Abstract
Methods for accurately measuring biophysical parameters are a key component for quantitative evaluation regarding to various forest applications. Conventional in situ measurements of these parameters take time and expense, encountering difficultness at locations with heterogeneous microtopography. To obtain precise biophysical data in such situations, we deployed an unmanned aerial system (UAS) multirotor drone in a cypress forest in a mountainous area of Japan. The structure from motion (SfM) method was used to construct a three-dimensional (3D) model of the forest (tree) structures from aerial photos. Tree height was estimated from the 3D model and compared to in situ ground data. We also analyzed the relationships between a biophysical parameter, diameter at breast height (DBH), of individual trees with canopy width and area measured from orthorectified images. Despite the constraints of ground exposure in a highly dense forest area, tree height was estimated at an accuracy of root mean square error = 1.712 m for observed tree heights ranging from 16 to 24 m. DBH was highly correlated with canopy width (R2 = 0.7786) and canopy area (R2 = 0.7923), where DBH ranged from 11 to 58 cm. The results of estimating forest parameters indicate that drone-based remote-sensing methods can be utilized to accurately analyze the spatial extent of forest structures.
Keywords:
UAV; UAS; drone; structure from motion; forest inventory; biophysical parameter; aerial survey 1. Introduction
Collecting accurate forest inventory information faster and more efficiently is one of the concerns and challenges of forest management [1]. There is a high demand for improved measurement methods for use in such programs as but not limited to Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation (REDD+; [2]), forests as carbon sinks for national CO2 reduction plan [3] and for meeting the challenges of modeling future climate scenarios by integrating terrestrial biogeochemical feedback [4]. By collecting accurate forest data, we can better estimate and interpret forest dimensions to evaluate various forest ecosystem services, such as biodiversity [5], carbon stocks and CO2 uptake [6,7], and aboveground biomass (AGB; [8]).
Conventional methods of collecting tree biophysical data rely on equipment that measures the sizes and heights of trees, such as measuring tapes and calipers [9]. Calipers, a device used to measure the distance between two opposite sides, can easily measure the diameter or cross-section of a tree trunk [10]. With advancements in equipment, modern methods of collecting forest inventory data include laser rangefinders [11], terrestrial light detection and ranging (LiDAR; [12,13]), and even smartphone applications [14], which improve efficiency and data quality. Although different methods can be used to collect forest data depending on various technologies and their suitability, the methods must always be used on the ground. This may be more efficient than using other conventional methods, but if the study area is located in an unpopulated or remote area, or in an extremely rugged terrain (e.g., in the mountains), difficulties arise and worker safety becomes a matter of great concern. We also have to be mindful of sampling designs, which depend on the available time and budget [9]. Given the difficulty of collecting detailed information using conventional methods [15], remote-sensing methods have been studied that involve multiple platforms (aircraft, satellites) and sensors (multispectral, radar, laser; [1,7,16,17,18]). Aerial methods such as airborne LiDAR [16,18] or photogrammetry [18] have been considered to collect more data in wider regions. These methods could be alternatives to continuous collection of forest data, which can also be used for monitoring purposes. The use of satellite images is still a challenging task. A number of applications can be used to collect forest biophysical parameters through spatial observations [19]; however, optical data can be limited in spatial/temporal resolution, and even with finer resolution data cloud cover makes proper estimation difficult [20]. Although synthetic aperture radar (SAR) is an alternative, it is still an undergoing task for the precise estimation, which is extremely site dependent [17,21,22,23,24,25].
Within this few years, utilizing the unmanned aerial system (UAS) is an emerging trend for collecting various spatial information [26]. Recent studies have reported the use of UAS in various analyses, including forestry applications [27,28]. Collecting aerial photos by UAS and processing them with the structure from motion (SfM) method is one of the major new approaches to analyzing forest structures [29,30]. SfM is a photogrammetric method of constructing a three-dimensional (3D) model based on multiple two-dimensional images (e.g., photos; [31]), which is receiving much attention in the remote sensing field with the use of airborne platforms. The advantage of UAS-borne data is that high-resolution images can be generated that clearly detect tree canopies [32]. Moreover, this technique can be used to construct 3D models of an area through photogrammetry. This means that there are possibilities for extracting forest inventory data from UAS-sensed information [18,29,30,32]. Digital surface models (DSMs) and ultra-fine resolution orthophotos can be directly utilized to estimate tree heights and canopy size. Usually, these data are difficult to extract correctly because the height of a tree depends on site conditions (higher/lower stem density; [33]), decreased interpretation of surface area at dense forest sites [30], or even exposure to light and wind [34,35]. In addition, directly estimating parameters in lower layers, such as DBH (Diameter at Breast Height), from DSM or orthophotos is also difficult because of tree canopies, particularly in dense forest environments. Therefore, extracting DBH information related to tree height remains challenging. In the various reports, utilizing airborne-based investigation methods, including UAS observations, relationships between canopy width or canopy area and DBH have rarely been reported. Results shown by Jucker et al. [36] present the relation of tree height and crown diameter with the stem diameter, which is utilizing airborne LiDAR information. From such works, we can determine that relations between the two parameters can be considered with relation, yet direct measurement of only canopy information and DBH is unclear with the use of photogrammetry. This is particularly true in the case of highly dense forests in Japan. Thus, our objective was to assess the use of UAS photogrammetry for estimating forest parameters, focusing on estimating DBH by canopy structure using both an ultra-fine resolution orthophoto and a 3D model constructed using the SfM method. We were interested in determining whether the method is applicable in mountainous areas with heterogeneous microtopography. We further investigated parameter settings for constructing the best fitting 3D model for estimating tree height.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
The study site was located at Otsu City, Shiga Prefecture, Japan. The Kiryu Hydrological Experimental Watershed (KEW), located between approximately 34.963°N, 135.9925°E, and 34.9667°N, 135.9955°E, is managed by the Department of Agriculture, Kyoto University, which monitors various environmental dynamics related to forestry and hydrology (http://www.bluemoon.kais.kyoto-u.ac.jp/kiryu-e/contents.html). KEW is primarily covered by evergreen conifer Japanese cypress (Chamaecyparis obtusa (Sieb. et Zucc.)) trees, most of which were planted in 1959. The forest also contains sparsely distributed Japanese red pine (Pinus densiflora) and broadleaf trees. Japanese cypress plantations are the second most common type of planted forests in Japan, accounting for almost 25% of the total area of planted forests and 10% of the entire forested area of Japan. The site was an ideal area for seeking out the aforementioned cypress trees to test the method and its potential applicability to other regions. The area has an average annual precipitation of 1654 mm and average annual temperature of 14.0 °C (1994–present). The elevation ranges from 190 to 255 m above mean sea level. A flux tower for meteorological observation was built at a southern location on the site to observe the airflow dynamics of the forest and atmospheric interactions. Figure 1 shows the overall area of the study site and its heterogeneous landscape.
