Abstract
Scarcity of information on the water productivity of different water, land, and other ecosystems in Africa, hampers the optimal allocation of the limited water resources. This study presents an innovative method to quantify the spatial variability of biomass production, crop yield, and economic water productivity, in a data scarce landscape of the Pangani Basin. For the first time, gross return from carbon credits and other ecosystem services are considered, in the concept of Economic Water Productivity. The analysis relied on the MODIS satellite data of 250 m and eight-day resolutions, and the SEBAL model, utilizing Monteith’s framework for ecological production. In agriculture, irrigated sugarcane and rice achieved the highest water productivities in both biophysical and economic values. Rainfed and supplementary irrigated banana and maize productivities were significantly lower than the potential values, reflecting a wide spatial variability. In natural landscapes, forest and wetland showed the highest biomass production. However, the transition to economic productivity was low but showed the potential to increase significantly when non-market goods and services were considered. Spatially explicit information, from both biophysical and economic water productivity, provides a holistic outlook of the socio-environmental and the economic water values of a land-use activity, and can identify areas for improvement, and trade-offs in river basins.
1. Introduction
The competition over water resources is escalating in many river basins, worldwide. Population growth and increasing food demands to meet not only local but also global needs imposes high pressures on the world’s fresh water resources. More water is also required to provide for the increasing energy demands from hydropower and biofuels [1]. Competition over water is not limited to the agricultural, domestic, and industrial sectors but also includes the natural environment. Ecosystem services provide essential functions that can be grouped in provisioning, regulating, as well as, habitat and cultural services [2,3]. While environmental water uses are fundamental for sustainable economic and social development in river basins, it is becoming clear that the natural environment consumes large amounts of the water resources, and that measures are required to safeguard natural capital [4,5,6].
The main water flux in a river basin is evapotranspiration, with a large part being consumed by the natural landscape. For example, in the Awash basin, Ethiopia, 49% of all evapotranspiration occurs in mosaic forested shrubland/grassland, and close to the open shrubland [7]. An analysis on the water consumption of different land-use classes for the Nile basin, showed that savannah is the largest water consumer at 38%, followed by pastures (9%), wetlands (7%), and rivers and lakes (7%), of the total evapotranspiration [8]. Of the total evaporative use of the Nile, thus, 61% is explained by environmental systems. Hence, the natural environment consumes large portions of rainfall (i.e., green water), and water from inundations and shallow groundwater tables (i.e., blue water). It is therefore legitimate, if not imperative, to include the economic value of natural ecosystems in the economic water productivity of river basins. So far, most authors have only considered agricultural goods when employing the concept of Economic Water Productivity [9,10,11,12]. Valuing the water consumption in a river basin should go beyond the marketable crops and encapsulate financial rewards for the sequestration of atmospheric carbon, heat, and other forms of ecosystem services. Payment for Ecosystem Services (PES) is an emerging topic that is gradually implemented by policy makers, in several basins, both in the developed and the developing countries. Some PES programs involve contracts between the consumers of ecosystem services and the suppliers of these services. However, the majority of the PES programs are funded by governments and involve intermediaries, such as non-government organizations [13].
Natural environments, such as forests and wetlands provide a wealth of ecosystem goods and services, in terms of delayed peak runoff, due to the retention of excess rainfall, sufficient catchment water yield that ensures base flow in the dry season, sustaining rainfall by means of atmospheric moisture recycling, reduced erosion, and improved water quality, from which the downstream societies benefit. Natural ecosystem goods and services also provide a buffer to the local communities, during periods of droughts, in semi-arid African landscapes [14]. Degradation of such environments reduces such benefits, significantly. Similarly, increased withdrawals in upper catchments directly affect the downstream ecosystems, such as wetlands, riparian vegetation, and delta and estuarine ecosystems. Due to the undesirable upstream developments, most perennial tributaries in our study area, i.e., the Pangani River Basin in Tanzania, have actually become seasonal in the last few decades [15].
Costanza et al. [16] estimated the global value of ecosystem services, in 2011, to be US$ 125 trillion a year, with a loss of up-to US$ 20 trillion per year, from 1997, due to land-use change. The study highlighted the magnitude of the ecosystem services and the urgent need for policies that promote environmental conservation. In the United States, farmers are paid an amount of US$ 1.8 billion per year to conserve soil and water on a 1.4 million hectare of “environment-friendly” land, i.e., 1285 US$ ha−1 year−1 [17]. Similarly, the Chinese government has a program for not clearing forests, which compensates an amount of US$ 50 billion, annually, to the local farming communities [18].
It is clear that optimal water use is indispensable to the river basins that are disappearing due to the prevailing competition over water resources [19]. Ecological and hydrological integrity is central to sustainable water resource use. Crop water productivity expresses the returns per unit of water consumed in river basins, and this can either be expressed biophysically, economically, or socially [20,21,22,23,24,25,26]. Therefore, water productivity (kg m−3 and $ m−3) can be a key indicator to assess the effective use of water, although never as a sole purpose [27]. Increasing the water productivity of crops is needed to achieve the broad objectives of increasing food production and, thus, the income and livelihoods of local communities in the river basin. Water productivity gains in agriculture would secure water resources for other landscape uses and the ecosystem services, as more crop is produced with less drops of water [28,29]. Farm practices to increase the physical water productivity are well documented in the literature. They include supplementary irrigation, soil water conservation, deficit irrigation, and the right use of fertilizers and pesticides, amongst other interventions.
Environmental biomass production that has high environmental and social values, often has little or no market price [3,30,31,32,33]. The situation is poised to change due to the emerging market of carbon credits. The Kyoto Protocol allows industrial emissions of carbon into the atmosphere to be offset by sequestration, in forests and other forms of permanent green landscapes [34]. Carbon trading appeared as a potential business in the early 21st century, which more recently has been hampered by the economic crisis, since 2008, and fewer industrial activities, resulting in a dramatic drop in carbon prices. Many economists, however, maintain that putting a price on carbon and allowing for carbon trading is a crucial element of the global climate policy [35,36].
There is, however, a systematic lack of data on the water productivity of natural vegetation. Moreover, natural vegetation is highly heterogeneous, with a large spatial coverage. A Measurement-Reporting-Planning-Monitoring (MRPM) system is required to quantify such water productivities. This paper demonstrates that estimates based on remote sensing can achieve this. Much progress has been made recently using remotely-sensed data, in spatial water productivity analysis [37]. In few cases, these have been complemented by modelling approaches to estimate water productivity. Van Dam et al. [38] combined a soil-physical simulation model with SEBAL, and Mainuddin and Kirby [39] used FAO’s CROPWAT for their model [40]. At a global scale, water productivity models have been developed, WATPRO (WATer PROductivity) is a model that has been developed for wheat water productivity [41] and GEPIC (GIS-based Environmental Policy Integrated Climate model) is an agro-ecosystem model to assess the global water productivity [42]. Finally, remote sensing data on water productivity has been complemented by using crop-yield statistics [43]. More recently, Yan and Wu [44] and Zhang et al. [45] presented the spatial-temporal crop water productivity for winter wheat, in China, using remotely-sensed estimates of evapotranspiration (ET). Only one study has reported on the economic water productivity, using a combination of remote sensing and economic analysis, for two main market crops, bananas, and sugarcane [12]. So far, few studies have included a valuation, and none have included natural land-use types or non-market-based crops. The objective of this paper is, therefore, to present a basin-wide analysis of the bio-physical (biomass and yield) and economic water productivity of both agricultural and natural land uses in a river basin.
2. Study Area
The Upper Pangani River Basin has an area of 13,400 km2, which is about 30% of the entire Pangani River Basin, and it is shared by Kenya and Tanzania (Figure 1). The climate is highly varied and mainly influenced by topography. The higher elevation ranges, centered around Mt. Kilimanjaro at 5880 m and Mt. Meru at 4565 m, predominantly have a tropical humid climate and receive nearly 2500 mm year−1 of rainfall [46,47]. The area is covered mainly by dense tropical rainforest and afro-alpine natural vegetation. The middle to lower catchments have a sub-humid to semi-arid climate. The rainfall is highly variable and ranges between 1000–2000 mm year−1, in the middle to upper catchments, and 300–800 mm year−1, in the lower catchments of the Upper Pangani River Basin. The middle catchment is dominated by agriculture, while a large expansive area in the lower catchment is dominated by natural shrublands and bushlands. A large part of this area is conserved for wildlife, mainly in the Kenyan part of the basin, in the Tsavo West and the Amboseli National parks.
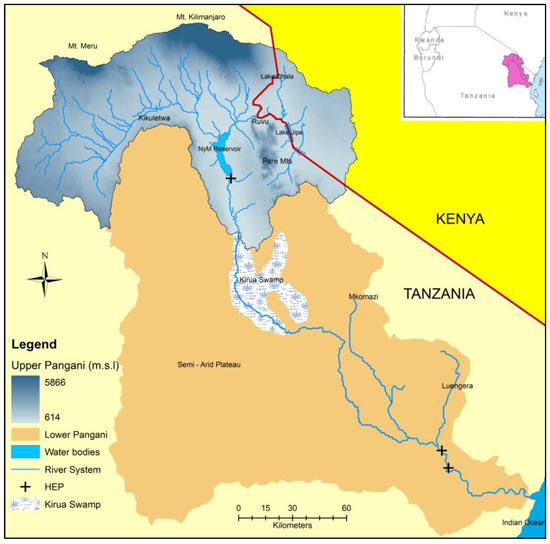
Figure 1.
