Long-Term Arctic Snow/Ice Interface Temperature from Special Sensor for Microwave Imager Measurements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Used Data
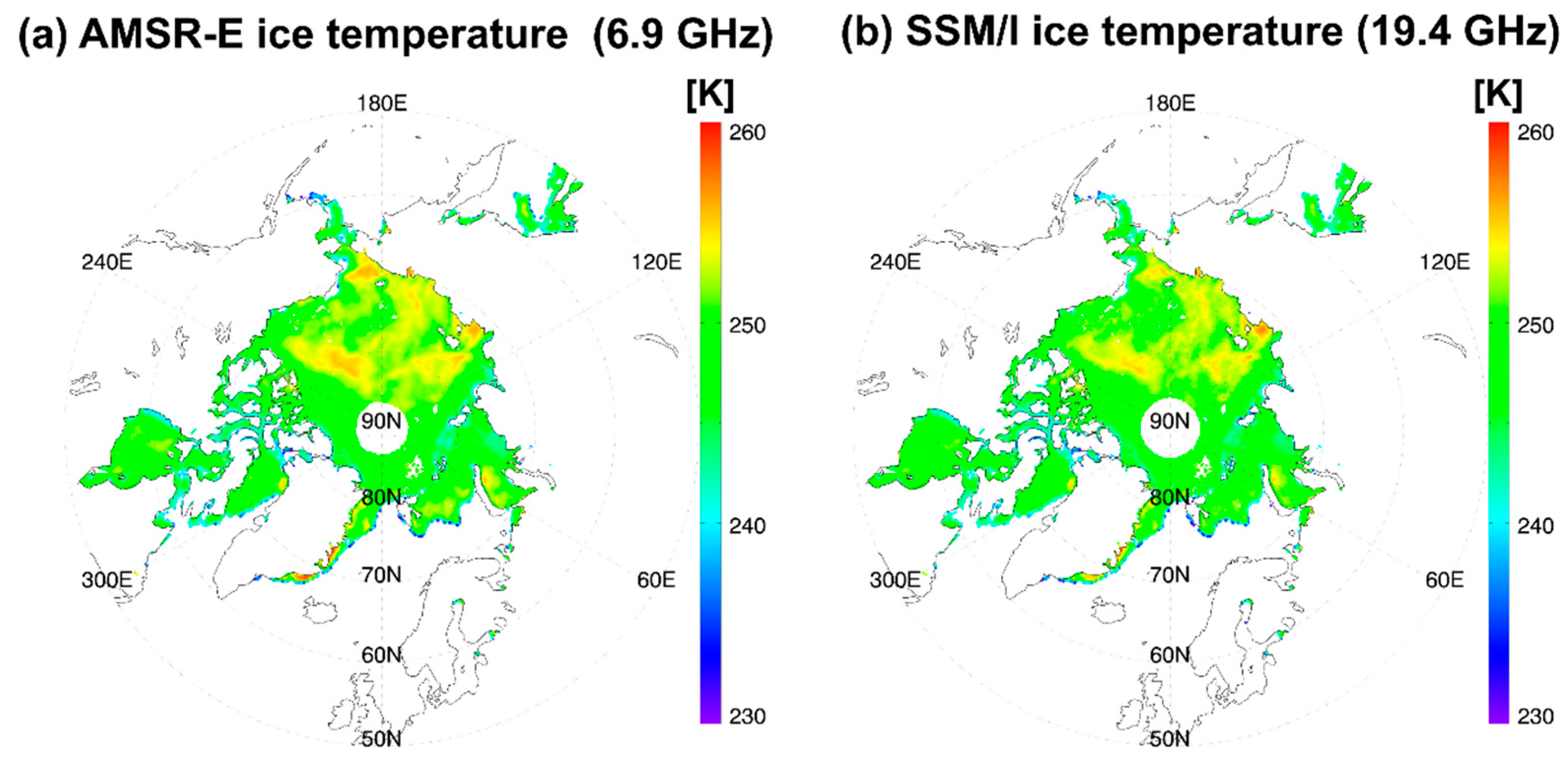
2.1. Passive MW Data
2.2. CRREL Buoy Measurements
3. Theoretical Background and Methodology
3.1. Simple Snow/Ice Model for Radiative Transfer
3.2. Apparent Emissivity
3.3. Correction Factor
3.4. Development of the SSM/I-Only Algorithm for the Correction Factor
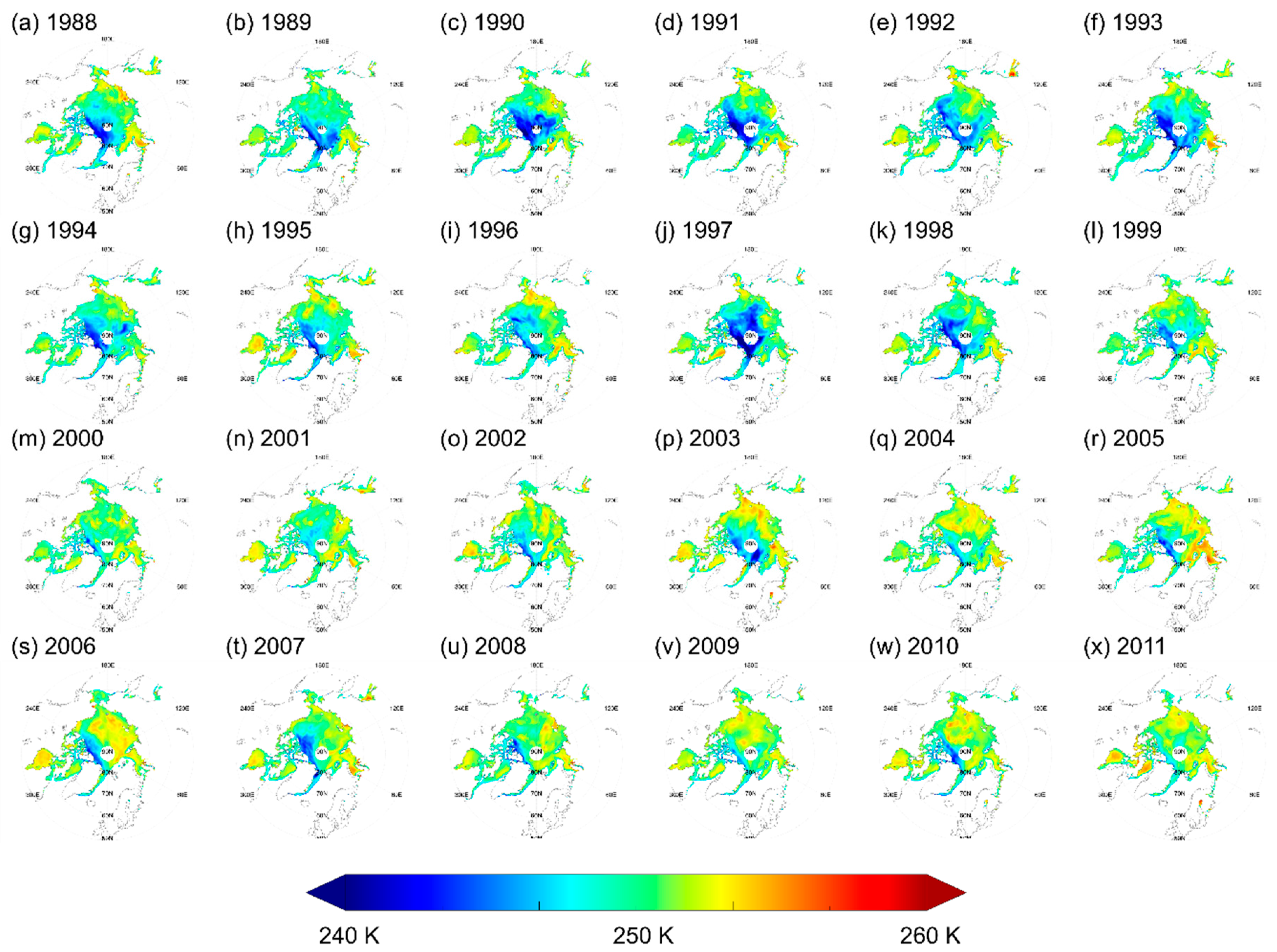
4. SSM/I Snow/Ice Interface Temperature (SIIT)
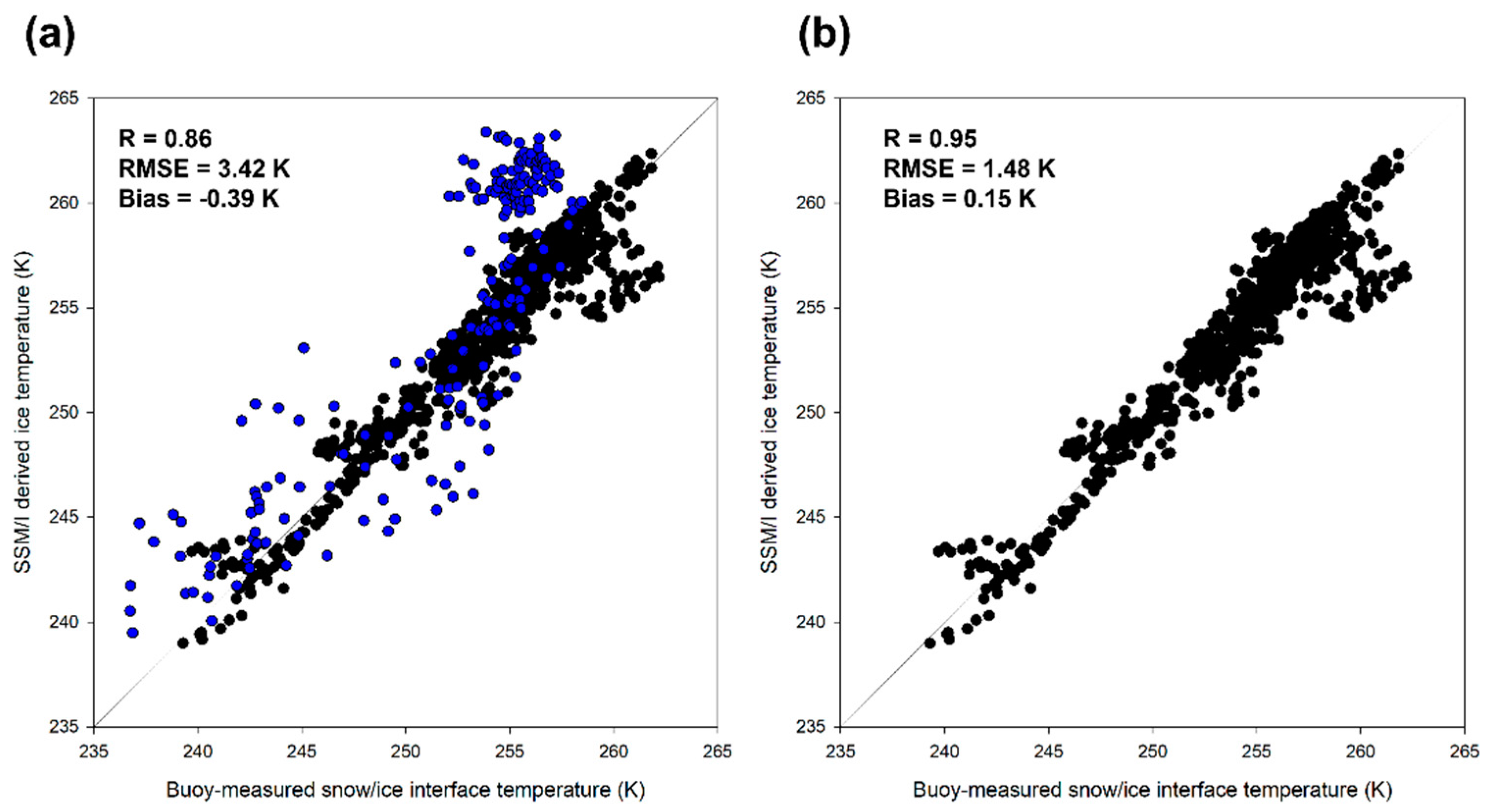
Validation against the Buoy Snow/Ice Interface Temperature
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Hansen, J.; Ruedy, R.; Sato, M.; Lo, K. Global surface temperature change. Rev. Geophys. 2010, 48, RG4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.D.; Wigley, T.M.L. Estimation of global temperature trends: What’s important and what isn’t. Clim. Chang. 2010, 100, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, N.A.; Parker, D.E.; Horton, E.B.; Folland, C.K.; Alexander, L.V.; Rowell, D.P.; Kent, E.C.; Kaplan, A. Global analyses of sea surface temperature, sea ice, and night marine air temperature since the late nineteenth century. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symon, C.; Arris, L.; Heal, B. (Eds.) Arctic Climate Impact Assessment; Cambridge Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004; p. 1042. [Google Scholar]
