Sustainable Complex Triangular Cells for the Evaluation of CO2 Emissions by Individuals instead of Nations in a Scenario for 2030
Abstract
:1. Introduction
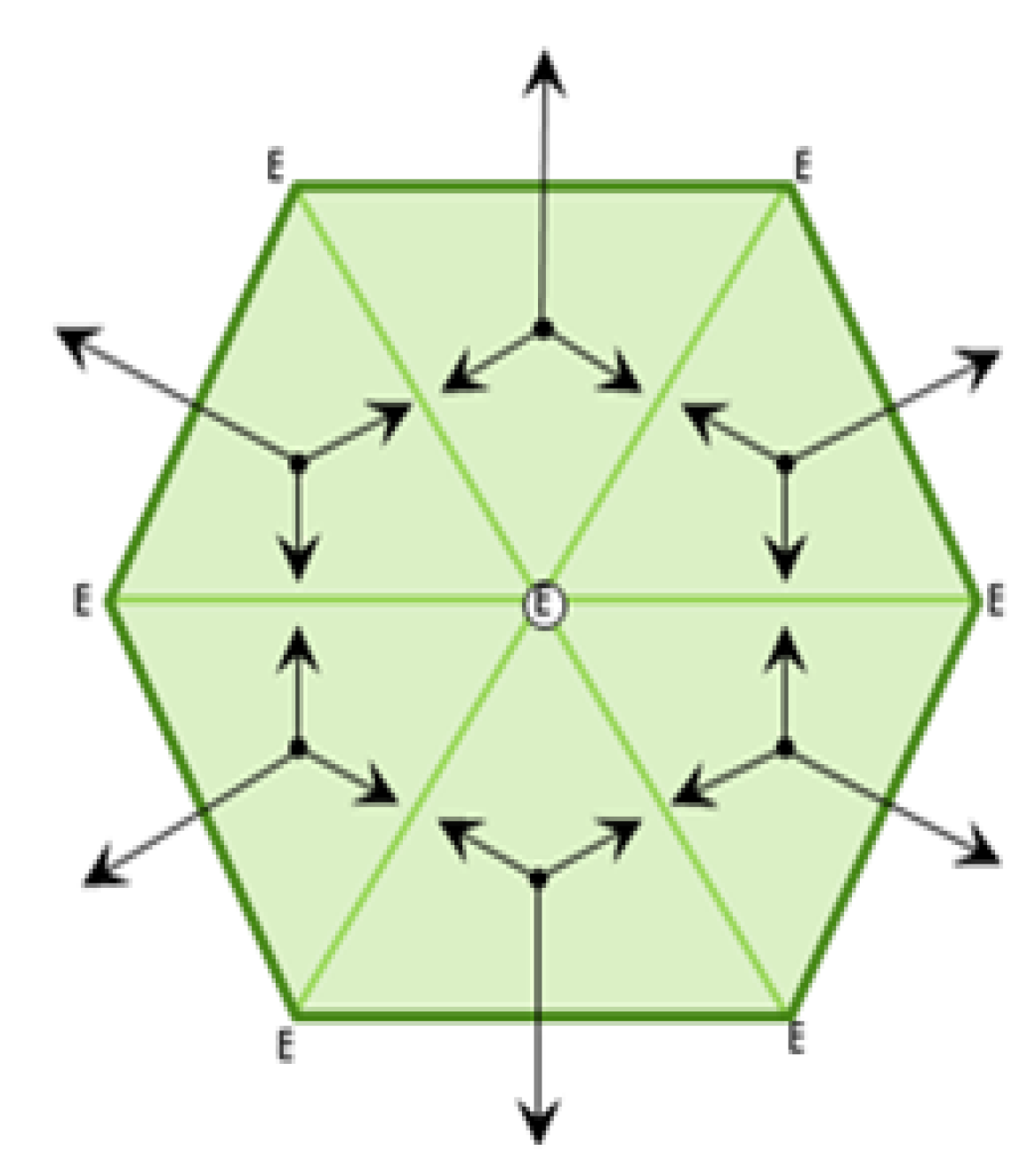
2. Sustainable Complex Triangular Cells: A Three-Dimensional View
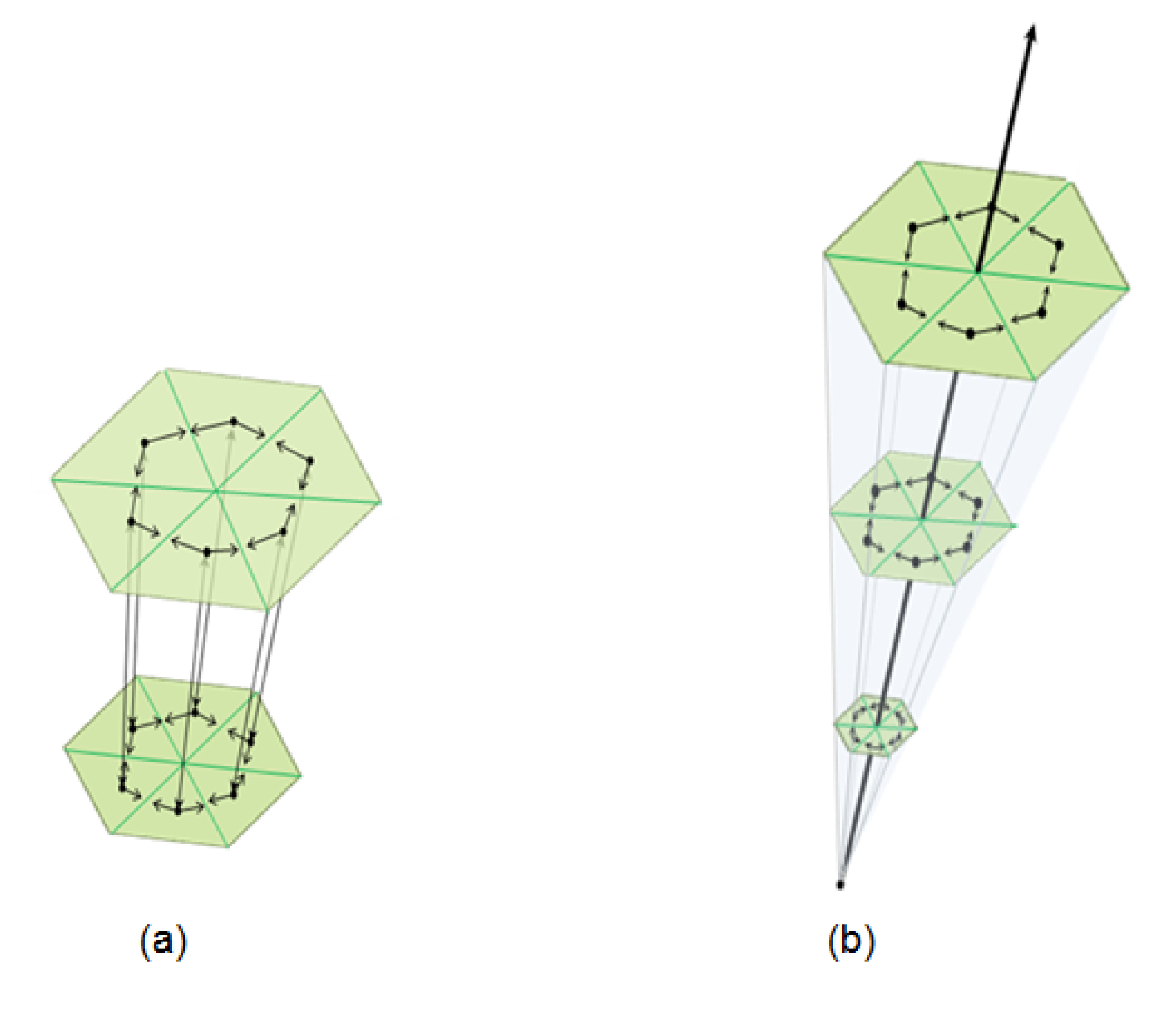
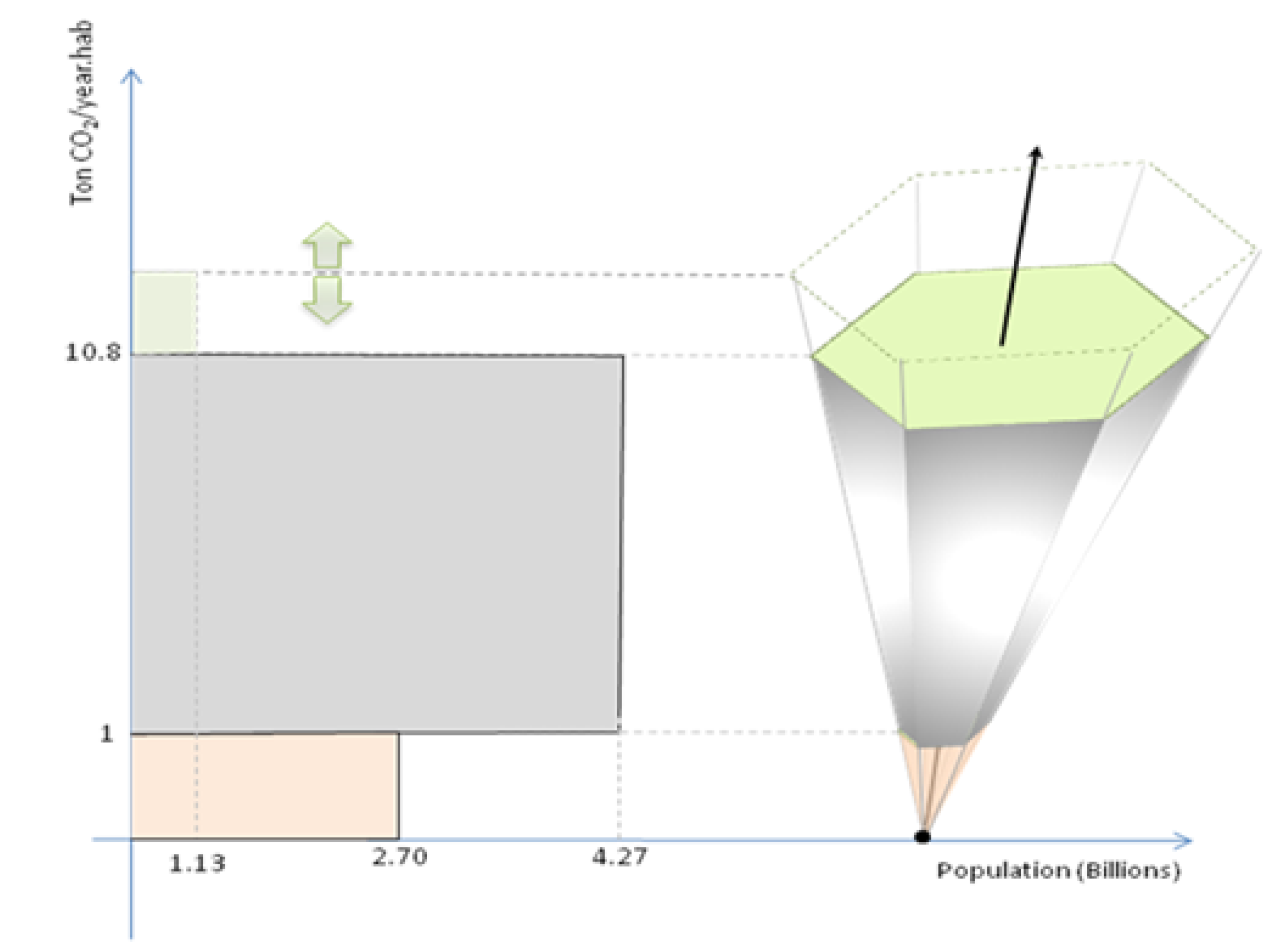
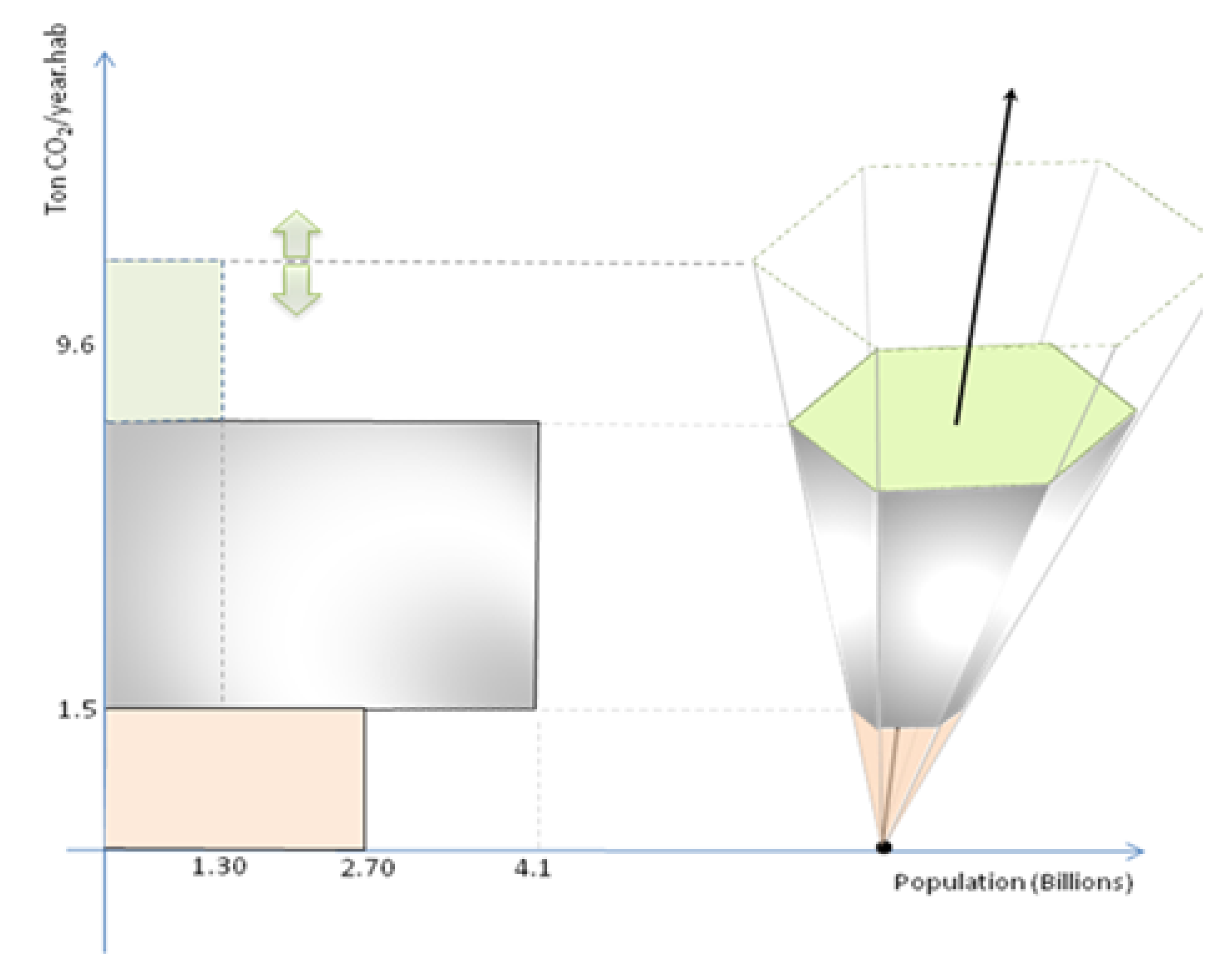
3. Three-Dimensional Model Applied to Chakavraty et al. Scenarios for CO2 Emission until 2030
4. Human Cooperation: Regular Hexagonal Pyramid
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Hansen, J.; Sato, M.; Ruedy, R. Percetion of climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E2415–E2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, R.A. Soot is Warming the World Even More Than Thought. Science 2013, 339, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matonse, A.H.; Pierson, D.C.; Frei, A.; Zion, M.S.; Anandhi, A.; Schneiderman, E.; Wright, B. Investigating the Impact f Climate Change on New York City’s Primary Water. Clim. Chang. 2013, 116, 437–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, T.M. The Closing Door of Climate Targets. Science 2013, 339, 280–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randerson, J.T. Global Warning and Tropical Carbon. Nature 2013, 494, 319–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J. Predicting Climate Change Effects on Agriculture from Ecological Niche Modeling: Who Profits, Who Loses? Clim. Chang. 2013, 116, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, P.M.; Pearson, D.; Booth, B.B.; Friedlingstein, P.; Huntingford, C.; Jones, C.D.; Luke, C.M. Sensitivity of Tropical Carbon to Climate Change Constrained by Carbon Dioxide Variability. Nature 2013, 494, 341–344. [Google Scholar]