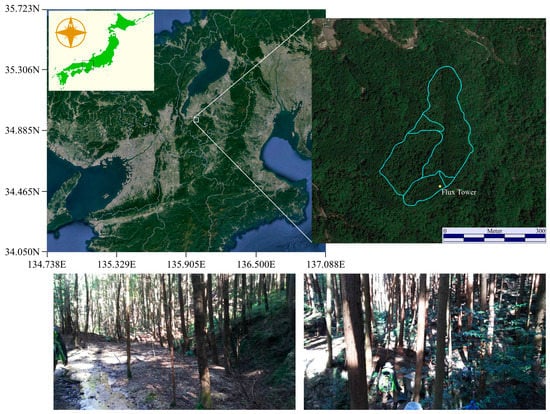
Figure 1.
Location of the study area, the Kiryu Experimental Watershed (KEW) (Shiga Prefecture). The outer border indicated in the enlarged image (right) represents the watershed, whereas the inner lines indicate sub-watersheds. The bottom images represent the general landscape of the KEW. The map images are from Google Earth (Pro ver. 7.3.0.3832, Google Inc., Mountain View, CA, USA) [37].
2.2. Photogrammetry 3D Model Construction
2.2.1. Collection and Processing of Aerial Photos
On 9 May 2017, a flight was conducted at KEW to collect aerial photos of the region. A DJI Phantom 4 Pro multicopter UAS (DJI, Shenzhen, China) was utilized to collect observational data. The multicopter took off from the top of the flux tower (29 m) and ascended to an altitude of approximately 110 m (an additional 80 m from the tower). This was to ensure that no objects were in the way during flight. DJI Ground Station Pro was used to perform the automatic flight and to take photos of the area. The camera was set to face vertically toward the surface, and the forward and side overlaps were both set to 85% for the photo shoots.
The collected photos were processed with the 3D modeling software Agisoft PhotoScan Pro version 1.3.1 (Agisoft LLC, St. Petersburg, Russia). This software performs automatic photogrammetric processing of images that can be used to generate 3D data such as DSMs and can also process and compute mosaicked orthorectified imagery. The SfM method works by extracting features (points) within the images and matching those features to pair the images; then, the camera position is estimated and the object is reconstructed from the features and the camera position. Further details can be found in Yi et al. [38]. Table 1 shows the overall process and parameter settings for generating point clouds and the orthophoto of the test site. Before generating a dense point cloud, we manually deleted several points that were interpreted as inaccurate projections. To collect information on the height of the trees, we also generated a digital terrain model (DTM) of the area by extracting the lowest points from the dense data point cloud and interpolating them using the inverse distance weighting (IDW) method to generate a model representing the ground surface. Several parameter settings were used to select ground points to generate and compare multiple DTMs, in order to determine which one best represented the surface information. Three parameters constituted the main criteria for extracting ground points from the point cloud information: cell size (m), maximum angle (degrees), and maximum distance (m). Further explanations are given in the Discussion section. A total of 23 models was produced with different parameter settings: DTMcell10 (cell:10, angle:20, distance:0.5), DTMcell20 (cell:20, angle:20, distance:0.5), DTMcell30 (cell:30, angle:20, distance:0.5), DTMcell40 (cell:40, angle:20, distance:0.5), DTMcell50 (cell:50, angle:20, distance:0.5), DTMcell60 (cell:60, angle:20, distance:0.5), DTMcell70 (cell:70, angle:20, distance:0.5), DTMcell80 (cell:80, angle:20, distance:0.5), DTMcell90(cell:90, angle:20, distance:0.5) DTMcell100 (cell:100, angle:20, distance:0.5), DTMd025 (cell:60, angle:20, distance:0.25), DTMd1(cell:60, angle:20, distance:1), DTMd2(cell:60, angle:20, distance:2), DTMd4(cell:60, angle:20, distance:4), DTMd8(cell:60, angle:20, distance:8), DTMd16(cell:60, angle:20, distance:16), DTMa1(cell:60, angle:1, distance:1.3), DTMa5(cell:60, angle:5, distance:1.3), DTMa10(cell:60, angle:10, distance:1.3), DTMa15(cell:60, angle:15, distance:1.3), DTMa20(cell:60, angle:20, distance:1.3), DTMa25(cell:60, angle:25, distance:1.3), and DTMa30(cell:60, angle:30, distance:1.3). Unfortunately, the area was covered by a very dense quantity of trees, which made it difficult to visualize the ground surface. Moreover, because of this dense canopy and the surrounding terrain, it was difficult to receive accurate GPS information on the site; therefore, we did not collect additional ground control points (GCP) for calibrating the model during the SfM procedure, and only the tagged GPS information was used. The generated resolution of the orthophoto and terrain models varied; therefore, the terrain model was resampled to match the orthophoto using the cubic convolution method. Further analyses were carried out using the processed data.

