Hyperspectral and LiDAR Fusion Using Deep Three-Stream Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- A three-stream CNN is designed in the proposed framework, which can effectively extract high-level features from spectral as well as spatial and elevation features produced by EPs. This baseline allows us to simultaneously take advantage of heterogeneous complementary features (from HSI and LiDAR) to achieve higher discriminating power during classification tasks.
- The proposed framework progressively combines low-level features (obtained by extinction profiles) with high-level features (obtained by CNN) for invariant feature learning. This consideration could significantly reduce the salt and pepper noise, as well as further promote the classification performance.
- A novel fusion scheme is proposed based on multi-sensor composite kernels, where three different base kernels for spectral, spatial and elevation features are taken into account. To be more specific, the MCK scheme provides us with an efficient framework for multi-sensor data fusion, where complementary information from heterogeneous features can be joint used for accurate classification by establishing and optimizing the corresponding MCK.
2. Methods
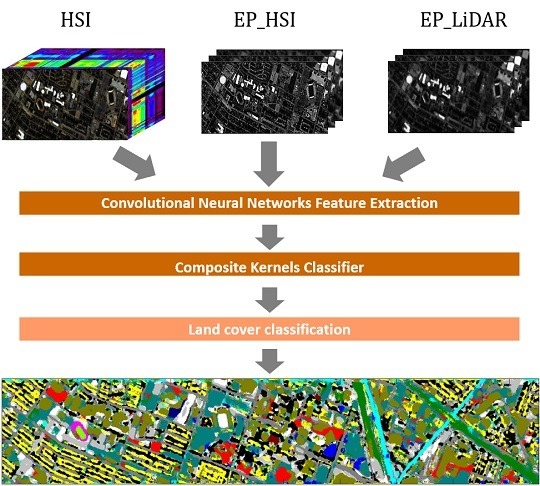
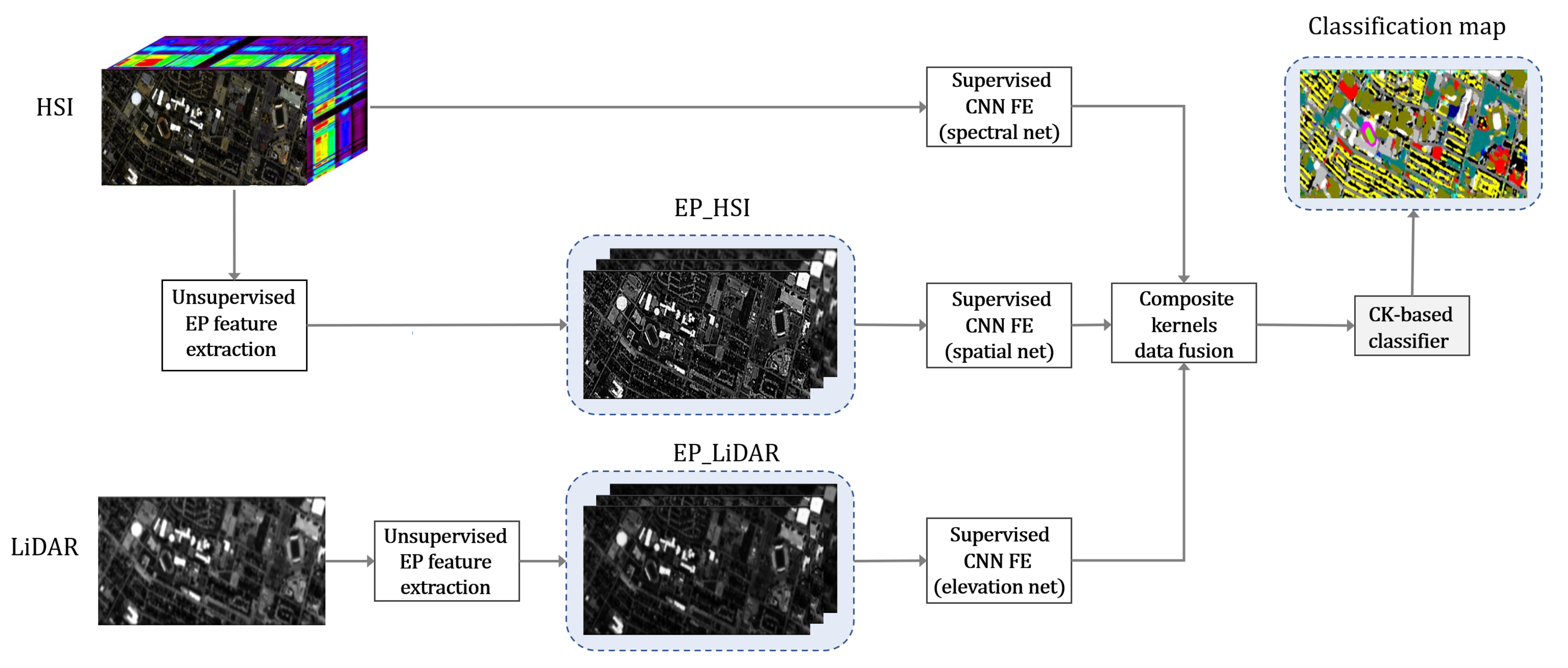
2.1. Workflow of the Proposed Fusion Framework
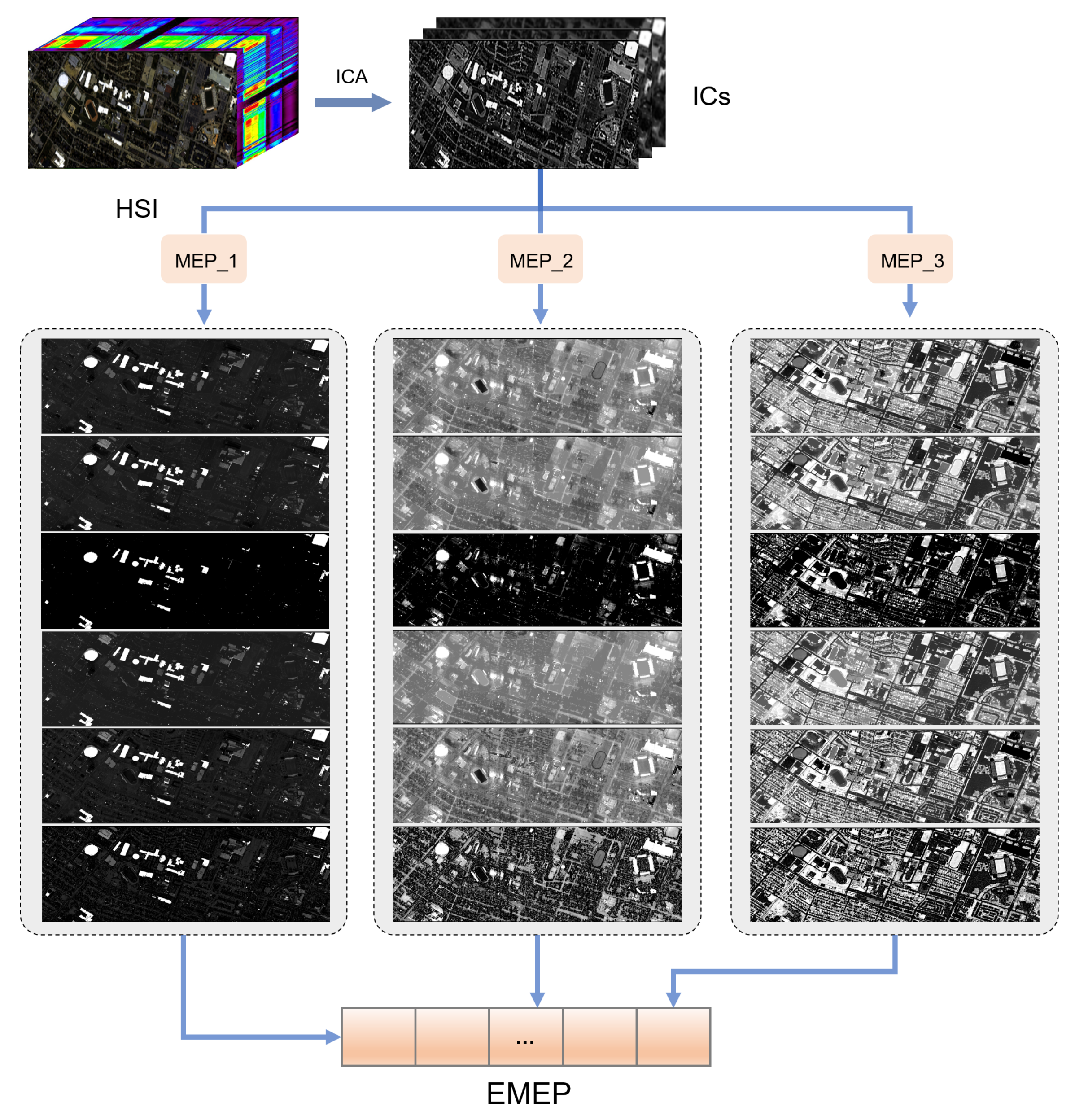
2.2. Extinction Profiles
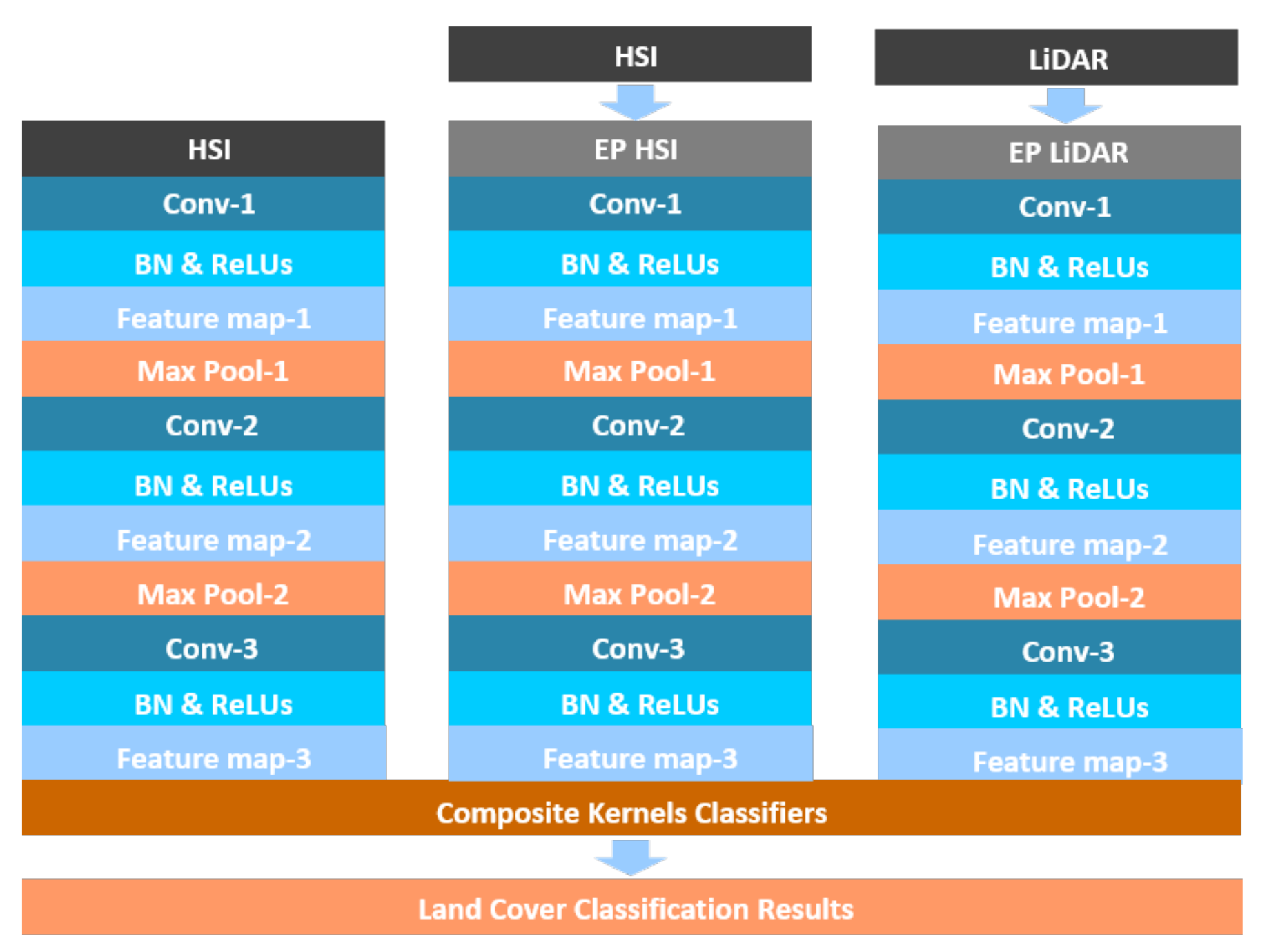
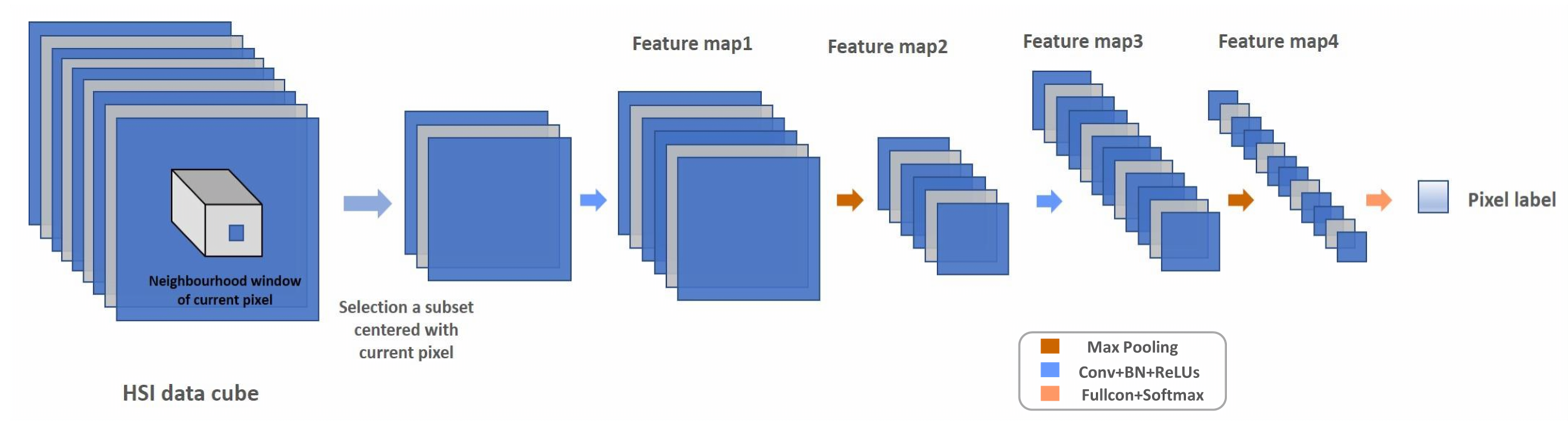
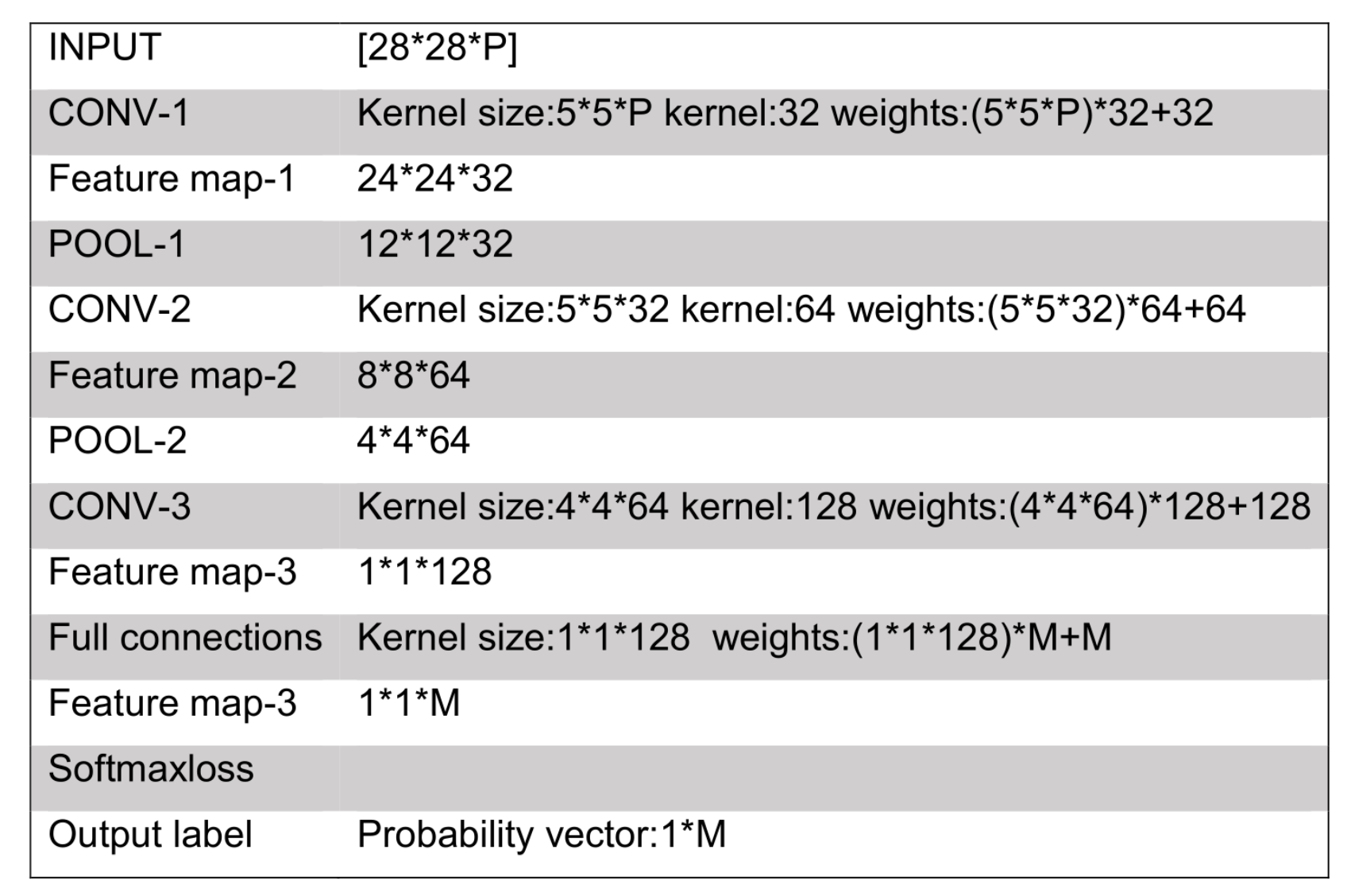
2.3. Convolutional Neural Networks Feature Extraction
2.4. Data Fusion Using Multisensor Composite Kernels
3. Experiment
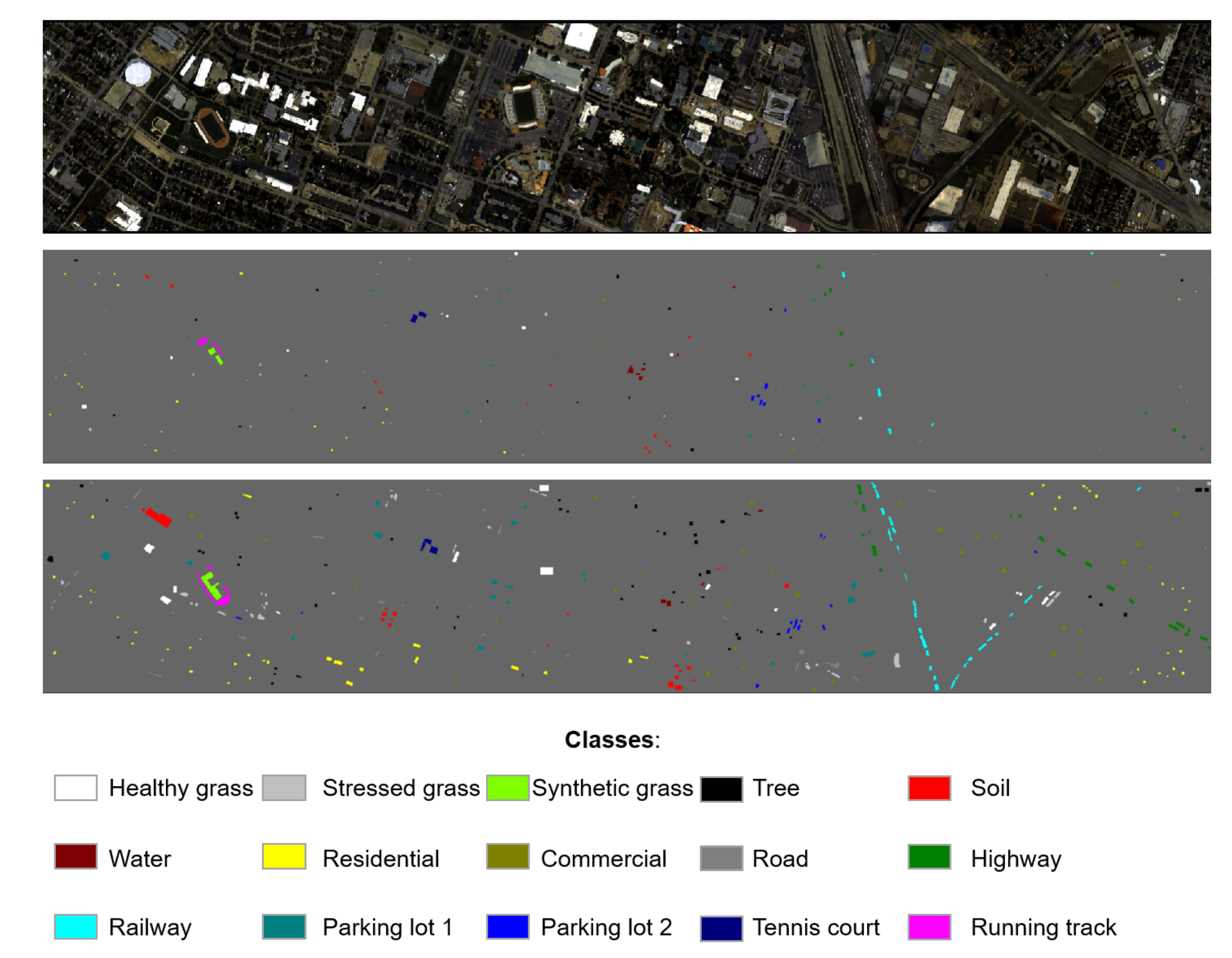
3.1. Data Descriptions
3.2. Algorithm Setup
4. Discussion
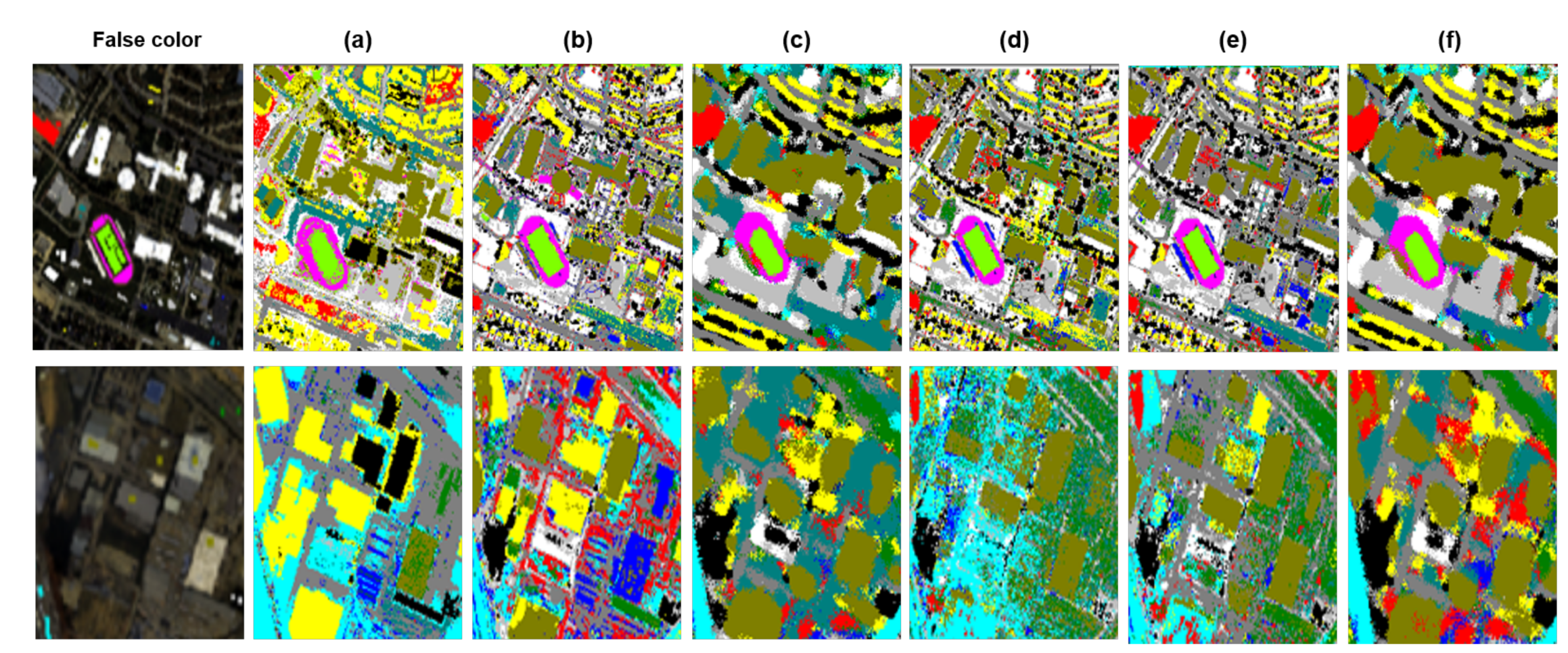
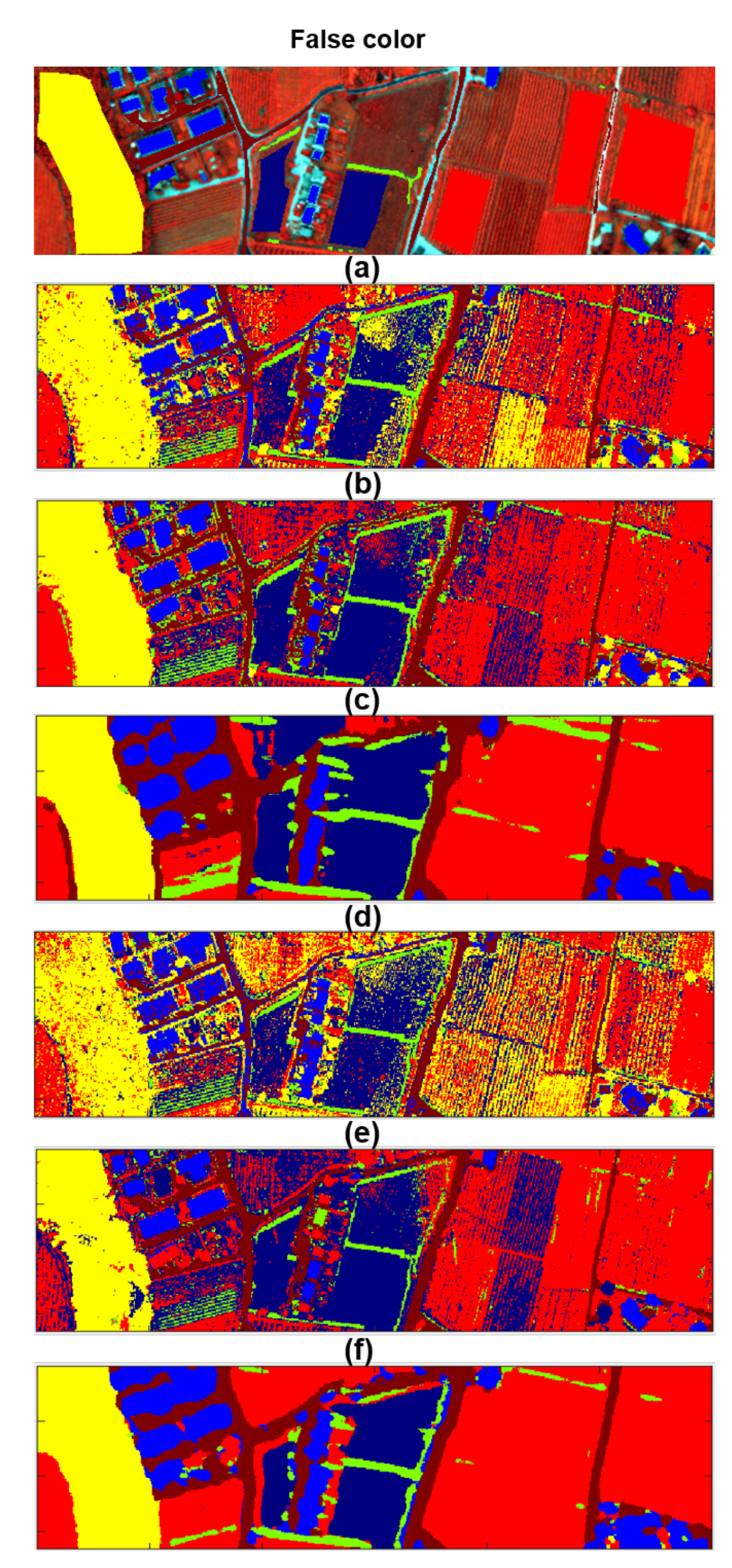
4.1. Classification Results
4.2. Comparison to State-of-the-Art
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benediktsson, J.; Ghamisi, P. Spectral-Spatial Classification of Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Images; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ghamisi, P.; Yokoya, N.; Li, J.; Liao, W.; Liu, S.; Plaza, J.; Rasti, B.; Plaza, A. Advances in Hyperspectral Image and Signal Processing: A Comprehensive Overview of the State of the Art. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2017, 5, 37–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eitel, J.U.; Höfle, B.; Vierling, L.A.; Abellán, A.; Asner, G.P.; Deems, J.S.; Glennie, C.L.; Joerg, P.C.; LeWinter, A.L.; Magney, T.S.; et al. Beyond 3-D: The new spectrum of lidar applications for earth and ecological sciences. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 372–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höfle, B.; Hollaus, M.; Hagenauer, J. Urban vegetation detection using radiometrically calibrated small-footprint full-waveform airborne LiDAR data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 67, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamba, P.; Acqua, F.D.; Dasarathy, B.V. Urban remote sensing using multiple data sets: Past, present, and future. Inf. Fusion 2005, 6, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Pizurica, A.; Bellens, R.; Gautama, S.; Philips, W. Generalized graph-based fusion of hyperspectral and LiDAR data using morphological features. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Liao, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Scheunders, P.; Philips, W. Fusion of Hyperspectral and LiDAR data for Classification of Cloud-shadow Mixed Remote Sensing Scene. IEEE J-STARS 2017, 10, 53768–3781. [Google Scholar]
- Ghamisi, P.; Höfle, B.; Zhu, X.X. Hyperspectral and LiDAR Data Fusion Using Extinction Profiles and Deep Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE J-STARS 2017, 10, 3011–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasti, B.; Ghamisi, P.; Plaza, J.; Plaza, A. Fusion of Hyperspectral and LiDAR Data Using Sparse and Low-Rank Component Analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 6354–6365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Ghamisi, P.; Jia, X.; Gu, Y. Deep Fusion of Remote Sensing Data for Accurate Classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 53–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasti, B.; Ghamisi, P.; Gloaguen, R. Hyperspectral and LiDAR Fusion Using Extinction Profiles and Total Variation Component Analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 3997–4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ghamisi, P.; Li, W. Classification of hyperspectral and LIDAR data using extinction profiles with feature fusion. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 8, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamisi, P.