Accuracy of Environmental Monitoring in China: Exploring the Influence of Institutional, Political and Ideological Factors
Abstract
:All the questions had received splendidly drafted answers: answers not open to doubt, since they were not the result of human thoughts (always liable to error), but were the outcome of official labours.Lev Tolstoj, 1877 [1]
1. Introduction
2. Structure and Methods
3. Environmental Monitoring Data in China: Discrepancies and Concerns over Accuracy
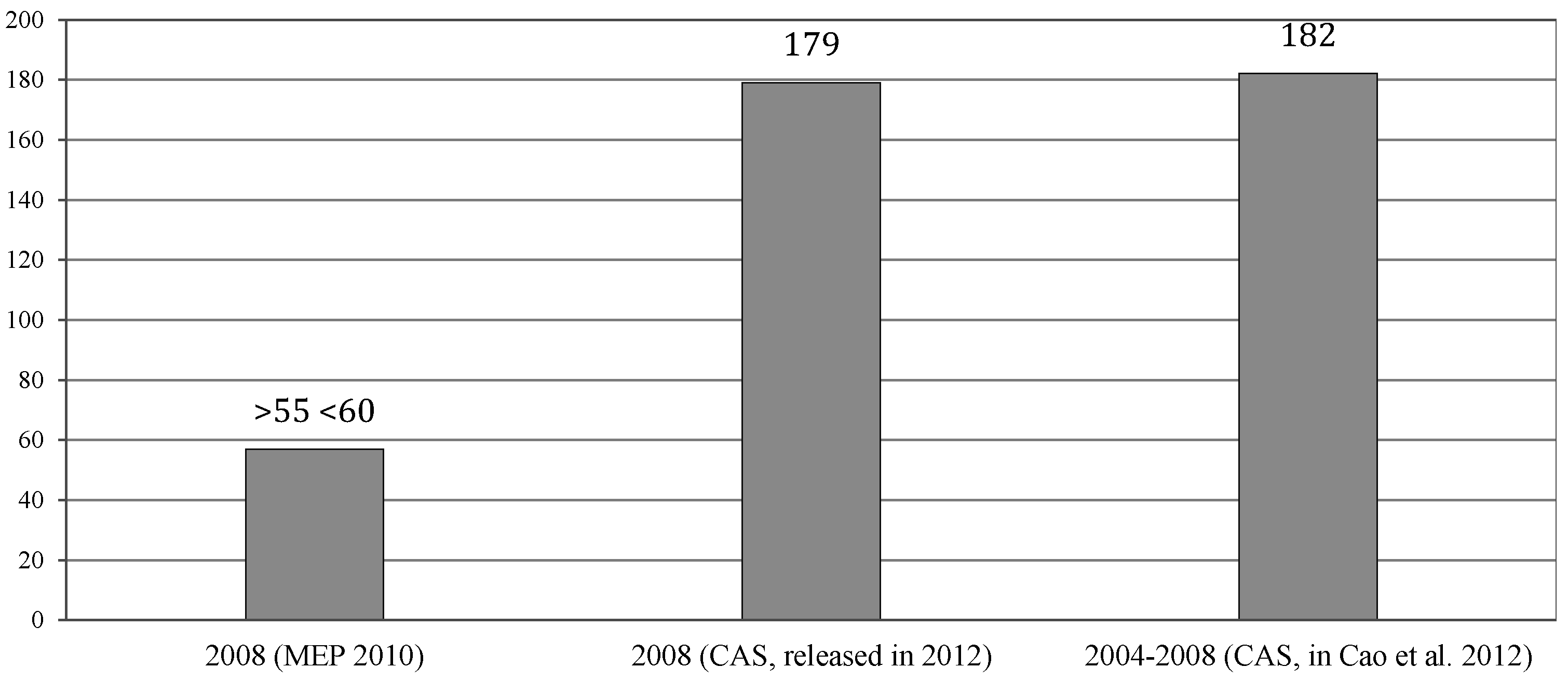
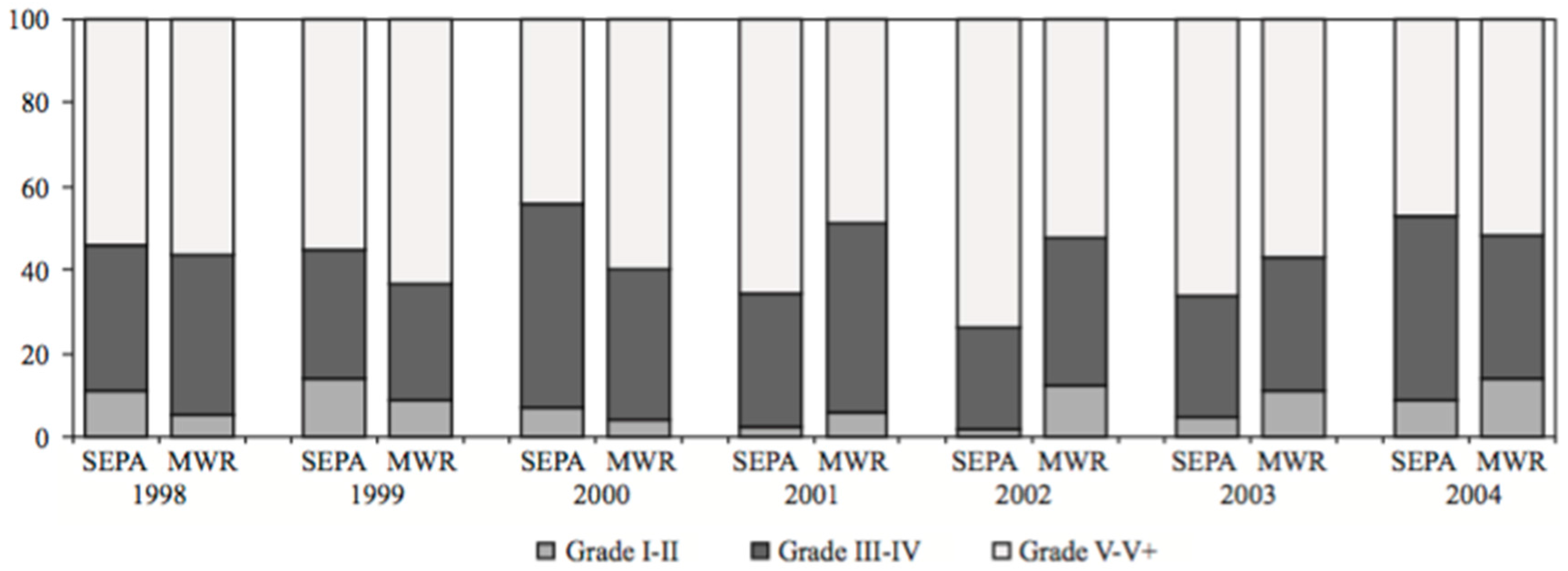
3.1. Air Pollution
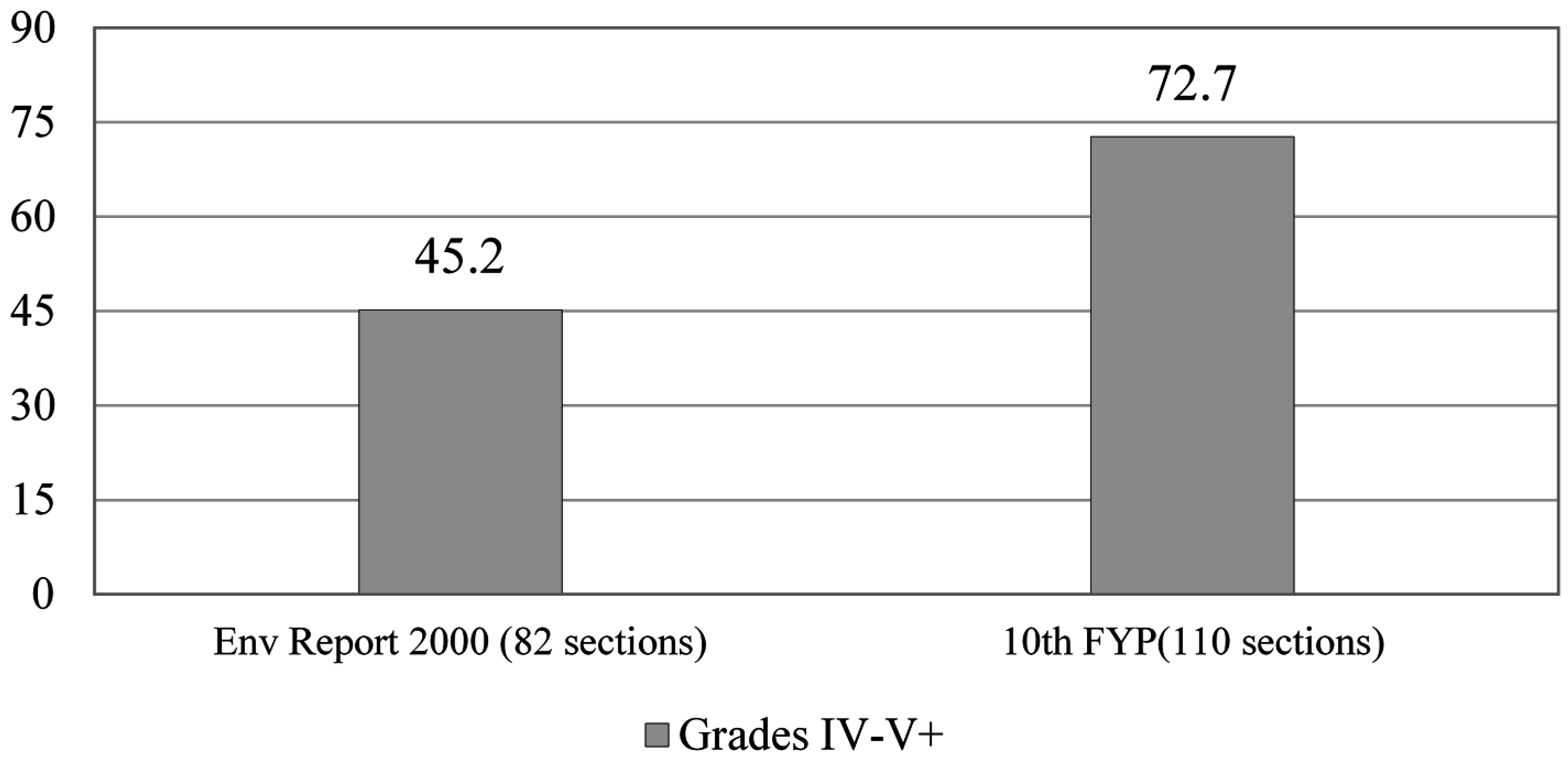
3.2. Water
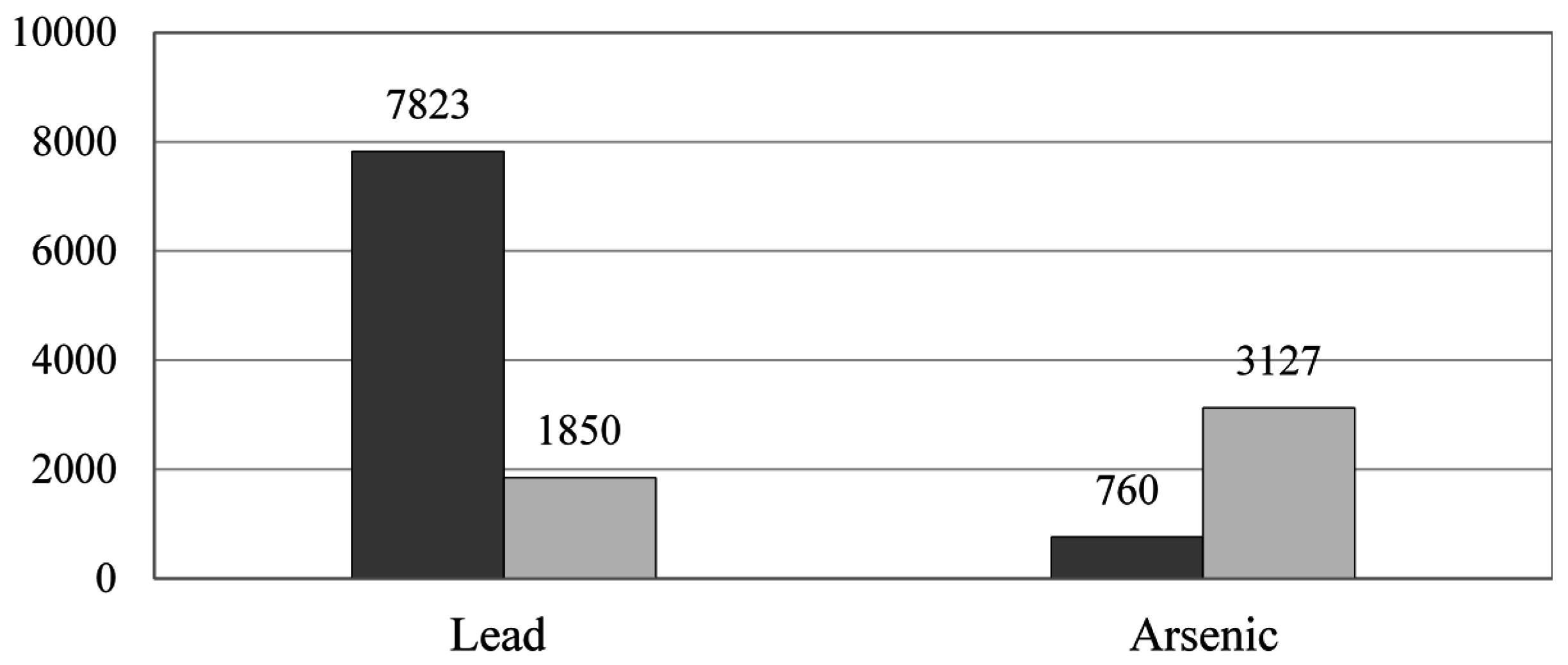
3.3. Soil
4. Non-Technical Factors Influencing Data Accuracy
4.1. Bureaucratic Incentives
4.2. Institutional Goals
When we try to investigate soil pollution we often have difficulties in accessing the field. Recently, we have found significant obstacles in a case study site [in Southern China]. We had already been there and found evidence of heavy metal pollution that was causing harm to the people’s health. The local authorities are scared that if we go there again the people might notice that there’s something wrong [with soil pollution] and get angry.[80]
4.3. Private Interests
For companies, the smaller is the extent of problems revealed by environmental data, the smaller is the likelihood of facing issues in terms of social responsibility and discharge fees. Even Environmental Protection Bureaus are also sceptical of these data [because] Chinese companies have an unwritten tradition of concealing […] data to avoid paying more taxes and sewage charges. Most of data from enterprises are clearly unreal. Data about emissions on SO2 and NOx according to national regulation should be provided [by companies] to Environmental Protection Bureaus, but in reality they often refuse and the regulation is not enforced. The problem is that Environmental Protection Bureaus usually don’t collect data independently, as such there is no third-party oversight, and companies are free to hide environmental issues.[92]
