Bioactivity of Phycocolloids against the Mediterranean Protozoan Leishmania infantum: An Inceptive Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Algal Materials and Phycocolloid Extractions
2.2. Cytotoxic Essay
2.3. Activity of Phycocolloids in L. infantum Promastigote Cultures
2.4. Activity of Phycocolloids in Trypanosoma cruzi Cultures
2.5. Statistical Analysis
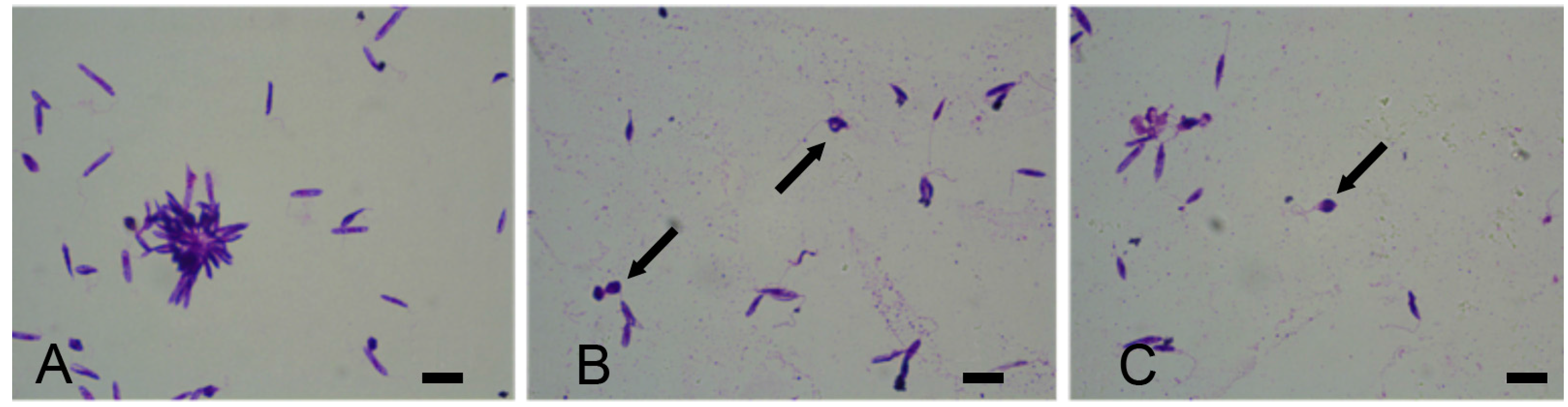
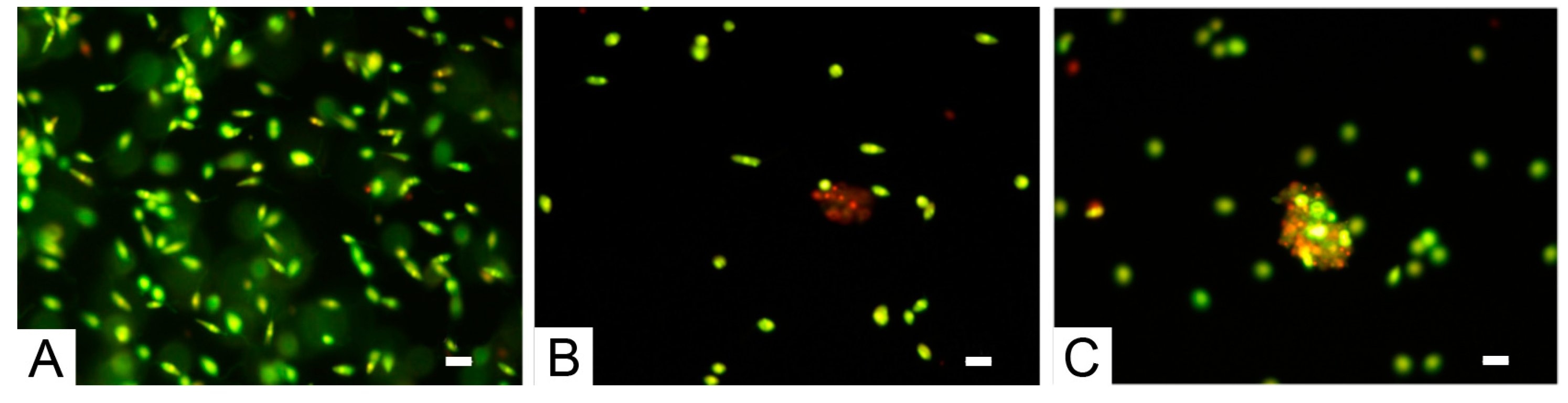
3. Results
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chanda, S.; Dave, R.; Kaneria, M.; Nagani, K. Seaweeds: A novel, untapped source of drugs from sea to combat Infectious diseases, in Current Research, Technology and Education Topics. In Applied Microbiology and Microbial Biotechnology; Méndez-Vilas, A., Ed.; Formatex: Badajoz, Spain, 2010; pp. 473–480. [Google Scholar]
- Genovese, G.; Leitner, S.; Armeli Minicante, S.; Lass-Flörl, C. The Mediterranean red alga Asparagopsis taxiformis has antifungal activity against Aspergillus species. Mycoses 2013, 56, 516–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, G.; Yu, G.; Zhang, J.; Ewart, H.S. Chemical Structures and Bioactivities of Sulfated Polysaccharides from Marine Algae. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 196–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parthiban, C.; Parameswari, K.; Saranya, C.; Hemalatha, A.; Anantharaman, P. Production of Sodium Alginate from Selected Seaweeds and Their Physiochemical and Biochemical Properties. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 2012, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Fouladvand, M.; Barazesh, A.; Farokhzad, F.; Malekizadeh, H.; Sartavi, K. Evaluation of in vitro anti-Leishmanial activity of some brown, green and red algae from the Persian Gulf. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 15, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Freile-Pelegrin, Y.; Robledo, D.; Chan-Bacab, M.J.; Ortega-Morales, B.O. Antileishmanial properties of tropical marine algae extracts. Fitoterapia 2008, 79, 374–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genovese, G.; Tedone, L.; Hamann, M.T.; Morabito, M. The Mediterranean Red Alga Asparagopsis: A Source of Compounds against Leishmania. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehnhardt Pires, C.; Rodrigues, S.; Bristot, D.; Gaeta, H.; de Oliveira Toyama, D.; Lobo Farias, W.; Toyama, M. Evaluation of Macroalgae Sulfated Polysaccharides on the Leishmania (L.) amazonensis Promastigote. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabina, H.; Aliya, R. Bioactive assessment of selected marine red algae against Leishmania major and chemical constituents of Osmundea pinnatifida. Pak. J. Bot. 2011, 43, 3053–3056. [Google Scholar]
- Manna, L.; Reale, S.; Vitale, F.; Gravino, A.E. Evidence for a relationship between Leishmania load and clinical manifestations. Res. Vet. Sci. 2009, 87, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desjeux, P. Leishmaniasis: Current situation and new perspectives. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2004, 27, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvar, J.; Vélez, I.D.; Bern, C.; Herrero, M.; Desjeux, P.; Cano, J.; Jannin, J.; den Boer, M. Leishmaniasis Worldwide and Global Estimates of Its Incidence. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamey, G. The world’s most neglected diseases. BMJ 2002, 325, 176–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerin, P.J.; Olliaro, P.; Sundar, S.; Boelaert, M.; Croft, S.L.; Desjeux, P.; Wasunna, M.K.; Bryceson, A.D.M. Visceral leishmaniasis: Current status of control, diagnosis, and treatment, and a proposed research and development agenda. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2002, 2, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athukorala, Y.; Lee, K.-W.; Kim, S.-K.; Jeon, Y.-J. Anticoagulant activity of marine green and brown algae collected from Jeju Island in Korea. Bioresour. Thecnol. 2007, 98, 1711–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, K.; Matsuura, Y.; Bacic, A.; Liao, M.; Hori, K.; Miyazawa, K. Anticoagulant properties of a sulfated galactan preparation from a marine green alga Codium cylindricum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2001, 28, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minghou, J. Processing and Extraction of Phycocolloids. FAO Corporate Document Repository. Available online: http://www.fao.org/docrep/field/003/ab728e/ab728e08.htm (accessed on 23 October 2016).