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Phinn, S. Land-cover classification using both hyperspectral and LiDAR data. Int. J. Image Data Fusion 2015, 6, 189–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamisi, P.; Cavallaro, G.; Wu, D.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Plaza, A. Integration of LiDAR and Hyperspectral Data for Land-cover Classification: A Case Study. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1707.02642. [Google Scholar]
- Pesaresi, M.; Benediktsoon, J.A. A new approach for the morphological segmentation of high-resolution satellite imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 39, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamisi, P.; Mura, M.D.; Benediktsson, J.A. A Survey on Spectral Spatial Classification Techniques Based on Attribute Profiles. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 2335–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mura, M.D.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Waske, B.; Bruzzone, L. Morphological Attribute Profiles for the Analysis of Very High Resolution Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 3747–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L. Supervised Segmentation of Very High Resolution Images by the Use of Extended Morphological Attribute Profiles and a Sparse Transform. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 1409–1413. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Marpu, P.R.; Plaza, A.; Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Benediktsson, J.A. Genralized Composite Kernel Framework For Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 4816–4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mura, M.D.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Bruzzone, L. Modeling structural information for building extraction with morphological attribute filters. In Image and Signal Processing for Remote Sensing XV; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2009; Volume 7477. [Google Scholar]
- Khodadadzadeh, M.; Li, J.; Prasad, S.; Plaza, A. Fusion of Hyperspectral and LiDAR Remote Sensing Data Using Multiple Feature Learning. IEEE J-STARS 2015, 8, 2971–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamisi, P.; Souza, R.