Assessing Wheat Frost Risk with the Support of GIS: An Approach Coupling a Growing Season Meteorological Index and a Hybrid Fuzzy Neural Network Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Research Framework for Assessing Wheat Frost Risk
2.3. Hazard Assessment of Wheat Frost Risk
2.3.1. Threshold Temperature of Wheat Frost Hazard
2.3.2. Wheat Frost Hazard Assessment Method
2.4. Vulnerability Assessment of Wheat Frost Risk
2.4.1. Diffuse Historical Records Using the Information Diffusion Method
2.4.2. Vulnerability Curving of Winter Wheat Based on Diffused Historical Disaster Data
3. Results
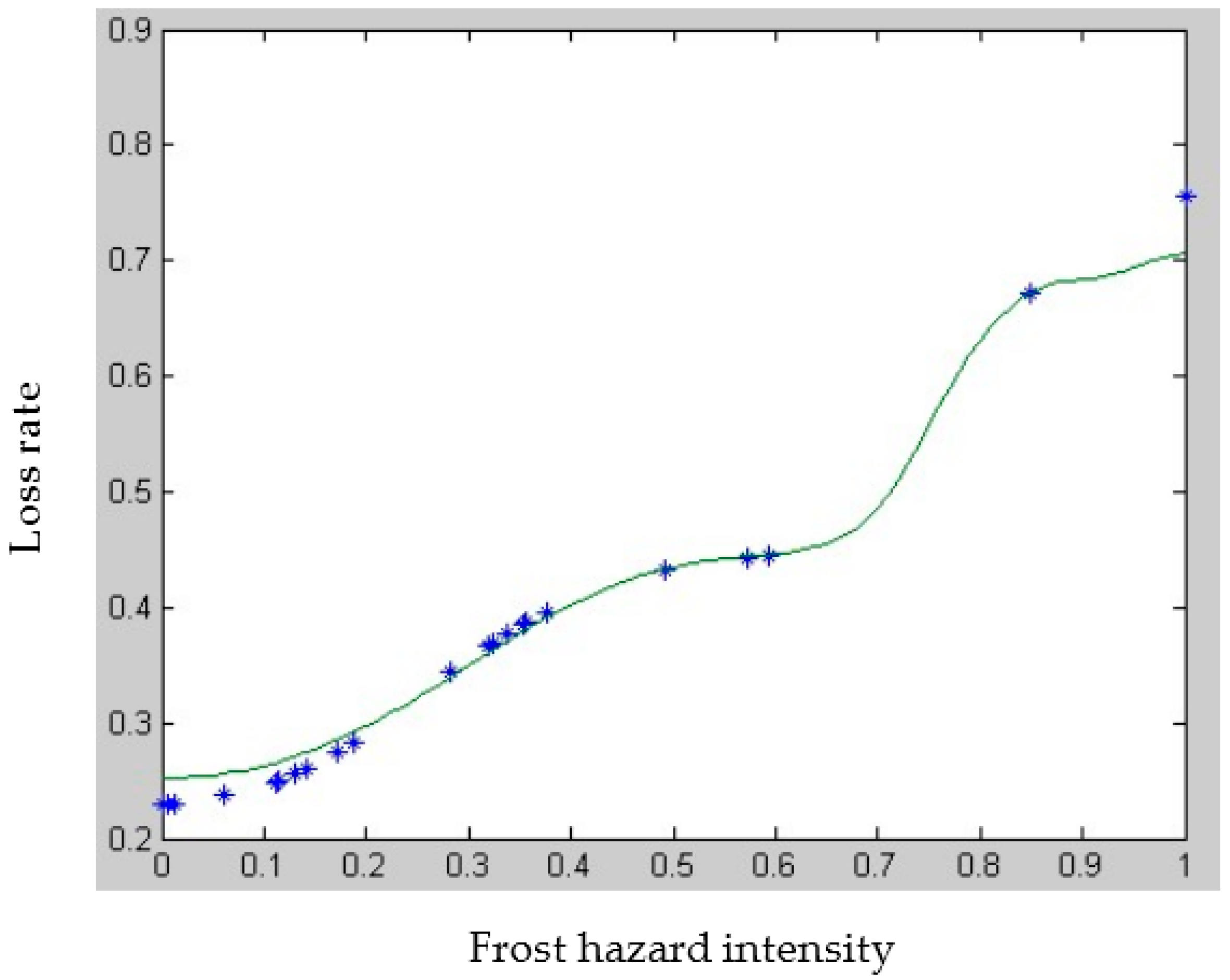
3.1. Vulnerability Cure of Wheat Subjected to Frost
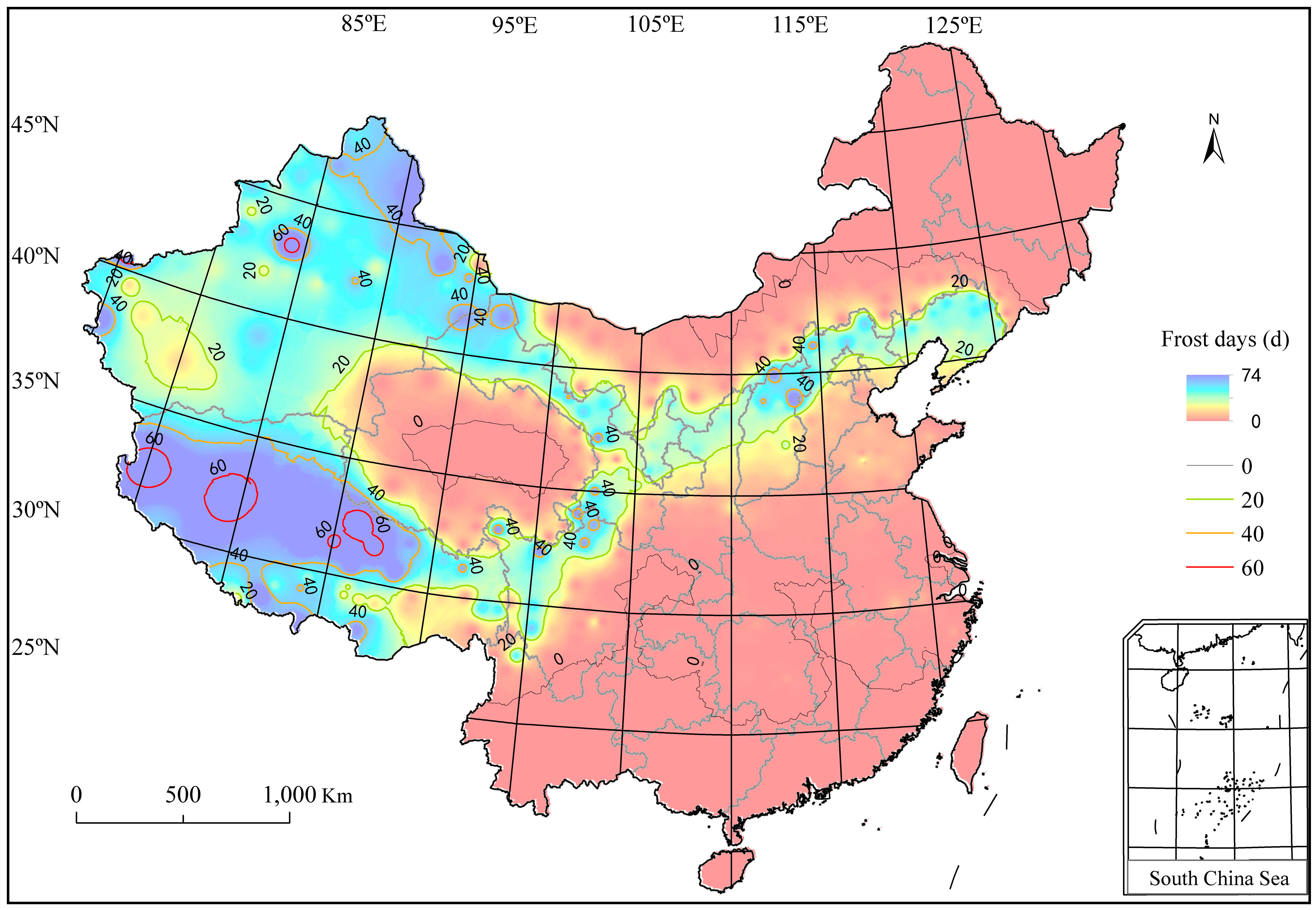
3.2. Wheat Frost Days in China
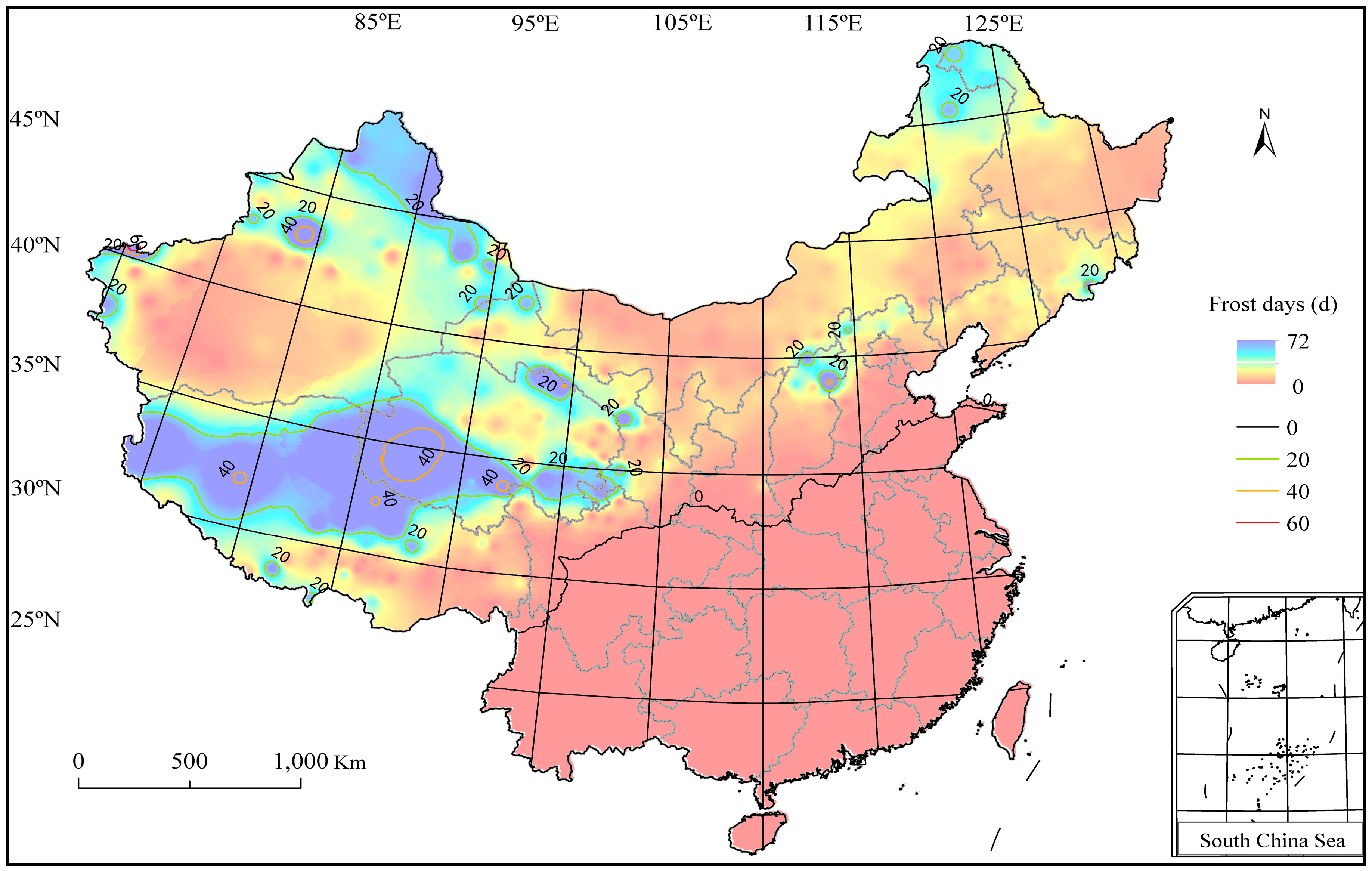
3.3. Wheat Frost Hazard in China
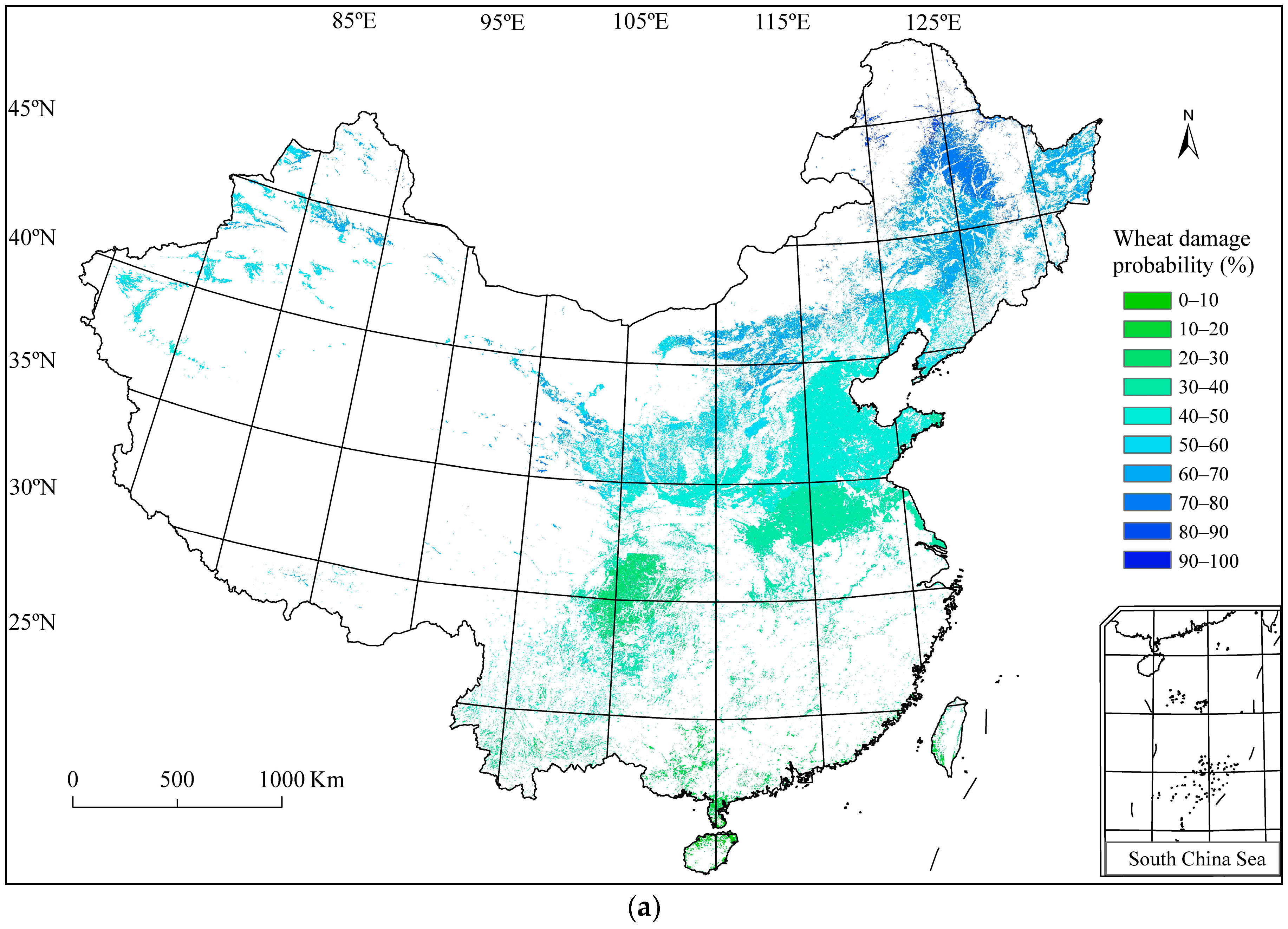
3.4. Wheat Frost Risk in China
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Papagiannaki, K.; Lagouvardos, K.; Kotroni, V.; Papagiannakis, G. Agricultural losses related to frost events: Use of the 850 hPa level temperature as an explanatory variable of the damage cost. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 14, 2375–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heino, R.; Brázdil, R.; Førland, E.; Tuomenvirta, H.; Alexandersson, H.; Beniston, M.; Pfister, C.; Rebetez, M.; Rosenhagen, G.; Rösner, S.; et al. Progress in the study of climate extremes in northern and central Europe. Clim. Chang. 1999, 42, 151–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonsal, B.R.; Zhang, X.; Vincent, L.A.; Hogg, W.D. Characteristics of daily and extreme temperature over Canada. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 1959–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easterling, D.R. Recent changes in frost days and the frost-free season in the United States. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 83, 1327–1332. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.H.; Wang, H.J.; Ge, Q.S. The decreasing spring frost risks during the flowering period for woody plants in temperate area of eastern China over past 50 years. J. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Hanson, P.J.; Mac, P.W.; Kaiser, D.P.; Yang, B.; Nemani, R.; Pallardy, S.G.; Meyers, T. The 2007 eastern US spring freezes: Increased cold damage in a warming world? Bioscience 2008, 58, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannell, M.G.R.; Smith, R.I. Climatic warming, spring budburst and frost damage on trees. J. Appl. Ecol. 1986, 23, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobin, A.; Tarquis, A.M.; Dalezios, N.R. Preface “Weather related hazards and risks in agriculture”. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 2599–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.S.; Wang, D.L.; Zhang, Q.; Chi, Y.G.; Wang, C.Y.; Kiribuchi-Otobe, C.; Yoshida, H. Cause analysis of frost dam to winter wheat in Huang-Huai-Hai plain during 2004–2005. J. Nat. Disasters 2005, 14, 51–55, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.S.; Wang, D.L.; Zhong, X.