Possible Futures towards a Wood-Based Bioeconomy: A Scenario Analysis for Germany
Abstract
:1. Introduction: The Wood-Based Bioeconomy—Aims, Perspectives and Uncertainties
2. Scenario Analysis: Methodology and Inputs
3. Scenario Analysis
3.1. Status Quo: Current State and Further Perspectives of the Wood-Based Bioeconomy in Germany
| No. | Strategies and Programmes | Content |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | “National Policy Strategy on Bioeconomy” (German Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture) [4] | Main strategies concerning the material recovery of biogene resources, including wood |
| 2 | “National Research Strategy BioEconomy 2030” (German Federal Ministry for Education and Research) [32] | |
| 3 | “Action Plan on Material Usage of Renewable Raw Materials” (German Federal Ministry for Consumer Protection, Food and Agriculture) [42] | |
| 4 | “National Biomass Action Plan for Germany” (German Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation and Reactor Safety/German Federal Ministry for Consumer Protection, Food and Agriculture) [43] | |
| 5 | “Perspectives for Germany. Our strategy for sustainable development” (German Federal Government) [56] | Overarching guidelines for a sustainable development |
| 6 | “Ideas. Innovation. Prosperity. High-Tech-Strategy 2020 for Germany” (German Federal Ministry for Education and Research) [57] | Important strategies regarding Research and Development |
