Complementarity of Hydro, Photovoltaic, and Wind Power in Rio de Janeiro State
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Rio de Janeiro’s Context
3. Power Modelling
3.1. Wind Energy
3.2. Hydro Energy
3.3. Photovoltaic Energy
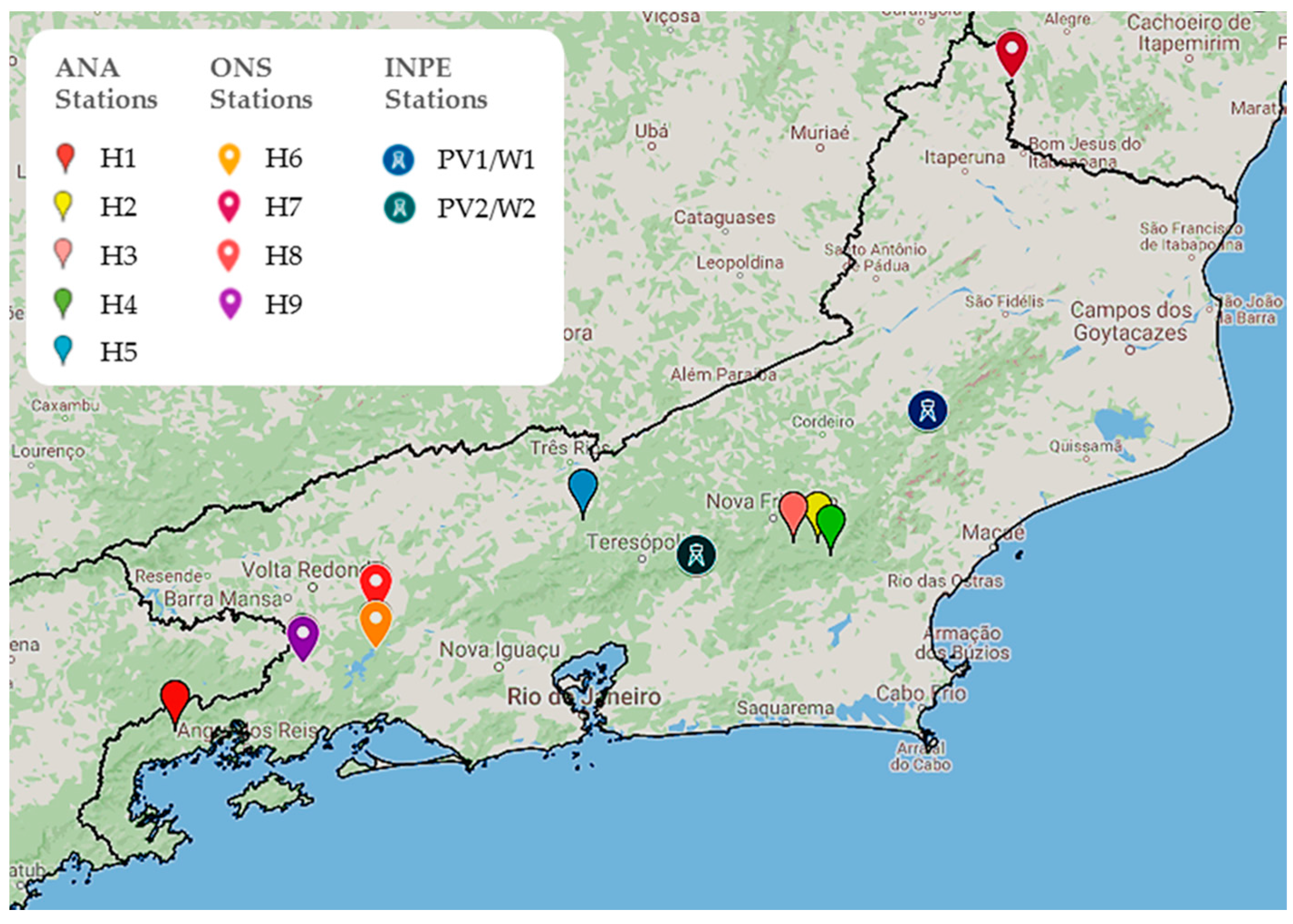
4. Database
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Linear Correlation
5.2. Verification
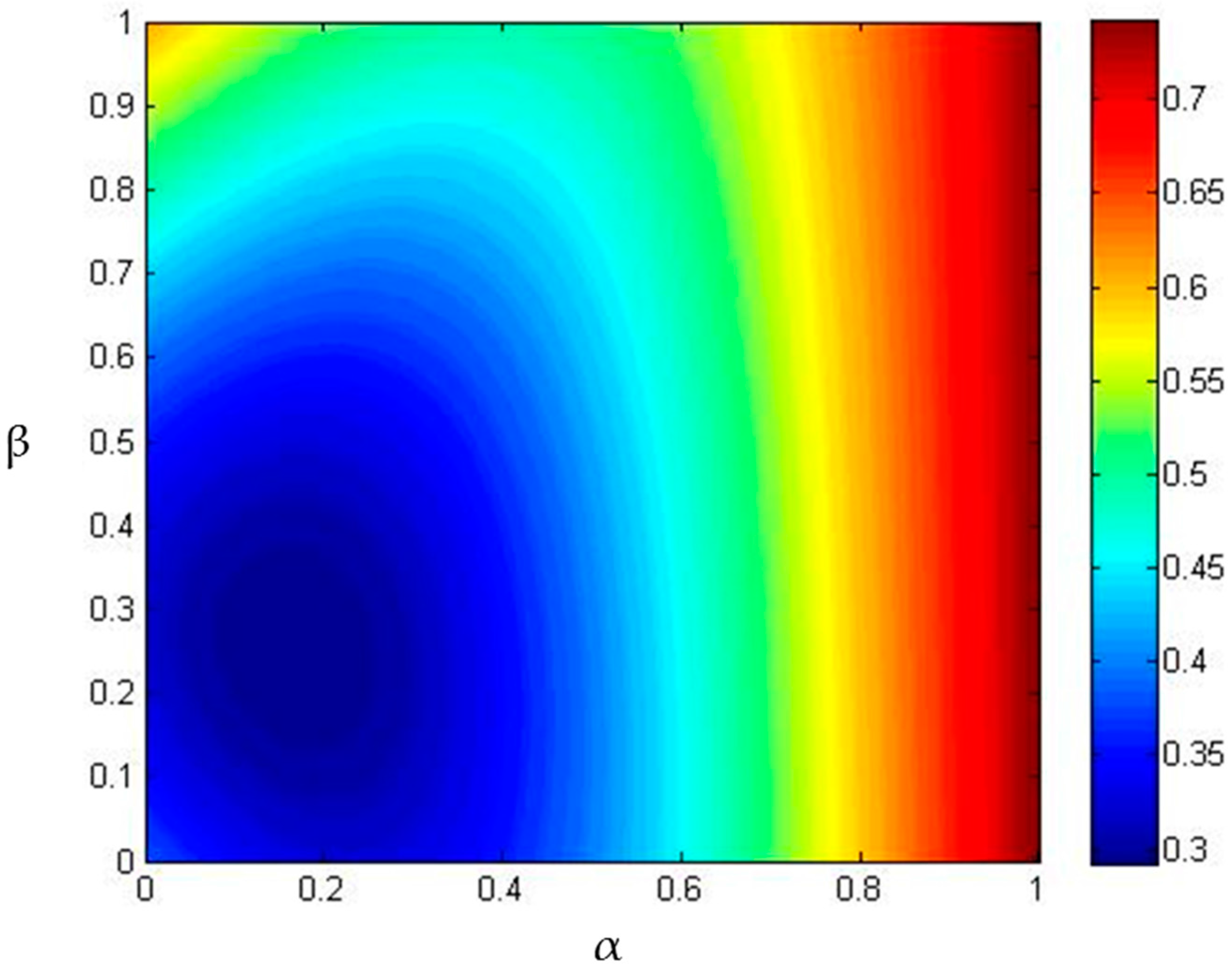
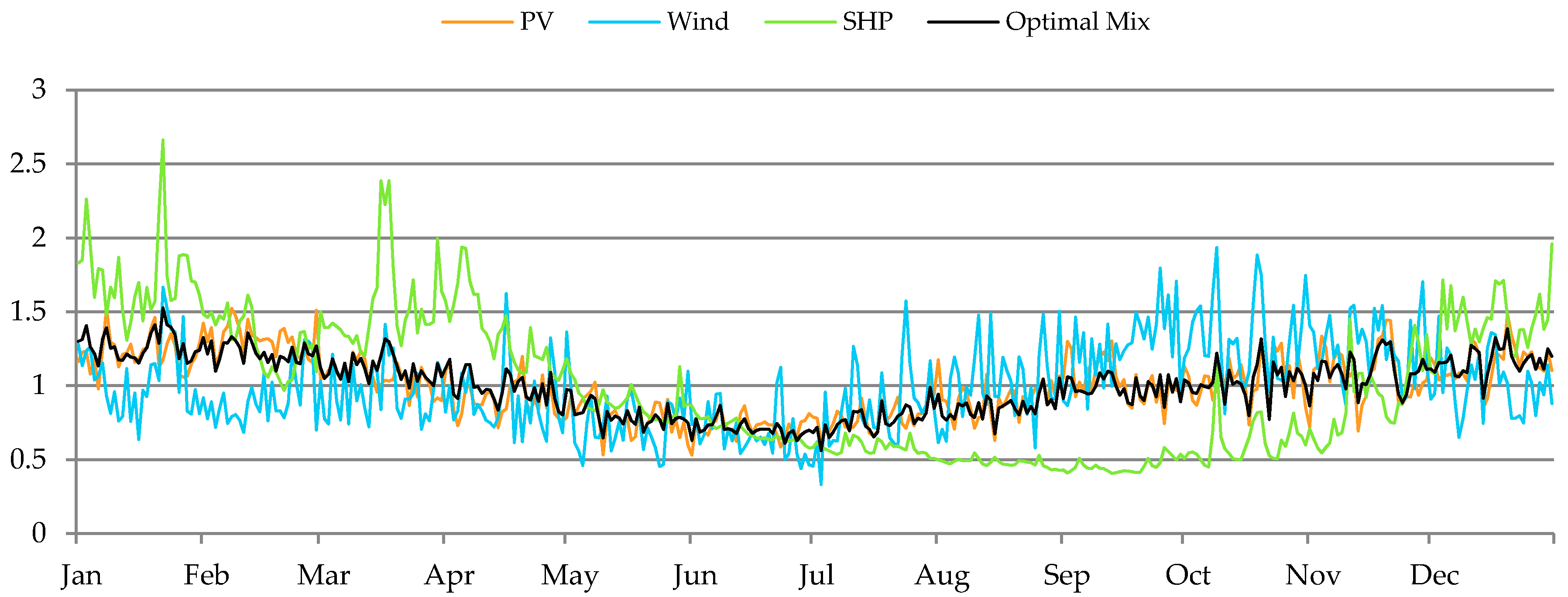
5.3. Renewable Energy Optimal Mix
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Abbreviation | Data Origin | Category | City | River |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PV1 | Inpe | Global Solar Radiation | Santa Maria Madalena | - |
| PV2 | Inpe | Global Solar Radiation | Teresópolis | - |
