Measuring the Interprovincial CO2 Emissions Considering Electric Power Dispatching in China: From Production and Consumption Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Research Methods
2.1. Basic Method
2.2. Measurement of CO2 Emissions from the Perspective of Production
2.3. Measurement of CO2 Emissions from the Perspective of Consumption
2.4. CO2 Emission Responsibility
2.5. Other Measuring Methods
3. Empirical Analysis
3.1. Data
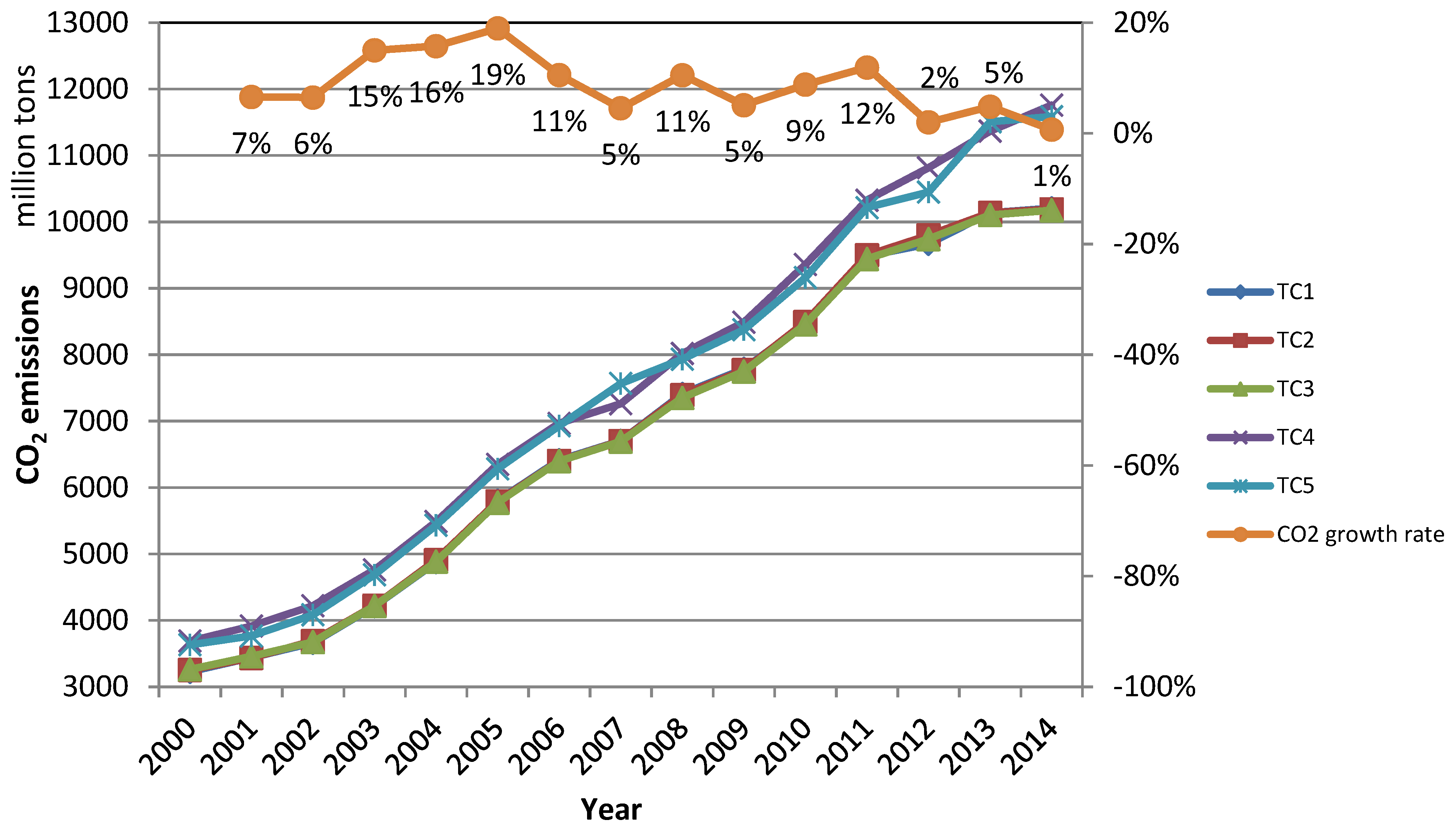