The Upper and Lower Pangani River Basin (HEP = Hydro-Electric Power plant).
Rainfall has a bimodal pattern, with a long rain season, during the months of March to May (Masika season) and the short rain season (Vuli season), in the months of November and December. The agricultural seasons follow the rainfall. Rainfed agriculture, in particular the cultivation of maize during the Masika season, is dominant in the middle catchments of the Upper Pangani River Basin. However, rainfed agriculture is unreliable and produces low yields, mainly due to low and unreliable rainfall pattern. Many farming households, therefore, depend on irrigation to supplement rainfall for food production. Irrigation development by smallholder farmers, during the last two centuries, has led to a complex and intricate network of small canals that rely on gravity water flow from springs and streams, in the upper catchments. Presently, about two thousand such irrigation canals exist in the Upper Pangani River Basin, some dating back to the 18th century [48]. Large scale irrigation is located in the lower catchments of the Upper Pangani River Basin, including the Tanzania Plantation Company (TPC) which produces sugarcane, and the Lower Moshi Irrigation scheme, producing rice and maize.
The increasing water use for agriculture has resulted in a decrease in the availability of river water and water from the groundwater table is no longer available [49]. Most wetlands and perennial rivers are drying up during the dry seasons, a clear sign that the river basin is closing [19]. This has also increased tensions and water related conflicts between water users [48,50]. It is believed that information on bio-physical and economic water productivity could assist in informing future water allocation or re-allocation strategies that seek to achieve a balance between the optimal social, environmental, and economical uses of the limited water resources, in the Pangani river basin.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Remotely-Sensed Data for Assessing Ecological Productivity
3.1.1. Actual Evaporation
Values for actual evapotranspiration (ET) were taken from a study by Kiptala et al. [47] who used the SEBAL algorithm [51]. The SEBAL methodology, including the details of the images and the processing steps, is explained in detail in Kiptala et al. [47]. ET data used for the water productivity analysis were available at 250 m and eight-day resolutions for the period 2008–2010, for the Upper Pangani River Basin.
3.1.2. Biomass Production
Biomass production (B) could be estimated as the dry matter production accumulated during the growing season or a calendar period, under consideration. B could be related to the absorbed photosynthetically active radiation (RAP) expressed in MJ m−2, and the Light-Use Efficiency (B) of plants (g MJ−1), using the relation developed by Monteith [52], Equation (1).
Plant leaves transmit and reflect solar radiation. Plant chlorophyll responds only to radiation in the 0.4 to 0.7 μm spectral regime, therefore, only a fraction of the total broadband shortwave radiation (K) is available for photosynthesis (RP). For the average 24 h conditions, the RP/ fraction is equal to 0.48 [53]. Light interception occurs only in the case of green leaves, filled with chlorophyll. RAP could, therefore, be computed using Equation (2).
The fraction f could be estimated directly from the normalized difference vegetation index, (NDVI) [54,55]:
ε for a particular crop is a constant if the environmental conditions are non-limiting [52]. However, water availability and temperature can impact ε, significantly. SEBAL uses the equations first published by Field et al. [56] to correct for the effect of heat variations (T1, T2) and soil moisture (W) on ε:
where ε′ is the maximum light-use efficiency under the optimal environmental conditions (g MJ−1). T1 and T2 are heat variations, based on the average temperature (Tav in °C) and the optimum temperature, during a time step, with a maximum leaf area index (Topt in °C). W is a water scalar that is defined by the ratio of actual over potential evapotranspiration to describe the land wetness conditions. Bastiaanssen and Ali [57] adopted the evaporative fraction (Λ), to define the water scalar of land mass.
For crops, the maximum light-use efficiency έ varies with different plant types (C3, C4, and CAM plants) if there is no water shortage [52,58]. The έ values have been provided for various crops, including banana, maize, rice, and sugarcane, from literature sources by Bastiaanssen and Ali [57]. Additional ε′ values from the more recent literature that included natural landscapes, have been presented in (see Section 3.3). For natural landscapes, tropical forests have a maximum light-use efficiency range of 1.5–2.6 g MJ−1 [59,60]. Shrublands and woodlands, and wetlands (high vegetation grass) have lower values and range between 0.8–1.6 g MJ−1 [61,62].
Radiation, water, and carbon fluxes were measured on typical savannah sites, in Niger, as part of the Hydrologic Atmospheric Pilot Experiment in the Sahel (HAPEX-SAHEL) [63]. The non-linear impact of soil moisture and ε appeared to be an essential process. A good synopsis has been provided by Prince [64], for applications with remote sensing.
3.1.3. Crop Yield
The conversion from total biomass development to the actual yield, such as cereal grains, varies with the harvest index (Hi) and the water content of the crop, during the harvest [65].
where Hieff is the effective harvest index, corrected using the optimal moisture content of the product, after harvest (moi). Different crops have a specific harvest index range. Hi values for various crops were used in the calibration process (see Section 3.3). The harvest index is also influenced by the crop variety [44,66]. Furthermore, management and agronomic practices, such as the use of fertilizers, can increase crop yield, as well as the harvest index [23].
3.1.4. Carbon Sequestration
The accumulation of biomass is a result of Net Primary Production (NPP). The carbon assimilates are distributed across the various plant organs, including roots, shoots, tubers, stems, branches, leaves, flowers, and grains. This partitioning is plant-specific and the factors are empirically known. The ratio of the above and below ground biomass production, for natural landscapes, has been measured for several biomes. The total biomass will reach a maximum value, after the equilibrium, between photosynthesis and natural decay, due to the seasons and the age of the vegetation. Tropical rainforests with 40 m tall trees and above the age of 150 years, can reach up to 500 to 1000 ton above ground biomass, per hectare [67]. Global maps of above ground biomass for the Pangani basin suggest values in the order of 15 to 40 ton ha−1, depending on the type of ecosystem. A significant amount of biomass is also present in the soil.
Ponce-Hernandez et al. [68] estimated the below ground biomass to be 0.25–0.30 of the above ground biomass, using plant growth simulation models. Litter and woody debris will be formed, due to senescence and the age of vegetation. The decay of biomass will return carbon as carbon dioxide, back into the atmosphere, and partially into the soil organic carbon. The typical carbon pools considered are harvested wood, litter, dead wood, and soil organic matter. This applies to all types of vegetation.
The sequestration of carbon relates to various time scales—while litter and soil organic matter are generally conceived as short-term carbon storage, harvested wood will have much longer time scales. Carbon sequestration can be approximated as:
where ξ [-] relates carbon pools to accumulate above ground biomass production and χ [-] relates total biomass production to above ground biomass production. The carbon pool does not take into account the short-term carbon storage, such as plant leaves and litter that decay and may not change much over the years. The ξ χ factor is essentially the effective harvest index from biomass production for carbon sequestration, which is normally taken as 0.5, (see Section 3.3).
3.1.5. Economic Water Productivity
The biophysical water productivity, WPB/ET (kg m−3) is derived from plant biomass production and the actual evapotranspiration (ET). The approach is widely adopted and has been used in previous studies [41,44].
The crop (yield) water productivity, WPY/ET (kg m−3) was derived from WPB/ET, using the effective harvest index factor, , Equation (8).
The economic water productivity, WPEc/ET (US$ m−3) was derived by multiplying the WPY/ET with the net price of the product (Pn), Equation (9).
where Pn(i) = (Pg(i) − Pc(i)) ($ kg−1) was the net farm gate price for crop i, determined by subtracting the total production costs, Pc(i) ($ kg−1) from the gross farm gate price, Pg (i) ($ kg−1) [12]. The total production costs included both variable and fixed costs, incurred during the crop development. This approach of subtracting the cost of production from the gross production, relies on the fact that the value to a producer is exhausted by the summation of the values of the inputs required to produce it [69].
The production cost was based on estimates provided by the agricultural extension office (Moshi, Pangani, Tanzania) for crops grown in the Lower Moshi irrigation scheme; rice, maize, and vegetables. The farm gate prices for banana were based on field data on the smallholder farms, in the upper catchments of the river basin. The production costs included labor, fertilizers and pesticides costs, seedling, and harvesting and transportation expenses. Family labor and land was also included as variable costs, using the prevailing labor rates and land rent costs. For commercial sugarcane, the economic water productivity was determined from the net benefits of sugar (sucrose), per unit of water consumption. The Pg was based on the wholesale price (2010) for white sugar of Tsh. 941 (US$ 0.67) per kg. The farm gate sugar price was slightly higher than the world average price (2010) for processed sugar (white) of US$ 0.60 per kg [70]. Data on the production costs for TPC sugarcane plantation was not available. The cost of production was, therefore, estimated from the world averages. The production costs ranged between 45–70% and averaged at 58% of the world sugar price for the ten-year period of 2000–2009 [70]. The average value was used, disregarding the returns from bagasse (by-product), which constituted 90% of the total biomass. Table 1 provides the net gates prices for the main crops in the Upper Pangani River Basin.

