Simulation of Thermal Distribution and Airflow for Efficient Energy Consumption in a Small Data Centers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
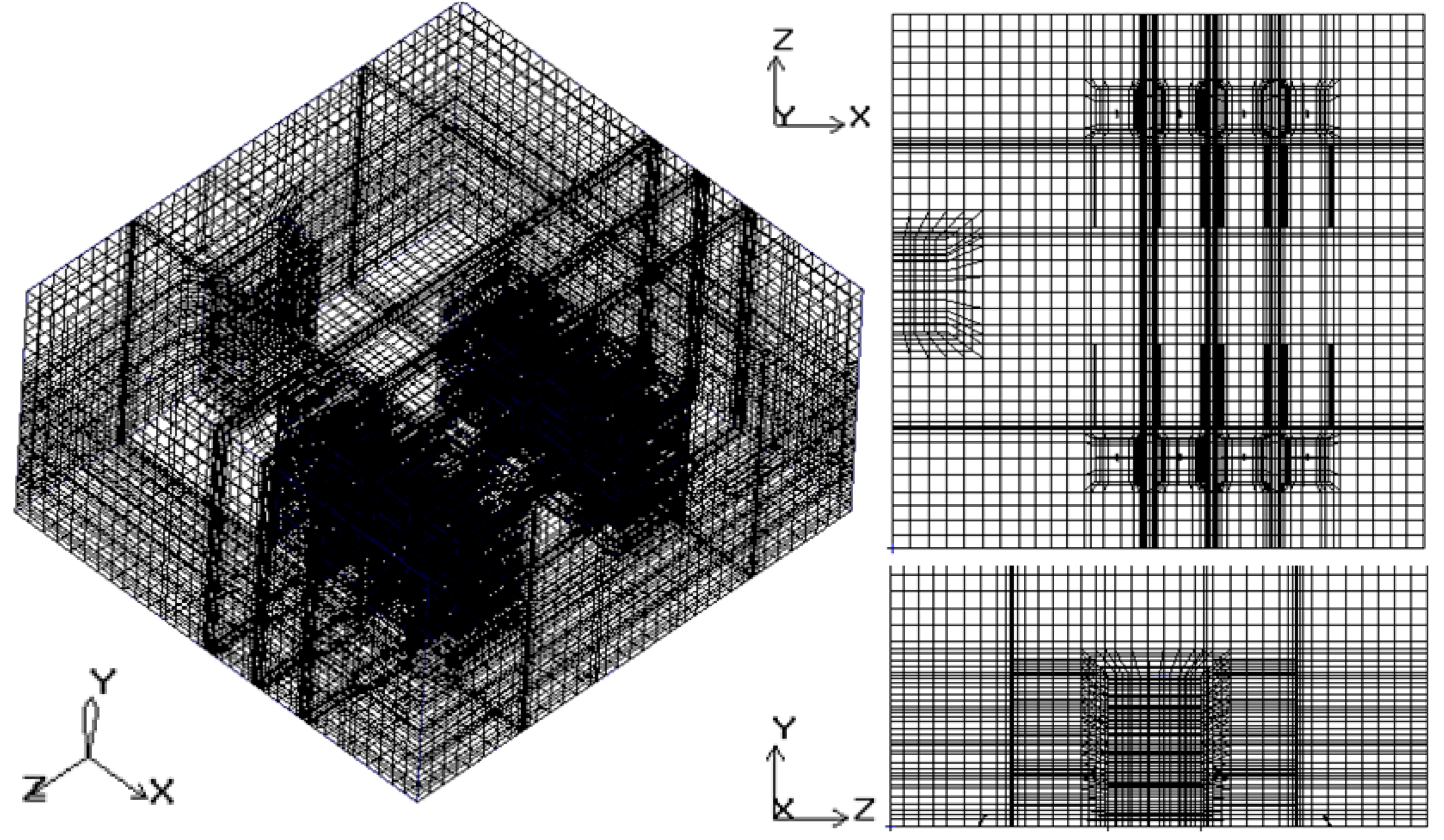
2.1. Physical Model of Data Center
2.2. Mathematical Model
2.2.1. Continuity and Momentum Equations
2.2.2. Turbulence Model