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Su, C.H.; Zhao, P.; Yan, X.Y.; Kiribuchi-Otobe, C.; Yoshida, H. Current situation and prospect of research on frost of winter wheat. J. Nat. Disasters 2005, 14, 72–78, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Eccel, E.; Rea, R.; Caffarra, A.; Crisci, A. Risk of spring frost to apple production under future climate scenarios: The role of phenological acclimation. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2009, 53, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigby, J.R.; Porporato, A. Spring frost risk in a changing climate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, J. Spring frosts in deciduous fruit trees—Morphological damage and flower hardiness. Sci. Hortic. 2000, 85, 155–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varazanashvili, O.; Tsereteli, N.; Amiranashvili, A.; Tsereteli, E.; Elizbarashvili, E.; Dolidze, J.; Qaldani, L.; Saluqvadze, M.; Adamia, S.; Arevadze, N.; et al. Vulnerability, hazards and multiple risk assessment for Georgia. Nat. Hazards 2012, 64, 2021–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laughlin, G.P.; Kalma, J.D. Frost Risk Mapping for Landscape Planning—A Methodology. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 1990, 42, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinoni, F.; Antolini, G.; Campisi, T.; Marletto, V.; Rossi, F. Characterisation of Emilia-Romagna region in relation with late frost risk. Phys. Chem. Earth 2002, 27, 1091–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, M.; Hajjam, S.; Khalili, A.; Kamali, G.A.; Stigter, C.J. Risk analysis of first and last frost occurrences in the Central Alborz Region, Iran. Int. J. Climatol. 2007, 27, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalma, J.D.; Laughlin, G.P.; Caprio, J.M.; Hamer, P.J.C. The Bioclima-Tology of Frost. Its Occurrence, Impact and Protection. Advances in Bioclimatology 2; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Crimp, S.; Bakar, K.S.; Kokic, P.; Jin, H.D.; Nicholls, N.; Howden, M. Bayesian space-time model to analyse frost risk for agriculture in Southeast Australia. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 2092–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollaway, K. NVT Victorian Winter Crop Summary 2014; The State of Victoria Department of Environment and Primary Industry: Brisbane, Australia, 2014.
- Lush, D. Queensland 2014 Wheat Varieties; Grains Research and Development Corporation and the State of Queensland, Department of Agriculture, Fisheries and Forestry: Brisbane, Australia, 2014.
- Matthews, P.; McCaffery, D.; Jenkins, L. Winter Crop Variety Sowing Guide 2014; NSW Department of Primary Industries: Sydney, Australia, 2014.
