Development of Himawari-8/Advanced Himawari Imager (AHI) Land Surface Temperature Retrieval Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Methodology
3. Results
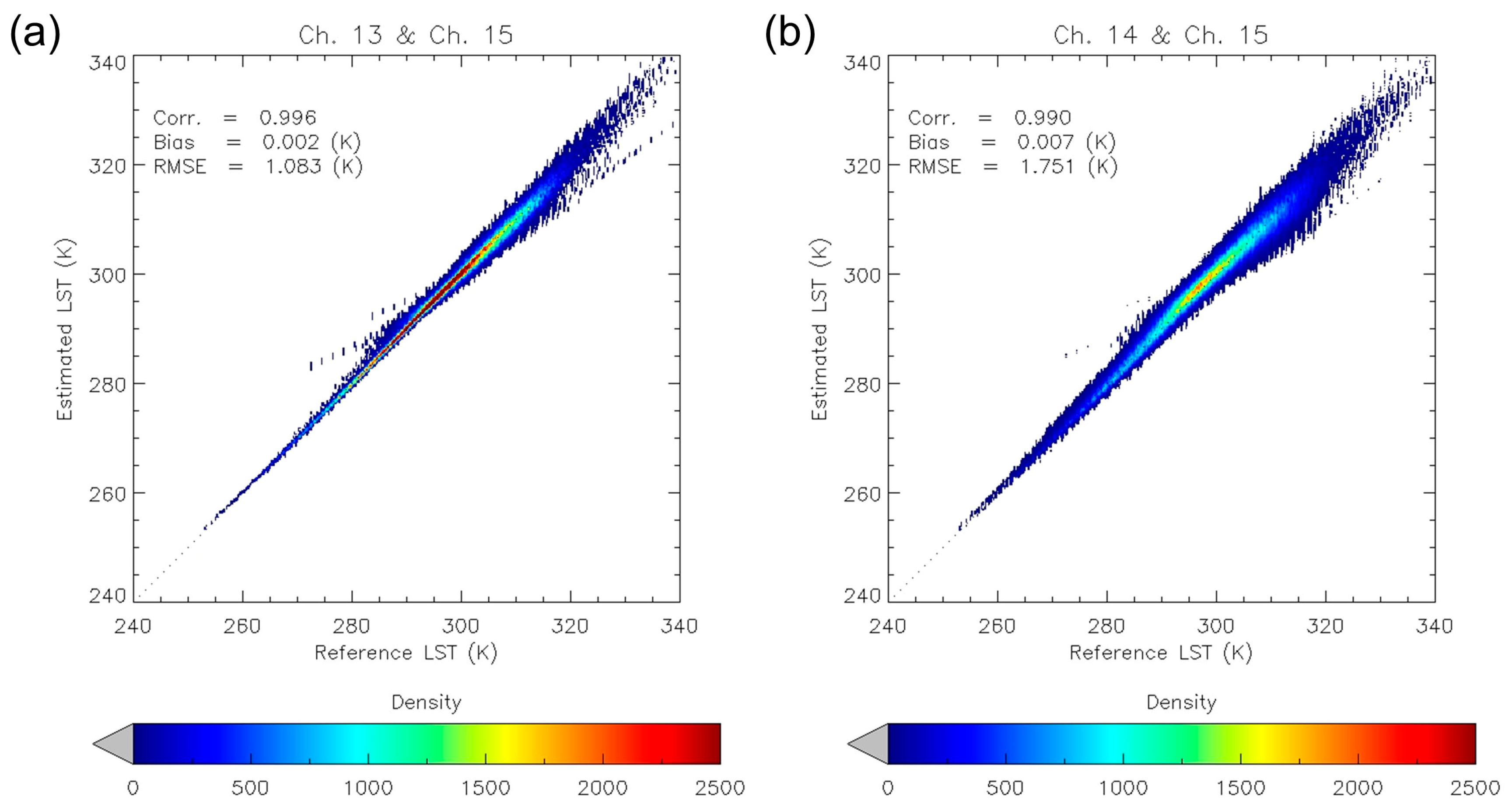
3.1. Results of Radiative Transfer Model Simulation
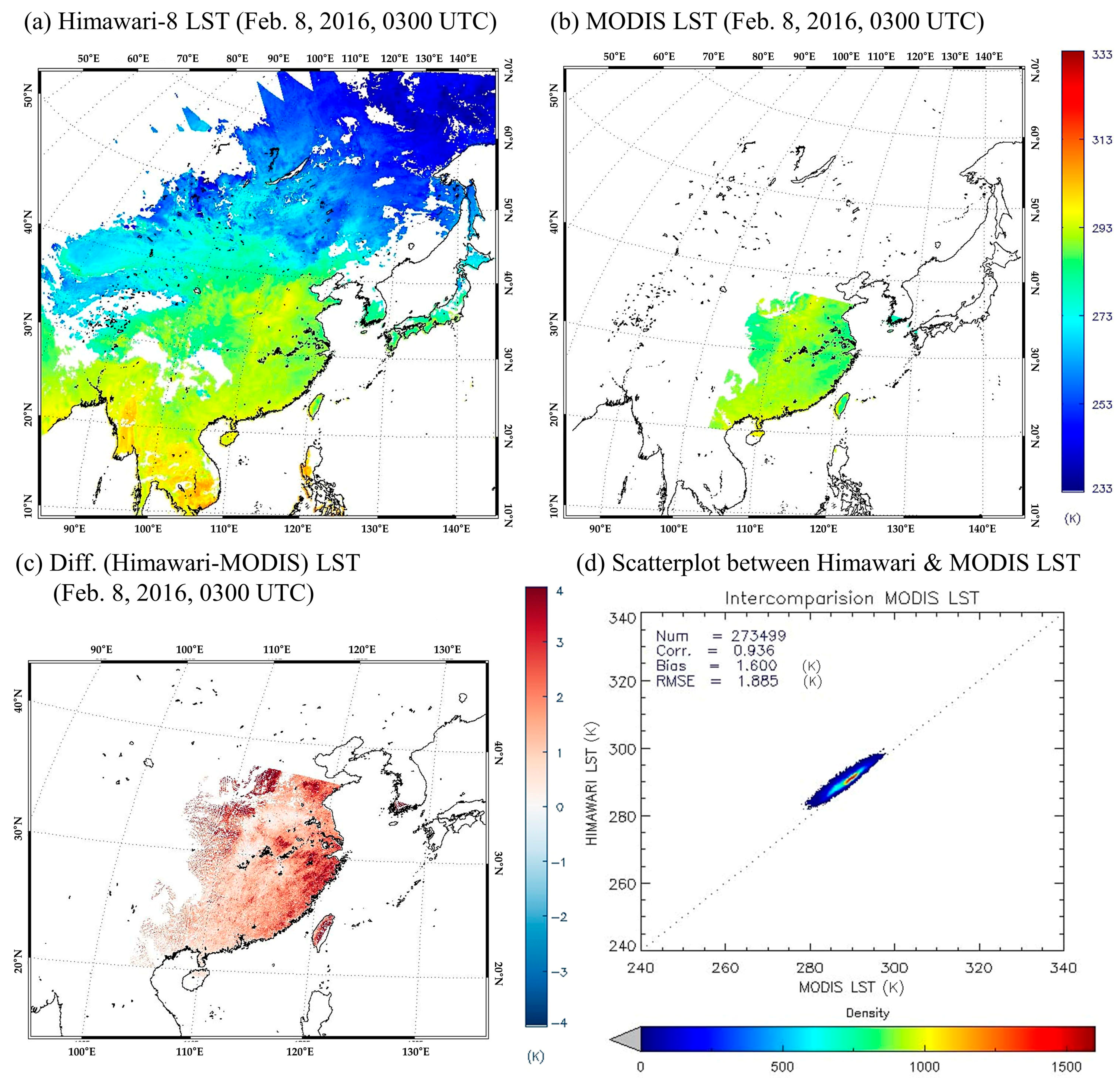
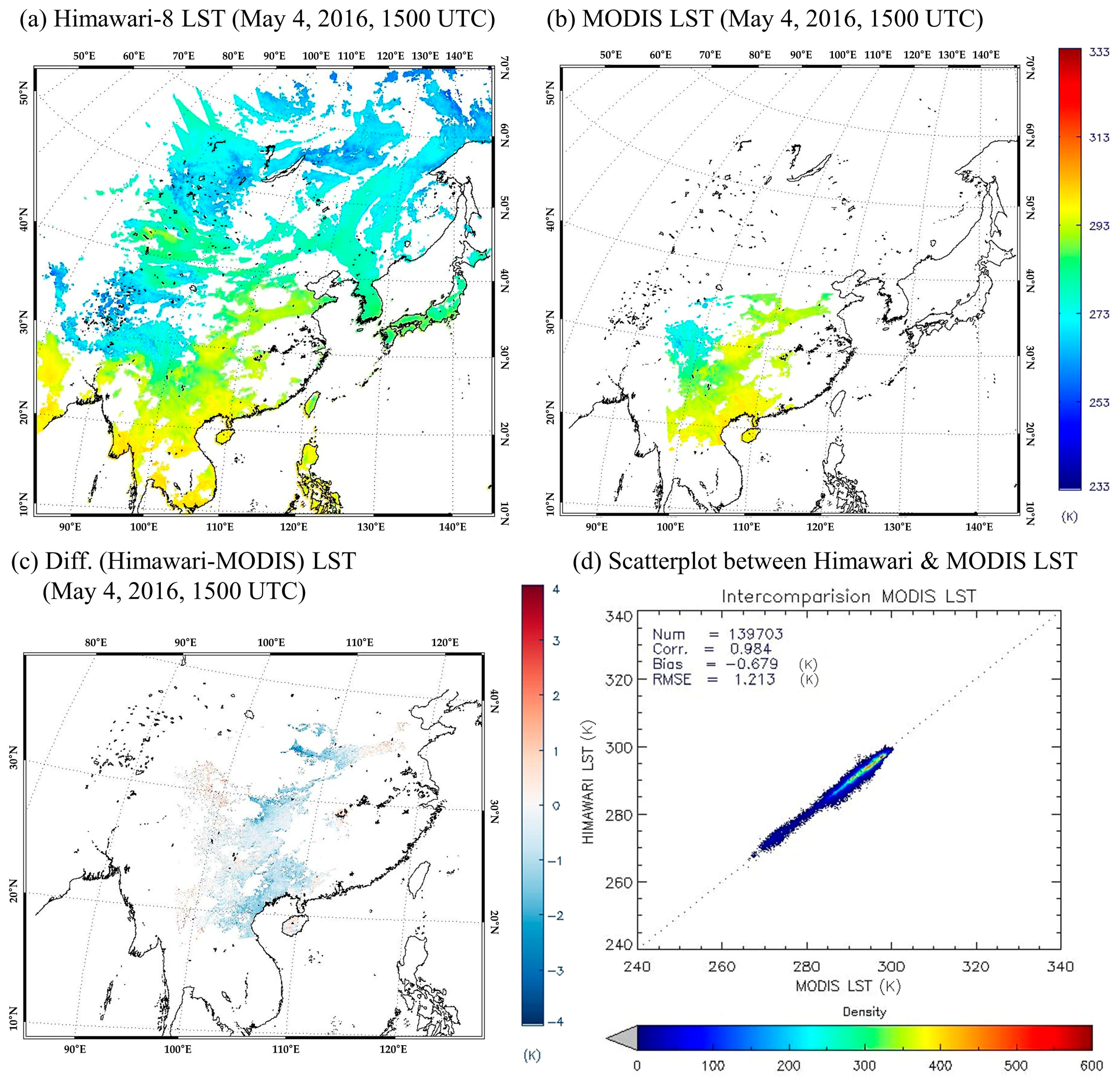
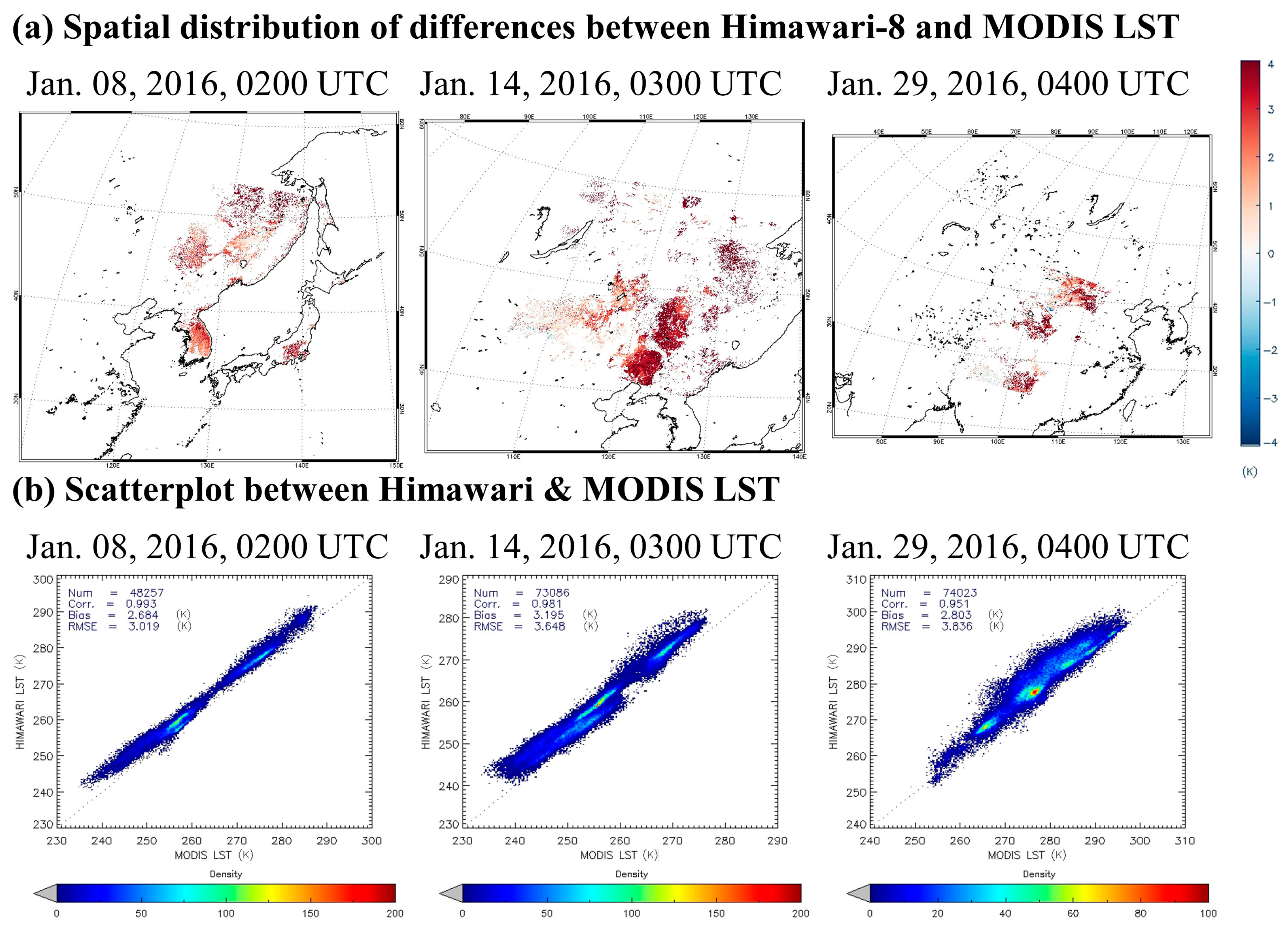
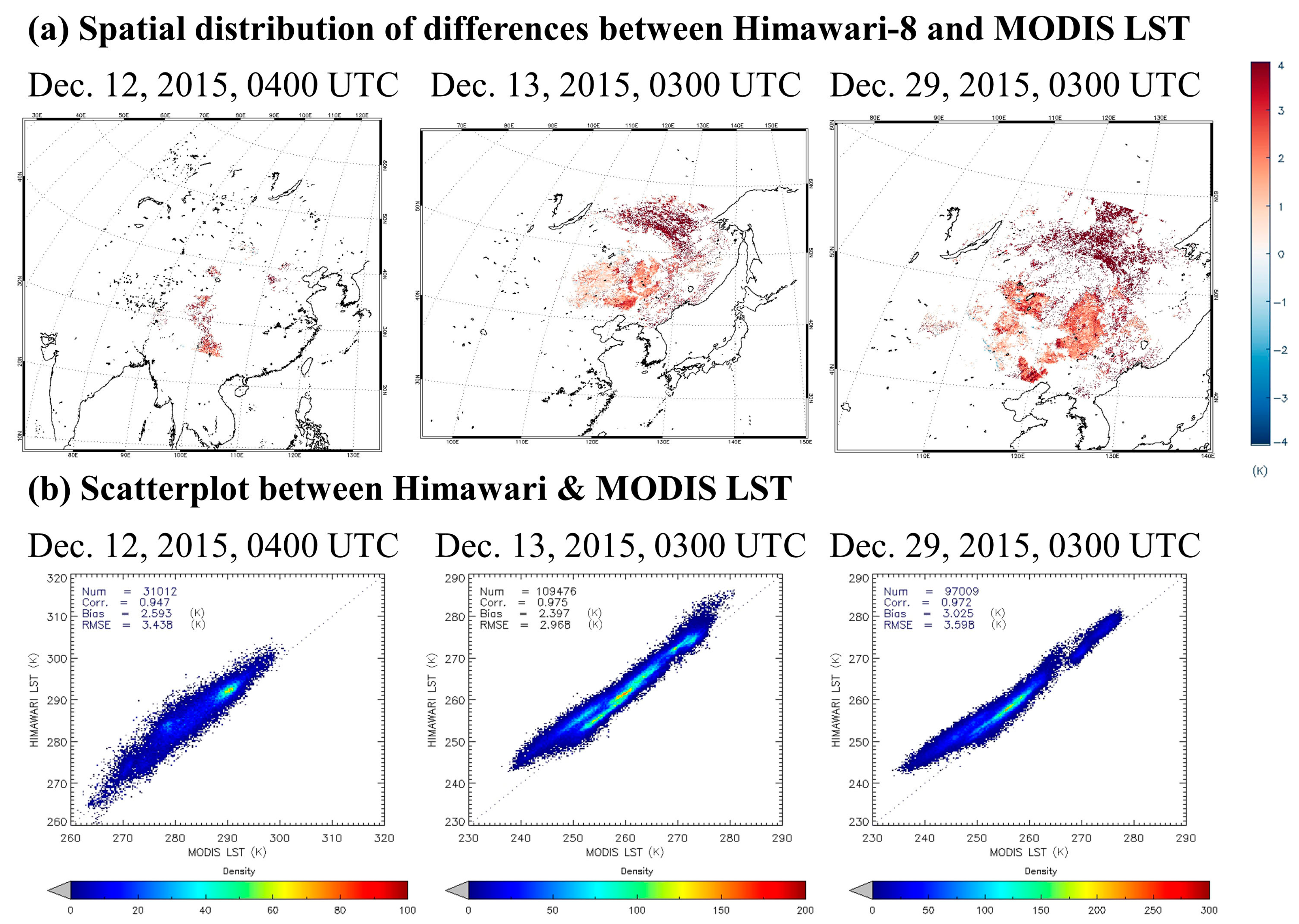
3.2. Cross-Validation Results Using MODIS LST
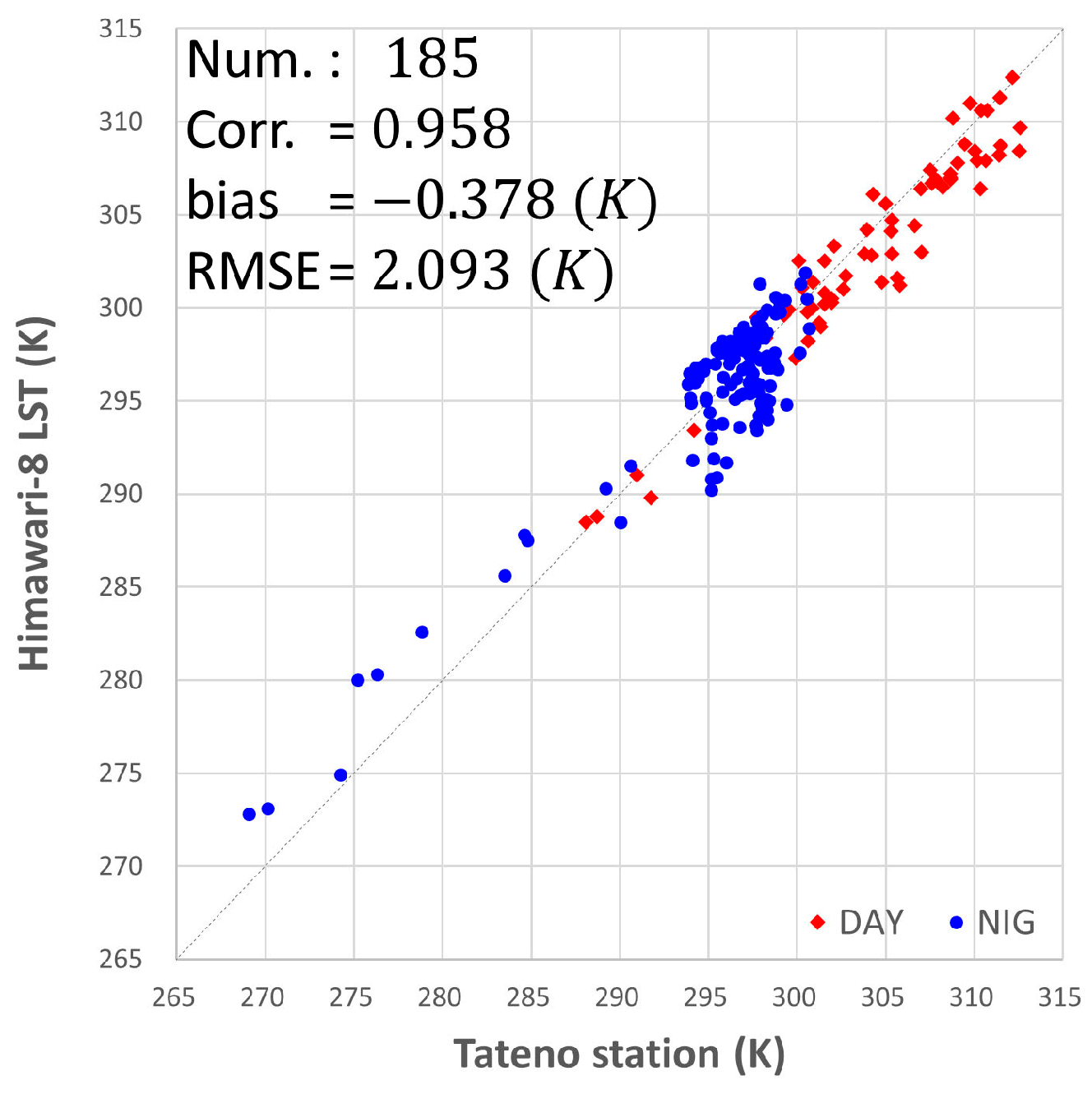
3.3. In Situ Validation Results Using Baseline Surface Radiation Network (BSRN)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dash, P.; Göttsche, F.; Olesen, F.; Fischer, H. Land Surface Temperature and Emissivity Estimation from Passive Sensor Data: Theory and Practice-Current Trends. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 2563–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbari, C.; Sobrino, J.; Mancini, M.; Hidalgo, V. Land Surface Temperature Representativeness in a Heterogeneous Area through a Distributed Energy-Water Balance Model and Remote Sensing Data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.K.; Sungmin, O.; Cassardo, C. Soil temperature response in Korea to a changing climate using a land surface model. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 53, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnieli, A.; Agam, N.; Pinker, R.T.; Anderson, M.; Imhoff, M.L.; Gutman, G.G.; Panov, N.; Goldberg, A. Use of NDVI and Land Surface Temperature for Drought Assessment: Merits and Limitations. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 618–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, P.; Song, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R. Toward the Estimation of Surface Soil Moisture Content using Geostationary Satellite Data Over Sparsely Vegetated Area. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 4112–4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, D.; Sheng, Y. The Impact of Energy Consumption on the Surface Urban Heat Island in China’s 32 Major Cities. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozenstein, O.; Agam, N.; Serio, C.; Masiello, G.; Venafra, S.; Achal, S.; Punkrin, E.; Karnieli, A. Diurnal emissivity dynamics in bare versus biocrusted sand dunes. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 506, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, M.S.; Baek, S.; Seol, K.H.; Cho, K. Advances in land modeling of KIAPS based on the Noah Land Surface Model. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 53, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barat, A.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, P.; Sarthi, P.P. Characteristics of Surface Urban Heat Island (SUHI) over the Gangetic Plain of Bihar, India. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 54, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, A.; Caselles, V.; Coll, C.; Sobrino, J.; Ottle, C. Thermal Remote Sensing of Land Surface Temperature from Satellites: Current Status and Future Prospects. Remote Sens. Rev. 1995, 12, 175–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tang, B.; Wu, H.; Ren, H.; Yan, G.; Wan, Z.; Trigo, I.F.; Sobrino, J.A. Satellite-Derived Land Surface Temperature: Current Status and Perspectives. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 131, 14–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillin, L.M. Estimation of Sea Surface Temperatures from Two Infrared Window Measurements with Different Absorption. J. Geophys. Res. 1975, 80, 5113–5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, F.; Li, Z. Temperature-Independent Spectral Indices in Thermal Infrared Bands. Remote Sens. Environ. 