1. Introduction
The rapid development of the global economy of last decades, coupled with the aggressive urbanization, puts rural communities into a predicament. To spur growth, the economy requires expanding volume of resources (natural, territorial, labor,
etc.) [
1]. In the majority of the developed countries, rural communities do not make a critical impact on the gross domestic product (GDP), but at the same time they concentrate essential volumes of resources, which are lacking in other industries. This is where the year-to-year choice arises: resources for economic growth in the short-term, or sustainable environment and preservation of rural communities for the next generations in the long-term [
2].
Whatever the case, rural communities are influenced by the industrialization and urbanization by all means. In such a shift from a “purely rural” to “industrially rural” society, the need for rural development to be sustainable becomes paramount [
3]. Sustainability for rural areas is more than just a sustainable economic growth. The concept of sustainability in rural areas should integrate environmental, economical, cultural and social factors. Every component is of importance. However, the last factor is the critical one. The specific character of the agricultural production stipulates the main bottleneck: possibilities to replace labor and land with capital in rural areas are limited [
4]. People, attracted by higher living standards in urban areas, tend to leave traditional rural areas of inhabitation in favor of bigger urban agglomerations [
5]. That is why the vital issue is how to retain rural inhabitants in their traditional environment by means of provision of sustainable employment and income.
According to Erokhin, Heijman, and Ivolga [
4], apart from the agricultural sector itself, rural areas do not provide many employment opportunities for local citizens. At the same time, one of the most valuable competitive advantages of rural areas over urban ones is that they harmoniously combine natural and cultural values into a unique mixture of attractions. The increasing trend of last decades in the developed countries (and of last years in the developing part of the world) is rural tourism. Tourism is an effective tool to attract investments and promote interest in rural ways of life, traditions and local identities of rural areas. As an alternative source of income in addition to the traditional agricultural production, rural recreation is especially important in developing countries and economies in transition, where investments in agriculture and volume of state support are lower in comparison to the developed countries of the EU and the USA [
6]. The diversity of rural culture in various countries (and even in particular rural areas within a country) provides opportunities to build attractive and competitive tourist products [
7]. Potentially, rural tourism provides alternative employment opportunities, which give rural inhabitants a sustainable income that is competitive in comparison to that of urban territories.
Economies in transition are those, which are emerging from a socialist-type command economy towards a market-based economy [
8]. They undergo a set of structural transformations intended to develop market-based institutions. Although the term usually covers the countries of Central and Eastern Europe and the Former Soviet Union, in a wider sense the definition of economy in transition refers to all countries, which attempt to change their basic constitutional elements towards market-style fundamentals. Such countries still face many problems while starting to develop their domestic rural tourist industries. In many cases, people do not know how to start, what particular steps to take and what identities to promote. A methodology is required to provide a tool for evaluating the capacities and potentials of rural settlements in the sphere of rural tourism. The development of such a universal methodology has been an area of research among a range of scientists and experts [
3]. However, as rural areas are very different from each other, with completely different sets of advantages and weaknesses, there is no “one-size-fits-all” formula for all rural communities. The potential of rural tourism to ensure the sustainable rural development is a generally accepted idea [
9]. The question is how every particular rural community may benefit from rural tourism, and what steps should be taken.
Rural communities have to be equipped with certain tools, applicable in their efforts to establish and develop tourist infrastructure. The present paper focuses on several administrative regions of Southern Russia to find out ways to evaluate rural area potentials to make them attractive for tourists, provide rural dwellers with alternative sources of income and ensure sustainable development of rural settlements. The present research begins with an overview of existing approaches to rural tourism and sustainable rural development, which will provide the background for the development of the methodology of assessment of rural tourism potentials. We examined administrative regions, districts and rural settlements of the North Caucasus Federal District of Russia and displayed three levels of rural tourism development, where with the help of the personal field research and the Delphi approach, we evaluated rural tourism potentials and suggested particular models of rural tourism to be introduced in various rural settlements.
2. Approaches to Rural Tourism and Sustainable Rural Development
There are many approaches to the definition of rural tourism. Zdorov interprets rural tourism as city dwellers vacationing in the countryside with a lease of the country dwelling [
10]. Almukhamedova and Vilenskaya refer to rural tourism as a kind of tourism, which facilitates the permanent residence of tourists in rural areas for the purpose of vacationing and/or involvement with agricultural activities [
11]. Fennel identifies rural tourism with farm tourism, where a large portion of the touristic experience is founded upon the cultural milieu of farms [
12]. However, rural tourism is not only the accommodation on farms. As stated by Ivolga and Erokhin, such a territorial approach to rural tourism limits opportunities for sustainable development and does not correspond to the real demands of rural communities [
13]. Their approach to rural tourism is concluded to be dedicated travels to rural areas with relatively undisturbed ecosystems and ethno-cultural complexes, which have a direct impact on the rural development and are subjects for control in the purposes of sustainable rural development [
13]. The given concept includes two major definitions. Firstly, rural tourism is referred to as an environmentally-oriented tourist product on the domestic and international tourist markets. Secondly, rural tourism is expected to act as one of the tools for sustainable rural development [
14]. Following this idea, Ivolga defines rural tourism as a kind of activity, related to organization of dedicated travels to rural areas, which provides tourists with a complex tourist product (accommodation, meals, excursion services and entertainment), reflects and preserves the natural and cultural identity of regions and ensures economic benefits for hosting communities through the development of employment opportunities and alternative sources of income for local population [
15].