| W1 | Inpe | Cube of Wind Speed | Santa Maria Madalena | - |
| W2 | Inpe | Cube of Wind Speed | Teresópolis | - |
| H1 | ANA | River Flow | Angra dos Reis | Mambucaba |
| H2 | ANA | River Flow | Nova Friburgo | Macaé |
| H3 | ANA | River Flow | Nova Friburgo | Macaé de Cima |
| H4 | ANA | River Flow | Nova Friburgo | Bonito |
| H5 | ANA | River Flow | Petrópolis | Fagundes |
| H6 | ONS | River Flow | Piraí/Rio Claro | Ribeirão das Lajes |
| H7 | ONS | River Flow | Guaçuí/São José do Calçado/Bom Jesus de Itabapoana | Itabapoana |
| H8 | ONS | River Flow | Piraí | Piraí |
| H9 | ONS | River Flow | Rio Claro | Piraí |
| WP | Proinfa | Wind Farm Power (Gargaú Power Plant) | São Francisco de Itabapoana | - |
| HP1 | Proinfa | Hydro Power (Tudelândia SHP) | Santa Maria Madalena | Santíssimo |
| HP2 | Proinfa | Hydro Power (Calheiros SHP) | Bom Jesus de Itabapoana/São José do Calçado | Itabapoana |
| HP3 | Proinfa | Hydro Power (Santa Rosa II SHP) | Bom Jardim/Cordeiro | Grande |
| HP4 | Proinfa | Hydro Power (Bonfante SHP) | Comendador Levy Gasparian/Simão Pereira | Paraibuna |
| HP5 | Proinfa | Hydro Power (Monte Serrat SHP) | Comendador Levy Gasparian/Simão Pereira | Paraibuna |
| HP6 | Proinfa | Hydro Power (Santa Fé SHP) | Comendador Levy Gasparian/Santana do Deserto/Três Rios | Paraibuna |
References
- US Energy Information Administration (EIA). International Energy Outlook 2016; EIA: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- Brazil. Brazilian Energy Balance 2015 Year 2014; Ministry of Mines and Energy/Energy Research Company: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2015.