2.3. Boundary Conditions
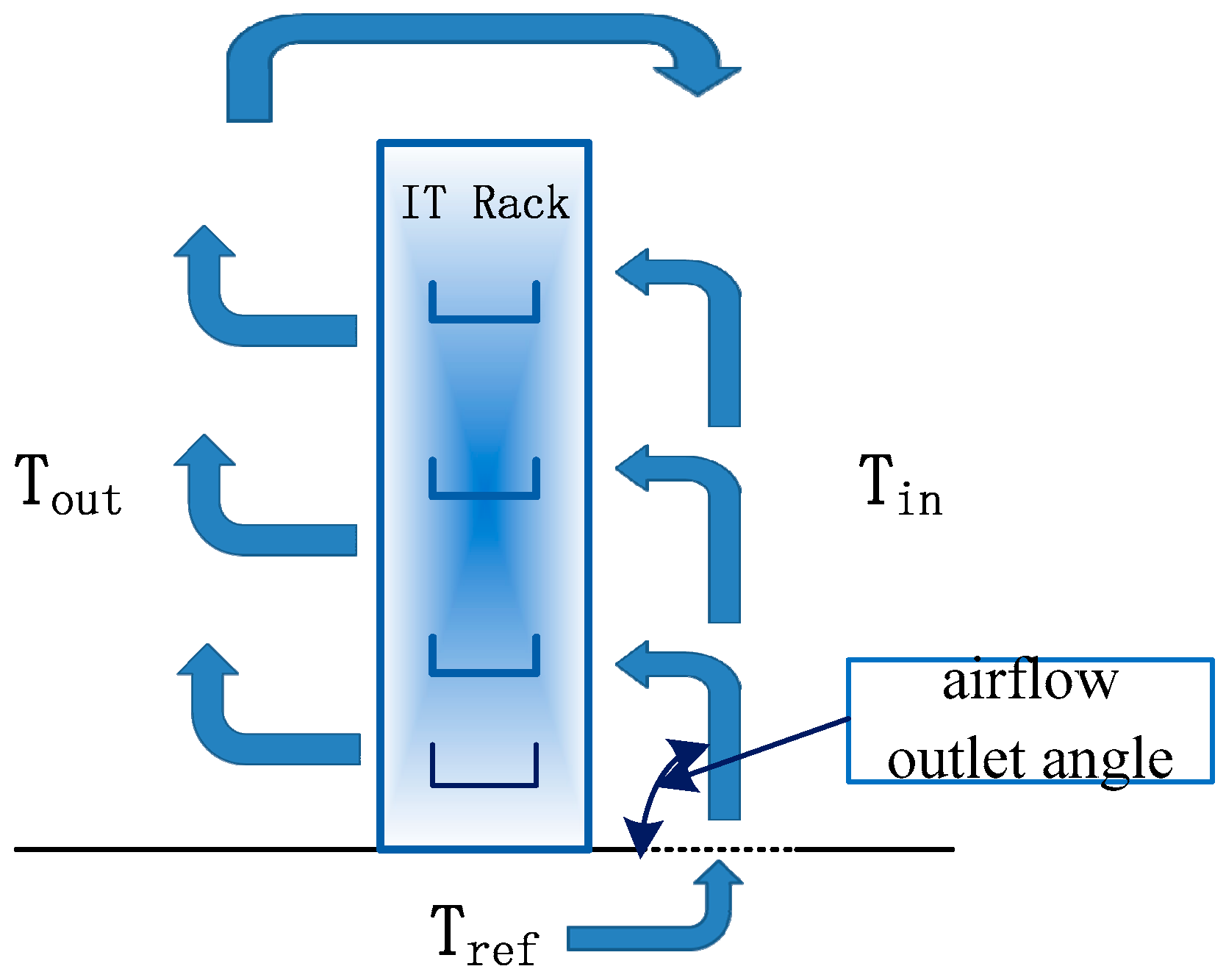
2.4. Evaluation Method
3. Results and Discussion
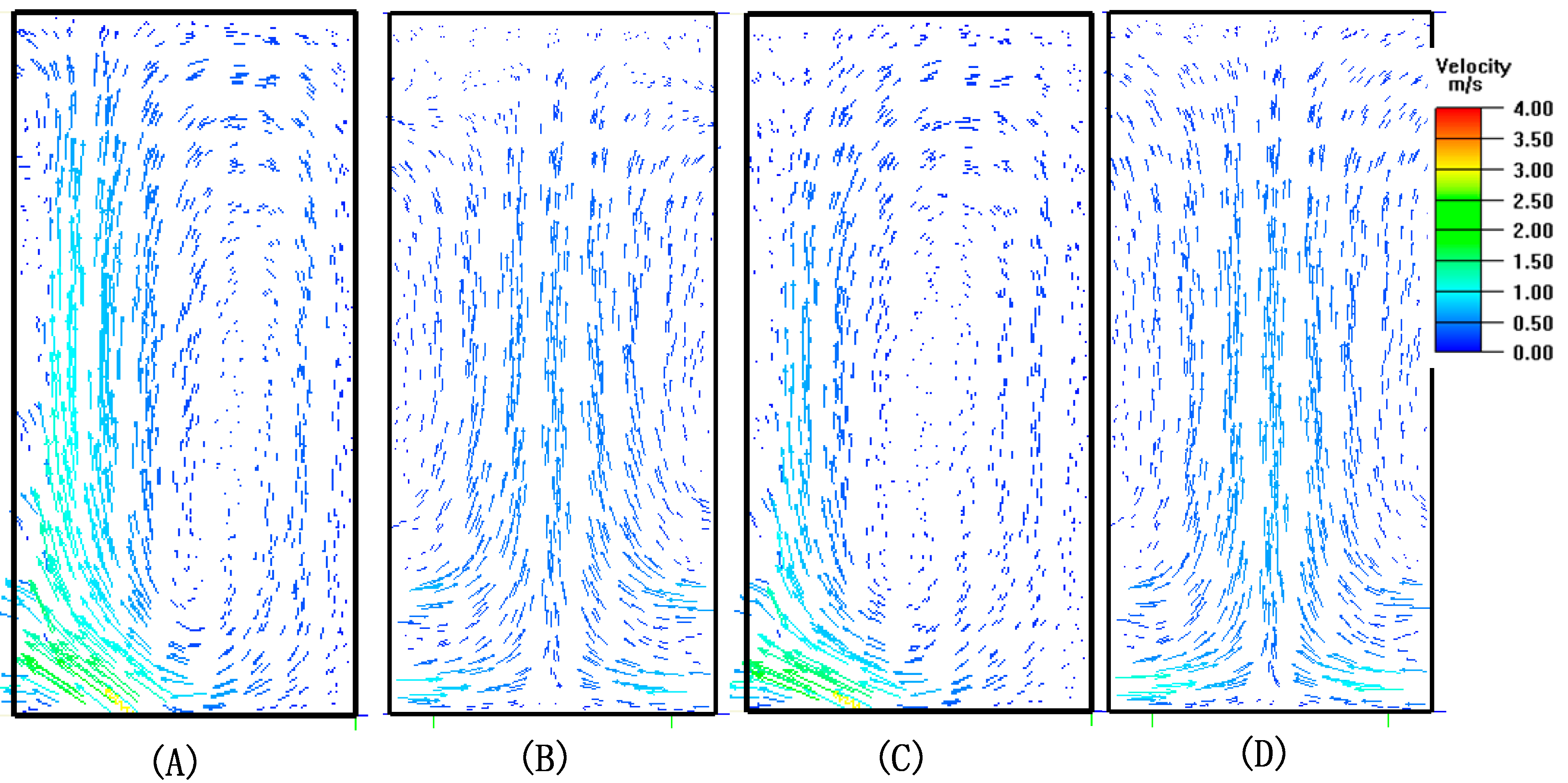
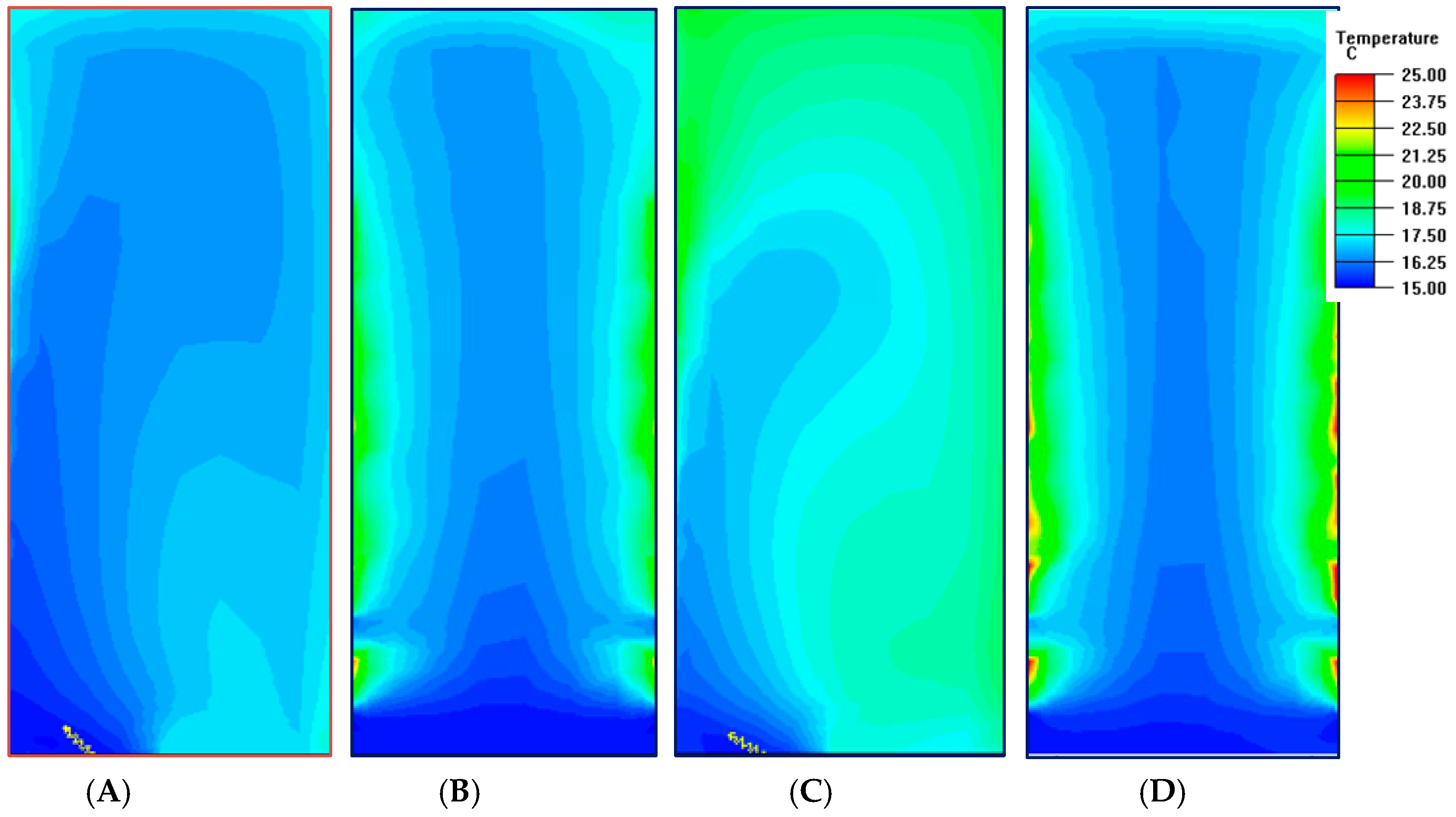
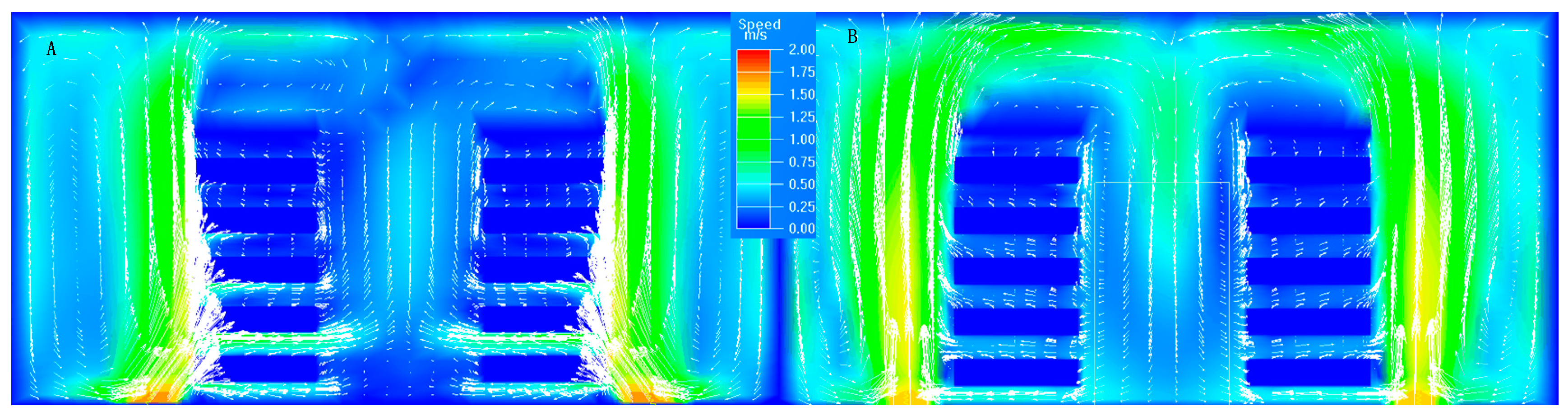
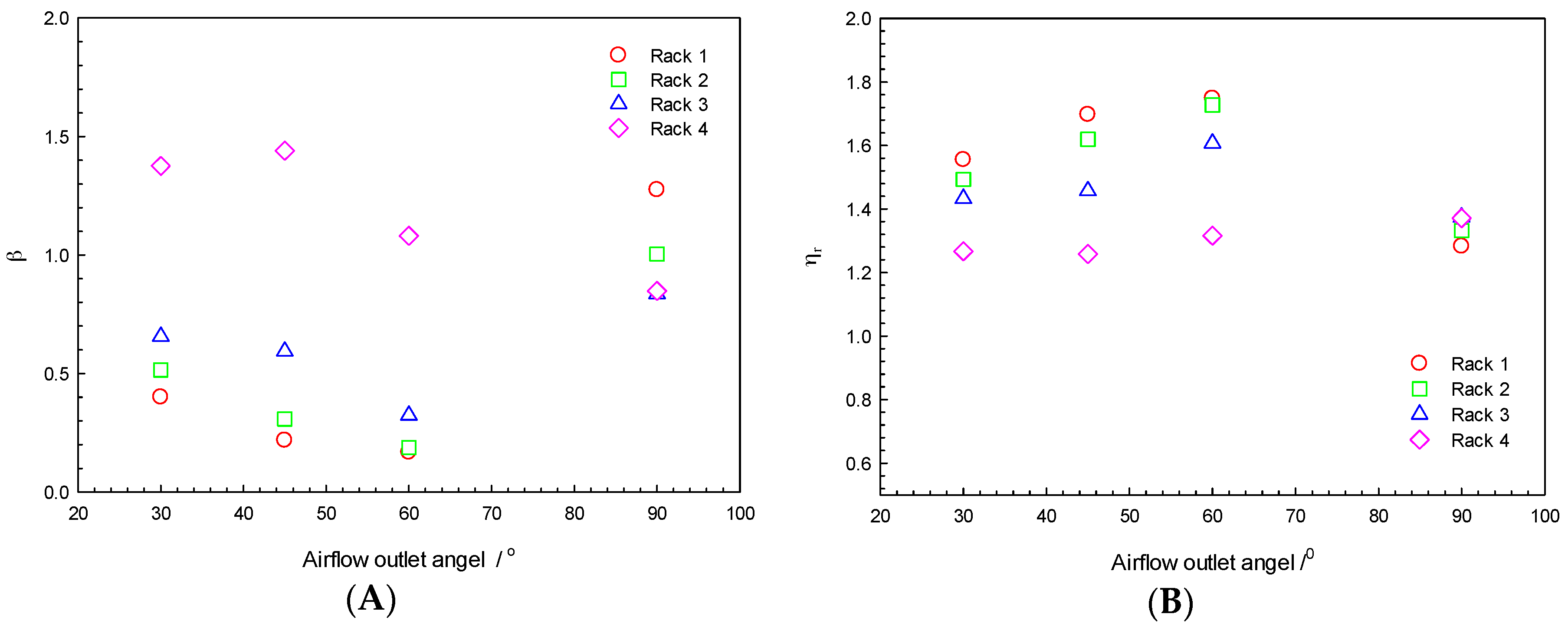
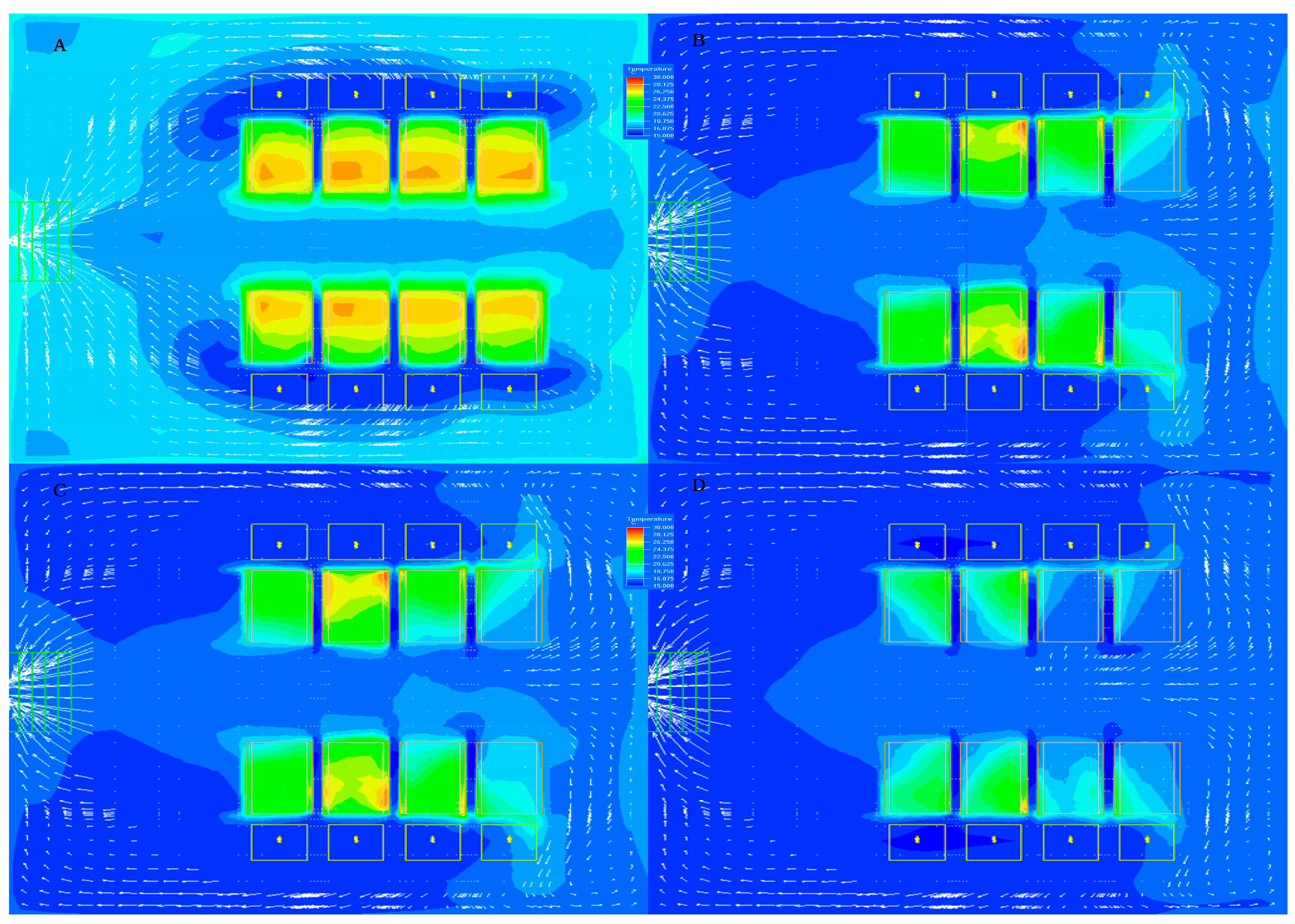