- Hambly, D.; Andrey, J.; Mills, B.; Fletcher, C. Projected Implications of Climate Change for Road Safety in Greater Vancouver, Canada. Clim. Chang. 2013, 116, 613–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.; Plattner, G.; Knutti, R.; Friedlingstein, P. Irreversible climate change due to carbon dioxide emissions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1704–1709. [Google Scholar]
- Meinshausen, M.; Meinshausen, N.; Hare, W.; Raper, S.C.B.; Frieler, K.; Knutti, R.; Frame, D.J.; Allen, M.R. Greenhouse-gas emissions targets for limiting global warning to 2 °C. Nature 2009, 458, 1158–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myles, R.; Frame, D.J.; Huntingford, C.; Jones, C.D.; Lowe, J.A.; Meinshausen, M.; Meinshausen, N. Warning Caused by Cumulative Carbon Emissions Towards the Trillionth Tonne. Nature 2009, 458, 1163–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.; Sato, M.; Kharecha, P.; Beerling, D.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Pagani, M.; Raymo, M.; Royer, D.L.; Zachos, J.C. Target atmosphere CO2: Where Should Humanity Aim. Open Atmos. Sci. J. 2008, 2, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Moore, B.; Karl, T.R.; Nobre, C. Monitoring and Prediction of The Earth’s Climate: A Future Perspective. J. Climate 2006, 19, 5001–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.; Sato, M. Greenhouse gas growth rates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 16109–16114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.; Nazarenko, L. Soot Climate Forcing via snow and ice Albedos. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.; Nazarenko, L.; Ruedy, R.; Sato, M.; Willis, J.; Del Genio, A.; Koch, D.; Lacis, A.; Lo, K.; Menon, S. Earth’s Energy Imbalance: Confirmation and implications. Science 2005, 308, 1431–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, M.E.; Bradley, R.S.; Hughest, M.K. Global temperature patterns and climate forcing over the past six centuries. Nature 1998, 392, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockstrom, J.; Steffen, W.; Noone, K.; Persson, A.; Chapin, F.S.; Lambin, E.F.; Lenton, T.M.; Scheffer, M.; Folke, C.; Schellnhuber, H.J.; et al. A Safe Operating Space for Humanity. Nature 2009, 461, 72–475. [Google Scholar]
- Flynn, K.; Blackford, J.C.; Baird, M.E.; Raven, J.A.; Clark, D.R.; Beardall, J.; Brownlee, C.; Fabian, H.; Wheeler, G.L. Changes in pH at the exterior surface of plankton with ocean acidification. Nat. Clim. Change 2012, 2, 510–513. [Google Scholar]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Shea, D.J. Atlantic hurricanes and natural variability in 2005. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Nathan, P.; Gillett, N.P.; Stone, D.A.; Stott, P.A.; Nozawa, T.; Karpechko, A.Y.; Heger, G.C.; Wehner, M.F.; Jones, F.D. Attribution of polar warming to human influence. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 750–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddall, M.; Stocker, T.F.; Clark, P.U. Constrains on future sea-level from past sea-level change. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, B.D.; Wiglet, T.M.L.; Glecker, P.J.; Bonfils, C.; Wehner, M.F.; AchutaRao, K.; Barnett, T.P.; Boyle, J.S.; Brüggeman, W.; Fiorino, M.; et al. Forced and unforced ocean temperature changes in Atlantic and Pacific tropical cyclogenesis