1990, 32, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, A.J. Land Surface Temperatures Derived from the Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer and the along-track Scanning Radiometer: 1. Theory. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1993, 98, 16689–16702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, A.; Rokugawa, S.; Matsunaga, T.; Cothern, J.S.; Hook, S.; Kahle, A.B. A Temperature and Emissivity Separation Algorithm for Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 1113–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, L.F.; DaCamara, C.C. Emissivity Maps to Retrieve Land Surface Temperature from MSG/SEVIRI. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 1834–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Li, Z.; Tang, B.; Zeng, F.; Li, C. Retrieval of Atmospheric and Land Surface Parameters from Satellite Based Thermal Infrared Hyperspectral Data using a Neural Network Technique. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 3485–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göttsche, F.; Olesen, F.; Trigo, I.F.; Bork-Unkelbach, A.; Martin, M.A. Long Term Validation of Land Surface Temperature Retrieved from MSG/SEVIRI with Continuous in-Situ Measurements in Africa. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.C. Land Surface Temperature Measurements from the Split Window Channels of the NOAA 7 Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1984, 89, 7231–7237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, M.S.; Jackson, R.D. Assessing the Spatial Distribution of Evapotranspiration using Remotely Sensed Inputs. J. Environ. Qual. 1991, 20, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, Y.H.; Lagouarde, J.P.; Imbernon, J. Accurate Land Surface Temperature Retrieval from AVHRR Data with use of an Improved Split Window Algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 1992, 41, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulivieri, C.; Castronuovo, M.; Francioni, R.; Cardillo, A. A Split Window Algorithm for Estimating Land Surface Temperature from Satellites. Adv. Space Res. 1994, 14, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Z.; Dozier, J. A Generalized Split-Window Algorithm for Retrieving Land-Surface Temperature from Space. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 892–905. [Google Scholar]
- Prata, A.; Cechet, R. An Assessment of the Accuracy of Land Surface Temperature Determination from the GMS-5 VISSR. Remote Sens. Environ. 1999, 67, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.; Pinker, R.T. Estimation of Land Surface Temperature from a Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-8). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, J.; Romaguera, M. Land Surface Temperature Retrieval from MSG1-SEVIRI Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 92, 247–254. [Google Scholar]
- Pinker, R.T.; Sun, D.; Hung, M.; Li, M.; Basara, J.B. Evaluation of Satellite Estimates of Land Surface Temperature from GOES Over the United States. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2009, 48, 167–180. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Tarpley, D.; Privette, J.L.; Goldberg, M.D.; Raja, M.R.V.; Vinnikov, Y.; Xu, Y. Developing Algorithm for Operational GOES-R Land Surface Temperature Product. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 936–951. [Google Scholar]
