Abstract
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) have become one of the major public health threats to the sustainable development of human beings. Among all of the STIs in China, three are listed as the notifiable infectious diseases, i.e., gonorrhea, syphilis, and HIV/AIDS, which demand more attention. This study aims to detect, describe, and compare the spatial-temporal clustering of these notifiable STIs in China and to relate spatial analysis results to epidemiologic trends during the past decade. A descriptive epidemiology analysis and a spatial autocorrelation analysis (global and local) are adopted to study the epidemiologic trends and spatial changing patterns of STIs respectively. The results indicated that there were regional disparities and spatial clusters in the spatial distribution of notifiable STIs in China. However, the incidence rates of the three notifiable STIs displayed relatively different characteristics in epidemiologic trends and the agglomeration level. Overall, the Yangtze River Delta region, the southwestern border area, and some other border regions are the places demanding more attention. In the end, we propose a three-dimensional prevention and control strategy, which focuses on not only the most-at-risk populations, but also the most-at-risk areas and most-at-risk timings. Besides, some measures targeting more than one STI should also be formulated.
1. Introduction
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), which are also referred to as venereal diseases, have been public health threats for centuries due to their high morbidity and mortality in both high- and low-income countries. Economically, STIs impose a heavy burden on the health expenditure of both households and national health systems around the world. The physical and psychological consequences resulting from STIs are also associated with the worsening conditions of individuals’ well-being [1]. Due to the malignant sexual, reproductive, and newborn health consequences, STIs impede sustainable human development in the 21st century.
As the biggest developing country in the world, China has been suffering from the epidemics of STIs for a long time. Among more than 30 STIs that can be infected or acquired predominantly through sexual contact, three are linked to the high incidence of illness and are therefore listed as the notifiable infectious diseases, which are highlighted in the Law of the People’s Republic of China on the Prevention and Treatment of Infectious Diseases [2]. Of the three notifiable sexually transmitted infections, two are classical STIs and currently curable, namely syphilis and gonorrhea, and one is human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)/AIDS that is incurable but susceptible to mitigation through treatment [3]. It is important to note that there are still other routes of transmission (blood, mother-to-child) of HIV/AIDS, but its transmission by sexual activities displays a substantial increase and has become a primary transmission mode in China recently [4]. According to the China Health and Family Planning Statistical Yearbook 2016 [5], syphilis, gonorrhea, and HIV/AIDS were all fairly active all over the country in 2015, with their reported cases ranking the third (433,974 reported cases), fifth (100,245 reported cases), and eighth (50,330 reported cases) among all of the 42 notifiable infectious diseases, respectively.
In literature, the academic world has been committed to improving policy designing for the control and prevention of notifiable STIs in China. First of all, the epidemiologic trends of STIs have always been the focus of numerous scholars. For instance, Chen et al. [6] reviewed the epidemiologic trends of STIs in China based on the national system of STI surveillance and concluded that the epidemic pattern of STIs in China is different from that in developed countries. Li and his colleagues [7] retrospectively studied the HIV/AIDS morbidity, mortality, and also the case fatality rate in China from 2004 to 2011. Tan et al. [8] used wavelet transformation and Fourier analysis to assess the temporal trends of monthly reported syphilis and gonorrhea cases in Guangdong province. Yan et al. [9] investigated the shift in the epidemiological features of HIV/AIDS in Fujian province. The epidemiologic trend analyses provided important evidence for understanding the epidemic situation. However, the temporal analysis alone is not enough for the making of targeted control programs.
In recent years, scholars have paid more and more attention to the spatial distribution of STIs epidemics in China. Peng et al. [10] applied spatial autocorrelation analysis to study the spatial distribution of HIV/AIDS in the Yunnan province. Targeted at Shenzhen, Wu et al. [11] conducted a spatial clustering analysis on the primary/secondary syphilis cases and detected the high-risk areas for spatially targeted control measures. Qian and his colleagues [12] introduced 17 provincial variables to the hierarchical clustering analysis for forming HIV/AIDS sub-epidemic areas in China. Zhang [13] analyzed the distribution patterns of the HIV/AIDS epidemic in a western provincial unit and explored its relationship with economic input factors. Chen et al. [14] implemented Kulldorff’s spatial scan statistic to identify spatial clusters of risky sexual behaviors and STIs in Guangzhou. Additional spatial analysis can be found in certain population groups, such as the HIV/AIDS spatial analysis among the elder adults (≥50 years old) in China [15], and spatial temporal analysis on the HIV/AIDS epidemic among young people (15–24 years old) [16].
Despite the accumulation of knowledge, few studies did a comprehensive spatial-temporal analysis on all of the notifiable STIs or compare their spatial changing patterns. However, the comparison of different spatial changing patterns of all of the notifiable STIs is of great importance for their prevention and control. The reasons can be twofold: firstly, the correlations of different STIs should not be ignored, many studies have proven that STIs can expedite the disease processes of each other, and many STIs even facilitate the acquisition of HIV/AIDS [15,16]. Secondly, unlike other infectious diseases, STIs share the same route of infection, similar high-risk population groups and overlapping prevention and control measures, which provides great possibilities for their combined prevention and treatment. This study is initiated to detect, describe, and compare the spatial-temporal clustering of notifiable STIs at the provincial level and to relate spatial analysis results (global and local) to epidemiologic trends during the past decade, we hope that this study can provide more region-oriented evidence for control and prevention policy making of STIs in China.