Special attention should also be paid to the diversification of income opportunities in rural areas by means of rural tourism. For the purposes of the current research the issues of unemployment and depopulation in rural areas, and perspectives of alternative income opportunities are addressed in the works of Kundius and Chermyanina [
16], Jelocnik and Ivolga [
17], Bondarenko [
18], and Kneafsey [
19], along with the issues of intensification of economic initiatives in the rural areas through the development of special economic zones of tourist and recreational type [
20].
International practices and success stories concerning the sphere of sustainable rural development by means of tourism are borrowed from the works of Cvijanovic and Vuković (investigations of perspectives of rural tourism in separate localities of Serbia and other Danube countries) [
21], Vuković, Kljajić, and Arsić (research of the role of rural tourism in the promotion of multifunctional agriculture) [
22], Erokhin
et al. (comparative analysis of various practices of rural tourism and rural development in Russia and countries of the Eastern Europe) [
23], Abrham (assessment of effectiveness of clusters in rural tourism in the countries of Visegrad Group) [
24], and Gannon (comparison of various cases in the sphere of rural tourism and their influence on the development of rural communities in the economies in transition) [
25].
Since the paper addresses cases of various regions, some of the regional approaches to rural tourism have been modified from the cases of the Carpathian region (research by Popović, Milijić and Vuković) [
26] and the region of Suva Planina of the Republic of Serbia (work by Randelović, Stefanović, and Azemović) [
27].
3. Methodology
The methodology for evaluating the rural tourism potentials of rural settlements presented in this paper has been developed with regard to the previous research in this field, primarily made by Rusinova, who elaborated the efficiency rating for the use of resource potential of rural communities [
28]; Floysand and Jakobsen, who explained approaches to the commodification of rural areas [
29]; and Volkov, who presented a strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats (SWOT)-analysis of the rural tourism potential in Russia and analyzed major problems of this industry with particular attention to the regions of Russia [
30].
Having studied a wide range of theoretical and practical approaches to rural tourism, for the purposes of this research we have emphasized major social and economic impacts of rural tourism to sustainable rural development, which are (1) establishment of new employment opportunities and alternative sources of income for rural people; (2) retention of economically active population and young people in rural areas, lower migration outflows; (3) establishment of a market for local agricultural and organic products, local specialties and products of folk crafts; (4) preservation of the natural, environmental and cultural heritage of rural areas. The abovementioned parameters are accepted as a basis for the development of the methodology for evaluating the rural tourism potentials of selected rural settlements.
The methodology included six groups of factors: economic, distribution of population, environmental, cultural, infrastructural and psychological.
Analysis was made based on the case of southern Russia (North Caucasus Federal District—NCFD). The district was selected as a model because of its predominance of rural territories, its high share of local citizens, its involvement in agricultural production, its reputation of a tourist destination and its unique environmental advantages for the development of rural tourism.
The research methodology was based on the Delphi approach. During the initial stages of designing the research concept, the author investigated many potential methods of enquiry. As the aim of the research was to develop a tool to evaluate rural tourism potentials that could be generalized for implementation in various regions and worldwide, the author desired to canvas professional academic and practitioner opinions from experts in the field. After considering many qualitative research methods, the author chose the Delphi method because of its appropriateness for this particular study and its flexibility with small samples.
The Delphi method is beneficial when other methods are not adequate or appropriate for data collection. According to Linstone [
31] (p. 275), there are two circumstances where Delphi techniques are most appropriate: (1) “the problem does not lend itself to precise analytical techniques but can benefit from subjective judgments on a collective basis”; (2) “individuals who need to interact cannot be brought together in a face-to-face exchange because of time or cost constraints”. Both circumstances, emphasized by Linstone, are applicable to the specifics of this study.
First, the broad range of subject parameters included in the concept of a “rural tourism potential” in different regions suggests this is very subjective. The Delphi method thus provided a means for achieving research aims, insofar as the structured communication process let to the summarization of various objective and subjective factors, which affect rural tourism at the regional, district and community levels.
Second, since the research was carried out on those three levels and included seven administrative regions of the North Caucasus Federal District, Russia, the experts were drawn from those spaced apart regions. Ninety-five experts in total were chosen who represented local authorities, universities, businesses and local communities.
The panels of selected experts were given the questionnaires (different for each level) to solicit specific information about the potential of rural development in the region, district, or community. On the regional level, a group of 14 experts (two from each region) was asked to verify and rate the potential of rural tourism for selected regions based on the set of six pre-identified parameters. The research goal was to obtain consensus regarding the region most suitable for the development of rural tourism. The Delphi array on the district level included eight respondents (representing authorities, university experts and businessmen of Stavropol Krai), who were questioned on seven parameters. The Delphi array on the community level included 73 respondents—inhabitants of six rural settlements of the Predgorny district, Stavropol Krai, who were surveyed on six parameters. The authors felt that identifying the specifics of rural tourist potentials in particular districts and communities would benefit from this wide range of opinions.