In one case, in a meeting with company employees during a field investigation, when several researchers questioned the discrepancies of data reported in documents provided by the company, the managers and their employees became very tense, immediately asked to collect back the materials [and] promised to give back the correct data […] In [another] case the researchers asked to visit a company, but instead they were shown around the industrial park. When they asked to visit the places where environmental problems were most severe, the requests were politely rejected for various reasons.[92]
4.4. Interactions between Public and Private Interests
When we drafted the report concerning the environmental risks posed by [a major hydro-power project] […] and submitted it for comments to our local partner [which had commissioned the study], its representatives told us that the report was too negative, and asked us to modify it to make it appear ‘better’. We reported this suggestion back to our leaders, who later gave us the go-ahead to modify the report according to our partner’s suggestion.[96]
4.5. Ideology and Political Culture
I already love this place. I really do. These days I’ve been reading news reports talking about China’s scientific development policies. I think this is really wonderful: where else in the world policy makers put science above everything else?[106]
5. Environmental Monitoring and Current Political Trends
Under the pressure of interests […], both government bodies, companies, organizations and single individuals have a strong tendency to manipulate, either by falsifying or concealing information. Local statistics are managed by local governments, and as such are subject to the interference by local leaders who aspire at better positions. Against such background, it is difficult to ensure accuracy and reliability of data.([28], online)
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Tolstoy, L. Anna Karenina; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- EC Joint Research Centre. Environmental Monitoring. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/jrc/en/research-topic/environmental-monitoring (accessed on 7 December 2015).
- Lovett, G.M.; Burns, D.A.; Driscoll, C.T.; Jenkins, J.C.; Mitchell, M.J.; Rustad, L.; Shanley, J.B.; Likens, G.E.; Haeuber, R. Who needs environmental monitoring? Front. Ecol. Environ. 2007, 5, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biber, E. The Challenge of Collecting and Using Environmental Monitoring Data. Ecol. Soc. 2013, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, A.; Martonakova, H.; Guziova, Z. (Eds.) Environmental Governance Sourcebook; UNDP Regional Bureau for Europe and the Commonwealth of Independent States: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2003.
- Joint Committee for Guides in Metrology (JCGM). International Vocabulary of Metrology, 3rd ed.; JCGM: Sèvres Cedex, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanem, D.; Zhang, J. ‘Efforless Perfection’: So Chinese cities manipulate air pollution data? J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2014, 68, 203–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdieu, P. Il Mestiere di Scienziato. Corso al College de France 2000–2011; Feltrinelli: Milano, Italy, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dijik, T.A. Ideology and Discourse. A