3.2. Overall National CO2 Emission Analysis
3.3. Interprovincial CO2 Emission Analysis of Different Measuring Methods
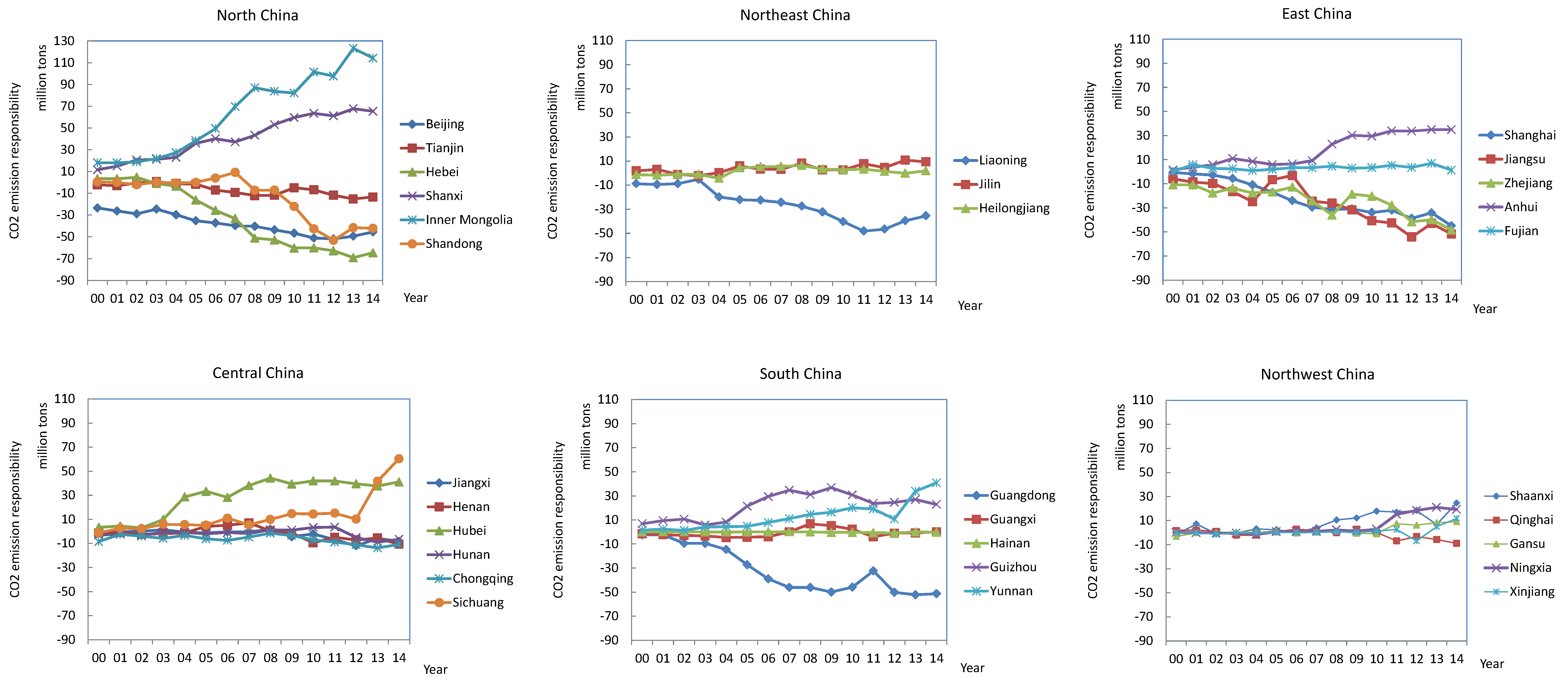
3.4. Interprovincial CO2 Emission Responsibility Analysis
4. Conclusions and Policy Enlightenments
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xinhuanet. UN Climate Chief Hails China-U.S. Announcement on Climate Change. Available online: http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/china/2014-11/13/c_133785521.htm (accessed on 30 March 2016).