4. Discussion
Rural tourist product may be developed in two ways: through the “traditional” rural tourism (farm accommodation, agricultural activities, etc.) and other “alternative” types of rural recreation (environmental, ethnographical, cultural, etc.). The way of development determines the set of approaches to the organization of rural tourism in a particular rural community.
According to the approach stated above, rural tourism includes not only an accommodation in rural areas, but also a wide range of recreational activities. In practice, “traditional” rural tourism is exceeded in abundance by its various alternative (more complex) forms. In general, an attractive and competitive rural tourist product is to include other types of tourist activities, apart from an accommodation itself [
32]. According to Dragulanesku and Drutu, a rural tourist product is synthesized from mass and alternative tourism, where mass tourism includes cultural weekend trips to popular resort destinations, while alternative rural tourism puts emphasis on the understanding of the way of living of rural people and the local natural environment [
3]. In this case, a tourist product may be targeted on a wider market segment, and consequently lead to an establishment of more employment opportunities for local inhabitants.
However, the combinations of traditional and alternative types of rural tourism vary widely depending on the particular rural community. There are several concepts and related types of rural tourism, which are determined by peculiarities of the historical development of particular territories and recreational systems, social and economic conditions and rural infrastructure. Ivolga emphasizes four models of rural tourism depending on the regional peculiarities: Western European (promotion of alternative sources of income for rural people through new employment opportunities), Eastern European (redirection of tourist flows from traditional tourist centers to rural areas), Asian (large-scale projects and promotion of regional identities through historical, cultural and ethnographic programs in rural areas) and English-American (provision of recreational opportunities for rural inhabitants in rural areas) [
15]. Sharing this classification, we would like to expand it with a fifth model, which is the model used in Russia and the former republics of the Soviet Union, now referred to as the countries of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS). The countries of the CIS, 23 years after the collapse of the Soviet Union, are still undergoing a variety of economic, social and industrial reforms as they attempt to make a transfer to market economies. Rural tourism and related rural infrastructure to support tourism were never developed in those countries under the Soviet Union. Today, however, the CIS countries recognize the economic potential of rural tourism and are making efforts to develop the tourist infrastructure and identify specific national attractions [
33].
The resource potential of the CIS countries and Russia is favorable for the development of rural tourism: there is a high cultural and natural diversity as well as a rich historical and cultural potential, and there are vast areas of agricultural land of appropriate quality and environmental conditions and well preserved local traditions and identities. Unfortunately, despite having such huge potentials, most of the rural areas in the CIS countries and Russia are underdeveloped. Despite the essential differentiation of countries in the context of development of rural tourism and the implementation of various practices, the overall tendencies are more or less the same. We have summarized four major tendencies from Ivolga [
15], Erokhin [
13], Heijman [
4], Almukhamedova and Vilenskaya [
11]:
- (1)
Seasonal character of rural tourism (tourists prefer to come during summer or winter, but not in spring or autumn) [
15];
- (2)
Limited opportunities for implementation of high-qualified labor force (until now most of the employees with high qualifications have left rural areas and are seeking better jobs and financial benefits in cities) [
4];
- (3)
“Erosion” of the local cultural and ethnographic environment (it is easier to offer tourists some popular product or service than to develop a new one on the basis of the local identity and to promote it) [
13];
- (4)
Shortage of financial and labor resources for traditional agricultural production [
11].
Having common problems and shortages regarding the development of rural tourism, countries and regions have different conditions and competitive advantages. In order to develop rural tourism in an effective and sustainable manner, those parameters have to be identified and measured, and then taken as a basis for the recommendations for a particular rural community.
The analysis was conducted on the case of the southern part of Russia, the North Caucasus Federal District (NCFD), which includes seven administrative entities of the Russian Federation (
Figure 1).
The region of the NCFD was chosen as a model for our research for four reasons: the majority of its territories are rural; the majority of inhabitants are involved in agricultural production or related activities of rural type (
Table 1); the region is widely known in Russia and neighbor countries as a tourist destination; the region has unique natural and environmental advantages for the development of rural tourism.
Table 1.
Main statistics on rural activities of the North Caucasus Federal District (NCFD) administrative entities in 2013.
Table 1.
Main statistics on rural activities of the North Caucasus Federal District (NCFD) administrative entities in 2013.
| Indicator | Republic of Chechnya | Republic of Dagestan | Republic of Ingushetia | Republic of Kabardino—Balkaria | Republic of Karachaevo—Cherkessia | Republic of North Osetia—Alania | Stavropol Krai |
|---|
| Gross regional product (GRP) per capita, Euro | 1864.1 | 3350.6 | 1677.7 | 2751.3 | 3185.5 | 3324.7 | 4004.2 |
| Share of agriculture in GPR, % | 10.3 | 15.0 | 10.1 | 19.1 | 22.3 | 19.2 | 13.2 |
| Rural inhabitants, percentage of the total population of the region, % | 64.7 | 57.6 | 57.5 | 43.9 | 55.9 | 35.7 | 43.1 |
| Average size of rural settlement, people | 1042 | 947 | 517 | 893 | 1058 | 1152 | 1654 |
| Average size of rural household, people | 2.9 | 4.1 | 2.3 | 3.1 | 3.4 | 3.0 | 3.2 |
| Employment level in rural territories, % | 56.2 | 55.9 | 38.6 | 58.7 | 57.6 | 60.6 | 60.5 |
| Employed in agriculture, percentage of the gainfully employed population of the region, % | 9.2 | 19.9 | 3.1 | 15.6 | 18.1 | 13.1 | 16.0 |
| Average nominal wages of rural people, employed in agriculture, Euros per month | 330.9 | 431.3 | 272.8 | 298.2 | 277.0 | 324.6 | 342.2 |
| Average per capita income of rural people in comparison to average Russian level, % | 66.6 | 86.8 | 54.9 | 60.0 | 55.8 | 65.4 | 68.9 |
The analysis of rural tourism potentials of various administrative entities of the NCFD was made on the basis of six groups of factors: economic, distribution of population, environmental, cultural, infrastructural and psychological (
Table 2).
