Constructing Ecological Security Patterns Using Remote Sensing Ecological Index Multi-Scenario Simulation and Circuit Theory: A Case Study of Xishuangbanna, a Border City
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Research Progress on Ecological Security Patterns
2.2. Research Progress on Remote Sensing Ecological Index and Simulation Models
2.3. Research Limitations and Research Hypotheses
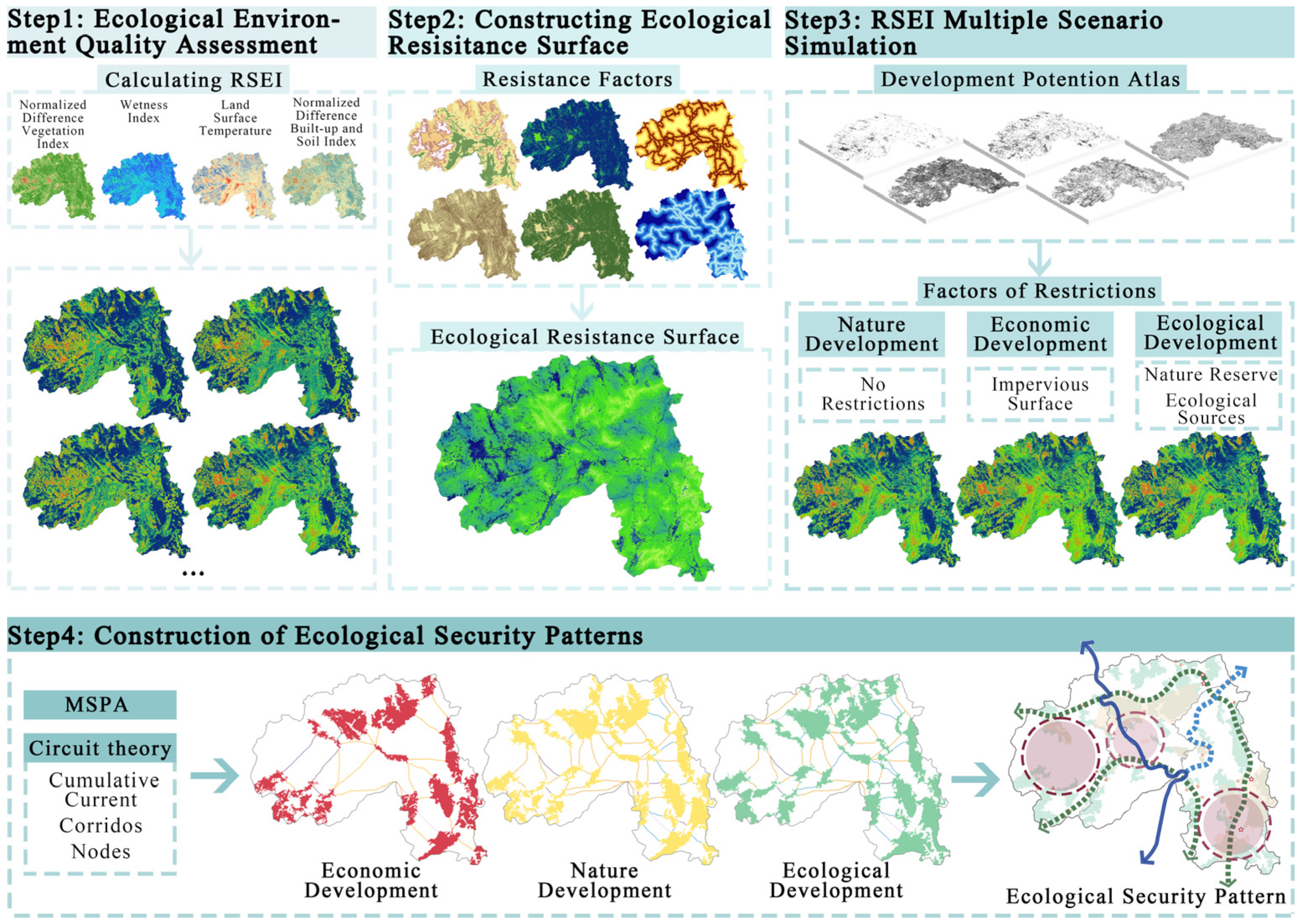
3. Materials and Methods
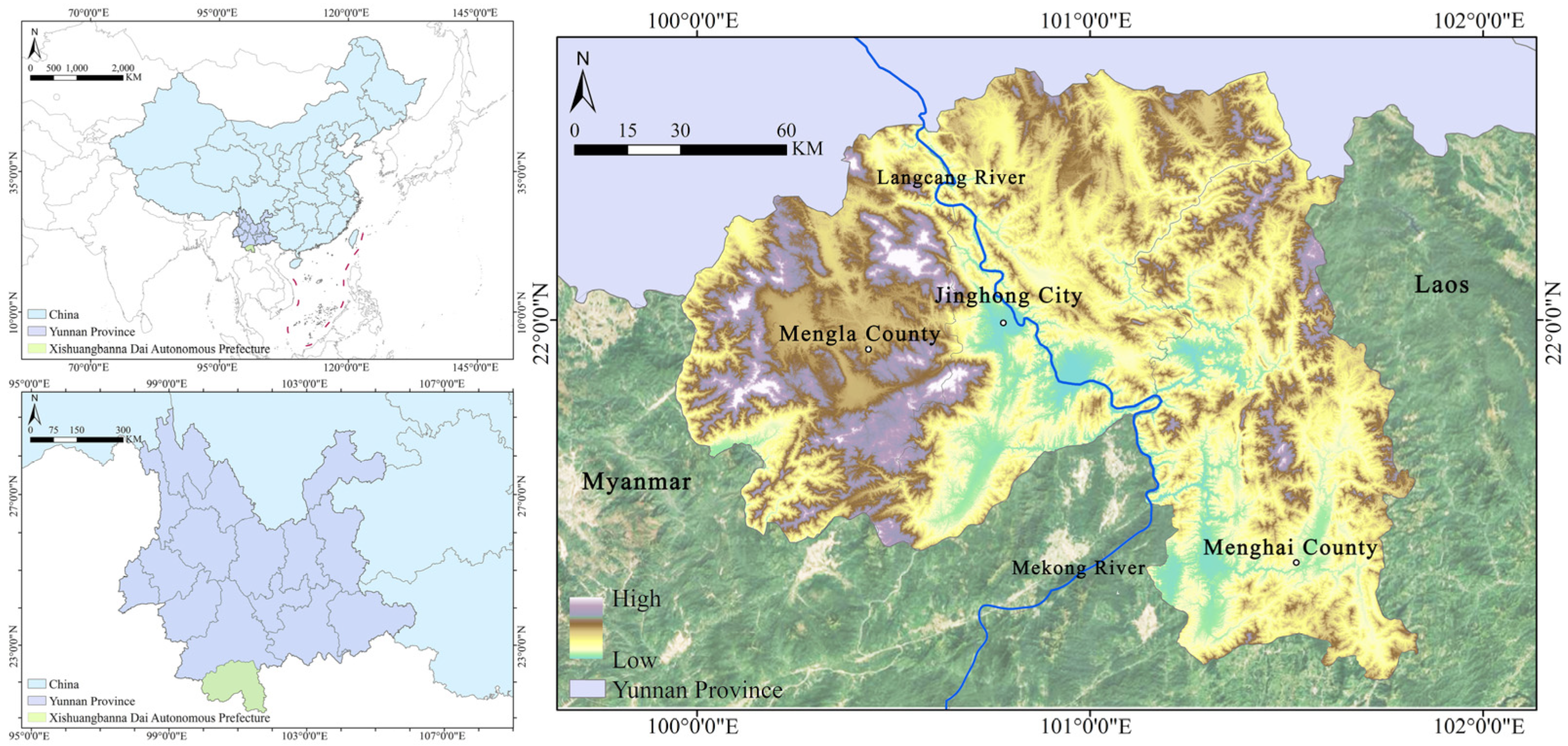
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Data Sources and Processing
3.3. Methods
3.3.1. Calculate the RSEI
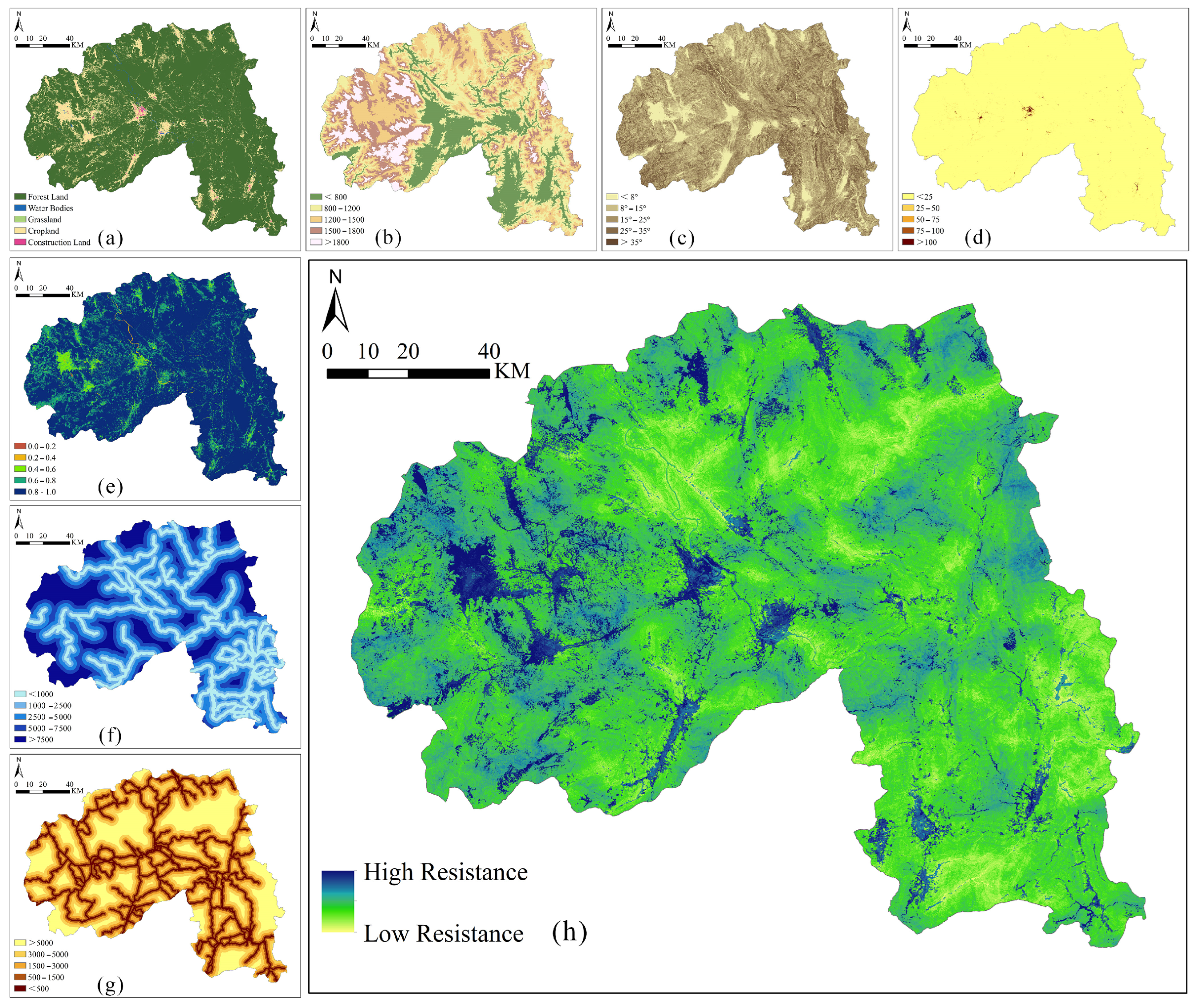
3.3.2. Constructing Ecological Resistance Surface
3.3.3. Multiple Scenario Simulations
3.3.4. Determination of Ecological Sources
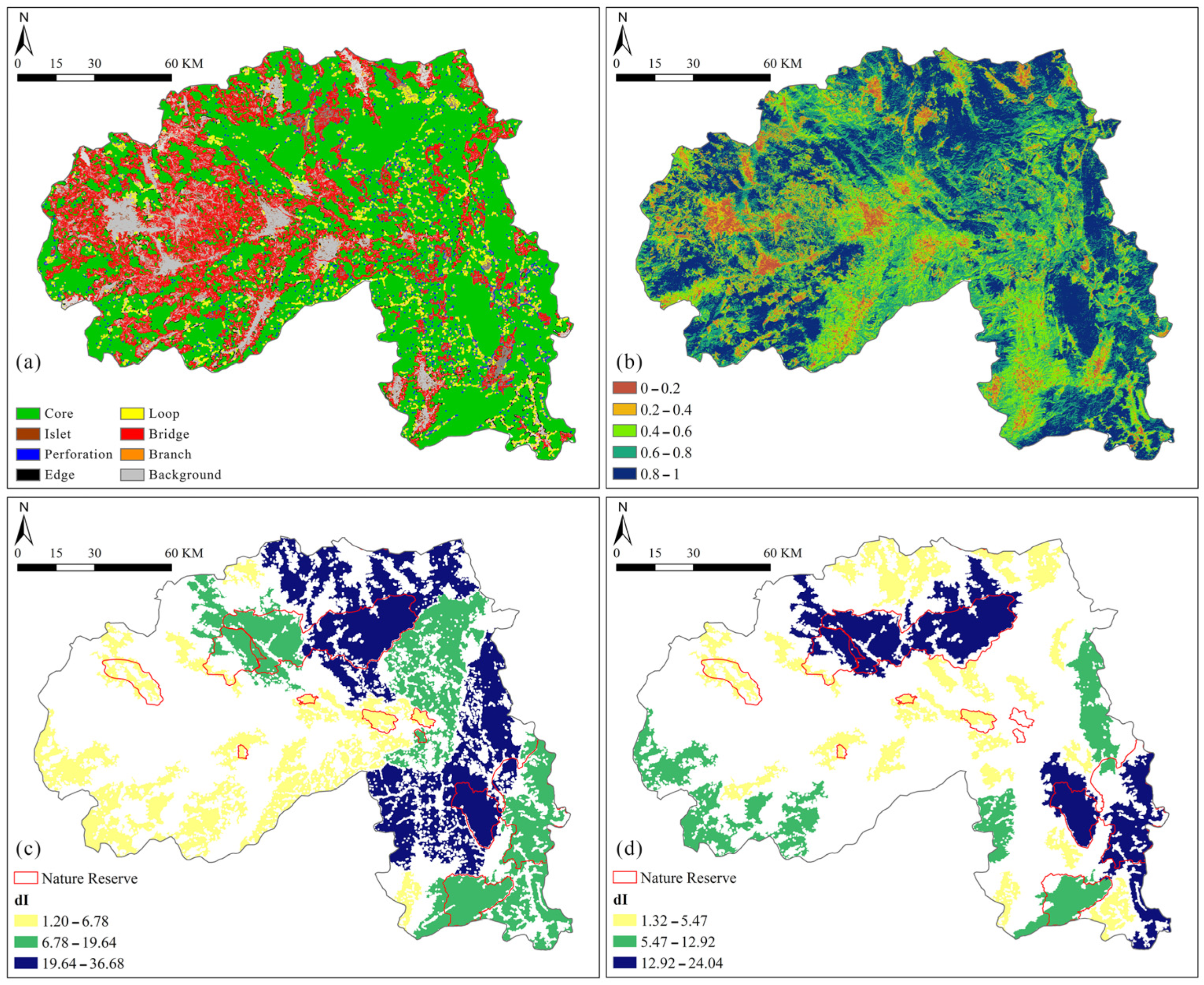
3.3.5. Extract Ecological Elements
3.3.6. Evaluation of Ecological Network Structure
4. Results
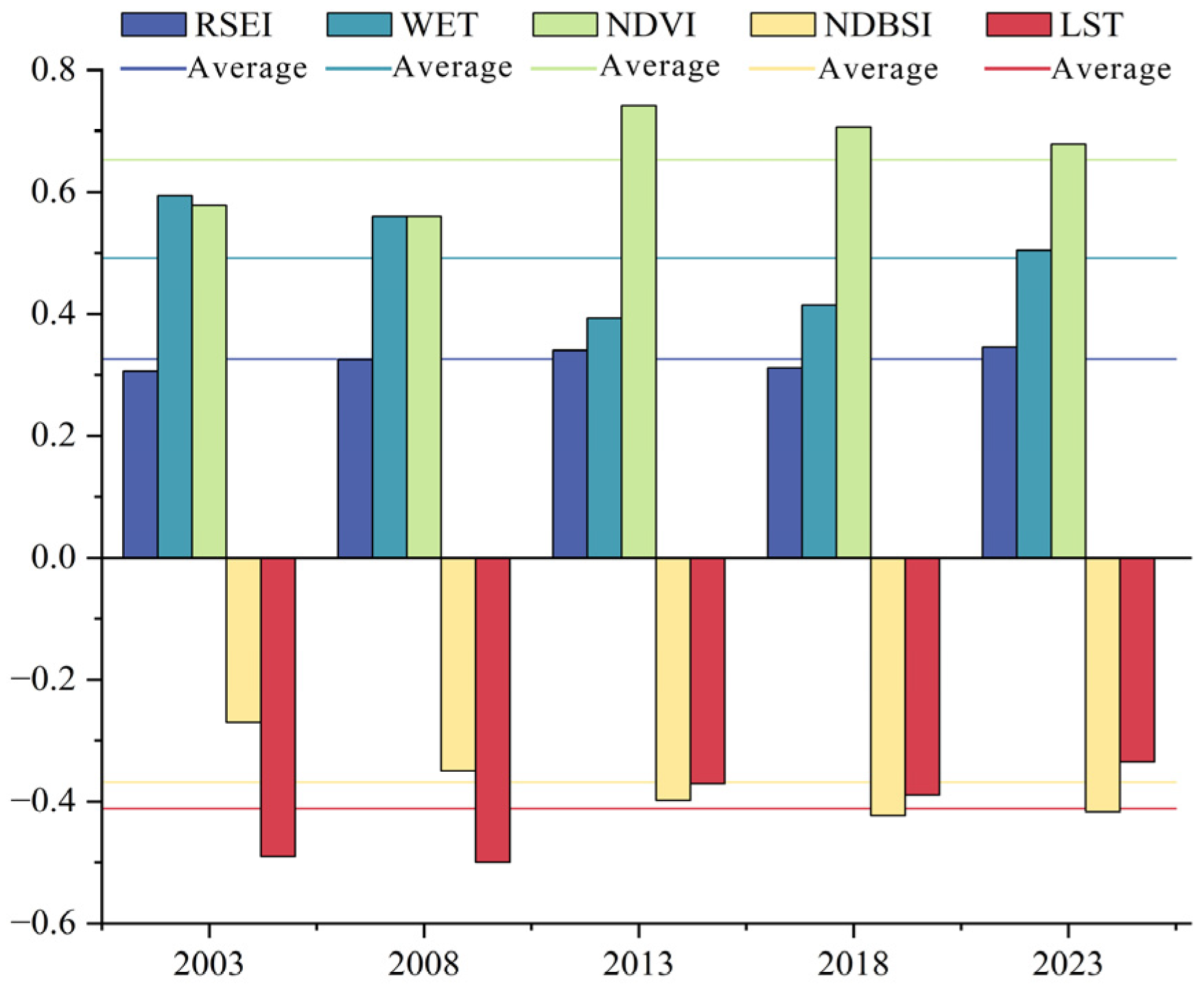
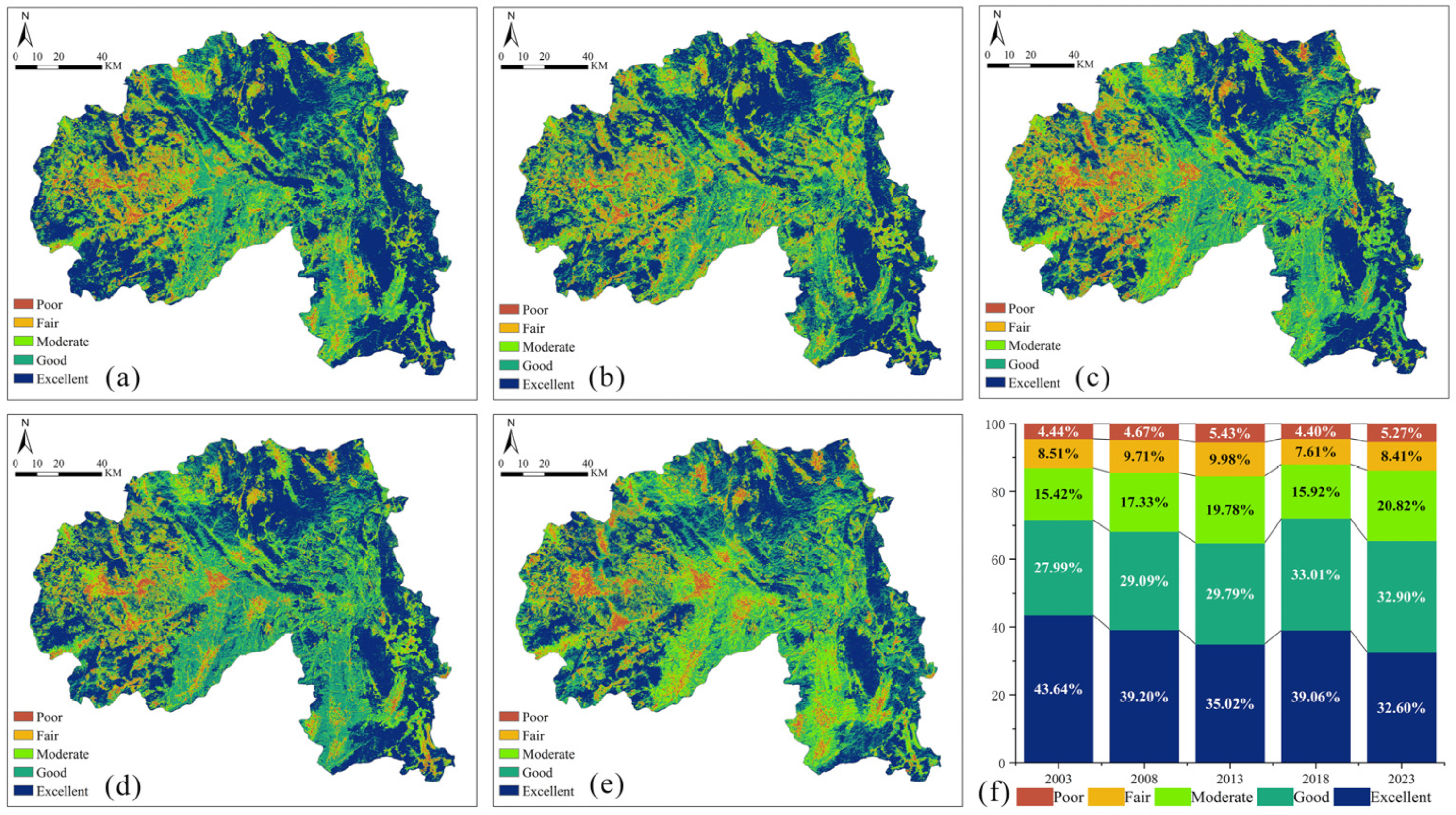
4.1. RSEI Feature Analysis
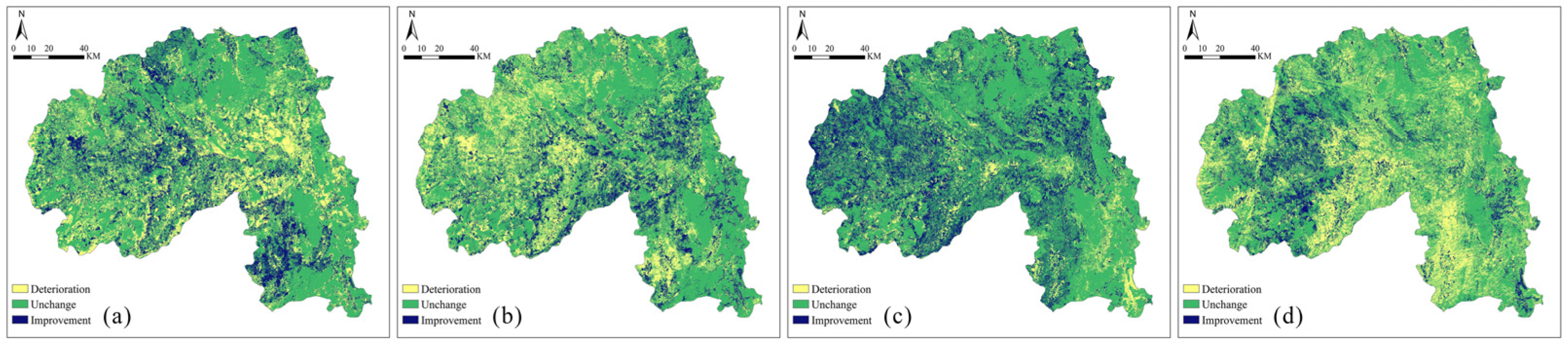
4.2. RSEI Temporal and Spatial Variation Analysis
4.3. Ecological Resistance Surface Analysis
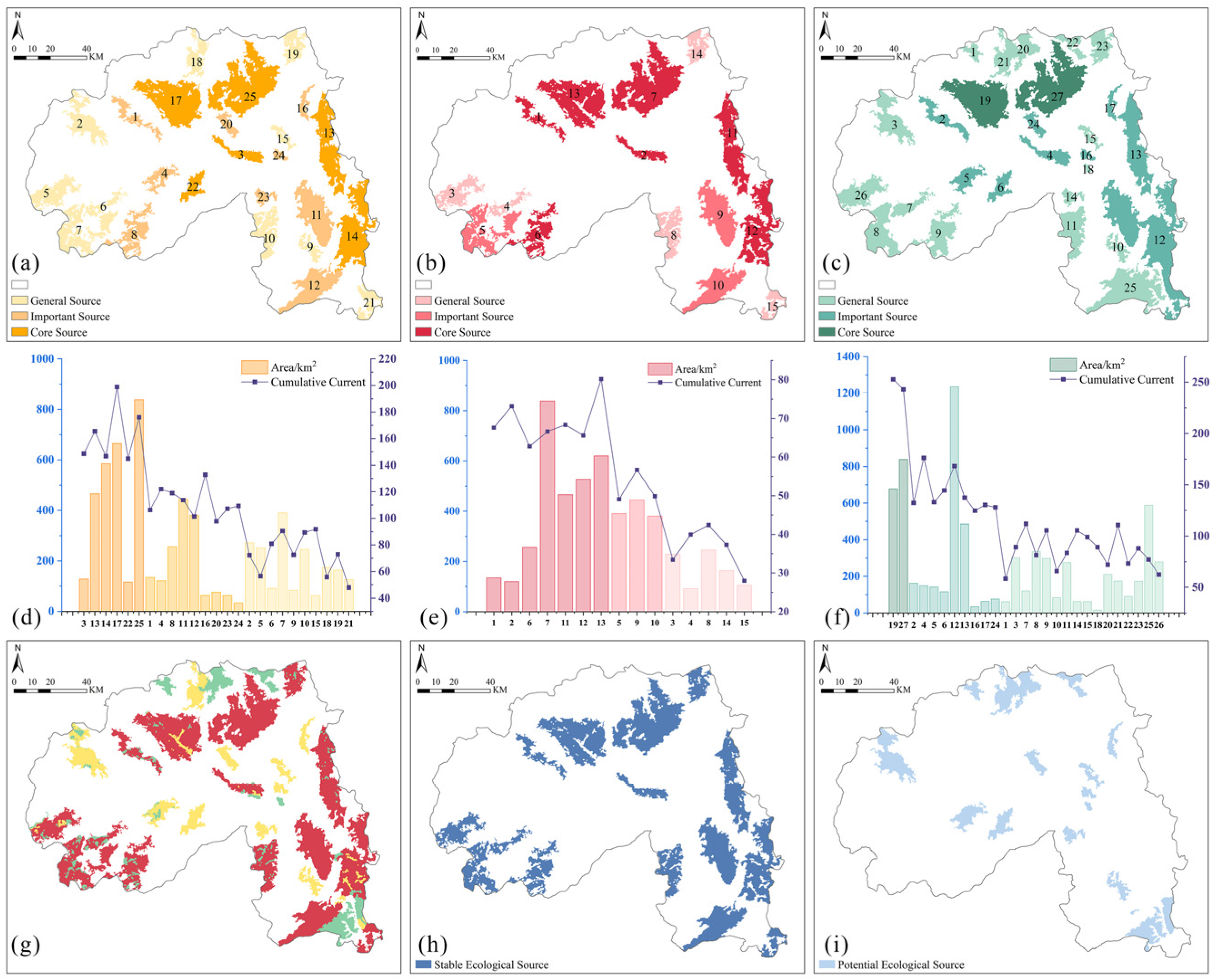
4.4. Comparison of Ecological Source Identification Analysis
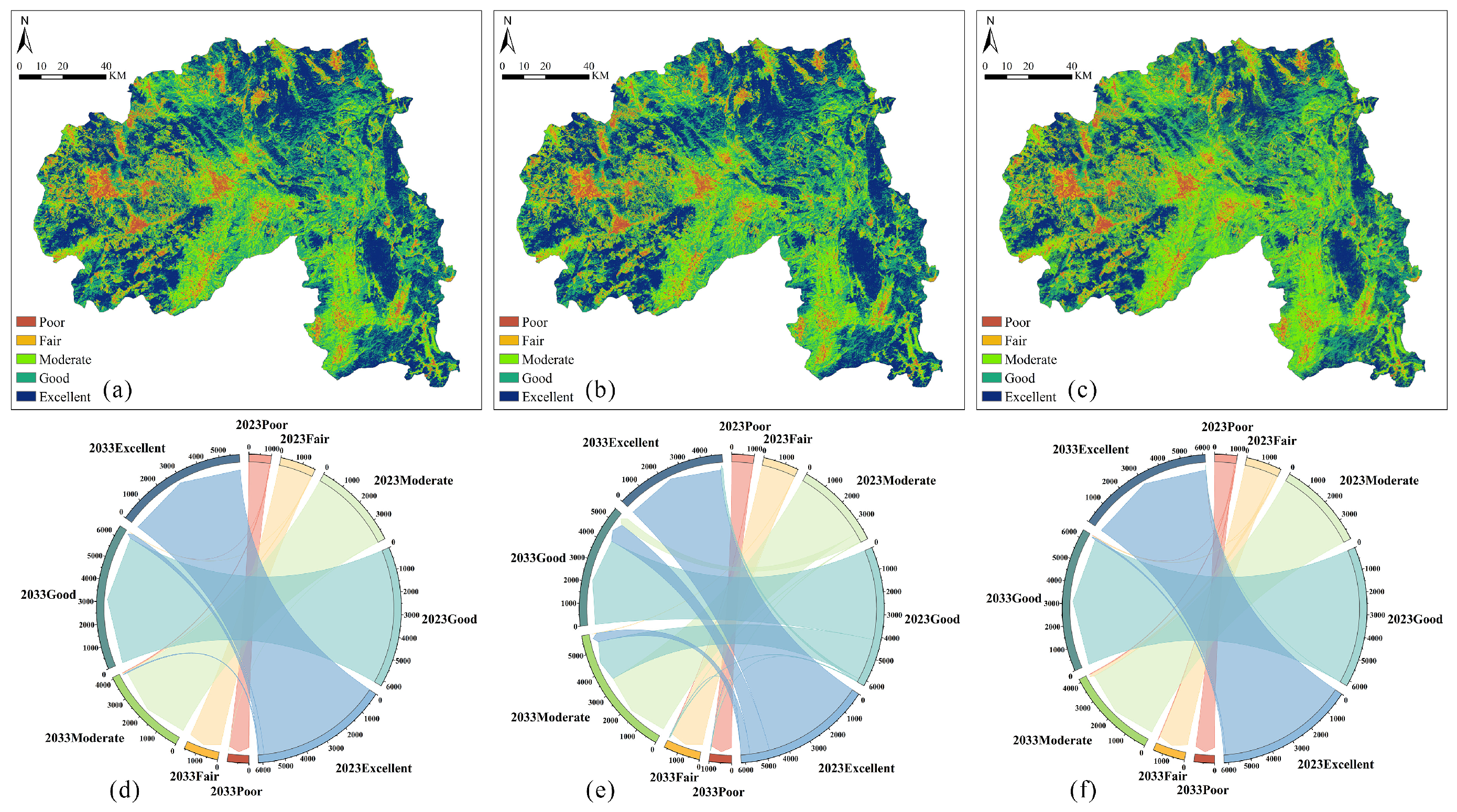
4.5. Multi-Scenario Simulation Analysis
4.5.1. Comparative Analysis of Ecological Sources Under Multi-Scenario Simulations
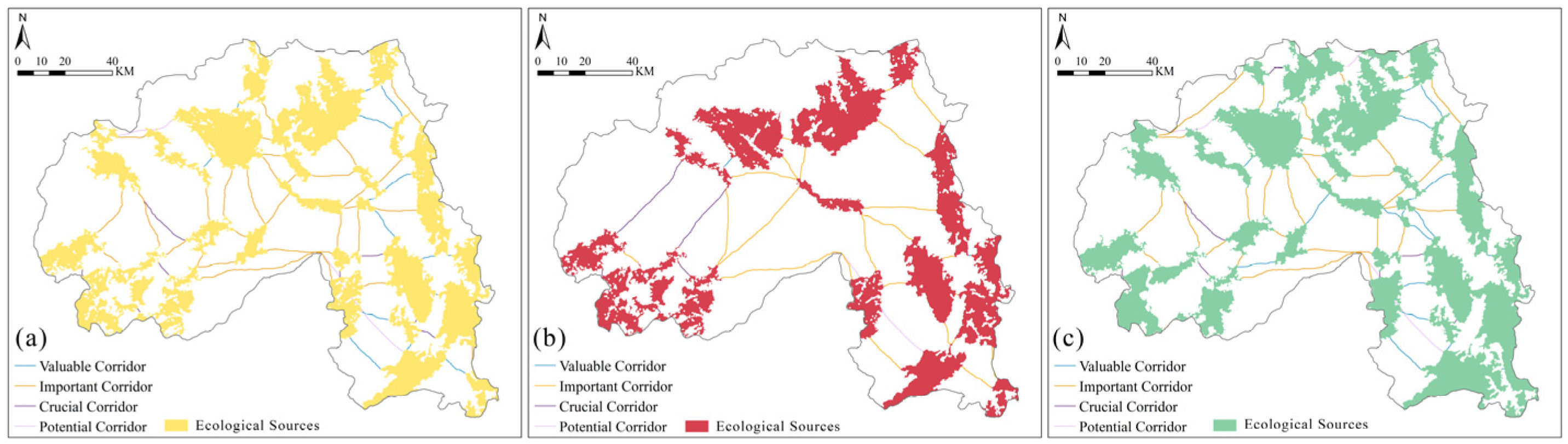
4.5.2. Comparative Analysis of Ecological Corridors Under Multi-Scenario Simulations
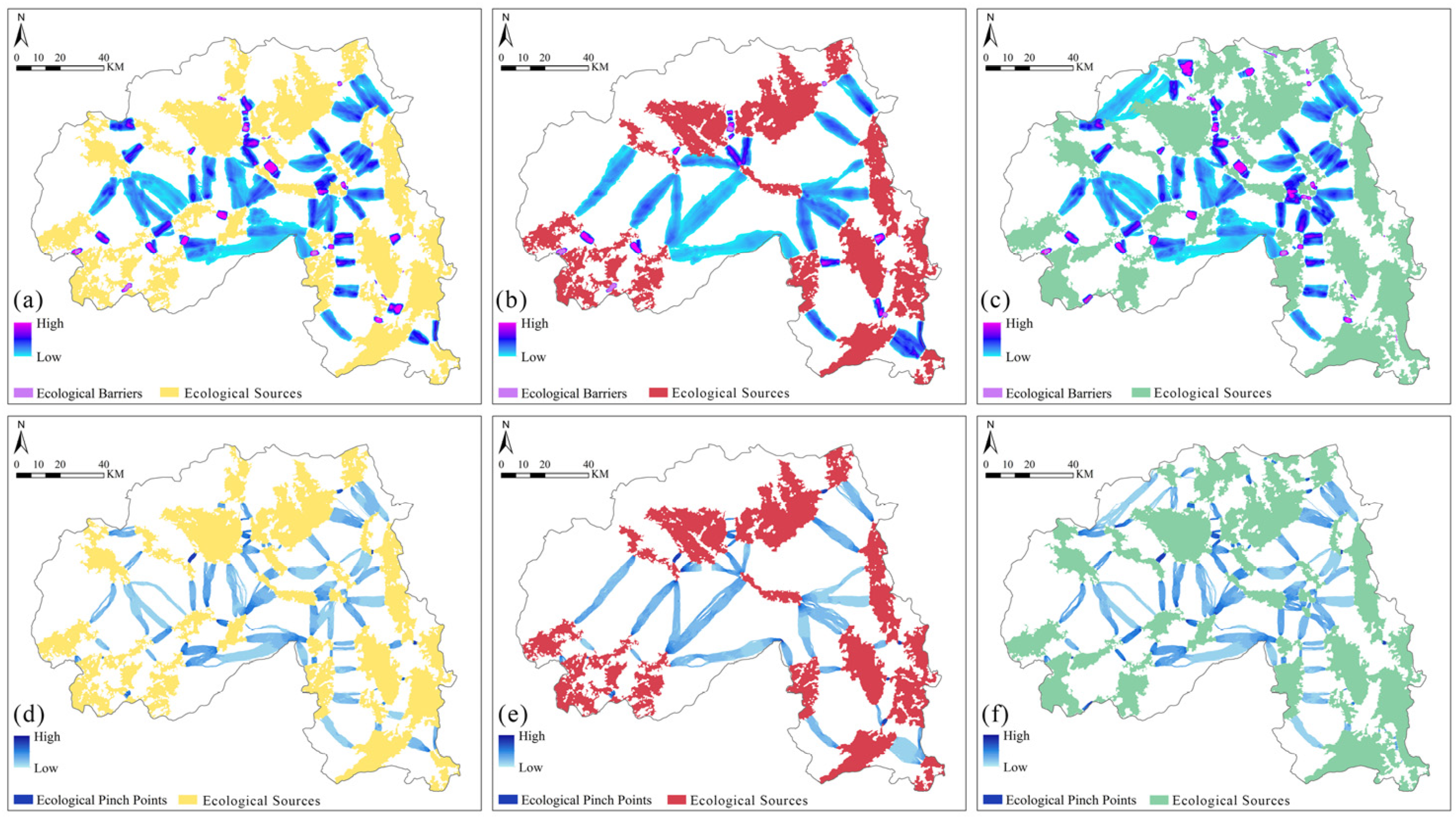
4.5.3. Comparative Analysis of Ecological Nodes Under Multi-Scenario Simulations
4.5.4. Analysis of Ecological Network Structure
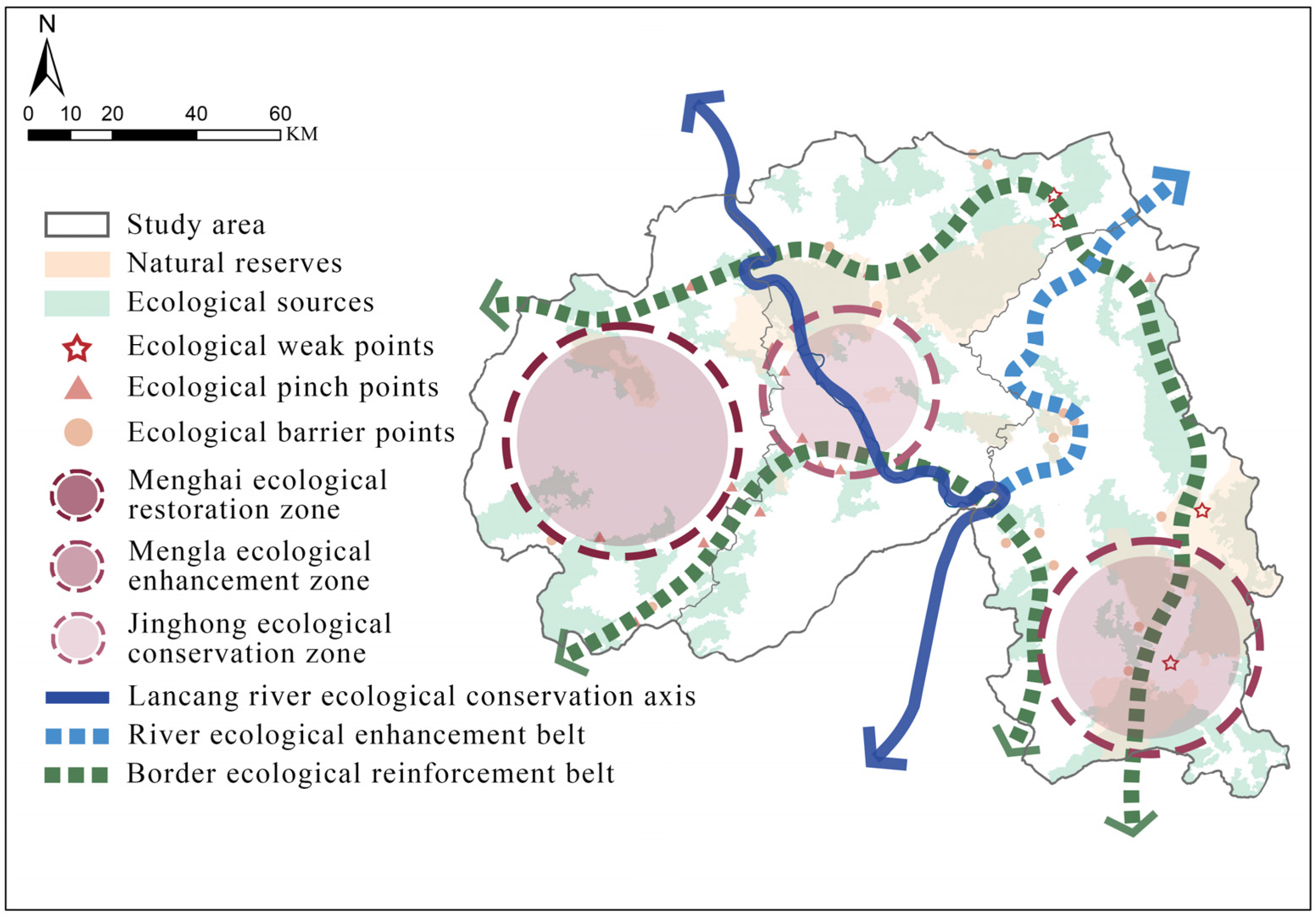
4.6. Construction of Ecological Security Pattern
4.6.1. “One Axis”—Lancang River Ecological Conservation Axis
4.6.2. “Two Corridors”—Two Border Ecological Enhancement Belts and One River
Ecological Reinforcement Belt
4.6.3. “Three Zones”—Menghai Ecological Restoration Zone, Mengla Ecological
Enhancement Zone, Jinghong Ecological Conservation Zone
5. Discussion