- Sobrino, J.; Jiménez-Muñoz, J.; Brockmann, C.; Ruescas, A.; Danne, O.; North, P.; Heckel, A.; Davies, W.; Berger, M.; Merchant, C. Land Surface Temperature Retrieval from Sentinel 2 and 3 Missions. In Proceedings of the Sentinel-3 OLCI/SLSTR and MERIS/(A) ATSR Workshop, Frascati, Italy, 15–19 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, A.; Suh, M. Evaluation of Land Surface Temperature Operationally Retrieved from Korean Geostationary Satellite (COMS) Data. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3951–3970. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Cho, A.; Choi, Y.; Suh, M. Improvements of a COMS Land Surface Temperature Retrieval Algorithm Based on the Temperature Lapse Rate and Water Vapor/Aerosol Effect. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1777–1797. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Choi, Y.Y.; Suh, M.S. Improvement of COMS land surface temperature retrieval algorithm by considering diurnal variation of air temperature. Korean J. Remote Sens. 2016, 32, 435–452. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmit, T.J.; Gunshor, M.M.; Menzel, W.P.; Gurka, J.J.; Li, J.; Bachmeier, A.S. Introducing the Next-Generation Advanced Baseline Imager on GOES-R. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 86, 1079–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Ho, C. Earth and Environmental Remote Sensing Community in South Korea: A Review. Remote Sens. Appl. 2015, 2, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessho, K.; Date, K.; Hayashi, M.; Ikeda, A.; Imai, T.; Inoue, H.; Kumagai, Y.; Miyakawa, T.; Murata, H.; Ohno, T.; et al. An Introduction to Himawari-8/9—Japan’s New-Generation Geostationary Meteorological Satellites. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2016, 94, 151–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yu, Y.; Tarpley, D.; Gottsche, F.; Olesen, F. Evaluation of GOES-R Land Surface Temperature Algorithm using SEVIRI Satellite Retrievals with in Situ Measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 3812–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Ishikawa, H.; Oku, Y.; Hu, Z. An algorithm for land surface temperature retrieval using three thermal infrared bands of Himawari-8. J. Meteorl. Soc. Jpn. 2018, 96, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.I.; Chung, S.R.; Baek, S. Development of cloud detection algorithm for GK-2A/AMI. In Proceedings of the 7th Asia-Oceania/2nd AMS-Asia/2nd KMA Meteorological Satellite User’s Conference, Songdo City, Korea, 24–27 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sobrino, J.A.; Li, Z.L.; Stoll, M.P.; Becker, F. Improvements in the split-window technique for land surface temperature determination. IEEE Trans. Geosci Remote Sens. 1994, 32, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Muñoz, J.C.; Sobrino, J.A. A generalized single-channel method for retrieving land surface temperature from remote sensing data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valor, E.; Caselles, V. Mapping land surface emissivity from NDVI: Application to European, African, and South American areas. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 57, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, W.C.; Wan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Y.Z. Classification-based emissivity for land surface temperature measurement from space. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 2753–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z. MODIS Land-Surface Temperature Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (LST ATBD); Institute for Computational Earth System Science: Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Petitcolin, F.; Zhang, R. A physically based algorithm for land surface emissivity retrieval from combined mid-infrared and thermal infrared data. Sci. China Ser. E 2000, 43, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, A.R.; Abbott, E.A.; Gilson, L.; Hulley, G.; Jiménez-Muñoz, J.C.; Sobrino, J.A. Residual errors in ASTER temperature and emissivity standard products AST08 and AST05. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3681–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masiello, G.; Serio, C.; De Feis, I.; Amoroso, M.; Venafra, S.; Trigo, I.F.; Watts, P. Kalman filter physical retrieval of surface emissivity and temperature from geostationary infrared radiances. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 3613–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masiello, G.; Serio, C.; Venafra, S.; Liuzzi, G.; Göttsche, F.; Trigo, I.F.; Watts, P. Kalman filter physical retrieval of surface emissivity and temperature from SEVIRI infrared channels: A validation and intercomparison study. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 2981–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasi, M.G.; Liuzzi, G.; Masiello, G.; Serio, C.; Telesca, V.; Venafra, S. Surface parameters from SEVIRI observations through a Kalman filter approach: Application and evaluation of the scheme to the southern Italy. Tethys J. Weather Clim. West. Mediterr. 2016, 13, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.H.; Suh, M.S. Improvement of infrared channel emissivity data in COMS observation area from recent MODIS data (2009–2012). Korean J. Remote Sens. 2014, 30, 109–126. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caselles, E.; Valor, E.; Abad, F.; Caselles, V. Automatic classification-based generation of thermal infrared land surface emissivity maps using AATSR data over Europe. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verhoef, W.; Bach, H. Simulation of hyperspectral and directional radiance images using coupled biophysical and atmospheric radiative transfer models. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 87, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guanter, L.; Richter, R.; Kaufmann, H. On the application of the MODTRAN4 atmospheric radiative transfer code to optical remote sensing. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 1407–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Muñoz, J.C.; Sobrino, J.A.; Mattar, C.; Franch, B. Atmospheric correction of optical imagery from MODIS and Reanalysis atmospheric products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2195–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berk, A.; Anderson, G.; Acharya, P.; Chetwynd, J.; Bernstein, L.; Shettle, E.; Matthew, M.; Adler-Golden, S.M. MODTRAN4 User’s Manual; Air Force Research Laboratory: Hanscom AFB, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Borbas, E.; Seemann, S.W.; Huang, H.-L.; Li, J.; Menzel, W.P. Global Profile Training Database for Satellite Regression Retrievals with Estimates of Skin Temperature and Emissivity. In Proceedings of the 14th International ATOVS Study Conference, Beijing, China, 25–31 May 2005; pp. 763–770. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Z. New refinements and validation of the collection-6 MODIS land-surface temperature/emissivity product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigo, I.F.; Monteiro, I.T.; Olesen, F.; Kabsch, E. An assessment of remotely sensed land surface temperature. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coll, C.; Wan, Z.; Galve, J.M. Temperature-based and radiance-based validations of the V5 MODIS land surface temperature product. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frey, C.M.; Kuenzer, C.; Dech, S. Quantitative comparison of the operational NOAA-AVHRR LST product of DLR and the MODIS LST product V005. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 7165–7183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Liang, S. Evaluation of ASTER and MODIS land surface temperature and emissivity products using long-term surface longwave radiation observations at SURFRAD sites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1556–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, P. Land Surface Temperature and Emissivity Retrieval from Satellite Measurements. FZKA. 2005. Available online: http://d-nb.info/97521960x/34/ (accessed on 25 October 2018).
