Science, Technology and Innovation through Entrepreneurship Education in the United Arab Emirates (UAE)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. UAE and Entrepreneurship Education
2.1. Entrepreneurship Education and Cultural Barriers in UAE
2.2. Skills Development through Entrepreneurial Education
3. Theory and Hypotheses
3.1. Entrepreneurship Theories
3.2. Hypotheses Development
3.2.1. Entrepreneurship Education
3.2.2. Self-Confidence as Predictor and Mediating Role of Positive Attitude
3.2.3. Locus of Control as a Predictor
3.2.4. Risk Taking Propensity as Predictor
3.2.5. Moderating Role of Fortitude
4. Research Methodology
4.1. Participants
4.2. Measurements
4.3. Statistical Test
4.4. Hypotheses Testing
5. Conclusions
6. Discussion
7. Limitations
8. Reforms to Enhance Science, Technology, and Innovation in UAE
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hall, J.K.; Martin, M.J.C. Disruptive technologies, stakeholders and the innovation value-added chain: A framework for evaluating radical technology development. R&D Manag. 2005, 35, 273–284. [Google Scholar]
- Hallami, M.O.; Horne, C.; Huang, V.Z. Technological Innovation in the United Arab Emirates: Process and Challenges. Trans. Corp. Rev. 2013, 5, 46–59. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. The World Investment Report, Transnational Corporations and the Internationalization of R&D; United Nation Publication: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Dutot, V.; van Horne, C. Digital Entrepreneurship Intention in a Developed vs. Emerging Country: An Exploratory Study in France and the UAE. Trans. Corp. Rev. 2015, 7, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarbush, S. Strength in Knowledge—MENA Acceleration Research, Development and Innovation; Global Arab Network: Dubai, UAE, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mubadala. Patent Application No. PCT/IB2008/000438. 2010. Available online: http://mubadala.ae (accessed on 14 June 2016).
- Emirates News Agency. Scientific Research Budget in Government Universities Is Low; WAM: Abu Dhabi, UAE, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Van Horne, C.; Huang, V.; Al Awad, M. UAE GEM Report 2011; Zayed University: Abu Dhabi, UAE, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Souitaris, V.; Zerbinati, S.; Al-Laham, A. Do entrepreneurship programmes raise entrepreneurial intention of science and engineering students? The effect of learning, inspiration and resources. J. Bus. Ventur. 2007, 22, 566–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Duysters, G.; Cloodt, M. The role of entrepreneurship education as a predictor of university students’ entrepreneurial intention. Int. Entrep. Manag. J. 2014, 10, 623–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzah, H.; Yahya, Z.; Sarip, A.G.; Adnan, Y.M. Impact of entrepreneurship education programme (EEP) on entrepreneurial intention of real estate graduates. Pac. Rim Prop. Res. J. 2016, 22, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, J.J. The Entrepreneurial Organization; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, A.B.; Soufani, K. Entrepreneurship education and training in Canada: A critical assessment. Educ. Train. 2002, 44, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, S.; Varadarajan, D. Students’ attitude towards entrepreneurship: Does gender matter in the UAE? Foresight 2013, 15, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.K.; Wong, P. Entrepreneurial interest of university students in Singapore. Technovation 2004, 24, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turker, D.; Selcuk, S.S. Which factors affect entrepreneurial intention of university students? J. Eur. Ind. Train. 2009, 33, 142–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosterbeek, H.; van Praag, M.; Ijsselstein, A. The impact of entrepreneurship education on entrepreneurship skills and motivation. Eur. Econ. Rev. 2010, 54, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Graevenitz, G.; Harhoff, D.; Weber, R. The effects of entrepreneurship education. J. Econ. Behav. Organ. 2010, 76, 90–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quality Assurance Agency. Enterprise and Entrepreneurship Education: Guidance for UK Higher Education Providers. Quality Assurance Agency for Higher Education. 2012. Available online: http://www.qaa.ac.uk/en/Publications/Documents/enterprise-entrepreneurship-guidance.pdf (accessed on 14 July 2016).
- The Abu Dhabi Economic Vision 2030. Available online: https://www.ecouncil.ae/PublicationsEn/economic-vision-2030-full-versionEn.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2016).
- Nicola, M. Middle East: The Rising Importance of SMEs (Special Report Standard Chartered Bank). 2009. Available online: http://research.standardchartered.com (accessed on 7 August 2016).
- Baumol, W. The Free-Market Innovation Machine: Analyzing the Growth Miracle of Capitalism; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Van Stel, A.J. Empirical Analysis of Entrepreneurship and Economic Growth; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wennekers, S.; van Stel, A.J.; Thurik, R.; Reynolds, P.D. Nascent entrepreneurship and the level of economic development. Small Bus. Econ. 2005, 24, 293–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Nowais, S. Education System to Get Overhaul. Gulf News On-Line. Available online: http://www.gulfnews.com/Articles/print2.asp?ArticleID=141170 (accessed on 10 August 2016).
- Ferris-Lay, C. UAE Schools Failing to Equip Pupils for Workplace. Arabian Business News. Available online: http://www.arabianbusiness.com/uae-schools-failingequip-pupils-for-workplace-360042.html (accessed on 10 August 2016).
- Godwin, L.N.; Stevens, C.E.; Brenner, N.L. Forced to play by the rules? Theorizing how mixed sex founding teams benefit women entrepreneurs in male-dominated contexts. Entrep. Theory Pract. 2006, 30, 623–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrohan, D.; Erogul, M.S.; Vellinga, N.; Tong, Q. Global Entrepreneurship Monitor, National Report, United Arab Emirates 2009; College of Business Sciences, Zayed University: Abu Dhabi, UAE, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, G.; Parmer, N. Problems Facing Entrepreneurs and SMEs in the UAE. The National. 2011. Available online: http://www.thenational.ae/thenationalconversation/industry-insights/finance/problems-facing-entrepreneurs-and-smes-in-the-uae (accessed on 13 August 2016).
- Mahfouz, E. Tadros. The Arab Gulf States and the Knowledge Economy: Challenges and Opportunities. Available online: http://www.agsiw.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/Tadros_Knowledge-Economy_Rev1.pdf (accessed on 13 August 2016).