Table 1.
Parameter settings for the workflow for generating 3D models (PhotoScan Pro).
2.2.2. Forest Inventory Ground Survey
A ground survey was carried out at KEW to collect actual ground information on the biophysical parameters of individual trees. A measuring tape was used to collect the DBH information of the sampled trees, and a laser rangefinder (Impulse 200, Laser Technology, Inc., Centennial, CO, USA) was used to measure tree height. A total of 51 individual samples were collected from the cypress trees in the vicinity of the flux tower so that they could be clearly recognized from the aerial images; however, the trees were randomly chosen to collect various sizes and heights. The distances and the direction from the tower were recorded for each of the sampled trees, and their locations were later matched to the aerial images. This was done because the density of the forest environment made it difficult to receive sufficient GPS signal to identify the locations from geographical coordinates.
2.2.3. Estimating and Analyzing Tree Parameters
Using the processed data and images, which were generated through the SfM method, we compared the tree parameters that could be extracted from the processed data with the actual ground data collected from the ground survey. The following equation was used to generate a canopy height model (CHM; [18]) to represent potential tree height:
CHM = DSM − DTM.
Then, we compared the height from the CHM to the actual ground data to assess the accuracy of the estimate. As previously mentioned, we generated multiple DTMs based on different parameters. We analyzed and computed different CHMs computed with different DTMs by assessing the root mean square error (RMSE) of the estimated tree heights.
As for the DBH information, we performed regression analyses for two parameters and the observed DBH data. The first parameter was the canopy width, which was easily measured using Quantum GIS (using a measuring tool) (ver. 2.18.13. QGIS Development Team, Open Source Geospatial Foundation) on the generated ultra-fine orthophoto. The width was measured twice per tree in both horizontal and vertical length, and the average was computed. We computed the second parameter, the canopy area of the individual trees, by constructing individual polygons covering the canopy area and calculating the area covered by each polygon. The investigation was conducted to see how well the canopy structure could predict the DBH. For quantifying the statistical significance of the relationships, Pearson’s correlation analysis was performed to compute the level of significance between the two variables (p-value).
2.3. Automatic Canopy Extraction
In reality, to obtain a full visual of the whole forested area, it is not a smart way to construct each polygon manually for individual trees. We have tested to see if automated extraction of canopy area is possible using the set of UAS data. Here, we implemented the watershed segmentation method found in the SAGA (System for Automated Geoscientific Analysis) GIS platform ver. 5.0.0 [39]. The method works as if the canopy shape tends to form like watersheds in the DSM/CHM data with the z-axis reversed. We have used the DSM for the test. First, for the original image results with small artifacts such as within the border of the canopy area, in order to smooth the data, a Gaussian filter was performed with a standard deviation 95%, circle kernel type and radius of 20. On the filtered DSM, a classical watershed algorithm was implemented and the segmented areas were computed. In SAGA, there are two parameters that need to be set. One is the method option, to either choose local minima or maxima. This determines the starting point of the flooding (filling) from the bottom of the valley like the normal watersheds (in our case, the lowest point of the canopy) or from the top of the slope (in our case, the top of the canopy) for local minima and maxima, respectively. We chose the local maxima option. The second is the merging option for the segments; however, we have left this option for “do not join”. Other options are left as default. The result is checked through visual interpretation on the ortho image.
3. Results
3.1. Orthophoto, DSM, DTM and CHM
The orthophoto was generated from the 696 photos collected in the aerial survey. The resolutions of the orthophoto and the DSM (DTM) were approximately 2.85 and 5.7 cm, respectively, and we resampled the terrain models to 2.85 cm using the cubic convolution method. The coverage of the area was 26.8 ha, and the total error was 5.56 m (x error: 3.07 m, y error: 0.53 m, z error: 4.61 m, xy error: 3.12 m). Although a large area was generated (covering the whole KEW), our individually sampled trees were from a relatively smaller area (0.72 ha); therefore, we extracted the areas of interest for further analysis. By comparing the analysis of multiple CHM data with the ground data, we found that the parameters that best described the ground surface information, the DTM generated from the classified point clouds, were a cell size of 60 m, a maximum angle of 25° and a maximum distance of 1.3 m (DTMa25). In Figure 2, the trends in RMSE when we compared the different parameter settings for generating DTMs by extracting the ground points are shown for each parameter. We used these DTM data in further analyses computing CHM. Graphical images of the orthophoto, DSM, DTM, and CHM are shown in Figure 3.
