Impact of China’s Recycling Subsidy Policy in the Product Life Cycle
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Policy Description, Causal Relationship and Simulation Model
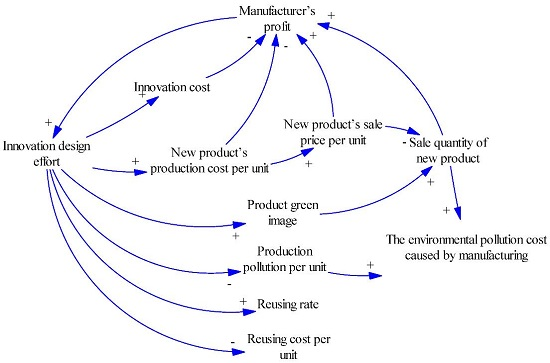
2.1. Manufacturing and Usage Subsystem
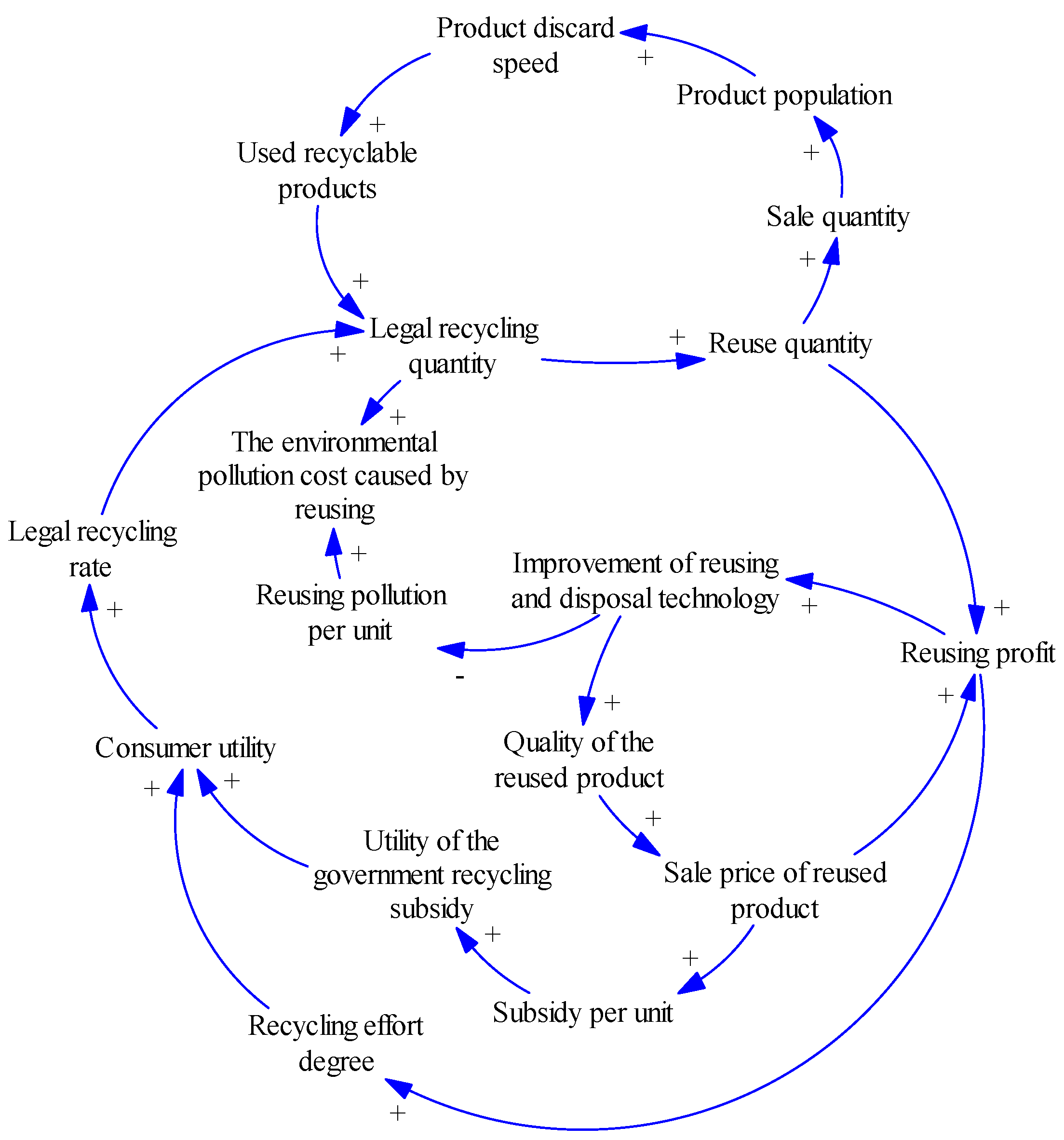
2.2. Recycling and Reuse Subsystem
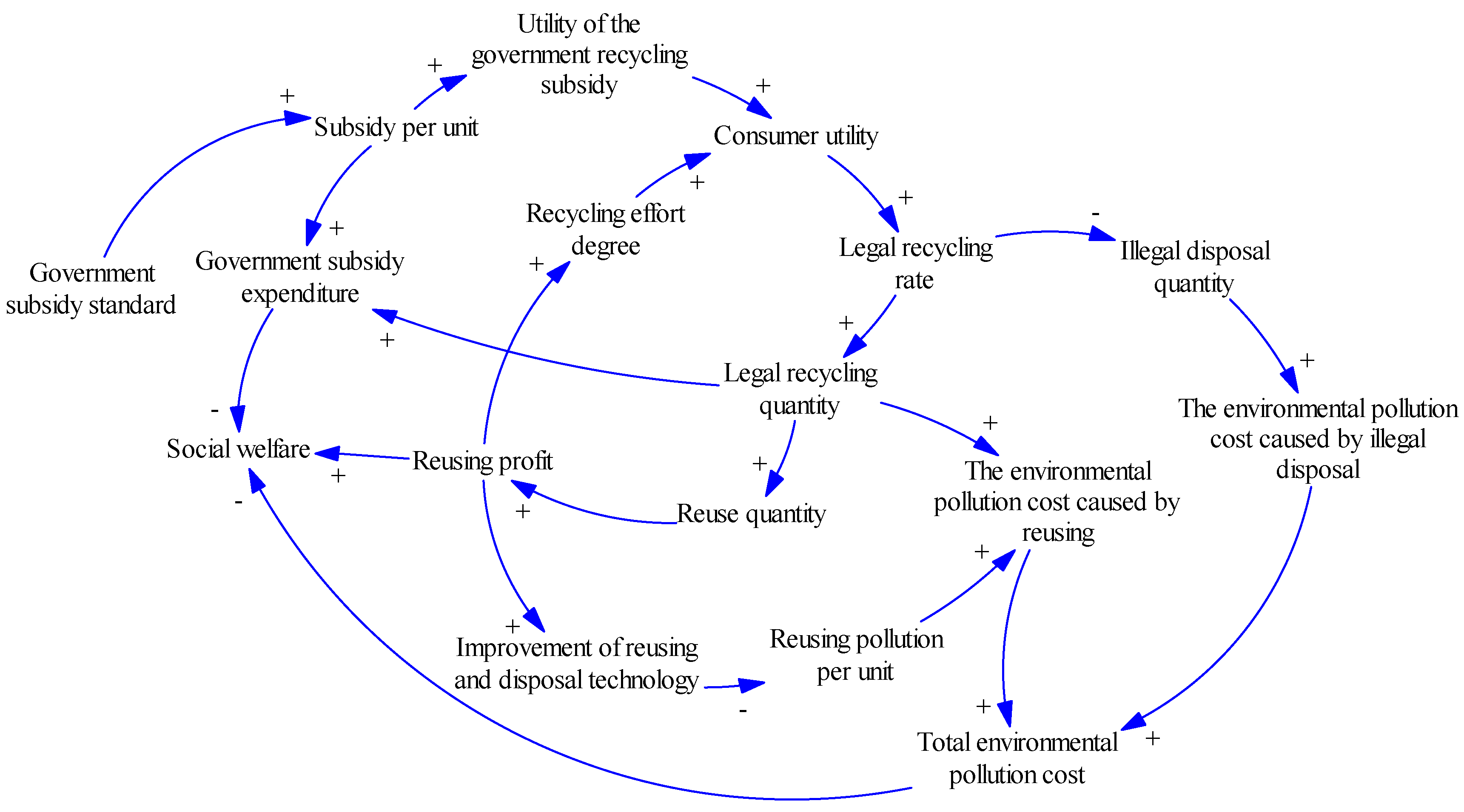