Table 2.
Six groups of factors in the sphere of rural tourism and three levels of influence.
Table 2.
Six groups of factors in the sphere of rural tourism and three levels of influence.
| Region | District | Rural Community |
|---|
| Group 1: Economic factors |
| Level of effective demand in the NCFD, and South Federal District (neighbor district) | Potential labor force (qualitative and quantitative parameters, and their differentiation in the republics of the North Caucasus and Stavropol Krai) |
| Development of agricultural production |
| Development of rural households and private subsidiary local farming |
| Group 2: Distribution of population |
| Number of urban agglomerations in the region | System of rural settlements (number of settlements and network) | Types of rural settlements (traditional Cossack villages, mountain settlements, remote animal-breeding settlements) |
| Location of the region in relation tourban agglomerations in the neighbor regions (cities of Moscow, Krasnodar and Rostov-on-Don) | Proximity to urban agglomerations (air, rail and road connections with Moscow and neighboring urban agglomerations of Krasnodar and Rostov-on-Don). International flight connections via Mineralnye Vody and Stavropol airports. | Population (number of people, density) |
| Share of population living in rural areas |
| Group 3: Environmental factors |
| Natural and climatic conditions | Landscape complexes: mountain resorts of Kabardino-Balkaria and Karachaevo-Cherkessia, spa resorts of Stavropol Krai | Particular natural objects and places of attraction (natural landscapes, mountains, spa resorts, historical places of interest) |
| Environmental conditions (region of the Caucasus Mineral Waters, “healing climate” resorts) |
| Group 4: Cultural factors |
| Regional brand (history, traditions, awareness of regional identities) | Particular cultural and historical objects and places of attraction |
| Group 5: Infrastructural factors |
| Transport accessibility | Tourist and recreational infrastructure, including accommodation |
| Group 6: Psychological factors |
| Interest in rural tourism and recreation among population | Hospitability of rural people and willingness to host tourists. Local perceptions of hospitality among various nationalities, inhabiting southern parts of Russia (Cossacks and mountain dwellers) |
| Social networking |
The working hypothesis is that the abovementioned factors determine various combinations of rural tourism, in particular rural communities. Their interrelations affect three levels (region, district, community) in a different manner. Each level has its own set of factors and parameters.
There are two major restrictions of the proposed methodology:
- (1)
Some of the factors are not measurable, hence it is not possible to construct any mathematical model to assess their influence on rural tourism in the rural community. That is why the methodology assumes rough estimates of those factors.
- (2)
Groups do not have equal degrees of influence. Economic factors of Group 1 have superiority and directly affect rural tourism. However, there are factors that influence indirectly.
5. Results
The evaluation was conducted on three levels, which diverge from each other in the sets of indicators.
Level 1: Region. The major differentiating factors at the regional level are those of Group 1 and Group 2. Economic factors and distribution of population make it possible to assess the potential of rural tourism. However, such an evaluation is rather general, that is why we adopted the procedure of the structure modeling in order to make the results more applicable. The implemented structure model included the following indicators:
- (1)
Group 1: Gross Regional Product (GRP) in agriculture per capita (R1).
- (2)
Group 2: Share of the rural population in small and medium rural settlements (200–500 inhabitants) (R2) and number of urban agglomerations in the region (potential of urban agglomerations) (R3).
- (3)
Group 3: Natural and climatic conditions of the region (R4).
- (4)
Group 4: Number of historical and cultural objects of the federal importance (R5).
- (5)
Group 5: Development of transport networks (number of airports, railroad network, etc.) (R6)
The Delphi approach was implemented: fourteen experts were surveyed (two people from each region) from July–August 2014. Parameters are rated between 0 (the lowest) and 10 (the highest) and weighted as the average of the 14 independent evaluations. The resulting parameter (R) for each region is calculated as an average value of six parameters. Results are presented in the
Table 3.
Table 3.
Assessment of the potential of rural tourism for selected regions of Russia (Level 1).
Table 3.