- IBGE—Regional Accounts 2014: Five States Account for Nearly Two Thirds of Brazilian GDP. Available online: http://saladeimprensa.ibge.gov.br/en/noticias.html?view=noticia&id=1&busca=1&idnoticia=3315 (accessed on 19 April 2017).
- IBGE—Population Estimates for the Brazilian Municipalities and Federation Units on July 1, 2016. Available online: http://www.ibge.gov.br/english/estatistica/populacao/estimativa2016/estimativa_dou.shtm (accessed on 19 April 2017).
- Christo, E.S.C.; Costa, K.A.; Meza, L.A.; Rosa, C.O.C.S. Life Cycle Inventory for Energy System in Rio de Janeiro State. In Proceedings of the VI International Conference on Life Cycle Assessment, Lima, Peru, 13–16 July 2015; Pontifical Catholic University of Peru: Lima, Peru, 2015; p. 437. [Google Scholar]
- Hoicka, C.E.; Rowlands, I.H. Solar and wind resource complementarity: Advancing options for renewable electricity integration in Ontario, Canada. Renew. Energy 2011, 36, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, P.S.; de Almeida, A.T. Multi-objective optimization of a mixed renewable system with demand-side management. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 1461–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bett, P.E.; Thornton, H.E. The climatological relationships between wind and solar energy supply in britain. Renew. Energy 2016, 87, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beluco, A.; de Souza, P.K.; Krenzinger, A. A dimensionless index evaluating the time complementarity between solar and hydraulic energies. Renew. Energy 2008, 33, 2157–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.R.; Pimenta, F.M.; Assireu, A.T.; Spyrides, M.H.C. Complementarity of Brazil’s hydro and offshore wind power. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 56, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François, B.; Borga, M.; Creutin, J.D.; Hingray, B.; Raynaud, D.; Sauterleute, J.F. Complementarity between solar and hydro power: Sensitivity study to climate characteristics in Northern-Italy. Renew. Energy 2016, 86, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François, B.; Hingray, B.; Raynaud, D.; Borga, M.; Creutin, J.D. Increasing climate-related-energy penetration by integrating run-of-the river hydropower to wind/solar mix. Renew. Energy 2016, 87, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantão, M.P.; Bessa, M.R.; Bettega, R.; Detzel, D.H.M.; Lima, J.M. Evaluation of hydro-wind complementarity in the Brazilian territory by means of correlation maps. Renew. Energy 2017, 101, 1215–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Anjos, P.S.; da Silva, A.S.A.; Stošić, B.; Stošić, T. Long-term correlations and cross-correlations in wind speed and solar radiation temporal series from Fernando de Noronha Island, Brazil. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2015, 424, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heide, D.; von Bremen, L.; Greiner, M.; Hoffmann, C.; Speckmann, M.; Bofinger, S. Seasonal optimal mix of wind and solar power in a future, highly renewable Europe. Renew. Energy 2010, 35, 2483–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, L.; Wang, H.; Dai, S.; Qi, Z. Analysis on the hourly spatiotemporal complementarities between China’s solar and wind energy resources spreading in a wide area. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2013, 56, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANEEL—Generation Information Bank. Available online: http://www2.aneel.gov.br/aplicacoes/capacidadebrasil/capacidadebrasil.cfm (accessed on 16 July 2016).
