Abstract
For a long time, the traditional pattern of urban-rural human settlements has been shaped in reference to the existence of the urban-rural dual structure. In this paper, we put forward the notion of triaxiality of human settlements, and used the standards conversion entropy weight method to measure and calculate degrees of livability of human settlements, so as to prove the existence of triaxiality of human settlements within the same unit at the micro-scale level, and conduct an empirical study on the spatial-temporal evolution, system attributes and formation mechanisms of the triaxiality of human settlements in 10 districts (counties) of Dalian (Years 2002–2011). Results showed that: (1) Spatial evolution of human settlements presents triaxiality. Administrative divisions do not play a full and predominant role in the unit division of human settlements. The number of distribution districts (counties) within different units of human settlements tends to be balanced, there is spatial variation of tertiary units in the human settlements of Dalian, and the transition area of human settlements occupies the leading position in the unit division of human settlements; (2) Human settlements also exhibit triaxiality at different development stages during the period of evolution. The fluctuation changes of degrees of livability of the human settlements of Dalian within the past 10 years have been relatively stable, with a trend of small scale decline and obvious manifestations of stage differences; (3) The system attributive characters of human settlements presents triaxiality. There also exists differentiations of system and area in human settlements within the same unit; (4) Industrialization and urbanization have led to the collapse of part of the urban-rural dual structure, while the differentiation of ternary structure of the economic and social structure, and living environment and life style leads to the triaxiality of human settlement.
1. Introduction
The idea of the unit division of human settlements was conceived in early urban planning in foreign countries: Howard put forward the idea of the “garden city” and tried to solve the urban problem from the perspective of the “urban-rural” dual structure [1]; Geddes promoted “regionalism” and emphasized that the basic framework of planning should extend the regular scope of the urban unit [2]; Mumford advocated the building of pluralistic zones with the tertiary unit of “urban combination”, “urban-rural combination”, “artificial-natural combination” and human-oriented [3]; Doxiadis, founder of the Sciences of Human Settlements, emphasized the study by integrating all human settlements including the three units of rural, town and urban and the five major systems of nature, human, society, house and network of human settlements [4,5,6]. International scientific scholars have conducted rich studies on human settlements in different units and results of the latest research mainly focus on: risk of human settlements [7]; ways to re-establish and restore human settlements after major disasters [8]; rank-scale of human settlements [9]; quality assessment and the continuity of human settlements under different space scales [10]; human settlement analysis under climate change [11]; urban sprawl [12]; rural settlements [13]; informal human settlements [14], etc. The findings of research on urban unit human settlements in China are most remarkable. (1) They include the theoretical basis of urban human settlements: the definition of intension and extension [15]; (2) The evaluation of the contents of urban human settlement: satisfaction [16]; Characteristics and Spatial-temporal Differences [17]; attraction [18]; livability [19]; natural suitability [20]; mismatch degree [21], etc. (3) The study on urban human settlements with different geographical space scales and hierarchies [22]; (4) Study of the correlation between urban human settlements and the contents of other sciences: information theory for human settlements [23]; coordinated development of urban human settlement environment and economy [24]; (5) Study of urban human settlements with special scale of space and time: peri-urban areas in urbanization [25]; less developed areas in periods of economic transition [26]; resettlement areas in urbanization and fringe areas in metropolises, etc. [27]. The human settlements in rural units constitute an important component of the Complex Giant System of human settlements, and the research results mainly focus on:
- (1)
- The evaluation of the contents of rural human settlement, quality difference and its driving factors [28], satisfaction degree and optimization strategy [29], progress and prospects on the research [30].
- (2)
- Study of rural human settlements under different positive space behaviors [31].
- (3)
- Study of the correlation between rural human settlements and special geographical phenomena [32].
- (4)
- Study on the influencing factors and driving mechanisms of rural human settlements [26].
The town is the transitional residential area between the country and city, and which is an organic and cohesive part of human settlement systems. The study of human settlements in the town unit is also concerned with:
- (1)
- Study of the comfort index of the human settlements of towns and their connectors [33].
- (2)
- Study of the characteristics that place a demand on town human settlements based on different subjects, etc. [34].
Overall, the study of human settlements in urban units is comparatively mature and the human settlements of rural units are being improved day by day, but the comprehensive and systematic discussion and study of human settlements in the three units of urban, transition area (town) and rural is relatively insufficient. In this paper, we defined preliminarily the triaxiality of human settlements on the basis of relevant studies [35,36,37,38]: the contents of this study concerning triaxiality mainly include human settlements, human settlement activities and human settlement culture; the triaxiality of the study scale mainly includes macro triaxiality and micro triaxiality, with the macro scale existing in human settlements comprised of the three units of urban, transition area (town) and rural; the micro scale refers to human settlements where the three subunits of the core area, transition area and fringe area exist in a similar way within the same unit (as shown in Figure 1).
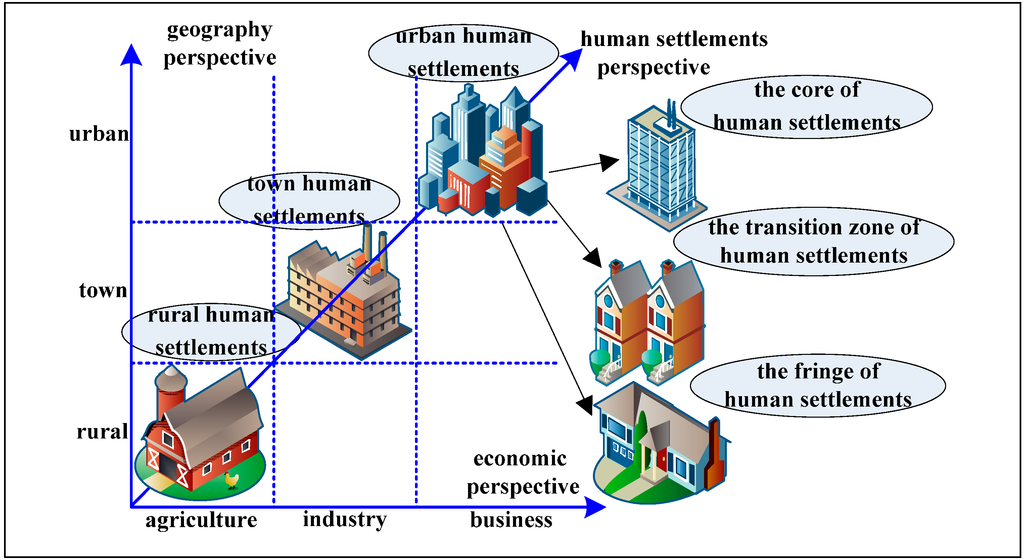
Figure 1.
