial Resolution Multispectral and Hyperspectral Imagery: A Comparison. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Space Agency (ESA). GMES Sentinel-2: Mission Requirements Document; Technical Report; ESA: Paris, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Barensky, S. Contrat Signé Pour Sentinel 2C et 2D. Aerospatium. 2016. Available online: https://www.aerospatium.info/contrat-signe-pour-sentinel-2c-et-2d/ (accessed on 4 January 2018).
- Segl, K.; Richter, R.; Kuster, T.; Kaufmann, H. End-to-End Sensor Simulation for Spectral Band Selection and Optimization with Application to the Sentinel-2 Mission. Appl. Opt. 2012, 51, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miglani, A.; Ray, S.S.; Pandey, R.; Parihar, J.S. Evaluation of EO-1 Hyperion Data for Agricultural Applications. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2008, 36, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drusch, M.; Del Bello, U.; Carlier, S.; Colin, O.; Fernandez, V.; Gascon, F.; Hoersch, B.; Isola, C.; Laberinti, P.; Martimort, P.; et al. Sentinel-2: ESA’s Optical High-Resolution Mission for GMES Operational Services. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkman, M.; Pearlman, J.; Liao, L.; Jarecke, P. EO-1/Hyperion Hyperspectral Imager Design, Development, Characterization, and Calibration; Technical Report; TRW Space and Electronics Group: Lyndhurst, OH, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wu, T.; Liu, K.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L. Evaluation of the Chinese Fine Spatial Resolution Hyperspectral Satellite TianGong-1 in Urban Land-Cover Classification. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopinto, E.; Ananasso, C. The Prisma Hyperspectral Mission. In Proceedings of the 33rd Symposium Towards Horizon 2020, Matera, Italy, 3–6 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga, T.; Tsuchida, S.; Iwasaki, A.; Tanii, J.; Kahimura, O.; Rokugawa, S. Current Status of Hyperspectal Imager Suite (HISUI). In Proceedings of the Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Melbourne, Australia, 21–26 July 2013; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Feingersh, T.; Dor, E.B. SHALOM—A Commercial Hyperspectral Space Mission. In Optical Payloads for Space Missions, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2016; Chapter 11; pp. 247–263. [Google Scholar]
- HyspIRI Mission Concept Team. HyspIRI Comprehensive Development Report; Technical Report; Jet Propulsion Laboratory: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2015.
- EnMAP Ground Segment Team. Spaceborne Imaging Spectroscopy Mission Compilation. 2015, p. 42. Available online: http://docplayer.net/53492560-Spaceborne-imaging-spectroscopy-mission-compilation-the-enmap-ground-segment-team.html (accessed on 4 December 2017).
- Calvin, W.; Pace, E. Utilizing HyspIRI Prototype Data for Geological Exploration Applications: A southern California Case Study. Geosciences 2016, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, S.; Gamet, P.; Lefevre-Fonollosa, M.J. HYPXIM A hyperspectral satellite defined for science, security and defence users. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Hyperspectral Image and Signal Processing, Evolution in Remote Sensing, Lisbon, Portugal, 6–9 June 2011; ESA: Frascati, Italy; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Thenkabail, P.S.; Enclona, E.A.; Ashton, M.S.; Van Der Meer, B. Accuracy Assessments of Hyperspectral Waveband Performance for Vegetation Analysis Applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 91, 354–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, T.; Huete, A. Discrimination and Biophysical Characterization of Cerrado Physiognomies with EO-1 Hyperspectral Hyperion. In Proceedings of the Simpósio Brasileiro de Sensoriamento Remoto, Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 5–10 April 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hochberg, E.J.; Roberts, D.A.; Dennison, P.E.; Hulley, G.C. Special issue on the Hyperspectral Infrared Imager (HyspIRI): Emerging science in terrestrial and aquatic ecology, radiation balance and hazards. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 167, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, K.L.; Roberts, D.A.; Dennison, P.E.; Alonzo, M.; Peterson, S.H.; Beland, M. Differentiating Plant Species within and across Diverse Ecosystems with Imaging Spectroscopy. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 167, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibanda, M.; Mutanga, O.; Rouget, M. Comparing the Spectral Settings of the New Generation Broad and Narrow Band Sensors in Estimating Biomass of Native Grasses Grown under Different Management Practices. GISci. Remote Sens. 2016, 53, 614–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaglio Laurin, G.; Puletti, N.; Hawthorne, W.; Liesenberg, V.; Corona, P.; Papale, D.; Chen, Q.; Valentini, R. Discrimination of Tropical Forest Types, Dominant Species, and Mapping of Functional Guilds by Hyperspectral and Simulated Multispectral Sentinel-2 Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 176, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.J.; Shrestha, R.; Spaete, L.P.; Glenn, N.F. Combining Airborne Hyperspectral and LiDAR Data Across Local Sites for Upscaling Shrubland Structural Information: Lessons for HyspIRI. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 167, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asner, G.P.; Heidebrecht, K.B. Imaging Spectroscopy for Desertification Studies: Comparing AVIRIS and EO-1 Hyperion in Argentina Drylands. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1283–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demuro, M.; Chisholm, L. Assessment of Hyperion for Characterizing Mangrove Communities. In Proceedings of the International Conference the AVIRIS 2003 Workshop, Pasadena, CA, USA, 24 February 2003; pp. 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Koedsin, W.; Vaiphasa, C. Discrimination of Tropical Mangroves at the Species Level with EO-1 Hyperion Data. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3562–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbane, C.; Guttler, F.; Alleaume, S.; Ienco, D.; Teisseire, M. Monitoring the Phenology of Mediterranean Natural Habitats with Multispectral Sensors: An Analysis Based on Multiseasonal Field Spectra. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Quebec, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014; pp. 3934–3937. [Google Scholar]