5.1. Proactive Management Is Crucial for Addressing Ecological Degradation
5.2. Complementing and Confirming Existing Research
5.3. Hypothesis Verification Analysis
Connectivity and Minimal Ecological Risk
5.4. Future Prospects for Constructing an ESP Against the Backdrop of Human-Nature Synergy
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RSEI | Remote Sensing Ecological Index |
| LUCC | Land Use and Land Cover Change |
| MSPA | Morphological Spatial Pattern Analysis |
| NDS | Natural Development Scenario |
| EDS | Economic Development Scenario |
| ECS | Ecological Conservation Scenario |
References
- Zhang, X.Q. The trends, promises and challenges of urbanisation in the world. Habitat Int. 2016, 54, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimm, S.L.; Jenkins, C.N.; Abell, R.; Brooks, T.M.; Gittleman, J.L.; Joppa, L.N.; Raven, P.H.; Roberts, C.M.; Sexton, J.O. The biodiversity of species and their rates of extinction, distribution, and protection. Science 2014, 344, 1246752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, B.; Liu, Y.; Meadows, M.E. Ecological restoration for sustainable development in China. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2023, 10, nwad033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chase, J.M.; Blowes, S.A.; Knight, T.M.; Gerstner, K.; May, F. Ecosystem decay exacerbates biodiversity loss with habitat loss. Nature 2020, 584, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Giulio, M.; Holderegger, R.; Tobias, S. Effects of habitat and landscape fragmentation on humans and biodiversity in densely populated landscapes. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2959–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahern, J. Planning for an extensive open space system: Linking landscape structure and function. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1991, 21, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.L.; He, D.M.; Wang, H.; Zhong, R.H.; Duan, X.W.; Deng, B.W.; Zhang, E.W.; Li, Y.W. Water yield service in the Lancang-Mekong River Basin: Cross-border changes and driving factors. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 176, 113725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.W.; Wang, Y.; Yan, M.Y.; Chiaka, J.C. Impact of cross-border transportation corridorsonchanges of land use and landscape pattern: A case study of the China-Laos railway. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2024, 241, 104924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, T.; Jian, P.; Hong, J.; Yifan, L.; Dongmei, X. Trade-off between comprehensive and specific ecosystem characteristics conservation in ecological security pattern construction. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2024, 49, e02776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodson, M.; Marvin, S. ‘Urban ecological security’: A new urban paradigm? Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2009, 33, 193–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Long, J.; Zhang, W.; Yang, J.T. Spatiotemporal evolution and driving factors of eco-environmental quality in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration in China. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 25631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.Y.; Xu, K.J.; Li, W.; Tian, Q.J.; Fan, Q.C.; Fang, S.W.; Shen, J.Y.; Jia, M.Y.; Tian, J. Spatiotemporal evolution and influencing mechanism of urbanization and ecological environmental quality between 2000 and 2020 in Henan Province, China. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2025, 37, 101492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Liu, Q.Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, T.; Li, M.Y. Constructing ecological security patterns using remote sensing ecological index and circuit theory: A case study of the Changchun-Jilin-Tumen region. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Pan, L.; Wang, Q.; Chen, P.; Yan, C.; Liu, L. Research on urban ecological network under the threat of road networks—A case study of wuhan. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, H.; Huang, Y. The complex ecological network’s resilience of the Wuhan metropolitan area. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, H.; Shan, L.; Xiao, F. Constructing and optimizing urban ecological network in the context of rapid urbanization for improving landscape connectivity. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 132, 108319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Yang, Z.; Xu, X. Ecological Corridors Analysis Based on MSPA and MCR Model—A Case Study of the Tomur World Natural Heritage Region. Sustainability 2020, 12, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, E.; Reheman, R.; Zhou, Z.; Tao, S. Evaluation of landscape ecological security pattern via the “pattern-function-stability” framework in the Guanzhong Plain Urban Agglomeration of China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liang, X.; Li, X.; Xu, X.; Ou, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Pei, F. A future land use simulation model (FLUS) for simulating multiple land use scenarios by coupling human and natural effects. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 168, 94–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thayn, J.B.; Sampeck, K.; Spaccapaniccia, M. Refining Hernando de Soto’ s Route Using Electric Circuit Theory and CircuitScape. Prof. Geogr. 2016, 68, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.H.; Yin, H.W.; Nobukazu, N.; Zong, Y.G. Urban green space network development for biodiversity conservation: Identification based on graph theory and gravity modeling. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 95, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, B.H.; Dickson, B.G.; Keitt, T.H.; Shah, V.B. Using circuit therory to model connectivity in ecology, evolution, and conservation. Ecology 2008, 89, 2712–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Huang, X.; Wu, D.; Wang, Z.; Yang, H. Optimization of ecological security patterns considering both natural and social disturbances in China’s largest urban agglomeration. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 180, 106647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincón, V.; Velázquez, J.; Gutiérrez, J.; Hernando, A.; Khoroshev, A.; Gómez, I.; Herráez, F.; Sánchez, B.; Luque, J.P.; García-abril, A.; et al. Proposal of new Natura 2000 network boundaries in Spain based on the value of importance for biodiversity and connectivity analysis for its improvement. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 108024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.Y.; Liu, X.L.; Jia, Y.Y. Construction and evolution of river basin ecological network based on circuit theory and MSPA: A case study of Dawen River Basin. Ecol. Model. 2025, 510, 111364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurrutxaga, M.; Rubio, L.; Saura, S. Key connectors in protected forest area networks and the impact of highways: A transnational case study from the Cantabrian Range to the Western Alps (SW Europe). Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 101, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, K.S. Remote sensing change detection for ecological monitoring in united states protected areas. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 182, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Xu, W.H.; Lu, N.; Huang, S.D.; Wu, C.; Wang, L.G.; Dai, F.; Kou, W.L. Assessment of spatial-temporal changes of ecological environment quality based on RSEI and GEE: A case study in Erhai Lake Basin, Yunnan province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Q. A remote sensing urban ecological index and its application. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 7853–7862. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/287524109_A_remote_sensing_urban_ecological_index_and_its_application (accessed on 4 December 2025).
- Firozjaei, M.K.; Fathololoumi, S.; Weng, Q.; Kiavarz, M.; Alavipanah, S.K. Remotely Sensed Urban Surface Ecological Index (RSUSEI): An Analytical Framework for Assessing the Surface Ecological Status in Urban Environments. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.S.; Xu, H.Q. A new remote sensing index for assessing the spatial heterogeneity in urban ecological quality: A case from Fuzhou City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, H.L.; Xiang, N.; Lv, C.Y.; Hu, P.; Cai, C.Y.; Li, J. Dynamic assessment and prediction of