Multidisciplinary Introduction; Pompeu Fabra University: Barcelona, Spain, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Saich, T. Governance and Politics of China, 3rd ed.; Palgrave & McMillan: Houndmills, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, W.W. Chinese Politics in the Hu Jintao Era, New Leaders, New Challenges; M.E. Sharpe: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- China Daily. Ecological Civilization. China Daily. 24 October 2007. Available online: http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/opinion/2007–10/24/content_6201964.htm (accessed on 26 May 2016).
- Central Committee of the CPC, State Council. Ecological Civilization System Comprehensive Reform Plan. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/guowuyuan/2015–09/21/content_2936327.htm (accessed on 26 June 2016).
- PRWeb. China Environmental Monitoring Instrument Market and Industry Size, Share, Growth, Opportunity, Trends and Forecast Report 2013–2015. PRWeb. 21 October 2014. Available online: http://www.prweb.com/releases/2014/10/prweb12261166.htm (accessed on 7 December 2015).
- China Daily. China Increasing Investment in Environmental Protection. China Daily. 13 August 2015. Available online: http://europe.chinadaily.com.cn/business/2015–08/13/content_21589192.htm (accessed on 8 August 2016).
- Julian, Z.; Yan, Y.; Christina, H.; Claire, W. China’s Environment. Big Issues, Accelerating Effort, Ample Opportunities. Goldman Sahcs. 13 July 2015. Available online: http://www.goldmansachs.com/our-thinking/pages/interconnected-markets-folder/chinas-environment/report.pdf (accessed on 8 August 2016).
- Xinhua. China Pays for PM2.5 Monitoring, U.S. Biz Gains. Xinhua. 5 March 2012. Available online: http://www.china.org.cn/environment/2012–03/05/content_24805519.htm (accessed on 8 August 2016).