- Suess, S.; Van Der Linden, S.; Okujeni, A.; Leitão, P.J.; Schwieder, M.; Hostert, P. Using Class Probabilities to Map Gradual Transitions in Shrub Vegetation from Simulated EnMAP Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 10668–10688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão, P.J.; Schwieder, M.; Suess, S.; Okujeni, A.; Galvão, L.S.; van der Linden, S.; Hostert, P. Monitoring Natural Ecosystem and Ecological Gradients: Perspectives with EnMAP. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 13098–13119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwieder, M.; Leitão, P.J.; Suess, S.; Senf, C.; Hostert, P. Estimating Fractional Shrub Cover Using Simulated EnMAP Data: A Comparison of Three Machine Learning Regression Techniques. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 3427–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, M.; Christian, B.; Joshi, N.; Vyas, D.; Marpu, P.; Krishnayya, N. Hyperspectral Data Dimensionality Reduction and the Impact of Multi-seasonal Hyperion EO-1 Imagery on Classification Accuracies of Tropical Forest Species. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2014, 80, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagendra, H. Using Remote Sensing to Assess Biodiversity. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 2377–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feret, J.B.; Asner, P. Tree Species Discrimination in Tropical Forests Using Airborne Imaging Spectroscopy. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, S.; Kneubühler, M. Application of Hyperion Data to Agricultural Land Classification and Vegetation Properties Estimation in Switzerland. In Proceedings of the XXth ISPRS Congress, Istanbul, Turkey, 12–23 July 2004; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Mariotto, I.; Thenkabail, P.S.; Huete, A.; Slonecker, E.T.; Platonov, A. Hyperspectral versus Multispectral Crop-Productivity Modeling and Type Discrimination for the HyspIRI Mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 139, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvão, L.S.; Formaggio, A.R.; Tisot, D.A. Discrimination of Sugarcane Varieties in Southeastern Brazil with EO-1 Hyperion Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 94, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvão, L.S.; Ponzoni, F.J.; Liesenberg, V.; dos Santos, J.R. Possibilities of Discriminating Tropical Secondary Succession in Amazônia Using Hyperspectral and Multiangular CHRIS/PROBA Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinform. 2009, 11, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, U.; Antoniadis, A.; Carfora, M.F.; Colandrea, P.; Cuomo, V.; Franzese, M.; Pignatti, S.; Serio, C. Statistical classification for assessing prisma hyperspectral potential for agricultural land use. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgani, F.; Bruzzone, L. Classification of Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Images with Support Vector Machines. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1778–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M.; Mather, P.M. Assessment of the Effectiveness of Support Vector Machines for Hyperspectral Data. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2004, 20, 1215–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostan, S.; Ortak, M.A.; Tuna, C.; Akoguz, A.; Sertel, E.; Ustundag, B.B. Comparison of Classification Accuracy of Co-located Hyperspectral & Multispectral Images for Agricultural Purposes. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Agro-Geoinformatics (Agro-Geoinformatics 2016), Tianjin, China, 18–20 July 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Thenkabail, P.S.; Enclona, E.A.; Ashton, M.S.; Legg, C.; De Dieu, M.J. Hyperion, IKONOS, ALI, and ETM+ Sensors in the Study of African Rainforests. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 90, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey III, E.; Rangoonwala, a.; Nelson, G.; Ehrlich, R. Mapping the Invasive Species, Chinese Tallow, with EO1 Satellite Hyperion Hyperspectral Image Data and Relating Tallow Occurrences to a Classified Landsat Thematic Mapper Land Cover Map. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 1637–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.R.; Townsend, P.A.; Zganjar, C.E. Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Gap Dominance by Low-Canopy Lianas Detected Using EO-1 Hyperion and Landsat Thematic Mapper. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 2104–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, G.A.; Lucas, K.L.; Blossom, G.A.; Holiday, C.L.L.; Mooneyhan, D.S.; Fastring, D.R.; Holcombe, T.R.; Griffith, J.A. Remote Sensing and Mapping of Tamarisk along the Colorado River, USA: A Comparative Use of Summer-Acquired Hyperion, Thematic Mapper and Quickbird Data. Remote Sens. 2009, 1, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengra, B.W.; Johnston, C.A.; Loveland, T.R. Mapping an Invasive Plant, Phragmites australis, in Coastal Wetlands Using the EO-1 Hyperion Hyperspectral Sensor. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apan, A.; Held, A.; Phinn, S.; Markley, J. Detecting Sugarcane ”Orange Rust” Disease Using EO-1 Hyperion Hyperspectral Imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.C.; Coops, N.C.; Hilker, T.; Wulder, M.A.; Carroll, A.L. Detecting Mountain Pine Beetle Red Attack Damage with EO-1 Hyperion Moisture Indices. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 2111–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Bhattacharya, B.K.; Rajak, D.R.; Chattopadhayay, C.; Patel, N.K.; Parihar, J.S. Disease Detection in Mustard Crop using EO-1 Hyperion Satellite Data. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2006, 34, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samiappan, S.; Prasad, S.; Bruce, L.M.; Robles, W. NASA’s Upcoming HyspIRI Mission—Precision Vegetation Mapping with Limited Ground Truth. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 July 2010; pp. 3744–3747. [Google Scholar]
- Chemura, A.; Mutanga, O.; Dube, T. Separability of Coffee Leaf Rust Infection Levels with Machine Learning Methods at Sentinel-2 MSI Spectral Resolutions. In Precision Agriculture; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Hamzeh, S.; Ali, A.; Kazem, S.; Bartholomeus, H.; Herold, M. Assessing the Accuracy of Hyperspectral and Multispectral Satellite Imagery for Categorical and Quantitative Mapping of Salinity Stress in Sugarcane Fields. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinform. 2016, 52, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, H.; Migdall, S.; Spannraft, K.; Hank, T.; Mauser, W. Potential and challenges of using Sentinel-2 for smart farming. In Proceedings of the First Sentinel-2 Preparatory Symposium, Frascati, Italy, 23–27 April 2012; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, R.; Yu, Q.; Gong, P.; Biging, G.S. EO-1 Hyperion, ALI and Landsat 7 ETM+ Data Comparison for Estimating Forest Crown Closure and Leaf Area Index. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 457–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locherer, M.; Hank, T.; Danner, M.; Mauser, W. Retrieval of Seasonal Leaf Area Index from Simulated EnMAP Data through Optimized LUT-based Inversion of the PROSAIL Model. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 10321–10346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegmann, B.; Jarmer, T.; Beyer, F.; Ehlers, M. The Potential of Pan-Sharpened EnMAP Data for the Assessment of Wheat LAI. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 12737–12762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, K.; Hank, T.; Mauser, W. Preparatory Analyses and Development of Algorithms for Agricultural Applications in the Context of the EnMAP Hyperspectral Mission. Proceedings of SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering, Toulouse, France, 22 October 2010; Volume 7824, pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, R.; Gong, P.; Yu, Q. Comparative Analysis of EO-1 ALI and Hyperion, and Landsat ETM+ data for Mapping Forest Crown Closure and Leaf Area Index. Sensors 2008, 8, 3744–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, P.; Pu, R.; Biging, G.S.; Larrieu, M.R. Estimation of Forest Leaf Area Index Using Vegetation Indices Derived from Hyperion Hyperspectral Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1355–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Han, X.; Niu, Z.; Dong, J. An Evaluation of EO-1 Hyperspectral Hyperion Data for Chlorophyll Content and Leaf Area Index Estimation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, D.A.; Gamon, J.A. Relationships between Leaf Pigment Content and Spectral Reflectance across a Wide Range of Species, Leaf Structures and Developmental Stages. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 81, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Cerrillo, R.M.; Trujillo, J.; de la Orden, M.S.; Hernández-Clemente, R. Hyperspectral and Multispectral Satellite Sensors for Mapping Chlorophyll Content in a Mediterranean Pinus sylvestris L. Plantation. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinform. 2014, 26, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addabbo, P.; Focareta, M.; Marcuccio, S.; Votto, C.; Ullo, S.L. Contribution of Sentinel-2 Data for Applications in Vegetation Monitoring. Acta Imeko 2016, 5, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnert, L.W.; Meyer, H.; Meyer, N.; Reudenbach, C.; Bendix, J. A Hyperspectral Indicator System for Rangeland Degradation on the Tibetan Plateau: A Case Study towards Spaceborne Monitoring. Ecol. Ind. 2014, 39, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wang, L.; Niu, Z.; Gao, S.; Wu, M. Nondestructive Estimation of Canopy Chlorophyll Content Using Hyperion and Landsat/TM Images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 2159–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, M.; Makarau, A.; Segl, K.; Richter, R. Estimating the Influence of Spectral and Radiometric Calibration Uncertainties on EnMAP Data Products-Examples for Ground Reflectance Retrieval and Vegetation Indices. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 10689–10714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.R.; Miura, T.; Gao, X. Land Cover Conversion and Degradation Analyses through Coupled Soil-Plant Biophysical Parameters Derived from Hyperspectral EO-1 Hyperion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1268–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandler, H.; Brenning, A.; Samimi, C. Potential of Space-Borne Hyperspectral Data for Biomass Quantification in an Arid Environment: Advantages and Limitations. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 4565–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numata, I.; Roberts, D.A.; Chadwick, O.A.; Schimel, J.P.; Galvão, L.S.; Soares, J.V. Evaluation of Hyperspectral Data for Pasture Estimate in the Brazilian Amazon Using Field and Imaging Spectrometers. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1569–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.; Büscher, O.; Jandewerth, M. Estimation of Biomass Potential Based on Classification and Height Information. In Proceedings of the International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing (ISPRS): ISPRS Hannover Workshop 2013, Hannover, Germany, 21–24 May 2013; Volume XL-1/W1, pp. 263–268. [Google Scholar]
- Sibanda, M.; Mutanga, O.; Rouget, M. Discriminating Rangeland Management Practices Using Simulated HyspIRI , Landsat 8 OLI , Sentinel 2 MSI, and VENUS Spectral Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 3957–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibanda, M.; Mutanga, O.; Rouget, M. Examining the Potential of Sentinel-2 MSI Spectral Resolution in Quantifying above Ground Biomass across Different Fertilizer Treatments. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 110, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monty, J.G.; Daughtry, C.S.T.; Crawford, M. Assessing Crop Residue Cover Using Hyperion Data. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Boston, MA, USA, 6–11 July 2008; pp. 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Bannari, A.; Staenz, K.; Champagne, C.; Khurshid, K.S. Spatial Variability Mapping of Crop Residue Using Hyperion (EO-1) Hyperspectral Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 8107–8127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, P.A.; Foster, J.R.; Chastian, R.A., Jr.; Currie, W.S. Canopy Nitrogen in the Forests of the Central Appalachian Mountains Using Hyperion and AVIRIS. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeil, B.E.; de Beurs, K.M.; Eshleman, K.N.; Foster, J.R.; Townsend, P.A. Maintenance of Ecosystem Nitrogen Limitation by Ephemeral Forest Disturbance: An Assessment Using MODIS, Hyperion, and Landsat ETM+. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotzler, S.; Hill, J.; Buddenbaum, H.; Stoffels, J. The Potential of EnMAP and Sentinel-2 Data for Detecting Drought Stress Phenomena in Deciduous Forest Communities. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 14227–14258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciraolo, G.; Capodici, F.; D’Urso, G.; Goffredo, L.L.; Antonino, M. Mapping Evapotranspiration on Vineyards: The Sentinel-2 Potentiality. In Proceedings of the First Sentinel-2 Preparatory Symposium, Frascati, Italy, 23–27 April 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- White, J.C.; Gómez, C.; Wulder, M.A.; Coops, N.C. Characterizing Temperate Forest Structural and Spectral Diversity with Hyperion EO-1 Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1576–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nink, S.; Hill, J.; Buddenbaum, H.; Stoffels, J.; Sachtleber, T.; Langshausen, J. Assessing the Suitability of Future Multi- and Hyperspectral Satellite Systems for Mapping the Spatial Distribution of Norway Spruce Timber Volume. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 12009–12040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clasen, A.; Somers, B.; Pipkins, K.; Tits, L.; Segl, K.; Brell, M.; Kleinschmit, B.; Spengler, D.; Lausch, A.; Förster, M. Spectral Unmixing of Forest Crown Components at Close Range, Airborne and Simulated Sentinel-2 and EnMAP Spectral Imaging Scale. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 15361–15387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerdink, S.K.; Roberts, D.A.; King, J.Y.; Roth, K.L.; Dennison, P.E.; Amaral, C.H.; Hook, S.J. Linking Seasonal Foliar Traits to VSWIR-TIR Spectroscopy across California Ecosystems. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 322–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.A.; Dennison, P.E.; Roth, K.L.; Dudley, K.; Hulley, G. Relationships between Dominant Plant Species, Fractional Cover and Land Surface Temperature in a Mediterranean Ecosystem. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 167, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, M.; Thenkabail, P. Developing in situ non-destructive estimates of crop biomass to address issues of scale in remote sensing. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 808–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, F.; Perry, S.; Caballero, A. Integrated Multispectral and Hyperspectral Mineral Mapping, Los Menucos, Rio Negro, Argentina, Part II. EO-1 Hyperion/AVIRIS comparisons and landsat TM. In Proceedings of the 11th JPL Airborne Geoscience Workshop, Pasadena, CA, USA, 4–8 March 2002; pp. 2–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard, B.E.; Crowley, J.K. Mineral Mapping on the Chilean-Bolivian Altiplano Using Co-Orbital ALI, ASTER and Hyperion Imagery: Data Dimensionality Issues and Solutions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 99, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldhoff, G.; Bubenzer, O.; Bolten, A.; Koppe, W.; Bareth, G. Spectral Analysis of Aster, Hyperion, and Quickbird Data for Geomorphological and Geological Research in Egypt (Dakhla Oasis, Western Desert). Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2008, XXXVII, 1201–1206. [Google Scholar]
- Leverington, D.W. Discrimination of Geological End Members Using Hyperion Imagery: Preliminary Results, Big Bend National Park, TEXAS. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Boston, MA, USA, 7–11 July 2008; Volume 2, pp. 40–41. [Google Scholar]
- Leverington, D.W. Discrimination of Sedimentary Lithologies Using Hyperion and Landsat Thematic Mapper Data: A Case Study at Melville Island, Canadian High Arctic. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 233–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cudahy, T.J.; Hewson, R.; Huntington, J.F.; Quigley, M.A.; Barry, P.S. The Performance of the Satellite-Borne Hyperion Hyperspectral VNIR-SWIR Imaging System for Mineral Mapping at Mount Fitton, South Australia. In Proceedings of the Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS 2001), Sydney, Australia, 9–13 July 2001; pp. 314–316. [Google Scholar]
- Gersman, R.; Ben-Dor, E.; Beyth, M.; Avigad, D.; Abraha, M.; Kibreab, A. Mapping of Hydrothermally Altered Rocks by the EO-1 Hyperion Sensor, Northern Danakil Depression, Eritrea. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 3911–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, W.; Cheng, Q.; Jing, L.; Chen, Y.; Guo, X.; Ding, H.; Liu, Q. Mineral Mapping in the Western Kunlun Mountains Using Tiangong-1 Hyperspectral Imagery. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2016, 34, 012011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesche, N.K.; Rogass, C.; Lubitz, C.; Brell, M.; Herrmann, S.; Mielke, C.; Tonn, S.; Appelt, O.; Altenberger, U.; Kaufmann, H. Hyperspectral REE (Rare Earth Element) Mapping of Outcrops-Applications for Neodymium Detection. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 5160–5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bösche, N.K. Detection of Rare Earth Elements and Rare Earth Oxides with Hyperspectral Spectroscopy. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Potsdam, Potsdam, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mielke, C.; Boesche, N.K.; Rogass, C.; Segl, K.; Kaufmann, H. Multi- and Hyperspectral Satellite Sensors for Mineral Exploration, New Applications to the Sentinel-2 and EnMAP Mission. In Proceedings of the 34th EARSeL Symposium, Poland, Warsaw, 16–20 June 2014; pp. 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Mielke, C.; Boesche, N.K.; Rogass, C.; Kaufmann, H.; Gauert, C.; de Wit, M. Spaceborne Mine Waste Mineralogy Monitoring in South Africa, Applications for Modern Push-Broom Missions: Hyperion OLI and EnMAP/Sentinel-2. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 6790–6816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielke, C.; Rogass, C.; Boesche, N.; Segl, K.; Altenberger, U. EnGeoMAP 2.0-Automated hyperspectral mineral identification for the German EnMAP space mission. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogge, D.; Rivard, B.; Segl, K.; Grant, B.; Feng, J. Mapping of NiCu-PGE Ore Hosting Ultramafic Rocks Using Airborne and Simulated EnMAP Hyperspectral Imagery, Nunavik, Canada. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 302–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, F.A.; Taranik, J.V.; Calvin, W.M.; Michaels, J.; Littlefield, E.F.; Coolbaugh, M.; Martini, B.A. Characterization of Hydrothermal Systems Using Simulated HyspIRI Data. In Proceedings of the IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 5–12 March 2011; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Kruse, F.A.; Taranik, J.V.; Coolbaugh, M.; Michaels, J.; Littlefield, E.F.; Calvin, W.M.; Martini, B.A. Effect of Reduced Spatial Resolution on Mineral Mapping Using Imaging Spectrometry-Examples Using Hyperspectral Infrared Imager (HyspIRI)-Simulated Data. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 1584–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducart, D.F.; Silva, A.M.; Labouré, C.; Toledo, B.; Assis, L.M.D. Mapping Iron Oxides with Landsat-8/OLI and EO-1/Hyperion Imagery from the Serra Norte Iron Deposits in the Carajás Mineral Province, Brazil. Braz. J. Geol. 2016, 46, 331–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoya, N.; Chan, J.C.W.; Segl, K. Potential of Resolution-Enhanced Hyperspectral Data for Mineral Mapping Using Simulated EnMAP and Sentinel-2 Images. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.L.; Gong, P.; Zhu, Z.L. A Spectral Index for Estimating Soil Salinity in the Yellow River Delta Region of China Using EO-1 Hyperion Data. Pedosphere 2010, 20, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldi, F.; Palombo, A.; Santini, F.; Pascucci, S.; Pignatti, S.; Casa, R. Evaluation of the Potential of the Current and Forthcoming Multispectral and Hyperspectral Imagers to Estimate Soil Texture and Organic Carbon. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 179, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldi, F.; Palombo, A.; Pascucci, S.; Pignatti, S.; Santini, F.; Casa, R. Reducing the Influence of Soil Moisture on the Estimation of Clay from Hyperspectral Data: A Case Study Using Simulated PRISMA Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 15561–15582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, C.; Oltra-Carrió, R.; Bacha, S.; Lagacherie, P.; Briottet, X. Evaluating the Sensitivity of Clay Content Prediction to Atmospheric Effects and Degradation of Image Spatial Resolution Using Hyperspectral VNIR/SWIR Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 164, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malec, S.; Rogge, D.; Heiden, U.; Sanchez-Azofeifa, A.; Bachmann, M.; Wegmann, M. Capability of Spaceborne Hyperspectral EnMAP Mission for Mapping Fractional Cover for Soil Erosion Modeling. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 11776–11800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulos, G.P.; Arvanitis, K.; Sigrimis, N. Hyperion hyperspectral imagery analysis combined with machine learning classifiers for land use/cover mapping. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 3800–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Arfa, J.; Bergès, J.C.; Beltrando, G.; Rim, K.; Zargouni, F. Mapping the Land Cover in Coastal Gabes Oases Using the EO-1 Hyperion Hyperspectral Sensor. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference, Vienna, Austria, 12–17 April 2015; Volume 17, p. 4314. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Gong, P. Land-use/Land-cover Classification with Multispectral and Hyperspectral EO-1 Data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2007, 73, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakovels, D.; Filipovs, J.; Brauns, A.; Taskovs, J.; Erins, G. Land Cover Lapping in Latvia Using Hyperspectral Airborne and Simulated Sentinel-2 Data. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Remote Sensing and Geoinformation of the Environment, Paphos, Cyprus, 4–8 April 2016; Volume 9688, pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Törmä, M.; Lewiński, S.; Aleksandrowicz, S.; Esch, T.; Metz, A.; Smith, G.; Lamb, A.; Turlej, K. Seasonality of Land Cover Types as Basis for Improved Land Cover Classification within Pan-European Area Frame Sampling Scheme. In Proceedings of the First Sentinel-2 Preparatory Symposium, Frascati, Italy, 23–27 April 2012; Ouwehand, L., Ed.; ESA: Frascati, Italy, 2012. Number August 2015. p. 900. [Google Scholar]
- Törmä, M.; Hatunen, S.; Härmä, P.; Järvenpää, E. Sentinel-2 Images and Finnish Corine Land Cover Classification. In Proceedings of the First Sentinel-2 Preparatory Symposium, Frascati, Italy, 23–27 April 2012; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, M.L.; Kilham, N.E. Mapping of Land Cover in Northern California with Simulated Hyperspectral Satellite Imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 119, 228–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.L. Mapping Land Cover with Hyperspectral and Multispectral Satellites Using Machine Learning and Spectral Mixture Analysis. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 513–516. [Google Scholar]
- Hunger, S.; Karrasch, P.; Wessollek, C. Evaluating the Potential of Image Fusion of Multispectral and Radar Remote Sensing Data for the Assessment of Water Body Structure. In Proceedings of the Remote Sensing for Agriculture, Ecosystems, and Hydrology, Edinburgh, UK, 25 October 2016; Volume 9996, pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Pande, H.; Tiwari, P.S. High-Resolution and Hyperspectral Data Fusion for Classification. New Advances in Image Fusion. Miao, Q., Ed.; 2013. Chapter 4. pp. 57–77. Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/books/new-advances-in-image-fusion/high-resolution-and-hyperspectral-data-fusion-for-classification (accessed on 4 December 2017).
- Falcone, J.A.; Gomez, R. Mapping Impervious Surface Type and Sub-Pixel Abundance Using Hyperion Hyperspectral Imagery. Geocarto Int. 2005, 20, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, R.M.; Fusilli, L.; Pascucci, S.; Pignatti, S.; Santini, F. Hyperspectral Sensor Data Capability for Retrieving Complex Urban Land Cover in Comparison with Multispectral Data: Venice City Case Study (Italy). Sensors 2008, 8, 3299–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okujeni, A.; van der Linden, S.; Hostert, P. Extending the Vegetation-Impervious-Soil Model Using Simulated EnMAP Data and Machine Learning. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heldens, W.; Heiden, U.; Esch, T.; Stein, E.; Müller, A. Can the Future EnMAP Mission Contribute to Urban Applications? A Literature Survey. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 1817–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.A.; Quattrochi, D.A.; Hulley, G.C.; Hook, S.J.; Green, R.O. Synergies between VSWIR and TIR Data for the Urban Environment: An Evaluation of the Potential for the Hyperspectral Infrared Imager (HyspIRI) Decadal Survey Mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Provincial, S.; Alchanatis, V. The Potential of Airborne Hyperspectral Images to Detect Leaf Nitrogen Content in Potato. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 5888–5889. [Google Scholar]
- Giardino, C.; Brando, V.E.; Dekker, A.G.; Strömbeck, N.; Candiani, G. Assessment of Water Quality in Lake Garda (Italy) Using Hyperion. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 109, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, R.; Bell, S. A Protocol for Improving Mapping and Assessing of Seagrass Abundance along the West Central Coast of Florida Using Landsat TM and EO-1 ALI/Hyperion Images. Proc. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 83, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, H.; Hieronymi, M.; Röttgers, R.; Krasemann, H.; Qiu, Z. Hyperspectral Differentiation of Phytoplankton Taxonomic Groups: A Comparison between Using Remote Sensing Reflectance and Absorption Spectra. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 14781–14805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogashawara, I.; Mishra, D.R.; Mishra, S.; Curtarelli, M.P.; Stech, J.L. A Performance Review of Reflectance Based Algorithms for Predicting Phycocyanin Concentrations in Inland Waters. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4774–4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudorff, C.M.; Galvão, L.S.; Novo, E.M.L.M. Reflectance of Floodplain Waterbodies Using EO-1 Hyperion Data from High and Receding Flood Periods of the Amazon River. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 2713–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Casey, B.; Arnone, R.; Weidemann, A.; Parsons, R.; Montes, M.J.; Gao, B.C.; Goode, W.; Davis, C.; Dye, J. Water and Bottom Properties of a Coastal Environment Derived from Hyperion Data Measured from the EO-1 Spacecraft Platform. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2007, 1, 011502. [Google Scholar]
- Devred, E.; Turpie, K.R.; Moses, W.; Klemas, V.V.; Moisan, T.; Babin, M.; Toro-Farmer, G.; Forget, M.H.; Jo, Y.H. Future Retrievals of Water Column Bio-Optical Properties Using the Hyperspectral Infrared Imager (HyspIRI). Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 6812–6837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hestir, E.L.; Brando, V.E.; Bresciani, M.; Giardino, C.; Matta, E.; Villa, P.; Dekker, A.G. Measuring freshwater aquatic ecosystems: The need for a hyperspectral global mapping satellite mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 167, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, T.W.; Cavanaugh, K.C.; Siegel, D.A. Remote Monitoring of Giant Kelp Biomass and Physiological Condition: An Evaluation of the Potential for the Hyperspectral Infrared Imager (HyspIRI) Mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 167, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Feng, L.; Hardy, R.F.; Hochberg, E.J. Spectral and Spatial Requirements of Remote Measurements of Pelagic Sargassum macroalgae. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 167, 229–246. [Google Scholar]