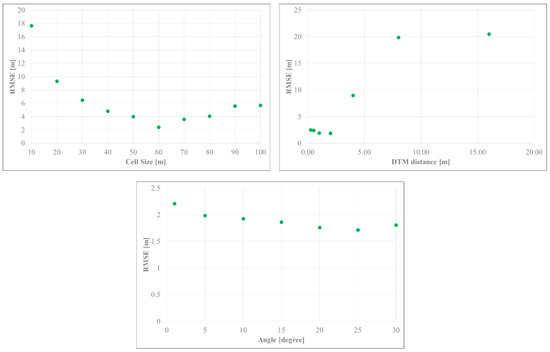
Figure 2.
Root mean square error (RMSE) of tree heights in terrain models generated using various parameter settings to extract the ground points.
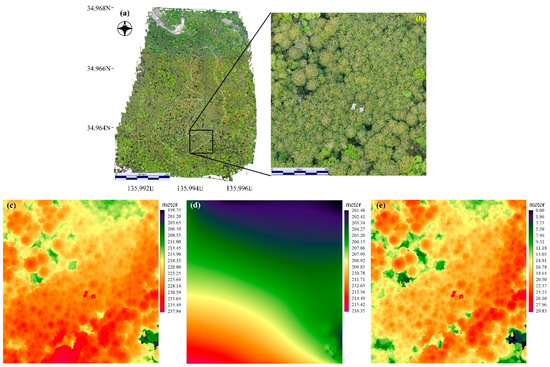
Figure 3.
Graphical images of the (a) orthophoto; (b) area of focus within the study site; (c) digital surface model; (d) digital terrain model; and (e) canopy height model.
3.2. Tree Height, DBH Analysis
Using the CHM data, we extracted the maximum heights of the individual trees (from constructed polygon data) and compared them with the actual ground data. Figure 4 shows the relationship between the estimated height and the reference height. Given the highly dense forested area, shorter trees were not considered because they were impossible to detect from the aerial view. Therefore, mostly taller trees were measured and used as samples, with a resultant height range of 16 to 24 m. The RMSE of the estimate was 1.712 m (R2 = 0.2076).
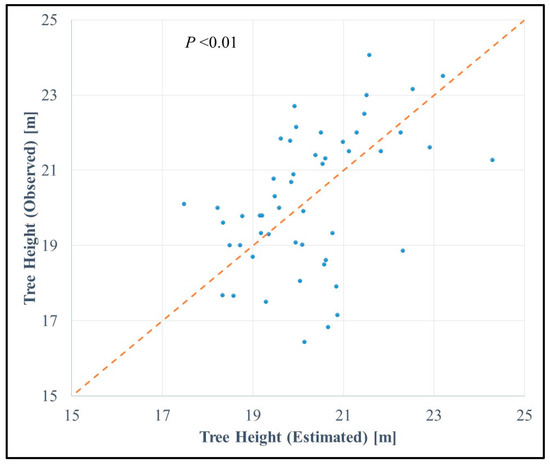
Figure 4.
The relationship between estimated and observed tree heights. The dotted line in the center indicates 1:1. The Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) was calculated as 1.712 m (R2 = 0.2076, linear trend).
Figure 5a,b show the relationship between canopy width and canopy area and DBH. There was an obvious strong linear relationship between canopy width and DBH (R2 = 0.7786). As mentioned previously, the relationship between height and DBH can be difficult to observe because height can vary depending on various environmental conditions, in particular the heterogeneity of the microtopography; therefore, we estimated DBH from canopy information instead. In the case of the Japanese cypress trees, canopy width was highly correlated with DBH; moreover, the canopy area also showed a strong relationship with DBH (R2 = 0.7923). For the DBH–canopy size relationship, the best fitting trend line was a second-order polynomial function. Along with the comparison, we found that extracting DBH from canopy information gave better results than using tree height (Figure 6), as we observed some outliers.
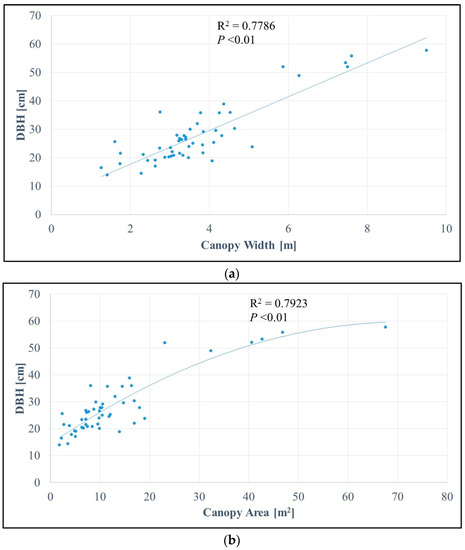
Figure 5.
Analysis of the relationships between observed Diameter at Breast Height (DBH) and (a) canopy width (m) and (b) canopy area (m2). The former shows a linear relationship of R2 = 0.7786, and the latter shows a second-order polynomial regression line as the reference (R2 = 0.7923). Pearson’s correlation analysis indicates the probability value (p-value) of less than 0.01.
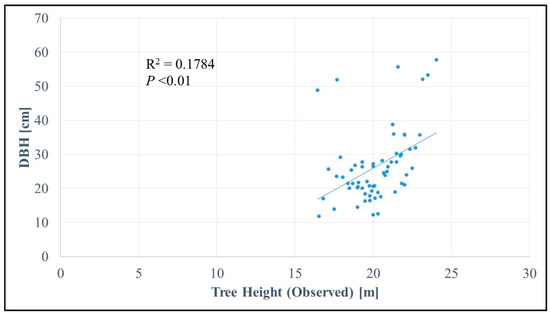
Figure 6.