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data Resources
To better monitor the new cases of notifiable infectious diseases, the Chinese government built the Diseases Reporting Information System (DPRI), which ensures that the local medical institutions to report the infected cases within 24 h (even 2 h for a few diseases, such as Severe Acute Respiratory Syndromes). First-diagnosis doctors and laboratory personnel are responsible for the record and report by means of report cards and Internet. With several procedures, such as amendments, supplementary reports, and reexamination, the data for all of the notifiable infectious diseases are summarized by the national Center for Diseases Control and Prevention (CDC).
We obtained the year-end incidence data of the three notifiable STIs in mainland China during 2005 and 2015 from China’s Health and Family Planning Statistical Yearbook (it is also referred to as China's Health Statistical Yearbook before the merge of National Population and Family Planning Commission and National Health Ministry in 2013). Please see the Supplementary Material Tables S1–S3 for the incidence data in each provincial unit during 2005–2015. Its relevant population data was obtained from the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS). The data were collected at the provincial level in Mainland China, excluding Hong Kong and Macao. Please see the Supplementary Material Figure S1 for the Chinese administrative divisions and their names.
2.2. Descriptive Epidemiology Analysis
Epidemiology analysis includes the temporal trends of STIs incidence rates across the nation and also in each provincial unit. Incidence rates are expressed as the number of new cases per 100,000 population in each year. This study uses the box plots to illustrate the temporal trends of the incidence rates and also the differences between provincial units. To better demonstrate the trends of incidence of notifiable STIs, the observation time is divided into two equal periods (2005–2010, 2010–2015). The growth rates of the incidence rates in each sub-period were calculated. The subsequent spatial studies also focus on these three time points (2005, 2010, and 2015).
2.3. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
Spatial autocorrelation analysis is often employed to investigate the geographical relationship of the research targets in a number of continuous geographical units. Figure 1 is an illustration of spatial autocorrelation, in which each square represents a geographical unit and the color stands for the incidence of notifiable STIs in the provincial units in China. The darker the color, the higher the incidence rate. The figure on the left reflects the pattern of random distribution. The one in the middle reveals a positive spatial autocorrelation, which implies the clustering of similar values. It indicates either the clustering of provincial units with high incidence rates of STIs, or low incidence rates, i.e., high-high clustering pattern or low-low clustering pattern. However, if a provincial unit with a high incidence rate is surrounded by units with low ones, or vice versa, it indicates a negative spatial autocorrelation, as shown in the figure on the right.

Figure 1.
An illustration of spatial autocorrelation.
Drawing data across a time span of 10 years, this study attempts to delineate the time-geography of STIs in China. Among all of the indicators for spatial autocorrelation, Moran’s I is one of the universally adopted indicators to explore the spatial distribution of infectious diseases and has been widely used in other studies [17,18,19,20,21,22,23]. Specifically, the global and local Moran’s I are both employed in this study to examine the geographical distribution patterns of STIs. They both illustrate to what extent, similar and discrepant values of geographic units are clustered in the research area.
2.3.1. Spatial Weight Matrix
Before conducting the autocorrelation analysis, a spatial weight matrix, which contains the geographical information of observation units, needs to be established. Whether two geographical units border with each other or not is taken as the standard of spatial weight measurement. If provincial unit i and j border with each other, then the value of is 1; if not, then the value will be 0. Although separated by a narrow strait, we still consider Hainan and Guangdong as bordering provinces, as the population exchange and mobility of the two provinces are massive. As there are 31 provincial units in total, the 31 × 31 spatial weight matrix has been established as follows. In addition, because each provincial unit may have a different number of neighbors, we have row-standardized the matrix.
2.3.2. Global Moran’s I
Global Moran’s I drops between the realm from −1 to 1. Approaching 0 means a more random distribution of the high/low values (the incidence rate of STIs). If approaching 1, it signifies that there is a clear concentration of similar values (provincial units of high STIs incidence with high ones or units of low incidence rates with low ones), while a number approaching −1 represents a concentration of different values. Formula (2) explains how the global Moran’s I is calculated, and stand for the incidence rates of the three notifiable STIs in provincial units i and j, whereas is the mean value. , which has been explained in the previous section, is the spatial weight matrix.
2.3.3. Local Moran’s I
Local Moran’s I is used to indicate the spatial autocorrelation of each principal units with the surrounding units. It is also understood as “Local indicator of spatial association”, which is shortened as LISA [24]. Formula (3) shows the calculation process of local Moran’s I.
As the indicator only focuses on one certain unit and its bordering region, the sum of j will be limited to the adjacent units of i. is a constant across all of the provincial units. It is consistent and is used to estimate the variance. In like vein, the value of local Moran’s I is also a number from −1 to 1 and the value can be explained exactly in the same way as that of the global Moran’s I. The function of local Moran’s I lies in the detection of spatial clusters, which helps to reveal the spatial-temporal changing patterns of STIs across the past 10 years [25].
2.3.4. Corresponding Mapping Tools
This study provides three kinds of maps: hierarchical maps, univariate LISA cluster maps, and clustering frequency maps. In order to create a hierarchical map, data of the incidence rates of notifiable STIs in the 31 provinces were classified into four classes (better, good, bad, worse) by the method of natural breaks, which shows the minimum differences between the incidence rates of three STIs in the same group and the maximum difference across groups [26]. After that, the data was loaded into China’s administrative division vector diagram with a provincial boundary.