- Daniele, B.; Haiyan, W.; Lisa, P.; Andrea, C.; Elisa, G. Soil environmental management Systems for Contaminated Sites ion China and the EU. Common Challenges and Perspectives for Lesson Drawing. Land Use Policy 2015, 48, 286–298. [Google Scholar]
- Yixiang, D.; Daniele, B.; Paolo, F.; Angela, M.; Andrea, C.; Yun, Z.; Antonio, M. China’s Water Environmental Management towards Institutional Integration. A Review of Current Progress and Constraints vis-a-vis the European Experience. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 113, 285–298. [Google Scholar]
- Economy, C.E. China’s environmental challenge: Political, social and economic implications. Testimony before the Congressional Executive Commission on China Roundtable on the Environment. Council on Foreign Relations. 27 January 2003. Available online: http://www.cfr.org/china/chinas-environmental-challenge-political-social-economic-implications/p5573 (accessed on 26 June 2016).
- Mol, A.P.J. Environmental Governance through Information: China and Vietnam. Singap. J. Trop. Geogr. 2009, 30, 114–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Environment News. Deepen the Implementation of Environmental Protection Reform Measures. Huanjing Bao. 26 April 2016. Available online: http://news.xinhuanet.com/politics/2016-04/26/c_128933549.htm (accessed on 26 June 2016).
- Xinhua. China to Complete Environmental Supervision Reform in Two Years. Xinhua. 11 March 2016. Available online: http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/2016–03/11/c_135179328.htm (accessed on 10 June 2016).
- Huang, Y. Is China Serious About Pollution Control? Councils on Foreign Relations. 20 November 2015. Available online: http://www.cfr.org/china/china-serious-pollution-controls/p37270 (accessed on 20 June 2016).
- Ge, C.; Weng, Z.; Li, H.; Ha, C. Implication of Administrative Talk to Environmental Supervision in China: A Case Study of Anyang City. Chin. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 7, 56–60. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- China Scholarship Council. Major National Key State Laboratories List. Available online: http://www.csc.edu.cn/uploads/出国/教育部主管国家重点实验室名单.xls (accessed on 30 November 2015).
- Xinhua. Environment Ministry Targets Fake Air Quality Data. Xinhua. 1 April 2015. Available online: http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/2015-04/01/c_134117345.htm (accessed on 7 December 2015).
- Wu, X.; Hong, G.; Liu, Q. National Vertical Management Needed for Environmental Data. Zhongguo fazhan guancha. 19 March 2013. Available online: http://theory.people.com.cn/n/2013/0319/c40531-20836763.html (accessed on 10 June 2015).
- McGarrity, J. China Promises Crackdown on Fake Air Quality Data. Chinadialogue. 2 April 2015. Available online: https://www.chinadialogue.net/blog/7828-China-promises-crackdown-on-fake-air-quality-data/en (accessed on 10 June 2015).
- Waggoner, P.E. Forest Inventories. Discrepancies and Uncertainties; Resources for the Future: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Herbstein, F.H. Crystalline Molecular Complexes and Compounds: Structures and Principles; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2005; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, J.E.; Krumholz, H.M.; Gal, B.; Ross, J.S. Reporting of Results in ClinicalTrials.gov and High-Impact Journals. JAMA 2014, 311, 1063–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aylward, M.J.; Rogers, T.; Duane, P.G. Inaccuracy in patient handoffs: Discrepancies between resident-generated reports and the medical record. Minn. Med. 2011, 94, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- CPB Netherlands Bureau for Economic Policy Analysis. Modelling the Reporting Discrepancies in Bilateral Data; CPB: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2007; Available online: http://www.cpb.nl/en/publication/modelling-reporting-discrepancies-bilateral-data (accessed on 7 December 2015).
- Lieberthal, K.G.; Lampton, D.M. (Eds.) Bureaucracy, Politics, and Decision Making in Post-Mao China; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1992.
- Lieberthal, K.G.; Oksenberg, M. (Eds.) Policy Making in China. Leaders, Structures, and Processes; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1988.
- Mertha, A. “Fragmented Authoritarianism 2.0”: Political Pluralization in the Chinese Policy Process. China Q. 2009, 200, 995–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S.Q. Inconsistencies in air quality metrics: ‘Blue Sky’ days and PM10 concentrations in Beijing. Environ. Res. Lett. 2008, 3, 034009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S.Q. Official Air Pollution Data in Beijing Still Failing the Public. China Dialogue. 15 October 2012. Available online: https://www.chinadialogue.net/article/show/single/en/5212-Official-air-pollution-data-in-Beijing-still-failing-the-public (accessed on 10 June 2015).
- Chen, Y.; Jin, G.Z.; Kumar, N.; Shi, G. Gaming in Air Pollution Data? Lessons from China. National Bureau of Economic Research Working Paper Series 18729. Available online: http://www.nber.org/papers/w18729.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2015).
- Cao, J.; Xu, H.; Xu, Q.; Chen, B.; Kan, H. Fine Particulate Matter Constituents and Cardiopulmunary Mortality in a Heavily Polluted Chinese City. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiuzi, F.; Zhongnan, F.; Boas, S.B.V.; George, J. An Investigation of the Quality of Air Data in Beijing. 2014. Available online: http://are.berkeley.edu/~sberto/BeijingJuly16.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2015).