Analysis of the relationship between observed tree height (m) and Diameter at Breast Height (DBH) (cm). At larger DBH values, observed tree height does not correspond to the growing trend (outliers).
3.3. Canopy Segmentation
Automated method for canopy area extraction was tested. Figure 7 shows the visual imagery of the segment borders (yellow lines) generated from the watershed method and it is overlaid on the ortho image. As an overall of the interpretation, small canopy and large canopy both can be extracted using such methods. Although we can see slight over segmentation (segment borders slightly larger) or under segmentation (segments not merged within one canopy) within the scene, it can be said that it is able to extract the canopy area even in such a highly dense forested area. To improve the automated method, developing a better 3D model of the area could enhance the result. Here, the result of the possibilities of automated extraction is shown; however, we will not go into detail, since our primary objective is not to seek methods for obtaining best results in the segmentation process. This should become our next task for collecting wide area inventory data.
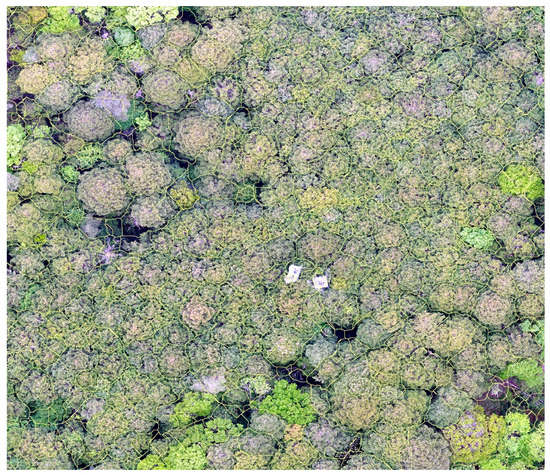

Figure 7.
Results of the watershed segmentation method for delineating the individual canopy area. Although slight differences in segments can be seen, overall, it can perform extraction rather well even in the highly dense forested areas.
4. Discussion
4.1. DTM Generation
A critical point when estimating tree height from 3D models constructed with the SfM method is to generate DTM data of reliable quality. By subtracting the pure terrain information from the DSM, we obtained information on the height of surface objects. We found several other studies that used similar methods to estimate tree heights (extracting DSM by DTM). Ota et al. [18] modeled the aboveground biomass (AGB) by estimating tree heights from aerial photos compared to LiDAR in tropical forests in Cambodia. They computed the DTM by extracting the ground points using local minima of 10 m ×10 m. This was compared for both SfM-derived and LiDAR-derived points, and both methods resulted in a good final AGB when the CHM was computed using the DTM from LiDAR points. A large variation in AGB resulted when the terrain data were extracted from SfM point cloud data, and it is expected that 10 m × 10 m local minima cannot delineate the ground information but instead collect false points from nonground areas. Wallace et al. [29] used the Lasground tool in Lastools to compute DTM data; this tool uses a similar procedure to that provided in Photoscan, in which initial points are selected to generate a triangular irregular network (TIN) surface, and then adjustments are made for additional points with set parameters. Their estimated tree heights were approximately RMSE (R2) 0.92 m (0.84) and 1.30 m (0.68) for LiDAR-based and SfM-based methods, respectively. Their study area was a sclerophyll eucalyptus forest in Australia that seemed to have had a relatively open canopy; therefore, it could be easily estimated even using the SfM method.
PhotoScan provides an automated procedure for extracting the lowest elevation point from the point cloud data generated, and interpolation is performed to develop a spatial distribution of the terrain data. We proceeded to generate DTM using this option. The difficulty of this method is setting the parameters to determine which points to extract as the ground points. Three parameters are provided: cell size, maximum angle, and maximum distance. Although some other studies have used the same options to generate DTMs [32], the optimal parameters for extraction are usually not described. Here, we further discuss the parameter settings for generating the best fitting models.
The cell size parameter operates within the range of a given cell size (in meters), selecting the lowest points determined as ground points, and then triangulates the selected points to generate an initial approximation of the terrain model [40]. Through multiple iterations, together with other parameter settings, this generates more points and eventually classifies all of the points. The optimal size for this parameter in our study was 60 m. This parameter may change based on the nature of the environment (depending on the site). When the cell size decreased or increased from this value, it resulted in a higher RMSE for tree height estimates (Figure 3). Decreasing the cell size led to selecting the lowest points from the canopy area, whereas increasing the cell size led to errors in selecting the lowest points within that cell area. It would be inappropriate in a region expected to have highly variable topography (it excludes the true ground points of certain areas). This was evident when the DSM–DTM difference was 0 m when the cell size was small, and the difference between the estimated tree height and observed tree height was larger when the cell size was increased (overestimation).