- Shackley, B.; Zaicou-Kunesch, C.; Dhammu, H.; Shankar, M.; Amjad, M.; Young, K. Wheat Variety Guide for Western Australia 2014; Department of Agriculture and Food, Western Australia: Brisbane, Australia, 2014.
- Wheeler, B. Wheat variety sowing guide 2014. In South Australia Sowing Guide; Heaslip, J., Eldredge, L., Treloar, M., Shannon, D., Eds.; SA Grain Industry Trust and Grains Research and Development Corporation: Brisbane, Australia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, B.Y.; Chenu, K.; Dreccer, M.F.; Chapman, S.C. Breeding for the future: What are the potential impacts of future frost and heat events on sowing and flowering time requirements for Australian bread wheat (Triticum aestivium) varieties? Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 18, 2899–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, B.Y.; Chapman, S.C.; Christopher, J.T.; Frederiks, T.M.; Chenu, K. Frost trends and their estimated impact on yield in the Australian wheat belt. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 3611–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potop, V.; Zahranicek, P.; Turkott, L.; Stepanek, P.; Soukup, J. Risk occurrences of damaging frosts during the growing season of vegetables in the Elbe River lowland, the Czech Republic. Nat. Hazards 2014, 71, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.L.; Wang, D.L.; Zhao, P.; Yan, X.Y.; Su, C.H. Occurrence of frost temperature in Huanghuai wheat production zone after wheat elongation. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2007, 15, 17–20, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Levitt, J. Response of Plant to Environmental Stress; Academic Press: London, UK, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Sakai, A.; Larcher, W. Frost Survival of Plant; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, J.J. Climate Change 2001: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability: Contribution of Working Group II to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Cutter, S.L. Vulnerability to environmental hazards. Prog. Hum. Geogr. 1996, 20, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, N. Vulnerability, risk and adaptation: A conceptual framework. Tyndall Cent. Clim. Chang. Res. Work. Pap. 2003, 38, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan, C.A. Quantifying water vulnerability: A multi-dimensional approach. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2011, 25, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.J.; Li, J.; Ye, X.Y.; Wang, Z.Q.; Zhu, A.X.; Wang, J.A. An EPIC model-based vulnerability assessment of wheat subject to drought. Nat. Hazards 2015, 78, 1629–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaikie, P.; Cannon, T.D.; Davis, I.I.; Wisner, B. At Risk: Natural Hazards, People’s Vulnerability and Disasters; Routledge: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations International Strategy for Disaster Reduction (UN/ISDR). Living with Risk. A Global Review of Disaster Reduction Initiatives; United Nations: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, B.L., II; Kasperson, R.E.; Matson, P.A.; McCarthy, J.J.; Corell, R.W.; Christensen, L.; Eckley, N.; Kasperson, J.X.; Luers, A.; Martello, M.L.; et al. A framework for vulnerability analysis in sustainability science. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 8074–8079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, B.L., II; Matson, P.A.; McCarthy, J.J.; Corell, R.W.; Christensen, L.; Eckley, N.; Hovelsrud-Broda, G.K.; Kasperson, J.X.; Kasperson, R.E.; Luers, A.; et al. Illustrating the coupled human-environment system for vulnerability analysis: Three case studies. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 8080–8085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Sha, Y.Z.; Bai, Y.M. Regional distribution of main agrometeorological disaster and disaster mitigation strategies in China. J. Nat. Disasters 2003, 12, 82–97, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Shi, P.J. Atlas of Nature Disaster Risk of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, P.J. Natural Disasters in China. In IHDP/Future Earth-Integrated Risk Governance Project Series; Jaeger, C., Shi, P.J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, X.; Mei, X.; Li, Y.; Yoshida, H.; Zhao, P.; Wang, X.; Han, L.; Hu, X.; Huang, S.; Huang, J.; et al. Changes in Frost Resistance of Wheat Young Ears with Development During Jointing Stage. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2008, 194, 343–349, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.X.; He, W.X.; Sun, Z.F.; Zhong, X.L. Climatological study on frost damage of winter wheat in China. Acta Agron. Sin. 1999, 25, 333–340, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Qi, X.X.; Vitousek, P.M.; Liu, L.M. Provincial food security in China: A quantitative risk assessment based on local food supply and demand trends. Food Secur. 2015, 7, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, M.P.; Fuller, A.M.; Kaniouras, S.; Christophers, J.; Fredericks, T. The freezing characteristics of wheat at ear emergence. Eur. J. Agron. 2007, 26, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.F. Frost Disasters and Defense Technology; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2001; pp. 81–82. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, S.Z.; Wang, J.T.; Ran, X.Z.; Wang, Z.T.; Xiao, J.H.; Li, Y.L. The frequency of late frost injury and its preventing method in wheat planted area in Huanghuai. Meteorol. J. Henan 2005, 4, 40–41, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.Y.; Zhuang, D.F.; Zhang, Z.X.; Gao, Z.Q.; Deng, X.Z. The establishment of land-use spatial-temporal database and its relative studies in China. Geo-Inform. Sci. 2002, 3, 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.Y.; Liu, M.L.; Zhuang, D.F.; Zhang, Z.X.; Deng, X.Z. The space analysis of land use pattern change of recent China. Sci. China (Ser. D) 2002, 32, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar]