- Ali, M. Al-Khouri Digital identity: Transforming GCC economies. Innovation 2014, 16, 184–194. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, M.H.; Davis, D.L.; Allen, J.W. Fostering corporate entrepreneurship: Cross-cultural comparisons of the importance of individualism versus collectivism. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 1994, 25, 65–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofstede, G. Cultures and Organizations. Software of the Mind: Intercultural Cooperation and Its Importance for Survival; Harper Collins: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, M.H.; Avila, R.A.; Allen, J.W. Individualism and the modern corporation: Implications for innovation and entrepreneurship. J. Manag. 1993, 19, 595–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gohary, H.; O’Leary, S.; Radway, P. Investigating the Impact of Entrepreneurship Online Teaching on Science and Technology Degrees on Students attitudes in Developing Economies: The case of Egypt. Int. J. Online Mark. 2012, 2, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Entrepreneurship Educators Programme: Economic Impact Potential, Report for National Council of Graduate Entrepreneurship. 2010. Available online: http://www.ncge.org.uk/publication/ieepreport.pdf (accessed on 15 August 2016).
- Shaw, K.E. Higher Education in the Gulf: Problems and Prospects; University of Exeter Press: Exeter, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Higher Education in the United Arab Emirates 2016 Strategic Goals. Available online: https://www.mohesr.gov.ae/En/AboutTheMinistry/Pages/StrategicGoals.aspx (accessed on 10 August 2016).
- Wiseman, A.W.; Alromi, N.H. The Employability Imperative: Schooling for Work as a National Project; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kautonen, T.; van Gelderen, M.; Fink, M. Robustness of the theory of planned behaviour in predicting entrepreneurial intentions and action. Entrep. Theory Pract. 2015, 39, 655–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, T.; Plewa, C.; Struwig, M. Entrepreneurship perceptions and career intentions of international students. Educ. Train. 2011, 53, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattab, T.; Albouy, C.; Lasram, F.B.R.; Somot, S.; Le Loc’h, F.; Leprieur, F. Towards a better understanding of potential impacts of climate change on marine species distribution: A multi scale modelling approach. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2014, 23, 1417–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, M.K. Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises in Malaysia Role and Issues; University Utara Malaysia Press: Sintok, Malaysia, 2002; ISBN 9832479231. [Google Scholar]
- Armanurah, M.; Abdul Razak, A.; Syahrina, A. Kepentingan pendidikan keusahawanan kepada organisasi dan Negara. In Proceedings of the National Conference on Skills and Competencies in Education, Selangor, Malaysia, 2012; pp. 101–106. (In Malayan)
- Mahmood, R.; Foster, S.A.; Logan, D. The GeoProfile metadata, exposure of instruments, and measurement bias in climatic record revisited. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 26, 1091–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, D.; Fritzsche, F.; Tekalign, M.; Lehmann, J.; Zech, W. Soil organic matter composition in the sub-humid Ethiopian highlands as influenced by deforestation and agricultural management. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, J.A. The chronology and intellectual trajectory of American entrepreneurship education 1876–1999. J. Bus. Ventur. 2003, 18, 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, J.C. The impact of an entrepreneurship education program on entrepreneurial competencies and intention. J. Small Bus. Manag. 2013, 51, 447–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, L.R.; Sloof, R.; van Praag, M. The effect of early entrepreneurship education: Evidence from a field experiment. Eur. Econ. Rev. 2014, 72, 76–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, J.; Manimala, J.M. Higher education’s role in entrepreneurship and economic development. Local Econ. Employ. Dev. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeng Kiat, O.; Shuhymee, A. A study among university students in business start-ups in Malaysia: Motivations and obstacles to become entrepreneurs. Int. J. Bus. Soc. Sci. 2012, 3, 181–192. [Google Scholar]
- Zuhairah, A.A.G.; Herna, M.; Zarinah, H. Legal eagle entrepreneurship education for law students: Special reference to International Islamic University Malaysia. Pertan. J. Soc. Hum. 2014, 22, 83–98. [Google Scholar]
- Berma, M.; Shamshubaridah, R.; Faridah, S.; Shazlinda, M.Y. Developing an entrepreneurship education eco-system at University Kebangsaan Malaysia (UKM): A critical analysis on teaching, learning and knowledge development. In Proceedings of the Teaching and Learning Convention, Selangor, Malaysia, 2012; pp. 1–36.
- Malaysia Qualification Register (MQR). Search for Qualifications Public Government Institutions; Malaysian Qualifications Agency: Selangor, Malaysia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Higher Education in the United Arab Emirates (2016a). Guide on Higher Education in the United Arab Emirates in the Academic Year 2013/2014. Available online: http://www.mohesr.gov.ae/En/ServicesIndex/Documents/UAE-factbook24Feb-en-CDversion.pdf (accessed on 5 August 2016).
- Pittaway, L.; Cope, J. Entrepreneurship Education: A Systematic Review of the Evidence. Int. Small Bus. J. 2007, 25, 479–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GEM Report on Entrepreneurship in the United Arab Emirates. Available online: http://www.gemconsortium.org/country-profile/130 (accessed on 6 August 2016).