The schematic diagram of the triaxiality of human settlements.
In this paper, we put forward the triaxiality of human settlements for the first time. We used the standards conversion entropy weight method and the SPSS (Statistical Product and Service Solutions) hierarchical clustering and dimensionality reduction factor analysis to measure and calculate degrees of livability for human settlements on the basis of the data of micro scales from 10 districts (counties) of Dalian (Years 2002–2011), so as to prove the existence of triaxiality of human settlements within the same unit at the micro-scale level and conducted an initial study on the spatial-temporal evolution characteristics, system attributes and formation mechanisms of the triaxiality of human settlements.
2. Date and Methods
The study area, Dalian, belongs to the Liaoning province, located at 121.2°E–121.7°E, 38.8°N–39.1°N, the area is 12,573.85 km2, and the population is about 5.903 million (2012). The data sources of the study area are the Liaoning Province Statistical Yearbook, Dalian Municipal Statistical Yearbook and the China City Statistical Yearbook, published between 2003 and 2012, the Dalian 2002–2011 Dalian Environmental Quality Communiqué and contemporary statistical yearbooks of various districts (counties) of Dalian, and the Statistical Communiqué of Dalian on National Economic and Social Development, etc. Parts of the historical data are mainly from the Dalian Archive, Dalian Real Estate Archive, Dalian Environmental Monitoring Center, Landscaping management office of Dalian Urban Construction Bureau and the Statistical Information Consultation Service Center of the Dalian Statistical Bureau.
We referenced the Evaluation index system of the prize of human settlements of China (Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China 2010), The science evaluation standard of livable city (Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China 2007) and national standards, in combination with the local laws and regulations of environmental protection, sewage with emissions of Liaoning province, and on the basis of predecessors’ research results [39,40]. We designed a set of layered index systems: these index systems proceeded from the basic concept of human settlements, and on the basis of emphasis on such five major systems as population, society, habitation, support, and environment. We designed in accordance with the diversity of study units of human settlements and the actual conditions of the division of districts (counties) in Dalian and we considered principles such as irreplaceability, feasibility, integrity and systematic coherence. We added the natural system, divided the properties of index in each system, and selected some of them which are typical to serve as the basic indexes for the evaluation system of triaxiality of human settlements in Dalian. These index systems are composed of six comprehensive index layers and 37 single indexes (Table 1).
Entropy is a physics-based concept that was introduced to information theory by Shannon. The entropy weight method [41,42] can overcome not only the subjectivity which may be produced using the Delphi method to determine weight, but also the repeatability of attributes incurred by too many indexes in the Complex Giant System, suitable for evaluation of objective data and pluralistic comprehensive indexes. However, when conducting evaluation on degrees of livability of human settlements using the entropy weight method, we often encounter some non-logical values that do not conform to the mathematical algorithm: (1) Forward indexes, 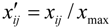 ; reverse indexes,
; reverse indexes, 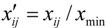 in the case of zero, whereby we could not continue operation; and (2) Natural logarithm, in the case that the index value in the matrix is negative, whereby we could neither calculate the specific weight directly nor take the logarithm. There are two main methods to improve the entropy value method: the efficiency coefficient method and the standardized transformation method. For the use of the efficiency coefficient method, it is required to add subjective ingredients, which cannot reflect objective results; the evaluation results of the standardized transformation method are not only objective but also unique. In this paper, we adopted the standardized transformation method for use in data processing. The specific procedures are as follows:
in the case of zero, whereby we could not continue operation; and (2) Natural logarithm, in the case that the index value in the matrix is negative, whereby we could neither calculate the specific weight directly nor take the logarithm. There are two main methods to improve the entropy value method: the efficiency coefficient method and the standardized transformation method. For the use of the efficiency coefficient method, it is required to add subjective ingredients, which cannot reflect objective results; the evaluation results of the standardized transformation method are not only objective but also unique. In this paper, we adopted the standardized transformation method for use in data processing. The specific procedures are as follows:
- (1)
- Original matrix: X = {xij}m×n (0 ≤ i ≤m,0 ≤ j ≤n), xij represents the index value of No. j index of No. i city (district and county).
- (2)
- Standardized processing of data:
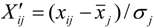 , where xj represents the average value of No. j index value, and σj represents the standard deviation of No. j index value.
, where xj represents the average value of No. j index value, and σj represents the standard deviation of No. j index value. - (3)
- Elimination of negative value:
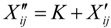 , K represents the scope of translation of axes.
, K represents the scope of translation of axes. - (4)
- Calculation of the weight of No. i city (prefecture and county) of No. j index:
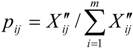 .
. - (5)
- Entropy value of index:
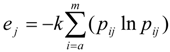 , k = 1/ln m, ej ∊[0,1].
, k = 1/ln m, ej ∊[0,1]. - (6)
- Differential coefficient: gj = 1 − ej.
- (7)
- Calculation of weight of No. j index.
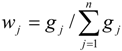
- (8)
- Calculation of degrees of livability of human settlements (Degrees of Livability):
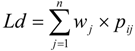 .
.

Table 1.
The evaluation index system of the triaxiality of human settlements.
| Comprehensive Index Layer | Single Index Layer |
|---|---|
| Natural system | mean temperature (°C); precipitation (mm); sunshine hours (t); average wind speed (m/s); average barometric pressure (HPa); windy days (day); extreme maximum temperature (°C); extreme minimum temperature (°C) ; frost-free season (day) |
| Population system | sex ratio (%); natural population growth rate (‰); aging rate (%); divorce rate (‰);The proportion of primary industry practitioners (%);The proportion of secondary and tertiary industry practitioners (%) |
| Social system | The registered urban unemployment rate (%);The proportion of the added value of primary industry (%);The proportion of the added value of secondary and tertiary industries (%);The per capita GDP (yuan);The proportion of science and technology spending (%); The proportion of education spending (%); The per capita total amount of social consumer goods (yuan); The average annual wage of staff and workers in urban (yuan) |
| Living system | The proportion of investment in real estate development (%); The proportion of investment in residential development (%); The population density of built-up area (People/km2) |
| Support system | Middle school teacher-student ratio; primary schoolteacher-student ratio; The number of hospitals (s); Ten thousand people have hospital beds (s); Ten thousand people with the doctor (s) |
| Environmental system | The mean of PM10 (mg/m3); The mean of SO2 (mg/m3); The mean of NO2 (mg/m3); The mean of natural dustfall (km2·30day); The frequency of acid rain (%); road traffic noise (dB); regional environmental noise (dB) |
3. Results and Discussion
According to the above evaluation index system, we used the standard conversion entropy weight method, SPSS hierarchical clustering and dimensionality reduction factor analysis to measure and calculate the degrees of livability of human settlements (Table 2).We used these methods to prove the existence of the triaxiality of human settlements within the same unit at the micro-scale level. We then conducted an empirical study of the spatial-temporal evolution characteristics and system attribute characteristics of the triaxiality of human settlements in 10 districts (counties) of Dalian (Years 2002–2011). Finally, we conducted a preliminary study on the formation mechanism of the triaxiality of human settlements.