- Codification Commission of National Atlas. National Agricultural Atlas of the People’s Republic of China; SinoMaps Press: Beijing, China, 1989.
- Alexander, D. Confronting Catastrophe-New Perspectives on Natural Disasters; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Crichton, D. Natural Disaster Management; Tudor Rose: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Dilley, M.; Chen, R.S.; Deichmann, U.; Lerner-Lam, A.L.; Arnold, M.; Agwe, J.; Buys, P.; Kjekstad, O.; Lyon, B.; Yetman, G. Natural Disaster Hotspots: A Global Risk Analysis; Disaster Risk Management Series No. 5; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Hu, G.F.; Yue, Y.J.; Ye, X.Y.; Li, M.; Zhao, J.T.; Wan, J.H. GIS-based risk assessment of cotton hail disaster and its spatiotemporal evolution in China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.M.; Yue, Y.J.; Su, Y. Frost Hazard Risk Assessment of Winter Wheat: Based on the Meteorological Indicator at Different Growing Stages. J. Catastrophol. 2009, 24, 45–50, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- China Meteorological Administration. Degree of Crop Frost Damage (QX/T 88-2008); The National Standard of the People’s Republic of China; China Meteorological Administration: Beijing, China, 2008. (In Chinese)
- Huang, C.F.; Lueng, Y. Estimating the relationship between isoseismal area and earthquake magnitude by hybrid fuzzy-neural-network method. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1999, 107, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.F.; Moraga, C. A diffusion-neural-network for learning from small samples. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 2004, 35, 137–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.F. Information matrix method for risk analysis of natural disaster. J. Nat. Disasters 2006, 15, 1–10, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.F. Risk Assessment of Natural Disaster Theory and Practice; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Liu, G. The study of a method of regional environmental risk assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 3290–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, H.; Saghatoleslami, N.; Rahim, M.R. Prediction of Water Activity Coefficient in TEG-Water System Using Diffusion Neural Network (DNN). Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 2000, 24, 167–176. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Yue, Y.J.; Shen, H.; Wang, J.A. Analysis of Wheat Vulnerability to Frost Disaster Based on Hybrid Model of Fuzzy Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 4th Annual Meeting of Risk Analysis Council of China Association for Disaster Prevention, Changchun, China, 16–17 August 2010. (In Chinese with English Abstract).