- Van Praag, C.M. Successful Entrepreneurship; Edward Elgar: Cheltenham, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, L.; Hannon, P.D.; Smith, A. Enacting entrepreneurial intent: The gap between students’ needs and higher education capabilities. Educ. Train. 2004, 48, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syahrina, A.; Armanurah, M.; Habshah, B.; Norashidah, H.; YengKiat, O. Tracer study of bachelor in entrepreneurship program: The case of Universiti Utara Malaysia. Int. J. Educ. Res. 2013, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Millán, J.M.; Congregado, E.; Román, C.; van Praag, M.; van Stel, A. The value of an educated population for an individual’s entrepreneurship success. J. Bus. Ventur. 2013, 29, 612–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, G. Human Capital: A Theoretical and Empirical Analysis with Special Reference to Education, 3rd ed.; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Mincer, J. Investment in human capital and personal income distribution. J. Political Econ. 1958, 66, 281–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennaioli, N.; La Porta, R.; Lopez-de-Silanes, F.; Shleifer, A. Human capital and regional development. Q. J. Econ. 2013, 128, 105–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaegel, C.; Koenig, M. Determinants of entrepreneurial intent: A meta-analytic test and integration of competing models. Enterp. Theory Pract. 2014, 38, 291–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, A.J.; Hulsink, W. Putting entrepreneurship education where the intention to act lies. An Investigation into the Impact of Entrepreneurship Education on Entrepreneurial Behaviour. Acad. Manag. Learn. Educ. 2015, 14, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.; Akbar, S.; Dalziel, M. The journey to develop educated entrepreneurs: Prospects and problems of Afghan businessmen. Educ. Train. 2011, 53, 433–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZainalAbidin, M.; Golnaz, R.I.; Amin, M.A.; Ezhar, T. Work culture and developing agri-entrepreneurial skills among farmers. Am. J. Econ. Bus. Admin. 2011, 3, 490–497. [Google Scholar]
- Grilo, I.; Irigoyen, J.M. Entrepreneurship in the EU: To wish and not to be. Small Bus. Econ. 2006, 26, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The American Dream. Available online: http://www.loc.gov/teachers/classroommaterials/lessons/american-dream/students/thedream.html (accessed on 21 July 2016).