2.3. Recycling Subsidy Subsystem
2.4. Stock and Flow Diagram of the SD Model
3. Data and Simulation Setup
- (1)
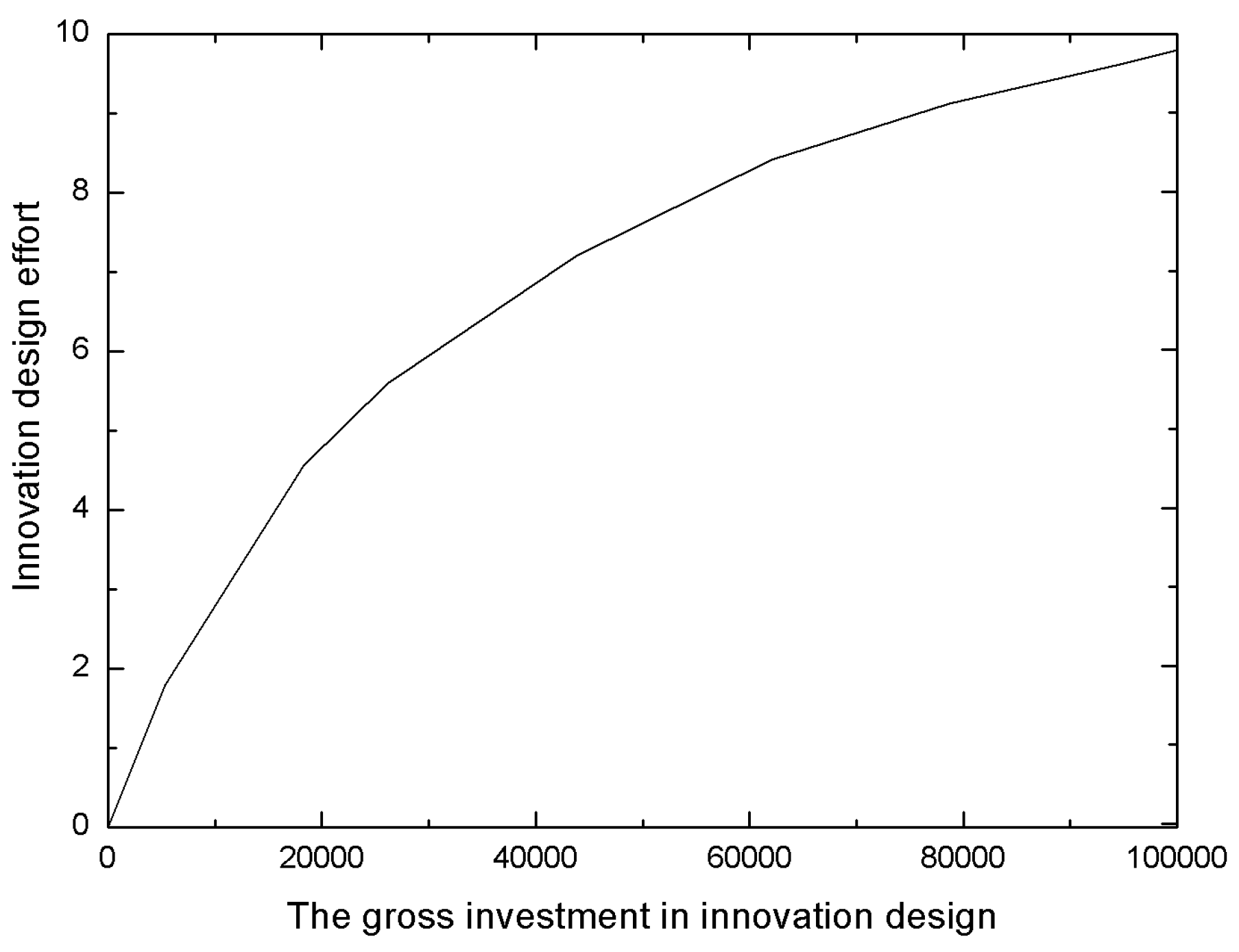
- Innovation-related function
- (2)
- New product’s unit production cost and sale price
- (3)
- New product sales quantity and product population
- (4)
- Discard rate and legal recycling rate
- (5)