- Zhang, X.F.; Ren, Z.H.; Chen, H.L.; Chen, D.; Zou, C.H.; Jin, G.Q. Risk assessment and influence of winter late frost on winter yield. J. Basic Sci. Eng. 2006, 14, 321–328, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, X.L.; Wang, D.L.; Li, Y.Z.; Zhao, P.; Yan, X.Y.; Sun, Z.F. Risk assessment of frost damage in wheat. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2007, 18, 102–107, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.D.; Zhang, X.F. A research on accessing method of frost damage in winter wheat in Huanghai area. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2009, 7454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


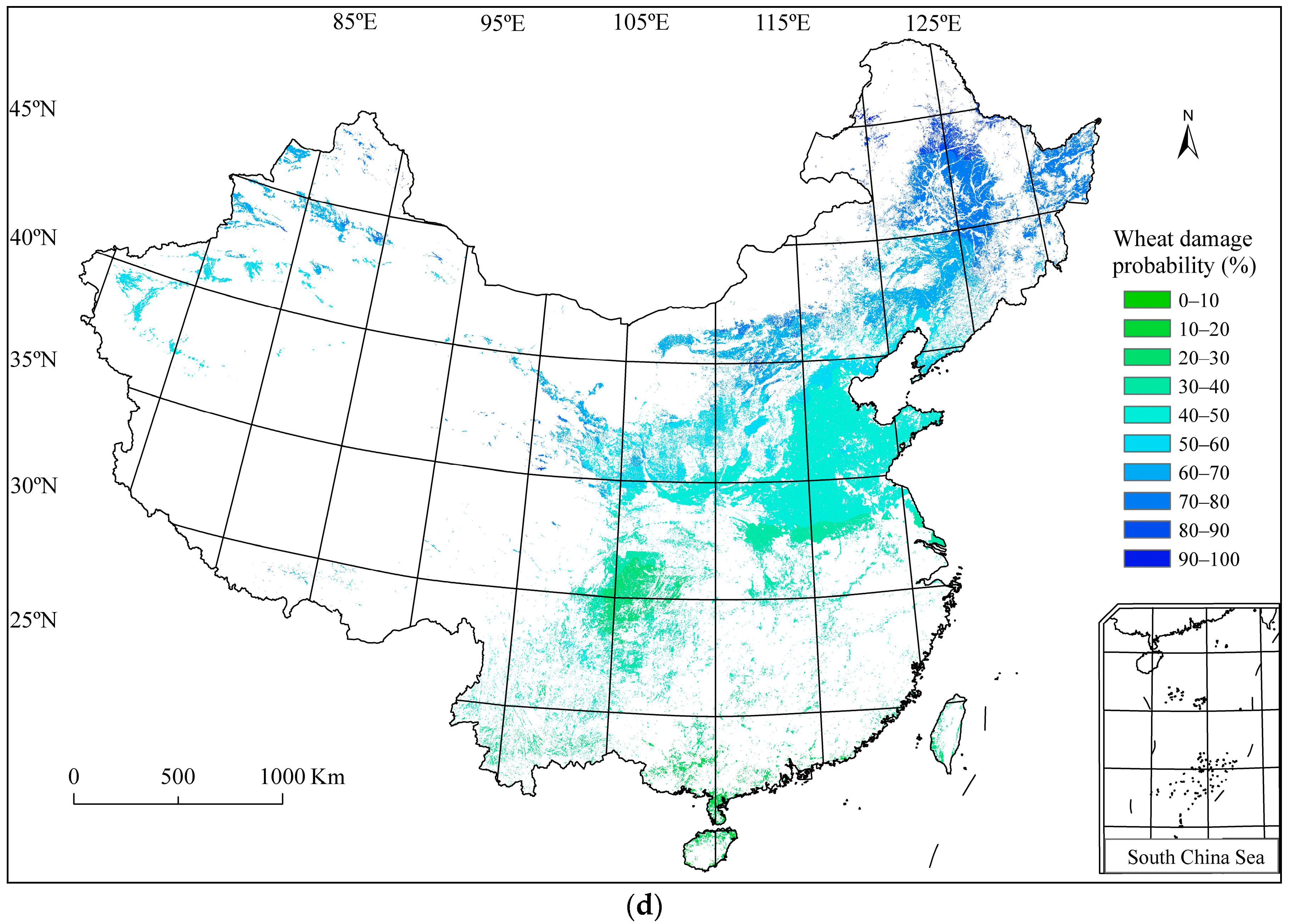

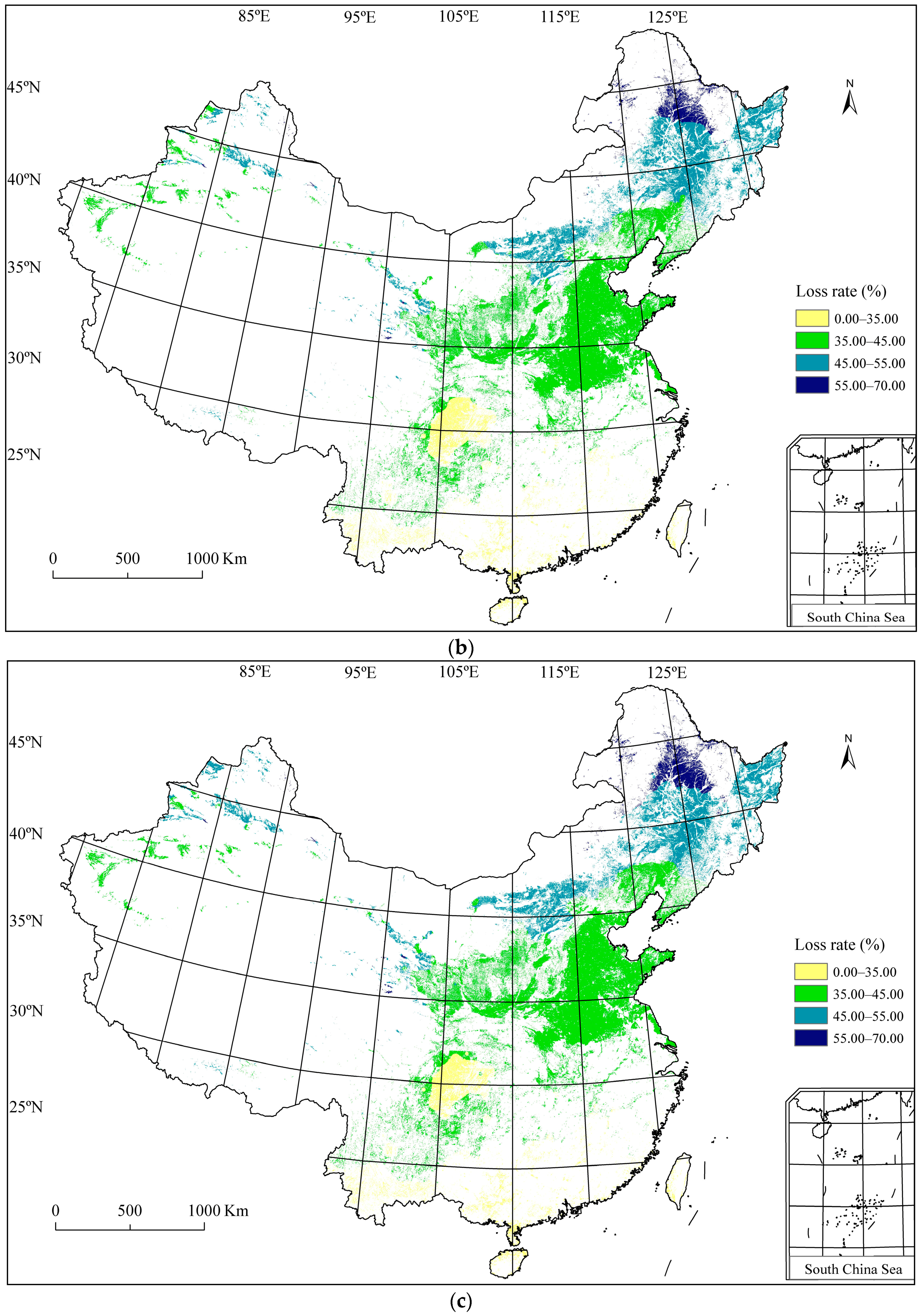
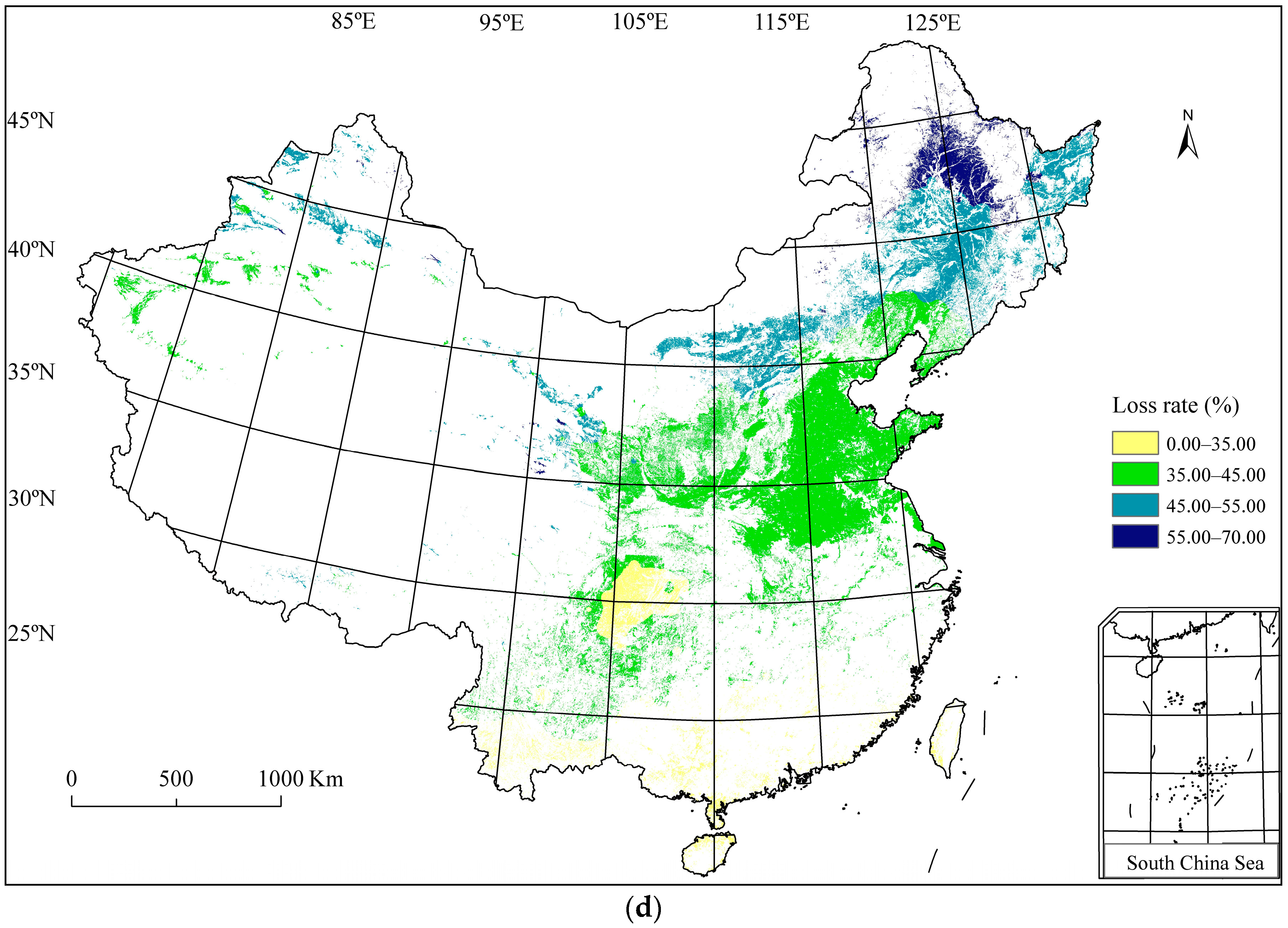
| Wheat Planting Regions | Seedling Stage (mm/dd) | Flowering Stage (mm/dd) | Harvest Stage (mm/dd) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Shanxi | 9/21–4/20 | 4/21–5/20 | 5/21–6/11 |
| Shandong, Shannxi | 10/1–3/31 | 4/1–4/30 | 5/1–6/11 |
| Henan | 10/11–3/20 | 3/21–4/20 | 4/21–6/11 |
| Anhui, Jiangsu | 10/21–3/10 | 3/11–4/20 | 4/21–6/1 |
| Shanghai | 10/21–2/29 | 3/1–4/20 | 4/21–6/1 |
| Guizhou | 10/21–2/10 | 2/11–3/20 | 3/21–5/21 |
| Chongqing | 11/1–1/20 | 1/21–2/29 | 3/1–5/1 |
| Hubei | 11/1–2/29 | 3/1–4/10 | 4/11–6/1 |
| Hunan | 11/1–2/20 | 2/21–3/31 | 4/1–5/21 |
| Jiangxi | 11/1–2/10 | 2/11–3/31 | 4/1–5/11 |
| Sichuan | 11/1–1/31 | 2/1–3/10 | 3/11–5/11 |
| Yunnan | 11/1–1/31 | 2/1–2/29 | 3/1–/5/1 |
| Zhejiang | 11/11–2/20 | 2/21–4/10 | 4/11–5/11 |
| Fujian | 11/11–1/31 | 2/1–2/29 | 3/1–5/11 |
| Guangdong, Guangxi | 11/11–12/31 | 1/1–1/31 | 2/1–4/1 |
| Liaoning | 9/11–4/30 | 5/1–5/31 | 6/1–7/11 |
| Gansu | 9/11–4/30 | 5/1–5/31 | 6/1–7/21 |