- Zhou, P.; Zhou, X.; Fan, L.W. On estimating shadow prices of undesirable outputs with efficiency models: A literature review. Appl. Energy 2014, 130, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, K.L. Regional differences of environmental efficiency of China’s energy utilization and environmental regulation cost based on provincial panel data and DEA method. Math. Comp. Model. Dyn. 2013, 58, 1074–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wei, Y.M. China’s regional industrial energy efficiency and carbon emissions abatement costs. Appl. Energy 2014, 130, 617–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Choi, Y. A note on the evolution of directional distance function and its development in energy and environmental studies 1997–2013. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2014, 33, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.W.; Chiu, Y.H.; Chiu, C.M. Driving factors behind carbon dioxide emissions in China: A modified production-theoretical decomposition analysis. Energy Econ. 2015, 51, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Lin, B.Q. Impacts of urbanization and industrialization on energy consumption/CO2 emissions: Does the level of development matter? Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 1107–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.Q.; Moubarak, M.; Ouyang, X.L. Carbon dioxide emissions and growth of the manufacturing sector: Evidence for China. Energy 2014, 76, 830–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.M.; Zhao, R.; Liu, T.S.; Zhao, J.F. Does urbanization lead to more direct and indirect household carbon dioxide emissions? Evidence from China during 1996–2012. J. Clean Prod. 2015, 102, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Z.F.; Pan, S.Y.; Yu, H.; Wei, Y.M. Potential impacts of industrial structure on energy consumption and CO2 emission: A case study of Beijing. J. Clean Prod. 2015, 103, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, C.M.; Liu, L.; Guo, H.; Liu, G.D.; Li, Y.W.; Deng, S.H. Investigation of carbon dioxide emission in China by primary component analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, N.; Xu, F.; Sha, J.H. Simulation Analysis of China’s Energy and Industrial Structure Adjustment Potential to Achieve a Low-carbon Economy by 2020. Sustainability 2013, 5, 5081–5099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Hu, Z.; Wang, K.; Fu, P. Spatial Distribution of Energy Consumption and Carbon Emission of Regional Logistics. Sustainability 2015, 7, 9140–9159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.Y.; Guo, Z.Q.; Zheng, Y.H.; Zhang, X.P. Scenarios Analysis of the Energies’ Consumption and Carbon Emissions in China Based on a Dynamic CGE Model. Sustainability 2014, 6, 487–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. The 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories. Available online: http://www.ipcc-nggip.iges.or.jp/public/2006gl/index.html (accessed on 30 March 2016).
- Long, X.L.; Naminse, E.Y.; Du, J.G; Zhuang, J.C. Nonrenewable energy, renewable energy, carbon dioxide emissions and economic growth in China from 1952 to 2012. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y.; Zhao, L.L.; Bian, Y.W. Measuring regional efficiency of energy and carbon dioxide emissions in China: A chance constrained DEA approach. Comput. Oper. Res. 2016, 66, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.T.; Wesley, B.J.; Lacombe, D.J. Province-Level convergence of China’s carbon dioxide emissions. Appl. Energy 2015, 150, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Lin, B.Q. Factors affecting carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions in China’s transport sector: A dynamic nonparametric additive regression model. J. Clean Prod. 2015, 101, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, K.Z. Convergence of carbon dioxide emissions in different sectors in China. Energy 2014, 65, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.K.; Zhang, Y.X.; Lu, X.; Nielsen, C.P.; Bi, J. Understanding China’s carbon dioxide emissions from both production and consumption perspectives. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.Y.; Xu, A. Regional difference and influential factors of china’s urban carbon emissions. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2011, 21, 8–14. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.D.; Zhao, M.Z.; Wang, C.X.; Li, B. Calculation of carbon dioxide emissions considering secondary energy deployment among provinces in China. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2012, 22, 69–75. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, N. Industrial Carbon Emissions of China’s Regions: A Spatial Econometric Analysis. Sustainability 2016, 8, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, J.J. The Effects of Coal Switching and Improvements in Electricity Production Efficiency and Consumption on CO2 Mitigation Goals in China. Sustainability 2015, 7, 9540–9559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics PR China. China Energy Statistical Yearbook, 2000–2015; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2004–2016. (In Chinese)
- Analysis of the Current Situation of City Heating Industry. Available online: http://finance.glinfo.com/12/1115/12/C72E318E8E751202.html (accessed on 30 March 2016). (In Chinese)
- 2014 Baseline Emission Factors for Regional Power Grids in China. Available online: http://cdm.ccchina.gov.cn/archiver/cdmcn/UpFile/Files/Default/20150204155537627092.pdf (accessed on 24 May 2016). (In Chinese)
- 2013 Baseline Emission Factors for Regional Power Grids in China. Available online: http://cdm.ccchina.gov.cn/archiver/cdmcn/UpFile/Files/Htmleditor/201310/20131024151336847.pdf (accessed on 24 May 2016). (In Chinese)
- 2012 Baseline Emission Factors for Regional Power Grids in China. Available online: http://cdm.ccchina.gov.cn/WebSite/CDM/UpFile/File2975.pdf (accessed on 24 May 2016). (In Chinese)
- 2011 Baseline Emission Factors for Regional Power Grids in China. Available online: http://cdm.ccchina.gov.cn/WebSite/CDM/UpFile/File2720.pdf (accessed on 24 May 2016). (In Chinese)
- 2010 Baseline Emission Factors for Regional Power Grids in China. Available online: http://cdm.ccchina.gov.cn/WebSite/CDM/UpFile/File2552.pdf (accessed on 24 May 2016). (In Chinese)
- 2009 Baseline Emission Factors for Regional Power Grids in China. Available online: http://cdm.ccchina.gov.cn/WebSite/CDM/UpFile/File2333.pdf (accessed on 24 May 2016). (In Chinese)
- 2008 Baseline Emission Factors for Regional Power Grids in China. Available online: http://cdm.ccchina.gov.cn/WebSite/CDM/UpFile/2008/20081230102527637.pdf (accessed on 24 May 2016). (In Chinese)
- 2007 Baseline Emission Factors for Regional Power Grids in China. Available online: http://cdm.ccchina.gov.cn/WebSite/CDM/UpFile/File1364.pdf (accessed on 24 May 2016). (In Chinese)
- Baseline Emission Factors for Regional Power Grids in China. Available online: http://cdm.ccchina.gov.cn/WebSite/CDM/UpFile/2006/2006121591135575.pdf (accessed on 24 May 2016). (In Chinese)
| Item | CO2 Emission Factors | Item | CO2 Emission Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| raw coal | 1.98 t/t | liquefied natural gas | 2.84 t/t |
| cleaned coal | 2.49 t/t | crude oil | 3.10 t/t |
| other washed coal | 0.79 t/t | gasoline | 3.18 t/t |
| coal briquette | 1.72 t/t | kerosene | 3.15 t/t |
| coke | 3.02 t/t | diesel | 3.18 t/t |
| coke oven gas | 7.42 t/(104 m3) | fuel oil | 3.13 t/t |
| natural gas | 21.84 t/(104 m3) | liquefied petroleum gas | 2.98 t/t |
| Regions | 2003–2005 | 2004–2006 | 2005–2007 | 2006–2008 | 2007–2009 | 2008–2010 | 2009–2011 | 2010–2012 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North | 1.1208 | 1.1169 | 1.0069 | 0.9914 | 0.9803 | 1.0021 | 1.0302 | 1.058 |
| Northeast | 1.2404 | 1.2561 | 1.1293 | 1.1109 | 1.0852 | 1.0935 | 1.112 | 1.1281 |
| East | 0.9421 | 0.954 | 0.8825 | 0.8592 | 0.8367 | 0.8244 | 0.81 | 0.8095 |
| Central | 1.2899 | 1.2783 | 1.1255 | 1.0871 | 1.0297 | 0.9944 | 0.9779 | 0.9724 |
| Northwest | 1.1257 | 1.1225 | 1.0246 | 0.9947 | 1.0001 | 0.9913 | 0.972 | 0.9578 |
| South | 1.0119 | 1.0608 | 0.9987 | 0.9762 | 0.9489 | 0.9344 | 0.9223 | 0.9183 |
| Regions | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North | 0.979 | 0.984 | 0.970 | 0.911 | 0.971 | 0.984 | 0.938 | 0.904 |