Table 2.
Score and ranking of the livability degree of human settlements of the districts (counties) in Dalia.
| Year | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | |||||||
| Regional | score | rank | score | rank | score | rank | score | rank | score | rank | score | rank | |
| Zhongshan | 3.81 | 7 | 3.39 | 8 | 3.86 | 5 | 4.79 | 4 | 4.01 | 4 | 4.57 | 3 | |
| Xigang | 4.32 | 4 | 3.66 | 6 | 5.41 | 1 | 5.29 | 2 | 4.80 | 1 | 4.58 | 2 | |
| Shahekou | 4.62 | 2 | 4.36 | 2 | 4.04 | 4 | 4.86 | 3 | 4.41 | 2 | 5.25 | 1 | |
| Ganjingzi | 4.11 | 6 | 3.50 | 7 | 4.51 | 2 | 3.80 | 5 | 3.07 | 7 | 3.47 | 5 | |
| Lvshunkou | 4.63 | 1 | 4.34 | 3 | 3.53 | 7 | 3.12 | 8 | 2.78 | 9 | 2.70 | 8 | |
| Jinzhou | 4.39 | 3 | 3.80 | 5 | 3.35 | 8 | 3.15 | 7 | 2.88 | 8 | 3.23 | 6 | |
| Wanfangdian | 3.65 | 8 | 3.83 | 4 | 3.68 | 6 | 3.20 | 6 | 3.08 | 6 | 2.79 | 7 | |
| Pulandian | 3.51 | 9 | 2.98 | 9 | 2.92 | 9 | 2.16 | 9 | 2.30 | 10 | 1.62 | 10 | |
| Zhuanghe | 3.34 | 10 | 2.62 | 10 | 2.64 | 10 | 2.58 | 10 | 3.40 | 5 | 2.04 | 9 | |
| Changhai | 4.13 | 5 | 4.76 | 1 | 4.34 | 3 | 5.33 | 1 | 4.37 | 3 | 4.20 | 4 | |
| Year | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | Complex | ||||||||
| Regional | score | rank | score | rank | score | rank | score | rank | score | rank | |||
| Zhongshan | 4.76 | 2 | 5.34 | 1 | 3.93 | 3 | 5.16 | 1 | 4.36 | 3 | |||
| Xigang | 4.12 | 4 | 4.63 | 3 | 4.04 | 2 | 4.92 | 2 | 4.58 | 2 | |||
| Shahekou | 4.88 | 1 | 4.95 | 2 | 3.74 | 4 | 4.75 | 3 | 4.59 | 1 | |||
| Ganjingzi | 3.53 | 5 | 4.09 | 5 | 3.07 | 6 | 4.15 | 4 | 3.73 | 5 | |||
| Lvshunkou | 3.19 | 6 | 3.08 | 7 | 2.86 | 7 | 3.16 | 7 | 3.34 | 7 | |||
| Jinzhou | 3.11 | 7 | 3.19 | 6 | 4.46 | 1 | 3.64 | 6 | 3.52 | 6 | |||
| Wanfangdian | 2.70 | 9 | 2.70 | 8 | 2.40 | 8 | 2.46 | 9 | 3.05 | 8 | |||
| Pulandian | 2.76 | 8 | 2.66 | 9 | 1.95 | 9 | 2.43 | 10 | 2.53 | 10 | |||
| Zhuanghe | 2.12 | 10 | 2.24 | 10 | 1.93 | 10 | 2.49 | 8 | 2.54 | 9 | |||
| Changhai | 4.20 | 3 | 4.49 | 4 | 3.66 | 5 | 3.90 | 5 | 4.34 | 4 | |||
3.1. Triaxiality of Spatial Distribution of Human Settlements
We divided degrees of livability of urban human settlements into three units (Table 3): core area of urban human settlements (Levels 1 and 2), transitional area of urban human settlements (Levels 1 and 2), and fringe area of urban human settlements (Levels 1 and 2). We divided each unit into two levels in accordance with the numerical magnitude. We deemed as the main category all the individuals (variants) of the comprehensive score of degrees of livability of urban human settlements in 10 districts (counties) of Dalian (years 2002–2011).We used SPSS hierarchical clustering and conducted decomposition layer by layer in accordance with the principle of distance (square Euclidean distance) similarity until each entity engaged in clustering formed an independent categor.

Table 3.
The distribution of the triaxiality of human settlements of the districts (counties) in Dalian (2002–2011).
| Unit | Livable Fringe Area | Livable Transition Area | Livable core area | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level | Level 2 | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 1 |
| Standard | 1.17–2.25 | 2.25–2.88 | 2.88–3.52 | 3.52–4.15 | 4.15–4.78 | 4.78–5.41 |
| 2002 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 0 |
| 2003 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| 2004 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 2005 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 4 |
| 2006 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 2007 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 1 |
| 2008 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 2009 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 2010 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 0 |
| 2011 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
Spatial evolution of human settlements presents triaxiality; as a result, administrative divisions do not play a predominant role in the unit division of human settlements fully (as shown in Figure 2 and Table 3). The first unit is the core area of human settlements, mainly including the three districts (counties) of Zhongshan District, Xigang District and Shahekou District, with a range of degrees of livability for human settlements of 4.15–5.14, which has been stable for a long time, is relatively high and has relatively great disparity with other districts (counties); the second unit is the transition area of human settlements, mainly including the three districts (counties) of Changhai County, Ganjingzi District and Jinzhou District, with a range of livable degrees of human settlements of 2.88–4.15, which has small disparity with other districts (counties), but the overall degree of livability is relatively high. The third unit is the fringe area of human settlements, mainly including the four districts (counties) of Zhuanghe City, Pulandian City, Wafangdian City, and Lushunkou District. The range of degrees of livability of human settlements is 1.17–2.88, and the range still has a significant disparity with other districts (counties) which are located in the transition area and the core area of human settlements, as compared to a relatively large growth rate in 2002–2011.