ecological environment quality in Tongren based on RSEI and CA-Markov—Taking Tongren, Guizhou Province as an example. Environ. Prot. Sci. 2025, 51, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atiyeh, A.; Thomas, B.; Mojgan, B.; Narges, S.; Omid, G.; Hamid, R.P. Leveraging GEE and machine learning algorithm in dynamic modeling of eco-environmental quality. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2025, 27, 100818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Z.; Guan, Q.Y.; Sun, Y.F.; Du, Q.Q.; Xiao, X.; Luo, H.P.; Zhang, J.; Mi, J.M. Simulation of future land use/cover change (LUCC) in typical watersheds of arid regions under multiple scenarios. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 335, 117543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Guan, Q.; Clarke, K.C.; Liu, S.; Wang, B.; Yao, Y. Understanding the drivers of sustainable land expansion using a patch-generating land use simulation (PLUS) model: A case study in Wuhan, China. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2021, 85, 101569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Tao, F.; Liu, R.; Wang, Z.; Leng, H.; Zhou, T. Multi-scenario simulation and ecological risk analysis of land use based on the PLUS model: A case study of Nanjing. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 85, 104055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Li, X.T.; Du, S.J.; Liu, C.; Shi, Z.W.; Yan, C. Spatial-temporal evolution analysis of multi-scenario land use and ecosystem services base on PLUS-Invest model: A case study in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. Sustain. Futures 2025, 10, 101154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Song, Y.; Hsu, W.-L. Integrating Ecosystem Services and Key Species Distribution to Construct a Sustainable Ecological Security Pattern in a Plateau Urban Agglomeration. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Liang, Z.; Yu, H.R.; Zhang, Q.; Fan, X. Spatial-temporal differentiation and multi-scenario simulation of landscape ecological risk assessment in Fenhe River Basin based on PLUS model. Ecol. Sci. 2024, 43, 35. Available online: http://www.ecolsci.com/CN/Y2024/V43/I1/35 (accessed on 4 December 2025).