Assessment of the potential of rural tourism for selected regions of Russia (Level 1).
| Region | Parameters | Resulting Parameter (R) |
|---|
| R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 |
|---|
| Republic of Chechnya | 6.23 | 7.11 | 5.01 | 8.22 | 3.10 | 6.15 | 5.97 |
| Republic of Dagestan | 6.09 | 8.12 | 6.47 | 8.31 | 4.08 | 6.49 | 6.59 |
| Republic of Ingushetia | 4.17 | 9.20 | 5.63 | 8.04 | 3.16 | 4.14 | 5.72 |
| Republic of Kabardino-Balkaria | 6.16 | 8.54 | 7.40 | 9.24 | 5.61 | 5.30 | 7.04 |
| Republic of Karachaevo-Cherkessia | 7.21 | 8.02 | 7.09 | 8.14 | 5.55 | 6.12 | 7.02 |
| Republic of North Osetia—Alania | 7.36 | 8.26 | 7.84 | 8.11 | 6.23 | 7.47 | 7.55 |
| Stavropol Krai | 8.59 | 6.30 | 9.17 | 6.97 | 8.10 | 8.95 | 8.01 |
The potential of Stavropol Krai in the sphere of rural tourism is rated the highest among the regions of the NCFD. The region has the highest GRP in agriculture per capita (R1), potential of urban agglomerations (R3), number of historical and cultural objects (R5), and the most developed transport networks (R6) among the surveyed regions. Negative (or less advantageous) factors for the development of rural tourism in Stavropol Krai are the lower share of rural population in comparison with the neighboring regions (R2) and less favorable natural conditions (R4).
Having determined the most favorable (model) region of the surveyed group, we were able to continue the analysis at the second level (district).
Level 2: District. The major differentiating factors at this level are those, which characterize the most favorable areas of rural tourism within the particular region. We used the same methodology as we implemented for the Level 1. The structure model included the following indicators:
- (1)
Group 1: Employed in agriculture and related rural areas (D1).
- (2)
Group 2: Number of rural settlements (D2) and proximity to urban agglomerations (D3)
- (3)
Group 3: Places of environmental and landscape attraction (D4).
- (4)
Group 4: Number of historical and cultural objects (D5).
- (5)
Group 5: Development of tourist infrastructure (D6).
- (6)
Group 6: Support of local citizens (D7).
Stavropol Krai includes 26 districts, which were surveyed by eight experts representing regional authorities (the Ministry of Agriculture of Stavropol Krai, the Ministry of Economic Development of Stavropol Krai and the Tourist Information Center of Stavropol Krai), universities (Stavropol State Agrarian University, North-Caucasus Federal University) and three tourist agencies. Results are presented in the
Table 4.
Table 4.
Evaluation of the potential of rural tourism for districts of Stavropol Krai (Level 2).
Table 4.
Evaluation of the potential of rural tourism for districts of Stavropol Krai (Level 2).
| District | Parameters | Resulting Parameter (D) |
|---|
| D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 | D6 | D7 |
|---|
| Aleksandrovsky | 8.10 | 7.85 | 5.96 | 5.21 | 4.55 | 5.94 | 6.14 | 6.25 |
| Andropovsky | 7.11 | 7.84 | 5.42 | 5.13 | 3.62 | 4.82 | 5.01 | 5.56 |
| Apanasenkovsky | 7.23 | 7.99 | 5.02 | 5.20 | 3.14 | 4.80 | 5.61 | 5.57 |
| Arzgirsky | 6.92 | 8.65 | 2.00 | 3.17 | 1.25 | 3.33 | 5.08 | 4.34 |
| Blagodarnensky | 6.95 | 7.16 | 5.28 | 5.61 | 3.11 | 5.44 | 4.71 | 5.47 |
| Budennovsky | 6.06 | 6.93 | 6.84 | 5.14 | 5.07 | 5.91 | 5.74 | 5.96 |
| Georgievsky | 6.28 | 7.13 | 8.15 | 6.97 | 7.09 | 7.18 | 6.97 | 7.11 |
| Grachevsky | 7.16 | 8.15 | 6.10 | 4.22 | 5.13 | 5.92 | 5.89 | 6.08 |
| Izobilnensky | 6.27 | 8.18 | 5.93 | 5.14 | 5.99 | 7.03 | 5.16 | 6.24 |
| Ipatovsky | 8.97 | 8.84 | 6.18 | 5.11 | 5.01 | 6.98 | 6.12 | 6.74 |
| Kirovsky | 7.82 | 9.14 | 4.12 | 6.17 | 4.20 | 5.27 | 4.97 | 5.96 |
| Kochubeevsky | 7.36 | 9.04 | 5.10 | 4.95 | 4.95 | 4.97 | 5.07 | 5.92 |
| Krasnogvardeysky | 6.96 | 8.24 | 4.00 | 5.24 | 4.82 | 4.89 | 5.49 | 5.66 |
| Kursky | 7.88 | 9.08 | 3.15 | 5.61 | 4.28 | 5.07 | 4.11 | 5.60 |
| Levokumsky | 6.33 | 9.81 | 3.07 | 4.22 | 3.17 | 4.31 | 4.32 | 5.03 |
| Mineralovodsky | 5.08 | 6.94 | 9.11 | 9.14 | 7.88 | 9.24 | 9.26 | 8.09 |
| Neftekumsky | 6.33 | 9.74 | 2.18 | 2.54 | 2.61 | 3.04 | 5.12 | 4.51 |
| Novoaleksandrovsky | 8.84 | 8.14 | 5.14 | 4.97 | 4.81 | 6.27 | 6.21 | 6.34 |
| Novoselitsky | 8.08 | 8.41 | 5.45 | 5.02 | 4.15 | 5.04 | 4.92 | 5.87 |
| Petrovsky | 7.11 | 7.14 | 6.25 | 6.21 | 5.12 | 4.98 | 4.56 | 5.91 |
| Predgorny | 5.02 | 6.12 | 10.00 | 9.89 | 9.99 | 10.00 | 9.57 | 8.66 |
| Sovetsky | 7.15 | 8.24 | 4.97 | 4.18 | 3.01 | 4.00 | 5.16 | 5.24 |
| Stepnovsky | 6.85 | 8.16 | 4.08 | 4.07 | 2.00 | 3.19 | 5.17 | 4.79 |
| Trunovsky | 6.93 | 7.94 | 5.18 | 5.14 | 4.06 | 5.27 | 5.15 | 5.67 |
| Turkmensky | 6.02 | 9.14 | 2.10 | 2.13 | 2.47 | 2.04 | 5.26 | 4.17 |
| Shpakovsky | 5.64 | 5.24 | 9.84 | 9.86 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 9.52 | 8.59 |
Three districts (Predgorny, Shpakovsky and Mineralovodsky) were rated as the most favorable for development of rural tourism. These regions are located close to the biggest urban agglomerations of Stavropol Krai (the cities of Stavropol and Pyatigorsk), have the most favorable environmental conditions (spa springs), landscape attractions (mountains) and developed tourist infrastructure (region of Caucasus Mineral Waters). Local citizens are accustomed to hosting tourists and aware of rural tourism.