Table 1.
Net farm gate prices for crops under irrigation from 2008–2010 in the Upper Pangani River Basin.
For natural land cover, the economic productivity may be inferred from the social and economic benefits of carbon sequestration. Here, we assumed that the value of ecosystem services was equal to the value of the net amount of additional carbon sequestered. This was obviously a conservative assumption since there are other ecosystem services, such as erosion control, nutrient recycling, waste treatment, provision of raw materials, habitat (genetic diversity), and cultural services that are provided by natural land cover [3,30]. According to the Interagency Working Group on Social Cost of Carbon [71], the benefits of carbon sequestration varies from $5 to $65 per ton of carbon, estimated from the social cost of carbon emission. Coffee farmers in Mexico received an amount of US$ 13 per ton of carbon sequestered [72], while the shadow price of carbon, used by the major global oil and gas companies, such as the Shell Oil Company, ranges between $28 and $80 per tC [73]. These values are consistent with the compensation market prices of between US$ 5 to 30, per ton CO2 equivalent—on the emerging carbon offset markets [33,74]. A conservative fixed price estimate of US$ 15 per ton of CO2 was used in this study.
3.2. Boundary Conditions for Water Productivity Assessment
For the spatial analysis of the economic water productivity, a detailed land use and land cover map was required. This study utilized the land use and land cover (LULC) classification for the Upper Pangani River Basin by Kiptala et al. [75]. The LULC types were derived using phenological variability of vegetation (from MODIS) for the same period of analysis, 2008 to 2010. Sixteen classes (including water bodies) were identified, of which smallholder maize (including supplementary irrigated) and shrublands were the two dominant classes, covering half of the area. The LULC classification achieved an overall accuracy of 85%, with individual classes achieving more than 70% accuracy.
Additional information on irrigation water uses was required to assess the economic water productivity of blue water use. The actual evapotranspiration (ET) comprises of evapotranspiration from precipitation (P) and irrigation water use (Qb). Qb was supplied either through river water abstraction and/or groundwater. Qb was estimated using the STREAM model (Spatial Tools for River basin Environmental Analysis and Management), a hydrological model developed specifically for the Upper Pangani Basin [76]. The STREAM model utilized the remotely-sensed ET, soil moisture, and P to simulate Qb at 250 m and an eight-day resolution. During low flows, Qb consumed nearly 50% of the river flow in the river basin. Qb estimates were comparable to the field estimates of net irrigation, with less than a 20% difference [76].
3.3. Calibration and Validation
The biomass parameters NDVI, evaporative fraction (Λ), and the incoming solar radiation () were derived from the SEBAL model. The other parameters T1 and T2 (Equation (4)), were computed using field-based Tav and Topt, derived from the maximum LAI or NDVI in the plant growing season. Only two parameters were, therefore, left for calibration–the maximum light-use efficiency (έ and the effective harvest index (Hieff).
The έ values were adjusted within the experimentally-verified parameter ranges, from the literature. The actual yield data were used to derive the field-based harvest index that was compared with the permissible Hieff range for the moisture content of the product, during harvest (moi). The actual yield data were taken from the field measurements and the yield records from the main stakeholders, in the Pangani River Basin.
Table 2 shows the experimentally-verified ranges of έ and Hieff for the four main crops grown in the Upper Pangani River Basin.

Table 2.
Crop biomass parameters ranges for calibration.
Table 3 shows the specific parameter values for the light-use efficiency and the harvest indices from the calibration process for agricultural landscapes. For more information on the calibration and validation process of the specific crops, see Supplementary data, S1.

Table 3.
Calibrated crop biomass parameters from calibration against secondary data and their ranges reported in the literature.
Since there were no actual yield data for the natural land cover, the average values of έ, as reported in the literature, were used.
It was expected that the actual light-use efficiency (ε) would be spatially corrected by the spatial environmental factors that were highly variable (due to the large topographical range in the river basin), from the computation of Equation (4). In the natural forest cover (dense forest and afro-alpine), an average έ value of 2.0 g MJ−1 was used from the permissible ranges for tropical rain forest. Similarly, average ἑ values of 1.0 and 1.2 g MJ−1 were adopted for the shrublands, the woodlands, and the wetlands, respectively.
The effective harvest index for carbon sequestration were derived from the literature. Carbon quantities were estimated to be 0.43–0.55 of the above-ground biomass production [68,87,88,89]. An average carbon conversion factor of 0.5 to the annual accumulated dry biomass was, therefore, adopted for this study (Table 4).

Table 4.
Maximum light-use efficiency and the harvest index for natural land cover.
3.4. Uncertainty Analysis of Biomass Production
Biomass production is related to vegetation growth and, therefore, has a temporal distribution due to seasonal variability. In remote sensing, the vegetation growth is accounted for by the phenological variability of NDVI over the cropping season or the given time period [47]. Biomass production for a given land-use type does not, therefore, follow a normal distribution. The nonparametric statistical inference is a technique to assess the uncertainty for data that do not follow a normal distribution [91]. The nonparametric bootstrapping technique was, therefore, used to estimate the confidence of mean biomass production. The pixel values of biomass were used as the sample population for the analysis. The bootstrapping method draws random samples with replacement from the original population sample, each time calculating the mean or the variance [92]. The process was repeated a thousand times and a plot of the distribution of the sample means was made. The 95% confidence interval for the mean was determined by finding the 2.5th and 97.5th percentiles on the constructed distribution. The statistical software Minitab Inc [93] was used in the analysis.
4. Results
4.1. Biomass Production
Figure 2a shows the spatial distribution of the mean annual biomass production, in the Upper Pangani River Basin, based on calculations using Equation (1), during a period of three years (2008–2010). The biomass growth covers fifteen land-use types (except water bodies) with the two large (commercial) irrigation schemes, Lower Moshi (rice), and TPC (sugarcane), as shown in Figure 2b,c, respectively. The key drivers of the spatial variability were the biophysical characteristics of different LULC types while the temporal variability was influenced by the precipitation, and the inter-seasonal/intra-seasonal variation of the climate conditions, during the period of analysis, in the river basin (also see Figure S1 and Table S3, in the supplementary data). High biomass production was observed in the mountainous areas and in the main irrigation systems. The lower catchment areas that experienced low rainfall had a lower biomass growth. In the dry year of 2009, the biomass production was suppressed for most of the LULC types, in the lower catchment, while it was enhanced in the land-cover-types, such as irrigated bananas and coffee, afro-alpine and dense forests, and the wetlands that had a sufficient water supply. Further information on the calibration and validation results for different crops is provided in the supplementary materials.
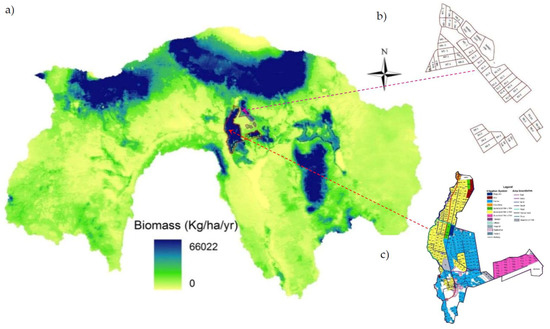
Figure 2.
(a) Spatial variability of biomass growth in the Upper Pangani River Basin; (b) the Lower Moshi irrigation scheme; (c) the Tanzania Plantation Company (TPC) sugarcane irrigation scheme.
4.2. Variability in Biomass Production
The uncertainty for biomass production has been assessed through the confidence interval (CI) of the mean for each land-use type. The lower and the upper bound confidence levels were estimated at 95% confidence limits, using the bootstrap non-parametric technique [92]. The uncertainty was greatly influenced by spatial coverage of the land-use types, within topographical or ecological zones. Urban and barelands had the highest uncertainty of 8% and 17%, respectively. The other land-use types had lower uncertainties of less than 2% (Figure 3; also see Section 4.4.1). The results showed that the mean values of biomass production were representative for the given land-use classes.
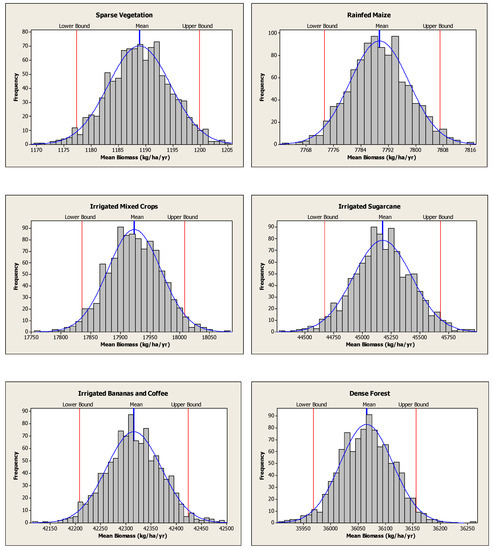
Figure 3.
Frequency distribution of the estimated annual mean biomass, from the bootstrap, at 95% confidence limits for the selected land-use types in the Upper Pangani River Basin, for the period of 2008–2010.