- Sweezy, P.M. Professor Schumpeter’s theory of innovation. In The Review of Economic Statistics; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1943; pp. 93–96. [Google Scholar]
- McClelland, C.A. The acute international crisis. World Politics 1961, 14, 182–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, R.C.; Shiffrin, R.M. Human memory: A proposed system and its control processes. Psychol. Learn. Motiv. 1968, 2, 89–195. [Google Scholar]
- Shelly, A.B.; Seung, Y.C. Factors that influence informal learning in the workplace. J. Workplace Learn. 2008, 20, 229–244. [Google Scholar]
- Dean, T.J.; McMullen, J.S. Toward a theory of sustainable entrepreneurship: Reducing environmental degradation through entrepreneurial action. J. Bus. Ventur. 2007, 22, 50–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogan, N.; Wallach, M.A. Certainty of judgment and the evaluation of risk. Psychol. Rep. 1960, 6, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Prasad, J. A Conceptual and Operational Definition of Personal Innovativeness in the Domain of Information Technology. Inf. Syst. Res. 1998, 9, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMullan, W.E.; Long, W.A.; Wilson, A. MBA concentration on entrepreneurship. J. Small Bus. Entrep. 1985, 3, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, B.; Schunk, D.H. Handbook of Self-Regulation of Learning and Performance; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Akerlind, G.S. Growing and developing as a university teacher—Variation in meaning. Stud. Higher Educ. 2003, 28, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavani, C.M.; Losh, S.C. Motivation, self-confidence and expectations as predictors of the academic performances among our high school students. Child Study J. 2003, 33, 141–151. [Google Scholar]
- Krech, D.; Crutchfield, R.S. Theory and Problems of Social Psychology; MacGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Fuson, W.M. Attitudes: A note on the concept and its research consequences. Am. Sociol. Rev. 1942, 7, 856–857. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, D.T. The indirect assessment of social attitudes. Psychol. Bull. 1950, 47, 15–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajzen, I.; Timko, C.; White, J.B. Self-monitoring and the attitude–behavior relation. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1982, 42, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretorius, T.B. Fortitude as Stress Resistance: Development and Validation of the Fortitude Questionnaire (FORQ); University of the Western Cape: Bellville, South Africa, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Hazan, C.; Shaver, P. Romantic love conceptualized as an attachment process. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1987, 52, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, M.; Collins, A.; Medeira, N.; Slater, J. Barriers to start-up and their effect on aspirant entrepreneurs. Educ. Train. 2003, 45, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pithers, R.T.; Soden, R. Critical thinking in education: A review. Educ. Res. 2000, 42, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, L.; Blackwell, A. Gender bias in incomes of art and design graduates. Ind. High. Educ. 1999, 13, 323–329. [Google Scholar]
- Ihmeideh, F.M.; Al-Omari, A.A.; Al-Dababneh, K.A. Attitudes toward Communication Skills among Students’-Teachers’ in Jordanian Public Universities. Aust. J. Teach. Educ. 2010, 35, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotter, J.B. Generalized expectancies for internal versus external control of reinforcement. Psychol. Monogr. 1966, 80, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bateman, T.S.; Crant, J.M. The proactive component of organizational behavior: A measure and correlates. J. Organ. Behav. 1993, 14, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spector, P.E. Behavior in organizations as a function of employee’s locus of control. Psychol. Bull. 1982, 91, 482–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.S. Cognitive Therapy: Basics and Beyond; Guilford: New York, NU, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Bandura, A. Psychology of chance encounters and life paths. Am. Psychol. 1982, 37, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritson, K.K. Impact of journaling on students’ self-efficacy and locus of control. Insight 2008, 3, 75–83. [Google Scholar]
- Entrialgo, M.; Fernanderz, E.; Vazquez, C.J. The effect of organizational context on SME’s entrepreneurship: Some Spanish evidence. Small Bus. Econ. 2001, 16, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.S.; Mueller, S.L. A case for comparative entrepreneurship: Assessing the relevance of culture. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2000, 31, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, A.; Kerman, K.; Meric, B.; Ozsoz, M. Methylene Blue as a Novel Electrochemical Hybridization Indicator. Electroanalysis 2001, 13, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockhaus, R.H. The psychology of entrepreneur. In Encyclopedia of Entrepreneurship; Kent, C.A., Sexton, D.L., Vesper, K.H., Eds.; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1982; pp. 39–71. [Google Scholar]
- Littunen, H. Entrepreneurship and the characteristics of the entrepreneurial personality. Int. J. Entrep. Behav. Res. 2000, 6, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liles, P.R. Who Are the Entrepreneurs? MSU Bus. Top. 1974, 22, 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Pretorius, T.B.; Heyns, P.M. Fortitude as Stress-Resistance: Development and Validation of the Fortitude Questionnaire (FORQ); University of the Western Cape: Cape Town, South Africa, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Deniz, G.; Erten, G.; Kücüksezer, U.C.; Kocacik, D.; Karagiannidis, C.; Aktas, E.; Akdis, C.A.; Akdis, M. Regulatory NK cells suppress antigen-specific T cell responses. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B.; Lee, J.Y.; Podsakoff, N.P. Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. J. Appl. Psychol. 2003, 88, 879–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, M. Society and the Adolescent Self-Image; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, D.N. Jackson Personality Inventory Manual; Research Psychologists Press: Goshen, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, T.C.M.; Klockaras, J. Anchor point effects on the equivalence of questionnaire items. J. Educ. Meas. 1982, 19, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurt, H.T.; Joseph, K.; Cook, C.D. Scales for the measurement of innovativeness. Hum. Commun. Res. 1977, 4, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, H.J.M. A Questionnaire Measure of Achievement Motivation. J. Appl. Psychol. 1970, 54, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pintrich, R.R.; DeGroot, E.V. Motivational and self-regulated learning components of classroom academic performance. J. Educ. Psychol. 1990, 82, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiseman, A.W.; Anderson, E. ICT-integrated education and national innovation systems in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries. Comput. Educ. 2014, 59, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