| 7 | “6th Energy Research Programme of the Federal Government” (Federal Ministry of Economics and Technology) [58] | |
| 8 | “Strengthening Germany‘s Role in the Global Knowledge Society. Strategy of the Federal Government for the Internationalisation of Science and Research” (German Federal Ministry for Education and Research) [59] | |
| 9 | “Health Research Framework Programme of the Federal Government” (German Federal Ministry for Education and Research) [60] | Important strategies regarding health and nature protection |
| 10 | “National Strategy on Biological Diversity” (German Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation and Reactor Safety) [61] | |
| 11 | “Forestry Strategy 2020” (German Federal Ministry for Consumer Protection, Food and Agriculture) [62] | Strategies regarding wood and forests in general |
| 12 | “Increased wood use” (German Federal Ministry for Consumer Protection, Food and Agriculture) [63] | |
| 13 | “Joint instruction on the procurement of wood products” (Federal Ministry of Transport, Building and Urban Affairs) [64] |
3.2. Identification of Generally Relevant Influence Factors
| Societal Categories | Generally Relevant Influence Factors | |
|---|---|---|
| Society/Consumers | 1A | Public influence |
| 1B | Environmental awareness | |
| 1C | Risk and innovation attitude | |
| 1D | Willingness to pay for bio-based products | |
| 1E | Voting behavior (supporting sustainable politics) | |
| Economy/Producers | 2A | Globalisation and global economic development (oil price/exports) |
| 2B | Domestic economic development | |
| 2C | Supply and demand for wood | |
| 2D | Willingness to invest in innovations | |
| 2E | Focus on short term- or long term-oriented profit | |
| 2F | Site conditions (e.g., establishment of businesses, infrastructure) | |
| Politics | 3A | Energy and climate policies |
| 3B | Technology, innovation and research policies | |
| 3C | Forest, environmental and nature conservation policies | |
| 3D | Support of the circular flow economy | |
| 3E | Support of local value chains | |
| 3F | Direction of economic, competition, tax, industry and agricultural policies | |
| 3G | Regional planning and development (e.g., role of federal states and regional associations) | |
| Technology | 4A | Innovations along the value chain of wood (including products) |
| 4B | Innovations for the exploitation of fossil resources (non-conventional) | |
| Environment | 5A | Climate change |
| 5B | Biomass availability/forest structure | |
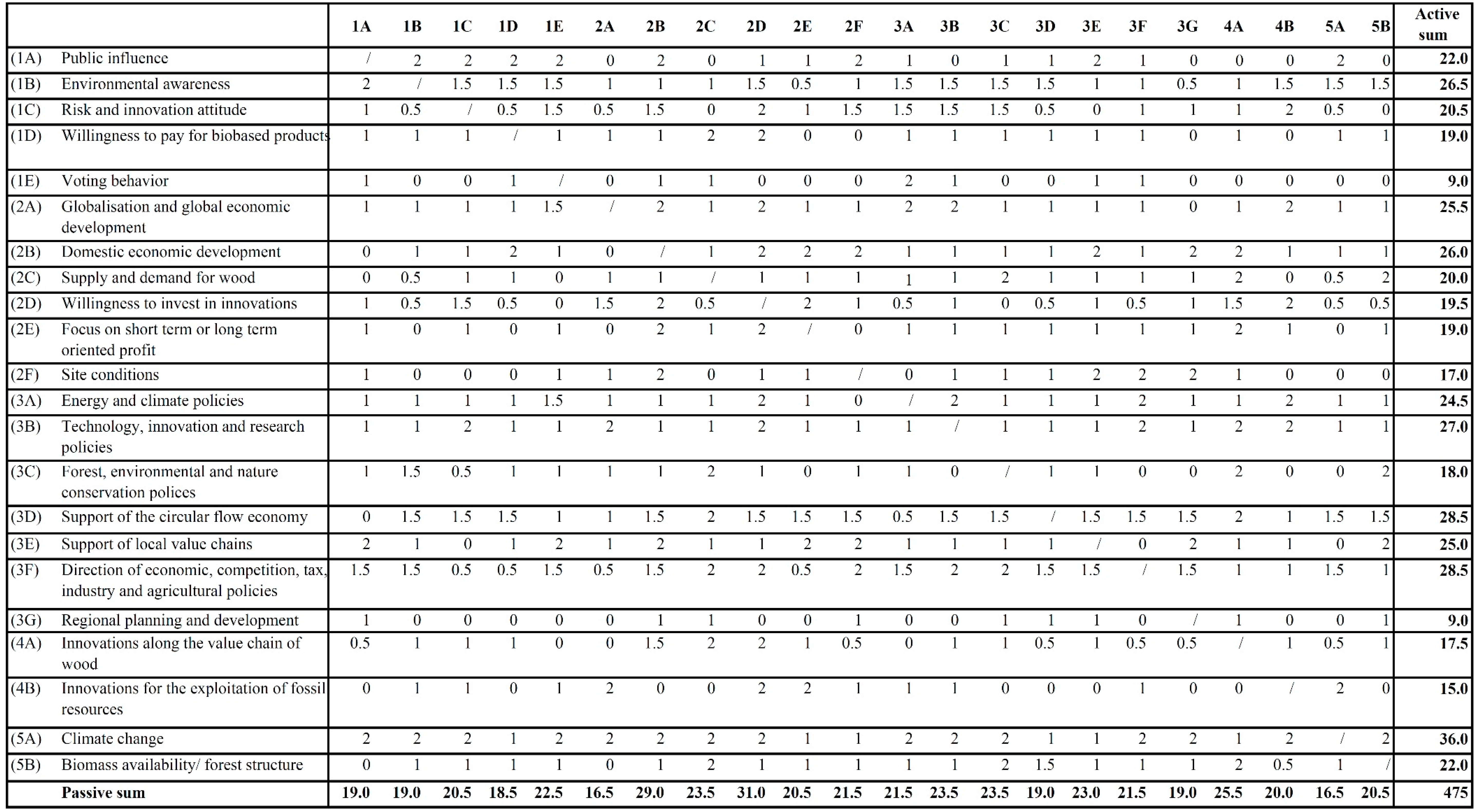
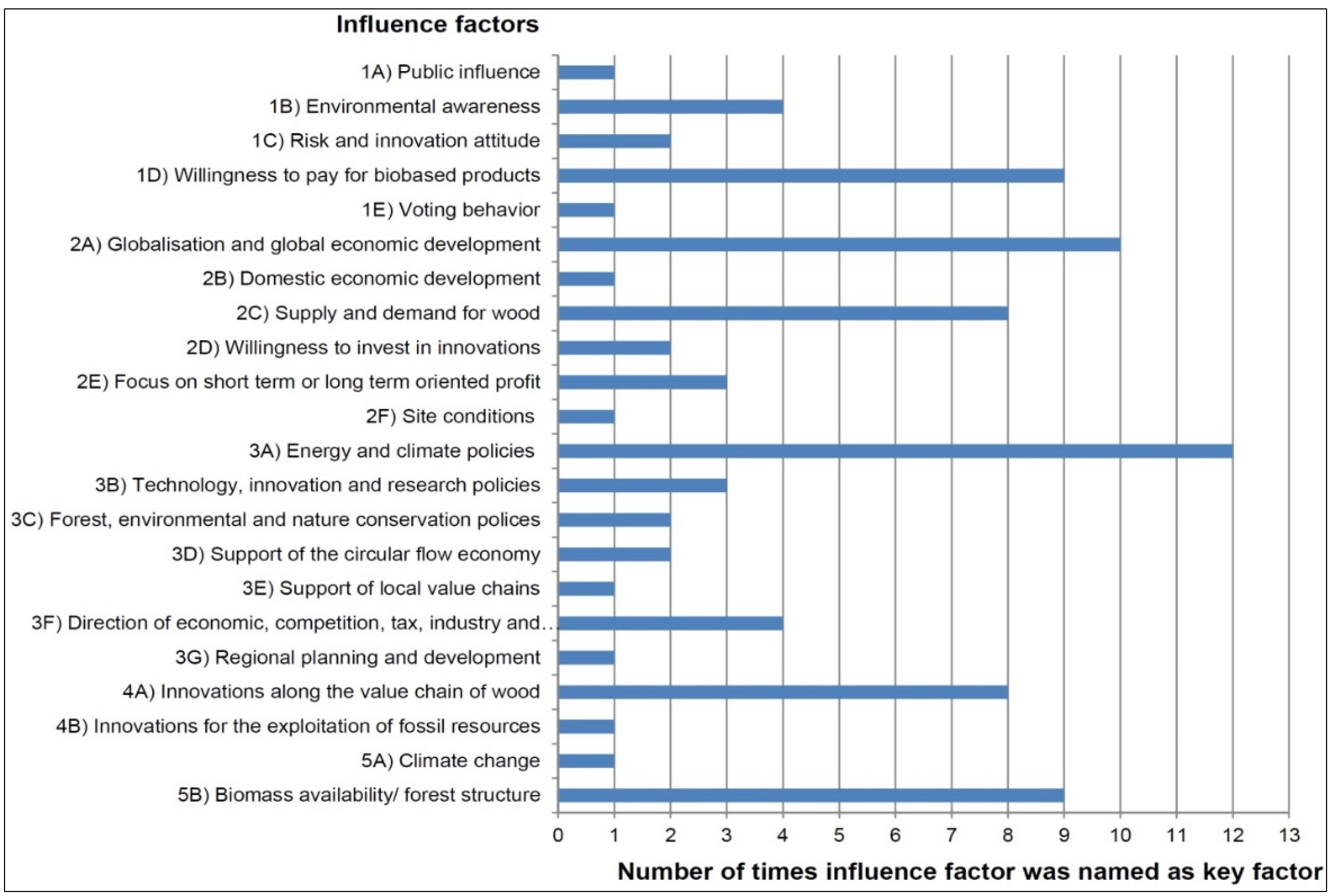
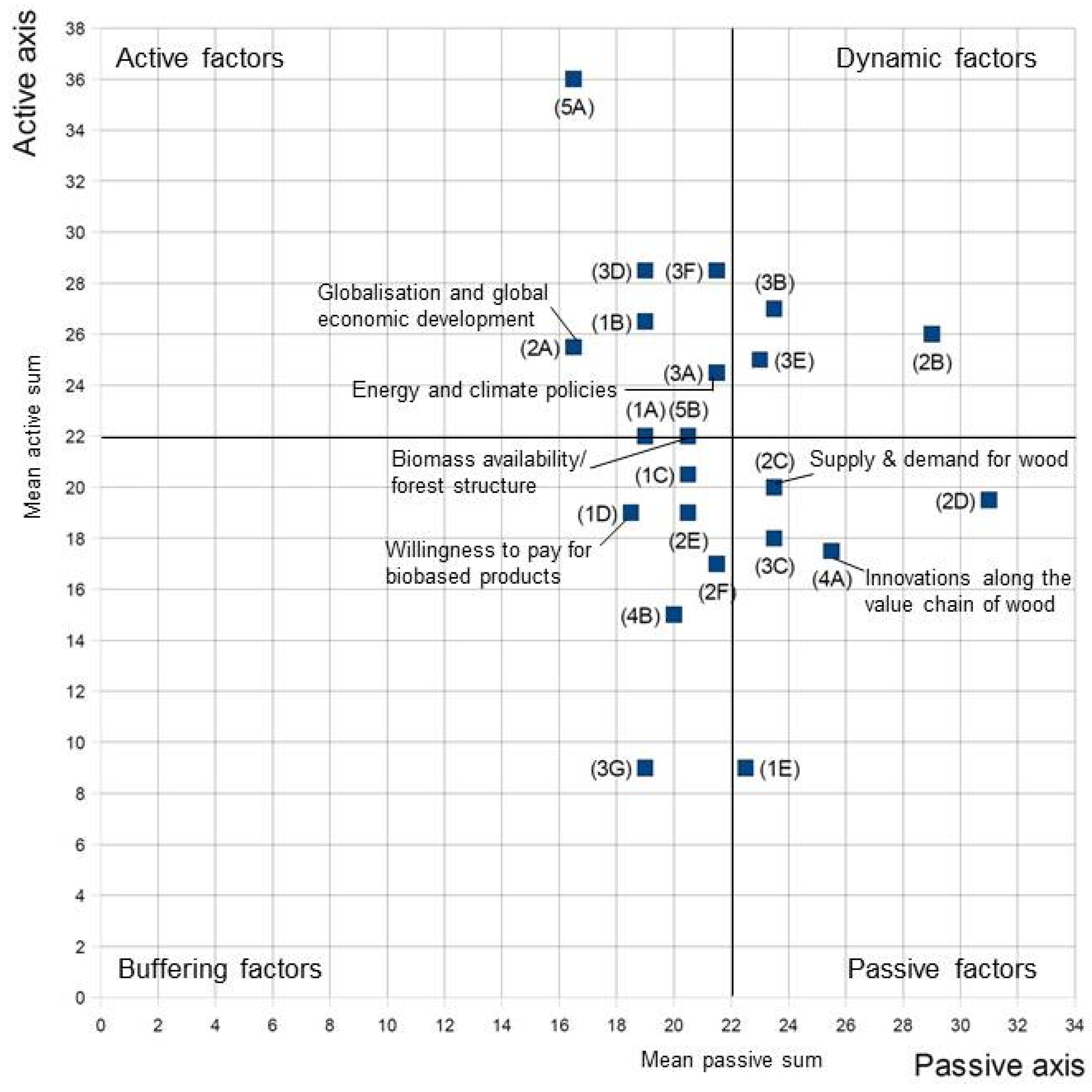
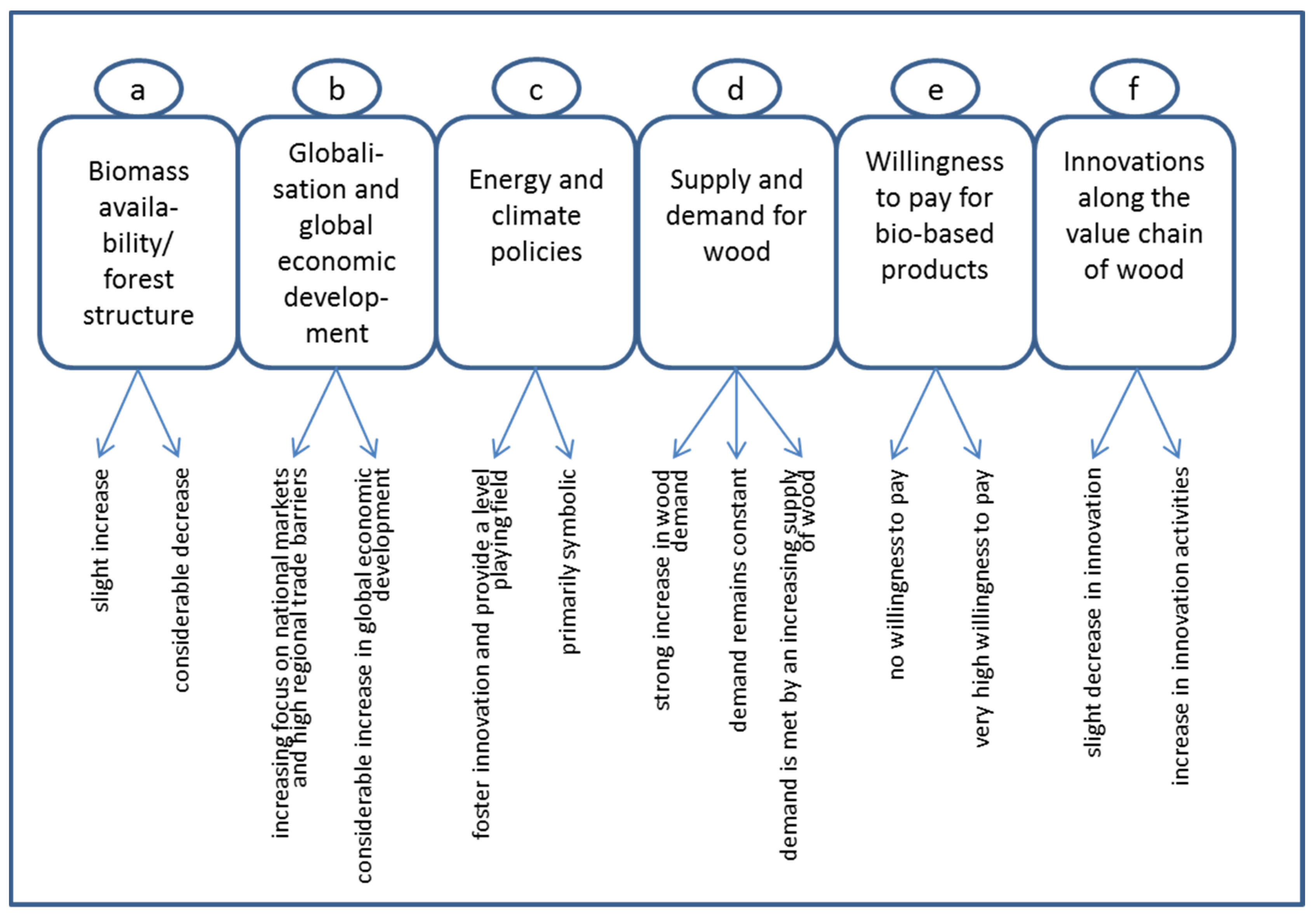
3.3. Third Step: Characteristics of “Key Influence Factors” and Projections