The map, which highlights the areas with significant local Moran’s I, is known as a univariate LISA cluster map. Based on the incidence rates (value size) and local Moran’s I (positive or negative), the cluster areas are divided into four types of clustering patterns, namely, high-high (HH), high-low (HL), low-low (LL), and low-high (LH) clusters. The threshold level of significance is 0.05. It is ordinary that in most spatial autocorrelation analysis, only some of the geographical units can reach the significant level.
Clustering frequency map is a sum of all of the clustering patterns of three STIs across all of the provincial units in China at 2005, 2010, and 2015, respectively, which serves as a direct visualization of the clustering patterns of notifiable STIs in China.
2.4. Softwares
The global Moran’s I and local Moran’s I values were measured using software GeoDa (Version 1.8.61, GitHub, San Francisco, CA, USA). Hierarchical maps, univariate LISA cluster maps, and cluster frequency maps were developed with ArcGIS (Version 10.0, Redlands, CA, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Epidemiological Trends
Table 1 summarizes the incidence rate of three notifiable STIs from 2005 to 2015, while Figure 2 visualizes such trends in box plots annually. Many details can be concluded from Table 1. HIV experienced a dramatic increase in terms of the incidence rate from 2005 to 2010, and the trend continued and rocketed up further in some provinces in the second half period. For example, the incidence rate in Sichuan was 0.11 (Unit: 1/100,000, the same below) in 2005, a comparatively moderate figure across all the provincial units. However, the epidemic shot up in the subsequent 5 years, increasing by 1664% and this trend continued with a substantial growth rate of 392% from 2010 to 2015. The final incidence rate was 9.55 in Sichuan after the boom of HIV epidemic and this figure ranked high among all of the provincial units in China.

Table 1.
Growth of incidence of sexually transmitted diseases in China (1/100,000).
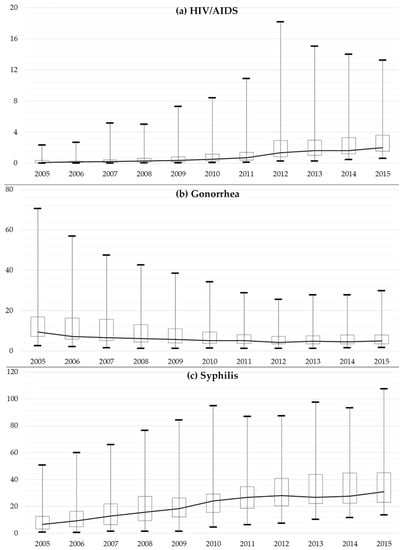
Figure 2.
Box plots of the incidence rates of three notifiable sexually transmitted infections (STIs) from 2005 to 2015 (1/100,000).
It should be highlighted that this trend was not incidental but a general trend throughout China. The only exception was Henan, which went through a downward trend (−33%) of HIV incidence in the first five years. The incidence rate of HIV in Henan was the highest in 2005 (2.35), and its number was 3.26 in 2015, a very moderate growth rate in China. Equally noticeable is that some provincial units were originally not so outstanding in terms of the incidence rates of HIV. However, with a constant and substantial increase in the 2-successive period, the incidence rates in Guangxi and Yunnan finally reached 13.25 and 12.31 in 2015, ranking as the top two among all the provincial units. Their original figures were 1.85 and 0.72. They were the only two provinces whose incidence rates were higher than 10. Although the incidence rates in some provincial units remained low in the end, say, Neimenggu (0.83) and Hebei (0.92), it is obvious that almost all of them experienced a considerable growth.
The black line in Figure 2 indicates the median value of STIs incidence across the provinces and it signifies the continued growing trend of HIV/AIDS in the past decade. The box plots diagram also indicates that the maximum reported number in one provincial unit went up before 2012 and then decreased gradually thereafter. The situation for gonorrhea showed a reversed picture. It can be summarized from Figure 2 that the maximum number of reported cases in one province dropped until 2012, and then stayed at a stable level. There is no obvious increase in the median value of all the provincial units across the past decade. Table 1 suggests that the provincial units went through a decrease in the incidence rate of gonorrhea in the first five years, with Beijing achieving the biggest decrease of −67%. Its incidence rate constantly dropped from 26.93 to 8.83, and finally to 5.14 in 2015. Shanghai had the highest incident rate of gonorrhea in 2005, whose figure was 70.62. It finally plummeted to 29.82, with an increase rate of −60% and 6% in the two time breaks. This was still the highest incidence rate in 2015 and it was closely followed by the bordering province Zhejiang, whose incidence rate was 29.41. A majority of the provincial units continued the downward trend in the second five years. However, it should be noted that the incidence in Hainan suddenly jumped up with an increase of 96%, reaching a standard even higher than 2005. It was rarely seen throughout the country.
As to Syphilis, its incidence rate constantly grew in most of the provincial units in the past 10 years, with Xizang having the most rapid growth (903% for the first five years and 341% for the second). Its incidence rate started from 0.76 in 2005 and ended up with 33.57 in 2015. Although the growth rate was rather outstanding, its incidence rate was not among the top group. The provincial unit with the highest incidence rate of syphilis in 2015 was Xinjiang, whose figure was 107.51, rising from 10.08 in 2005. The provincial units with the lowest incidence rate after a 10-year growth were Hebei (13.05), Shandong (15.00), and Henan (17.04) in 2015. It should also be noticed that the epidemic had been continued to grow in the second five years, although the growth rate is not as high as that of HIV. The box plots draw a similar picture, with the median value of reported cases in all provincial units going up substantially.