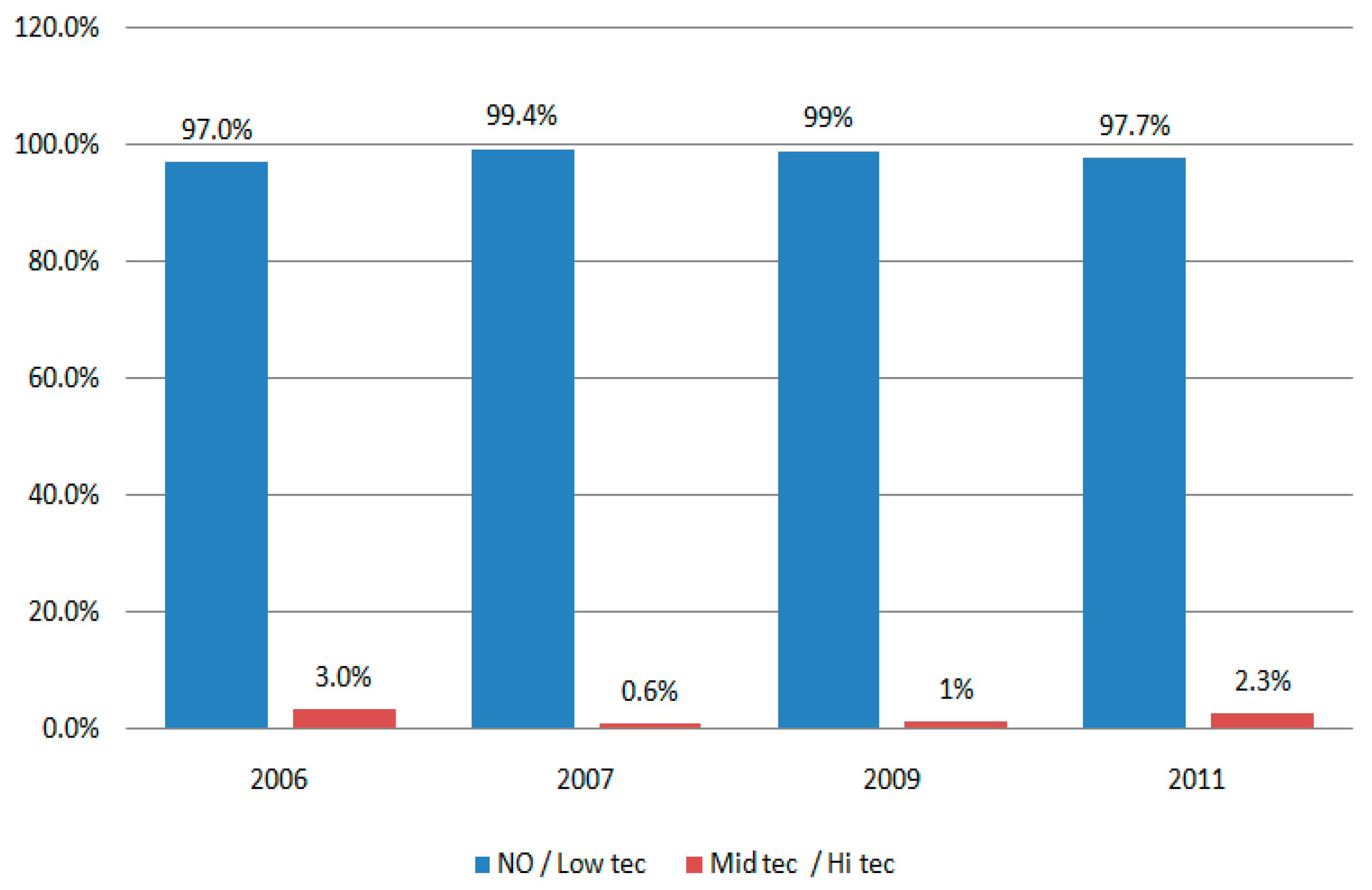
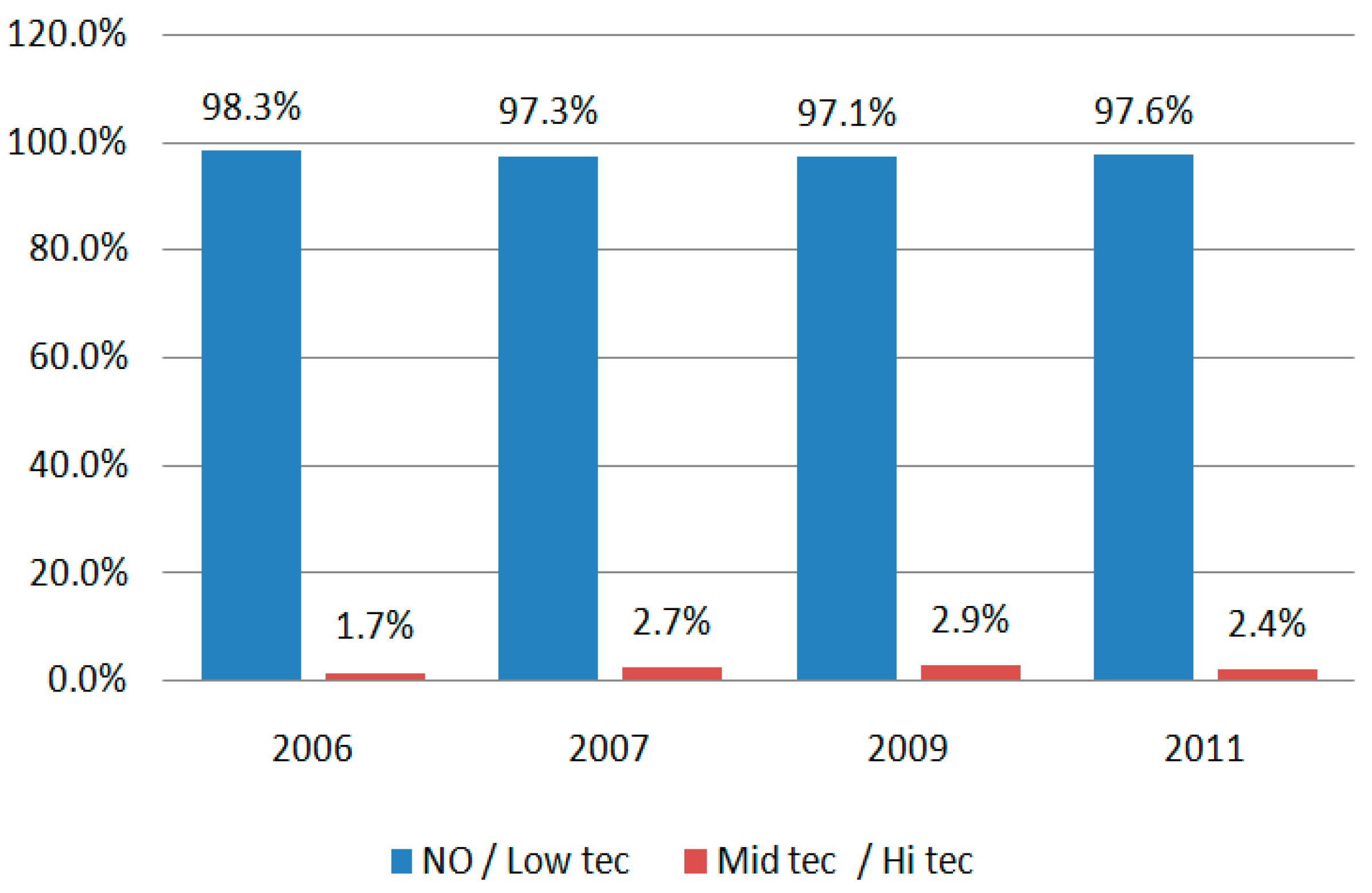
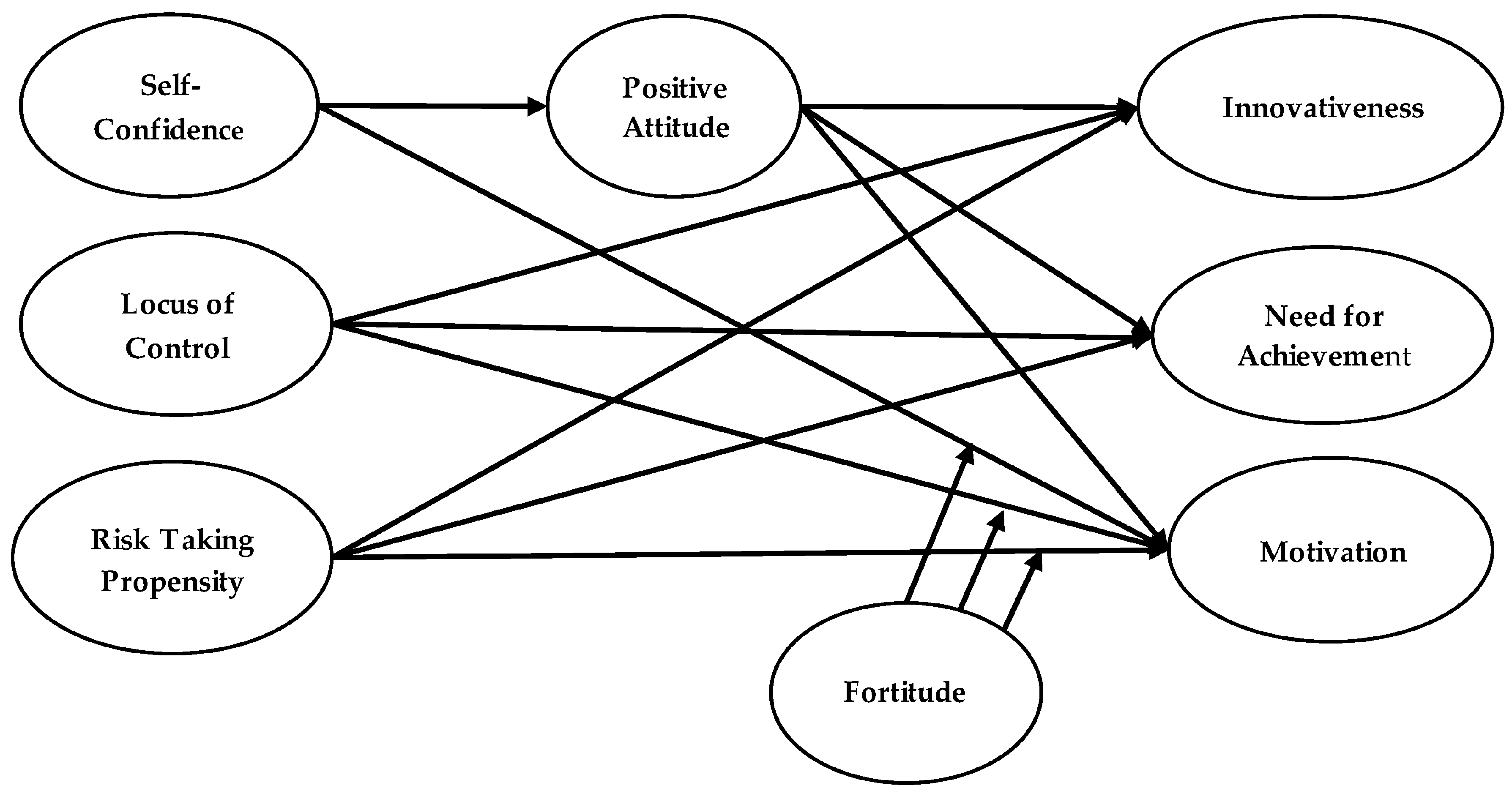
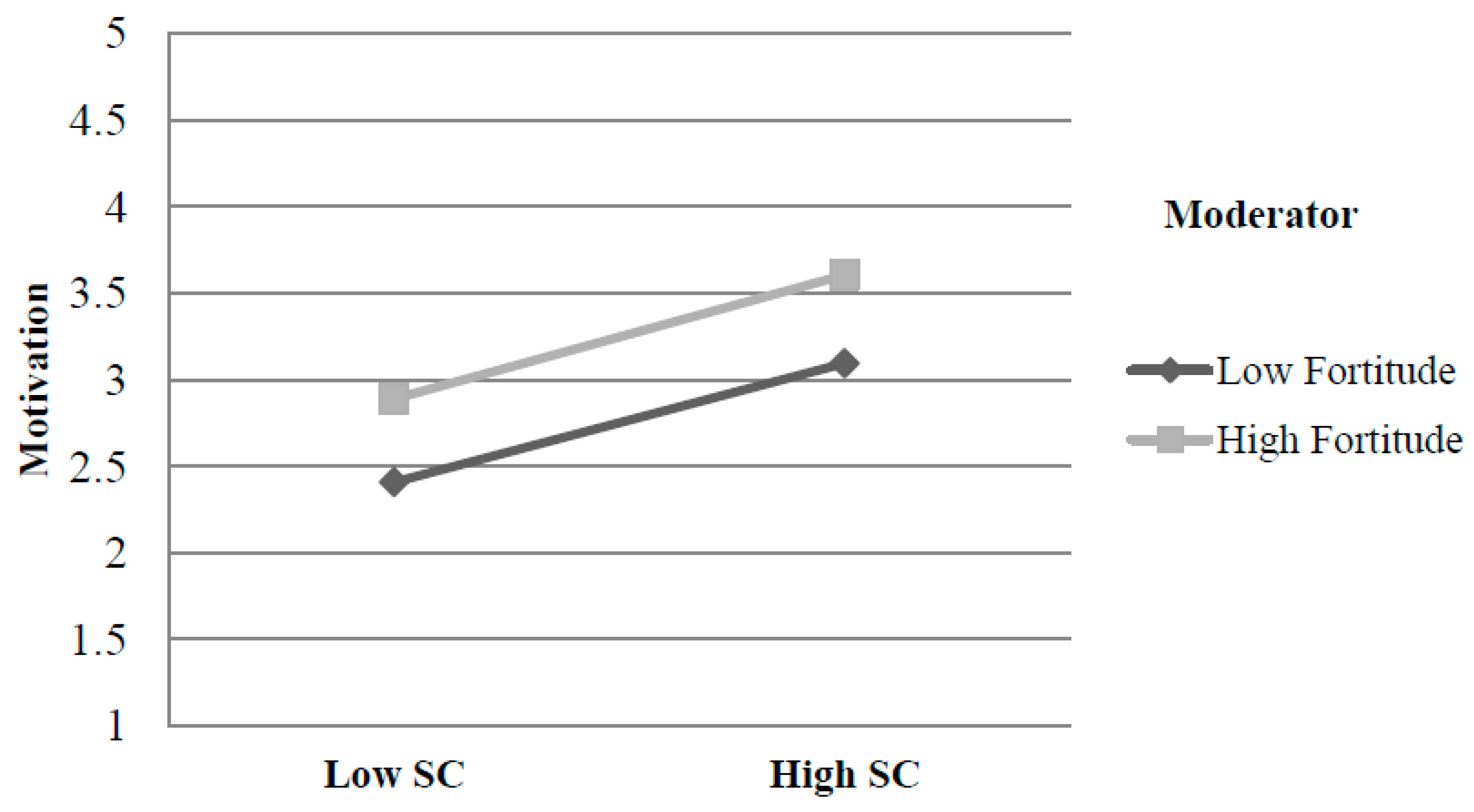
| R | R-seq | MSE | F | df1 | df2 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model I | 0.329 | 0.108 | 0.474 | 14.950 | 2 | 247 | 0.000 |
| Model II | 0.471 | 0.221 | 0.437 | 35.112 | 2 | 247 | 0.000 |
| Model III | 0.522 | 0.272 | 0.344 | 46.212 | 2 | 247 | 0.000 |
| Coeff | Se | T | p | LLCI | ULCI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model I | Constant | 3.898 | 0.387 | 10.079 | 0.000 | 3.137 | 4.660 |
| PA | 0.103 | 0.063 | 01.631 | 0.104 | −0.021 | 0.228 | |
| SC | 0.250 | 0.065 | 03.852 | 0.000 | 0.122 | 0.378 | |
| Model II | Constant | 2.754 | 0.372 | 7.413 | 0.000 | 2.022 | 3.486 |
| PA | 0.116 | 0.061 | 1.911 | 0.057 | −0.004 | 0.236 | |
| SC | 0.394 | 0.062 | 6.319 | 0.000 | 0.271 | 0.516 | |
| Model III | Constant | 2.680 | 0.330 | 8.128 | 0.000 | 2.030 | 3.329 |
| PA | 0.262 | 0.054 | 4.866 | 0.000 | 0.156 | 0.369 | |
| SC | 0.279 | 0.055 | 5.056 | 0.000 | 0.171 | 0.388 |
| Effect | Boot SE | Boot LLCI | Boot ULCI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model I | PA | 0.049 | 0.030 | −0.003 | 0.114 |
| Model II | PA | 0.056 | 0.034 | −0.008 | 0.126 |
| Model III | PA | 0.126 | 0.038 | 0.063 | 0.212 |
| Estimate | S.E. | C.R. | p | Label | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model I | Inn | <--- | LC | 0.160 | 0.053 | 3.023 | 0.003 | par_4 |
| NFA | <--- | LC | 0.240 | 0.053 | 4.509 | 0.000 | par_5 | |
| Mot | <--- | LC | 0.227 | 0.049 | 4.658 | 0.000 | par_6 | |
| Model II | Inn | <--- | RTP | 0.217 | 0.053 | 4.076 | 0.000 | par_4 |
| NFA | <--- | RTP | 0.226 | 0.055 | 4.127 | 0.000 | par_5 | |
| Mot | <--- | RTP | 0.286 | 0.049 | 5.874 | 0.000 | par_6 |
| Estimate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model I | Inn | <--- | LC | 0.188 |
| NFA | <--- | LC | 0.275 | |
| Mot | <--- | LC | 0.283 | |
| Model II | Inn | <--- | RTP | 0.250 |
| NFA | <--- | RTP | 0.253 | |
| Mot | <--- | RTP | 0.349 |
| R | R-seq | MSE | F | df1 | df2 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model I | 0.522 | 0.273 | 0.410 | 30.712 | 3 | 246 | 0.000 |
| Model II | 0.419 | 0.176 | 0.465 | 18.987 | 3 | 246 | 0.000 |
| Model III | 0.402 | 0.162 | 0.473 | 15.834 | 3 | 246 | 0.000 |
| Model I | Coeff | Se | T | p | LLCI | ULCI | |
| constant | 1.943 | 2.564 | 0.758 | 0.449 | −3.107 | 6.994 | |