- Serreze, M.C.; Francis, J.A. The Arctic amplification debate. Clim. Chang. 2006, 76, 241–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comiso, J.C.; Hall, D.K. Climate trends in the Arctic as observed from space. WIREs Clim. Chang. 2014, 5, 389–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroeve, J.C.; Kattsov, V.; Barrett, A.; Serreze, M.; Pavlova, T.; Holland, M.; Meier, W.N. Trends in Arctic sea ice extent from CMIP5, CMIP3 and observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 39, L16502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, I. Comparing and contrasting the behavior of Arctic and Antarctic sea ice over the 35 year period 1979–2013. Ann. Glaciol. 2015, 56, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bintanja, R.; Selten, F.M. Future increases in Arctic precipitation linked to local evaporation and sea-ice retreat. Nature 2014, 509, 479–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Screen, J.A.; Simmonds, I. Declining summer snowfall in the Arctic: Causes, impacts and feedbacks. Clim. Dyn. 2012, 38, 2243–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattsov, V.B.; Walsh, J.E. Twentieth-century trends of Arctic precipitation from observational data and a climate model simulation. J. Clim. 2012, 13, 1362–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopec, B.G.; Feng, X.; Michel, F.A.; Posmentier, E.S. Influence of sea ice on Arctic precipitation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bintanja, R.; Andry, O. Toward a rain-dominated Arctic. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.; Screen, J.A.; Furtado, J.C.; Barlow, M.; Whittleston, D.; Coumou, D.; Francis, J.; Dethloff, K.; Entekhabi, D.; Overland, J.; et al. Recent Arctic amplification and extreme mid-latitude weather. Nat. Geosci. 2014, 7, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, J.A.; Vavrus, S.J. Evidence for a wavier jet stream in response to rapid Arctic warming. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 014005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Xiao, Y.; Yao, Y.; Dai, A.; Simmonds, I.; Franzke, C.L.E. Impact of Ural blocking on winter warm Arctic-cold Eurasian anomalies. Part I: Blocking-induced amplification. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 3925–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Curry, J.A.; Wang, H.; Song, M.; Horton, R.M. Impact of declining Arctic sea ice on winter snowfall. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 4074–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kug, J.-S.; Jeong, J.-H.; Jang, Y.-S.; Kim, B.-K.; Folland, C.K.; Min, S.-K.; Son, S.-W. Two distinct influences of Arctic warming on cold winters over North America and East Asia. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 759–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Screen, J.A. Influence of Arctic sea ice on European summer precipitation. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 044015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-M.; Sohn, B.-J. Retrieving the refractive index, emissivity, and surface temperature of polar sea ice from 6.9 GHz microwave measurements: A theoretical development. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 2293–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, W.; Kroodsma, R.; Kummerow, C.D.; McKague, D.S. Fundamental climate data records of microwave brightness temperature. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-M.; Sohn, B.-J.; Shi, H. Impact of ice surface and volume scatterings on the microwave sea ice apparent emissivity. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, W.; Sapiano, M.R.P.; Horsman, J.; Kummerow, C. Improved geolocation and earth incidence angle information for a fundamental climate data record of the SSM/I sensors. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 1504–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comiso, J.C. Bootstrap Sea Ice Concentration from Nimbus-7 SMMR and DMSP SSM/I-SSMIS, Version 3; NASA National Snow and Ice Data Center Distributed Active Archive Center: Boulder, CO, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polashenski, C.; Perovich, D.; Richter-Menge, J.; Elder, B. Seasonal ice mass-balance buoys: Adapting tools to the changing Arctic. Ann. Glaciol. 