Other districts of the region have various restricting factors, but are still favorable for the development of some special types of rural tourism. There are districts that are unsuitable for rural tourism (Turkmensky, Arzgirsky, and Neftekumsky), because of unfavorable climatic conditions and low historical and cultural attractiveness. Those disadvantages are not compensated, not even by the high number of rural settlements and agricultural specialization.
Level 3: Community. The following factors are considered as the most influencing for the rural tourism at the rural community level:
- (1)
Group 1: Number of rural households and private subsidiary farming in the community (C1)
- (2)
Group 2: Types of rural settlements (size and specialization) (C2) and density of rural population (C3).
- (3)
Group 3: Particular natural objects and places of attraction (C4).
- (4)
Group 4: Particular cultural and historical objects and places of attraction(C5).
- (5)
Group 6: Social networking in the community (C6).
Since we had defined the Predgorny district as the most favorable one in Stavropol Krai for development of rural tourism, we continued our analysis on the case of six rural settlements, located within the administrative borders of this district (
Table 5). The Delphi array included 73 questionnaires, obtained from the inhabitants of six rural settlements of the Predgorny district.
Table 5.
Evaluation of the potential of rural tourism for settlements of the Predgorny district (Level 3).
Table 5.
Evaluation of the potential of rural tourism for settlements of the Predgorny district (Level 3).
| Settlement | Parameters | Resulting Parameter (C) |
|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 |
|---|
| Bekeshevskaya | 8.14 | 7.96 | 9.12 | 7.02 | 6.35 | 7.41 | 7.67 |
| Borgustanskaya | 7.52 | 6.24 | 8.07 | 6.20 | 6.13 | 8.94 | 7.18 |
| Etoka | 6.02 | 6.28 | 7.15 | 8.84 | 7.26 | 6.55 | 7.02 |
| Pyatogorsky | 6.20 | 4.98 | 6.33 | 8.71 | 7.93 | 6.16 | 6.72 |
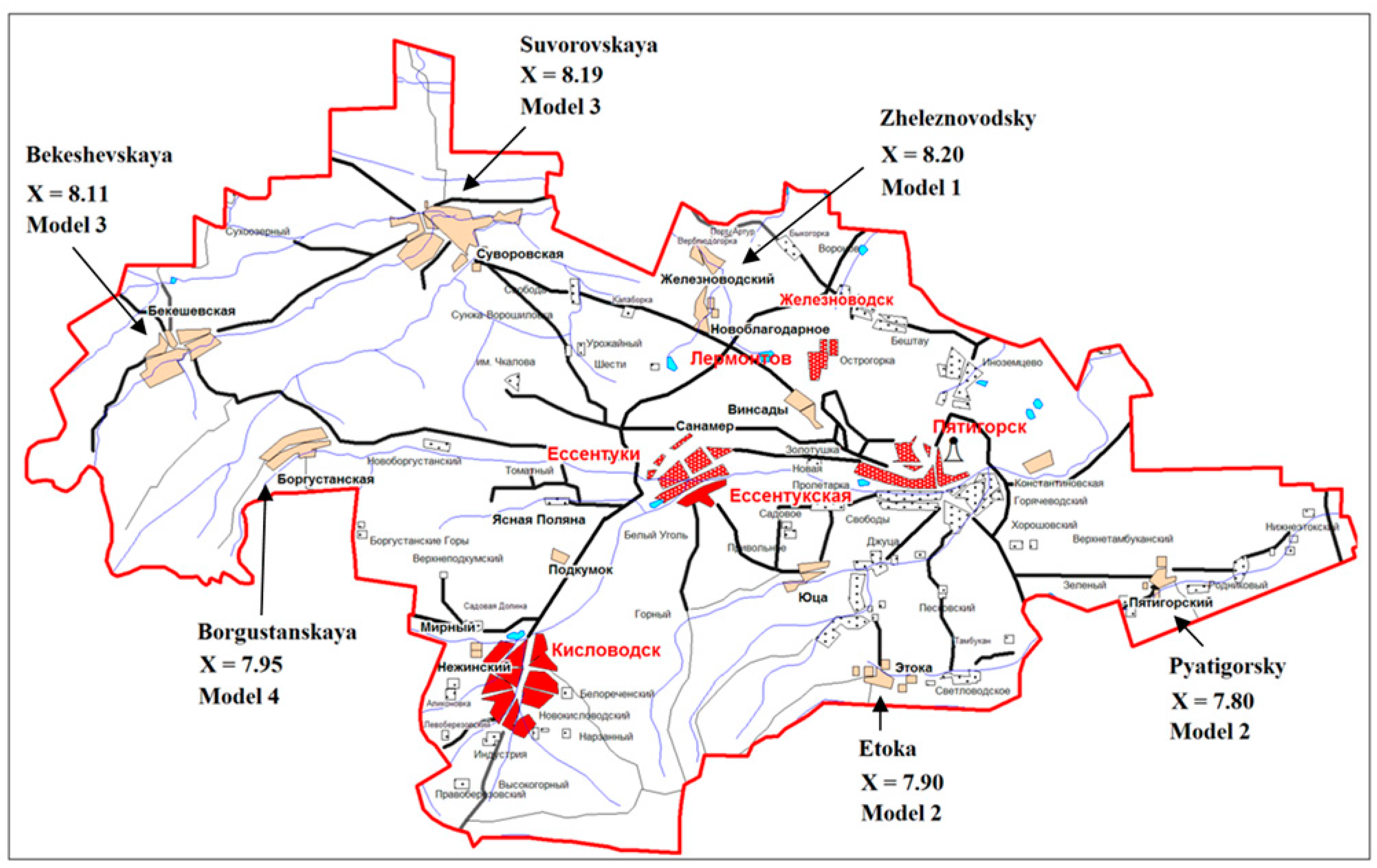
| Suvorovskaya | 9.07 | 7.89 | 8.79 | 6.27 | 7.14 | 8.23 | 7.90 |
| Zheleznovodsky | 7.05 | 6.02 | 8.04 | 9.91 | 9.20 | 7.34 | 7.93 |
Summarizing the conducted analysis of various factors, which affect rural tourism at the regional, district and community levels, we determined the resulting formula as follows:
where:
X—resulting rating of rural settlement on potential of rural tourism;
n—levels of analysis (n = 3);
Ra—factor of regional level;
Db—factor of district level;
Cc—factor of community level.
The resulting ratings of the selected settlements of the Predgorny district are presented in
Figure 2.
Figure 2.
Rural settlements of the Predgorny district: resulting ratings and models of rural tourism. Source: author’s development.
Figure 2.
Rural settlements of the Predgorny district: resulting ratings and models of rural tourism. Source: author’s development.