| For | 0.248 | 0.427 | 0.581 | 0.562 | −0.593 | 1.088 | |
| SC | 0.351 | 0.454 | 0.772 | 0.441 | −0.544 | 1.245 | |
| int_1 | 0.007 | 0.075 | 0.094 | 0.925 | −0.141 | 0.155 | |
| Interactions: int_1 = SC X For | |||||||
| Model II | Coeff | Se | T | p | LLCI | ULCI | |
| constant | 5.681 | 0.047 | 120.157 | 0.000 | 5.588 | 5.774 | |
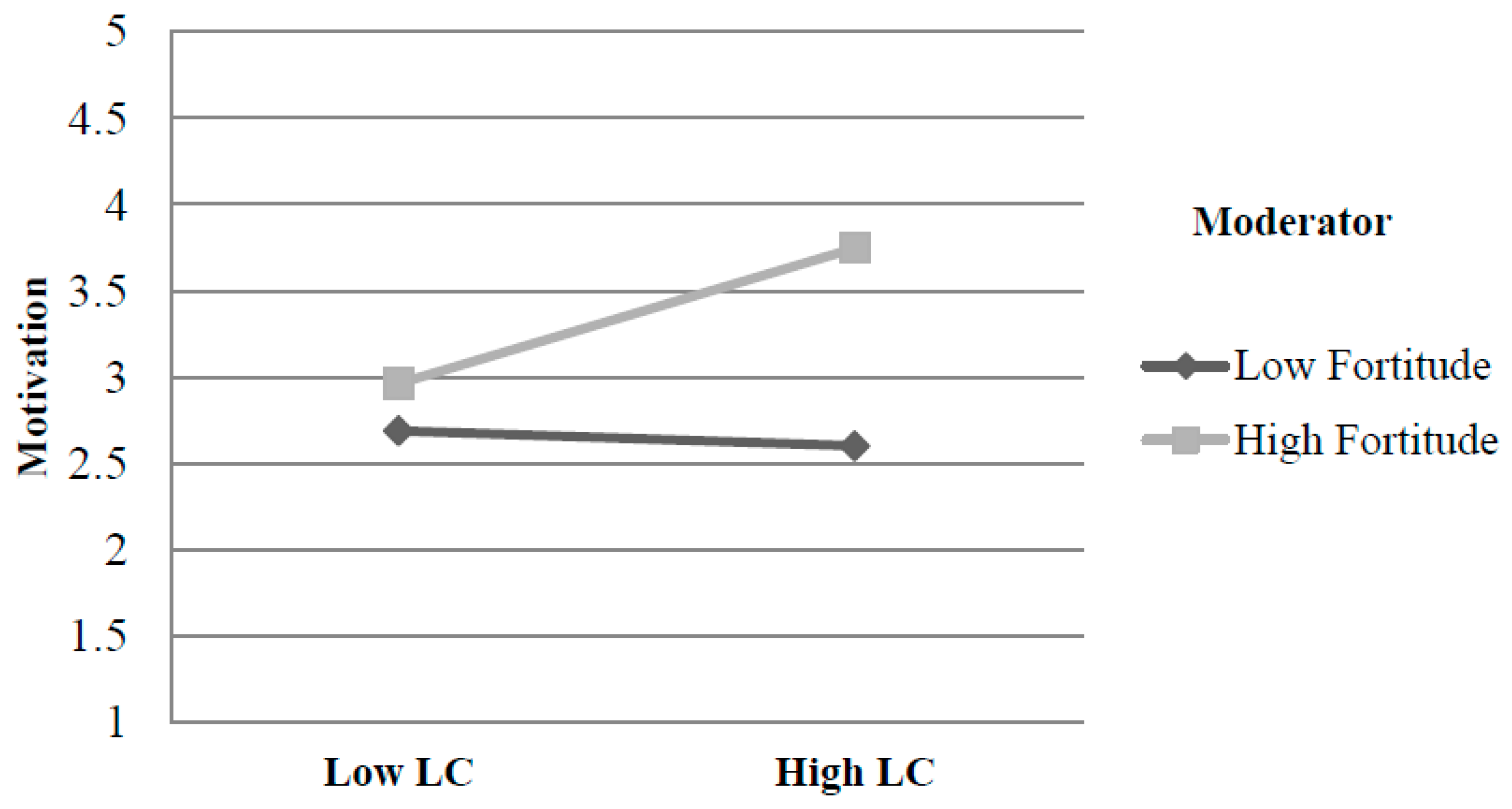
| For | 0.355 | 0.070 | 5.038 | 0.000 | 0.216 | 0.493 | |
| LC | 0.174 | 0.055 | 3.184 | 0.002 | 0.066 | 0.282 | |
| int_1 | 0.218 | 0.074 | 2.925 | 0.004 | 0.071 | 0.364 | |
| Interactions: int_1 = LC X For | |||||||
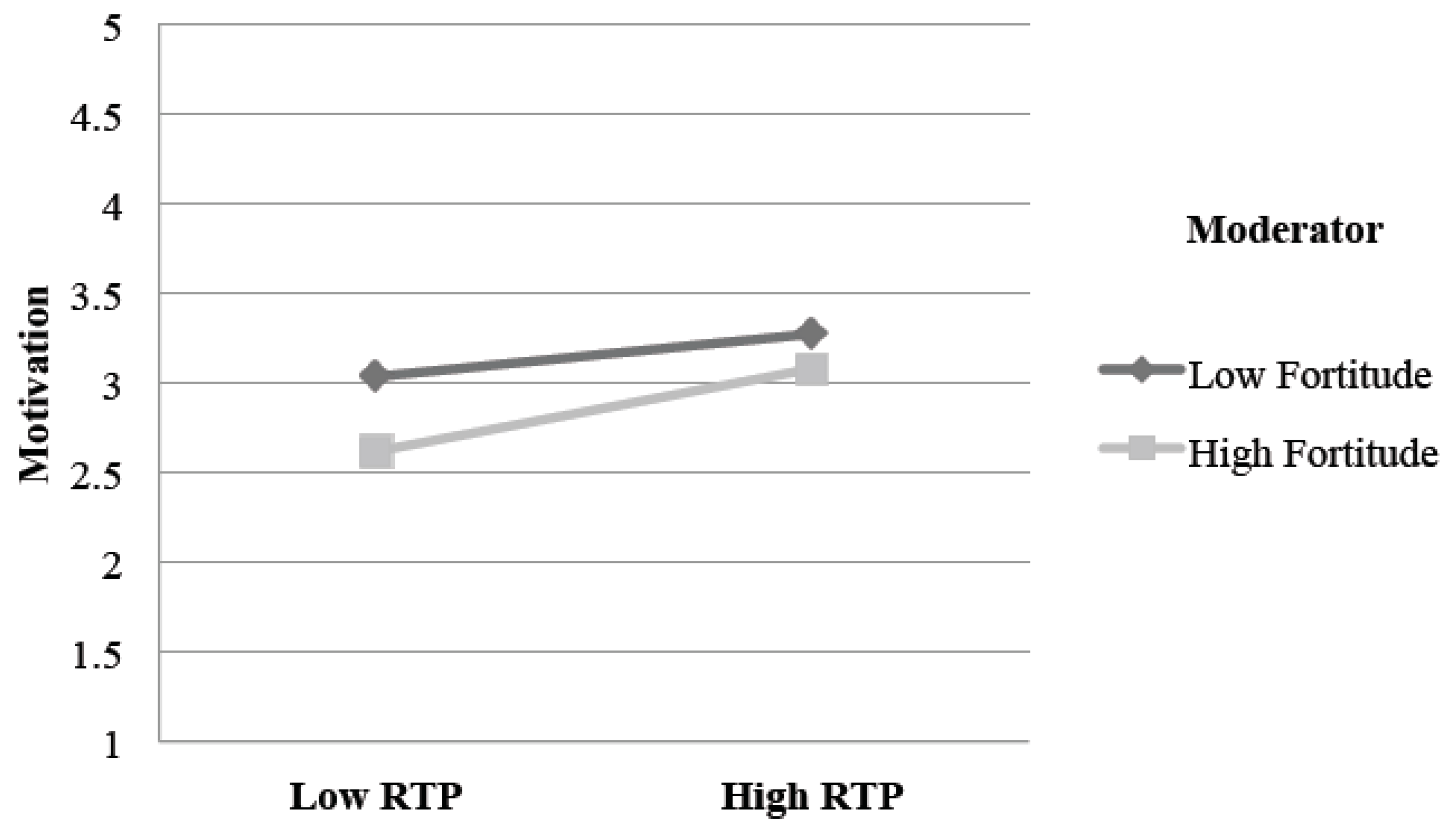
| Model III | Coeff | Se | T | p | LLCI | ULCI | |
| Constant | 4.382 | 2.342 | 1.871 | 0.063 | −0.231 | 8.995 | |
| For | 0.064 | 0.386 | 0.165 | 0.869 | −0.696 | 0.823 | |
| RTP | −0.154 | 0.445 | −0.346 | 0.730 | −1.031 | 0.723 | |
| int_1 | 0.055 | 0.073 | 0.758 | 0.449 | −0.088 | 0.199 | |
| Interactions: int_1 = RTP X For | |||||||
| For | Effect | Se | T | p | LLCI | ULCI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −0.666 | 0.029 | 0.057 | 0.516 | 0.606 | −0.082 | 0.140 |
| 0 | 0.174 | 0.055 | 3.184 | 0.002 | 0.066 | 0.282 |
| 0.666 | 0.319 | 0.088 | 3.635 | 0.000 | 0.146 | 0.492 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hameed, I.; Khan, M.B.; Shahab, A.; Hameed, I.; Qadeer, F. Science, Technology and Innovation through Entrepreneurship Education in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). Sustainability 2016, 8, 1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8121280
Hameed I, Khan MB, Shahab A, Hameed I, Qadeer F. Science, Technology and Innovation through Entrepreneurship Education in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). Sustainability. 2016; 8(12):1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8121280
Chicago/Turabian StyleHameed, Irfan, Muhammad Babar Khan, Atif Shahab, Imran Hameed, and Faisal Qadeer. 2016. "Science, Technology and Innovation through Entrepreneurship Education in the United Arab Emirates (UAE)" Sustainability 8, no. 12: 1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8121280
APA StyleHameed, I., Khan, M. B., Shahab, A., Hameed, I., & Qadeer, F. (2016). Science, Technology and Innovation through Entrepreneurship Education in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). Sustainability, 8(12), 1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8121280