The maximum distance and the maximum angle help determine how to add the next selected ground points to the initial DTM. In our case, for the maximum distance parameter, lower RMSE was observed at distance settings of around 1–2 m, and RMSE increased dramatically when the distance settings were increased. Increasing the distance parameter gave falsely selected points that were similar in position to the DSM (on tree canopy), leading to an estimated tree height of 0 m (the difference between DSM and DTM becomes null). This was particularly notable when the distance value was set to 8 m. In contrast, when the value was set too low, it did not delineate the terrain characteristics of KEW, resulting in a rougher estimation of tree height. If the area of interest is rather flat in terms of topography and does not require consideration of a variety of elevations and slopes, lower distance and angle values may be preferred [41]. However, in the case of areas with rugged terrain, such as our study site (shown in Figure 1), adjusting parameters to higher distance and angle values may be key to generating precise DTMs. In such heterogeneous topographies, LiDAR may be one option for collecting ground information. LiDAR can penetrate canopy layers, reaching the ground layer even in dense forests [42]; thus, the LiDAR system may be a viable alternative to help enhance the quality of the model.
4.2. Forest Parameter Extraction Using UAS
In this study, we took on the challenge of investigating DBH from information that could be observed and collected purely from UAS surveys: canopy information. This was based on several discussions that DBH growth may rely on different factors that might affect estimation from tree height information alone, and it was also borne out by our observations (Figure 6). The literature indicates that DBH height trajectory may differ depending on leaf amounts [43]. Light availability and wind play roles in tree architecture [34,35,44], as does water availability [45]. Therefore, instead of estimating DBH from tree heights, we focused on estimating it from the canopy structure. The relationship between canopy width and DBH showed an increasing linear trend, and the relationship between crown area and DBH showed an increasing polynomial-like relationship (Figure 5). Our analysis showed that canopy information is highly correlated with individual tree DBH, and this can shed light on ways to achieve better quality forest inventories even at larger spatial dimensions using UASs. Observing tree width manually for each individual tree may be difficult in large areas (particularly when stem density is high); however, using the canopy area information and computing the area with an automated method, such as watershed segmentation [46], creates possibilities for collecting inventory data through UAS remote sensing and automated extraction, as we have shown here in our work.
Looking at the canopy by area rather than width can result in better interpretations of the total structure, as tree formations may not always be circular but may be elliptical or even more complex in shape (Figure 3a). If this is the case, then more precise interpretations of forest status can be visualized spatially, leading to better estimation of parameters such as AGB. This method could shed light on relationship analyses made with satellite data (e.g., SAR data), in which it is usually mentioned that collecting actual ground data for relationship analysis with forest parameters is better at larger sample sizes (e.g., 1 ha) to avoid bias; however, collecting such data in large areas at multiple locations is a very time-consuming and difficult task [47]. For example, Němec [11] showed that forest inventory field work, covering a 200 ha area with plot dimensions of 2000 m × 1000 m, required 14 people working for 25 days using calipers and laser rangefinders to measure DBH and tree height, respectively. In our study, we spent less than 1 h collecting aerial photos of an approximately 27 ha area and took 23 h to process the whole procedure (Table 1), although this time depends on machine processing power. Where conducting flights and processing can be done alone, the potential efficiency and possibilities of utilizing UASs for surveys can be seen. Thus, if the spatial distribution of forest parameters can be produced using a UAS-based method in a continuous landscape instead of conventional ground surveys, the necessary actual ground data can be easily obtained and better matched with such resources as satellite information (because they are already in the form of grid cells). Therefore, we believe that spatial information collected from drones can become a bridge for linking point information from the ground to larger spatial expanses observed from space. For tree height information, because of the characteristics of the environment, taller trees were the primary samples. Shorter trees cannot be distinguished or interpreted in densely forested areas (because taller trees cover them); therefore, future studies should try to find areas in which shorter trees can be detected and examine whether there are differences in modeling taller and shorter trees using SfM.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we estimated tree parameters by constructing an ultra-fine orthophoto and a 3D model from a large number of photos taken with a multicopter UAS and processed them using the SfM method. The computed 3D model of the forest structure and the terrain information led to the development of a satisfactory CHM of the area indicating tree height information. This was shown to be a good estimate even in extremely dense forests in the rugged mountainous areas, and it was accurate enough to provide a rough estimate of tree heights. Individual tree canopies were easy to extract from the orthophoto because of the ultra-fine resolution of the image (2.85 cm/pixel). The canopy width and area were examined with in situ data collected in a ground survey, and a strong relationship was found between both canopy width and canopy area and DBH. These findings can enhance the collection of forest inventory observations utilizing multicopter UAS to cover a larger spatial area. Tree height and DBH information are crucial when evaluating forest status, and the drone-based method utilizing multicopter UAS aided not only in collecting forest parameters but also in performing continuous operational monitoring. We will further investigate the extraction of forest parameters in different environmental systems and examine the use of these parameters for making accurate estimates. We will also attempt relationship analysis with existing satellite information and explore the influence of the local environment (temperature, water availability, etc.) on the structural growth of trees, a potential method of estimating local site productivities.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology for Science Research (JSPS KAKENHI; grant number 15H05625), the Environment Research and Technology Development Fund (4-1506) of Environmental Restoration and Conservation Agency, Japan, and the Research Institute for Humanity and Nature (RIHN; Project No. 14200117).
Author Contributions
K.I. took the lead in designing the research, collecting, analyzing the data and writing the manuscript. T.Y. has collected and analyzed the data. M.I. and Y.K. contributed in data collection as well as revising the manuscript. All authors contributed substantially to the work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hyyppä, J.; Schardt, M.; Haggren, H.; Koch, B.; Lohr, U.; Scherrer, H.U.; Paananen, R.; Luukkonen, H.; Ziegler, M.; Hyyppä, H.; et al. HIGH-SCAN: The first European-wide attempt to derive single-tree information from laserscanner data. Photogramm. J. Finl. 2001, 17, 43–53. [Google Scholar]
- Di Lallo, G.; Mundhenk, P.; Zamora López, S.E.; Marchetti, M.; Köhl, M. REDD+: Quick Assessment of Deforestation Risk Based on Available Data. Forests 2017, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climate Focus. Forests and Land Use in the Paris Agreement. The Paris Agreement Summary. 2015. Available online: http://www.climatefocus.com/publications/cop21-paris-2015-climate-focus-overall-summary-and-client-briefs (accessed 27 November 2017).