3.2. Global Spatial Autocorrelation
Table 2 shows the global spatial autocorrelation of STIs and their test results. For HIV/AIDS and syphilis, the test reaches the significance threshold for most of the years and as to gonorrhea, the data from all of the selected years are significant. In general, the global Moran’s I for HIV/AIDS increased throughout the past 10 years from around 0.0293 to about 0.3402, suggesting a stronger spatial autocorrelation and an increasing geographical unevenness in its epidemiologic trends. The value of Moran’s I implies a clear tendency in spatial autocorrelation as compared with other research of infectious diseases. Regarding gonorrhea, after experiencing a slight decrease in its global Moran’s I, its degree of spatial autocorrelation increased moderately and finally reached around 0.47 in 2015. This value is extremely high, indicating that imperative measures is needed to control the epidemic in certain hot-spot geographical units. The spatial autocorrelation of syphilis had been turning less significant in the past ten years. Its global Moran’s I went down from 0.3789 to 0.1099, implying that the geographical unevenness of the disease is less obvious than it used to be.

Table 2.
Global spatial autocorrelation analysis and test results.
3.3. Local Spatial Autocorrelation
Figure 3 illustrates the hierarchy maps of the incidence rate of HIV and its univariate LISA cluster maps. From the hierarchy map, it can be concluded that although the general incidence rate of HIV/AIDS increased, the middle provincial units were no longer the most plagued provinces of HIV. However, the situation in the southwest provinces deteriorated dramatically from 2010 to 2015, with the provinces reporting the highest level of incidence of HIV/AIDS expanded from Guangxi, to the adjacent provincial units of Yunnan, Sichuan, and Chongqing. The LISA maps demonstrate a more direct and appalling trend of the epidemics of HIV/AIDS. In 2005, only LL clustering pattern was found in the northeast provinces of Neimenggu, Heilongjiang, Jilin, and Liaoning. Nevertheless, the LL clustering pattern shrank in 2010 with two HL pattern appearing (Xinjiang and Henan). What is worse, Yunnan and Guangxi showed a HH clustering pattern as well. In 2015, such HH regions further stretched to bordering provinces of Guizhou and Hunan, indicating the spreading trend of the disease. At the same time, the LL pattern was detected as well in a large territory of the middle and north provinces including Henan, Hebei, Jilin, Liaoning, and Neimenggu.
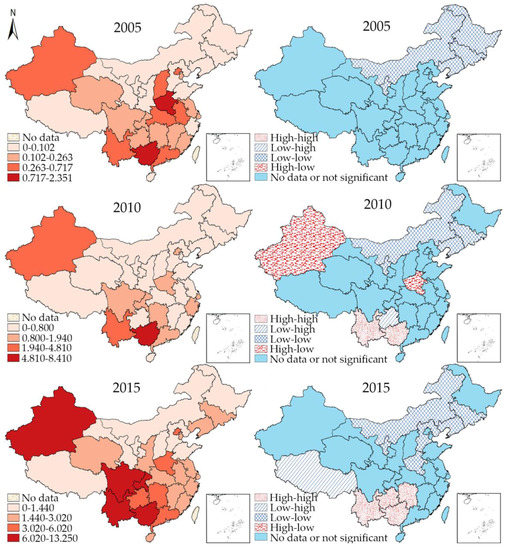
Figure 3.
Hierarchy map (left) and univariate local indicator of spatial association (LISA) cluster map (right) of HIV/AIDS in 2005, 2010, and 2015.
The epidemic trend of gonorrhea was the other way around. Figure 4 is the hierarchy and LISA cluster maps of gonorrhea. The incidence rate of gonorrhea in the past ten years was comparatively stable. The highest incidence rate has always been in Shanghai, and Zhejiang. The epidemic was also serious in the coastal provinces such as Jiangsu, Fujian, Guangdong, and Guangxi in southern and eastern China. Most of the middle, western, and northern provincial units had a lower incidence rate in the observation period. The LISA maps highlighted the hot spots and cold spots of gonorrhea, with the former always concentrating in the east coastal provincial units, namely, Jiangsu, Shanghai, Zhejiang, and Fujian. However, new hot spot regions gradually appeared as HL patterns emerged in Xinjiang, Beijing, and Neimenggu, gradually. The LL pattern was sporadically detected in some northern and middle provinces.
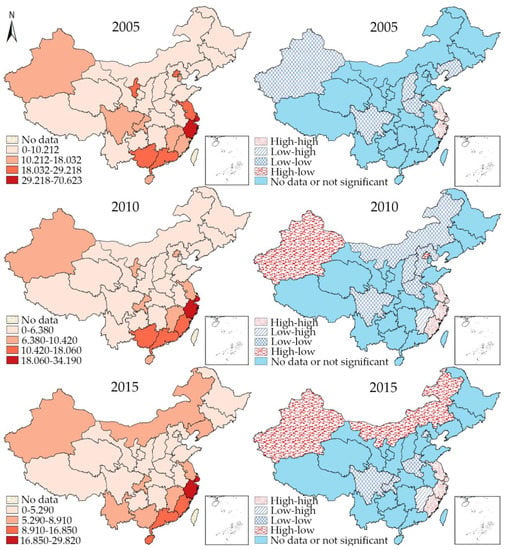
Figure 4.