regions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13905–13910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuel, K. Increasing destructiveness of tropical cyclones over the past 30 years. Nature 2005, 436, 686–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peza, A.B.; Simmonds, I. The first South Atlantic hurricane: Unprecedented blocking, how shear and climate change. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, 5712–5717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, M. Use of complex adaptive systems for modeling global Change. Ecosystems 1998, 1, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurz, W.A.; Dymond, C.C.; Stinson, G.; Rampley, G.J.; Neilson, E.T.; Carroll, A.L.; Ebata, T.; Safranyik, L. Mountain pine beetle and forest carbon feedback to climate change. Nature 2008, 452, 987–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenoir, J.; Gégout, J.C.; Marquet, P.A.; Ruffray, P.; Brisse, H. A significant upward shift in plant species optimum elevation during the 20th century. Science 2008, 320, 1768–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, C.; Karoly, D.; Vicarelli, M.; Neofotis, P.; Wu, Q.; Casassa, G.; Menzel, A.; Root, T.L.; Estrella, N.; Seguin, B.; et al. Attributing physical and biological impacts to anthropogenic climate change. Nature 2008, 453, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC, Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis; Report of Working Group I; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007.
- IPCC, Climate Change 2007: Mitigation of Climate Change; Report of Working Group III; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007.
- Chakravarty, S.; Chikka, A.; Coninck, H.; Pacala, S.; Socolow, R.; Tavoni, M. Sharing global CO2 emission reductions among one billion high emitters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 11884–11888. [Google Scholar]
- WWF. Living Planet Report. Available online: http://awsassets.panda.org/downloads/living_planet_report.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2012).
- Sthel, M.S.; Tostes, J.G.R. Sustainable Complex Triangular Cells: Case Study—Envira River Isolated Indians in Western Amazon. J. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 5, 92–104. [Google Scholar]
- Sthel, M.S.; Tostes, J.G.R.; Tavares, J.R. Current energy crisis and its economic and environmental consequences: intense human cooperation. Nat. Sci. 2013, 5, 244–252. [Google Scholar]
- Rifkin, J. The Empathic Civilization: The Race to Global Consciousness in a World in Crisis; Penguin: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rifkin, J. The Third Industrial Revolution: How Lateral Power Is Transforming Energy, the Economy, and the World; Palgrave Macmillan: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Parrish, J.K.; Edelstein-Keshet, L. Complexity, Pattern, and Evolutionary Trade-Offs in Animal Aggregation. Science 1999, 284, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, E. A general framework for analyzing sustainability of social-ecological systems. Science 2009, 325, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P. Collective intelligence. Nat. Geosci. 2007, 88, 40–57. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, G. All Together Now-Pull. Science 2007, 317, 1338–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.; Lauder, H. Collective Intelligence. In Social Capital: Critical Perspectives; Baron, S., Field, J., Schuller, T., Eds.; University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Sunstein, C. Infotopia: How Many Minds Produce Knowledge; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bak, P. How Nature Works: The Science of Self-Organized Criticality; Copernicus Books: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, K.; Barton, M.; Hurtado, A.M. The Emergence of Human Uniqueness: Characters Underlying Behavioral Modernity. Evol. Anthropol. 2009, 18, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sear, R.; Marlowe, F.W. How universal are human mate choices? Size does not matter when Hadza foragers are choosing a mate. Biol. Lett. 2009, 5, 606–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlowe, F.W. What Explains Hadza Food Sharing. Res. Eco. Anthr. 2004, 23, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, R. Paleoclimate and Human Evolution. Evol. Anthropol. 2007, 16, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menocal, P.B. Climate and Human Evolution. Science 2011, 331, 540–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.R.; Stringer, C.B. Human Evolution out of Africa: The Role of Refugia and Climate Change. Science 2012, 335, 1317–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerling, T.E.; Wynn, J.G.; Andanje, S.A.; Bird, M.I.; Korir, D.K.; Levin, N.E.; Mace, W.; Macharia, A.N.; Quade, J.; Remien, C.H. Woody Cover and Hominin Environments in the past 6 Million years. Nature 2011, 476, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmesan, C.; Matthews, J. Biological Impacts of Climate Change. Available online: http://www.sinauer.com/groom-demo/pdfs/GroomChapter10.pdf (accessed on 2 November 2012).