The number of distribution districts (counties) within different units of human settlements tends to be balanced. As shown in Figure 3, between 2002 and 2006, the difference in the number of districts (counties) in the three units was relatively great. Here, we see the number of districts (counties) in the transition areas of human settlements presenting a trend of steady decrease; the number of districts (counties) in the fringe areas of human settlements presents a trend of increase in time and in the core area of human settlements it is relatively stable; between 2006 and 2011, the number of distribution districts (counties) within different units of human settlements presents a balanced trend on the whole in spite of fluctuations.
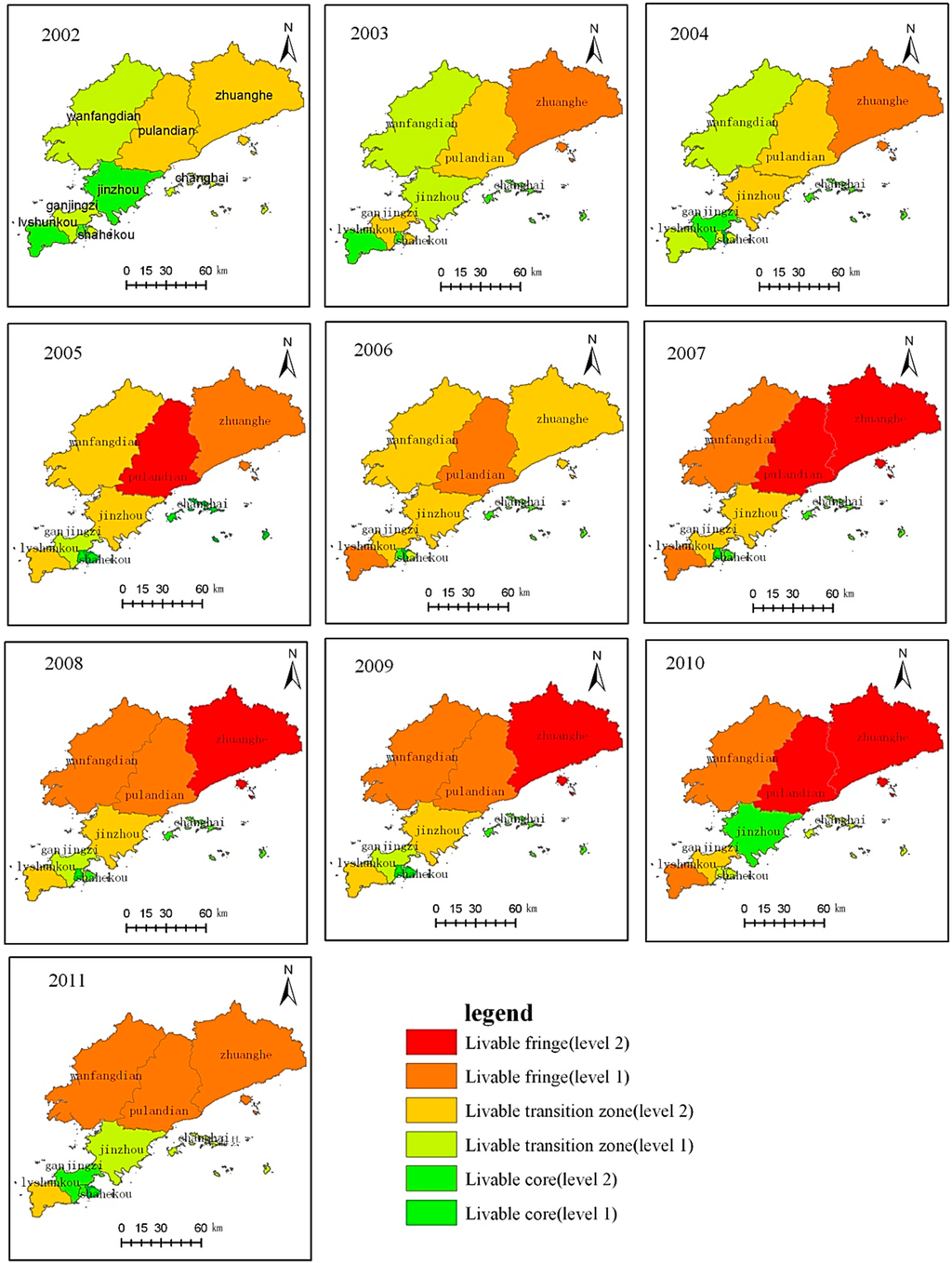
Figure 2.
The temporal evolution pattern of the triaxiality of human settlements.
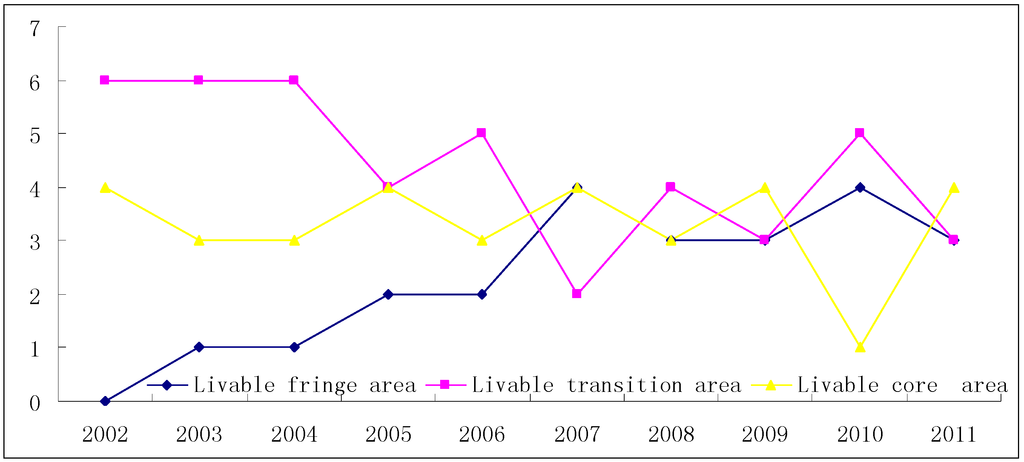
Figure 3.
The distribution of the districts (counties) of the triaxiality of human settlements in Dalian (2002–2011).