- Sobrino, J.A.; Jiménez-Muñoz, J.C.; Paolini, L. Land surface temperature retrieval from LANDSAT TM 5. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 90, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atitar, M.; Sobrino, J.A. A split-window algorithm for estimating LST from Meteosat 9 data: Test and comparison with in situ data and MODIS LSTs. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Muñoz, J.C.; Sobrino, J.A. A single-channel algorithm for land-surface temperature retrieval from ASTER data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2010, 7, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Duan, S.B.; Ren, H.; Labed, J.; Li, Z.L. Algorithm Development for Land Surface Temperature Retrieval: Application to Chinese Gaofen-5 Data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.-S.; Park, Y.-Y.; Yeom, J.-M. Detection of change in vegetation in the surrounding desert areas of North China and Mongolia with multi-temporal satellite images. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 51, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyoshi, K.; Akatsuka, S.; Takeuchi, W.; Sobue, S. Hourly LST Monitoring with Japanese Geostationary Satellite MTSAT-1R over the Asia-Pacific Region. Asian J. Geoinform. 2014, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Trigo, I.F.; Peres, L.F.; DaCamara, C.C.; Freitas, S.C. Thermal land surface emissivity retrieved from SEVIRI/Meteosat. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Bi, Y.; Li, Z.L.; Xia, J. Generalized split-window algorithm for estimate of land surface temperature from Chinese geostationary FengYun meteorological satellite (FY-2C) data. Sensors 2008, 8, 933–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, A.J. Land surface temperatures derived from the Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer and the along-track scanning radiometer: 2. Experimental results and validation of AVHRR algorithms. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1994, 99, 13025–13058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z.L. Validation of the land-surface temperature products retrieved from Terra Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coll, C.; Galve, J.M.; Sanchez, J.M.; Caselles, V. Validation of Landsat-7/ETM+ thermal-band calibration and atmospheric correction with ground-based measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, J.A.; Jiménez-Muñoz, J.C.; Sòria, G.; Ruescas, A.B.; Danne, O.; Brockmann, C.; Ghent, D.; Remedios, J.; North, P.; Merchant, C.; et al. Synergistic use of MERIS and AATSR as a proxy for estimating Land Surface Temperature from Sentinel-3 data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 179, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Li, Z.L. Radiance-based validation of the V5 MODIS land-surface temperature product. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 5373–5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z. New refinements and validation of the MODIS land-surface temperature/emissivity products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijima, O. Basic and Other Measurements of Radiation at Station Tateno (2016–08); Aerological Observatory, Meteorological Agency: Tokyo, Japan, 2016; Available online: https://doi.org/10.1594/PANGAEA.867410 (accessed on 25 October 2018).