4.3. Water Yield
The mean annual water yields (P-ET) for the sixteen LULC are presented in Table 5. The water supply is an important ecosystem service, especially for the forest ecosystem [94]. The water yields and snow storage, offers the water regulation services to downstream catchment [2,3]. From Table 5, it can be seen that the ice caps and afro-alpine forests generated significant water yields. The other natural ecosystems with large land masses—dense forest, bushlands, and sparse vegetation, also contributed substantial amounts of water flows to the river basin. The water yields provided essential water flows for irrigation, wetlands and swamps, the water bodies (lakes, reservoirs), and hydropower, in the Pangani river system.

Table 5.
The water yields for various land use and land cover (LULC) types in the Upper Pangani River Basin, for the period of 2008–2010.
4.4. Water Productivity
4.4.1. Biomass and Crop Water Productivity
The water productivity in terms of the above-ground biomass and actual evapotranspiration (WPB/ET) was computed based on Equation (7) (Table 6). The highest WPB/ET was realized in irrigated agriculture, with sugarcane providing the highest WPB/ET of 4.4 kg m−3. Dense and afro-alpine forests also attained the high values of 2.4 and 1.4 kg m−3, respectively, due to a high biomass production. Land cover types with low-biomass growth, such as barelands or sparse vegetation, had the lowest WPB/ET values (Table 6).

Table 6.
Average above-ground biomass (B), actual evapotranspiration (ET), and water productivity (WPB/ET) in the Upper Pangani River Basin, for the period of 2008–2010.
The coefficient of variation (CV) of the mean (pixel) values of WPB/ET has been presented for each land-use type. For the natural land-use types, a high level of CV (greater than 0.3) was related to high levels of heterogeneity of the land cover. For rainfed and irrigated croplands, the CV was low to moderately high (0.1–0.3), compared to the more homogeneous irrigation systems, which have a CV of 0.05 [21]. The biomass water productivity was converted into crop or yield productivity (WPY/ET), using their corresponding effective harvest indices.
For sugarcane, the estimated WPB/ET of 4.36 kg m−3 was within the range reported in literature (3.5–5.5 kg m−3) [12,95,96,97]. The average WPY/ET of 9.6 kg m−3 sugarcane (1.1 kg m−3 sucrose) compared well with the crop water productivity data reported for irrigated sugarcane of between 4.0–11.1 kg m−3, in India, and 7.4 kg m−3, in Thailand [39]. The average yield for sucrose (1.1 kg m−3) was also consistent with the estimates of 1.1–1.3 kg m−3, in the Incomati Basin [12]. There was no significant difference between the water productivities of the furrow and sprinkler irrigation systems. Drip irrigation systems produced lower yields (average of 92 tons ha−1), with a lower actual ET usage, thus, resulting in a statistically similar WPY/ET (9.6 kg m−3), compared to the other irrigation technologies.
WPB/ET for rice of 1.5 kg m−3 was within the range (0.6–1.6 kg m−3) reported in the literature [39,98,99,100,101]. For irrigated bananas, the average WPB/ET and WPY/ET was 3.2 and 2.8 kg m−3, respectively. The average WPB/ET for irrigated banana was in the range of 1.4–5.5 kg m−3 in the Nico Coelho irrigation scheme, Pernambuco, Brazil [102]. The WPY/ET was also consistent with estimates of 2.8 kg m−3, for the banana crop, in the Incomati Basin [12]. The water productivity WPB/ET for rainfed maize (with supplementary irrigation) was 1.0 kg m−3, while that for irrigated maize was 2.0 kg m−3. The water productivity translated to WPY/ET of 0.35 and 0.70 kg m−3, for rainfed and irrigated maize crops. The low productivity for rainfed maize was explained by the low yields that were generally associated with water stress, due to long dry spells during the growing seasons. The result was consistent with a recent study that showed that the water productivity for irrigated agriculture was twice that of rainfed agriculture, in the Indus Basin [21]. In general, the maize productivity WPB/ET was within the range reported in literature of 1.1–2.7 kg m−3 [100]. The yield productivity WPY/ET was also consistent with the range of 0.40 to 0.70 kg m−3 for irrigated maize, in Mkoji, Great Ruaha river basin, in Tanzania [20].
For natural landscape, the WPB/ET was high for the natural tropical forest because of the high biomass production associated with the favourable rainfall, throughout the year. WPB/ET for dense forests averaged 2.4 kg m−3, which was within the range of 2–3 kg m−3, for the closed forests, in the Nile Basin, for the year 2007 [103]. The relatively high WPB/ET value for the wetlands and swamps of 1.6 kg m−3 was consistent with the values found for natural wetlands, in the Nile Basin of 1.5 kg m−3 [104], and could be explained by year round access to water. The WPB/ET for shrublands, bushlands, sparse vegetation, and barelands, located in the lower parts of the Upper Pangani, were lower than 0.5 kg m−3, mainly because of the low rainfall. In natural grasslands, the average biomass production of 2.6 tons ha−1 represented a WPB/ET of 0.4 kg m−3 (Table 6). The water productivity was low, compared to good pastures or forage (alfalfa), grown for commercial purposes, under irrigation, which ranged between 1.0–2.6 kg m−3 [104]. The low productivity might be attributed to low rainfall and could possibly be combined with overgrazing.
The relationship between the average B and ET, for various landscapes, is presented in Figure 4.
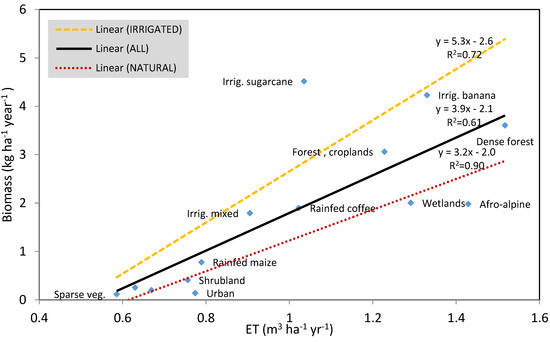
Figure 4.
Variation between the biomass and actual evapotranspiration (ET) for agricultural and natural landscapes, using average values, for the period of 2008–2010, in the Upper Pangani River Basin.
There was a strong linear relationship between the B and the ET, in irrigated (R2 = 0.72) and natural (R2 = 0.90) landscapes. It was observed that biomass production in irrigated agriculture was more enhanced than in rainfed agriculture and natural landscapes. Most of the irrigated crops (maize, banana, and vegetables) were under supplementary irrigation, where only some blue water was added in critical times, to supplement the rainfall. This improves the water availability for the crops. In commercial sugarcane (fully irrigated), irrigation combined with soil fertility management, provides optimal conditions for plant development.
Figure 4 shows the scope for increasing water productivity. Additional water storage (through water harvesting) and the subsequent water use by rainfed systems, would result in a significant increase in the biomass production. This can be observed by comparing rainfed maize and irrigated mixed crops (maize, beans, and vegetables), where the biomass production increases by 130%, with only a difference of 15% in ET. It is noteworthy that the different kinds of plants (C3, C4, and CAM plants) have different water-use efficiency, in terms of B and ET, in their positioning in Figure 4. As such C4 crops, such as sugarcane and maize are more water-efficient, than C3 crops, such as rice [23]. Figure 4 can also implicitly provide (from water use) the shadow value or the opportunity cost of keeping the natural ecosystems in good conditions. These values provide baseline data that can be used for a detailed environmental valuation and modelling.
Figure 5 presents the water productivities (that relates to land use), in the Upper Pangani Basin.
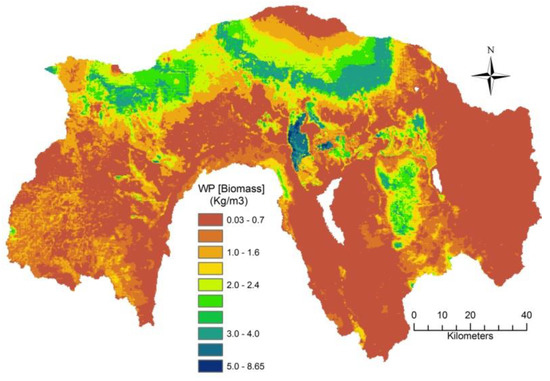
Figure 5.
Water Productivity (Biomass) for the period of 2008–2010, in the Upper Pangani River Basin.
4.4.2. Economic Water Productivity
The economic water productivity was computed from the crop yields and the net production values, using Equation (9). Table 7 provides the yield and the corresponding economic water productivity for the main crops in the basin.

Table 7.
Crop yield and economic water productivity for main agricultural crops in the Upper Pangani River Basin.
WPEc/ET values for the irrigated crops show that sugarcane and bananas have a higher economic water productivity (0.31$ m−3), compared to those of vegetables (0.29$ m−3), rice (0.18$ m−3), and maize (0.13$ m−3). The average WPEc/ET for rice was within the range of 0.10–0.25$ m−3 that has been reported in the literature [23,103]. Rice and maize have relatively stable local markets and are the preferred crops in the Lower Moshi irrigation scheme. The banana and vegetable markets are controlled by middlemen and the market is volatile. The Pg for banana and vegetable crops was about 44% of the retail prices of the produce, at the local markets. The high difference was mainly attributed to the high transport and brokerage costs.