- Caixin. Beijing Releases PM2.5 Air Quality Readings. Caixin. 1 January 2012. Available online: http://english.caixin.com/2012-01-21/100350762.html (accessed on 9 August 2016).
- Wentao, W.; Primbs, T.; Tao, S.; Simonich, S.L.M. Atmospheric Particulate Matter Pollution during the 2008 Beijing Olympics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 5314–5320. [Google Scholar]
- Xibuwang (CnWest). Calling into Question the Battle between Officials and Society over Blue Skies Data in Xi’an. In Shanghai Environmental Protection Bureau; 10 August 2012. Available online: http://www.sepb.gov.cn/fa/cms/shhj//shhj5082/shhj2254/2012/08/73871.htm (accessed on 10 June 2015). [Google Scholar]
- Huashang Bao. In the Past Ten Years Xi’an PM2.5 Reached Lowest Levels on July, Highest in January. Huashang Bao. 2 July 2014. Available online: http://hsb.hsw.cn/2014–07/02/content_8541815.htm (accessed on 10 August 2016).
- Department of Environmental Protection of Shaanxi Province. Environmental Report of Shaanxi Province 2009; Department of Environmental Protection of Shaanxi Province: Xi’an, China, 2010. Available online: http://www.shaanxi.gov.cn/0/1/65/365/370/83864.htm (accessed on 10 August 2016).
- Department of Environmental Protection of Shaanxi Province. Environmental Report of Shaanxi Province 2008; Department of Environmental Protection of Shaanxi Province: Xi’an, China, 2009. Available online: http://www.shaanxi.gov.cn/0/1/65/365/370/67494.htm (accessed on 10 August 2016).
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of China. Ambient Air Quality Standards Draft for Suggestions—Explanatory Notes. 2010. Available online: http://www.mep.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/bgth/201011/W020101130374443039627.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2016). [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, S.; Xu, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhen, Z.; Zhang, G.; Wei, J.; Shen, J.; Yao, D. Variations in Concentrations of Different Size Fractions of Atmospheric Particulate Matter from Jinghe National Climate Reference Observatory in Xi’an, China. J. Earth Environ. 2012, 3, 1085–1090. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fujikura, R.; Kaneko, S.; Nakayama, H.; Sawazu, N. Coverage and Reliability of Chinese Statistics Regarding Sulfur Dioxide Emissions during the Late 1990s. Environ. Econ. Policy Stud. 2006, 7, 415–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Liu, Z.; Geng, Y.; Lindner, S.; Hubacek, K. The gigatonne gap in China’s carbon dioxide inventories. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 672–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The World Bank. Addressing China’s Water Scarcity; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z. Evaluation of the Implementation of Water Pollution Prevention and Control Plans in China: The Case of Huai River Basin; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; Available online: http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/824051468018234962/Evaluation-of-the-implementation-of-water-pollution-prevention-and-control-plans-in-China-the-case-of-Huai-River-Basin (accessed on 31 December 2016).
- Qin, L. China Needs Consistent Data on Water Pollution If Promised Improvements Are to Be Met. China Dialogue. 18 May 2016. Available online: https://www.chinadialogue.net/article/show/single/en/8922-Clear-as-mud-how-poor-data-is-thwarting-China-s-water-clean-up (accessed on 9 August 2016).
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of China. 2011 National Coastal Environmental Quality Report; Ministry of Environmental Protection of China: Beijing, China, 2011. Available online: http://jcs.mep.gov.cn/hjzl/jagb/2011jagb/ (accessed on 9 August 2014).
- State Oceanic Administration of China. 2011 Coastal Environmental Quality Report; State Oceanic Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2012. Available online: http://www.coi.gov.cn/gongbao/huanjing/201207/t20120709_23185.html (accessed on 9 August 2014).
- China Water Risk. Are the Data Real? China Water Risk. 9 July 2014. Available online: http://chinawaterrisk.org/resources/analysis-reviews/pollution-is-the-data-real/ (accessed on 1 August 2014).
- International Business Times. 50 Percent of Water In China May Be Unsafe To Drink. International Business Times. 17 May 2012. Available online: http://www.ibtimes.com/50-percent-water-china-may-be-unsafe-drink-698930 (accessed on 10 June 2015).
- Jing, G.; Hongqiao, L. The Dirty Truth about Water Quality. Caixin Online. 7 May 2012. Available online: http://english.caixin.com/2012-05-07/100387511.html (accessed on 10 June 2015).
- Xinhua. China Focus: Soil pollution data remains secret, stirs public concern. Xinhua. 9 May 2013. Available online: http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/china/2013–05/09/c_124689362.htm (accessed on 8 August 2013).
- Teng, Y.; Wu, J.; Lu, S.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, X.; Song, L. Soil and soil environmental quality monitoring in China: A review. Environ. Int. 2014, 69, 177–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, B.; Yang, L. A Review of Heavy Metal Contaminations in Urban Soils, Urban Road Dusts and Agricultural Soils from China. Microchem. J. 2010, 94, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, A. Heavy Metal pollution in Hunan soil exceeds China’s limits by 1500 times. South China Morning Post. 2 December 2014. Available online: http://www.scmp.com/news/china/article/1653877/heavy-metal-pollution-hunan-soil-exceeds-chinas-limits-1500-times (accessed on 10 June 2015).