Hierarchy map (left) and univariate LISA cluster map (right) of gonorrhea in 2005, 2010, and 2015.
Figure 5 shows the hierarchy and univariate LISA cluster maps of syphilis in the year 2005, 2010, and 2015. The hierarchy maps indicate that in 2005, the incidence of syphilis was mostly detected in the eastern coastal provinces, with Zhejiang and Shanghai ranking the highest, while the epidemic in most other provinces was less serious. Throughout the ensuing 10 years, the general incidence rate increased slightly in these provincial units, yet the overall infections in some other provinces grew much more rapidly, particularly in Xinjiang. New hot spots emerged during the decade. As to the LISA maps, the most noticeable characteristic is that the concentration of HH clusters of syphilis infection gradually shrank from Jiangsu, Shanghai, Zhejiang, and Fujian, and finally disappeared in 2015. In parallel, the LL clusters also reduced from many middle and northern provincial units to Henan, Shandong, Tianjin, and Beijing in 2015. The other two types of clustering were not significant for most of the time, except that in 2015, Ningxia revealed a LH clustering pattern. In general, the HH clusters of provincial units dropped significantly during the observation period.
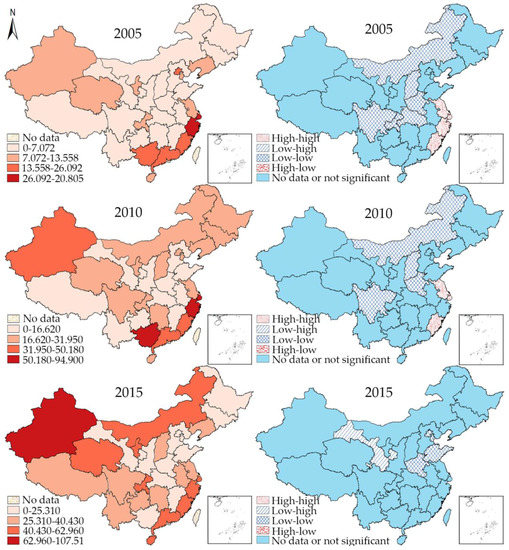
Figure 5.
Hierarchy map (left) and univariate LISA cluster map (right) of syphilis in 2005, 2010, and 2015.
3.4. Frequency Summary of the Spatial-Temporal Clusters
Despite the relatively different epidemiologic trends and spatial changing patterns of three notifiable STIs, a spatial demonstration of STIs as a whole on the national scale is necessary due to their overlapping prevention and intervention approaches, as well as similar most-at-risk-populations (MARPs). Figure 6 is the summary of all the high (including HH and HL) and low (LL and LH) distribution patterns of all three STIs. In general, Shanghai and Jiangsu were mostly plagued with STIs and they appeared over five times in HH or HL clustering patterns. They are particularly affected by syphilis and gonorrhea. Other hot spot regions include border provinces such as Guangxi, Yunnan, and Xinjiang, with the former two especially prominent in the incidence rate of HIV/AIDS. In contrast, many of the northern and middle provinces appeared in LL or LH distribution patterns several times. Sichuan, Henan, and Neimenggu appeared in LL or LH patterns over five times, followed by Liaoning and Shanxi (four times). Other provinces include Ningxia and Jilin (three times), Jiangxi, Chongqing, Hebei, and Beijing (two times).
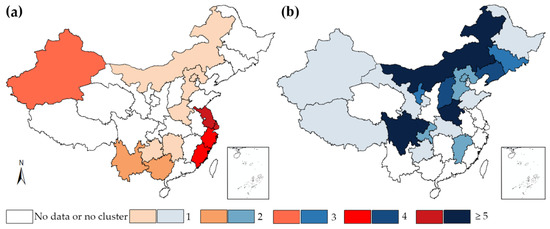
Figure 6.
Frequency of cluster occurrence among notifiable STIs during 2005, 2010, and 2015. (a) for high–high and high–low clusters and (b) for low–low and low–high clusters.
4. Discussion
In order to improve the knowledge of notifiable STIs prevention and control in China, the investigation of epidemiologic trends and spatial changing patterns are of vital importance. Nevertheless, existing studies paid little attention to the comparison of different STIs’ spatial changing patterns and seldom related them to epidemiologic trends. The findings of this study, therefore, supplement previous studies and serve as references for policy makers to develop disease-combined and region-oriented STI control and prevention strategies.