- Carmichael, J.; Degraff, W.G.; Gazdar, A.F.; Minna, J.D.; Mitchell, J.B. Evaluation of a tetrazolium-based semiautomated colorimetric assay: Assessment of chemosensitivity testing. Cancer Res. 1987, 47, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Castelli, G.; Galante, A.; Verde, V.L.; Migliazzo, A.; Reale, S.; Lupo, T.; Piazza, M.; Vitale, F.; Bruno, F. Evaluation of Two Modified Culture Media for Leishmania infantum Cultivation Versus Different Culture Media. J. Parasitol. 2014, 100, 228–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limoncu, M.E.; Balcioglu, I.; Yereli, K.; Ozbel, Y.; Ozbilgin, A. A new experimental in vitro culture medium for cultivation of Leishmania species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 2430–2431. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Solano-Gallego, L.; Rodríguez-Cortés, A.; Iniesta, L.; Quintana, J.; Pastor, J.; Espada, Y.; Portús, M.; Alberola, J. Cross-sectional serosurvey of feline leishmaniasis in ecoregions around the northwestern Mediterranean. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 76, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baneth, G.; Shaw, S.E. Chemotherapy of canine leishmaniosis. Vet. Parasitol. 2002, 106, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinnell, R.J.; Courtenay, O. Transmission, reservoir hosts and control of zoonotic visceral leishmaniasis. Parasitology 2009, 136, 1915–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deniz, T.; Kaiser, M.; Brun, R.; Yardely, V.; Schmidt, T.J.; Tosun, F.; Ruedi, P. Antitrypanosomal and antileishmanial activities of flavonoids and their analogues: In vitro, in vivo, structure-activity relationship and quantitative structure—Activity relationship studies. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1352–1364. [Google Scholar]
- Laurienzo, P. Marine Polysaccharides in Pharmaceutical Applications: An Overview. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2435–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Rodríguez, A.D.; Berlinck, R.G.S.; Fusetani, N. Marine pharmacology in 2007–8: Marine compounds with antibacterial, anticoagulant, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antimalarial, antiprotozoal, antituberculosis, and antiviral activities; affecting the immune and nervous system, and other miscellaneous mechanisms of action. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C 2011, 153, 191–222. [Google Scholar]