- Arneth, A.; Harrison, S.P.; Zaehle, S.; Tsigaridis, K.; Menon, S.; Bartlein, P.J.; Feichter, J.; Korhola, A.; Kulmala, M.; O’Donnell, D.; et al. Terrestrial biogeochemical feedbacks in the climate system. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zellweger, F.; Baltensweiler, A.; Ginzler, C.; Roth, T.; Braunisch, V.; Bugmann, H.; Bollmann, K. Environmental predictors of species richness in forest landscapes: Abiotic factors versus vegetation structure. J. Biogeogr. 2016, 43, 1080–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Kim, S.; Hong, S.; Kim, K.; Kim, E.; Im, J.; Heo, J. Effects of national forest inventory plot location error on forest carbon stock estimation using k-nearest neighbor algorithm. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 81, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, K.; Tateishi, R. Estimation of CO2 Sequestration by the Forests in Japan by Discriminating Precise Tree Age Category Using Remote Sensing Techniques. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 15082–15113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, P.; Korhonen, L.; Gautam, B.; Tokola, T. Effect of field plot location on estimating tropical forest above-ground biomass in Nepal using airborne laser scanning data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 94, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhl, M.; Magnussen, S.S.; Marchetti, M. Sampling Methods, Remote Sensing and GIS Multiresource Forest Inventory; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- West, P.W. Tree and Forest Measurement, 3rd ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Němec, P. Comparison of modern forest inventory method with the common method for management of tropical rainforest in the Peruvian Amazon. J. Trop. For. Sci. 2015, 27, 80–91. [Google Scholar]
- Moskal, L.M.; Zheng, G. Retrieving Forest Inventory Variables with Terrestrial Laser Scanning (TLS) in Urban Heterogeneous Forest. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauwens, S.; Bartholomeus, H.; Calders, K.; Lejeune, P. Forest Inventory with Terrestrial LiDAR: A Comparison of Static and Hand-Held Mobile Laser Scanning. Forests 2016, 7, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vastaranta, M.; Latorre, E.G.; Luoma, V.; Saarinen, N.; Holopainen, M.; Hyyppä, J. Evaluation of a Smartphone App for Forest Sample Plot Measurements. Forests 2015, 6, 1179–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, V.R.; Cordell, K.C.; Zarnoch, S.J.; Green, G.T.; Poudyal, N.; Fox, S. The Forest Service Safety Survey: Results from an Employee-Wide Safety Attitude Survey; e-General Technical Report SRS-GTR-191; U.S. Department of Agriculture Forest Service, Southern Research Station: Asheville, NC, USA, 2014; p. 58.
- Hyyppä, J.; Yu, X.; Hyyppä, H.; Vastaranta, M.; Holopainen, M.; Kukko, A.; Kaartinen, H.; Jaakkola, A.; Vaaja, M.; Koskinen, J.; et al. Advances in Forest Inventory Using Airborne Laser Scanning. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 1190–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Widyorini, R.; Kawai, S.; Omura, Y.; Sanga-Ngoie, K.; Supriadi, B. Backscattering Characteristics of L-Band Polarimetric and Optical Satellite Imagery over Planted Acacia Forests in Sumatra, Indonesia. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2012, 6, 063525. [Google Scholar]
- Ota, T.; Ogawa, M.; Shimizu, K.; Kajisa, T.; Mizoue, N.; Yoshida, S.; Takao, G.; Hirata, Y.; Furuya, N.; Sano, T.; et al. Aboveground Biomass Estimation Using Structure from Motion Approach with Aerial Photographs in a Seasonal Tropical Forest. Forests 2015, 6, 3882–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolter, P.T.; Townsend, P.A.; Sturtevant, B.R. Estimation of forest structural parameters using 5 and 10 meter SPOT-5 satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2019–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asner, G.; Palace, M.; Keller, M.; Pereira, M.; Silva, J.; Zweede, J. Estimating canopy structure in an Amazon forest from laser rangefinder and IKONOS satellite observations. Biotropica 2002, 34, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckman, A.; Baker, J.; Honzak, M.; Lucas, R. Tropical Forest Biomass Density Estimation Using JERS-1 SAR: Seasonal Variation, Confidence Limits, and Application to Image Mosaics. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 63, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fransson, J.E.S.; Israelsson, H. Estimation of Stem Volume in Boreal Forests Using ERS-1 C- and JERS-1 L-Band SAR Data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 20, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, R.M.; Armston, J.; Fairfax, R.; Fensham, R.; Accad, A.; Carreiras, J.; Kelley, J.; Bunting, P.; Clewley, D.; Bray, S.; et al. An Evaluation of the ALOS PALSAR L-Band Backscatter—Above Ground Biomass Relationship Queensland, Australia: Impacts of Surface Moisture Condition and Vegetation Structure. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2010, 3, 576–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, O.; Aziz, H.K.; Rahman, K.A. Remotely Sensed L-Band SAR Data for Tropical Forest Biomass Estimation. J. Trop. For. Sci. 2011, 23, 318–327. [Google Scholar]