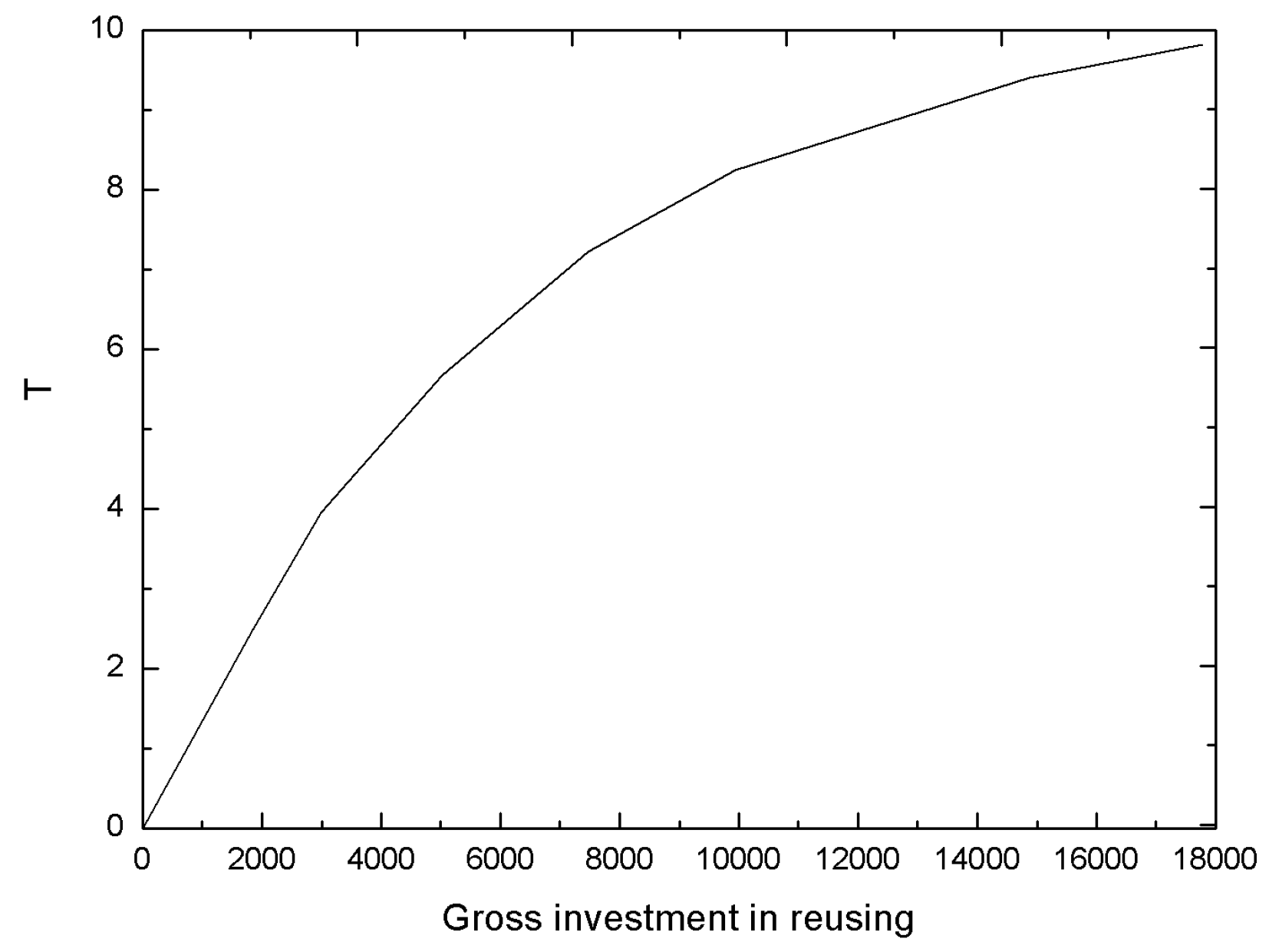
- Reuse rate and reuse cost per unit
- (6)
- Sale price of the reused product
- (7)
- Environmental cost
4. Simulation Analysis, Results and Discussions
4.1. Analysis of the CRS-Policy Impact
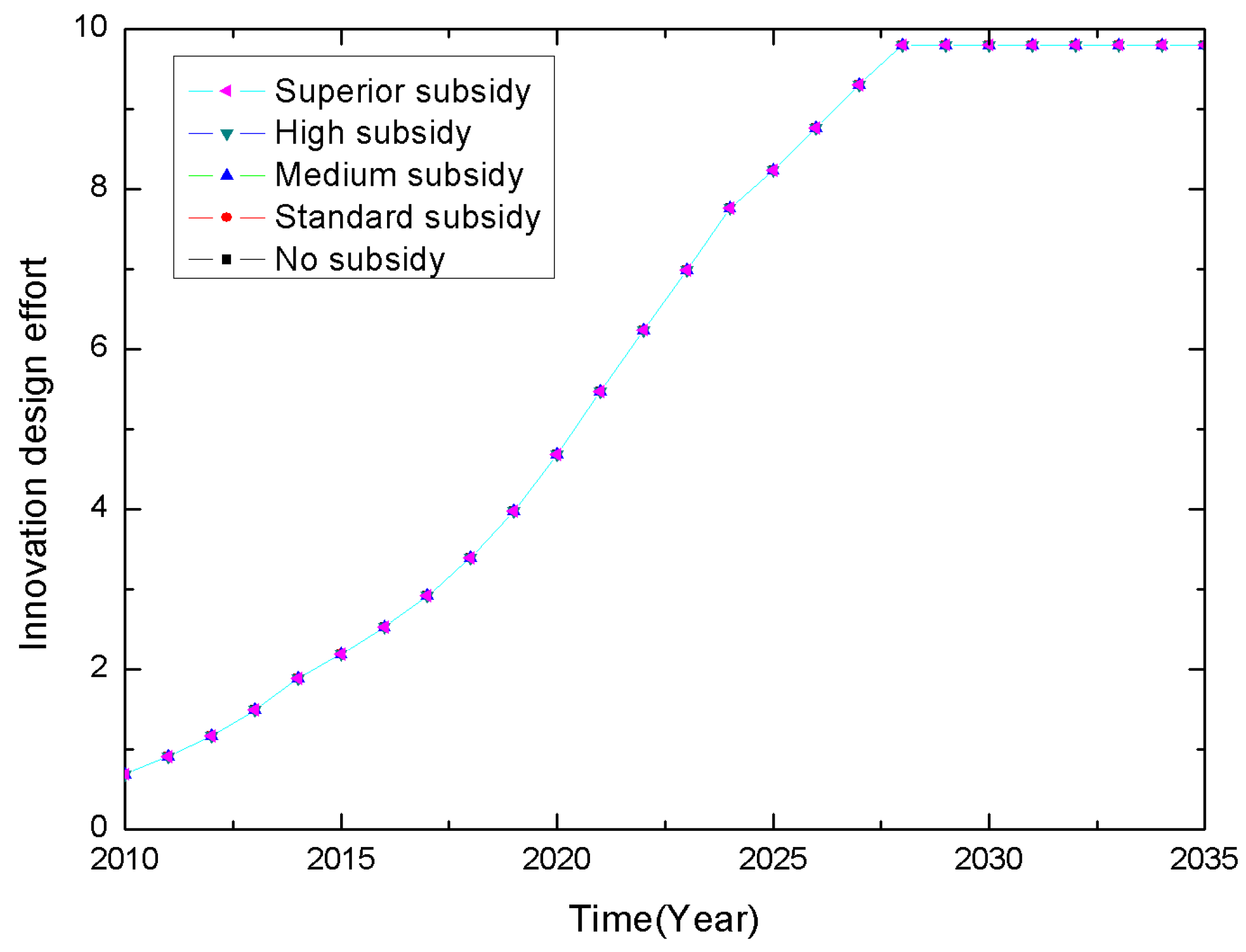
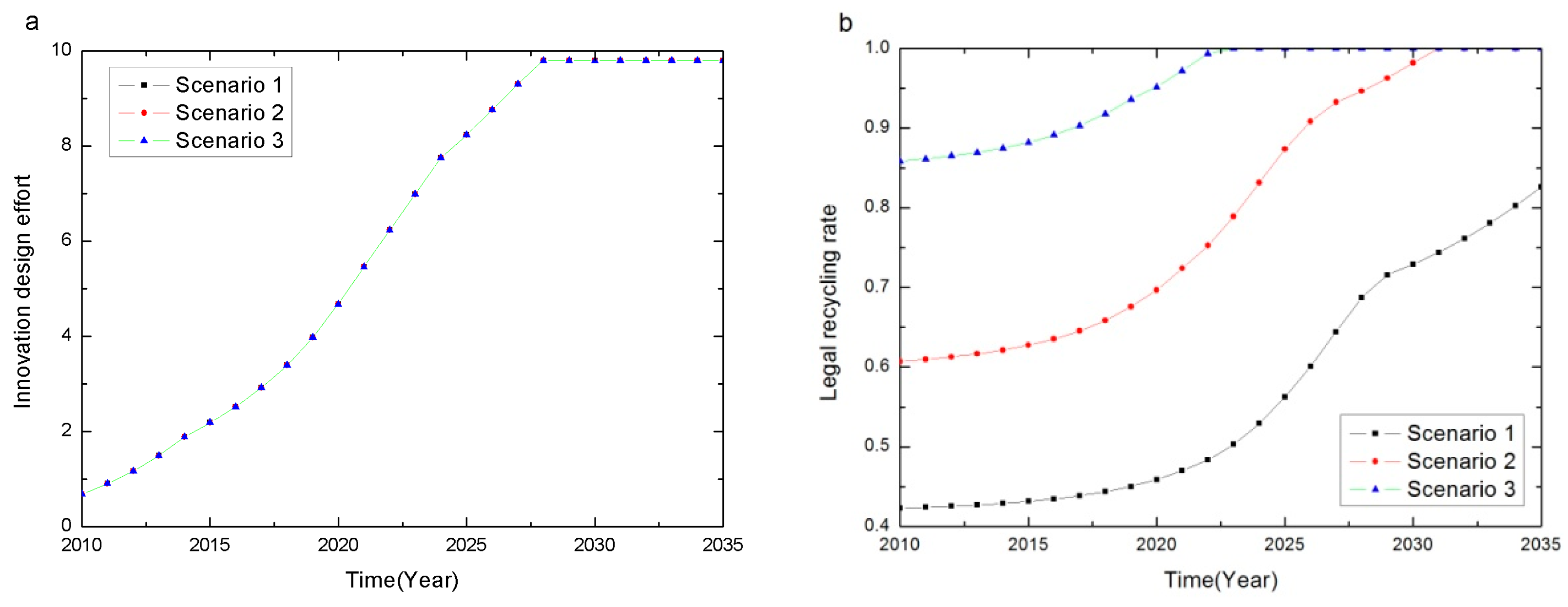
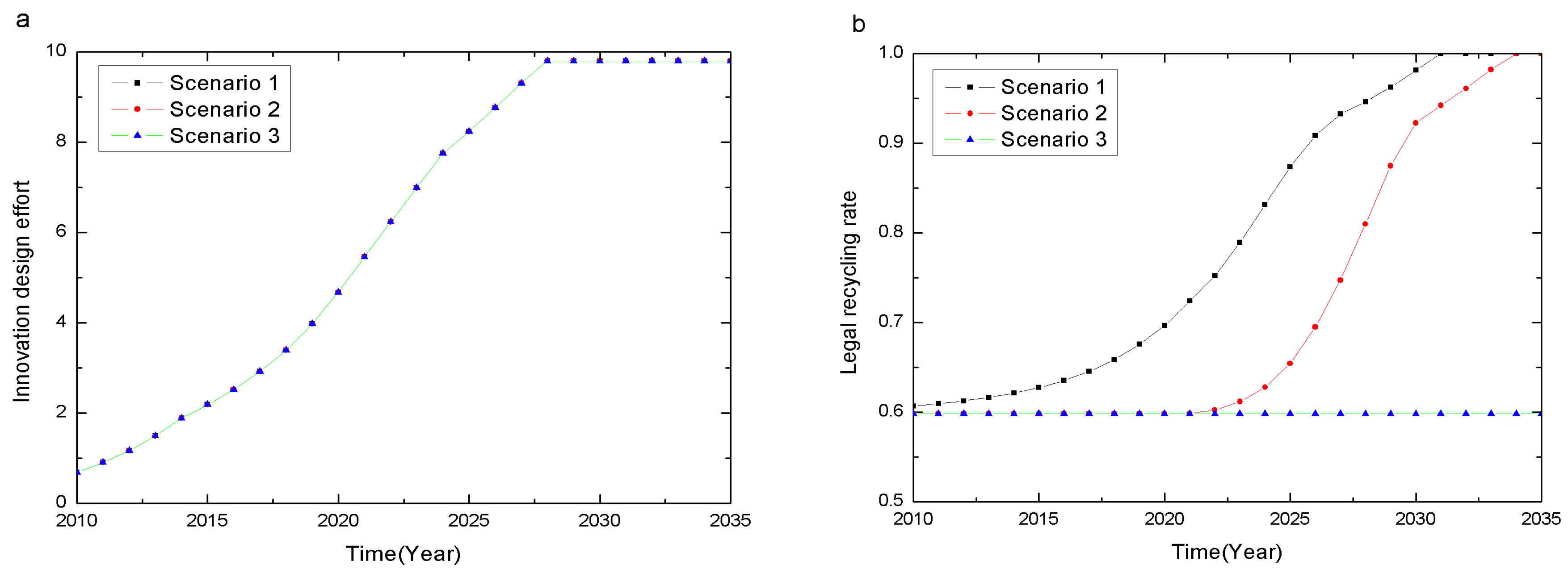
4.1.1. Preventative Impact