The economic water productivity for the commercial sugarcane of 0.31$ m−3 was higher in 2008/10, compared to that of the Incomati basin (2004/05)—0.20$ m−3 [12]. Since the biomass and crop yield productivities were similar, the difference could be attributed to the high sugarcane prices during the two periods [70].
For pastures (grasslands and scattered croplands), the economic water productivity was assessed using the biomass production that was grazed or harvested mainly for livestock. The assumption here was that the grass consumed by the livestock could otherwise have been purchased as dry feeding forage (hay), in assessing the economic water productivity. Using an effective harvest index of 0.70, for dry grass, at 15% moisture (harvest index of 1 and field moisture of 50%); the WPY/ET became 0.28 kg m−3. The market price for hay (dry grass) was approx. 0.18$ kg−1 (20 kg hay market price averaged Tsh. 5000). This implied, thus, that the WPEc/ET could be approximately 0.025$ m−3, using a cost of production factor of 0.5. The productivity (natural grasslands) was approximately three times less than rainfed maize (0.07$ m−3), despite the small difference (20% in average) in water usage (ET). However, the grassland’s water yield was higher than rainfed maize (Table 5), thus, providing additional ecosystem services to the catchment.
The dense forest and afro-alpine forest, with an annual average biomass growth of 20 tons ha−1 yr−1 and 36 tons ha−1 yr−1 (Table 6) had carbon storage of between 10–18 tons C ha−1 yr−1. The economic potential for the carbon storage in the forest would, therefore, range between 150–270 US$ ha−1 yr−1. Using the water productivity of carbon yield (from biomass), WPY/ET (CO2) of 0.7–1.2 kg m−3, the WPEc/ET translated to a range of between 0.01–0.02 US$ m−3. The WPEc/ET was low (about 15 times less), compared to irrigated agriculture, despite high WPB/ET values (Table 6). This was mainly attributable to the low carbon market prices. The low cost of carbon market prices t has been observed by Batjes [33] was the greatest hindrance for a quicker implementation of the CO2 mitigation measures, in agriculture. However, there were prospects that the situation was poised to change with emerging markets for carbon trading, where countries (through their industries) trade to meet their CO2 obligations specified by the Kyoto Protocol.
Shrublands and bushlands also provided for carbon storage. The annual biomass production ranged between 2–4 ton ha-1 and the carbon storage would, thus, range between 0.5–1.0 ton C ha−1 yr−1. However, other provisioning and regulatory services for these biomes, such as providing grazing fields for wildlife and food for local populations, as well as water regulation, added significant value to this land use [30].
Table 8 presents the yield and economic water productivity for the natural landscapes, based on hay and carbon sequestration. The economic value for carbon was expected to increase by 25–30%, when the below-ground biomass production was considered.

Table 8.
Yield and economic water productivity for natural landscapes in the Pangani River Basin.
Figure 6 presents the spatial crop yield and the economic water productivities, in the Upper Pangani Basin. Both productivities accounted for the CO2 storage for forest and shrublands, hay for grasslands, and the harvestable yield for irrigated and rainfed agriculture.
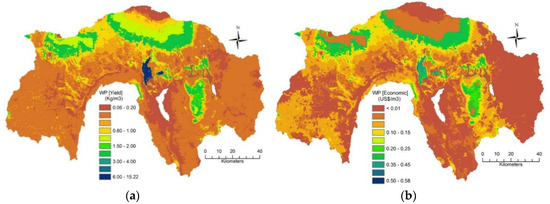
Figure 6.
(a) Water Productivity (Yield). (b) Water Productivity (Economic) for the period of 2008–2010.
4.4.3. Economic Water Productivity for Irrigation Water Use
Crop water use (actual ET) comprised both precipitation (P) and net irrigation (blue water) withdrawal (Qb). Table 9 shows the percentage of Qb to the total actual water use (ET), for the main irrigated crops in the Upper Pangani River Basin, extracted from Kiptala et al. [47]. The economic water productivity, in terms of blue water (WPEc/ETb) was derived by dividing the total economic water productivity (WPEc/ETb) by the blue-water-use factor (Qb/ET).

Table 9.
Economic water productivity for the main irrigated crops expressed in terms of net irrigation water use, for the period of 2008–2010.
5. Discussion
Apart from carbon storage, natural biomes provide other valuable services that may relate to ecological production, of which some are not monetized. Water yields generated by natural landscapes are consumed in agricultural and urban landscapes, generating economic value, whilst generating some disservices [105,106]. Trade-offs between the natural and anthropogenic landscapes are, therefore, not always clear. Fanaian et al. [107] provided a good and systematic overview of how to undertake local economic valuation of ecosystem services, by way of assessing tradeoffs of alternative resource use, in a river system. In this paper, we argued to infer the extent of the value of the ecosystem services provided by the natural biomes, to go beyond the CO2 sequestration, alone, and to consider the benefits, as presented in Table 8. The results from this study have been compared to the ranges of economic values (2007 prices), provided by De Groot et al. [3], based on over three thousand peer-reviewed studies, some in the tropical climate. Of interest are the tropical forest, woodlands, grasslands, inland wetlands, and fresh water lakes that constitute much of the natural ecosystems in the Upper Pangani River Basin.
The economic value for provisioning services for tropical forests was estimated to be at 2695 US$ ha−1yr−1 from ninety-six case studies, at a standard error rate of 13%. From the water use for dense and afro-alpine forests, in the Upper Pangani River Basin, the water productivity equaled 0.19 US$ m−3, which was ten times greater than the derived value for carbon storage (Table 8). Furthermore, the water value could significantly increase to 0.34 US$ m−3 (5264 US$ ha−1 yr−1), if the other ecosystem services (water and climate regulation, erosion control, nutrient recycling) were also considered.
The shrublands provided primarily food and pasture to livestock, wildlife, and even local communities, in the form of plant leaves and fruits. This part of biomass was not accounted for in carbon sequestration. From the literature, the economic value of shrublands was estimated at 1305 US$ ha−1 yr−1, based on twenty-one case studies, with a standard error of 4%, for which 90% of the value was derived from food [3]. The assessment was consistent with the shrublands areas in the Africa savanna, including Pangani, which hosts a wide variety of wildlife, and pastoralists keeping cattle. Considering the water use for the shrublands in the Upper Pangani River Basin, the water productivity equaled 0.17 US$ m−3. Habitat (genetic diversity) and cultural services of the shrublands further increased the water productivity to 0.38 US$ m−3. On the other hand, bushlands provide ornamental and generic resources, such as medicine to the local communities [30], which was estimated at 253 US$ ha−1 yr−1 [3], equivalent to a water value of 0.04 US$ m−3, in the Upper Pangani River Basin. Considering habitat services, the economic value of the bushlands would increase to 1588 US$ ha−1 yr−1 or a water value of 0.24 US$ m−3. These water values, for both the shrublands and bushlands, were much significantly higher than the economic benefits from carbon sequestration (<0.004 US$ m−3), given in Table 8.
Inland wetland is known to provide the greatest value in ecosystem services, in the form of water flow (and disturbance) regulation, water treatment, food production, and recreation. Although most of the functions are not directly related to biomass, its total economic value (2007 prices levels) was estimated to be at 25,682 US$ ha−1 yr−1 [3]. The valuation was consistent with earlier estimates (1994 price levels) of 15,000 US$ ha−1 yr−1 [30]. The provisioning services that relate to ecological productions (biomass), such as food, pasture, and raw materials was estimated to be much lower, at 1659 US$ ha−1 yr−1. The average value was based on estimates from a hundred and sixty-eight case studies, at an 11% standard error rate. The economic value from the provisioning services was 0.13 US$ m−3 from water use (evapotranspiration) of 1300 mm yr−1. The water value would increase to 2.0 US$ m−3, if all the other regulating and habitat services (2007 price levels) were considered.
The fresh water lakes also provide substantially high values, in terms of water supply, water treatment, food (fish and grazing land), and recreation services. The water value from fifteen case studies, at a 17% standard error rate, was estimated to be at 1914 US$ ha−1 yr−1 [3]. In the Pangani River Basin, the Lake Jipe and Lake Chala provide these provisioning services. Considering the evaporation rate of 2000 mm yr−1, the water value equaled to 0.10 US$ m−3. Costanza et al. [30] argued that additional water regulation services, provided by the wetlands, should also be added to the freshwater lakes. Thus, recreational services would increase the water value of the fresh water lakes to 0.4 US$ m−3. However, these natural biomes are located close to each other in the Upper Pangani River Basin and the water regulation may only be offered by one, or partly, by all.
The comparison of the results for natural landscapes, derived in Table 8 (based on CO2 and pastures), against the literature reviewed, showed that the biophysical analysis, based on carbon storage and pastures only, significantly underestimates the total economic value of the natural ecosystem services. However, a local ecosystem valuation needs to be undertaken to explicitly derive the total value of ecosystem services, generated by each natural biome. This will reduce the chances of avoiding double counting, especially for parallel ecosystem services supported by nearby natural landscapes. As such the biophysical data and the baseline water values, provided in this study, provide boundary conditions for a further detailed economic valuation.
For irrigated agriculture, the economic (blue) water productivity (WPEc/ETb) showed higher values for smallholder crops (banana, vegetables, and maize) using a less net irrigation, Qb, compared to the fully irrigated rice and sugarcane (Table 9). This, thus, imply that during periods of physical water scarcity, the opportunity cost for blue water (scarce) resources is much higher than that of precipitation.