First of all, we would like to compare the epidemiologic trends and overall agglomeration level of the three notifiable STIs. As for the former, this study further extends the study of Zhang and Wilson [27], who reviewed the trends in notifiable infectious diseases before 2010 and discovered the different epidemiologic trends in notifiable STIs. As reported previously, the nationwide incidence rate of HIV/AIDS increased dramatically during 2005–2015, that of syphilis has also been growing but with a slower speed during the same time. In comparison, the incidence rate of gonorrhea dropped at first but remained stable in the second five years. However, the epidemiologic trends differ greatly between provincial units, thus resulting in the changes in agglomeration level and clustering areas. The results of global Moran’s I indicate that the incidence rate of all the notifiable STIs tended to aggregate at the provincial level. The significant global Moran’s I of gonorrhea, syphilis, and HIV/AIDS at most observation time points meet our expectations as the spatial cluster feature is an inherent attribute of the infectious diseases. It is also consistent with other studies on the STIs [15,16]. However, the trends of global Moran’s I reflect the diverse spatial distribution characteristics of notifiable STIs. The rapid increase in the incidence of HIV/AIDS is accompanied by the swift growth of its global Moran’s I, indicating the ever increasing unevenness and deteriorating conditions in the geography of HIV/AIDS epidemics (certain regions are more plagued with the disease and it has been expanding to surrounding regions). In comparison, the agglomeration level of syphilis decreased during the whole period, with its global Moran’s I reducing from 0.3789 in 2005 to 0.1099 in 2015. It is worth mentioning that the global Moran’s I of gonorrhea showed a slow growth despite the decreasing trend of its incidence. To conclude, the rapid increase of HIV/AIDS and syphilis incidence, as well as the stable incidence of gonorrhea, revealed the serious situation of STIs prevention and control confronting the Chinese health sector. The reasons can be twofold. First, higher levels of population mobility in contemporary China have significantly multiplied the possibility of STI transmission. This does not only involve the labor migration, but also the mobility of female sex workers [28]. Besides, the emergence of antimicrobial resistance in all bacterial STIs and the particular problem of resistant gonorrhea present a challenge to STIs prevention, control, and elimination [29].
Secondly, the summary of the spatial cluster frequency provides important evidence for targeted prevention and control programs. The results of local spatial autocorrelation analysis, i.e., detection of spatial clusters, have confirmed the significant spatial variation in STIs epidemic at the provincial level and specified two priority areas: south-western border area (Yunnan, Guangxi) and the Yangtze River Delta region (Zhejiang, Shanghai, Jiangsu). It means that the clusters of STIs have gone beyond the provincial level and exhibited a trend of regionalization. Among the three STIs, HIV/AIDS is particularly prominent in the former region, while gonorrhea and syphilis in the latter. In 2015, Yunnan and Guangxi were the only two provincial units whose incidence rate of HIV/AIDS exceeded 10/100,000. It is in he Yunnan province that the first case of HIV/AIDS was discovered in 1985 in China [10]. One of its underlying causes is probably the heroin trafficking route starting from the “Golden Triangle”, which opens the door for HIV/AIDS transmission in China. There are a large number of injection-drug users in Yunnan and the illegal trade across the borders is rampant. In addition, the high mobility of a mass population might be accredited as the catalyst for the high incidence of HIV as well. The border provinces are insufficient in prevention measures, and therefore quite a number of the population are exposed to high-risk behaviors, namely, incorrect use of condoms, etc. [30].
In comparison, the Yangtze River Delta region is the clustering area of both gonorrhea and syphilis. It is one of the three most integrated and dynamic city-regions in China, consisting of four provincial units, i.e., Anhui, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Shanghai. In addition to Shanghai, the core city, there are a number of regional center cities, such as Hangzhou and Nanjing. Other cities such as Wenzhou, Ningbo, Wuxi, and Suzhou are also highly developed. In 2005, the HH clustering areas of syphilis mostly overlapped with that of gonorrhea, while their differences lie in the spatial-temporal changing patterns. The HH cluster areas of gonorrhea have been expanding while the other one has been shrinking. The incidence rate of gonorrhea in Shanghai, Jiangsu, and Zhejiang showed a HH cluster feature and were significant at every time point, with Fujian also being significant in 2015. In comparison, the HH cluster feature of syphilis in the three provincial units shrank, and finally disappeared completely.
Last but not least, there are some interactions between the epidemiologic analysis and the spatial-temporal analysis. In effect, the changes of agglomeration level and spatial-temporal clusters result from the unbalanced growth of the incidence of STIs. Therefore, we would like to discuss the results with a combination of the epidemiologic trends and spatial analysis. Generally, the epidemiologic trends and global Moran’s I make us better understand the STIs situation. When considered together, the growth rate of STIs incidence and the changes in Global Moran’s I imply relatively different scenarios for each STI. For instance, a decreasing incidence and an increasing global Moran’s I (gonorrhea) indicate the deteriorating situation in cluster areas; increasing incidence and decreasing global Moran’s I (syphilis) indicate the gradually spreading of the epidemic and an increase in incidence rate in most provincial units. Specifically, the spatial-temporal cluster analysis of incidence rates also provides implications for the phases of the STIs epidemics in some provincial units from a geographical perspective. For instance, owing to the high incidence and high growth rates in Yunnan, the incidence rate of HIV/AIDS in the Sichuan province, its neighboring province, increased 1664% during 2005–2010, the biggest jump among all of the provincial units. In like vein, during 2010–2015, the incidence of gonorrhea in most provincial units declined, while the continuously increasing incidence in Jiangxi (2%), Shandong (39%), and Henan (48%) can be attributed their geographical proximity.
To date, STIs have become one of the major challenges faced by the Chinese health sector. However, it is not the first time that the Chinese government faces the STI challenge. Before the founding of the People’s Republic of China, STIs were widespread, especially among the female sex workers in big cities [6]. Since the early 1950s, the Chinese government attacked STIs with massive treatment campaigns and structural measures, such as (1) the establishment of specialized agencies, (2) strikes on commercial sex, (3) reeducation camps for sex workers, and (4) increasing the availability of the diagnostic and treatment services [31]. Through 15-year efforts, STIs were officially reported eradicated in China by 1964. However, in the 1980s, STIs emerged again after China’s reform and opening-up policy [14].