Conclusion 1: The CRS-policy motivates the manufacturer’s innovation design effort, but different subsidies have no significant preventative impact on the manufacturing stage.
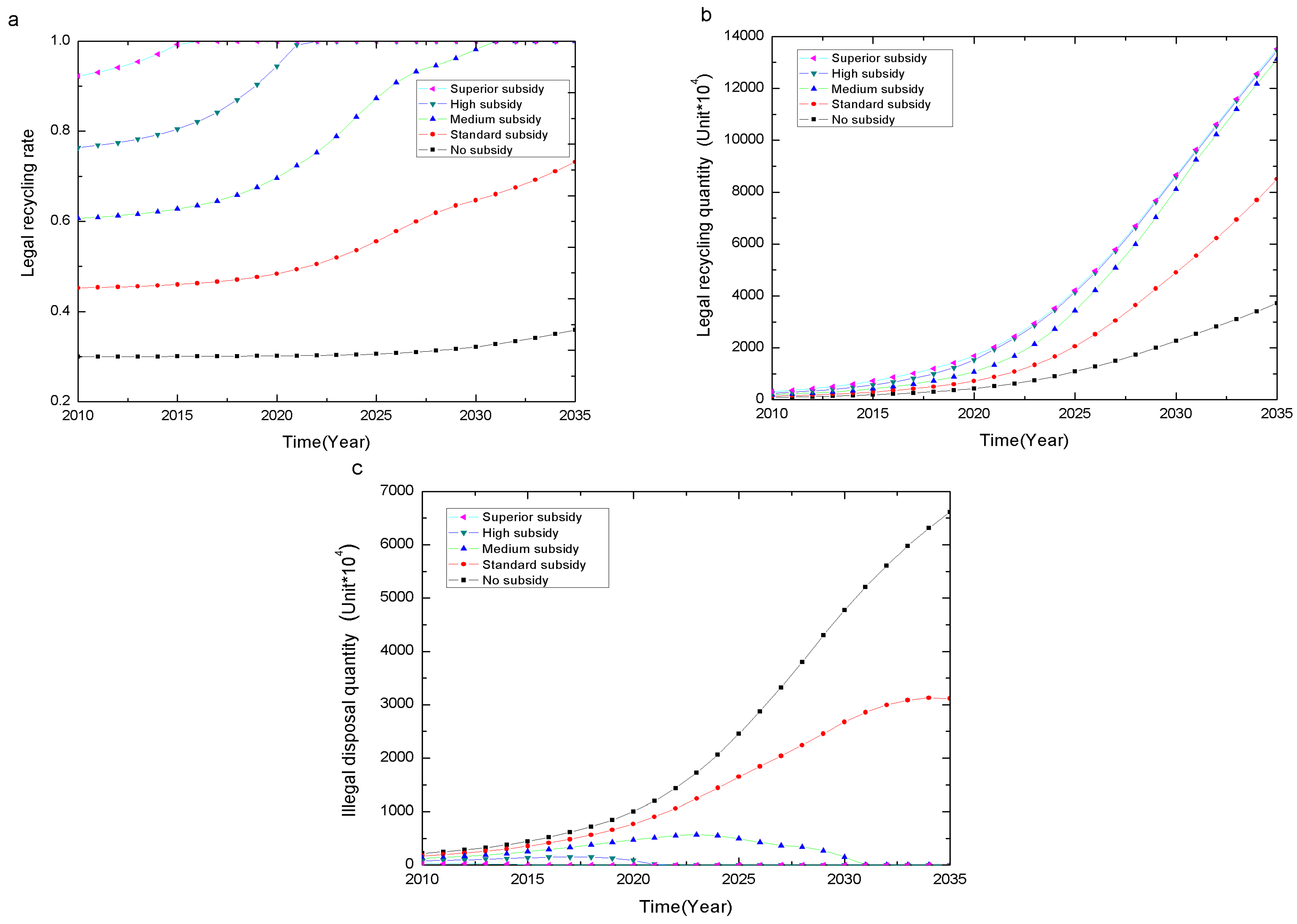
4.1.2. Regenerative Impact
Conclusion 2: CRS-policy levels have a significant regenerative effect on the recycling and reuse stage, and an optimal subsidy exists.