There is a spatial variation of tertiary units in human settlements of Dalian, and the transition area of human settlements occupies the leading position in unit division of human settlements, the core area of human settlements in the next place, with the fringe area of human settlements being the last. As shown in Table 3, there are 100 points in total on the time sequence of 10 years and space units of 10 districts (counties), where the core area of human settlements is 33 units, the transition area of human settlements is 44 units and fringe area of human settlements is 23 units.
3.2. Triaxiality of Time Evolution of Human Settlements
Triaxiality is presented at different development stages during the periodical evolution of human settlements. As shown in Figure 4, in the time sequence of 10 years, the outermost layer unit is composed of the four districts (counties) including Zhuanghe City, Pulandian City, Wafangdian City and Lvshunkou District .Together, these four districts have a rank of 7–10, which constitutes the fringe area of human settlements. The middle layer is composed of the three districts (counties) of Changhai County, Ganjingzi District and Jinzhou District, and their rank is 4–6, which constitutes the transition area of human settlements. The innermost layer unit is composed of the three districts (counties) of Zhongshan District, Xigang District and Shahekou District, with a ranking of 1–3, which is the core area of human settlements.
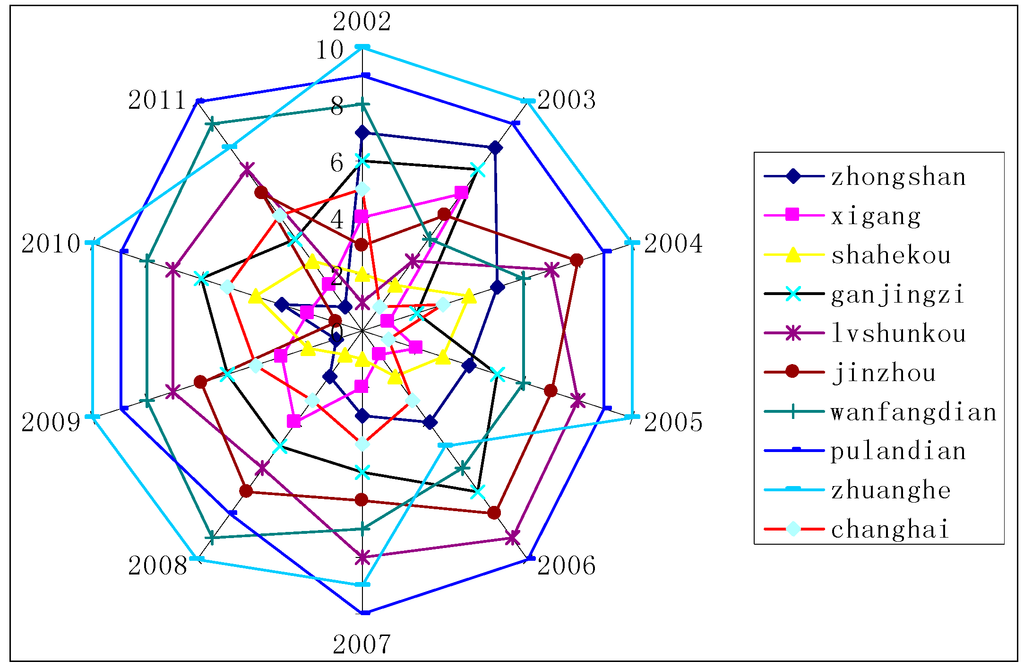
Figure 4.
The radar chart of the time evolution the triaxiality of human settlements in Dalia.
The fluctuation changes of degrees of livability of human settlements of Dalian within the past 10 years have been relatively stable, with a small-scale trend of decline. As shown in Figure 5, the fluctuation changes of degrees of livability of human settlements of Dalian within the past 10 years have not been great and have been relatively stable. The mean value of the degrees of livability decreased from a small scale of fluctuation of 4.05 in 2002 to 3.71 in 2011.
Human settlements demonstrate obvious stage differences. As shown in Figure 5, human settlements present two stages: the first stage (2002–2005): the numeral value of standard deviation is not large on the whole in spite of a trend of continuous increase, all distributed between 0.43 and 0.77. It indicates that the area differentiation of human settlements in 10 districts (counties) of Dalian at this stage is characterized by a rising trend year by year, but the change in area differentiation is not great. In the second stage (2005–2011), the standard deviation changes frequently fluctuating up and down significantly, and the overall numeral value was distributed between 0.85 and 1.13, indicating that the change in area differentiation of human settlements in 10 districts (counties) of Dalian at this stage was relatively great and the fluctuation change frequency relatively hig.
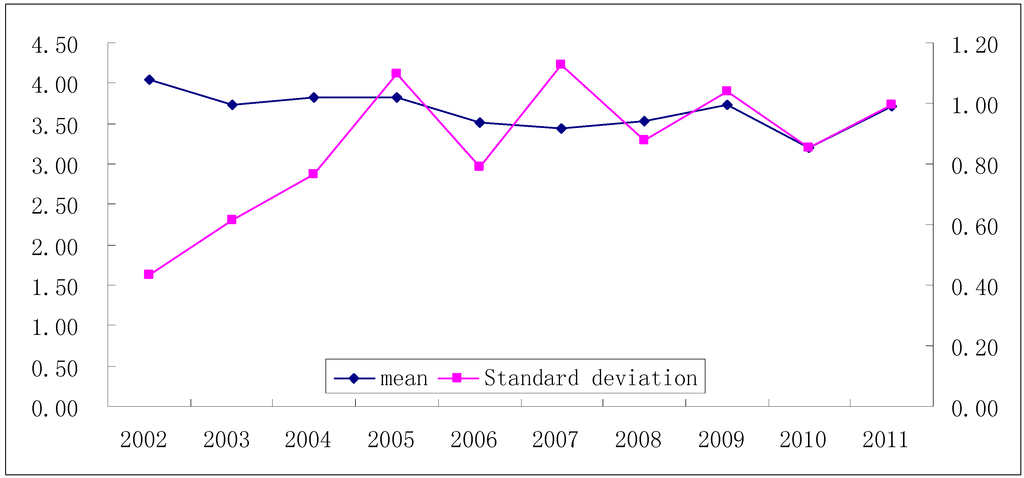
Figure 5.
The mean and standard deviation of the livability degree of human settlements in Dalian (2002–2011).