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Zhu, X.X.; Rittner, L.; Lotufo, R.A. Extinction Profiles for the Classification of Remote Sensing Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 5631–5645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamisi, P.; Souza, R.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Rittner, L.; Lotufo, R.; Zhu, X.X. Hyperspectral Data Classification Using Extended Extinction Profiles. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 1641–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamisi, P.; Höfle, B. LiDAR Data Classification Using Extinction Profiles and a Composite Kernel Support Vector Machine. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.X.; Tuia, D.; Mou, L.; Xia, G.S.; Zhang, L.; Xu, F.; Fraundorfer, F. Deep Learning in Remote Sensing: A Comprehensive Review and List of Resources. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2017, 5, 8–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mou, L.; Zhu, X.X.; Vakalopoulou, M.; Karantzalos, K.; Paragios, N.; Saux, B.L.; Moser, G.; Tuia, D. Multitemporal Very High Resolution from Space: Outcome of the 2016 IEEE GRSS Data Fusion Contes. IEEE J-STARS 2017, 10, 3435–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, L.; Ghamisi, P.; Zhu, X.X. Deep Recurrent Neural Networks for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 3639–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.; Lu, H.; Mou, L.; Li, W.; Wright, J.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Zhu, X.X.; Wang, J.; Yu, L.; et al. Long-Term Annual Mapping of Four Cities on Different Continents by Applying a Deep Information Learning Method to Landsat Data. IEEE J-STARS 2018, 10, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, H.; Li, C.; Jia, X.; Ghamisi, P. Deep Feature Extraction and Classification of Hyperspectral Images Based on Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 6232–6250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, L.; Bruzzone, L.; Zhu, X.X. Learning Spectral-Spatial-Temporal Features via a Recurrent Convolutional Neural Network for Change Detection in Multispectral Imagery. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1803.02642. [Google Scholar]