2011, 52, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comiso, J.C. Sea ice effective microwave emissivities from satellite passive microwave and infrared observations. J. Geophys. Res. 1983, 88, 7686–7704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masunaga, H.; Matsui, T.; Tao, W.; Hou, A.Y.; Kummerow, C.D.; Nakajima, T.; Bauer, P.; Olson, W.S.; Sekiguchi, M.; Nakajima, T.Y. Satellite Data Simulator Unit: A multisensory, multispectral satellite simulator package. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91, 1625–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, J.A.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 136, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-M.; Sohn, B.-J.; Kim, S.-J. Differentiating between first-year and multiyear sea ice in the Arctic using microwave-retrieved ice emissivities. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 5097–5112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, B.J.; Lee, S.-M. Analytical relationship between polarized reflectivities on the specular surface. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 2368–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Moore, R.K.; Fung, A.K. Microwave Remote Sensing: Active and Passive: Volume III: From Theory to Applications; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, S.; Pedersen, L.T.; Heygster, G.; Tonboe, R.; Kaleschke, L. Intercomparison of passive microwave sea ice concentration retrieval over the high concentration Arctic sea ice. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 112, C08004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastwood, S.; Lavergne, T.; Tonboe, R. Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document for the OSI SAF Global Reprocessed Sea Ice Concentration Product; EUMETSAT Network Satellite Application Facilities; EUMETSAT: Darmstadt, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cavalieri, D.J.; Crawford, J.P.; Drinkwater, M.R.; Eppler, D.T.; Farmer, L.D.; Jentz, R.R.; Wackerman, C.C. Aircraft active and passive microwave validation of sea ice concentration from the Defense Meteorological Program Special Sensor Microwave Imager. J. Geophys. Res. 1991, 96, 21989–22008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, N.; Johannessen, O.M.; Pedersen, L.T.; Tonboe, R.T. Retrievals of Arctic sea ice parameters by satellite passive microwave sensors: A comparison of eleven sea ice concentration algorithms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 7233–7246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Pinel, N.; Bourlier, C. Polarized infrared emissivity of 2D sea surfaces with one surface reflection. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, K. An Introduction to Atmospheric Radiation, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Petty, G.W.; Katsaros, K.B. The response of the SSM/I to the marine environment. Part II: A parameterization of the effect of the sea surface slope distribution on emission and reflection. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1994, 13, 617–628. [Google Scholar]