- Chen, Y.; Xu, C.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y. A 100 m gridded population dataset of China’s seventh census using ensemble learning and big geospatial data. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2024, 16, 3705–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.B.; Wang, W.; Song, Y.J.; Miao, L.G.; Ma, C. Ecological index evaluation of arid inflow area based on the modified remote sensing ecological index: A case study of Tabu River Basin at the northern foot of the Yin Mountains. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 523–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Zhang, X.; Li, G.H.; Wang, R.X. Construction of ecological corridor in Xishuangbanna Prefecture, Yunnan Province of southwestern China. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2024, 46, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Tamg, A.Q. Evaluaton of Asian elephant habitat network in Xishuanebanna based on InVEST-GraphTheory model. Acta Eoologica Sin. 2024, 44, 5206–5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Chen, K. Analysis of Blue Infrastructure Network Pattern in the Hanjiang Ecological Economic Zone in China. Water 2022, 14, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Liu, T.; Liang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Lv, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, Q. Uncovering the impacts of LUCC on ecological connectivity in suburban open-pit mining concentration areas: A pattern collection of changing relationships between ecological resistance and ecological network elements. Ecol. Model. 2024, 496, 110815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Jiang, H.L.; Zhang, S.H. Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Vegetation Cover and Multiscenario Simulation Prediction in Shenyang from 2000–2020. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2024, 39, 1555–1564. Available online: http://www.rsta.ac.cn/EN/10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2024.6.1555 (accessed on 4 December 2025).