Fortunately, the rapid development in screening technology brings great convenience for STI surveillance. Owing to China’s family planning policy, testing after marriage has become regular, which enables the Center for Disease Control and Prevention to document the health conditions for married women. However, the testing for unmarried men and women is still insufficient. Without basic knowledge of STIs, many people are diagnosed STIs when they have serious symptoms. Since STIs are highly private and the cultural atmosphere in China is rather conservative, knowledge promotion of STIs is restricted to sex education in communities. Little publicity of STIs has been seen on social media and other new media. What is worse, rapid urbanization, the growing mobility of the population, and changes in sexual behaviors result in a great difficulty of STIs prevention and control. By far, the most important tool to assist the control of STIs is early diagnosis and treatment of those infected, and therefore current STI prevention and control measures mainly focus on MARPs, such as the drug users, female sex workers (FSWs), and Men who have sex with men (MSM) [11,32]. Nevertheless, evidence from the epidemiologic trends and spatial changing patterns provide two new dimensions for targeted interventions, with its advantage lying in the detection of priority areas at a specific temporal-spatial spot for infectious diseases prevention and control. By means of the spatial-temporal data analysis, the government can not only focus on the MARPs, but also the most-at-risk areas (MARAs) and most-at-risk timings (MARTs). On the one hand, based on the spatial changing patterns of notifiable infectious diseases and the cluster frequency maps, southwest China, Yangtze River Delta region, some other border regions, and also their neighboring provincial units are the most-at-risk areas (MARAs), which should be the top priority areas for STIs prevention and control in China. In addition, the MARAs with more cluster frequency demand more attention and call for more disease-combined intervention programs. On the other hand, even though two geographical units may have similar incidence rates of STIs, they might be at totally different time points of the epidemiological trends, therefore the control and prevention measures should be tailored to the rising trend and epidemic season (MARTs) of epidemics.
With a limited scope and data availability, this study only targets STIs at the provincial level in China. However, the epidemiologic trends and spatial changing patterns of STIs are often across scales. Zooming into smaller scales, researchers may find more delicate distribution and clustering patterns of STIs, and therefore come up with more specific and solution-specific findings. Besides, the control and prevention of STIs require concerted efforts across scales. Covariates are also important for the analysis of the epidemiology of STIs, which is not the focus on this study. Hence, we call for future inter-scalar research on the distribution patterns and epidemiology trends of STIs.
5. Conclusions
China’s national health would be in jeopardy without effective control of infectious diseases. However, the prevention and control of each kind of infectious diseases on such a large territory is never an easy task. In this retrospective study, the notifiable STIs exhibit various temporal-spatial distribution characteristics among the provinces of China. Syphilis and HIV/AIDS, especially the latter, displayed a strong upwards trend, indicating that it is time to tackle with STIs more seriously.
To address the outbreaks of STIs, collaboration across provincial boundaries should be initiated through effective institutional arrangements, such as collaborative policy design for regional-oriented prevention and control measures. First, we propose the regional preference for the prevention and control programs. For instance, free condom distribution should increase in these priority areas and epidemic seasons, sex/health education should be enhanced, particularly at targeted regions, and most at risk populations (for instance, college students and migrants). Second, the STIs prevention measures should not be limited to the existing programs. For instance, rational sex education course in compulsory education should be guaranteed and optimized. Besides, promotion on television, mobile phones, and the Internet should be mobilized to spread the knowledge on STIs prevention and control.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/9/10/1784/s1, Figure S1: The administrative divisions of China, Table S1: The incidence of HIV/AIDS in each provincial unit during 2005–2015, Table S2: The incidence rate of gonorrhea in each provincial unit during 2005–2015, Table S3: The incidence rate of syphilis in each provincial unit during 2005–2015.