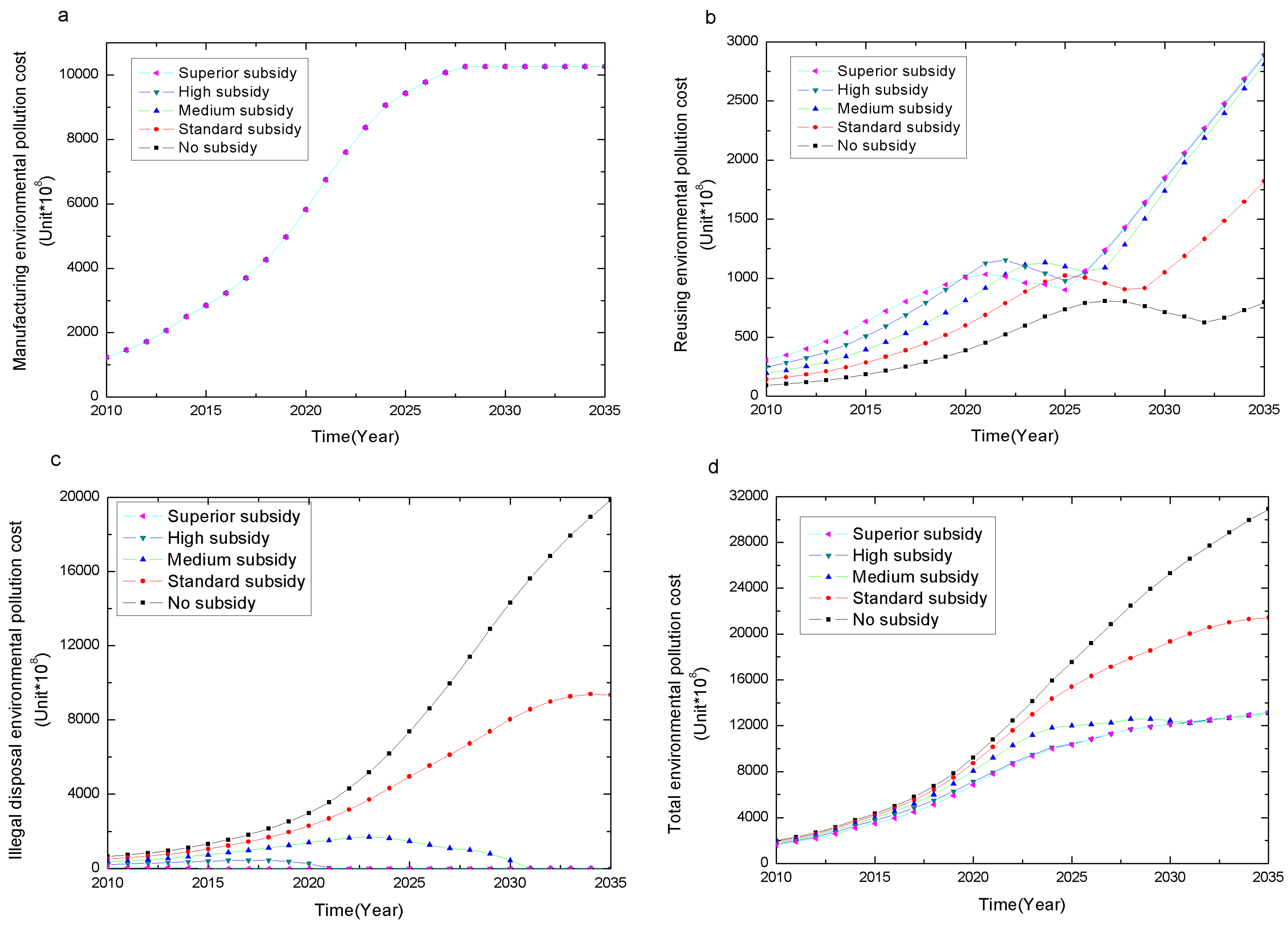
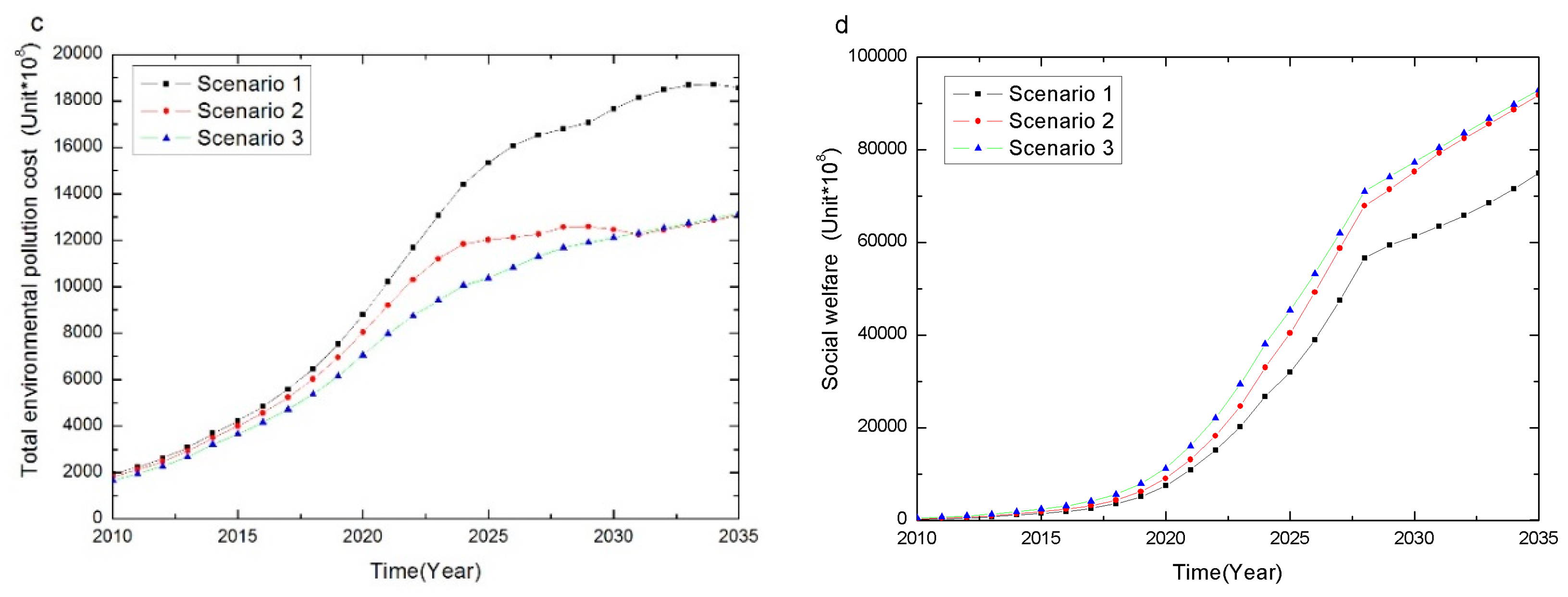
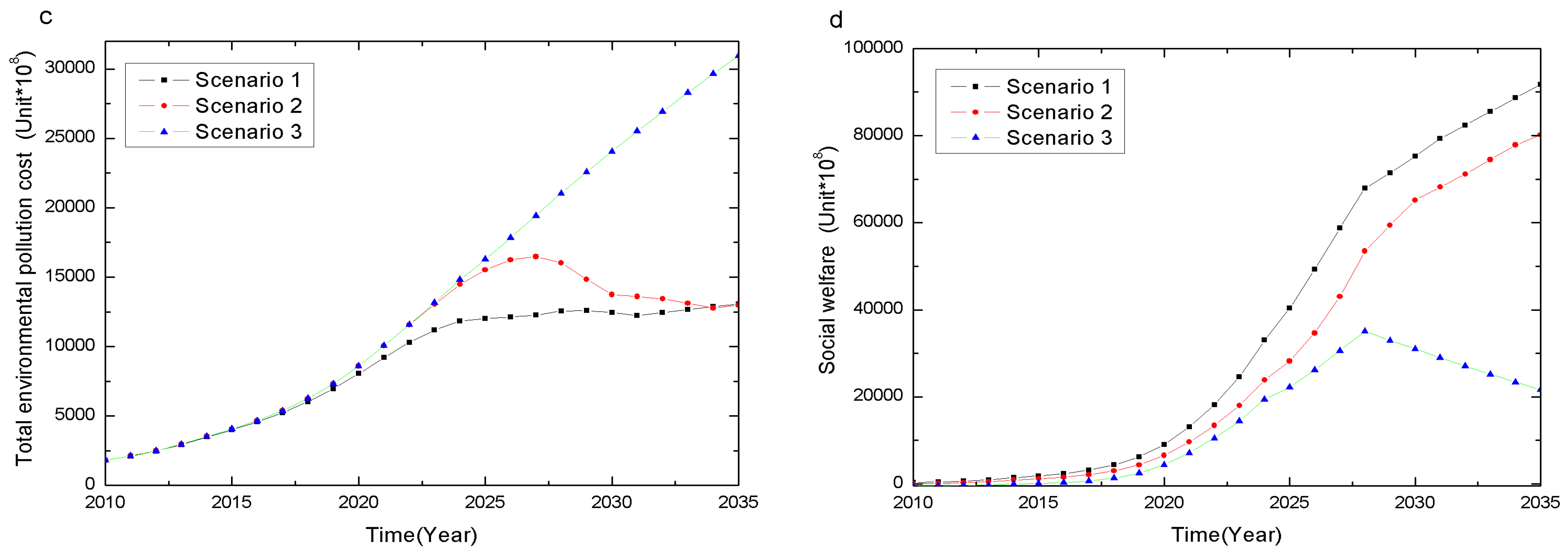
4.1.3. Environmental Pollution Cost
- (1)
- (2)
- The Recycling or disposal process may cause pollution cost to some extent, referred to as negative environmental effects. Different subsidies levels result in the following changes in the reuse EPC (Figure 7b).
- (3)
- Figure 7c reveals a clear pattern that a relative high subsidy will dramatically reduce the illegal disposal EPC, and eventually eliminate the illegal disposal EPC in the long term. The increasing illegal disposal EPC is incurred from the no or standard subsidy policies, suggesting that relative low subsidy policy is not effective in reducing illegal disposal EPC in the long run.
- (4)
- For the total EPC shown in Figure 7d, the subsidy incurs growing total EPC over time, but the higher subsidy tends to result in a much lower total EPC. Between 2010 and 2025, the superior subsidy leads to the lowest total pollution. Between 2025 and 2029, the high subsidy has the minimum overall pollution. Between 2030 and 2035, the middle subsidy has the minimum overall pollution. This finding implies the existence of a critical point of industry development, denoted by D. When industry development does not reach the critical point D, the higher subsidy generates less overall pollution. However, when industry development reaches the critical point D, an optimal subsidy S* exists that has the minimum overall negative environmental effect.