6. Conclusions
This paper presented the spatial water productivity in terms of bio-physical (biomass and yield) and economic benefits for different LULC in the Upper Pangani River Basin, in Eastern Africa. In agriculture, irrigated lands achieved the highest water productivity in terms of biomass, crop yield and economic productivity. The productivity for sugarcane and rice is high and within the ranges reported in the literature. In supplementary irrigated and rainfed systems, the productivity was moderate but significantly lower than the potential reported in literature. In natural ecosystems, natural forest and wetland that have access to abundant water resources achieved a relatively high biomass production, compared to the expansive shrublands and sparse vegetation. However, the economic productivity for the natural forest and wetlands was low, when computed using biomass-derived CO2 storage economic benefits, only. We found a linear relationship between biomass (and yield) and ET, in both agricultural and natural landscapes. As expected, biomass production in irrigated (and supplementary irrigated) agriculture was higher than in rainfed agriculture and natural ecosystems, in the Upper Pangani. This could be explained by better plant water and soil fertility management, in the irrigated landscapes, and a relatively low rainfall, in the rainfed landscapes. The relationship provides a scope for improved water productivity, especially for rainfed systems with supplementary irrigation and good agronomic practices. Molden et al. [23,28] provides the various ways of increasing the productivity of rainfed agriculture and crops, through supplementary irrigation (see also [24,108]).
The pixel results for biomass water productivity of a given land-use class showed large variations. The coefficient of variation (CV) was high for natural and conserved land uses (0.3–1.3). This was mainly due to the large topographical range of the land-use type which influence the environmental factors, such as rainfall and temperature. For agricultural land uses, the CV was lower (0.1–0.3), but nevertheless still higher than those reported for large-scale irrigation systems. The result could be explained by the high levels of intercropping that exists within the land-use types, dominated by smallholder irrigation system. Even so, the spatial analysis provided a further scope for increased water productivity, in agricultural plots that have a low biomass growth.
The economic productivity in terms of irrigation water use (Qb) was higher for the smallholder banana and maize, under supplementary irrigation, as compared to the fully-irrigated sugarcane and rice. In situations of physical water scarcity, the opportunity cost for blue water (scarce) resources was much higher than that of precipitation. It would, thus, be more prudent to allocate river water to the supplementary irrigated crops than to the fully irrigated crops that are grown during the dry season.
The market price for carbon sequestration was observed to significantly influence the water productivity for the natural forest ecosystems. The market price was observed to be lower than the social costs of carbon emissions, in the global market [33,71]. Nevertheless, the price was expected to increase, significantly, in the near future with the expected carbon trading, following the Kyoto Protocol [109]. Other ecosystem services from natural land cover, inferred from the literature, substantially increased the economic water productivity, especially for the wetlands, natural forests, and the shrublands. Advanced techniques for localized environmental and social ecosystem valuation for the natural environment, exist [110], but these techniques require specific expertise and are quite costly [111]. However, the biophysical data and baseline water values derived here, could therefore, provide boundary conditions for a further detailed economic or environmental modelling.
The social water value to the local populations is also a key factor, for consideration by policy makers, when interpreting the, water productivity indices. Banana, maize and rice provide staple food for local livelihoods and income, thus, enhancing food security and social well-being. On the other hand, sugarcane grown by the large-scale Tanzania Plantation Company that has a relatively high economic productivity and might not provide high benefits to local livelihoods. Trade-offs, therefore, have to be made between attaining high economic water productivities and social benefits in the Pangani river basin.
It is clear from the spatial water productivity maps that biomass production is closely correlated with economic water productivity. Water yields, carbon credits, and other ecosystem services provide insight into the water value that society attaches to a certain cultural and natural land-use activity. Standard payment for environmental services (PES) schemes also relates with efforts to enhance water yields, prevention of soil erosion, and carbon sequestration among others. A holistic approach that involves the improvement of both the biophysical and economic factors, through sustainable basin-wide interventions can, therefore, result into higher economic water productivity at a lower social and environmental cost. Such a comprehensive water productivity analysis will allow policy makers to quantify the foregone economic benefits for allocating water for socio-environmental gains. Moreover, the physical water productivity can inform the long-term basin strategies, based on future market trends and socio-economic scenarios. The remotely-sensed estimate of the economic water productivity that includes natural ecosystems would, therefore, provide vital information for the sustained green growth and socio-economic development, in many African river basins.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at http://www.mdpi.com/2072-4292/10/11/1802/s1, further information on the calibration and validation of the specific crops and additional information on biomass production. Table S1. Actual yield to biomass sampling data for rice in the Lower Moshi irrigation scheme; Table S2. Actual biomass to actual yield for sugarcane in the TPC irrigation scheme; Figure S1: Mean annual biomass production in the Upper Pangani River Basin for different land use types for the years 2008–2010; Table S3: Mean annual biomass production for different land use types in Upper Pangani River Basin for 2008–2010.
Author Contributions
J.K.K., Y.M. and W.G.M.B. designed the research; J.K.K. processed the data; J.K.K., M.M., Y.M., W.G.M.B. and P.v.d.Z. analyzed the data; J.K.K., M.M. and P.v.d.Z. wrote the paper.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
This research carried out in the framework of the Smallholder Systems Innovations (SSI) on the theme ‘Upscaling small-scale land and water system innovations in dryland agro-ecosystems for sustainability and livelihood improvements’. The project is funded by the Netherlands Ministry of Development Cooperation (DGIS) through the UNESCO-IHE Partnership Research Fund (UPaRF). We gratefully acknowledge data provided by the following organizations: Pangani Basin Water Office (Moshi, Tanzania), Tanzania Plantation Company—TPC (Moshi, Tanzania), Lower Moshi Irrigation Scheme (Moshi, Tanzania), and Zonal Irrigation Department (Moshi, Tanzania).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
References
- De Fraiture, C.; Giordano, M.; Liao, Y. Biofuels and implications for agricultural water use: Blue impacts of green energy. Water Policy 2008, 10, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Current States and Trends; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- De Groot, R.; Brander, L.; van der Ploeg, S.; Costanza, R.; Bernard, F.; Braat, L.; Christie, M.; Crossman, N.; Ghermandi, A.; Hein, L.; et al. Global estimates of the value of ecosystems and their services in monetary units. Ecosyst. Serv. 2012, 1, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockström, J.; Gordon, L.; Folke, C.; Falkenmark, M.; Engwall, M. Linkages among water vapor flows, food production, and terrestrial ecosystem services. Conserv. Ecol. 1999, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackernagel, M.; Onisto, L.; Bello, P.; Linares, A.C.; Falfán, I.S.L.; García, J.M.; Guerrero, A.I.S. National natural capital accounting with the ecological footprint concept (Analysis). Ecol. Econ. 1999, 29, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monfreda, C.; Wackernagel, M.; Deumling, D. Establishing national capital accounts based on detailed Ecological Footprint and biological capacity assessments. Land Use Policy 2004, 21, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, P.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Sood, A.; Hoogeveen, J.; Peiser, L.; Bastidas-Obando, E.; Dost, R.J. Spatial evapotranspiration, rainfall and landuse data in water accounting results for policy decisions in the Awash Basin. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 533–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Karimi, P.; Rebelo, L.; Duan, Z.; Senay, G.; Muthuwatte, L.; Smakhtin, V. Earth observation based assessment of the water production and water consumption of Nile Basin Agro-Ecosystems. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 10306–10334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijne, J.W.; Barker, R.; Molden, D.J. (Eds.) Economics of water productivity in managing water for agriculture. In Water Productivity in Agriculture—Limits and Opportunities for Improvements, Comprehensive Assessment of Water Management in Agriculture; CABI Publishing in Association with International Water Management Institute: Wallingford, UK, 2003; pp. 19–35. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Ferrero, N. Water productivity in irrigation systems. Water Int. 2003, 28, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.H.; Hoque, M.R.; Hassan, A.A.; Khair, A.A. Effects of deficit irrigation on wheat yield, water productivity and economic returns. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 92, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellegers, P.J.G.J.; Soppe, R.; Perry, C.J.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M. Combining remote sensing and economic analysis to support decisions that affect water productivity. Irrig. Sci. 2009, 27, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- . Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Payments for Ecosystem Services and Food Security; Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2011; 300p, ISBN 978-92-5-106796-3. [Google Scholar]
- Enfors, E.; Gordon, L. Dealing with drought: The challenge of using water system technologies to break dryland poverty traps. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2008, 18, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUCN. The Pangani River Basin: A Situation Analysis, 2nd ed.; IUCN Eastern Africa Region Office: Nairobi, Kenya, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Costanza, R.; de Groot, R.S.; Sutton, P.; van der Ploeg, S.; Anderson, S.J.; Kubiezewski, I.; Farber, I.; Turner, R.K. Changes in the global value of ecosystem services. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2014, 26, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubbs, M. Conservation Reserve Program (CRP): Status and Issues; Congressional Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Saah, D.; Troy, A. Developing an Ecosystem Service Value Baseline; USAID Cooperative Agreement No. AID-486-A-12-00009; Vietnam Forests and Deltas Program: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, J.; Keller, A.; Davids, G. River basin development phases and implications of closure. J. Appl. Irrig. Sci. 1998, 33, 145–163. [Google Scholar]