- Ghamisi, P.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, X.X. A Self-Improving Convolution Neural Network for the Classification of Hyperspectral Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 1537–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, L.H.; Schmitt, M.; Mou, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, X.X. Identifying Corresponding Patches in SAR and Optical Images With a Pseudo-Siamese CNN. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 784–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, L.; Chen, Y.; Ghamisi, P.; Benediktsson, J.A. Generative Adversarial Networks for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 5046–5063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, L.; Ghamisi, P.; Zhu, X.X. Unsupervised Spectral-Spatial Feature Learning via Deep Residual Conv-Deconv Network for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Peng, J.; Chen, C.L.P. Extreme Learning Machine With Composite Kernels for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE J-STARS 2015, 8, 2351–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamisi, P.; Plaza, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Plaza, A.J. Advanced Spectral Classifiers for Hyperspectral Images: A review. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2017, 5, 8–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vachier, C. Extinction values: A new measurement of persistence. In Proceedings of the 1995 IEEE Workshop on Nonlinear Signal and Image Processing, Halkidiki, Greece, 20–22 June 1995; pp. 245–257. [Google Scholar]
- Soille, P. Morphological Image Analysis: Principles and Applications, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y. The Handbook of Brain Theory and Neural Networks; Chapter Convolutional Networks for Images, Speech, and Time Series; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1998; pp. 255–258. [Google Scholar]
- Lecun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, C.; Zhao, C.; Yang, Y.; Fermüller, C.; Aloimonos, Y. LightNet: A Versatile, Standalone Matlab-based Environment for Deep Learning. arXiv, 2016; arXiv:1605.02766. [Google Scholar]
- Volpi, M.; Tuia, D. Dense Semantic Labeling of Subdecimeter Resolution Images With Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 881–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scherer, D.; Müller, A.; Behnke, S. Evaluation of Pooling Operations in Convolutional Architectures for Object Recognition. In Artificial Neural Networks–ICANN 2010; Diamantaras, K., Duch, W., Iliadis, L.S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 92–101. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, G.F. On the mean accuracy of statistical pattern recognizers. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1968, 14, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Chanussot, J.; Jia, X.; Benediktsson, J.A. Multiple Kernel Learning for Hyperspectral Image Classification: A Review. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 6547–6565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Wang, C.; You, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y. Representative Multiple Kernel Learning for Classification in Hyperspectral Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 2852–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camps-Valls, G.; Gomez-Chova, L.; Munoz, J.; Vila-Frances, J.; Calpe-Maravilla, J. Composite Kernels for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2005, 3, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camps-Valls, G.; Bruzzone, L. Kernel-based methods for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Huang, G.B.; Zhang, J.; Yin, J. Multiple kernel extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing 2015, 149, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debes, C.; Merentitis, A.; Heremans, R.; Hahn, J.; Frangiadakis, N.; van Kasteren, T.; Liao, W.; Bellens, R.; Pizurica, A.; Gautama, S.; et al. Hyperspectral and LiDAR Data Fusion: Outcome of the 2013 GRSS Data Fusion Contest. IEEE J-STARS 2014, 7, 2405–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.; Hinton, G.E. Rectified Linear Units Improve Restricted Boltzmann Machines. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML’10), Haifa, Israel, 21–24 June 2010; pp. 807–814. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch Normalization: Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing Internal Covariate Shift. arXiv, 2015; arXiv:1502.03167. [Google Scholar]



| HSI | LiDAR | Proposed Framework | Deep Fusion [10] | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classes | Train/Test | SVM | ELM | SVM | ELM | SVM | ELM | SVM | ELM | SVM | ELM | SVM | ELM | Softmax |
| Grass Healthy | 198/1053 | 84.14 | 90.98 | 38.89 | 6.36 | 76.45 | 72.27 | 58.88 | 62.30 | 78.16 | 80.82 | 76.92 | 76.92 | 81.58 |
| Grass Stressed | 190/1064 | 95.68 | 97.65 | 42.27 | 34.59 | 83.65 | 79.42 | 57.71 | 42.58 | 80.73 | 84.77 | 96.33 | 98.40 | 92.11 |