Conclusion 3: CRS-policy levels have no significant different impact on reducing environmental pollution at the manufacturing stage, but significantly affect reuse and illegal disposal environmental pollution, as well as overall environmental pollution. When the development of the recycling industry reaches a certain degree D, an optimal subsidy S* with the lowest overall environmental pollution exists. This optimal subsidy is negatively related to the industry development.
- (1)
- In the initial stage of industry development, the government should offer high subsidies. When the industry development has reached a more advanced stage, an optimal subsidy should be proposed with simultaneous considerations of recycling, legal and illegal disposal, and improvement in the reuse process technology.
- (2)
- The policy should provide incentives to recyclers to adopt more environmentally-friendly technology, to improve reuse process and to reduce negative environmental effect of the reuse activities.
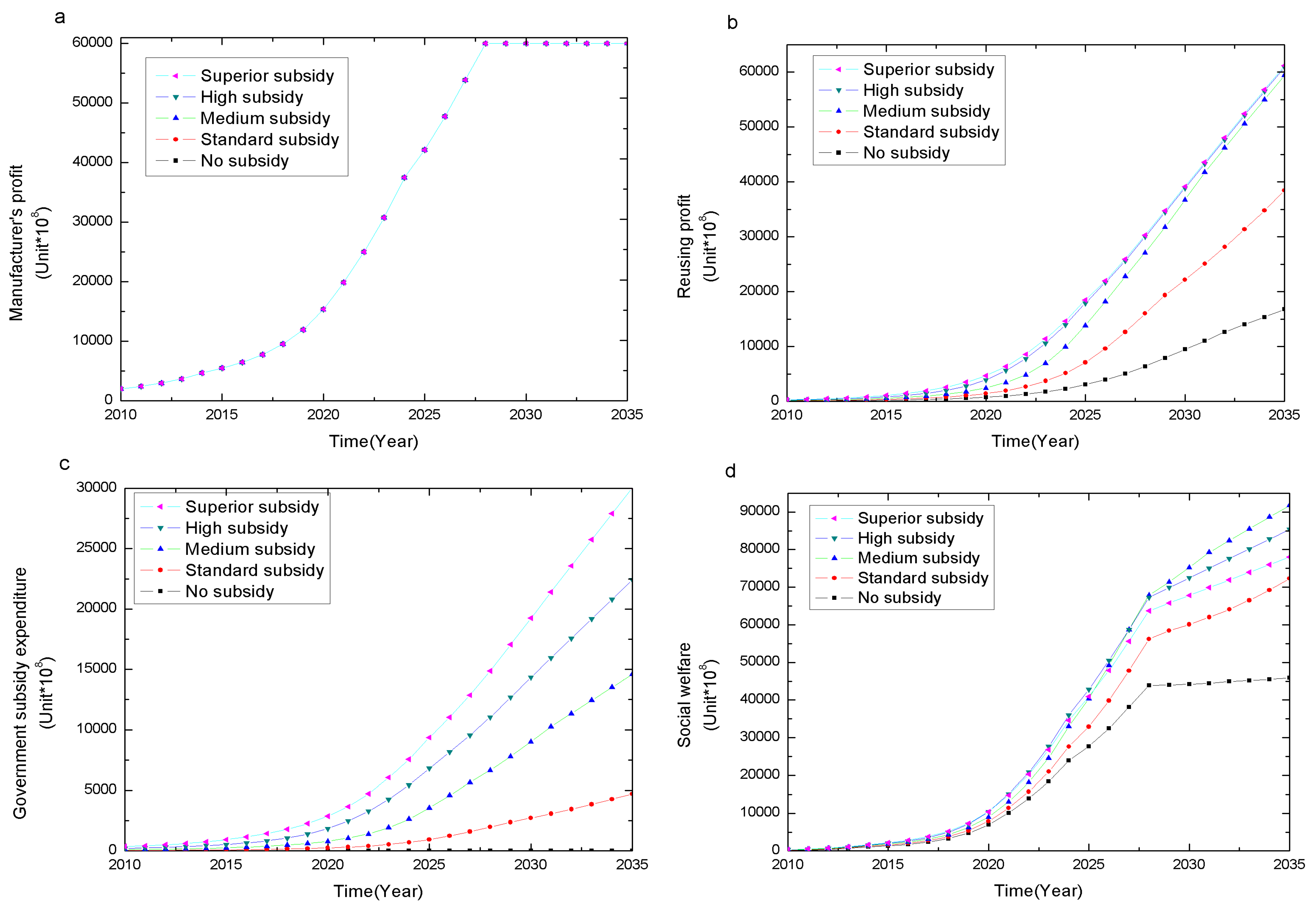
4.1.4. Economic and Social Welfare
Conclusion 4: CRS-policy levels have no significant different impact on the manufacturer’s profit but significantly affect the recycler’s profit, government subsidy expenditure and social welfare. When the development of the recycling industry reaches a certain degree, an optimal subsidy exists with the highest social welfare. This optimal subsidy is negatively related to industry development level.