- Warren, S.G.; Brandt, R.E. Optical constants of ice from the ultraviolet to the microwave: A revised compilation. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D14220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
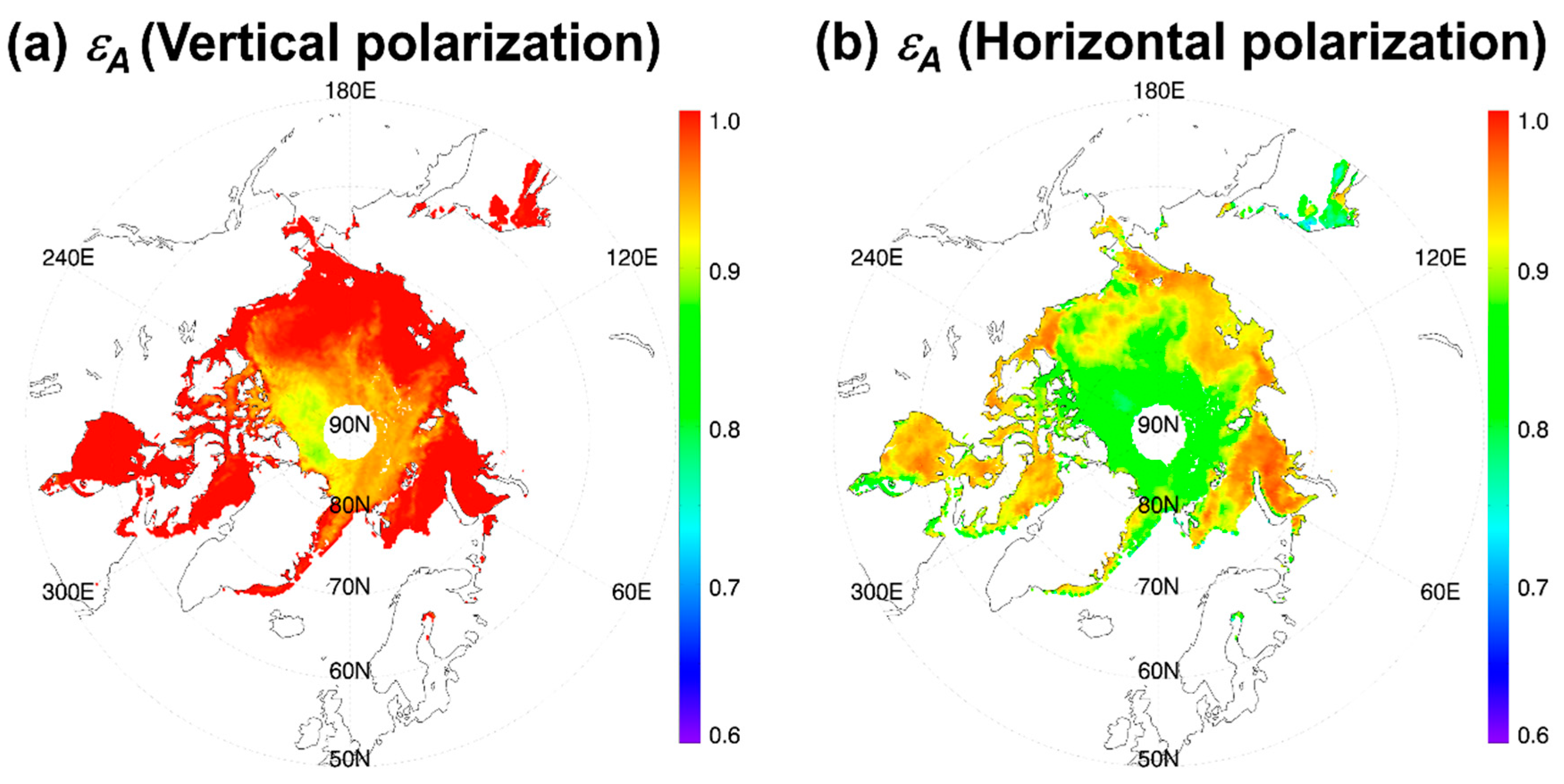
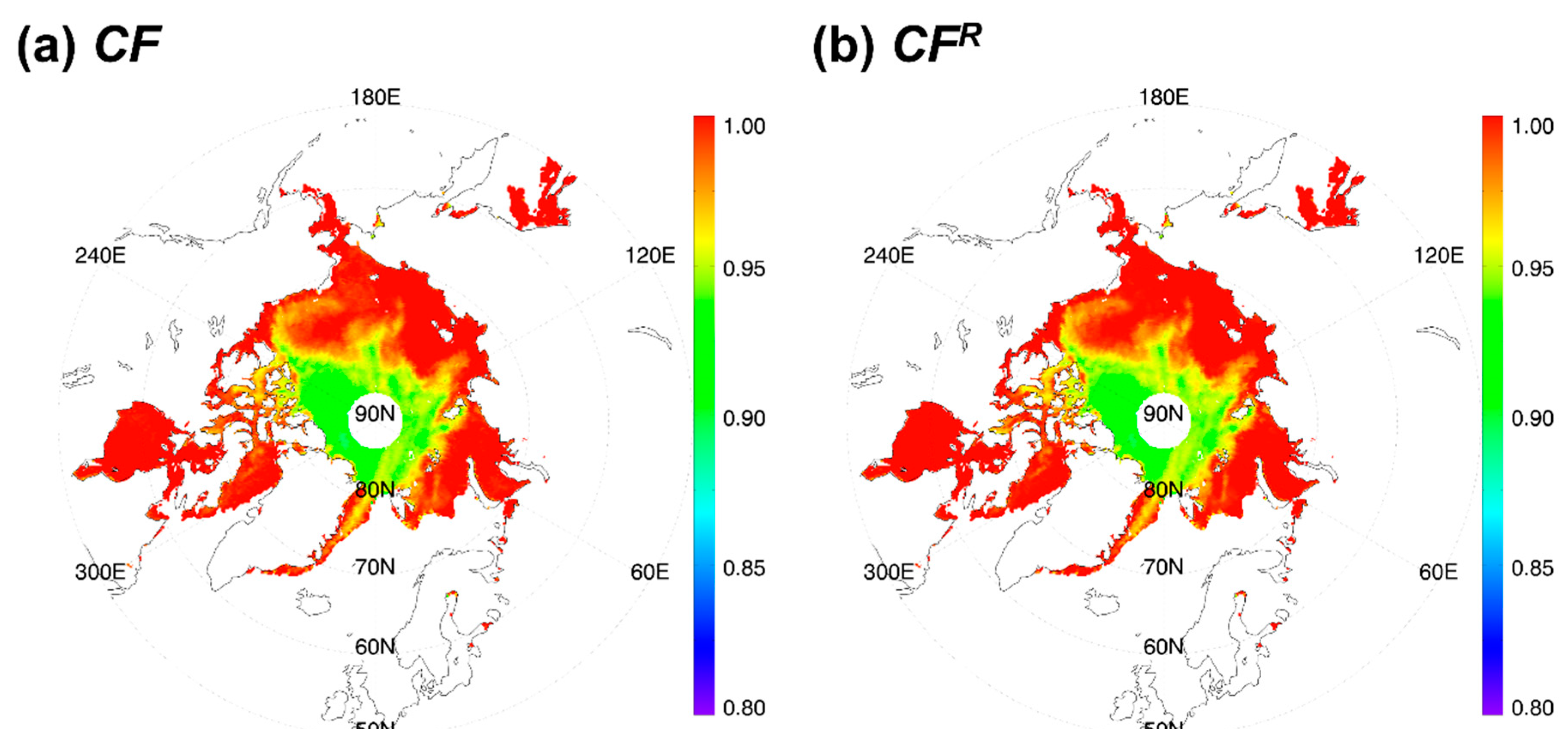
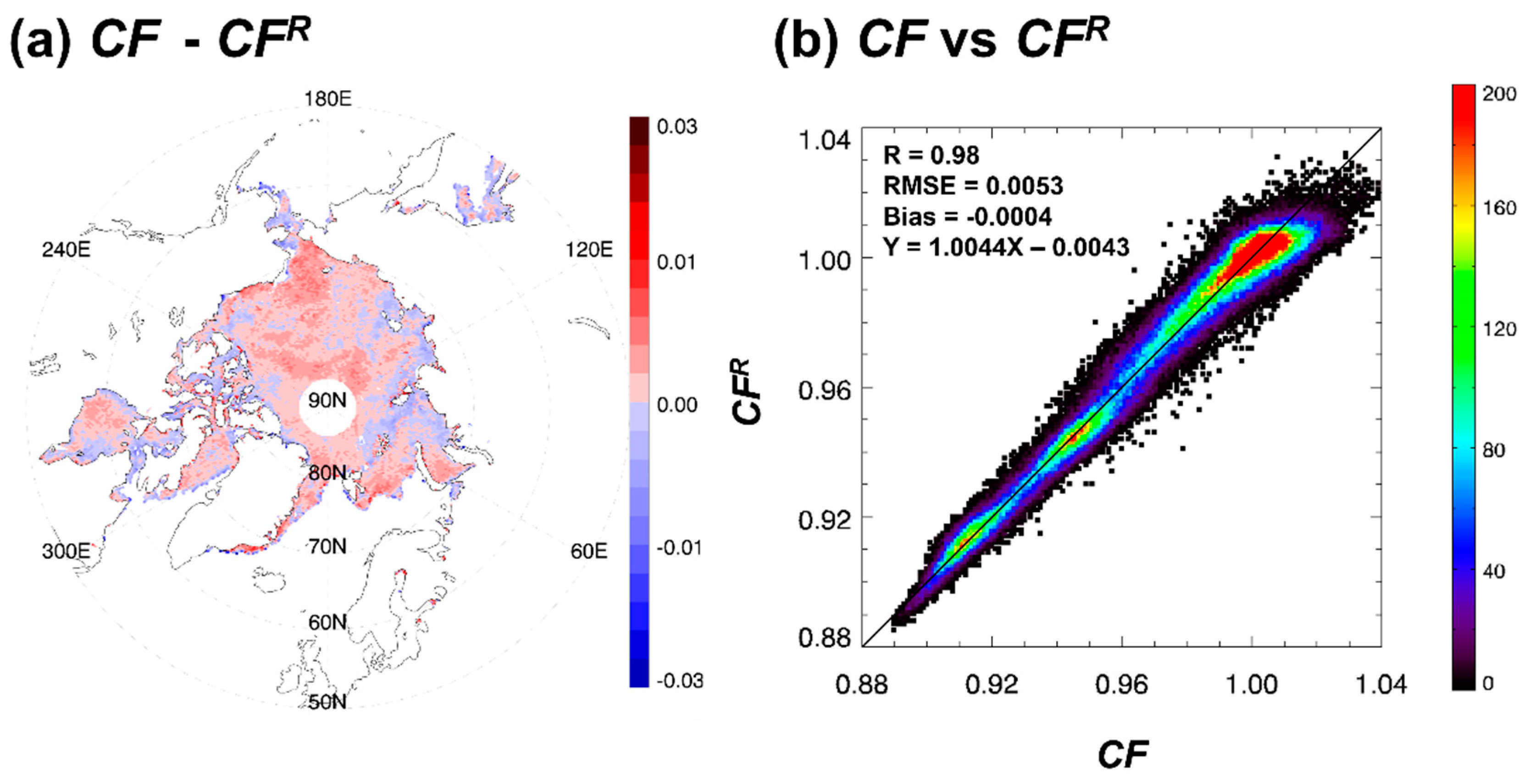
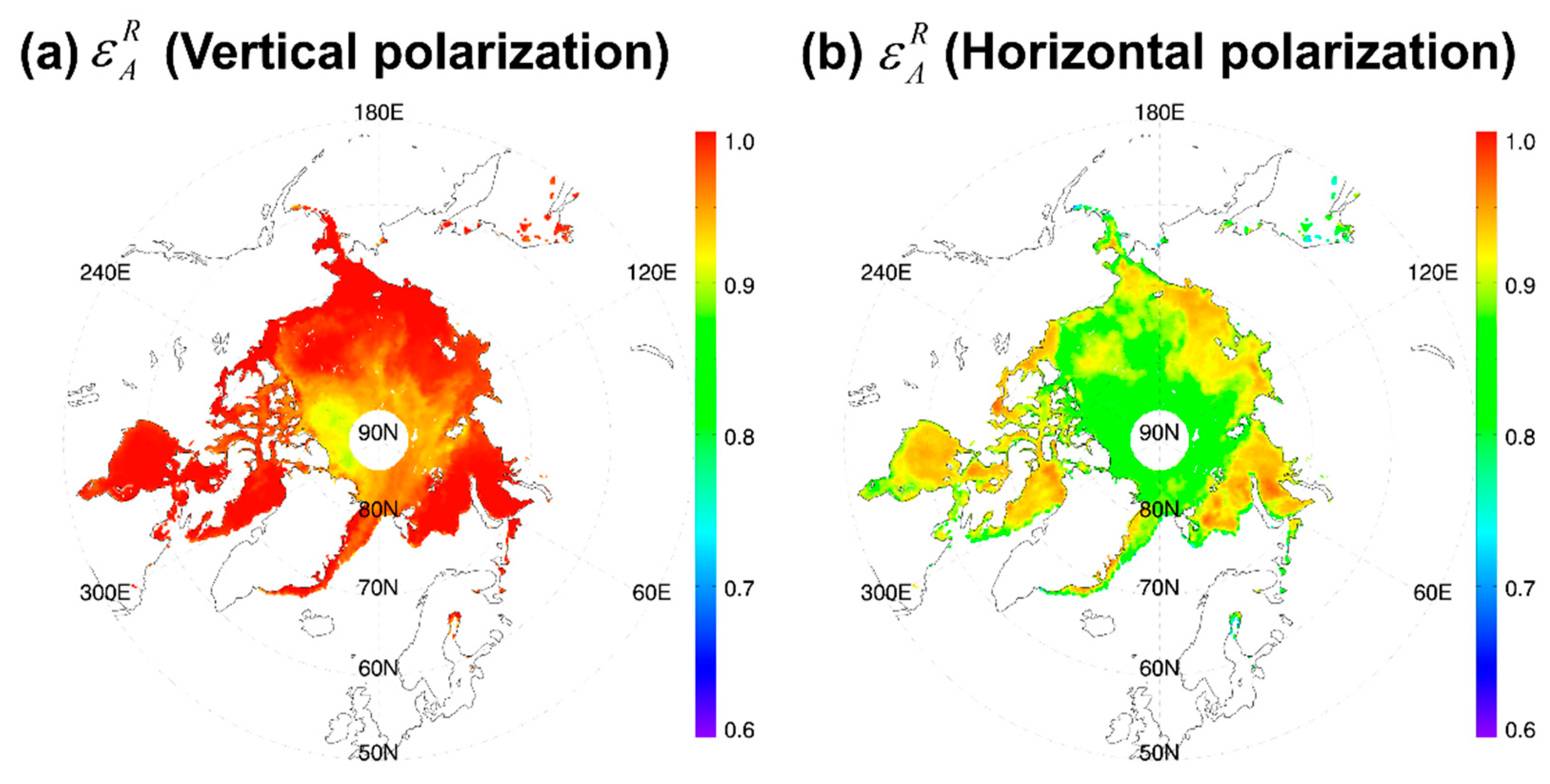

| Coefficients | a0 | a1 | a2 | a3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V-polarization | 0.48253852 | 0.00204367 | 0.0000556537 | −0.50878161 |
| H-polarization | 0.49223596 | 0.00201050 | −0.0000576901 | −0.52647698 |
| 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.9811 | 0.9839 | 0.9901 | 0.9798 | 0.9859 | 0.9745 | 0.9848 | 0.9897 | 0.9777 |
| # | Period | Starting Point | Ending Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 December 1993–28 February 1994 | 74.81°N, 138.55°W | 74.38°N, 154.19°W |
| 2 | 22 December 1997–28 February 1998 | 75.34°N, 150.05°W | 75.11°N, 159.66°W |
| 3 | 1 December 1997–28 February 1998 | 76.14°N, 147.46°W | 75.11°N, 159.59°W |
| 4 | 1 December 2003–29 February 2004 | 75.24°N, 135.07°W | 74.89°N, 141.07°W |
| 5 | 1 December 2006–28 February 2007 | 77.43°N, 139.35°W | 76.74°N, 139.14°W |
| 6 | 1 December 2006–2 February 2007 | 85.03°N, 128.78°E | 86.98°N, 125.96°E |
| 7 | 11 December 2007–27 February 2008 | 79.87°N, 155.15°W | 80.85°N, 151.78°W |
| 8 | 1 December 2007–28 February 2008 | 77.20°N, 135.27°W | 74.64°N, 135.14°W |
| 9 | 12 December 2007–23 February 2008 | 83.90°N, 112.91°W | 84.00°N, 109.63°W |