- China Environment Chamber of Commerce. Strengthening Environmental Management of Contaminated Sites Is an Extremely Urgent Matter. China Environment Chamber of Commerce. 25 April 2014. Available online: http://www.cecc-china.org/detail/19702.html (accessed on 13 April 2015).
- Bradsher, K. China Asks Other Nations Not to Release Its Air Data. New York Times. 5 June 2012. Available online: http://www.nytimes.com/2012/06/06/world/asia/china-asks-embassies-to-stop-measuring-air-pollution.html?_r=0 (accessed on 11 August 2016).
- Tsai, L. Quantitative Research and Issues of Political Sensitivity in Rural China. In Contemporary Chinese Politics. New Sources, Methods, and Field Strategies; Carlson, A., Gallagher, M.E., Lieberthal, K., Manion, M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010; pp. 246–265. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y. Between State and Peasant: Local Cadres and Statistical Reporting in Rural China. China Q. 2000, 163, 783–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch-Weser, I. The Reliability of China’s Economic Data: An Analysis of National Output; U.S.-China Economic and Security Review Commission Staff Research Project; U.S.-China Economic and Security Review Commission: Washington, DC, USA, 2013.
- Marinaccio, J. Power and Control of the Chinese Communist Party: An Introduction to China’s Cadre Management; Passerino Editore: Gaeta, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, W.; Yongheng, D.; Jun, H.; Randall, M.; Bernard, Y. Incentives and Outcomes: China’s Environmental Policy. Available online: http://www.ires.nus.edu.sg/workingpapers/IRES2013-004.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2016).
- Chung, C.K.L. Upscaling in Progress: The Reinvention of Urban Planning as an Apparatus of Environmental Governance in China. In Population Mobility, Urban Planning and Management in China; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 171–187. [Google Scholar]
- Asia-Europe Meeting (ASEM). ASEM Seminar on Sustainable Management of Water Resources in the Context of Urbanization—Changsha Declaration. Available online: http://www.aseminfoboard.org/documents/asem-seminar-sustainable-management-water-resources-context-urbanisation-changsha (accessed on 11 June 2016).
- Wuxi City Small Leading Group for the Planning and Construction of Lihu City. Unveiling the Beauty of Lihu Lake. Wuxi Well on Its Way towards Ecological Wellbeing; Phoenix Press Group and Phoenix Publishing House: Wuxi, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Economy, E. The River Runs Black: The Environmental Challenge to China’s Future; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Ortolano, L. Environmental Regulation in China: Institutions, Enforcement, and Compliance; Rowman and Littlefield: Lanham, MD, USA; Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Van Rooij, B. Implementation of Chinese Environmental Law: Regular Enforcement and Political Campaigns. Dev. Chang. 2006, 37, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CCTV. China to Set up Vertical System to Reduce Local Government Interference in Environment Protection. CCTV. 21 January 2016. Available online: http://newscontent.cctv.com/NewJsp/news.jsp?fileId=338000 (accessed on 9 August 2016).
- Informant Interview #0430, 2014 (collected by the author).
- Informant Interview #0715a, 2013 (collected by the author).
- Key Informant Interview #0315, 2014 (collected by the author).
- Kostka, G.; Mol Arthur, P.J. Implementation and Participation in China’s Local Environmental Politics: Challenges and Innovations. J. Environ. Policy Plan. 2013, 15, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Informant Interview #0610, 2014 (collected by the author).
- Public Statement #0109, 2012 (collected by the author).
- Liu, C. Peking University Report Says Government Is Lying about Air Pollution Problem. The Nanfang. 27 April 2015. Available online: https://thenanfang.com/bju-report-refutes-official-stance-beijing-air-pollution/ (accessed on 10 June 2015).
- BBC News. China Takes under the Dome Anti-Pollution Film Offline. BBC News. 7 March 2015. Available online: http://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-31778115 (accessed on 10 June 2015).
- Kotska, G. Barriers to the Implementation of Environmental Policies at the Local Level in China. World Bank Policy Research Working Paper 7016. Available online: http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/102001468220778402/pdf/WPS7016.pdf (accessed on 17 August 2016).
- Zhang, Z. Programs, Prices and Policies towards Energy Conservation and Environmental Quality in China; FEEM Fondazione Eni Enrico Mattei Research Paper Series No 60.2014; FEEM: Milan, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- David, S.; Kathy, C. False Emissions Reporting Undermines China’s Pollution Fight. Reuters. 17 January 2016. Available online: http://www.reuters.com/article/us-china-power-emissions-idUSKCN0UV0XS (accessed on 15 August 2016).
- Reuters. China Environment Bureau Says Coca-Cola Bottling Plant Falsified Pollution Data. Reuters. 22 October 2015. Available online: http://www.reuters.com/article/us-coca-cola-china-idUSKCN0SG0LL20151022 (accessed on 15 August 2016).