- Igbadun, H.E.; Mahoo, H.F.; Tarimo, A.K.P.R.; Salim, B.A. Crop water productivity of an irrigated maize crop in Mkoji sub-catchment of the Great Ruaha River Basin, Tanzania. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 85, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, P.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Molden, D.J.; Cheema, M.J. Basin-wide water accounting based on remote sensing data: an application for the Indus Basin. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 2473–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokwe, S. Water productivity in smallholder irrigation schemes in South Africa. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 1223–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molden, D.; Oweis, T.Y.; Steduto, P.; Kijne, J.W.; Hanjra, M.A.; Bindraban, P.S. Pathways for increasing agricultural water productivity. In Water for Food, Water for Life: A Comprehensive Assessment of Water Management in Agriculture; Earthscan: London, UK; International Water Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Zaag, P. Viewpoint—Water variability, soil nutrient heterogeneity and market volatility—Why sub-Saharan Africa’s Green Revolution will be location-specific and knowledge-intensive. Water Altern. 2010, 3, 154–160. [Google Scholar]
- Bossio, D.; Jewitt, G.; van der Zaag, P. Editorial—Smallholder system innovation for integrated watershed management in Sub-Saharan Africa. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 1683–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereres, E.; Orgaz, F.; Gonzalez-Dugo, V.; Testi, L.; Villalobos, F.J. Balancing crop yield and water productivity tradeoffs in herbaceous and woody crops. Funct. Plant Boil. 2014, 41, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molden, D.; Sakthivadivel, R. Water Accounting to Assess Use and Productivity of Water. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 1999, 15, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molden, D.; Oweis, T.Y.; Steduto, P.; Bindraban, P.; Hanjra, M.A.; Kijne, J. Improving agricultural water productivity: Between optimism and caution. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijne, J.; Barron, J.; Hoff, H.; Rockström, J.; Karlberg, L.; Gowing, J.; Wani, S.P.; Wichelns, D. Opportunities to Increase Water Productivity in Agriculture with Special Reference to Africa and South Asia; A Report Prepared by Stockholm Environment Institute, for the Swedish Ministry of Environment Presentation at CSD 16, N. Y. 14 May 2009; Stockholm Environment Institute: Stockholm, Sweden, 2009; 39p. [Google Scholar]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; de Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, L.M.; van Halsema, E.G.; Mahoo, F.H. Building a mosaic of values to support local water resources management. Water Policy 2006, 8, 415–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enfors, E.; Gordon, L. Analysing resilience in dryland agro-ecosystems: A case study of the Makanya catchment in Tanzania over the past 50 years. Land Degrad. Dev. 2007, 18, 680–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batjes, N.H. Projected changes in soil organic carbon stocks upon adoption of recommended soil and water conservation practices in the Upper Tana River catchment, Kenya. Land Degrad. Dev. 2014, 35, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedjo, R.A. Forest Carbon Sequestration: Some Issues for Forest Investments; Discussion Paper No. 01-34; Resources for the Future: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Pizer, W.A. Combining price and quantity controls to mitigate global climate change. J. Public Econ. 2002, 85, 409–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, N. The Economics of Climate Change: The Stern Review; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zwart, S.J.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M. SEBAL for detecting spatial variation of water productivity and scope for improvement in eight irrigated wheat systems. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 89, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dam, J.C.; Singh, R.; Bessembinder, J.J.E.; Leffelaar, P.A.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Jhorar, R.K.; Kroes, J.G.; Droogers, P. Assessing options to increase water use productivity in irrigated river basins using remote sensing and modelling tools. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2006, 22, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainuddin, M.; Kirby, M. Spatial and temporal trends of water productivity in the lower Mekong River Basin. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 1567–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration—Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements; FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Zwart, S.J.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; De Fraiture, C.; Molden, D.J. WATPRO: A remote sensing based model for mapping water productivity of wheat. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1628–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Williams, J.R.; Zehnder, A.J.B.; Yang, H. GEPIC—Modelling wheat yield and crop water productivity with high resolution on a global scale. Agric. Syst. 2007, 94, 478–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McVicar, T.R.; Zhang, G.; Bradford, A.S.; Wang, H.; Dawes, W.R.; Zhang, L.; Li, L. Monitoring regional agricultural water use efficiency for Hebei province on the North China Plain. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2002, 53, 55–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Wu, B. Integrated spatial–temporal analysis of crop water productivity of winter wheat in Hai Basin. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 133, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, H.; Lei, H.; Shao, H.; Liu, T. Winter Wheat Water Productivity Evaluated by the Developed Remote Sensing Evapotranspiration Model in Hebei Plain, China. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 384086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PBWO/IUCN. The Hydrology of the Pangani River Basin. Report 1: Pangani River Basin Flow Assessment Initiative; PBWO: Moshi, Tanzanian, 2006; 62p. [Google Scholar]
- Kiptala, J.K.; Mohamed, Y.; Mul, M.L.; van der Zaag, P. Mapping evapotranspiration trends using MODIS images and SEBAL model in a data scarce and heterogeneous landscape in Eastern Africa. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 8495–8510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujwahuzi, M.R. Water use conflicts in the Pangani basin. In Water Resources Management in the Pangani River Basin; Challenges and Opportunities; Ngana, J.O., Ed.; Dar es Salaam University Press: Dar es Salaam, Tanzania, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- PBWO/IUCN. Pangani River Basin Flow Assessment; Final Project Report; Pangani Basin Water Board: Moshi, Tanzanian; IUCN Eastern & Southern Africa Regional Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2009; 89p. [Google Scholar]
- Komakech, H.; Van Koppen, B.; Mahoo, H.; Van der Zaag, P. Pangani River Basin over time and space: On the interface of local and basin level responses. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 1740–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Menenti, M.; Feddes, R.A.; Holtslag, A.A.M. A remote sensing Surface Energy Balance Algorithm for Land (SEBAL) 1. Formulation. J. Hydrol. 1998, 212–213, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteith, J.L. Solar radiation and productivity in tropical ecosystems. J. Appl. Ecol. 1972, 9, 747–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, M.S.; Maas, S.J.; Pinter, P.J. Combining remote sensing and modeling for estimating surface evaporation and biomass production. Remote Sens. Rev. 1995, 12, 335–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatfield, J.L.; Asrar, G.; Kanemasu, E.T. Intercepted photosynthetically active radiation estimated by spectral reflectance. Remote Sens. Environ. 1984, 14, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asrar, G.; Myneni, R.B.; Choudhury, J. Spatial heterogeneity in vegetation canopies and remote sensing of absorbed photosynthetically active radiation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1992, 41, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, C.B.; Randerson, J.T.; Malmstrom, C.M. Global net primary production: Combining ecology and remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 1995, 51, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Ali, S. A new crop yield forecasting model based on satellite measurements applied across the Indus Basin, Pakistan. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2003, 94, 321–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.S.; Feddes, R.A.; Gilley, J.R.; Lesaffre, B. Water Use Efficiency; In Sustainability of Irrigated Agriculture; NATO ASI Series E: Applied Sciences; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 193–209. [Google Scholar]
- Heinsch, F.A.; Reeves, M.; Votava, P.; Kang, S.; Milesi, C.; Zhao, M.; Glassy, J.; Jolly, W.M.; Loehman, R.; Bowker, C.F.; et al. User’s Guide GPP and NPP (MOD17A2/A3) Products NASA MODIS Land Algorithm; NASA Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2003; 57p, Available online: http://www.academia.edu/4620715/Users_Guide_GPP_and_NPP_MOD17A2_A3_Products_NASA_MODIS_Land_Algorithm (accessed on 7 July 2013).
- Ibrom, A.; Oltchem, A.; June, T.; Kreilein, H.; Rakkibu, G.; Ross, T.; Panferov, O.; Gravenhorst, G. Variation in photosynthetic light-use efficiency in a mountainous tropical rain forest in Indonesia. Tree Physiol. 2008, 28, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobbs, D.C.; Cannell, M.G.R.; Crout, N.M.J.; Lawson, G.J.; Friend, A.D.; Arah, J. Complementarity of light and water use in tropical agro forests. 1. Theoretical model outline, performance and sensitivity. For. Ecol. Manag. 1997, 102, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncrief, J.; Monteny, B.; Verhoef, A.; Friborg, T.; Elbers, J.; Kabat, P.; de Bruin, H.; Soegaard, H.; Jarvis, P.; Taupin, J. Spatial and temporal variations in net carbon flux during HAPEX-Sahel. J. Hydrol. 1997, 188–189, 563–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goutorbe, J.P.; Lebel, T.; Dolman, A.J.; Gash, J.H.C.; Kabat, P.; Kim, Y.H.; Monteny, B.; Prince, S.D.; Sticker, A.; Tinga, A.; et al. An overview of HAPEX-Sahel: A study in climate and desertification. J. Hydrol. 1997, 188–189, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, S.D. A model of regional primary production for use with coarse-resolution satellite data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1991, 12, 1313–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donald, C.M.; Hamblin, J. The biological yield and harvest index of cereals as agronomic and plant breeding criteria. Adv. Agron. 1976, 28, 361–405. [Google Scholar]
- Steduto, P.; Hsiao, T.C.; Raes, D.; Fereres, E. AquaCrop—The FAO crop model to simulate yield response to water: I. Concepts and underlying principles. Agron. J. 2009, 101, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saatchi, S.S.; Harris, N.L.; Brown, S.; Lefsky, M.; Mitchard, E.T.A.; Salas, W.; Zutta, B.R.; Buermann, W.; Lewis, S.L.; Hagen, S.; et al. Benchmark map of forest carbon stocks in tropical regions across three continents. PNAS 2011, 108, 9899–9904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponce-Hernandez, R.; Koohafkan, P.; Antoine, J. Assessing Carbon Stocks and Modelling Win-Win Scenarios of Carbon Sequestration through Land-Use Changes; Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2004; 168p, ISBN 92-5-105168-5. [Google Scholar]
- Young, R.A. Determining the Economic Value of Water: Concepts and Methods; Resource for the Future: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; 374p. [Google Scholar]
- LMC International. Worldwide Survey of Sugar and HFCS Production Cost (2000–2009); Overseas Development Institute: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Interagency Working Group on Social Cost of Carbon. Social Cost of Carbon for Regulatory Impact Analysis under Executive Order 12866. US EPA Technical Support Document. 2009. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/oms/climate/regulations/scc-tsd.pdf (accessed on 13 August 2014).