Author Contributions
Bin Zhu and Yang Fu conceived and designed the study; Bin Zhu collected and analyzed the data; Bin Zhu and Yang Fu drafted the paper, Jinlin Liu and Ying Mao read and revised the draft critically. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Schleihauf, E.; Watkins, R.E.; Plant, A.J. Heterogeneity in the spatial distribution of bacterial sexually transmitted infections. Sex. Transm. Infect. 2009, 85, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, I.C.H.; Hao, Y.; Cai, J.; Ying, Y.; Schaible, B.J.; Yu, C.M.; Tse, Z.T.H.; Fu, K.W. Chinese social media reaction to information about 42 notifiable infectious diseases. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Health in 2015: From MDGs to SDGs; World Health Organization: Genova, Switherland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, N. Modeling sexual transmission of HIV/AIDS in Jiangsu province, China. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2013, 36, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health and Family Planning Commission of the PRC. China Health and Family Planning Statistical Yearbook 2016; Chinese Peking Union Medical College Press: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Chen, X.; Gong, X.; Liang, G.; Zhang, G. Epidemiologic trends of sexuallly transmitted diseases in China. Sex. Transm. Dis. 2000, 27, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Shen, Y.; Jiang, X.; Li, Q.; Zhou, X.; Lu, H. Clinical epidemiology of HIV/AIDS in China from 2004–2011. Biosci. Trends 2014, 8, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, N.X.; Tan, G.X.; Yang, L.; Yang, B.; Powers, K.A.; Emch, M.E.; Tucker, J.D. Temporal Trends in Syphilis and Gonorrhea Incidences in Guangdong Province, China. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 209, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Wu, S.; Chen, L.; Yan, P.; Qiu, Y. Shift in HIV/AIDS Epidemic in Southeastern China : A Longitudinal Study from 1987 to 2015. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.-H.; Cheng, Y.-J.; Reilly, K.H.; Wang, L.; Qin, Q.-Q.; Dingi, Z.-W.; Ding, G.-W.; Ding, K.-Q.; Yu, R.-B.; Chen, F.; et al. Spatial distribution of HIV/AIDS in Yunnan province, People’s Republic of China. Geospat. Health 2011, 5, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Tucker, J.D.; Hong, F.; Messina, J.; Lan, L.; Hu, Y.; Wen, L.; Zhang, C.; Feng, T.; Emch, M.E.; et al. Multilevel and spatial analysis of syphilis in Shenzhen, China, to inform spatially targeted control measures. Sex. Transm. Infect. 2013, 88, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, S.; Guo, W.; Xing, J.; Qin, Q.; Ding, Z.; Chen, F.; Zhihang, P.; Wang, L. Diversity of HIV/AIDS epidemic in China: A result from hierarchical clustering analysis and spatial autocorrelation analysis. AIDS 2014, 28, 1805–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Zhou, L.; Ma, D.; Liu, L.; Lu, R.; Yi, D.; Yi, D. The AIDS epidemic and economic input impact factors in Chongqing, China, from 2006 to 2012: A spatial-temporal analysis. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e006669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zhou, F.; Hall, B.J.; Wang, Y.; Latkin, C.; Ling, L.; Tucker, J.D. Spatial distribution and cluster analysis of risky sexual behaviors and STDs reported by Chinese adults in Guangzhou, China: A representative population-based study. Sex. Transm. Infect. 2016, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Li, Y.; Tang, W.; Guo, W.; Ding, Z.; Ding, G.; Wang, L.; Qin, Q.; Xu, Y.; Qian, S.; et al. HIV/AIDS Epidemic Among Older Adults in China During 2005–2012: Results From Trend and Spatial Analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 59, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, W.; Li, Y.; Mahapatra, T.; Feng, Y.; Li, M.; Chen, F.; Li, P.; Xing, J.; Qian, S.; et al. The HIV/AIDS epidemic among young people in China between 2005 and 2012: Results of a spatial temporal analysis. HIV Med. 2016, 18, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Sun, D.; Ding, S.; Zhang, B.; Du, Z.; Xue, F. Detecting Spatial-Temporal Clusters of HFMD from 2007 to 2011 in Shandong Province, China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins-melo, F.R.; Pinheiro, M.C.C.; Ramos, A.N., Jr.; Alencar, C.H.; Bezerra, F.S.; Heukelbach, J. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Schistosomiasis-Related Deaths, Brazil, 2000–2011. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1820–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Cai, S.; Zhang, H.; Lin, W.; Fan, Y.; Qiu, J.; Sun, L.; Chang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Nie, S. Spatial, temporal, and spatiotemporal analysis of malaria in Hubei Province, China from 2004–2011. Malar. J. 2015, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, E.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Wei, X. Spatial and temporal analysis of tuberculosis in Zhejiang Province, China, 2009–2012. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2016, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, C.; Pearl, D.L.; McEwen, S.A.; Sargeant, J.M.; Pollari, F.; Guerin, M.T. Area-level global and local clustering of human Salmonella Enteritidis infection rates in the city of Toronto, Canada, 2007–2009. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Yan, L.; Liang, S.; de Vlas, S.J.; Feng, D.; Han, X.; Zhao, W.; Xu, B.; Bian, L.; Yang, H.; et al. Spatial analysis of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, T.; Younus, M.; Muhammad, S.A. Spatial cluster analysis of human cases of Crimean Congo hemorrhagic fever reported in Pakistan. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2015, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anselin, L. Local Indicators of Spatial Association—Lisa. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraga, P.; Montes, F. Detection of spatial disease clusters with LISA functions. Stat. Med. 2011, 30, 1057–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Yang, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, B.; Lv, J. Research on geographical environment unit division based on the method of natural breaks (jenks). Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2013, XL-4/W3, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wilson, D.P. Trends in notifiable infectious diseases in Vhina: Implications for surveillance and population health policy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, R.Y.; Sharp, G.B.; Brown, K.; Smith, K.; Ding, G.; Jin, X.; Xu, J.; Dong, R.; Wang, N. Mobility, risk behavior and HIV/STI rates among female sex workers in Kaiyuan City, Yunnan Province, China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ison, C.A. Antimicrobial resistance in sexually transmitted infections in the developed world: implications for rational treatment. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 25, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Shi, X.; Mao, S.; Shi, N.; Hui, X. The spatial distribution pattern of human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immune deficiency syndrome in China. Geospat. Health 2016, 11, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, M.; Ping, G.; Fox, K.; Henderson, G. Sexuallly transmitted diseases in the People’s Republic of China. Sex. Transm. Dis. 2000, 27, 143–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behaviors, R.; Willem, J.; Van Wijngaarden, D.L.; Girault, P. The Epidemiology of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection, Sexually Transmitted Infections, and Associated The Epidemiology of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection. Sex. Transm. Dis. 2009, 36, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).