- Orhan, I.; Sener, B.; Atici, T.; Brun, R.; Perozzo, R.; Tasdemir, D. Turkish freshwater and marine macrophyte extracts show In vitro antiprotozoal activity and inhibit FabI, a key enzyme of Plasmodium falciparum fatty acid biosynthesis. Phytomedicine 2006, 13, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.; Wang, K.; Zhou, C.; Liu, J.; Zeng, X. Purification, antitumor and antioxidant activities in vitro of polysaccharides from the brown seaweed Sargassum pallidum. Food Chem. 2008, 111, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Species | Extract Concentrations | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 µg/mL | 40 µg/mL | 80 µg/mL | 160 µg/mL | |
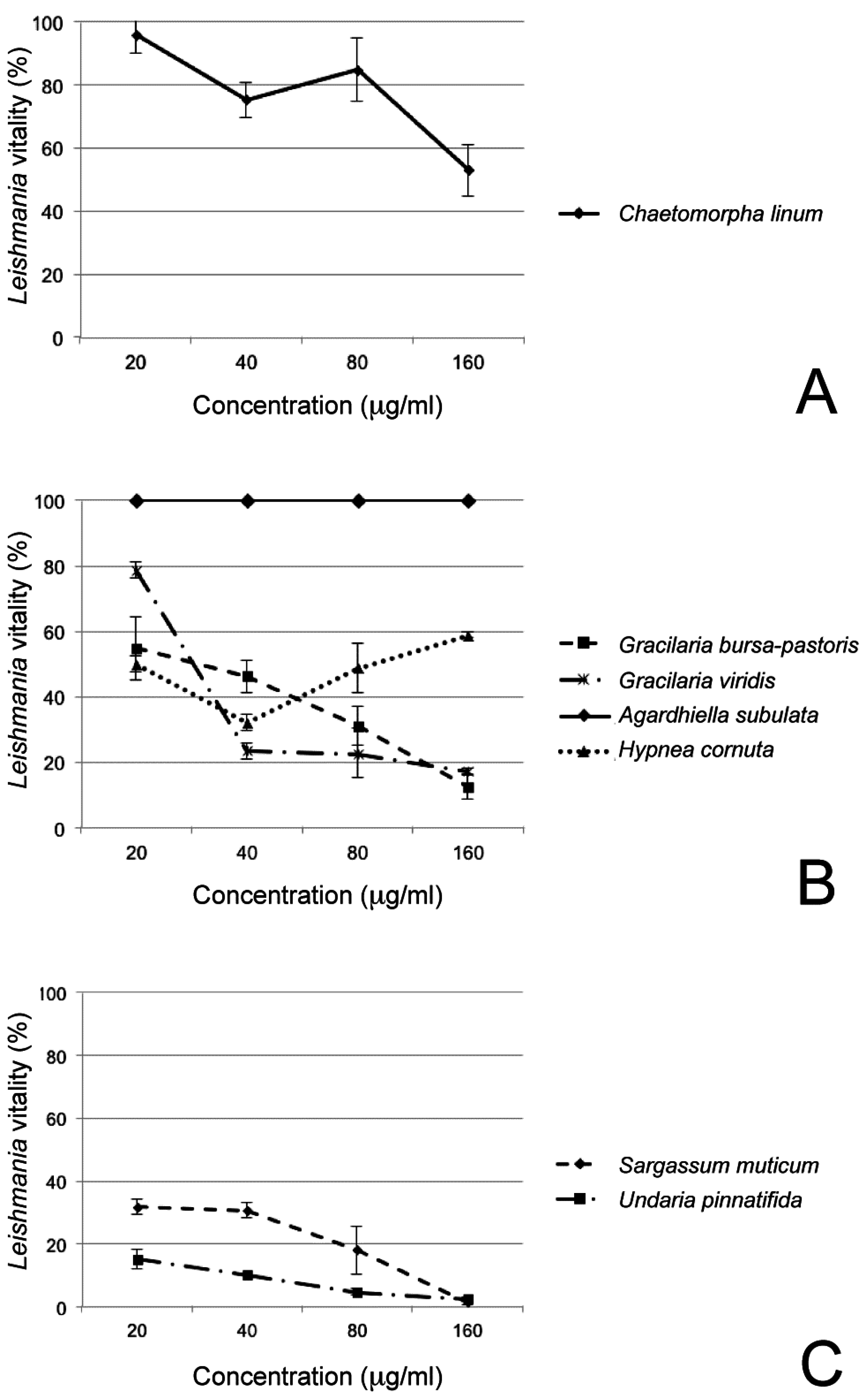
| Chaetomorpha linum | 95.87 ± 5.84 | 75.17 ± 5.40 | 84.73 ± 9.91 | 52.87 ± 8.10 |
| Gracilaria viridis | 78.62 ± 2.33 | 23.52 ± 2.34 | 22.59 ± 7.50 | 17.20 ± 0.84 |
| Hypnea cornuta | 49.94 ± 17.16 | 32.05 ± 18.15 | 48.73 ± 8.86 | 58.74 ± 15.59 |
| Gracilaria bursa-pastoris | 54.61 ± 9.51 | 46.21 ± 4.75 | 31.09 ± 5.93 | 12.50 ± 3.53 |
| Agardhiella subulata | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 |
| Sargassum muticum | 31.80 ± 2.33 | 30.60 ± 1.13 | 18 ± 1.15 | 1.50 ± 0.36 |
| Undaria pinnatifida | 15.16 ± 2.66 | 10.21 ± 0 | 4.64 ± 0.83 | 2.47 ± 0.48 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Armeli Minicante, S.; Michelet, S.; Bruno, F.; Castelli, G.; Vitale, F.; Sfriso, A.; Morabito, M.; Genovese, G. Bioactivity of Phycocolloids against the Mediterranean Protozoan Leishmania infantum: An Inceptive Study. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8111131
Armeli Minicante S, Michelet S, Bruno F, Castelli G, Vitale F, Sfriso A, Morabito M, Genovese G. Bioactivity of Phycocolloids against the Mediterranean Protozoan Leishmania infantum: An Inceptive Study. Sustainability. 2016; 8(11):1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8111131
Chicago/Turabian StyleArmeli Minicante, Simona, Silvia Michelet, Federica Bruno, Germano Castelli, Fabrizio Vitale, Adriano Sfriso, Marina Morabito, and Giuseppa Genovese. 2016. "Bioactivity of Phycocolloids against the Mediterranean Protozoan Leishmania infantum: An Inceptive Study" Sustainability 8, no. 11: 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8111131
APA StyleArmeli Minicante, S., Michelet, S., Bruno, F., Castelli, G., Vitale, F., Sfriso, A., Morabito, M., & Genovese, G. (2016). Bioactivity of Phycocolloids against the Mediterranean Protozoan Leishmania infantum: An Inceptive Study. Sustainability, 8(11), 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8111131