4.2. Analysis of the Market Factors’ Impact
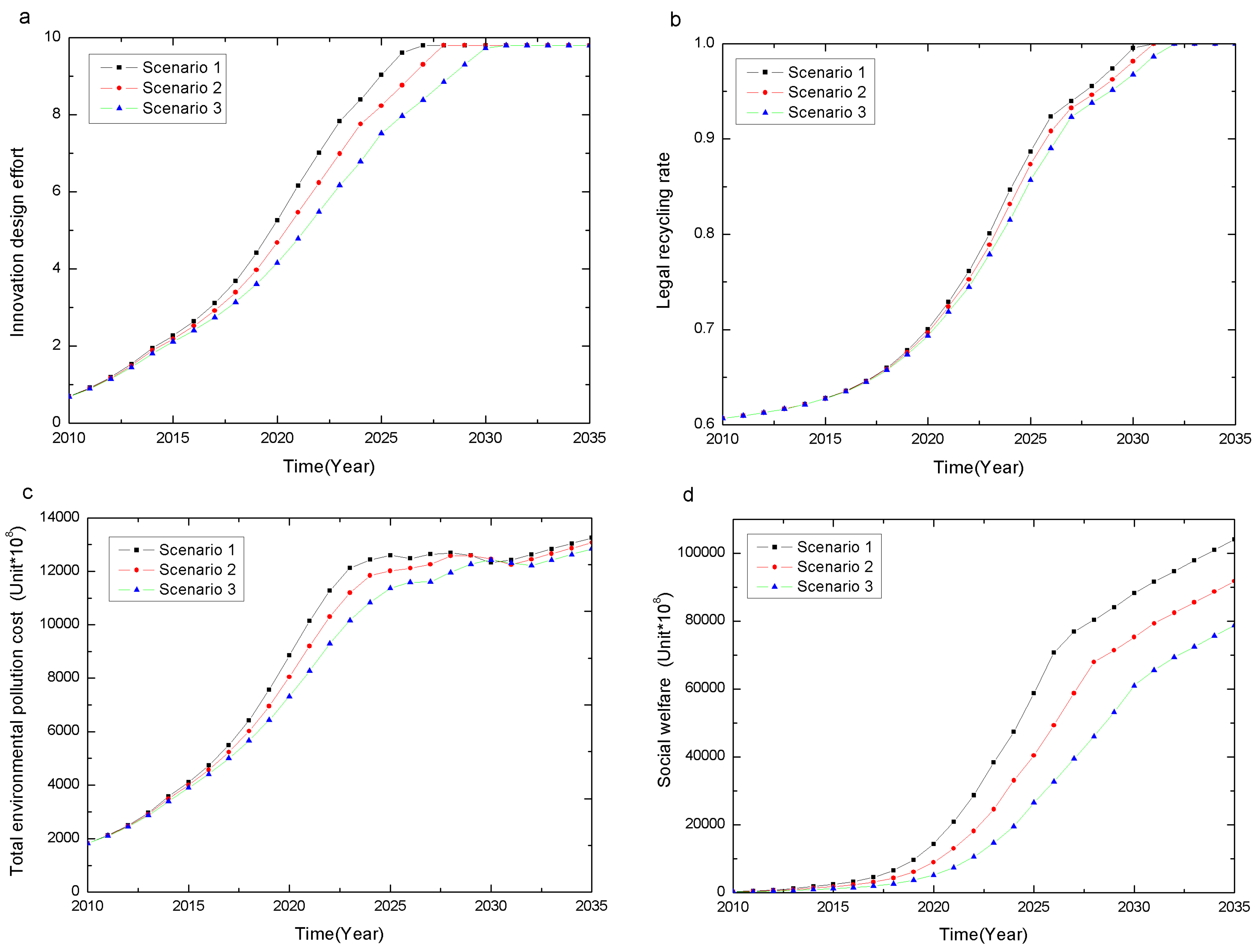
4.2.1. The Innovation Environment
Conclusion 5: Improvement in the upstream innovation environment would enhance the effectiveness of the CRS-policy in the manufacturing and recycling and reuse stages.
4.2.2. Consumer Environmental Awareness
Conclusion 6: An increase in consumer environmental awareness would enhance the effectiveness of the CRS-policy in the manufacturing and recycling and reuse stages.
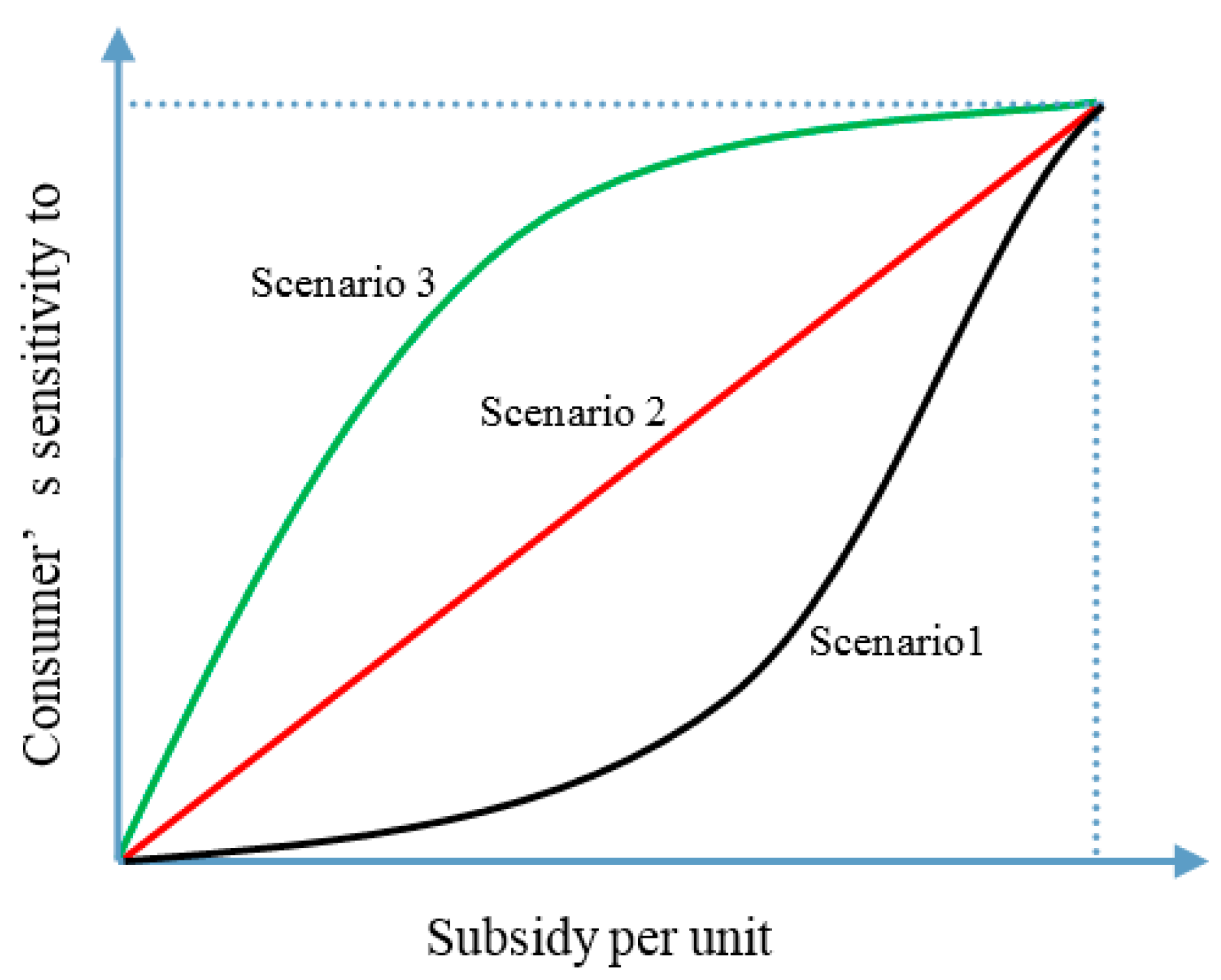
4.2.3. Consumer Sensitivity to the CRS-Policy
Conclusion 7: Improvement in consumer’s sensitivity to the recycling subsidy at the initial stage of the policy would enhance the effectiveness of the subsidy policy in the recycling and reuse stage.