| 10 | 11 December 2007–28 January 2008 | 81.98°N, 119.61°W | 82.01°N, 119.76°W |
| 11 | 1 December 2008–18 February 2009 | 82.57°N, 115.30°W | 82.09°N, 114.50°W |
| 12 | 1 December 2010–28 February 2011 | 77.02°N, 149.28°W | 76.23°N, 146.66°W |
| 13 | 1 December 2010–28 February 2011 | 75.32°N, 142.39°W | 74.10°N, 142.60°W |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.-M.; Sohn, B.-J.; Kummerow, C.D. Long-Term Arctic Snow/Ice Interface Temperature from Special Sensor for Microwave Imager Measurements. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1795. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10111795
Lee S-M, Sohn B-J, Kummerow CD. Long-Term Arctic Snow/Ice Interface Temperature from Special Sensor for Microwave Imager Measurements. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(11):1795. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10111795
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Sang-Moo, Byung-Ju Sohn, and Christian D. Kummerow. 2018. "Long-Term Arctic Snow/Ice Interface Temperature from Special Sensor for Microwave Imager Measurements" Remote Sensing 10, no. 11: 1795. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10111795
APA StyleLee, S.-M., Sohn, B.-J., & Kummerow, C. D. (2018). Long-Term Arctic Snow/Ice Interface Temperature from Special Sensor for Microwave Imager Measurements. Remote Sensing, 10(11), 1795. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10111795