- Iizuka, K.; Tateishi, R. Simple relationship analysis between L-band backscattering intensity and the stand characteristics of sugi (Cryptomeria japonica) and hinoki (Chamaecyparis obtusa) trees. Adv. Remote Sens. 2014, 3, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.; Gaston, K.J. Lightweight unmanned aerial vehicles will revolutionize spatial ecology. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2013, 11, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodbody, T.R.H.; Coops, N.C.; Marshall, P.L.; Tompalski, P.; Crawford, P. Unmanned aerial systems for precision forest inventory purposes: A review and case study. For. Chron. 2017, 93, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, J.P.; Watt, M.S.; Pearse, G.D.; Heaphy, M.; Dungey, H.S. Assessing very high resolution UAV imagery for monitoring forest health during a simulated disease outbreak. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 131, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, L.; Lucieer, A.; Malenovský, Z.; Turner, D.; Vopěnka, P. Assessment of Forest Structure Using Two UAV Techniques: A Comparison of Airborne Laser Scanning and Structure from Motion (SfM) Point Clouds. Forests 2016, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlambo, R.; Woodhouse, I.H.; Gerard, F.; Anderson, K. Structure from Motion (SfM) Photogrammetry with Drone Data: A Low Cost Method for Monitoring Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Forests in Developing Countries. Forests 2017, 8, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wu, L.; Gerke, M.; Wang, R.; Yang, H. Skeletal camera network embedded structure-from-motion for 3D scene reconstruction from UAV images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 121, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotidis, D.; Abdollahnejad, A.; Surový, P.; Chiteculo, V. Determining tree height and crown diameter from high-resolution UAV imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 2392–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saremi, H.; Kumar, L.; Stone, C.; Melville, G.; Turner, R. Sub-Compartment Variation in Tree Height, Stem Diameter and Stocking in a Pinus radiata D. Don Plantation Examined Using Airborne LiDAR Data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 7592–7609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashima, A.; Kume, A.; Yoshida, S.; Murakami, T.; Kajisa, T.; Mizoue, N. Discontinuous DBH-height relationship of Cryptomeria japonica on Yakushima Island: Effect of frequent typhoons on the maximum height. Ecol. Res. 2009, 24, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osada, N. Crown exposure to light and tree allometry of 11 tree species in a snowy cool-temperate forest in Japan. Plant Ecol. 2012, 213, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jucker, T.; Caspersen, J.; Chave, J.; Antin, C.; Barbier, N.; Bongers, F.; Dalponte, M.; van Ewijk, K.Y.; Forrester, D.I.; Haeni, M.; et al. Allometric equations for integrating remote sensing imagery into forest monitoring programmes. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Google Earth, V 7.1.8.3036. (24 March 2016), Kiryu Experimental Site, Shiga Prefecture, Japan. 34.9643°N, 135.9939°E, Eye alt 1.08 km. Gray Buildings © 2008 ZENRIN. Available online: http://www.earth.google.com (accessed on 4 August 2017).
- Yi, G.; Jianxin, L.; Hangping, Q.; Bo, W. Survey of structure from motion. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Cloud Computing and Internet of Things, Changchun, China, 13–14 December 2014; pp. 72–76. [Google Scholar]
- Conrad, O.; Bechtel, B.; Bock, M.; Dietrich, H.; Fischer, E.; Gerlitz, L.; Wehberg, J.; Wichmann, V.; Böhner, J. System for Automated Geoscientific Analyses (SAGA) v. 2.1.4. Geosci. Model Dev. Discuss. 2015, 8, 2271–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agisoft Photoscan User Manual, 2017. Professional Edition, Version 1.3. Available online: http://www.agisoft.com/pdf/photoscan-pro_1_3_en.pdf (accessed on 31 August 2017).
- Serifoglu Yilmaz, C.; Gungor, O. Comparison of the performances of ground filtering algorithms and DTM generation from a UAV-based point cloud. Geocarto Int. 2016, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitold, V.; Keller, M.; Morton, D.C.; Cook, B.D.; Shimabukuro, Y.E. Airborne lidar-based estimates of tropical forest structure in complex terrain: Opportunities and trade-offs for REDD+. Carbon Balance Manag. 2015, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumida, A.; Miyaura, T.; Torii, H. Relationships of tree height and diameter at breast height revisited: Analyses of stem growth using 20-year data of an even-aged Chamaecyparis obtusa stand. Tree Physiol. 2013, 33, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, S.X.; Lieffers, V.J.; Reid, D.E.B.; Rudnicki, M.; Silins, U.; Jin, M. Reducing stem bending increases the height growth of tall pines. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 3175–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otieno, D.; Li, Y.; Ou, Y.; Cheng, J.; Liu, S.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Jung, E.-Y.; Zhang, D.; Tenhunen, J. Stand characteristics and water use at two elevations in a sub-tropical evergreen forest in southern China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 194, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Hu, B.; Li, J.; Noland, T. Automated delineation of individual tree crowns from LiDAR data by multi-scale analysis and segmentation. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2012, 78, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.V.; Tateishi, R.; Kondoh, A.; Sharma, R.C.; Nguyen, H.T.; To, T.T.; Minh, D.H.T. Mapping Tropical Forest Biomass by Combining ALOS-2, Landsat 8, and Field Plots Data. Land 2016, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).