| Ningxia | 9/21–4/30 | 5/1–5/31 | 6/1–7/11 |
| Xinjiang | 9/11–4/30 | 5/1–5/31 | 6/1–7/11 |
| Tibet | 9/11–5/10 | 5/11–6/10 | 6/11–9/1 |
| Light Frost | Moderate Frost | Heavy Frost | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seedling Stage | Flowering Stage | Harvest Stage | Seedling Stage | Flowering Stage | Harvest Stage | Seedling Stage | Flowering Stage | Harvest Stage |
| −7.0–8.0 | 0.0–1.0 | −1.0–2.0 | −8.0–9.0 | −1.0–2.0 | −2.0–3.0 | −9.0–10 | −2.0–3.0 | −3.0–4.0 |
| Sample | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −18 | −0.8 | −5.5 | −6 | −10 | −4.6 | −0.6 | −9.9 | −3.7 | −8.8 | −10.9 | −3.7 | −15 | |
| 0.45 | 0.2 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.3 | 0.15 | 0.2 | 0.55 | 0.1 | 0.5 | |
| 0.446 | 0.231 | 0.274 | 0.283 | 0.369 | 0.260 | 0.230 | 0.367 | 0.249 | 0.344 | 0.385 | 0.249 | 0.432 | |
| Sample | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | |
| −25.6 | −11.6 | −11 | −3.8 | −10.4 | −10.9 | −0.4 | −6 | −17.4 | −2.2 | −4.3 | −30.1 | ||
| 0.65 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.25 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.33 | 0.15 | 0.8 | ||
| 0.671 | 0.396 | 0.386 | 0.250 | 0.376 | 0.385 | 0.23 | 0.283 | 0.443 | 0.237 | 0.256 | 0.757 |
| Frost Intensity Level | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probability | Once Every 2 Years | Once Every 5 Years | Once Every 10 Years | Once Every 20 Years |
| 0.00–10.00 | 0.66 | 0.35 | 0.11 | 0.08 |
| 10.00–20.00 | 2.61 | 2.47 | 2.49 | 2.39 |
| 20.00–30.00 | 9.22 | 8.29 | 7.54 | 7.10 |
| 30.00–40.00 | 18.27 | 15.52 | 15.03 | 13.74 |
| 40.00–50.00 | 23.06 | 25.61 | 26.32 | 26.97 |
| 50.00–60.00 | 16.53 | 14.73 | 14.23 | 14.03 |
| 60.00–70.00 | 22.57 | 20.46 | 18.38 | 18.02 |