The rating itself allows selecting rural communities with the highest potential for the development of rural tourism. However, since the resulting number is an average value, we implemented the cross-spectrum analysis of C
1–C
6 parameters that allow us to consider local differences of rural communities and to define various models of rural tourism as the most appropriate ones for each settlement (
Table 6).
Table 6.
Models of rural tourism for settlements of the Predgorny district.
Table 6.
Models of rural tourism for settlements of the Predgorny district.
| Model | Parameters | Conditions | Proposed Actions |
|---|
| Model 1 | High: C3, C4, C5( ≥ 8)Low: C1, C2, C6( < 8) | There are many objects of attraction (natural, cultural and historical), but the rural tourist infrastructure is underdeveloped. The settlement is located near urban agglomeration; the space is limited. | Reconstruction or establishment of new tourist objects in rural areas. Intensive development of the tourist infrastructure (possibly without involvement of additional land) |
| Model 2 | High: C4( ≥ 8)Low: C1, C2, C3, C5, C6( < 8) | Low level of development of tourist infrastructure.Settlements have natural attractions and free space. | Establishment of the tourist infrastructure. Construction of large and medium sized tourist facilities (guest houses, farms, etc.) with involvement of available land resources. |
| Model 3 | High: C1, C2, C3 ( ≥ 8)Low: C4, C5, C6( < 8) | Developed rural infrastructure, high density of population, many rural households to be potentially involved into the rural tourism. | Rural tourism on the basis of small family hotels and guesthouses, with a variety of rural activities. Remote rural settlements are favorable for weekend (or even longer) accommodations of tourists. |
| Model 4 | High: C3, C6 ( ≥ 8)Low: C1, C2, C4, C5 ( < 8) | Rural infrastructure is underdeveloped, however, there are many places of attraction. Rural people are highly involved in tourism through networking. | Development of new tourist products with the involvement of local people. Regional branding through networking and “word-of-mouth” advertising. Involvement of rural people as tourist guides. |
6. Contextualization of the Approach from a Global Perspective
The case study of the North Caucasus Federal District, Russia, presented in the paper, is a model, which may be easily utilized worldwide. As rural tourism is considered as one of the tools to ensure sustainable development of rural areas, the potential contextualization of the approach is wide.
According to Sillignakis [
34], in the shift from an “industrial” to a “risk” society, the need for rural development to be sustainable becomes paramount. The concept of sustainability integrates environmental, economic, cultural and social considerations.