3.3.1. Biomass Availability and Forest Structure
3.3.2. Globalisation and Global Economic Development
3.3.3. Energy and Climate Policies
3.3.4. Supply and Demand for Wood
3.3.5. Willingness to Pay for Bio-Based Products
3.3.6. Innovations along the Value Chain of Wood
3.4. Compilation of Projections into Scenarios
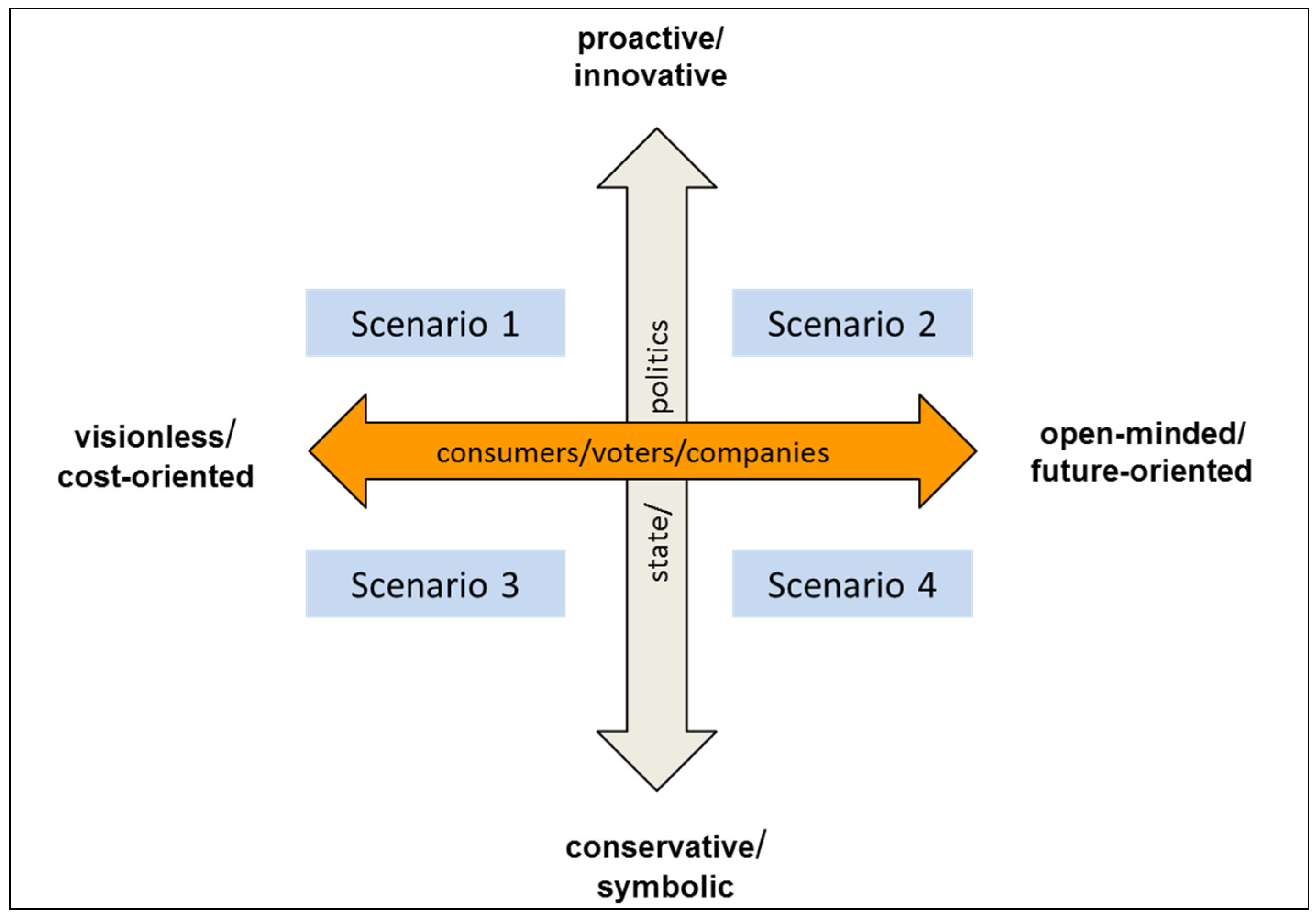
3.5. Storylines
4. Discussion: What Are the Implications of the Scenarios for Politics, Companies and Society?
4.1. Benefits and Challenges for Companies and the Society
4.2. The State’s Role in Balancing Stability and Flexibility under Uncertainty
4.3. Resource Availability and Distribution
4.4. Sustainability Concerns and the Bioeconomy
4.5. International Ramifications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vandermeulen, V.; van der Stehen, M.; Stevens, C.V.; van Huylenbroeck, G. Industry expectations regarding the transition towards a biobased economy. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefining 2012, 6, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission (EC). Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions. Innovating for Sustainable Growth: A Bioeconomy for Europe. {SWD(2012) 11 final}. Available online: ec.europa.eu/research/bioeconomy/pdf/official-strategy_en.pdf (accessed on 7 April 2015).
- Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF); Bundesministerium für Ernährung und Landwirtschaft (BMEL). Bioökonomie in Deutschland—Chancen für eine Biobasierte und Nachhaltige Zukunft; Bonn: Berlin, Germany, 2014; Available online: www.bmbf.de/pub/Biooekonomie-in-Deutschland_001.pdf (accessed on 7 April 2015). (In German)
- Bundesministerium für Ernährung und Landwirtschaft (BMEL). Nationale Politikstrategie Bioökonomie—Nachwachsende Ressourcen und Biotechnologische Verfahren als Basis für Ernährung, Industrie und Energie. Available online: https://www.bmbf.de/files/BioOekonomiestrategie.pdf (accessed on 18 January 2016). (In German)
- McCormick, K.; Kautto, N. The bioeconomy in Europe: An overview. Sustainability 2013, 5, 2589–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staffas, L.; Gustavsson, M.; McCormick, K. Strategies and policies for the bioeconomy and bio-based economy: An analysis of official national approaches. Sustainability 2013, 5, 2751–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michigan State University (MSU) Product Center and Shepherd Advisors. Future Scenarios for Michigan’s Bioeconomy: Planning Your Strategic Responses. Available online: http://productcenter.msu.edu/uploads/files/Future Scenarios for Michigans Bioeconomy.pdf (accessed on 18 January 2016).
- Edwards, R.; Szekeres, S.; Neuwahl, F.; Mahieu, V. Biofuels in the European Context: Facts and Uncertainties. Available online: ec.europa.eu/dgs/jrc/downloads/jrc_biofuels_report.pdf (accessed on 7 April 2015).