- ANEEL—Distributed Generation. Available online: http://www2.aneel.gov.br/scg/rcgMicro.asp (accessed on 7 September 2016).
- Silva, R.C.; Neto, I.D.; Seifert, S.S. Electricity supply security and the future role of renewable energy sources in Brazil. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 59, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eletrobras. Brazilian Hydroelectric Potential by Phase. Potencial Hidrelétrico Brasileiro por Estágio. Available online: http://eletrobras.com/pt/AreasdeAtuacao/geracao/sipot/Potencial%20Hidreletrico%20Brasileiro%20por%20Estagio%20-%20Dezembro%202015.pdf (accessed on 23 August 2016). (In Portuguese).
- Amarante, O.A.C.; Silva, F.J.L.; Rios Filho, L.G. Rio de Janeiro State’s Wind atlas. In Atlas Eólico do Estado do Rio de Janeiro; Secretária de Estado de Energia, da Indústria Naval e do Petróleo: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2002; p. 83. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- EPE. Technical Note 19/14: Distributed Photovoltaic Generation Insertion in Brazil. In Nota Técnica DEA 19/14: Inserção da Geração Fotovoltaica Distribuída no Brasil; EPE: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2014. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Twidell, J.; Weir, T. Renewable Energy Resources, 2nd ed.; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kaltschmitt, M.; Streicher, W.; Wiese, A. Renewable Energy; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Adrada, T.; Mancebo, J.A.; Martineza, C. Small Hydropower Plants (in Portuguese Pequenas Centrais Hidrelétricas); ONUDI: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kougias, I.; Szabó, S.; Monforti-Ferrario, F.; Huld, T.; Bódis, K. A methodology for optimization of the complementarity between small-hydropower plants and solar PV systems. Renew. Energy 2016, 87, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoplaki, E.; Palyvos, J.A. On the temperature dependence of photovoltaic module electrical performance: A review of efficiency/power correlations. Sol. Energy 2009, 83, 614–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INPE—Dados Históricos. Available online: http://sinda.crn2.inpe.br/PCD/SITE/novo/site/historico/index.php (accessed on 28 November 2015).
- ANA—Hidroweb: Sistema de Informações Hidrológicas. Available online: http://hidroweb.ana.gov.br/default.asp (accessed on 18 April 2016).
- ONS—Séries Históricas de Vazões. Available online: http://www.ons.org.br/operacao/vazoes_naturais.aspx (accessed on 15 February 2016).
- Eletrobras—Programa de Incentivo às Fontes Alternativas de Energia Elétrica (Proinfa). Available online: http://www.eletrobras.com/elb/ProinfA/data/Pages/LUMISABB61D26PTBRIE.htm (accessed on 17 July 2016).