4.2.4. Profit in the Recycling and Reuse Industry
Conclusion 8: An increase in the downstream recycling and reuse profit would enhance the effectiveness of the CRS-policy in the recycling and reuse stage.
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of interest
Appendix
| Parameters | Definition |
|---|---|
| The innovation cost coefficient. | |
| The innovation design effort of the manufacturer, which is a dimensionless parameter. [0,10]. | |
| Initial production cost per unit without any innovation effort. | |
| represents the cost increasing rate of the innovation, | |
| Market scale | |
| Consumer’s price sensitivity | |
| a | Consumer’s environmental awareness (CEA) |
| product innovation green coefficient, δ ∊ [0,1] and represents the product green image. | |
| New product’s unit sale price and reused product’s unit sale price, respectively. | |
| u | Consumer utility |
| Reusing rate, | |
| Value of the reused product quality, | |
| Manufacturing environmental pollution cost (manufacturing EPC), recycling and reusing EPC, illegal recycling and disposal EPC, respectively. | |
| Manufacturing EPC per unit, recycling and reusing EPC per unit and illegal recycling and disposal EPC per unit, respectively. | |
| T | The value of the improvement of reusing and disposal technology, |

References
- Tu, J.C.; Huang, H.S. Analysis on the relationship between green accounting and green design for enterprises. Sustainability 2015, 7, 6264–6277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksen, D.; Aras, N.; Karaarslan, A.G. Design and analysis of government subsidized collection systems for incentive-dependent returns. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2009, 119, 308–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Webster, S. Competition in remanufacturing and the effects of government subsidies. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2008, 111, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Zhao, Z.; Ke, H. Dual-channel closed-loop supply chain with government consumption-subsidy. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2013, 226, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krass, D.; Nedorezov, T.; Ovchinnikov, A. Environmental taxes and the choice of green technology. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2013, 22, 1035–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raz, G.; Druehl, C.T.; Blass, V. Design for the environment: Life-cycle approach using a newsvendor model. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2013, 22, 940–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plambeck, E.; Wang, Q. Effects of e-waste regulation on new product introduction. Manag. Sci. 2009, 55, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleber, R.; Zanoni, S.; Zavanella, L. On how buyback and remanufacturing strategies affect the profitability of spare parts supply chains. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2011, 133, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunter, R.H.; Flapper, S.D.P. Optimal core acquisition and remanufacturing policies under uncertain core quality fractions. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2011, 210, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simic, V.; Dimitrijevic, B. Production planning for vehicle recycling factories in the EU legislative and global business environments. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2012, 60, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnveden, G.; Ekvall, T.; Arushanyan, Y.; Bisaillon, M.; Henriksson, G.; Gunnarsson Östling, U.; Ljunggren Söderman, M.; Sahlin, J.; Stenmarck, Å.; Sundberg, J.; et al. Policy instruments towards a sustainable waste management. Sustainability 2013, 5, 841–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, I.H.; Ke, J.S. Determining advanced recycling fees and subsidies in “E-scrap” reverse supply chains. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, I.H.; Lee, Y.T.; Chang, P.Y. Socially optimal and fund-balanced advanced recycling fees and subsidies in a competitive forward and reverse supply chain. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 82, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeanjean, F. Subsiding the next-generation infrastructures. Consumer-side or supply-side. Info 2010, 12, 95–120. [Google Scholar]
- Lorentziadis, P.L.; Vournas, S.G. A quantitative model of accelerated vehicle-retirement induced by subsidy. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2011, 211, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poles, R. System dynamics modelling of a production and inventory system for remanufacturing to evaluate system improvement strategies. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2013, 144, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiadis, P.; Vlachos, D. The effect of environmental parameters on product recovery. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2004, 157, 449–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterman, J.D. Business Dynamics: Systems Thinking and Modeling for a Complex World; Irwin/McGraw-Hill: Boston, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Das, D.; Dutta, P. A system dynamics framework for integrated reverse supply chain with three-way recovery and product exchange policy. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2013, 66, 720–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Schaik, A.; Reuter, M.A. The time-varying factors influencing the recycling rate of products. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2004, 40, 301–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spengler, T.; Schroter, M. Strategic management of spare parts in closed-loop supply chains: A system dynamics approach. Interfaces 2003, 33, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, N.; Varela-Candamio, L.; Novo-Corti, I. A dynamic model for construction and demolition (C&D) waste management in Spain: Driving policies based on economic incentives and tax penalties. Sustainability 2014, 6, 416–435. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, M.; Peng, Y.; Chen, H. Post-seismic supply chain risk management: A system dynamics disruption analysis approach for inventory and logistics planning. Comput. Oper. Res. 2014, 42, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiadis, P.; Besiou, M. Sustainability in electrical and electronic equipment closed-loop supply chains: A system dynamics approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2008, 16, 1665–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.P.; Dong, Z.Y. Impact of technological innovation difficulty on high-tech enterprise optimal innovation investment: Based on analysis of agent-based model. Sci. Technol. Econ. 2014, 27, 44–48. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.S. Remanufacturing and Recycling Economy; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2007. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.H.; Zhu, J.W.; Zhang, T.Z.; Cui, P.F.; Tian, G.D.; Wang, H. Analysis of dynamic modeling and prediction of end-of-life vehicles. Comput. Commun. 2008, 26, 23–25. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mao, G.P.; Zhu, Y.W.; Wu, C. A study on the environmental influence comparison between engine manufacturing and remanufacturing. Automot. Eng. 2009, 31, 565–568. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Atasu, A.; Van Wassenhove, L.N.; Sarvary, M. Efficient take-back legislation. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2009, 18, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atasu, A.; Wassenhove, L.N. An operations perspective on product take-back legislation for e-waste: Theory, practice, and research needs. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2012, 21, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, X.; Fan, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, J. Impact of China’s Recycling Subsidy Policy in the Product Life Cycle. Sustainability 2016, 8, 781. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8080781
Chang X, Fan J, Zhao Y, Wu J. Impact of China’s Recycling Subsidy Policy in the Product Life Cycle. Sustainability. 2016; 8(8):781. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8080781
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Xiangyun, Junjie Fan, Yabing Zhao, and Jie Wu. 2016. "Impact of China’s Recycling Subsidy Policy in the Product Life Cycle" Sustainability 8, no. 8: 781. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8080781
APA StyleChang, X., Fan, J., Zhao, Y., & Wu, J. (2016). Impact of China’s Recycling Subsidy Policy in the Product Life Cycle. Sustainability, 8(8), 781. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8080781