- Jenkins, J.D. Political economy constraints on carbon pricing policies: What are the implications for economic efficiency, environmental efficacy, and climate policy design? Energy Policy 2014, 69, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahl, U. Bioökonomie für den Klima—Und Ressourcenschutz—Regulative Handlungskorridore. Study on behalf of NABU. Available online: https://www.nabu.de/imperia/md/content/nabude/gentechnik/studien/140821-nabu-biooekonomie-studie_2014.pdf (accessed on 30 October 2015). (In German)
- Unruh, G.C. Understanding carbon lock-in. Energy Policy 2000, 28, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unruh, G.C. Escaping carbon lock-in. Energy Policy 2002, 30, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, C.; Newell, R.G. Environmental and technology policies for climate mitigation. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2008, 55, 142–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, A.B.; Newell, R.G.; Stavins, R.N. A tale of two market failures: Technology and environmental policy. Ecol. Econ. 2005, 54, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubler, A.; Aguayo, F.; Gallagher, K.; Hekkert, M.; Jiang, K.; Mytelka, L.; Neij, L.; Nemet, G.; Wilson, C. Policies for the Energy Technology Innovation System (ETIS). In Global Energy Assessment—Toward a Sustainable Future; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA; The International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis: Laxenburg, Austria, 2012; pp. 1665–1744. [Google Scholar]
- Purkus, A.; Röder, M.; Gawel, E.; Thrän, D.; Thornley, P. Handling uncertainty in bioenergy policy design—A case study analysis of UK and German bioelectricity policy instruments. Biomass Bioenergy 2015, 79, 64–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- March, H.; Therond, O.; Leenhardt, D. Water futures: Reviewing water-scenario analyses through an original interpretative framework. Ecol. Econ. 2012, 82, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priess, J.A.; Hauck, J. Integrative scenario development. Ecol. Soc. 2014, 19, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, R.; Raudsepp-Hearne, C.; Atkinson-Palombo, C.; Bohensky, E.; Boyd, E.; Cundill, G.; Fox, H.; Ingram, S.; Kok, K.; Spehar, S.; et al. Linking futures across scales: A dialog on multiscale scenarios. Ecol. Soc. 2007, 12, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Alkemade, R.; van Oorschot, M.; Miles, L.; Nellemann, C.; Bakkenes, M.; ten Brink, B. GLOBIO3: A framework to investigate options for reducing global terrestrial biodiversity loss. Ecosystems 2009, 12, 374–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leadley, P.W.; Krug, C.B.; Alkemade, R.; Pereira, H.M.; Sumaila, U.R.; Walpole, M.; Marques, A.; Newbold, T.; Teh, L.S.L.; van Kolck, J.; et al. Progress towards the Aichi Biodiversity Targets: An Assessment of Biodiversity Trends, Policy Scenarios and Key Actions; Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Maes, J.; Hauck, J.; Paracchini, M. L.; Ratamäki, O.; Hutchins, M.; Termansen, M.; Furman, E.; Pérez-Soba, M.; Braat, L. Mainstreaming ecosystem services into EU policy. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2013, 5, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). What External Factors Will Drive the Bioeconomy to 2030? The Bioeconomy to 2030: Designing a Policy Agenda; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Gausemeier, J.; Fink, A.; Schlake, O. Scenario Management: An approach to develop future potentials. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 1998, 59, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rounsevell, M.D.A.; Metzger, M.J. Developing qualitative scenario storylines for environmental change assessment. Wiley Interdiscipl. Rev. Clim. Chang. 2010, 1, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Government Office for Science. Collection Foresight Projects. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/collections/foresight-projects (accessed on 18 January 2016).
- Steinmetz, J.; Bennett, C.; Håkonsson, D.D. A practitioner’s view of the future of organization design: Future trends and implications for Royal Dutch Shell. J. Organ. Des. 2012, 1, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Purkus, A.; Barth, V. Geothermal power production in future electricity markets—A scenario analysis for Germany. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carus, M.; Dammer, L. Food or non-food: Which agricultural feedstocks are best for industrial uses? Ind. Biotechnol. 2013, 9, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajaste, R. Chemicals from biomass—Managing greenhouse gas emissions in biorefinery production chains—A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 75, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limayem, A.; Ricke, S.C. Lignocellulosic biomass for bioethanol production: Current perspectives, potential issues and future prospects. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2012, 38, 449–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF). Nationale Forschungsstrategie BioÖkonomie 2030. Unser Weg zu einer bio-basierten Wirtschaft. Available online: https://www.bmbf.de/pub/biooekonimie.pdf (accessed on 26 October 2015). (In German)
- Bioeconomy Cluster. Available online: http://en.bioeconomy.de (accessed on 18 January 2016).
- Özkaynak, B.; Rodriguez-Labajos, B. Mutli-scale interaction in local scenariobuilding: A methodological framework. Futures 2012, 42, 995–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Verband der Chemischen Industrie e.V. (VCI). Die Deutsche Chemische Industrie 2030. VCI-Prognos-Studie. Available online: https://www.vci.de/vci/downloads-vci/publikation/langfassung-prognos-studie-30-01-2013.pdf (accessed on 7 April 2015).