- Kudela, R.M.; Palacios, S.L.; Austerberry, D.C.; Accorsi, E.K.; Guild, L.S.; Torres-Perez, J. Application of hyperspectral remote sensing to cyanobacterial blooms in inland waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 167, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, S.L.; Kudela, R.M.; Guild, L.S.; Negrey, K.H.; Torres-Perez, J.; Broughton, J. Remote Sensing of Phytoplankton Functional Types in the Coastal Ocean from the HyspIRI Preparatory Flight Campaign. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 167, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turpie, K.R.; Klemas, V.V.; Byrd, K.; Kelly, M.; Jo, Y.H. Prospective HyspIRI Global Observations of Tidal Wetlands. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 167, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhellemont, Q.; Ruddick, K. Acolite for Sentinel-2: Aquatic Applications of MSI Imagery. In Proceedings of the ESA Living Planet Symposium, Prague, Czech, 9–13 May 2016; Volume SP-740, pp. 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Toming, K.; Kutser, T.; Laas, A.; Sepp, M.; Paavel, B.; Nõges, T. First Experiences in Mapping Lakewater Quality Parameters with Sentinel-2 MSI Imagery. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ling, F.; Wang, Q.; Li, W.; Li, X. Water Bodies’ Mapping from Sentinel-2 Imagery with Modified Normalized Difference Water Index at 10-m Spatial Resolution Produced by Sharpening the SWIR Band. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, R.; Zhan, S.; Liu, H.; Tong, S.; Yang, B.; Xu, M.; Ye, Z.; Huang, Y.; Shu, S.; Wu, Q.; et al. Comparison of Satellite Reflectance Algorithms for Estimating Chlorophyll-a in a Temperate Reservoir Using Coincident Hyperspectral Aircraft Imagery and Dense Coincident Surface Observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 178, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltese, A.; Capodici, F.; Ciraolo, G.; Corbari, C.; Granata, A.; La Loggia, G. Planktothrix rubescens in Freshwater Reservoirs: The Sentinel-2 Potentiality for Mapping Phycocyanin Concentration. In Proceedings of the First Sentinel-2 Preparatory Symposium, Frascati, Italy, 23–27 April 2012; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Hedley, J.; Roelfsema, C.; Koetz, B.; Phinn, S. Capability of the Sentinel 2 mission for tropical coral reef mapping and coral bleaching detection. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakuta, S.; Ariyasu, E.; Asada, N.; Takeda, T.; Matsunaga, T. A Monitoring Method of Coral Bleaching by Using Hyperspectral Sensor. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Melbourne, Australia, 21–26 July 2013; pp. 1598–1601. [Google Scholar]
- Abrams, M. Beyond ASTER: Future VNIR-SWIR and TIR Hyperspectral Instruments. In Proceedings of the HyspIRI Science Workshop; Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA, USA, 15 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ustin, S.; Roberts, D.; Gardner, M.; Dennison, P. Evaluation of the Potential of Hyperion Data to Estimate Wildfire Hazard in the Santa Ynez Front Range, Santa Barbara, California. IEEE Int. Geosci. Remote Sens. Symp. 2002, 2, 7536–7538. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, Y.; Kim, Y. Application of Hyperion Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Data for Wildfire Fuel Mapping. Korean J. Remote Sens. 2007, 23, 21–32. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, D.A.; Dennison, P.E.; Gardner, M.E.; Hetzel, Y.; Ustin, S.L.; Lee, C.T. Evaluation of the Potential of Hyperion for Fire Danger Assessment by Comparison to the Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1297–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, E.R.J.; Wang, L.; Qu, J.J.; Hao, X. Remote Sensing of Fuel Moisture Content from Canopy Water Indices and Normalized Dry Matter Index. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2012, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Crowley, J.K.; Hubbard, B.E.; Mars, J.C. Analysis of Potential Debris Flow Source Areas on Mount Shasta, California, by Using Airborne and Satellite Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 87, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, H.E.; Diuk-Wasser, M.A.; Guan, Y.; Caskey, S.; Fish, D. Comparison of Three Satellite Sensors at Three Spatial Scales to Predict Larval Mosquito Presence in Connecticut Wetlands. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 2301–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numata, I.; Cochrane, M.A.; Galvëo, L.S. Analyzing the Impacts of Frequency and Severity of Forest Fire on the Recovery of Disturbed Forest Using Landsat Time Series and EO-1 Hyperion in the Southern Brazilian Amazon. Earth Interact. 2011, 15, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitri, G.H.; Gitas, I.Z. Mapping post-fire vegetation regeneration using EO-1 Hyperion. In Proceedings of the 6th Internation Workshop of the EARSeL Special Interest Group on Forest Fires, Thessaloniki, Greece, 27–29 September 2007; pp. 252–255. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Manso, A.; Fernández-Manso, O.; Quintano, C. Sentinel-2A Red-Edge Spectral Indices Suitability for Discriminating Burn Severity. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 50, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheson, D.S.; Dennison, P.E. Evaluating the Effects of Spatial Resolution on Hyperspectral Fire Detection and Temperature Retrieval. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 780–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arellano, P.; Tansey, K.; Balzter, H.; Boyd, D.S. Detecting the Effects of Hydrocarbon Pollution in the Amazon Forest Using Hyperspectral Satellite Images. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 205, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bonis, R.; Laneve, G.; Palombo, A.; Pascucci, S.; Pignatti, S.; Santini, F.; Ananasso, C. The potential impact of the next hyperspectral PRISMA mission on the natural and anthropogenic hazards management. In Proceedings of the IEEE 15th International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering (EEEIC), Rome, Italy, 10–13 June 2015; pp. 1643–1646. [Google Scholar]
- Thenkabail, P.S.; Mariotto, I.; Gumma, M.K.; Middleton, E.M.; Landis, D.R.; Huemmrich, K.F. Selection of Hyperspectral Narrowbands (HNBs) and Composition of Hyperspectral Twoband Vegetation Indices (HVIs) for Biophysical Characterization and Discrimination of Crop Types Using Field Reflectance and Hyperion/EO-1 Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thenkabail, P.S.; Lyon, G.J.; Huete, A. Advances in Hyperspectral Remote Sensing of Vegetation and Agricultural Crops. In Hyperspectral Remote Sensing of Vegetation; Thenkabail, P.S., Ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011; Chapter 1; pp. 3–29. [Google Scholar]