- Qian, Y.G.; Li, Z.L.; Nerry, F. Evaluation of land surface temperature and emissivities retrieved from MSG/SEVIRI data with MODIS land surface temperature and emissivity products. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 3140–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niclòs, R.; Galve, J.M.; Valiente, J.A.; Estrela, M.J.; Coll, C. Accuracy assessment of land surface temperature retrievals from MSG2-SEVIRI data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2126–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuyama, A.; Takahashi, M.; Date, K.; Hosaka, K.; Murata, H.; Tabata, T. Validation of Himawari-8/AHI radiometric calibration based on two years of in-orbit data. J. Meteorl. Soc. Jpn. 2018, 96, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
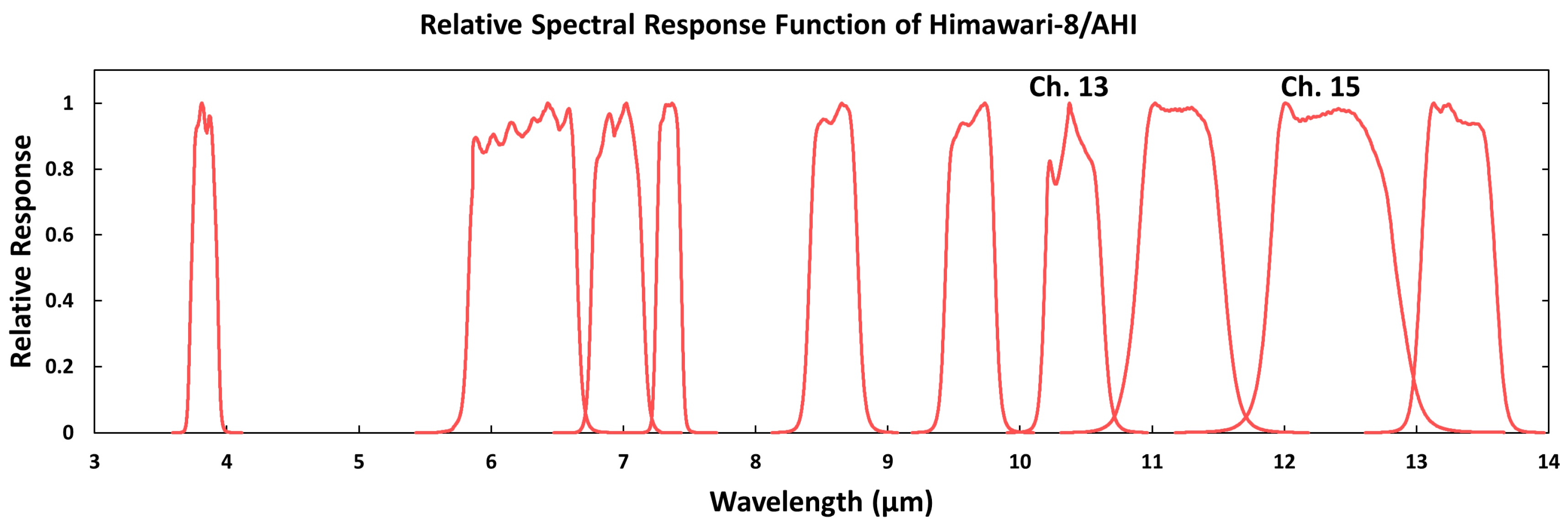
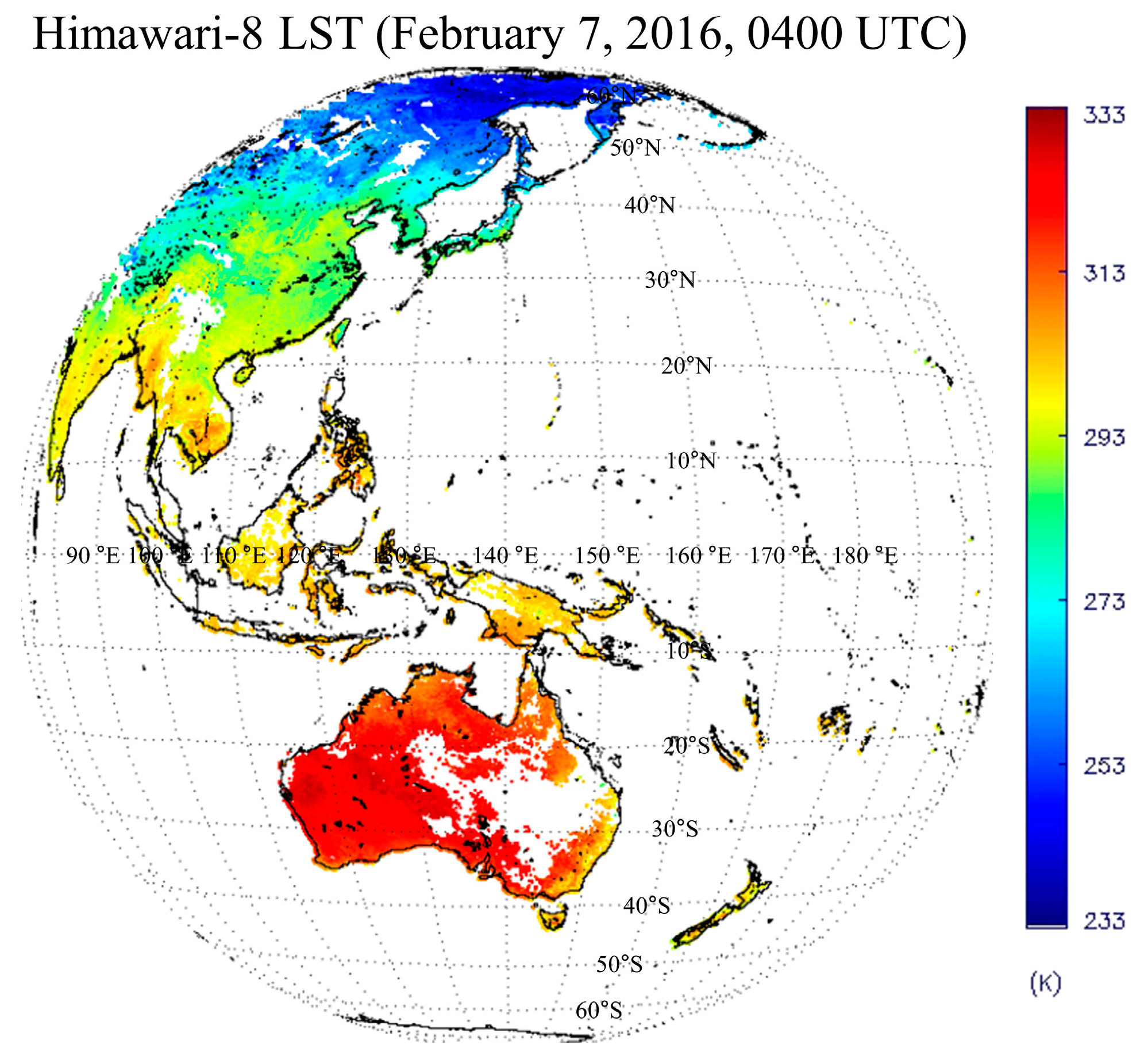
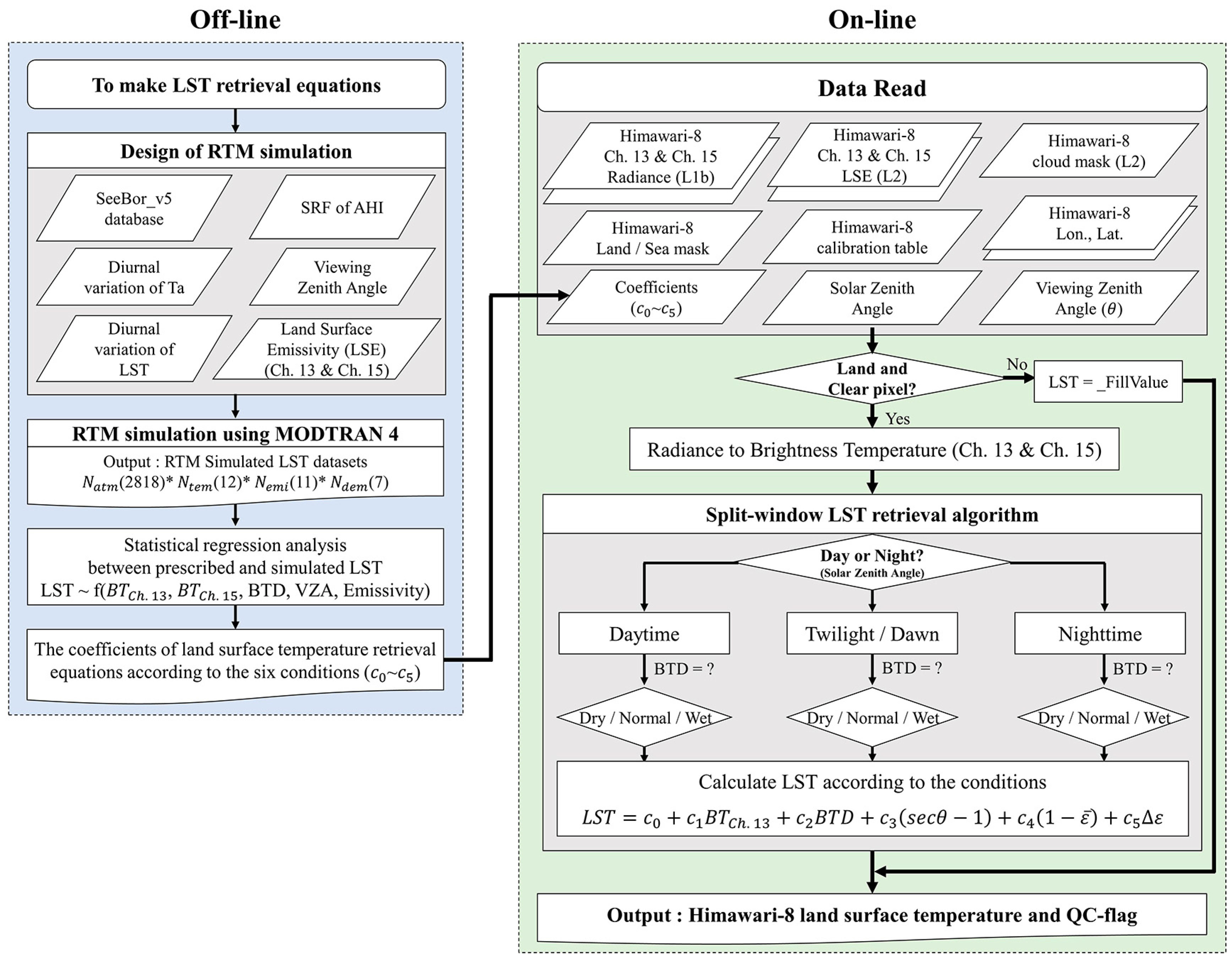
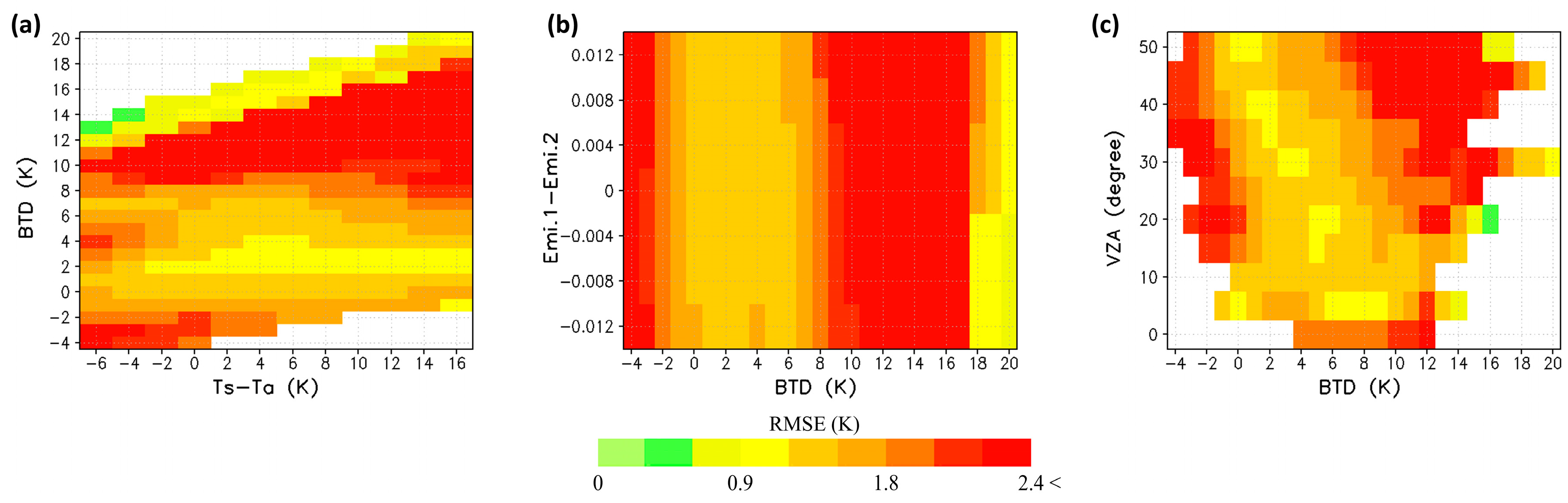

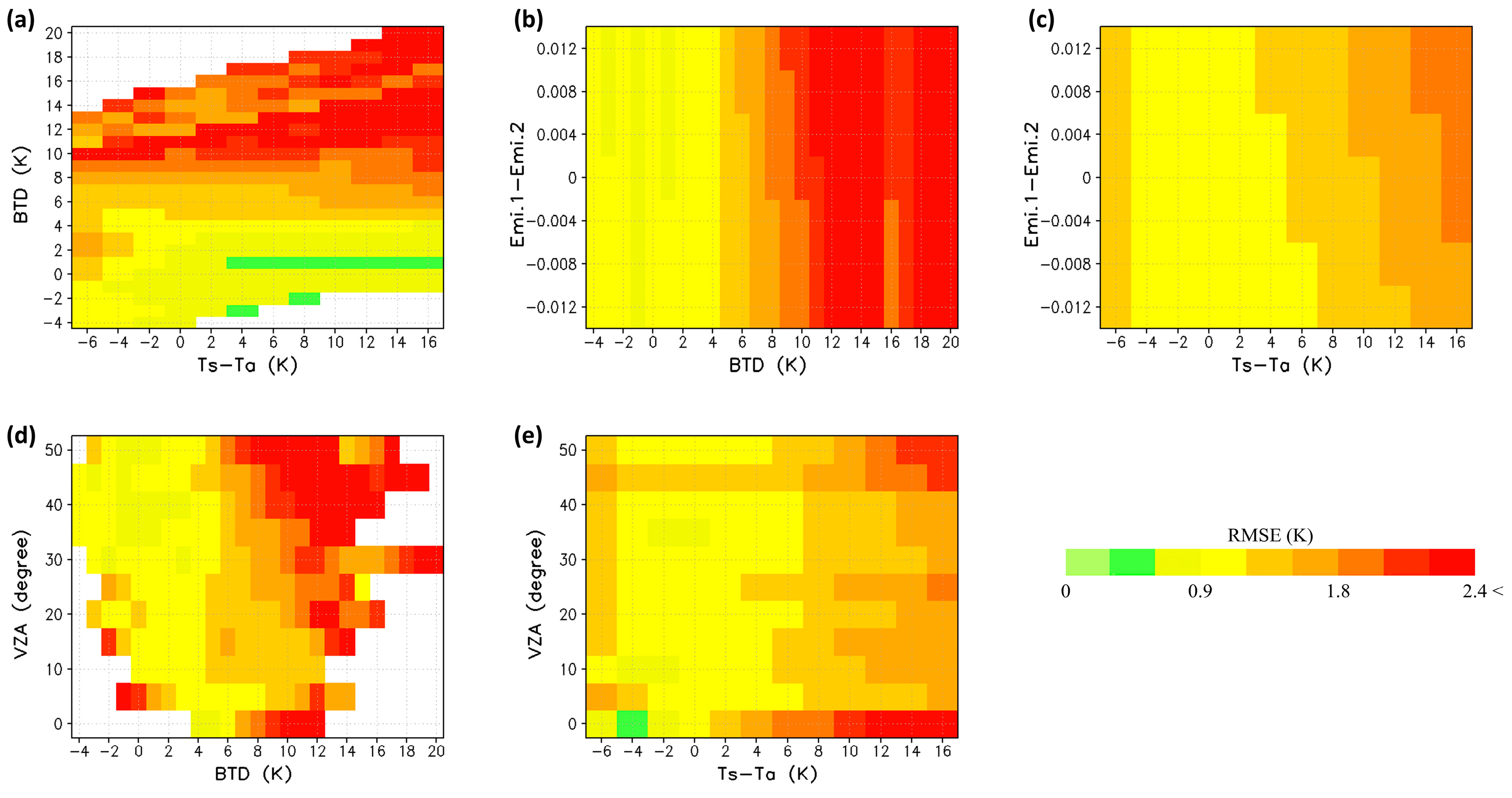


| Impacting Factors | Conditions |
|---|---|
| Atmospheric Profiles | 2818 SeeBor profiles (version 5) |
| (Viewing zenith angle < 50 °) | |
| Land Surface Temperature | Day: Ta − 2 K to Ta + 16 K (a step of 2 K) |
| Night: Ta − 6 K to Ta + 2 K (a step of 2 K) | |
| Air Temperature | Ta′ = Ta + (LST − Ta)/2 |
| Land Surface Emissivity | : 0.9478–0.9968 (a step of 0.0049) |
| −0.012 0.012 (a step of 0.004) | |
| If () > 1, = 0.9999 |