3.1. Effect of Airflow Outlet Angle of Tiles on Air Distribution
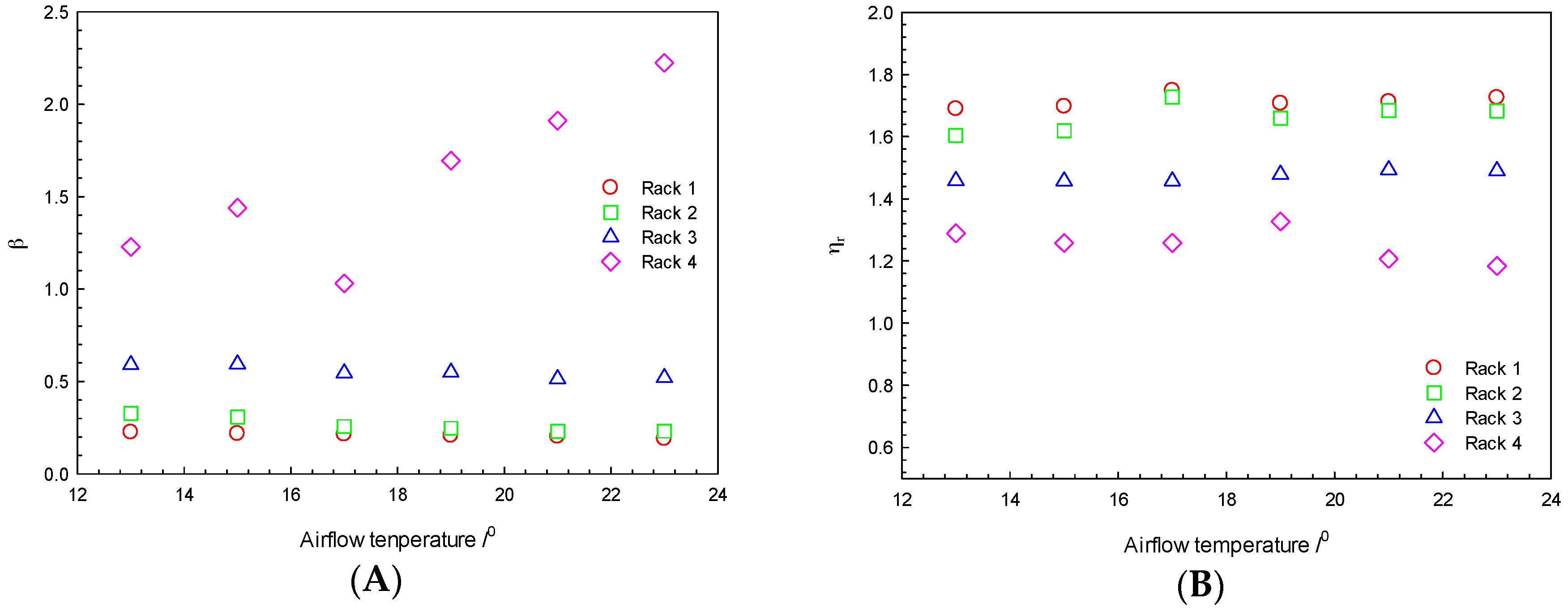
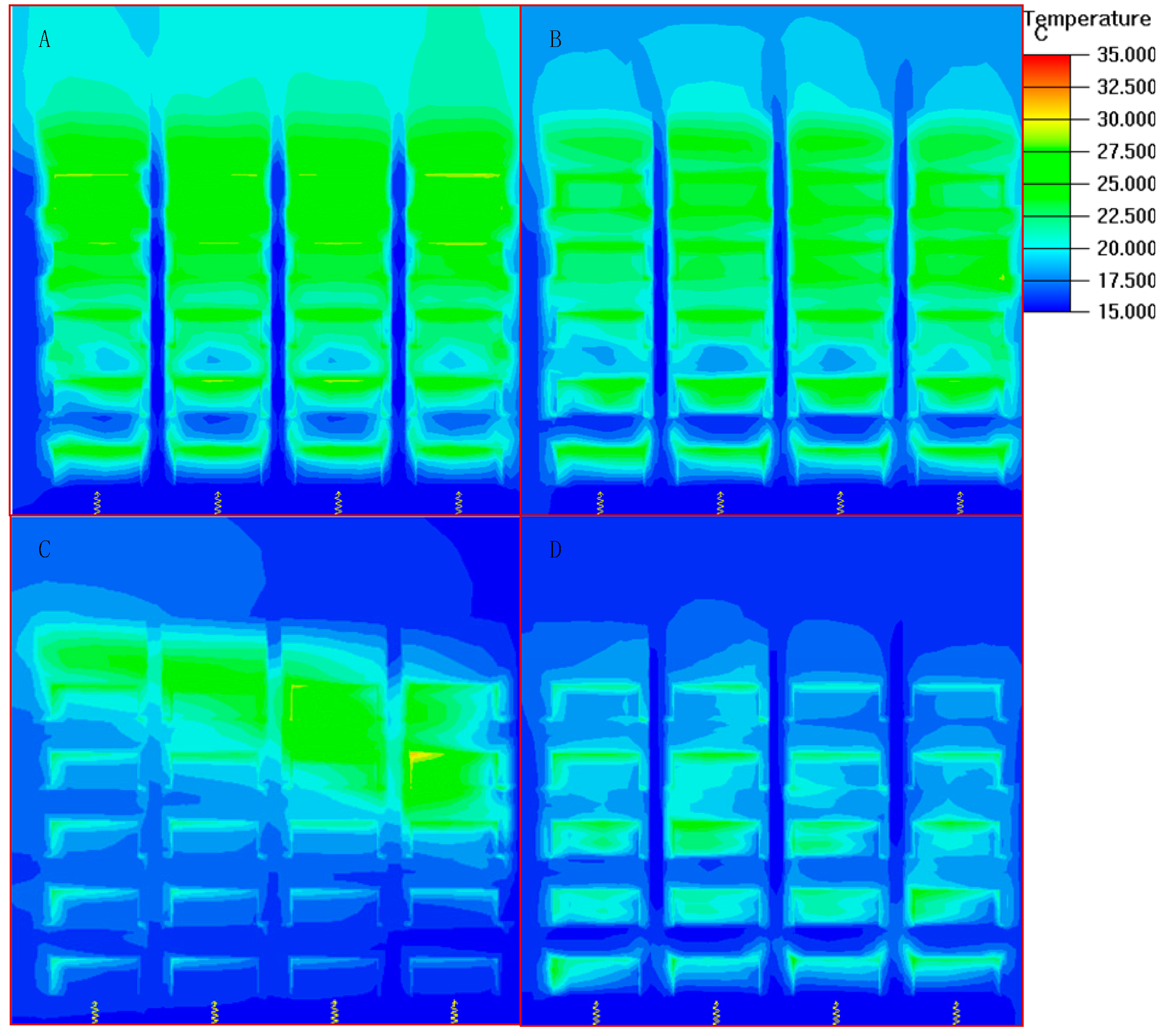
3.2. The Temperature of the Cold Air on the Airflow Distribution
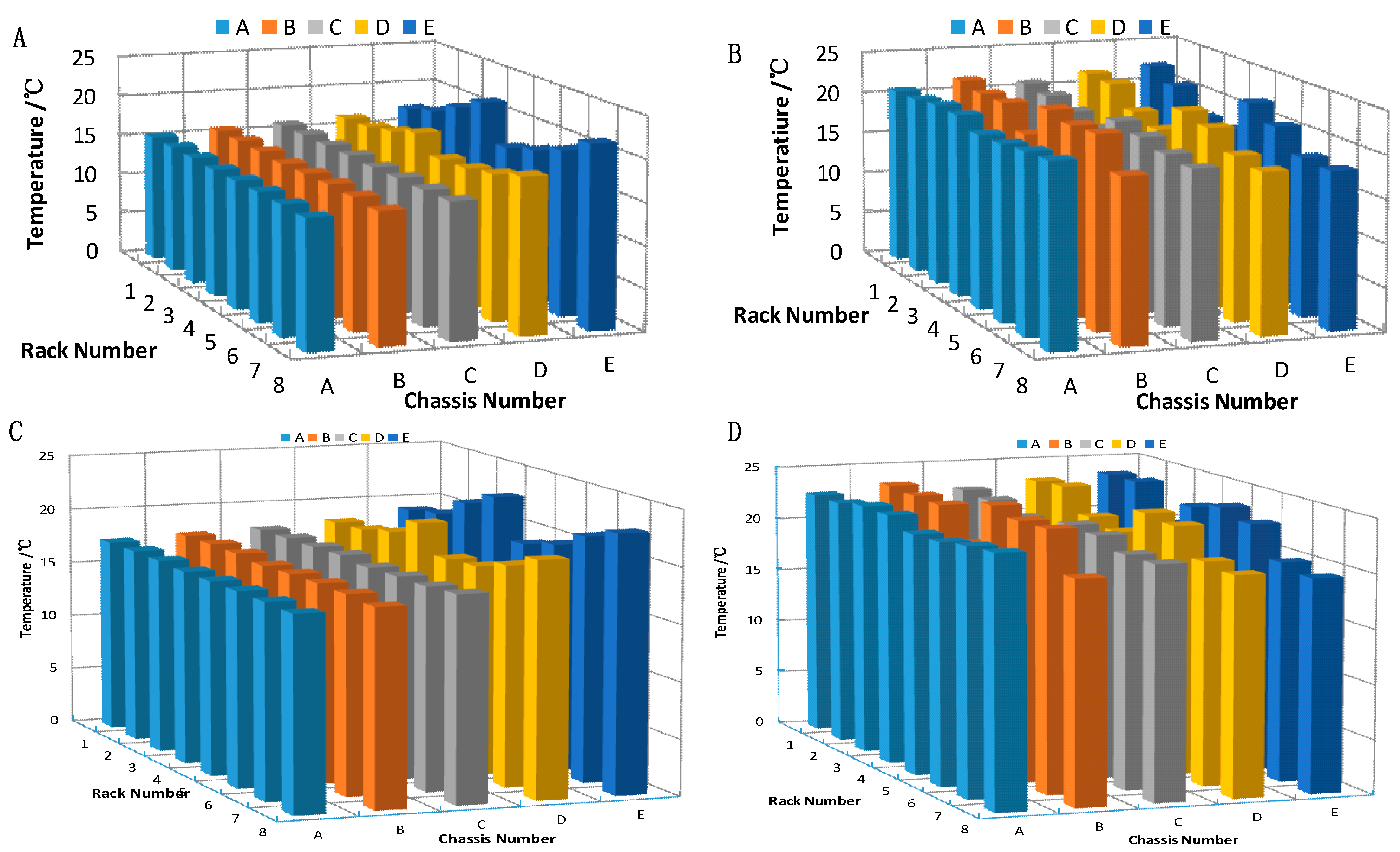
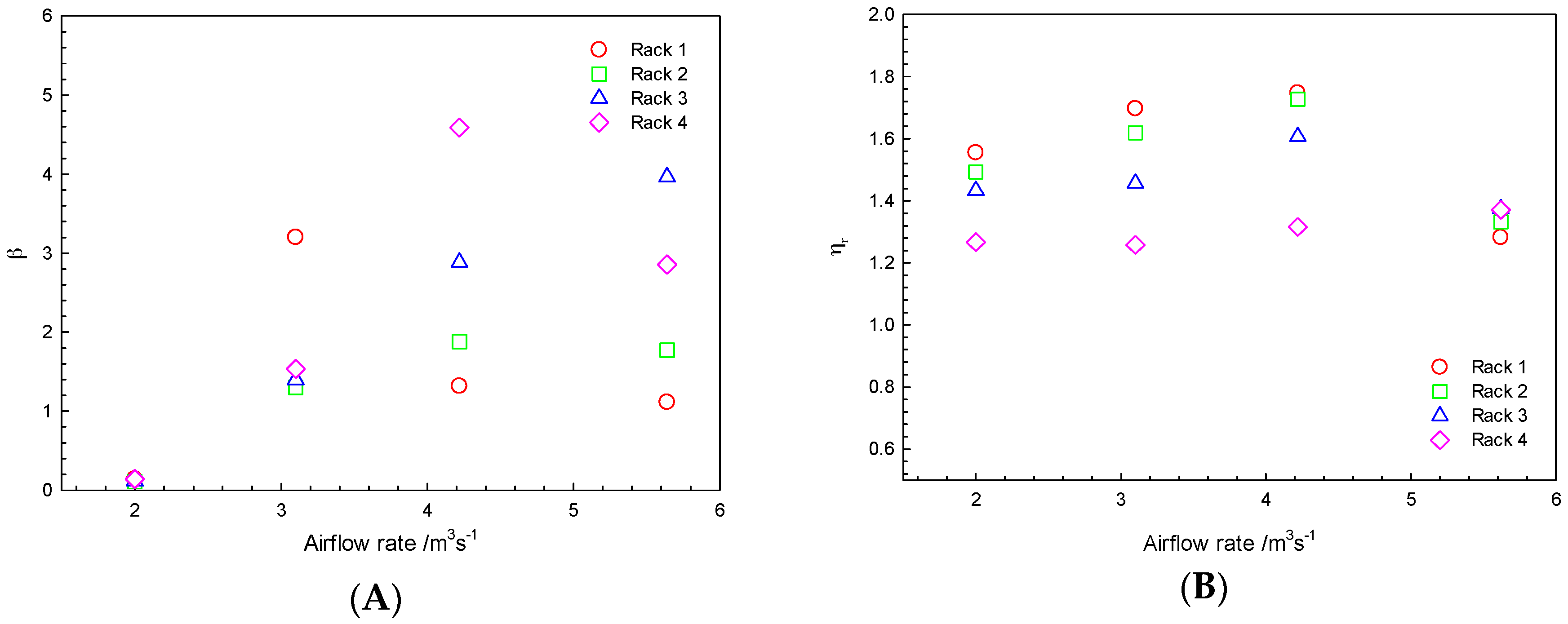
3.3 The Effect of Airflow Rate on the Air Distribution
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koomey, J.G. Growth in Data Center Electricity Use 2005 to 2010; Analytics Press: Oakland, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, J.; Bai, X. A review of air conditioning energy performance in data centers. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 625–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, J.; Delforge, P. Data Center Efficiency Assessment; Natural Resources Defense Council: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ristic, B.; Madani, K.; Makuch, Z. The water footprint of data centers. Sustainability 2015, 7, 11260–11284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehabi, A.; Ganguly, S.; Traber, K.; Price, H.; Horvath, A.; Nazaroff, W.W.; Gadgil, A.J. Energy Implications of Economizer Use in California Data Centers; Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory: Monterey, CA, USA, 2008.