- Steinmüller, K.; Schulz-Montag, B.; Veenhoff, S. Waldzukünfte 2100. Szenarioreport. Available online: http://www.z-punkt.de/fileadmin/be_user/D_CorporateForesight/Wald2100_Szenreport_090603_kons.pdf (accessed on 7 April 2015). (In German)
- Von Reibnitz, U. Szenario-Technik: Instrumente für die unternehmerische und persönliche Erfolgsplanung. Gabler Verlag: Wiesbaden, Germany, 1992. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Mißler-Behr, M. Auf der Suche nach Zukunftsbildern. Eine Regelbasis zur Szenarienauswahl. In Szenariotechnik—Vom Umgang mit der Zukunft; Wilms, F.E.P., Ed.; Haupt Verlag: Bern, Switzerland, 2006; pp. 215–240. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Fachagentur Nachwachsende Rohstoffe e.V. (FNR). Marktanalyse Nachwachsende Rohstoffe. Available online: http://fnr.de/marktanalyse/marktanalyse.pdf (accessed on 14 January 2016). (In German)
- Mantau, U. Holzrohstoffbilanz Deutschland—Entwicklungen und Szenarien des Holzaufkommens und der Holzverwendung von 1987 bis 2015; Universität Hamburg: Hamburg, Germany, 2012. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Dieter, M. Volkswirtschaftliche Betrachtung von holzbasierter Wertschöpfung in Deutschland. In Waldstrategie 2020 Tagungsband zum Symposium des BMELV, 10.-11. Dez. 2008, Berlin; Seintsch, B., Dieter, M., Eds.; Landbauforschung—vTI Agriculture and Forestry Research: Braunschweig, Germay, 2009; Volume 327, pp. 37–46. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Bundesministerium für Ernährung, Landwirtschaft und Verbraucherschutz (BMELV). Aktionsplan zur stofflichen Nutzung nachwachsender Rohstoffe; BMELV: Bonn, Germany, 2009. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Bundesministerium für Umwelt, Naturschutz und Reaktorsicherheit (BMU); Bundesministerium für Ernährung, Landwirtschaft und Verbraucherschutz (BMELV). Nationaler Biomasseaktionsplan für Deutschland—Beitrag der Biomasse für eine Nachhaltige Energieversorgung; BMU: Berlin, Germany; BMELV: Bonn, Germany, 2010. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Pannicke, N.; Gawel, E.; Hagemann, N.; Purkus, A.; Strunz, S. The political economy of fostering a wood-based bioeconomy in Germany. Ger. J. Agric. Econ. 2015, 64, 224–243. [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig, G.; Köck, W.; Tronicke, C.; Gawel, E. Der Rechtsrahmen für die Bioökonomie in Deutschland. Die Öffentliche Verwaltung (DÖV) 2015, 68, 41–54. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Gawel, E.; Purkus, A. The role of energy and electricity taxation in the context of the German energy transition. Z. Energiewirtschaft 2015, 39, 77–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Crijns-Grausa, W.; Lamb, L.; Gilbert, A. Ex-ante evaluation of EU ETS during 2013–2030: EU-internal abatement. Energy Policy 2015, 77, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isenmann, R.; von Hauff, M. Industrial Ecology: Mit Ökologie Zukunftsorientiert Wirtschaften; Elsevier: München, Germany, 2007. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- North, D.C. Institutions, Institutional Change and Economic Performance; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Purkus, A.; Gawel, E.; Deissenroth, M.; Nienhaus, K.; Wassermann, S. Market integration of renewable energies through direct marketing—lessons learned from the German market premium scheme. Energy Sustain. Soc. 2015, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German Institute for Standardization. DIN EN 15440:2011-05. Solid Recovered Fuels—Methods for the Determination of Biomass Content; German Version EN 15440:2011; Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- German Institute for Standardization. DIN EN 14995:2007-03. Plastics—Evaluation of Compostability—Test Scheme and Specifications; German Version EN 14995:2006; Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- German Institute for Standardization. Bio-Based Products—Sustainability Criteria; German Version FprEN 16751:2015; Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- German Institute for Standardization. Bio-Based Products—Life Cycle Assessment; German Version EN 16760:2015; Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard, A.W.; Gillespie, I.; Hirsch, M.; Begley, C. Biosecurity and sustainability within the growing global bioeconomy. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2011, 3, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Die Bundesregierung. Perspektiven für Deutschland—Unsere Strategie für eine nachhaltige Entwicklung. Available online: http://www.bundesregierung.de/Content/DE/_Anlagen/Nachhaltigkeit-wiederhergestellt/perspektiven-fuer-deutschland-langfassung.pdf?__blob=publicationFile (accessed on 30 October 2015). (In German)
- Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF). Ideen. Innovation. Wachstum—Hightech-Strategie 2020 für Deutschland. Available online: https://www.bmbf.de/pub/hts_2020.pdf (accessed on 26 October 2015).
- Bundesministerium für Wirtschaft und Technologie (BMWI). Forschung für eine Umweltschonende, Zuverlässige und Bezahlbare Energieversorgung—Das 6. Energieforschungsprogramm der Bundesregierung. Available online: https://www.bmwi.de/BMWi/Redaktion/PDF/E/6-energieforschungsprogramm-der-bundesregierung,property=pdf,bereich=bmwi2012,sprache=de,rwb=true.pdf (accessed on 18 January 2016). (In German)
- Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF). Deutschlands Rolle in der Globalen Wissensgesellschaft Stärken—Strategie der Bundesregierung zur Internationalisierung von Wissenschaft und Forschung. Available online: www.bmbf.de/pub/Internationalisierungsstrategie.pdf (accessed on 18 January 1016). (In German)
- Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF). Rahmenprogramm Gesundheitsforschung der Bundesregierung. Available online: http://www.gesundheitsforschung-bmbf.de/_media/Gesundheitsforschungsprogramm.pdf (accessed on 26 October 2015). (In German)
- Bundesministerium für Umwelt, Naturschutz und Reaktorsicherheit (BMU). National Strategy on Biological Diversity. Available online: https://biologischevielfalt.bfn.de/fileadmin/NBS/documents/Veroeffentlichungen/BMU_Natio_Strategie_en_bf.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2015).