- Christian, B.; Krishnayya, N.S.R. Classification of Tropical Trees Growing in a Sanctuary Using Hyperion (EO-1) and SAM Algorithm. Curr. Sci. 2009, 96, 1601–1607. [Google Scholar]
- Jafari, R.; Lewis, M.M. Arid Land Characterisation with EO-1 Hyperion Hyperspectral Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinform. 2012, 19, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, J.; Chan, J.C.W. Hyperspectral Imagery Super-Resolution by Spatial-Spectral Joint Nonlocal Similarity. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 2671–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, S.J.; McCleary, A.L.; Mena, C.F.; Shao, Y.; Tuttle, J.P.; González, A.; Atkinson, R. QuickBird and Hyperion Data Analysis of an Invasive Plant Species in the Galapagos Islands of Ecuador: Implications for Control and Land Use Management. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1927–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, B.; Asner, G.P. Invasive Species Mapping in Hawaiian Rainforests Using Multi-Temporal Hyperion Spaceborne Imaging Spectroscopy. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Leeuwen, M.V.; Romanczyk, P.; Kelbe, D.; Aardt, J.V. Assessing the Impact of Sub-Pixel Vegetation Structure on Imaging Spectroscopy via Simulation. In Proceedings of the Algorithms and Technologies for Multispectral, Hyperspectral, and Ultraspectral Imagery XXI, Baltimore, MA, USA, 21 May 2015; Volume 9472, pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Thorp, K.R.; French, A.N.; Rango, A. Effect of Image Spatial and Spectral Characteristics on Mapping Semi-Arid Rangeland Vegetation Using Multiple Endmember Spectral Mixture Analysis (MESMA). Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 132, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feilhauer, H.; Dahlke, C.; Doktor, D.; Lausch, A.; Schmidtlein, S.; Schulz, G.; Stenzel, S. Mapping the Local Variability of Natura 2000 Habitats with Remote Sensing. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2014, 17, 765–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicaksono, P. Mangrove above-ground carbon stock mapping of multi-resolution passive remote-sensing systems. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 1551–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loncan, L.; Almeida, L.B.; Bioucas-dias, M.; Briottet, X.; Chanussot, J.; Dobigeon, N.; Fabre, S.; Liao, W.; Licciardi, G.A.; Sim, M.; et al. Hyperspectral Pansharpening: A Review. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2015, 3, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Fu, D.; Sun, X.; Chen, H.; She, X. A Spatial-Temporal-Spectral Blending Model Using Satellite Images. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Novokuznetsk, Russian, 7–10 June 2016; Volume 34, pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasrodashti, E.K.; Karami, A.; Heylen, R.; Scheuders, P. Spatial Resolution Enhancement of Hyperspectral Images Using Spectral Unmixing and Bayesian Sparse Representation. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Chan, J.C.W.; Shen, Q. Image Fusion for Spatial Enhancement of Hyperspectral Image via Pixel Group Based Non-Local Sparse Representation. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Huang, B.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, H. Spatio-Spectral Fusion of Satellite Images Based on Dictionary-Pair Learning. Inf. Fusion 2014, 18, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briottet, X.; Marion, R.; Carrere, V.; Jacquemoud, S.; Chevrel, S.; Prastault, P.; D’Oria, M.; Gilouppe, P.; Hosford, S.; Lubac, B.; et al. HYPXIM: A new hyperspectral sensor combining science/defence applications. In Proceedings of the 3rd Workshop on Hyperspectral Image and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing (WHISPERS), Lisbon, Portugal, 6–9 June 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Pearlman, J.; Carman, S.; Segal, C.; Jarecke, P.; Clancy, P.; Browne, W. Overview of the Hyperion Imaging Spectrometer for the NASA EO-1 mission. In Proceedings of the Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Sydney, Australia, 9–13 July 2001; Volume 7, pp. 3036–3038. [Google Scholar]
- Kruse, F.A.; Boardman, J.W.; Huntington, J.F.; Mason, P.; Quigley, M.A. Evaluation and Validation of EO-1 Hyperion for Geologic Mapping. In Proceedings of the Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS 2002), Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2002; pp. 593–595. [Google Scholar]
- Nocita, M.; Kooistra, L.; Bachmann, M.; Müller, A.; Powell, M.; Weel, S. Predictions of Soil Surface and Topsoil Organic Carbon Content through the Use of Laboratory and Field Spectroscopy in the Albany Thicket Biome of Eastern Cape Province of South Africa. Geoderma 2011, 167–168, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnsleu, M.J.; Settle, J.J.; Cutter, M.; Lobb, D.; Teston, F. The PROBA/CHRIS mission: a low-cost smallsat for hyperspectral multiangle observations of the Earth surface and atmosphere. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Soc. 2004, 42, 1512–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, H.J. HJ-1 (Huan Jing-1: Environmental Protection & Disaster Monitoring Constellation). Available online: https://directory.eoportal.org/web/eoportal/satellite-missions/h/hj-1 (accessed on 4 January 2018).
- Corson, M.R.; Lucke, R.L.; Davis, O.; Snyder, A.; Korwan, R.; Mcglothlin, R.; Butcher, D.; Wood, L. The Hyperspectral Imager for the Coastal Ocean (HICO) on the International Space Station. In Oceans from Space; Barale, V., Gower, J., Alberotanza, L., Eds.; JRC: Venice, France, 2010; pp. 69–70. [Google Scholar]
- Arkhipov, S.A.; Baklanov, A.I.; Linko, V.M. Hyperspectral shooting apparatus for the Resurs-P spacecraft. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2014, 50, 978–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.; Avbelj, J.; Carmona, E.; Eckardt, A.; Gerasch, B.; Graham, L.; Günther, B.; Heiden, U.; Ickes, J.; Kerr, G.; et al. The New Hyperspectral Sensor Desis on the Multi-Payload Platform Muses Installed on the Iss. ISPRS Inter. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, XLI-B1, 461–467. [Google Scholar]
- Perkins, R.; Müller, R.; Carmona, E. The DESIS Hyperspectral Instrument—A New Space-Based Tool for Coastal Zone Monitoring; DLR: Cologne, Germany, 2017; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Keitha, D.J.; Schaeffer, B.A.; Lunetta, R.S.; Gould, R.W.; Rocha, K.; Cobb, D.J. Remote Sensing of Selected Water-Quality Indicators with the Hyperspectral Imager for the Coastal Ocean (HICO) Sensor. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 2927–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Meteorological Organization. Instrument: HYSI. Available online: https://www.wmo-sat.info/oscar/instruments/view/1048 (accessed on 4 January 2018).