| Grass Synthetic | 192/505 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 98.61 | 71.09 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 99.01 | 85.54 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 89.50 | 90.50 | 93.07 |
| Tree | 188/1056 | 98.96 | 94.70 | 61.84 | 29.64 | 81.82 | 81.91 | 68.94 | 62.97 | 96.02 | 88.35 | 93.75 | 96.12 | 94.22 |
| Soil | 186/1056 | 97.82 | 99.62 | 61.84 | 10.32 | 96.02 | 95.36 | 80.87 | 76.42 | 96.40 | 98.67 | 95.64 | 99.62 | 98.77 |
| Water | 182/143 | 95.10 | 88.81 | 74.83 | 66.43 | 95.80 | 92.31 | 76.92 | 76.92 | 95.80 | 95.80 | 95.10 | 95.80 | 97.90 |
| Residential | 196/1072 | 78.82 | 82.92 | 44.31 | 48.51 | 75.75 | 65.11 | 80.41 | 64.83 | 72.48 | 74.44 | 92.26 | 95.15 | 89.27 |
| Commercial | 191/1053 | 44.54 | 77.02 | 44.54 | 60.87 | 85.66 | 46.44 | 72.65 | 70.56 | 91.45 | 78.16 | 93.35 | 94.59 | 91.17 |
| Road | 193/1059 | 74.88 | 65.16 | 55.34 | 40.60 | 65.82 | 68.18 | 57.41 | 57.79 | 68.78 | 69.08 | 87.25 | 93.20 | 87.63 |
| Highway | 191/1036 | 79.83 | 77.61 | 9.07 | 36.39 | 75.77 | 66.22 | 67.95 | 64.00 | 73.65 | 74.13 | 85.04 | 88.42 | 90.06 |
| Railway | 181/1054 | 89.28 | 72.87 | 32.26 | 0 | 87.86 | 95.16 | 99.72 | 99.53 | 87.86 | 92.12 | 95.35 | 93.83 | 96.49 |
| Parking Lot 1 | 192/1041 | 63.11 | 41.02 | 33.62 | 0 | 79.54 | 75.31 | 74.26 | 77.23 | 84.05 | 82.90 | 92.03 | 92.41 | 84.63 |
| Parking Lot 2 | 184/285 | 75.79 | 68.42 | 34.04 | 39.30 | 81.40 | 75.09 | 55.09 | 65.61 | 77.89 | 78.95 | 79.65 | 84.56 | 81.75 |
| Tennis Court | 181/247 | 100.00 | 99.19 | 26.32 | 95.95 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Running Track | 187/473 | 98.10 | 98.73 | 32.56 | 95.56 | 99.37 | 98.73 | 73.78 | 86.89 | 99.15 | 98.73 | 77.59 | 87.74 | 86.26 |
| OA(%) | 82.66 | 81.80 | 44.80 | 33.45 | 82.77 | 77.27 | 73.76 | 69.71 | 84.75 | 84.23 | 90.22 | 92.57 | 90.60 | |
| AA(%) | 79.75 | 77.06 | 43.52 | 39.73 | 80.19 | 80.77 | 70.56 | 72.68 | 81.47 | 86.53 | 84.36 | 92.48 | 85.31 | |
| K | 0.8123 | 0.7939 | 0.4019 | 0.3826 | 0.8133 | 0.7939 | 0.7156 | 0.7073 | 0.8347 | 0.8557 | 0.8938 | 0.9193 | 0.8981 | |
| HSI | LiDAR | Proposed Framework | Deep Fusion [10] | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classes | Train/Test | SVM | ELM | SVM | ELM | SVM | ELM | SVM | ELM | SVM | ELM | SVM | ELM | Softmax |
| Apple trees | 129/3905 | 91.52 | 89.55 | 41.25 | 0 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 99.05 | 95.29 | 98.80 | 99.80 | 99.59 | 94.11 | 99.28 |