- Informant Interview #0613, 2015 (collected by the author).
- Key Informant Interview #0401, 2014 (collected by the author).
- Barry, N. SASAC and Rising Corporate Power in China. China Leadership Monitor, 12 March 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Economy, E. Environmental Enforcement in China. In China’s Environment and the Challenge of Sustainable Development; Kristen, A.D., Ed.; M.E. Sharpe: Armonk, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 102–120. [Google Scholar]
- Brodsgaard, K.E. Cadre and Personnel Management in the CPC. China Int. J. 2012, 10, 69–83. [Google Scholar]
- Informant Interview #0809, 2013 (collected by the author).
- Moorman, J.L.; Zhang, G. Promoting and Strengthening Public Participation in China’s Environmental Impact Assessment Process: Comparing China’s EIA Law and U.S. NEPA. Vt. J. Environ. Law 2007, 8, 282–335. [Google Scholar]
- Informant Interview #1102, 2014 (collected by the author).
- Bao, X. China’s EIA Industry Rife with Fraud. China Dialogue. 3 November 2014. Available online: https://www.chinadialogue.net/article/show/single/en/7449-China-s-EIA-industry-rife-with-fraud- (accessed on 10 August 2015).
- Qie, J. MEP Has Named 15 Companies Guilty of Producing Fraudulent Environmental Impact Assessments: The Participants to the Survey Had Not Filled in the Investigation Form. Legal Daily. 27 November 2015. Available online: http://www.thepaper.cn/newsDetail_forward_1401898 (accessed on 10 August 2015).
- Spence, J.D. The Search for Modern China; W.W. Norton & Company: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Elman, B.A. A Cultural History of Modern Science in China; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X. Deng Xiaoping Wenxuan—Di Er Juan; Renmin Chubanshe: Beijing, China, 1993; Volume II. [Google Scholar]
- Nature. The Future of Chinese Research-Editorial. Nature 2016, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhalgh, S. Just One Child. Science and Policy in Deng’s China; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA; Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Informant Interview #0715b, 2013 (collected by the author).
- Link, P. An Anatomy of Chinese; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Schoenals, M. Doing Things with Words in Chinese Politics: Five Studies; Center for Chinese Studies: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Daniele, B. Politicizzazione Della Ricerca Orientata Alle Politiche Pubbliche Nella Repubblica Popolare Cinese. In Proceedings of the XIV Conference of the Italian Association of Chinese Studies, Procida, Italy, 19–21 September 2013; Available online: http://www.aisc-org.it/AISC_Atti_XIV_Convegno_con_segnalibri.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2015).
- Tod, K.; Rongkun, L. Taking the Pulse: The One-Year Anniversary of China’s Open Government Information Measures. Wilson Center. 7 July 2011. Available online: https://www.wilsoncenter.org/publication/taking-the-pulse-the-one-year-anniversary-chinas-open-government-information-measures (accessed on 17 August 2016).
- Yang, G. The Internet and Emerging Civil Society in China. In Debating Political Reform in China: Rule of Law vs. Democratization; Zhao, S., Ed.; M.E. Sharpe: Armonk, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Larson, C. In China, a New Transparency on Government Pollution Data. Yale Environment 360. 20 December 2010. Available online: http://e360.yale.edu/featurein_china_a_new_transparency_on_government_pollution_data/2352/ (accessed on 10 June 2015).
- National Resources Defence Council (NRDC); Istitute of Public and Environmental Affairs (IPE). Cutting through the Fog with China’s First Pollution Information Transparency Index (PITI); NRDC-IPE: New York, NY, USA; Beijing, China, 2009; Available online: https://www.nrdc.org/international/piti/files/chinapiti.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2015).
- China Water Risk. Environmental Transparency in 120 Chinese Cities Revealed. China Water Risk. 9 June 2014. Available online: http://chinawaterrisk.org/notices/environmental-transparency-in-120-chinese-cities-revealed/ (accessed on 10 June 2015).
- Reuters. China to Toughen Inspection on Air Quality Data: Xinhua. Reuters. 1 April 2015. Available online: http://www.reuters.com/article/2015/04/02/us-china-pollution-idUSKBN0MT06H20150402 (accessed on 10 June 2015).

© 2017 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brombal, D. Accuracy of Environmental Monitoring in China: Exploring the Influence of Institutional, Political and Ideological Factors. Sustainability 2017, 9, 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9030324
Brombal D. Accuracy of Environmental Monitoring in China: Exploring the Influence of Institutional, Political and Ideological Factors. Sustainability. 2017; 9(3):324. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9030324
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrombal, Daniele. 2017. "Accuracy of Environmental Monitoring in China: Exploring the Influence of Institutional, Political and Ideological Factors" Sustainability 9, no. 3: 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9030324
APA StyleBrombal, D. (2017). Accuracy of Environmental Monitoring in China: Exploring the Influence of Institutional, Political and Ideological Factors. Sustainability, 9(3), 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9030324