3.3. Triaxiality of System Attributes of Human Settlements
We conducted dimensionality reduction factor analysis using SPSS statistical analysis software, selecting the average value, standard deviation and number of effective values of each initial variable in the analysis for invariable descriptive statistics. We also selected correlation matrixes as coefficients and the significance levels and sphericity of KMO and Bartlett for inspection, extracting factors of which with a characteristic value greater than 1, and selecting the maximum convergence iteration for principal component analysis, and finally calculating the numeral value of the scores of the six systems. The calculation formula Equation (1) is as follows:
zF = w1 × FAC1_1+ w2 × FAC2_1+ w3 × FAC3_1+…wi × FACn_1
Where: zF represents the comprehensive score of each system, wi represents the variance devoting rate of common factors after rotation, and FACn_1 presents the score of the No. n factor.
The system attributive character of human settlements presents triaxiality. As shown in Figure 6, the overall attribute of the six systems of human settlements is represented in the characteristics of three units. The comprehensive score of six systems of human settlements in Zhongshan District, Xigang District, Shahekou District and Ganjingzi District, and the overall distribution is above the 0 value line (lateral axis) and is the first unit of human settlements (the core area); the comprehensive score of six systems of human settlements in Lushunkou District, Jinzhou District, Wafangdian City and Pulandian City is −0.35 to −1.87, and the overall distribution is below the 0 line and above the −2 line and is the second unit of human settlements (transition area); the comprehensive score of six systems of human settlements in Zhuanghe City and Changhai County is −2.15 to −2.97, and the overall distribution is below the −2 straight line and above the −3 line and is the third unit of human settlements (fringe area).
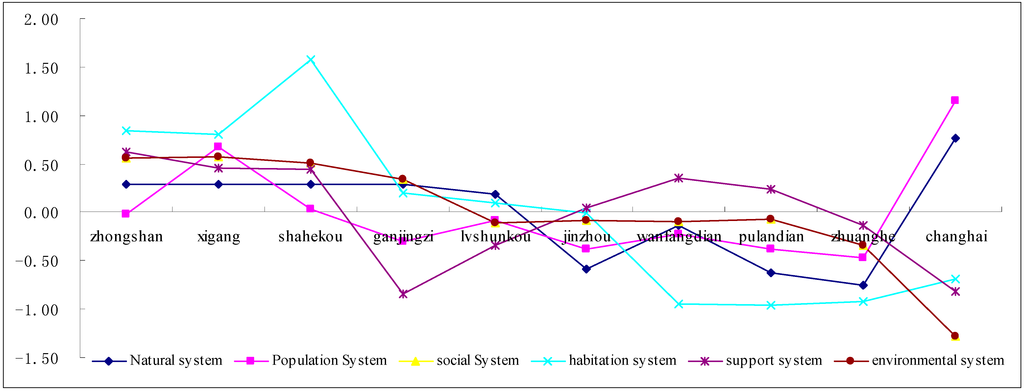
Figure 6.
The score of six systems of human settlements.
There also exists system and area differentiation in human settlements within the same unit: Firstly, there exists differentiation between different systems in the same unit. As shown in Figure 6, although Zhongshan District, Xigang District, and Shahekou District G all belong to the first unit (core area) of human settlements, the comprehensive score of the habitation system is 0.84–1.57, which is higher than that of the other systems. The population system score, which is far higher than that of the other systems, demonstrates relatively significant fluctuations. Secondly, the scores of different areas in the same system of the same unit also display differences. As shown in Figure 5, Zhuanghe City and Changhai County belong to the third unit (fringe area) of human settlements; the same population system, natural or environmental system, and support system all have obvious area differentiation. For instance, the score of the population system of Changhai County is 1.15, but the score of the population system of Zhuanghe City is −0.47, which indicates that the same population system has obvious area differentiation.
3.4. Formation Mechanism of Triaxiality of Human Settlements
The urban settlement pattern under the typical urban-rural dual structure is the residential quarter, and the rural settlement pattern is the village. The increasingly rapid pace of industrialization and urbanization has led to the collapse of part of the urban-rural dual structure, while all-around urbanization has not yet formed and is still in the transition period. The economic structure exists not only in new-type urban industry and modern agriculture, but also in town industry. Social population structures exist not only in typical urban populations and rural populations, but also among the “urban migrant workers” and “urban immigrants” in the process of “citizenization”. There also exists obvious differences in the living environments and life styles and the triaxial differentiation of economic structure, social structure, living environment and life style, which lead to the formulation of the triaxiality of human settlements (Figure 7).
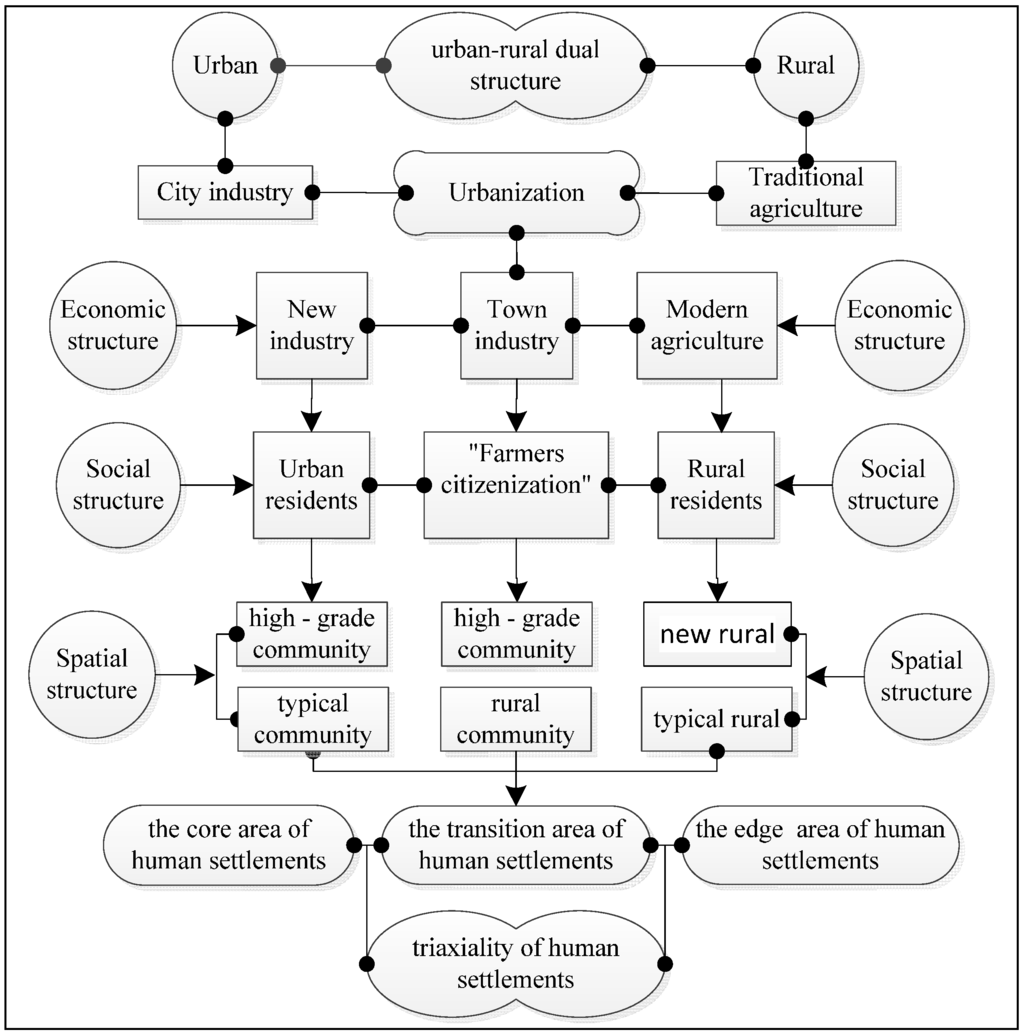
Figure 7.