| Conditions | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day | Moist | 67.1857 | 0.7448 | 2.07 | 1.096 | 63.061 | −75.1606 |
| Normal | 8.926 | 0.9651 | 0.9364 | −0.1385 | 56.8638 | −63.8708 | |
| Dry | 15.3567 | 0.9461 | 1.1996 | −1.411 | 48.5137 | −68.3093 | |
| Night | Moist | 44.5826 | 0.8205 | 2.0427 | 1.6411 | 58.5399 | −59.1371 |
| Normal | 12.1778 | 0.9535 | 0.9278 | −0.095 | 51.2696 | −51.8349 | |
| Dry | 20.3004 | 0.9279 | 1.0879 | −1.4883 | 47.2503 | −61.7212 | |
| Month | Day | Night | Total (Day + Night) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # of Scene | Corr. | Bias (K) | RMSE (K) | # of Scene | Corr. | Bias (K) | RMSE (K) | # of Scene | Corr. | Bias (K) | RMSE (K) | |
| Sep 2015 | 6 | 0.92 | 0.90 | 1.71 | 6 | 0.97 | −0.48 | 1.31 | 12 | 0.95 | 0.12 | 1.48 |
| Oct 2015 | 5 | 0.92 | 1.45 | 2.57 | 7 | 0.97 | 0.07 | 1.14 | 12 | 0.95 | 0.53 | 1.62 |
| Nov 2015 | 6 | 0.86 | 0.95 | 2.55 | 5 | 0.98 | 0.06 | 1.66 | 11 | 0.93 | 0.48 | 2.08 |
| Dec 2015 | 7 | 0.95 | 1.97 | 2.96 | 5 | 0.99 | 0.40 | 1.48 | 12 | 0.96 | 1.52 | 2.53 |
| Jan 2016 | 5 | 0.95 | 2.94 | 3.66 | 3 | 0.99 | −0.55 | 1.13 | 8 | 0.96 | 2.44 | 3.30 |
| Feb 2016 | 3 | 0.94 | 1.46 | 2.01 | 3 | 0.98 | 1.09 | 1.89 | 6 | 0.96 | 1.28 | 1.95 |
| Mar 2016 | 6 | 0.88 | 1.06 | 2.62 | 3 | 0.99 | 0.17 | 1.34 | 9 | 0.92 | 0.72 | 2.13 |
| Apr 2016 | 8 | 0.90 | 0.50 | 2.63 | 5 | 0.97 | 0.11 | 1.09 | 13 | 0.93 | 0.33 | 1.94 |
| May 2016 | 6 | 0.92 | −0.14 | 2.59 | 3 | 0.96 | −0.43 | 1.28 | 9 | 0.93 | −0.25 | 2.07 |