| Northeast | 0.856 | 0.922 | 1.039 | 1.037 | 1.082 | 1.072 | 1.055 | 0.995 |
| East | 0.965 | 0.946 | 0.761 | 0.979 | 0.940 | 0.904 | 0.894 | 0.882 |
| Central | 0.607 | 0.597 | 0.630 | 0.650 | 0.719 | 0.665 | 0.655 | 0.637 |
| Northwest | 0.754 | 0.697 | 0.766 | 0.762 | 0.811 | 0.749 | 0.752 | 0.749 |
| South | 0.582 | 0.600 | 0.587 | 0.643 | 0.594 | 0.690 | 0.725 | 0.697 |
| Regions | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | |
| North | 0.903 | 0.877 | 0.863 | 0.915 | 0.888 | 0.855 | 0.793 | |
| Northeast | 1.006 | 0.991 | 0.959 | 0.979 | 0.960 | 0.908 | 0.907 | |
| East | 0.862 | 0.822 | 0.806 | 0.820 | 0.830 | 0.778 | 0.778 | |
| Central | 0.575 | 0.577 | 0.589 | 0.659 | 0.593 | 0.623 | 0.566 | |
| Northwest | 0.725 | 0.718 | 0.705 | 0.709 | 0.696 | 0.676 | 0.622 | |
| South | 0.585 | 0.586 | 0.557 | 0.543 | 0.489 | 0.492 | 0.399 |
| Provinces | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) |
| Beijing | 91 | 129 | 134 | 144 | 92 | −29.5% | 3.3% | 11.0% | −29.2% |
| Tianjin | 116 | 123 | 124 | 131 | 116 | −5.4% | 1.0% | 7.2% | −5.7% |
| Hebei | 530 | 563 | 559 | 590 | 487 | −5.8% | −0.6% | 4.9% | −13.5% |
| Shanxi | 359 | 318 | 315 | 333 | 654 | 13.0% | −0.9% | 4.8% | 105.7% |
| Inner Mongolia | 386 | 323 | 276 | 294 | 429 | 19.6% | −14.4% | −8.8% | 32.9% |
| Shandong | 579 | 592 | 592 | 631 | 686 | −2.3% | 0.0% | 6.5% | 15.8% |
| Liaoning | 343 | 369 | 372 | 396 | 457 | −7.1% | 0.8% | 7.1% | 23.7% |
| Jilin | 174 | 170 | 164 | 173 | 184 | 2.4% | −3.3% | 1.5% | 8.2% |
| Heilongjiang | 196 | 194 | 189 | 201 | 262 | 0.9% | −2.5% | 3.3% | 34.8% |
| Shanghai | 169 | 191 | 196 | 196 | 167 | −11.8% | 2.2% | 2.6% | −12.5% |
| Jiangsu | 460 | 486 | 488 | 490 | 449 | −5.4% | 0.4% | 0.9% | −7.7% |
| Zhejiang | 282 | 305 | 334 | 336 | 287 | −7.8% | 9.5% | 10.0% | −6.2% |
| Anhui | 223 | 205 | 204 | 204 | 233 | 8.9% | −0.7% | −0.3% | 13.8% |
| Fujian | 155 | 152 | 180 | 181 | 135 | 2.1% | 18.5% | 19.1% | −10.9% |
| Jiangxi | 115 | 118 | 108 | 132 | 109 | −2.3% | −8.8% | 12.0% | −7.5% |
| Henan | 396 | 398 | 338 | 420 | 427 | −0.5% | −15.2% | 5.3% | 7.1% |
| Hubei | 251 | 222 | 255 | 302 | 228 | 13.1% | 15.2% | 36.2% | 2.8% |
| Hunan | 202 | 204 | 208 | 249 | 193 | −0.9% | 2.1% | 22.1% | −5.2% |
| Chongqing | 110 | 116 | 115 | 137 | 101 | −5.7% | −1.3% | 17.9% | −13.0% |
| Sichuan | 224 | 211 | 246 | 301 | 213 | 6.4% | 16.6% | 42.7% | 0.9% |
| Guangdong | 381 | 413 | 389 | 533 | 347 | −7.7% | −5.7% | 29.1% | −15.9% |
| Guangxi | 123 | 124 | 130 | 163 | 104 | −0.8% | 4.4% | 31.1% | −16.0% |
| Hainan | 25 | 25 | 23 | 29 | 32 | −0.7% | −7.1% | 15.3% | 27.0% |
| Guizhou | 177 | 155 | 146 | 177 | 198 | 13.8% | −6.3% | 13.9% | 27.3% |
| Yunnan | 148 | 135 | 147 | 183 | 141 | 9.5% | 8.5% | 35.2% | 4.3% |
| Shaanxi | 169 | 161 | 151 | 168 | 244 | 5.0% | −6.1% | 4.3% | 51.3% |
| Qinghai | 29 | 30 | 44 | 52 | 33 | −3.6% | 46.6% | 74.3% | 9.5% |
| Gansu | 108 | 106 | 112 | 128 | 131 | 1.8% | 5.6% | 20.5% | 23.7% |
| Ningxia | 89 | 83 | 74 | 84 | 104 | 6.4% | −11.7% | 1.2% | 24.7% |
| Xinjiang | 158 | 157 | 147 | 162 | 200 | 0.5% | −6.3% | 3.5% | 27.5% |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tao, X.; Wang, P.; Zhu, B. Measuring the Interprovincial CO2 Emissions Considering Electric Power Dispatching in China: From Production and Consumption Perspectives. Sustainability 2016, 8, 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8060506
Tao X, Wang P, Zhu B. Measuring the Interprovincial CO2 Emissions Considering Electric Power Dispatching in China: From Production and Consumption Perspectives. Sustainability. 2016; 8(6):506. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8060506
Chicago/Turabian StyleTao, Xueping, Ping Wang, and Bangzhu Zhu. 2016. "Measuring the Interprovincial CO2 Emissions Considering Electric Power Dispatching in China: From Production and Consumption Perspectives" Sustainability 8, no. 6: 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8060506
APA StyleTao, X., Wang, P., & Zhu, B. (2016). Measuring the Interprovincial CO2 Emissions Considering Electric Power Dispatching in China: From Production and Consumption Perspectives. Sustainability, 8(6), 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8060506