- Jauffraud, E.; Bassaler, P.; Coppo, P.; Taiti, A.; Battistelli, E.; Rossi, M. FLEX & SENTINEL 3: A TANDEM TO MONITOR VEGETATION. In Proceedings of the Living Planet Symposium, Prague, Czech Republic, 9–13 May 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Coppo, P.; Taiti, A.; Pettinato, L.; Francois, M.; Taccola, M.; Drusch, M. Fluorescence Imaging Spectrometer (FLORIS) for ESA FLEX Mission. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Instrument | MSI | Hyperion | TianGong-1 | PRISMA | HISUI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Platform name | Sentinel-2 | EO-1 | Shenzhou-8 | PRISMA | HISUI |
| Sensor type | Multispectral | Hyperspectral | Hyperspectral | Hyperspectral | Hyperspectral |
| Swath width (km) | 290 | 7.5 | 10 | 30 | 30 |
| Spectral range (nm) | 443–2190 | 357–2576 | 400–2500 | 400–2505 | 400–2500 |
| VNIR | 357–1000 | 400–1000 | 400–1010 | 400–970 | |
| SWIR | 900–2576 | 1000–2500 | 920–2500 | 900–2500 | |
| Spectral bands | 13 | 220 | 128 | 249 | 185 |
| Resolution | |||||
| Spatial (m) | 10–20–60 | 30 | 10 (VNIR) | 30 | 30 |
| 20 (SWIR) | |||||
| Temporal (day) | 5 | 16–30 | 14 to 7 | 2–60 | |
| Spectral (nm) | 15–180 | 10 | 10 (VNIR) | 10 | 10 (VNIR) |
| 23 (SWIR) | 12.5 (SWIR) | ||||
| SNR (30% albedo) | |||||
| VNIR | 89:1 to 168:1 | 144:1 to 161:1 | 200:1 | ≥450 at 620 nm | |
| 600:1 at 650 nm | |||||
| SWIR | 50:1 to 100:1 | 40:1 to 110:1 | 200:1 | ≥300:1 at 2100 nm | |
| 400:1 at 1550 nm | |||||
| 100:1 | |||||
| 200:1 at 2100 nm | |||||
| Objective | Earth observation | Earth observation | Scientific research and land imaging | Natural resources and atmosphere | Energy, vegetation monitoring |
| Country | Europe | USA | China | Italy | Japan |
| Organization | ESA | NASA | Chinese Academy of Science Physics | Agenzia Spaziale Italiana | Japanese Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry |
| Number of articles | 41 | 608 | 8 | 5 | 1 |
| Instrument | MSI | EnMAP HSI | SHALOM | HyspIRI | HypXIM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Platform name | Sentinel-2 | EnMAP | Improved Multi- | HyspIRI | HypXIM |
| Purpose Satellite-II | |||||
| Sensor type | Multispectral | Hyperspectral | Hyperspectral | Hyperspectral | Hyperspectral |
| Swath width (km) | 290 | 30 | 30 | 145–600 | 15 |
| Spectral range (nm) | 443–2190 | 420–2450 | 400–2500 | 380–2510 | 400–2500 |
| VNIR | 420–1000 | 400–1010 | 380–1400 | 400–1100 | |
| SWIR | 900–2450 | 920–2500 | 1400–2510 | 1100–2500 | |
| Spectral bands | 13 | 244 | 275 | 214 | 210 |
| Resolution | |||||
| Spatial (m) | 10–20–60 | 30 | 10 | 30 (60) | 8 |
| Temporal (day) | 5 | 27 (VZA ≥ 5) | 4 (VZA ≥ 30) | 5–16 | 3–5 |
| 4 (VZA ≥ 30) | |||||
| Spectral (nm) | 15–180 | 6.5 (VNIR) | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| 10 (SWIR) | |||||
| SNR (30% albedo) | |||||
| VNIR | 89:1 to 168:1 | 400:1 | 200:1 | 560:1 at 500 nm | ≥200:1 to 250:1 |
| >400:1 at 495 nm | 600:1 at 650 nm | ||||
| SWIR | 50:1 to 100:1 | 180:1 | 200:1 | 356 at 1500 nm | ≥100:1 |
| >180:1 at 2200 nm | 400:1 at 1550 nm | 236 at 2200 nm | |||
| 100:1 | |||||
| 200:1 at 2100 nm | |||||
| Objective | Earth observation | Earth observation | Land and ocean observation | Volcanic, vegetation, soil, exploration | Soil, urban, coastal, biodiversity |
| Country | Europe | Germany | Italy-Israël | USA | France |
| Organization | ESA | GFZ-DLR | ASI-ISA | JPL-NASA | CNES |
| Number of articles | 41 | 41 | 2 | 35 | 1 |
| Results | S2 | Hyperion | TG-1 | PRISMA | EnMAP | HISUI | SHALOM | HyspIRI | HypXIM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | 77.8% | 57.7% | 50.0% | 50.0% | 63.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 40.6% | 100.0% |
| (b) | 22.2% | 30.8% | 50.0% | 50.0% | 29.6% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 46.9% | 0.0% |
| (c) | 0.0% | 11.5% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 7.4% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 12.5% | 0.0% |
| Studies | 27 | 78 | 2 | 6 | 27 | 1 | 1 | 32 | 1 |
| Main Applications Topics | Applications | Resolutions | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spatial | Temporal | ||
| Vegetation and Agriculture | Monitoring/Status | +++ | +++ |
| Monitoring/Disease | +++ | +++ | |
| Classification | ++/+++ | +++ | |
| Geology and Soils | Mapping/Properties | ++/+++ | + |
| Exploration | +++ | + | |
| Land use | Classification/Changes | ++ | + |
| Urban | Classification/Changes | +++ | + |
| Water resources | Quality assessment | + | + |
| Bathymetry | + | + | |
| Classification of coastal ecosystems | + | + | |
| Component bloom | ++ | +++ | |
| Disaster | Prevention | ++ | +/+++ |
| Monitoring | ++/+++ | +++ | |
| Post-crisis | ++ | +/++ | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Transon, J.; D’Andrimont, R.; Maugnard, A.; Defourny, P. Survey of Hyperspectral Earth Observation Applications from Space in the Sentinel-2 Context. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020157
Transon J, D’Andrimont R, Maugnard A, Defourny P. Survey of Hyperspectral Earth Observation Applications from Space in the Sentinel-2 Context. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(2):157. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020157
Chicago/Turabian StyleTranson, Julie, Raphaël D’Andrimont, Alexandre Maugnard, and Pierre Defourny. 2018. "Survey of Hyperspectral Earth Observation Applications from Space in the Sentinel-2 Context" Remote Sensing 10, no. 2: 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020157
APA StyleTranson, J., D’Andrimont, R., Maugnard, A., & Defourny, P. (2018). Survey of Hyperspectral Earth Observation Applications from Space in the Sentinel-2 Context. Remote Sensing, 10(2), 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020157