| Jun 2016 | 3 | 0.94 | −0.82 | 2.54 | 4 | 0.97 | −0.38 | 1.26 | 7 | 0.96 | −0.49 | 1.58 |
| Jul 2016 | 5 | 0.92 | −0.82 | 2.51 | 5 | 0.88 | −0.04 | 1.39 | 10 | 0.89 | −0.23 | 1.66 |
| Aug 2016 | 6 | 0.91 | −0.19 | 1.94 | 4 | 0.95 | −0.38 | 1.27 | 10 | 0.94 | −0.30 | 1.56 |
| Total day and Average | 66 | 0.92 | 0.92 | 2.54 | 53 | 0.96 | −0.01 | 1.34 | 119 | 0.94 | 0.45 | 1.93 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, Y.-Y.; Suh, M.-S. Development of Himawari-8/Advanced Himawari Imager (AHI) Land Surface Temperature Retrieval Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 2013. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10122013
Choi Y-Y, Suh M-S. Development of Himawari-8/Advanced Himawari Imager (AHI) Land Surface Temperature Retrieval Algorithm. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(12):2013. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10122013
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Youn-Young, and Myoung-Seok Suh. 2018. "Development of Himawari-8/Advanced Himawari Imager (AHI) Land Surface Temperature Retrieval Algorithm" Remote Sensing 10, no. 12: 2013. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10122013
APA StyleChoi, Y.-Y., & Suh, M.-S. (2018). Development of Himawari-8/Advanced Himawari Imager (AHI) Land Surface Temperature Retrieval Algorithm. Remote Sensing, 10(12), 2013. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10122013