- Qian, X.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.X. Entransy and exergy analyses of airflow organization in data centers. Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 2015, 81, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, Y.; Kumar, P. Energy Efficient Thermal Management of Data Centers; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, C.D.; Sharma, R.; Bash, C.E. Thermal considerations in cooling large scale high compute density data centers. In Proceedings of the 2002 Inter Society Conference on Thermal Phenomena, San Diego, CA, USA, 30 May–2 June 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey, R.; Yogendra, J. Modeling of data center airflow and heat transfer: State of the art and future trends. Distrib. Parallel Databases 2007, 21, 193–225. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, M.; Darabidarabkhani, Y.; Shah, A.; Memon, J. Evaluating power efficient algorithms for efficience and carbon emissions in cloud data centers: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 51, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Mukherjee, T.; Sandeep, K.S.; Cayton, G.P. Sensor-based fast thermal evaluation model for energy efficient high-performance datacenters. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Sensing Information Processing, Bangalore, India, 15–18 December 2006; pp. 203–208. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Q.; Gupta, S.K.S.; Varsamopoulos, G. Energy-efficient, thermal-aware task scheduling for homogeneous, high performance computing data centers: A cyber-physical approach. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2008, 19, 1458–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Yang, J.; Park, W. Evaluation of air distribution system’s airflow performance for cooling energy savings in high-density data centers. Energy Build. 2014, 68, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Luo, J.; Song, A. Dynamic pricing based energy cost optimization in data center environments. Chin. J. Comput. 2013, 36, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, H.; Feng, Z.; Sun, C.; Jin, Z.; Long, Z. Optimization on air distribution and energy consumption of a small data center. J. Tianjin Univ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 47, 647–652. [Google Scholar]
- Axley, J.W.; Emmerich, S.J.; George, N.W. Modeling the performance of a naturally ventilated commercial building with a multizone coupled thermal/airflow simulation tool. ASHRAE Trans. 2002, 108, 1260–1275. [Google Scholar]
- Dols, W.S.; Emmerich, S.J.; Polidoro, B.J. Using coupled energy, airflow and indoor air quality software (TRNSYS/CONTAM) to evaluate building ventilation strategies. Build. Serv. Eng. Res. Technol. 2016, 37, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dols, W.S.; Emmerich, S.J.; Polidoro, B.J. Coupling the multizone airflow and contaminant transport software contam with energy plus using co-simulation. Build. Simul. 2016, 9, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alissa, H.A.; Nemati, K.; Puvvadi, U.L.N.; Sammaki, B.G.; Schneebeli, K.; Seymour, M.; Gregory, T. Analysis of airflow imbalances in an open compute high density storage data center. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 108, 937–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jin, F.; Jiang, L. CFD analysis of airflow configuration in the computer room. Refrig. Air Cond. Electr. Powder Mach. 2008, 28, 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, N.; Li, C.; Wang, M.A. Study on the influence of different inlet wind directions on airflow pattern of under floor air distribution system. World Sci. Tech. R D 2009, 31, 913–916. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, N.M.S.; Khan, M.M.K.; Rasul, M.G. Temperature monitoring and CFD Analysis of Data Centre. Procedia Eng. 2013, 56, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, I.N.; Tsui, Y.Y.; Wang, C.C. Improvements of Airflow Distribution in a Container Data Center. Energy Proc. 2015, 75, 1819–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Lim, T.; Kim, B.S. Measurements and predictions of the air distribution systems in high compute density(internet)data centers. Energy Build. 2009, 41, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Lü, X.; Remes, M. Investigation of air management and energy performance in a data center in Finland: Case study. Energy Build. 2011, 43, 3360–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.H.; Shokry, E.; Ahmadian Hosseini, A.J.; Ahmadi, G.; Calautit, J.K. Evaluation of airflow and thermal comfort in buildings ventilated with wind catchers: Simulation of conditions in Yazd City, Iran. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2016, 35, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartrand, T.A.; Farouk, B.; Haas, C.N. Countercurrent gas/liquid flow and mixing: Implications for water disinfection. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2009, 35, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhim, B. Multifaceted Analysis of Data Centre Cooling Using CFD, Experiment and Second Law of Thermodynamics. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia, March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Alkharabsheh, S.; Fernandes, J.; Gebrehiwot, B.; Agonafer, D.; Ghose, K.; Ortega, A.; Joshi, Y.; Sammakia, B. A brief overview of recent developments in thermal management in data center. J. Electron. Packag. 2015, 137, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.S.; VanGilder, J.W.; Iyengar, M.; Schmidt, R.R. Effect of rack modeling detail on the numerical results of a data center test cell. In Proceedings of the IEEE Intersociety Conference on Thermal and Thermomechanical Phenomena in Electronics Systems (ITHERM 2008), Lake Buena Vista, FL, USA, 28–31 May 2008; pp. 1183–1190. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, J.Z.; Hermansen, K.A.; Al-Saadi, S. The development of simplified rack boundary conditions for numerical data center models. ASHRAE Trans. 2012, 118, 436–449. [Google Scholar]
- Ansys Incorported. ANSYS FLUENT-Solver Release 10.0; Ansys Inc.: Canonsbury, PA, USA, 2005; p. 131. [Google Scholar]