The formation mechanism of triaxiality of human settlements.
Economic integration and urbanization are the fundamental driving forces for the formation of the triaxiality of human settlements. Economic integration has caused the rapid circulation and flow of people, material, information, funds and technology, resulting in the collapse of the urban and rural dual areal division of labor as viewed in the traditional sense and further challenged by the continuous enhancement of inter-zone linkage and cooperation. Urbanization has caused the differentiation of population, industry and habitation, and a situation where the two forms of urban and rural populations have been broken. The “transition area” and “urban fringe area” led by suburbanization and semi-urbanization, has gradually formed. Therefore, the triaxial settlement structure including the core area of human settlements, transition area of human settlements and fringe area of human settlements, with the urban, transition area (town) and rural as the spatial containers, has appeared.
Technology led by “Internet”, “architectural planning” and “urban transportation” is the booster for the formation of the triaxiality of human settlements. Weakening space attributes of the workplace and residence, widening consumption channels and changing work and life styles—resulting in a decrease in the rate of dependency of populations on the “urban area”—have led to the appearance of human settlements in transition areas and triaxiality of human settlements on the basis of traditional urban and rural dual human settlements.
Macro-control by the government led by rules and regulations and administrative divisions is the premise and guarantee for the formation of triaxiality of human settlements. Housing system reform has broken the “unification in unit” of the traditional habitation pattern. As a matter of fact, the household registration system reform has weakened the limit between the population structures of “resident” and “peasant”; land system reform has caused the “back three binary” industrial structure in the urban core area and the adjustment of administrative divisions has provided golden opportunity especially for development of urban fringe areas. All these factors provide system guarantees for the formation of triaxialit.
4. Conclusions
In this study, on the basis of the study of human settlements of urban, transition areas (town) and rural units, we put forward the triaxiality of human settlements, and used the standard conversion entropy weight method and the SPSS hierarchical clustering and dimensionality reduction factor analysis to measure and calculate degrees of livability for human settlements, so as to prove the existence of the triaxiality of human settlements within the same unit at the micro-scale level. Furthermore, we conducted an empirical study on spatial-temporal evolution, system attributes and formation mechanisms of triaxiality of human settlements in 10 districts (counties) of Dalian (Years 2002–2011).
Results showed that: spatial evolution of human settlements presents triaxiality. Administrative divisions do not play a full or predominant role in the unit division of human settlements and degrees of livability; the number of distribution districts (counties) within different units of human settlements tends to be balanced; there is spatial variation of tertiary units in degrees of livability of human settlements in Dalian; and the core area of human settlements does not occupy the leading position in unit division of human settlements.
Human settlements also exhibit triaxiality at different development stages during the evolution period of human settlements: the fluctuation changes of livable degrees of human settlements of Dalian within the past 10 years have been relatively stable, with a small scale trend of decline and obvious manifestations of stage differences.
The system attributive character of human settlements presents triaxiality. There also exists system and area differentiation in human settlements within the same unit: there exists differentiation between different systems in the same unit, and the scores of different areas in the same system of the same unit also are different. Industrialization and urbanization have led to the collapse of part of the urban-rural dual structure, and there exists differences in economic structure, social structure, living environment and life style, and the differentiation of ternary structure leads to the triaxiality of human settlements. In this study, we used the standard conversion entropy weight method and the SPSS hierarchical clustering and dimensionality reduction factor analysis to prove the existence of the triaxiality of human settlements within the same unit at the micro-scale level, as well as conducted an empirical study on the spatial-temporal evolution, system attributes and formation mechanisms of the triaxiality of human settlements in 10 districts (counties) of Dalian (Years 2002–2011). We conducted a preliminary study on triaxiality of human settlements systematically, and the research direction and thinking may be used for reference by relevant studies on urban human settlements, but more extensive and thorough research is required: (1) In this paper, we only analyzed the existence of triaxiality of human settlements of the core area, transition area and fringe area within the same unit (urban) at the micro-scale level; therefore, further comprehensive study on human settlements of the three units of urban, town and rural at the macro-scale level is still required; (2) In this paper, we only preliminarily analyzed the formation mechanisms of human settlements from dual to triaxial, so a thorough analysis on the formation mechanisms from triaxial to multivariate or even the disintegration of the unit into an all-around town (urban) is required; (3) In addition, the vagueness and complexity of “urban boundary” and “unit gradient” still remain as a major obstacle against the further understanding of triaxiality of human settlements.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by foundation items: The study of urban mimicry human settlements—in the case of Dalian (No. 41171137); The study of urban environmental justice issues of human settlements perspective—in the case of Dalian (No. 20132136110001); The program support excellent talents in Liaoning Province (No. 901214). The authors have no conflicts of interest related to this manuscrip.
Author Contributions
All authors were involved in the foundation items. All authors read and approved the final manuscrip.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interes.