| Buildings | 125/2778 | 84.67 | 78.04 | 84.88 | 65.08 | 98.78 | 99.42 | 96.22 | 73.72 | 99.32 | 99.60 | 99.89 | 100.00 | 90.03 |
| Ground | 105/374 | 96.52 | 94.12 | 37.70 | 0 | 96.52 | 92.25 | 58.29 | 61.50 | 32.62 | 69.79 | 71.93 | 73.80 | 54.01 |
| Wood | 154/8969 | 96.43 | 86.41 | 93.77 | 87.85 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 97.38 | 95.55 | 99.87 | 100.00 | 99.97 | 100.00 | 99.72 |
| Vineyard | 184/10317 | 78.32 | 56.50 | 74.07 | 97.96 | 99.64 | 99.12 | 61.11 | 67.12 | 99.88 | 95.95 | 99.62 | 99.93 | 99.34 |
| Roads | 122/3252 | 67.92 | 74.02 | 66.48 | 0 | 70.97 | 74.51 | 70.02 | 69.79 | 84.93 | 88.96 | 90.83 | 85.29 | 97.80 |
| OA(%) | 85.35 | 74.35 | 75.49 | 67.34 | 96.70 | 96.89 | 81.43 | 80.37 | 97.27 | 97.18 | 97.91 | 97.33 | 97.83 | |
| AA(%) | 73.63 | 79.77 | 56.88 | 35.84 | 80.84 | 94.22 | 68.87 | 67.16 | 73.63 | 92.66 | 79.47 | 92.19 | 77.17 | |
| K | 0.8067 | 0.7573 | 0.6740 | 0.3018 | 0.9558 | 0.9306 | 0.7646 | 0.7259 | 0.9634 | 0.9119 | 0.9729 | 0.9063 | 0.9710 | |
| Method in [8] | Method in [12] | Method in [9] | Method in [10] | Method in [11] | Proposed | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSI + LiDAR | GBFF | EPs Fusion | SLRCA | Deep Fusion | OTVCA | ||
| OA(%) | 83.33 | 91.02 | 89.93 | 91.30 | 91.32 | 92.45 | 92.57 |
| AA(%) | 82.21 | 91.82 | 91.02 | 91.95 | 91.96 | 92.69 | 92.48 |
| K | 0.8188 | 0.9033 | 0.8910 | 0.9056 | 0.9057 | 0.9181 | 0.9193 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Ghamisi, P.; Soergel, U.; Zhu, X.X. Hyperspectral and LiDAR Fusion Using Deep Three-Stream Convolutional Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10101649
Li H, Ghamisi P, Soergel U, Zhu XX. Hyperspectral and LiDAR Fusion Using Deep Three-Stream Convolutional Neural Networks. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(10):1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10101649
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hao, Pedram Ghamisi, Uwe Soergel, and Xiao Xiang Zhu. 2018. "Hyperspectral and LiDAR Fusion Using Deep Three-Stream Convolutional Neural Networks" Remote Sensing 10, no. 10: 1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10101649
APA StyleLi, H., Ghamisi, P., Soergel, U., & Zhu, X. X. (2018). Hyperspectral and LiDAR Fusion Using Deep Three-Stream Convolutional Neural Networks. Remote Sensing, 10(10), 1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10101649