- Eriksson, A.; Friend, A.D.; Lycett, S.J.; Singarayer, J.S.; Cramon-Taubadel, N.; Valdes, P.J.; Balloux, F.; Manica, A. Late Pleistocene Climate Change and the Global Expansion of Anatomically Moders Humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16089–16094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, S.C. Climatic Influences on the Evolution of Early Homo? Folia Primatol. 2007, 78, 365–388. [Google Scholar]
- Anton, S.C. Natural History of Homo Erectus. Yearbk. Phys. Anthropol. 2003, 46, 126–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menocal, P.B. African Climate Change and Faunal Evolution During the Pliocene-Pleistocene. Earth Plan. Sci. Lett. 2004, 220, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magill, C.R.; Ashley, G.M.; Freeman, K.H. Water, plants, and early human habitats in eastern Africa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magill, C.R.; Ashley, G.M.; Freeman, K.H. Ecosystem variability and early human habitats in eastern Africa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swedell, L.; Plummer, T. A Papionin Multilevel Society as a Model for Hominin Social Evolution. Int. J. Primatol. 2012, 33, 1165–1193. [Google Scholar]
- Tipple, B.J. Capturing Climate Variability during our Ancestors Earliest Day. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawks, J. Population Bottlenecks and Pleistocene Human Evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teaford, M.F.; Ungar, P.S. Diet and Evolution of the Earliest Human Ancestors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 13506–13511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, W.R.; Robertson, M.L. On Diet, Energy Metabolism, and Brain Size in Human Evolutio. Curr. Anthr. 1996, 37, 125–129. [Google Scholar]
- Ambrose, S.H. Did the Super-Eruption of Toba Cause Bottleneck? Reply to Gathorne-Hardy and Harcourt-Smith. J. Hum. Evol. 2003, 45, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.A.J. Environmental Impact of the Toba super-Eruption in South Asia. Paleo 2009, 284, 295–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampino, M.; Ambrose, S.H. Volcanic Winter in the Garden of Eden: The Toba Supereruption and Late Pleistocene Human Crash. Available online: http://specialpapers.gsapubs.org/content/345/71.full.pdf+html (accessed on 3 November 2012).
- Ambrose, S.H. Late Pleistocene Human Population Bottlenecks, Volcanic Winter and Differentiation of Modern Humans. J. Hum. Evol. 1998, 34, 623–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behar, D.M. The Dawn of Human Matrilineal Diversity. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 82, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luca, F.; Hudson, R.R.; Witonsky, D.B.; Di Rienzo, A. A Reduced Representation Approach to Population Genetic Analyses and Applications to human Evolution. Genome. Res. 2011, 21, 1087–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, S.S. Last of the Neanderthals. National Geographic 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, S.L.; Stiner, M.C. What’s a Mather to Do? The Division of Labor among Neandertals and Modern Humans in Eurasia. Curr. Anthropol. 2006, 47, 953–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, W.R. Food for thought dietary change was a driving force in human evolution. Scientific American 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Silk, J.B. Social Components of Fitness in Primate Groups. Science 2007, 317, 1347–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, A. The Social Origin of Mind. Science 2007, 317, 1326–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunbar, R.I.M.; Shultz, S. Evolution in the Social Brain. Science 2007, 317, 1344–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, J.; Davidson, B.J. Cell- Gazing Into the future: What Genes, Homo heidelbergensis and Punishment tell Us about Our Adaptive Capacity. Sustainability 2013, 5, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, R.; Richerson, P.J. Culture and the Evolution of Human Cooperation. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2009, 364, 3281–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehr, E.; Gachter, S. Altruistic Punishment in Humans. Nature 2002, 415, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrich, J. Cultural Group Selection Coevolutionary Processes and Large-Scale Cooperation. J. Econ. Behav. 2004, 53, 3–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennisi, E. On the Origin of Cooperation. Science 2009, 325, 1196–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaesen, K. Cooperative Feeding and Breeding and the Evolution of Executive Control. Biol. Philos. 2012, 27, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcloone, B. Collaboration and Human Social Evolution: Review of Michael tomasello’s Why we Cooperate. Biol. Philos. 2012, 27, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, S. Foundations of Social Evolution; Princeton Universty Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Burkart, J.M.; Hardy, S.B.; Schaik, C.P.V. Cooperative Breeding and Human Cognitive Evolution. Evol. Anthropol. 2009, 18, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmuller, R.; Johnstone, R.; Russel, A.F.; Bsharya, R. Integrating Cooperative Breeding into Theoretical Concepts of Cooperation. Behav. Proc. 2007, 76, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, S.; Gintis, H. A Cooperative Species: Human Reciprocity and its Evolution; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- De Waal, F.B.M. Putting the Altruism back into Altruism: The Evolution of Empathy. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2008, 59, 279–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, E.O. The Social Conquest of Earth; Liveright: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fowlen, J.H. Life interwoven. Nature 2012, 484. [Google Scholar]
- Upson, S.; Kuchment, A. Recommended: The Social Conquest of Earth. Available online: http://www.scientificamerican.com/article.cfm?id=recommended-apr-12 (accessed on 5 November 2012).
- Costa, R. Power of generosity. ISTOÉ independente. 2012, 2218, 80–86. Available online: http://www.istoe.com.br/reportagens/205685_O+PODER+DA+GENEROSIDADE (accessed on 5 November 2012). [Google Scholar]
- Angier, N.; Edward, O. Wilson’s New Take on Human Nature. Smithsonian magazine 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nowak, M.A. Five Rules for the Evolution of Cooperation. Science 2006, 314, 1560–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, M.A. Evolving Cooperation. J. Theor. Biol. 2012, 299, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, M.A.; Tarnita, C.E.; Wilson, E.O. The evolution of eusociality. Nature 2010, 466, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar]
- Tarnita, C.E.; Taubes, C.H.; Nowak, M.A. Evolutionary construction by staying together and coming together. J. Theor. Biol. 2013, 320, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veelen, M.; et al. Direct Reciprocity in Structured Populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9929–9934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, M.A. Why We Help: The Evolution of Cooperation. Scientific American 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Casti, J. X-Events—The Collapse of Everything; HarperCollins Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Sthel, M.; Tostes, J.G.; Tavares, J. Sustainable Complex Triangular Cells for the Evaluation of CO2 Emissions by Individuals instead of Nations in a Scenario for 2030. Sustainability 2013, 5, 1944-1959. https://doi.org/10.3390/su5051944
Sthel M, Tostes JG, Tavares J. Sustainable Complex Triangular Cells for the Evaluation of CO2 Emissions by Individuals instead of Nations in a Scenario for 2030. Sustainability. 2013; 5(5):1944-1959. https://doi.org/10.3390/su5051944
Chicago/Turabian StyleSthel, Marcelo, José Glauco Tostes, and Juliana Tavares. 2013. "Sustainable Complex Triangular Cells for the Evaluation of CO2 Emissions by Individuals instead of Nations in a Scenario for 2030" Sustainability 5, no. 5: 1944-1959. https://doi.org/10.3390/su5051944
APA StyleSthel, M., Tostes, J. G., & Tavares, J. (2013). Sustainable Complex Triangular Cells for the Evaluation of CO2 Emissions by Individuals instead of Nations in a Scenario for 2030. Sustainability, 5(5), 1944-1959. https://doi.org/10.3390/su5051944