| 70.00–80.00 | 6.21 | 10.75 | 13.73 | 14.87 |
| 80.00–90.00 | 0.88 | 1.76 | 2.03 | 2.62 |
| 90.00–100.00 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.15 | 0.17 |
| Risk Levels | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loss Rate (%) | Once Every 2 Years | Once Every 5 Years | Once Every 10 Years | Once Every 20 Years |
| 0.00–35.00 | 12.64 | 11.21 | 10.31 | 9.71 |
| 35.00–45.00 | 63.27 | 60.71 | 59.54 | 58.60 |
| 45.00–55.00 | 21.34 | 23.73 | 24.11 | 24.18 |
| 55.00–70.00 | 2.75 | 4.35 | 6.04 | 7.51 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yue, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Ye, X. Assessing Wheat Frost Risk with the Support of GIS: An Approach Coupling a Growing Season Meteorological Index and a Hybrid Fuzzy Neural Network Model. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8121308
Yue Y, Zhou Y, Wang J, Ye X. Assessing Wheat Frost Risk with the Support of GIS: An Approach Coupling a Growing Season Meteorological Index and a Hybrid Fuzzy Neural Network Model. Sustainability. 2016; 8(12):1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8121308
Chicago/Turabian StyleYue, Yaojie, Yao Zhou, Jing’ai Wang, and Xinyue Ye. 2016. "Assessing Wheat Frost Risk with the Support of GIS: An Approach Coupling a Growing Season Meteorological Index and a Hybrid Fuzzy Neural Network Model" Sustainability 8, no. 12: 1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8121308
APA StyleYue, Y., Zhou, Y., Wang, J., & Ye, X. (2016). Assessing Wheat Frost Risk with the Support of GIS: An Approach Coupling a Growing Season Meteorological Index and a Hybrid Fuzzy Neural Network Model. Sustainability, 8(12), 1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8121308