- Dester, M. Reliability of electricity supply regarding the integration of intermittent sources in Brazil’s power mix. IEEE Latin Am. Trans. 2016, 14, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Power Plant Classification | Power (kW) | % |
|---|---|---|
| Conventional Generation | ||
| Fossil Fuel Power Plants | 5,117,192.74 | 57.71% |
| Nuclear Power Plants | 1,990,000.00 | 22.44% |
| Large Hydropower Plants | 1,371,699.00 | 15.47% |
| Biomass Power Plants | 46,700.00 | 0.53% |
| Wind Farm | 28,050.00 | 0.32% |
| Small Hydropower Plants 1 | 309,977.64 | 3.50% |
| Distributed Generation | ||
| PV Panels | 3343.47 | 0.04% |
| Small Wind Generators | 2.00 | 0.00% |
| Total | 8,866,964.85 | 100.00% |
| PV1 | PV2 | W1 | W2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PV1 | 1.000 | |||
| PV2 | 0.849 | 1.000 | ||
| W1 | 0.316 | 0.276 | 1.000 | |
| W2 | 0.264 | 0.336 | 0.184 | 1.000 |
| PV1 | PV2 | W1 | W2 | H1 | H2 | H3 | H4 | H5 | H6 | H7 | H8 | H9 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PV1 | 1.000 | ||||||||||||
| PV2 | 0.690 | 1.000 | |||||||||||
| W1 | 0.140 | 0.060 | 1.000 | ||||||||||
| W2 | −0.152 | 0 | 0.249 | 1.000 | |||||||||
| H1 | −0.073 | −0.086 | 0.077 | 0.077 | 1.000 | ||||||||
| H2 | −0.073 | −0.074 | 0.084 | 0.097 | 0.577 | 1.000 | |||||||
| H3 | −0.080 | −0.069 | 0.068 | 0.095 | 0.534 | 0.845 | 1.000 | ||||||
| H4 | −0.087 | −0.069 | 0.085 | 0.118 | 0.545 | 0.720 | 0.675 | 1.000 | |||||
| H5 | −0.057 | 0 | 0.061 | 0 | 0.402 | 0.456 | 0.411 | 0.385 | 1.000 | ||||
| H6 | −0.090 | −0.097 | 0.073 | 0.052 | 0.745 | 0.555 | 0.486 | 0.552 | 0.463 | 1.000 | |||
| H7 | −0.051 | 0 | 0 | 0.074 | 0.413 | 0.426 | 0.395 | 0.503 | 0.391 | 0.355 | 1.000 | ||
| H8 | −0.090 | −0.096 | 0.076 | 0.054 | 0.745 | 0.555 | 0.485 | 0.553 | 0.462 | 0.999 | 0.355 | 1.000 | |
| H9 | −0.090 | −0.096 | 0.076 | 0.053 | 0.745 | 0.555 | 0.485 | 0.553 | 0.462 | 0.999 | 0.355 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| WP | W1 | W2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| WP | 1.000 | ||
| W1 | 0.816 | 1.000 | |
| W2 | 0.318 | 0.536 | 1.000 |
| HP1 | HP2 | HP3 | HP4 | HP5 | HP6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | 0.579 | 0.602 | 0.491 | 0.484 | 0.675 | 0.630 |
| H2 | 0.723 | 0.780 | 0.618 | 0.593 | 0.704 | 0.590 |
| H3 | 0.621 | 0.766 | 0.545 | 0.526 | 0.620 | 0.480 |
| H4 | 0.582 | 0.706 | 0.540 | 0.482 | 0.565 | 0.512 |
| H5 | 0.706 | 0.721 | 0.557 | 0.582 | 0.670 | 0.569 |
| H6 | 0.507 | 0.515 | 0.500 | 0.425 | 0.590 | 0.568 |
| H7 | 0.680 | 0.866 | 0.548 | 0.537 | 0.635 | 0.579 |
| H8 | 0.504 | 0.515 | 0.501 | 0.423 | 0.587 | 0.564 |
| H9 | 0.502 | 0.514 | 0.501 | 0.423 | 0.586 | 0.562 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Oliveira Costa Souza Rosa, C.; Costa, K.A.; Da Silva Christo, E.; Braga Bertahone, P. Complementarity of Hydro, Photovoltaic, and Wind Power in Rio de Janeiro State. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9071130
De Oliveira Costa Souza Rosa C, Costa KA, Da Silva Christo E, Braga Bertahone P. Complementarity of Hydro, Photovoltaic, and Wind Power in Rio de Janeiro State. Sustainability. 2017; 9(7):1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9071130
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Oliveira Costa Souza Rosa, Caroline, Kelly Alonso Costa, Eliane Da Silva Christo, and Pâmela Braga Bertahone. 2017. "Complementarity of Hydro, Photovoltaic, and Wind Power in Rio de Janeiro State" Sustainability 9, no. 7: 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9071130
APA StyleDe Oliveira Costa Souza Rosa, C., Costa, K. A., Da Silva Christo, E., & Braga Bertahone, P. (2017). Complementarity of Hydro, Photovoltaic, and Wind Power in Rio de Janeiro State. Sustainability, 9(7), 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9071130