- Bundesministerium für Ernährung, Landwirtschaft und Verbraucherschutz (BMELV). Waldstrategie 2020—Nachhaltige Waldbewirtschaftung—Eine gesellschaftliche Chance und Herausforderung; BMELV: Bonn, Germany, 2011. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Bundesministerium für Ernährung, Landwirtschaft und Verbraucherschutz (BMELV). Verstärkte Holznutzung—Zugunsten von Klima, Lebensqualität, Innovationen und Arbeitsplätzen (Charta für Holz). Available online: http://www.dhwr.de/fileadmin/user_upload/downloads/ChartaFuerHolz.pdf (accessed on 26 October 2015). (In German)
- Bundesministerium für Verkehr, Bau und Stadtentwicklung (BMVBS). Erlass zur Beschaffung von Holzprodukten; BMVBS: Berlin, Germany, 2011. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Krippner, R. Untersuchungen zu Einsatzmöglichkeiten von Holzleichtbeton im Bereich von Gebäudefassaden. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität München, Munich, Germany, 8 March 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Gärtner, S.; Hienz, G.; Keller, H.; Müller-Lindenlauf, M. Gesamtökologische Bewertung der Kaskadennutzung von Holz: Umweltauswirkungen Stofflicher und Energetischer Holznutzungssysteme im Vergleich; IFEU Heidelberg: Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- De Besi, M.; McCormick, K. Towards a bioeconomy in Europe: National, regional and industrial strategies. Sustainability 2015, 7, 10461–10478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welfe, A.; Gilbert, P.; Thornley, P. Increasing biomass resource availability through supply chain analysis. Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 70, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fachagentur Nachwachsende Rohstoffe e.V. (FNR). Bioenergy in Germany: Facts and Figures. January 2014. Available online: https://mediathek.fnr.de/media/downloadable/files/samples/b/a/basisdaten_9x16_2013_engl_web.pdf (accessed on 9 December 2015).
- Prognos AG; EWI—Institute of Energy Economics at the University of Cologne; GWS—Gesellschaft für Wirtschaftliche Strukturforschung. Entwicklung der Energiemärkte—Energiereferenzprognose. Projekt Nr. 57/12 des Bundesministeriums für Wirtschaft und Technologie. Available online: http://www.bmwi.de/DE/Mediathek/publikationen,did=644920.html (accessed on 6 January 2016). (In German)
- Hoefnagels, R.; Dornburg, V.; Faaij, A.; Banse, M. Analysis of the Economic Impact of Large-Scale Deployment of Biomass Resources for Energy and Materials in The Netherlands. Available online: edepot.wur.nl/164540 (accessed on 7 April 2015).
- Peck, P.; Bennett, S.; Bissett-Amess, R.; Lenhart, J.; Mozaffarian, H. Examining understanding, acceptance, and support for the biorefinery concept among EU policy-makers. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefining 2009, 3, 361–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewatripont, M.; Roland, G. The design of reform packages under uncertainty. Am. Econ. Rev. 1995, 85, 1207–1223. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann, P.; Creutzig, F.; Ehlers, M.-H.; Friedrichsen, N.; Heuson, C.; Hirth, L.; Pietecker, R. Carbon lock-out: Advancing renewable energy policy in Europe. Energies 2012, 5, 323–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.-J. Gradualism versus Big Bang: Speed and sustainability of reforms. Can. J. Econ. 1997, 30, 1234–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrás, S.; Edquist, C. The choice of innovation policy instruments. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2013, 80, 1513–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foxon, T.J.; Gross, R.; Chase, A.; Howes, J.; Arnall, A.; Anderson, D. UK innovation systems for new and renewable energy technologies: Drivers, barriers and systems failures. Energy Policy 2005, 33, 2123–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawel, E.; Loßner, M.; Herbes, C. EEWärmeG—Hindernisse und Potenziale im Wärmemarkt für Biomethan. Energiewirtschaftliche Tagesfragen 2013, 63, 48–53. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Piotrowski, S.; Carus, M.; Essel, R. Global bioeconomy in the conflict between biomass supply and demand. Nova Pap. 2015, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upham, P.; Riesch, H.; Tomei, J.; Thornley, P. The sustainability of forestry biomass supply for EU bioenergy: A post-normal approach to environmental risk and uncertainty. Environ. Sci. Policy 2011, 14, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfau, S.F.; Hagens, J.E.; Dankbaar, B.; Smits, A.J.M. Visions of sustainability in bioeconomy research. Sustainability 2014, 6, 1222–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londo, M.; Deurwaarder, E. Developments in EU biofuels policy related to sustainability issues: Overview and outlook. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefining 2007, 1, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batie, S.S. Wicked problems and applied economics. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2008, 90, 1176–1191. [Google Scholar]
- McCann, L. Transaction costs and environmental policy design. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 88, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsche, U.R.; Iriarte, L. Sustainability criteria and indicators for the bio-based economy in Europe: State of discussion and way forward. Energies 2014, 7, 6825–6836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hagemann, N.; Gawel, E.; Purkus, A.; Pannicke, N.; Hauck, J. Possible Futures towards a Wood-Based Bioeconomy: A Scenario Analysis for Germany. Sustainability 2016, 8, 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8010098
Hagemann N, Gawel E, Purkus A, Pannicke N, Hauck J. Possible Futures towards a Wood-Based Bioeconomy: A Scenario Analysis for Germany. Sustainability. 2016; 8(1):98. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8010098
Chicago/Turabian StyleHagemann, Nina, Erik Gawel, Alexandra Purkus, Nadine Pannicke, and Jennifer Hauck. 2016. "Possible Futures towards a Wood-Based Bioeconomy: A Scenario Analysis for Germany" Sustainability 8, no. 1: 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8010098
APA StyleHagemann, N., Gawel, E., Purkus, A., Pannicke, N., & Hauck, J. (2016). Possible Futures towards a Wood-Based Bioeconomy: A Scenario Analysis for Germany. Sustainability, 8(1), 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8010098