- AMBIO. Scolel te Programme Plan Vivo Annual Report 2009; San Cristobal de las Casas: Chiapas, Mexico, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank and Ecofys. State and Trends of Carbon Pricing 2017; Advanced Brief, Carbon Pricing Watch; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; Available online: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/26565 (accessed on 21 March 2018).
- Newell, R.G.; Pizer, W.A.; Raimi, D. Carbon Markets: Past, Present, and Future; Discussion Papers; Resources for the Future: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; 54p, Available online: http://www.rff.org/files/sharepoint/WorkImages/Download/RFF-DP-12-51.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2014).
- Kiptala, J.K.; Mohamed, Y.; Mul, M.; Cheema, M.J.M.; van der Zaag, P. Land use and land cover classification using phenological variability from MODIS vegetation in the Upper Pangani River Basin, Eastern Africa. J. Phys. Chem. Earth 2013, 66, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiptala, J.K.; Mul, M.L.; Mohamed, Y.; van der Zaag, P. Modelling stream flow and quantifying blue water using modified STREAM model in the Upper Pangani River Basin, Eastern Africa. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 2287–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, D.; Epema, G.F.; Goudriaan, J. Monitoring rice reflectance at field level for estimating biomass and LAI. Field Crops Res. 1998, 55, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschetti, M.; Bocchi, S.; Stroppiana, D.; Brivio, P.A. Estimation of parameters describing morpho-physiological features of Mediterranean rice varieties for modelling purposes. Ital. J. Agrometeorol. 2006, 3, 40–49. [Google Scholar]
- Boschetti, M.; Stroppiana, D.; Brivio, P.A.; Bocchi, S. Multi-year monitoring of rice crop phenology through time series analysis of MODIS images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 4643–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waclawovsky, A.J.; Sato, P.M.; Lembke, C.G.; Moore, P.H.; Souza, G.M. Sugarcane for bio-energy production: An assessment of yield and regulation of sucrose content. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2010, 8, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varlet-Grancher, C.; Bonhomme, R.; Charter, M.; Artis, P. Efficience de la conversion de l’energie solaire par un couvert vegetal. Acta Ecol./Ecol. Plant. 1982, 3, 3–26. [Google Scholar]
- Nyombi, K. Understanding Growth of East Africa Highland Banana: Experiments and Simulation. Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen University, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2010; 198p. [Google Scholar]
- Nyombi, K.; van Asten, P.J.A.; Corbeels, M.; Taulya, G.; Leffelaar, P.A.; Giller, K.E. Mineral fertilizer response and nutrient use efficiencies of East African highland banana (Musa spp., AAA-EAHB, cv. Kisansa). Field Crops Res. 2010, 117, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, D.W.; Fortescue, J.A.; Thomas, D.S. Environmental physiology of the bananas (Musa spp). Braz. J. Plant Physiol. 2008, 19, 463–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, S.J. Use of remotely sensed information in agricultural crop growth models. Ecol. Model. 1988, 41, 247–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, C.L.; Richardson, A.J.; Escobar, D.E.; Gerberman, A.H. Vegetation indices in crop assessments. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 35, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.A.J.; Gillespie, J.R.; Lugo, A.E. Biomass estimation methods for tropical forests with application to forest inventory data. For. Sci. 1989, 35, 881–902. [Google Scholar]
- Kilawe, E.C.; Lusambo, L.P.; Katima, J.H.Y.; Augustino, S.; Swalehe, N.O.; Lyimo, B. Above ground biomass equations for determination of carbon storage in plantation forests in Kilombero district, Tanzania. Int. For. Rev. 2011, 3, 317–321. [Google Scholar]
- Namayanga, L.N. Estimating Terrestrial Carbon Sequestered in Above Ground Woody Biomass from Remotely Sensed Data. SEBAL and CASA Algorithms in a Semi-Arid Area of Serowe—Botswana. Master’s Thesis, ITC, Enschede, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.; Bian, J.; Lei, G.; Huang, C. Estimating the maximal light use efficiency for different vegetation through the CASA Model combined with Time-series remote sensing data and ground measurements. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 3857–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Coulibaly, P.; Dibike, Y. Uncertainty analysis of statistical downscaling methods. J. Hydrol. 2006, 31, 357–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efron, B.; Tibshirani, R. An Introduction to the Bootstrap; Chapman and Hall: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Minitab Inc. MINITAB Statistical Software, Release 14 for Windows; State College: Pennsylvania, PA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ford, C.R.; Laseter, S.H.; Swank, W.T.; Vose, J.M. Can forest management be used to sustain water-based ecosystem services in the face of climate change? Ecol. Appl. 2011, 21, 2049–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, G.D. Water use by sugarcane. S. Afr. Sugar J. 1976, 60, 593–600, 627–635. [Google Scholar]
- Olivier, F.; Singels, A. Water use efficiency of irrigated sugarcane as affected by row spacing and variety. Proc. S. Afr. Sugar Technol. Assoc. 2003, 7, 347–351. [Google Scholar]
- Carr, M.K.V.; Knox, J.W. The water relations and irrigation requirements of sugar cane (Saccharum officinarum): A review. Exp. Agric. 2011, 47, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouman, B.A.M.; Humphreys, E.; Tuong, T.P.; Parker, R. Rice and water. Adv. Agron. 2006, 92, 187–237. [Google Scholar]
- Bouman, B.A.M.; Lampayan, R.M.; Tuong, T.P. Water Management in Rice: Coping with Water Scarcity; International Rice Research Institute: Los Baños, Philippines, 2007; 54p. [Google Scholar]
- Zwart, S.J.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M. Review of measured crop water productivity values for irrigated wheat, rice, cotton and maize. Agric. Water Manag. 2004, 69, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwart, S.J.; Leclert, L.M.C. A remote sensing based irrigation performance assessment: A case study of the Office du Niger in Mali. Irrig. Sci. 2010, 28, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Brito, R.A.L.; Bos, M.G.; Souza, R.A.; Cavalcanti, E.B.; Bakker, M.M. Low cost satellite data for monthly irrigation performance monitoring: Benchmarks for Nilo Coelho, Brazil. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2001, 15, 53–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molden, D.; Awulachew, S.B.; Conniff, K.; Rebelo, L.M.; Mohamed, Y.; Peden, D.; Kinyangi, J.; van Breugel, P.; Mukherji, A.; Cascão, A.; et al. Nile Basin Focal Project; Synthesis Report, Project Number 59; Challenge Program on Water and Food and International Water Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Grimes, D.W.; Wiley, P.L.; Sheesley, W.R. Alfalfa Yield and Plant Water Relations with Variable Irrigation. Crop Sci. 1991, 32, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Berkel, D.B.; Verburg, P.H. Spatial quantification and valuation of cultural services in an agricultural landscape. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 37, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Baggethun, E.; Barton, D.N. Classifying and valuing ecosystem services for urban planning. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 86, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanaian, S.; Graas, S.; Jiang, Y.; van der Zaag, P. An ecological economic assessment of flow regimes in a hydropower dominated river basin: The case of the lower Zambezi River, Mozambique. Sci. Total. Environ. 2015, 505, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI). Livestock and Fish Market Chains in Asia and Africa. Available online: www.ilri.org/node/1234 (accessed on 1 April 2014).
- Carbon Market Watch. What Is Needed to Fix the EU’s Carbon Market? Recommendations for the Market Stability Reserve and Future ETs Reform Proposals; Carbon Market Policy Briefing; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Economic Valuation of Water Resources in Agriculture; Turner, K., Georgiou, S., Clark, R., Brouwer, R., Eds.; FAO Water Reports; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2004; p. 204. [Google Scholar]
- Hermans, L.M.; Hellegers, P. A “New Economy” for Water for Food and Ecosystem; Synthesis Report for E-Forum Results; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2005; 19p. [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).