Among the contemporary challenges facing rural areas globally, Wakeford highlights demographic changes and social polarization [
35]. In rural areas, population numbers may conceal an ageing population, with younger people moving to the cities for highly rewarded employment opportunities. This means that fewer people work locally and traditional rural industries continue to lose qualified and effective labor force. Attractiveness of rural areas and effectiveness of agricultural production cannot be increased with just a bigger amount of investments into agricultural complex. Rural areas need more than farmer-based development, because the rural way of life is like a social paradigm, which is developed under an influence of a whole set of non-economic factors: social, cultural, historical, ethnic,
etc.The approach implemented in the paper is the application of the principle of sustainable development to tourism. Reid [
36] emphasizes that sustainable tourism seeks to sustain the quantity, quality and productivity of both human and natural resource systems over time, while respecting and accommodating the dynamics of such systems. Drawing on the OECD, research suggests that rural regions need to address the particular challenges of business capacity infrastructure, human capital, innovation and services [
37]. Tourism represents an important share of the service economy, both domestically and internationally, and the growth sector. According to Erokhin [
5], the development of rural tourism increases employment in rural areas, helps to retain people in rural areas (and even attract them from cities), improves the quality of life by the development of rural infrastructure and related industries. According to McGehee and Andereck [
38], development of rural tourism also has an essential social impact, since it supports historical-cultural diversity and traditions on the regional level.
What are the implications of these findings for other rural areas worldwide, besides the regions of Russia’s South? Local communities are becoming increasingly important in terms of actions taken to ensure their own sustainability, and, as Richards and Hall [
39] point out, are also forming part of wider alliances to preserve the environment globally. There is the recognition that to be sustainable, the preservation of local identities (environmental, cultural, social, historical,
etc.) must be grounded in the communities and societies, which exploit those identities [
34]. That is why stakeholders in rural areas (policymakers, community authorities, producers, rural dwellers) have increasingly turned to tourism as an alternative means of achieving economic growth and sustainable development through diversification [
5].
Butler [
40] observes that “tourism has emerged as one of the central means by which rural areas can adjust themselves economically, socially and politically to the new global environment”. The methodology presented in this paper is designed to support rural policymakers and other stakeholders in their efforts to identify local tourist destinations and assess the tourist capacity of each settlement. The set of indicators included in the model helps to assess two major components of tourist capacity: the quality of the environment and the quality of the recreation experience. Through identification and development of local tourist capacity, local communities are expected to sustain and create additional local incomes and employment, encourage the development of other sectors of domestic economy, retain human resources in rural areas, and contribute to the conservation of environmental and cultural resources.
7. Conclusions
Concluding the conducted analysis, we may highlight the novelty of the approach, which is that we have introduced the concept of a “rural tourism potential” and ranked the selected rural settlements according to their rural tourist capacity. The methodology is based on the evaluation of several groups of factors, which may be recognized as the most influential. The resulting rating of rural settlement on the potential of rural tourism is an arithmetical average of 19 parameters, divided into six groups on three levels: regional, district and local. The value of each parameter for each region, district and rural community is received through the survey of three targeted groups of experts representing local authorities, academic experts and professional practitioners in the sphere of rural tourism (Delphi approach). Each level involves different factors and results in different outcomes. The analysis at the regional level identifies territories for various forms of support of rural tourism on the national level. The evaluation of particular districts within the region allows identifying territories for the development of rural infrastructure. Analysis on the local level helps to formulate a certain course of action in the frame of particular models of rural tourism.
The application of the methodology to rural settlements of Stavropol Krai, Russia allows us to construct four models. Model 1 is based on the preferential reconstruction of existing tourist facilities and establishment of new ones. Model 2 presumes complete establishment of a tourist infrastructure in rural areas, with construction of large-scale tourist facilities and involvement of available land. The rural settlement of Model 3 is to develop accommodation and recreational facilities based on existing small and medium rural households. Model 4 awaits the high support from local citizens and their involvement in the development of tourist products and promotion of local brands and identities.
The methodology may be easily implemented to other regions of the country, as well as to other countries. The idea is to discover the existing strengths, attractions or identities, which every rural settlement has to a greater or lesser degree, and to turn them to advantages.
The application of the methodology helps regional authorities and other stakeholders to evaluate rural tourism potentials of various regions/districts/communities, to discover their specific advantages and disadvantages, and to analyze the indicators of rural tourism used in terms of policy relevance in order to assess their overall value, especially in an international context. Recent policy work of the OECD has highlighted the growing role of the regions in rural tourism development [
41]. Local governments now need to start to address how alternative types of economic activities in rural areas, such as rural tourism, will need to be adjusted to encourage the sustainable intensification in use of existing competitive advantages (environmental, natural, agricultural, cultural,
etc.) of a region. In many countries, regions now have a key competency for tourism policy and product development and promotion [
41]. In this connection the methodology described in the paper is of key importance. It allows the development of a system of ranking of rural settlements according to their rural tourist capacity at the regional level, which makes it comparable with other regions and with national and international data. This approach is in line with the OECD activities in the sphere of identification of the major elements to be considered when measuring the economic and social impacts of tourism at the sub-national level.