- Abanto, J.; Barrero, D.; Reggio, M.; Ozell, B. Airflow modeling in a computer room. Build. Environ. 2004, 39, 1393–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z. Thermal performance of a contained data center with fan-assisted perforations. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 102, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, C.D.; Bash, C.E.; Belady, C.; Stahl, L.; Sullivan, D. Computational fluid dynamics modeling of high compute density data centers to assure system inlet air specifications. In Proceedings of the Pacific Rim Technical Conference and Exposition of Packaging and Integration of Electronic and Photonic Systems (IPACK), Kauai, HI, USA, 8–13 July 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Dun, Z.; Qin, Y.; Guan, X. Simulation optimization and evaluation analysis of the data center airflow distribution. Build. Energy Effic. 2015, 43, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, T.; David, M.; Geer, J. Experimental and numerical dynamic investigation of an energy efficient liquid cooled chiller-less data center test facility. Energy Build. 2015, 91, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannaford, P. Ten steps to solving cooling problems cause by high-density server deployment. In Proceedings of the INTELEC 05-Twenty-Seventh International Telecommunications Conference, Berlin, Germany, 18–22 September 2005; pp. 609–616. [Google Scholar]
- Herrlin, M.K. Rack cooling effectiveness in data centers and telecom central offices: The Rack Cooling Index (RCI). ASHRAE Trans. 2005, 111, 725–731. [Google Scholar]
- Herrlin, M.K. Airflow and cooling performance of DC: Two performance metrics. ASHRAE Trans. 2008, 114, 182–187. [Google Scholar]
- Capozzoli, A.; Serale, G.; Liuzzo, L.; Chinnici, M. Thermal metrics for data centers: A critical review. Energy Procedia 2014, 62, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.R.; Cruz, E.E.; Iyengar, M.K. Challenges of data center thermal management. IBM J. Res. Dev. 2005, 49, 709–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanGilder, J.W.; Lee, T. A hybrid flow network-CFD method for achieving any desired flow partitioning through floor tiles of a raised-floor data center. Adv. Electron. Packag. 2003, 1, 377–382. [Google Scholar]
- Sorell, V.; Escalante, S.; Yang, J. Comparison of overhead and underfloor air delivery systems in a data center environment using CFD modeling. ASHRAE Trans. 2005, 111, 756–764. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.X. Energy Consumption and Air Distribution Simulation of a Substation Data Room; Zhejiang University: Hangzhou, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, S.; Schmidt, R.; Kelkar, K.M.; Radmehr, A.; Patankar, S.V. A Methodology for the Design of Perforated Tiles in Raised Floor Data Centers Using Computational Flow Analysis. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Technol. 2001, 24, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, K.; Patankar, S. Airflow distribution through perforated tiles in raised-floor data centers. Build. Environ. 2006, 41, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanGilder, J.W.; Schmidt, R. Airflow Uniformity through Perforated Tiles in a Raised-Floor Data Center. In Proceedings of the ASME 2005 Pacific Rim Technical Conference and Exhibition on Integration and Packaging of MEMS, NEMS, and Electronic Systems collocated with the ASME 2005 Heat Transfer Summer Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 17–22 July 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelmaksoud, W.A.; Khalifa, H.E.; Dang, T.Q.; Elhadidi, B.; Schmidt, R.R.; Iyengar, M. Experimental and Computational Study of Perforated Floor Tile in Data Centers. In Proceedings of the 12th IEEE Intersociety Conference on Thermal and Thermomechanical Phenomena in Electronics Systems (ITHERM), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2–5 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Arghode, V.K.; Kumar, P.; Joshi, Y.; Weiss, T.; Meyer, G. Rack Level Modeling of Air Flow Through Perforated Tile in a Data Center. ASME J. Electron. Packag. 2013, 135, 030902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, K.C.; Radmehr, A.; Patankar, S.V. Use of computational fluid dynamics for calculating flow rates through perforated tiles in raised-floor data centers. HVAC R Res. 2003, 9, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beitelmal, A.H. Numerical investigation of data center raised-floor plenum. In Proceedings of the ASME 2015 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Houston, TX, USA, 13–19 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Code for Design of Electronic Information System Room; GB 50174-2008; China Electronics Engineering Design Institute: Beijing, China, 2009.

| Length/m | Width/m | Height/m | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simulation of data center | 9.60 | 10.00 | 3.20 |
| Chassis | 0.683 | 0.448 | 0.0875 |
| Air conditioner | 0.765 | 0.560 | 1.940 |
| Pressure | Density | Body Force | Momentum | |
| Relaxation factor | 0.7 | 1 | 1 | 0.3 |
| Volume Fraction | Turbulent Kinetic Energy | Turbulent Dissipation Rate | Turbulent Viscosity | |
| Relaxation factor | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 1 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ni, J.; Jin, B.; Zhang, B.; Wang, X. Simulation of Thermal Distribution and Airflow for Efficient Energy Consumption in a Small Data Centers. Sustainability 2017, 9, 664. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9040664
Ni J, Jin B, Zhang B, Wang X. Simulation of Thermal Distribution and Airflow for Efficient Energy Consumption in a Small Data Centers. Sustainability. 2017; 9(4):664. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9040664
Chicago/Turabian StyleNi, Jing, Bowen Jin, Bo Zhang, and Xiaowei Wang. 2017. "Simulation of Thermal Distribution and Airflow for Efficient Energy Consumption in a Small Data Centers" Sustainability 9, no. 4: 664. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9040664
APA StyleNi, J., Jin, B., Zhang, B., & Wang, X. (2017). Simulation of Thermal Distribution and Airflow for Efficient Energy Consumption in a Small Data Centers. Sustainability, 9(4), 664. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9040664