References
- Howard, E. Garden Cities of Tomorrow; The Commercial Press: Beijing, China, 2002; pp. 17–18. [Google Scholar]
- Geddes, P. Cities in Evolution: An Introduction to the Town Planning Movement and to the Study of Civics; China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2012; pp. 91–119. [Google Scholar]
- Mumford, L. The City in History: Its Origins, Its Transformations and Its Prospects; China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 1989; pp. 356–378. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.Y. Introduction to Sciences of Human Settlements; China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2001; pp. 7–19. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.Y. Introduction to Sciences of Human Settlements; China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2001; pp. 97–112. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.Z.; Chen, L.; Yang, Y.Z. Research progress on human settlement evolution. Prog. Geog. 2013, 32, 710–721. [Google Scholar]
- McGranahan, G.; Balk, D.; Anderson, B. The rising tide: Assessing the risks of climate change and human settlements in low elevation coastal zones. Environ. Urban. 2007, 19, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornstein, L.; Lizarralde, G.; Gould, K.A.; Davidson, C. Framing responses to post-earthquake Haiti: How representations of disasters, reconstruction and human settlements shape resilience. Int. J. Disaster Resil. Built Environ. 2013, 4, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, W.J. On the Rank—Size Distribution for Human Settlements. J. Region. Sci. 2002, 42, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzounis, G.K.; Syrris, V.; Pesaresi, M. Multiscale quality assessment of Global Human Settlement Layer scenes against reference data using statistical learning. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 2013, 34, 1636–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magadza, C. Climate change impacts and human settlements in Africa: Prospects for adaptation. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2000, 61, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, S.; Ewing, R. A longitudinal study of changes in urban sprawl between 2000 and 2010 in the United States. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 128, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, W.R.; Medeiros, J.F.; Julião, G.R.; Ríos-Velásquez, C.M.; Marialva, E.F.; Desmouliére, S.J.; Pessoa, F.A.C. Anthropic effects on sand fly (Diptera: Psychodidae) abundance and diversity in an Amazonian rural settlement, Brazil. Acta Trop. 2014, 139, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, R.T. Exploring counter-conduct in upgraded informal settlements: The case of women residents in Makhaza and New Rest (Cape Town), South Africa. Habitat Inter. 2014, 44, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.M.; Xia, C.G.; Zhang, Y.J. Chinese Human Settlement research with Geography Perspective in recent 10 Years. Urban Dev. Stud. 2014, 21, 6–13. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, Y.G.; Xia, B. Study on difference in satisfaction on level on Human Settlements by different social stratums in Guang Zhou. China City Plan. Rev. 2013, 37, 40–44. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.M.; Jin, P.Y. Characteristics and Spatial-temporal Differences of Urban Human Settlement Environment in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2012, 32, 521–529. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.M.; Zhang, J.L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, L. Analysis of the attraction field of urban human settlements: A case study of Dalian. Geogr. Res. 2012, 31, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.P. Evaluation of urban human settlements livability—A case of comparison and analysis on China’s four municipalities. Econ. Geogr. 2010, 30, 1992–1997. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, H.M.; Ren, Z.Y. Evaluation of Nature Suitability for Human Settlement in Shanxi Province Based on Grid Data. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2009, 64, 498–506. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.M.; Tian, S.Z.; Yang, J.; Zhang, F.; Kong, F.Q. The preliminary study of mismatch degree of urban human settlements: Taking 14 cities in Liaoning Province as cases. Geogr. Res. 2014, 33, 687–697. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.M.; Tian, S.Z.; Zhang, F.; Yang, J.; Zhang, C.H. The evaluation of human settlements of urban special functional area scale: Taking 10 universities in Dalian as cases. Urban Probl. 2014, 2, 24–30. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, W.M. Information Theory for Human Settlements Research and Its Info-spectrum Images System. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2012, 67, 253–265. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Y.; Zeng, G.M.; Dong, L.S. Quantitative Evaluation of the Uncertainties in the Coordinated Development of Urban Human Settlement Environment and Economy: Taking Changsha City as an Example. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2007, 62, 397–406. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, N.; Cui, S.H.; Liu, Q.M.; Wen, C.; Chen, X.M. Study on the Characteristics of Community Human Settlements in Peri-urban Area during Urbanization: A Case of Jimei District, Xiamen City. Prog. Geogr. 2012, 31, 750–760. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.H.; Liu, P.L.; Dou, Y.D. Evolution characteristic and micro mechanism of rural human settlement in underdeveloped areas during the transition—A Case Study of Er-Cheng. Hum. Geogr. 2012, 27, 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, X.H.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhu, Y. The evolvement rules of human settlements system on metropolis fringe: A case study of Guangzhou. Geogr. Res. 2008, 27, 421–430. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.Z.; Wang, Q. Evaluation of rural human settlement quality difference and its driving factors in tourism area of southern Anhui Province. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2013, 68, 851–867. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.H.; Liu, C.M.; Zeng, J.X. An evaluation on the satisfaction degree and optimization strategy of rural human settlements—A Case Study of Jiuheyuan Town in Shishou City. Hum. Geogr. 2009, 24, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.H.; Zeng, J.X.; Hu, J. Progress and Prospects on the Research of Rural Human Settlement Environment. Geogr. Geo-Inform. Sci. 2008, 24, 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.H.; Zeng, J.X. Research on Rural Human Settlement Environment Based on the Changes of the Householders’ Spatial Behaviors. Geogr. Geo-Inform. Sci. 2009, 25, 84–88. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.J.; Zeng, J.X. Study on the longevity phenomena and human settlements in rural China: Taking Zhong xiang city as an example. Geogr. Res. 2008, 27, 421–430. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.L.; Liao, L.W.; Liu, C.L. Urban residential amenity index and its composition factors: The case of Changsha County in Hunan Province. Prog. Geogr. 2013, 32, 769–776. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Cheng, J.P.; Zhong, S.Y.; Li, Y. Empirical research of urban human settlement environment elements based on the needs of different subjects: A case study of Xintang Town, Guangzhou. Geogr. Res. 2013, 32, 307–316. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.H.; Sheng, S.H.; Bai, X.H. China’s ternary social structure and the integrative development of countryside and city. Economist 2003, 6, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.Y. The ternary is the philosophical foundation of the human settlements. Planners 1999, 15, 99–102. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.Y.; Hu, B.L. China’s ternary economic structure and the surplus labor migration of agriculture. Econ. Res. J. 1994, 4, 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.Q. The discussion of Ternary structure of China’s economy. Soc. Sci. China 1991, 3, 65–82. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.Z. Study on Intrinsic Meanings of the Livable City and the Evaluation System of Livable City. Urban Plan. Forum 2007, 3, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, E.X.; Luo, Y.M. The science evaluation standard of Livable city. Beijing Plan. Rev. 2007, 1, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.M.; Xia, B. Analysis of sustainable development ability of the urban ecosystem in Guangzhou City in the perspective of entropy. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2013, 68, 45–57. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.X.; Ma, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, Y. Dynamic evolution mode of regional dominance indexes of Chinese in bound tourism flows during 1993 to 2008: An empirical research based on modified entropy technology. Geogr. Res. 2012, 31, 257–268. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).