- Fu, S.T.; He, C.X.; Ma, J.K.; Wang, B.; Zhen, Z.L. Ecological environment quality of the Shanxi section of the Yellow River Basin under different development scenarios. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 35, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Dong, J.Q. Scenario-based ecological security patterns to indicate landscape sustainability: A case study on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 2175–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baste, I.A.; Watson, R.T. Tackling the climate, biodiversity and pollution emergencies by making peace with nature 50 years after the Stockholm Conference. Glob. Environ. Change 2022, 73, 102466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, J. Construction and optimization of regional ecological security patterns based on MSPA-MCR-GA Model: A case study of Dongting Lake Basin in China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 165, 112169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleyhl, B.; Baumann, M.; Griffiths, P.; Heidelberg, A.; Manvelyan, K.; Radeloff, V.C.; Zazanashvili, N.; Kuemmerle, T. Assessing landscape connectivity for large mammals in the Caucasus using Landsat 8 seasonal image composites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 193, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, A.; Rubio, X. Beyond Least Cost Paths: Circuit theory, maritime mobility and patterns of urbanism in the Roman Adriatic. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2022, 138, 105534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Lv, H.; Hu, X. Linking ecosystem services and landscape patterns to assess urban ecosystem health: A case study in Shenzhen City, China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 143, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.Y.; Li, C.; Wu, Z.F.; Zhang, L.; Ji, D.Q.; Cheng, J. Identifying Ecological Security Patterns and Prioritizing Ecological Corridors in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2022, 31, 652–662. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, A.M.; Yue, Q.F.; Zhao, X.Q.; Huang, P.; Ran, Y.J.; Gu, Z.X.; Shi, X.Y. Identification and restoration zoning of key areas for ecological restoration of territorial space in southwestern karst mountainous areas: A case study of Kaiyuan City in karst mountainous area of Southwest China. China Environ. Sci. 2023, 43, 6571–6582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.Y.; Chen, W.B.; Sheng, Z.Y.; Wang, P.Q.; Guan, F.Y. Ecological network construction and identification of important elements based on morphological spatial pattern analysis and circuit theory in Pingxiang City. J. Nat. Conserv. 2025, 86, 126902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Ma, R.; Xie, W.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Yin, L. Construction of Ecological Security Pattern Based on Ecosystem Services, Sensitivity, Connectivity, and Resistance—A Case Study in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain. Land 2024, 13, 2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.P.; Chen, W.B. Construction and evaluation of ecological network in Poyang Lake Eco-economic Zone, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 27, 1611–1618. Available online: https://www.cjae.net/CN/10.13287/j.1001-9332.201605.016 (accessed on 4 December 2025).
- Estes, J.A.; Terborgh, J.; Brashares, J.S.; Power, M.E.; Berger, J.; Bond, W.J.; Carpenter, S.R.; Essington, T.E.; Holt, R.D.; Jackson, J.B.C. Trophic Downgrading of Planet Earth. Science 2011, 333, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukesh, S.B.; Komal, C.; Rustam, P.; Alexander, K. Eco-environmental quality assessment based on pressure-state-response framework by remote sensing and GIS. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2021, 23, 100530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tölgyesi, C.; Csikós, N.; Temperton, V.M.; Buisson, E.; Silveira, F.A.O.; Lehmann, C.E.R.; Török, P.; Bátori, Z.; Bede-Fazekas, Á. Limited carbon sequestration potential from global ecosystem restoration. Nat. Geosci. 2025, 18, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.P.; Yu, H.P.; Han, D.L.; Zhang, G.L.; Wei, Y.; Huang, J.P.; An, L.L.; Liu, X.Y.; Ren, Y. Declines in global ecological security under climate change. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.P.; Zhang, Y.J. Transboundary Ecological Network Communities based on natural protected areas: A case study of the Mekong River Basin, Asia. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2024, 55, e03216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotlov, I.; Chernenkova, T.; Belyaeva, N. Vegetation Response Patterns to Landscape Fragmentation in Central Russian Forests. Land 2025, 14, 2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.K.; He, P.; Xu, J.; Hou, L.P. Research basis of ecological thresholds and regime shifts in China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 2015–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Zhou, B. Study on the Modern Change and Protection of “Long Forest” of Dai Nationality. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2024, 45, 255–258. Available online: https://ahny.cbpt.cnki.net/portal/journal/portal/client/paper/d0e4b1aa19f73e069b31201026936701 (accessed on 4 December 2025).
- Huang, Q.; Nan, C.F.; Bao, C.H.; Li, W.; Li, G.C. Ecological Value of the Natural Worship of Dai People in Xishuangbanna. J. Yunnan Agric. Univ. (Soc. Sci). 2017, 11, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, S.J. Traditional Culture and Biodiversity Conservation. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2011, 26, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker, R.R.; Aversa, J.; Papp, V.; Serre, B.M.; Mackay, B.R. Showcasing Relationships between Neighborhood Design and Wellbeing Toronto Indicators. Sustainability 2020, 12, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Data | Resolution | Database Sources | Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat5/7/8 | 30 m | Google Earth Engine | https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/datasets (accessed on 4 December 2025) |
| Population Density | 100 m | Figshare | https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.24916140.v1 (accessed on 4 December 2025) |
| LUCC | 30 m | Earth System Science Data | https://zenodo.org/records/15853565 (accessed on 4 December 2025) |
| Road | N/A | Open Street Map | http://www.openstreetmap.org (accessed on 4 December 2025) |
| River | N/A | ||
| Boundary | N/A | National Catalogue Service for Geographic Information | http://www.webmap.cn (accessed on 4 December 2025) |
| Nature Reserve | N/A | ||
| DEM | 30 m | Geospatial Data Cloud | http://www.gscloud.cn/ (accessed on 4 December 2025) |
| Factors | Weight | Level | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| LUCC | 0.303 | Forest Land | Water Bodies | Grassland | Cropland | Construction Land |
| NDVI | 0.207 | 0.8–1.0 | 0.6–0.8 | 0.4–0.6 | 0.2–0.4 | 0–0.5 |
| Distance to River (km) | 0.107 | <1 | 1–2.5 | 2.5–5 | 5–7 | >7.5 |
| Distance to Road (km) | 0.103 | >5 | 3–5 | 1.5–3 | 5–1.5 | <5 |
| DEM (km) | 0.101 | <0.8 | 0.8–1.2 | 1.2–1.5 | 1.5–1.8 | >1.8 |
| Slope (°) | 0.101 | <8 | 8–15 | 15–25 | 25–35 | >35 |
| Population Density (persons/km2) | 0.066 | <25 | 25–50 | 50–75 | 75–100 | >100 |
| Type | Natural Development Scenario | Economic Development Scenario | Ecological Conservation Scenario | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | F | M | G | E | P | F | M | G | E | P | F | M | G | E | |
| P | 0.405 | 0.286 | 0.187 | 0.093 | 0.029 | 0.559 | 0.441 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.952 | 0.027 | 0.011 | 0.007 | 0.003 |
| F | 0.145 | 0.285 | 0.341 | 0.188 | 0.041 | 0.074 | 0.385 | 0.541 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.555 | 0.146 | 0.157 | 0.142 |
| M | 0.051 | 0.137 | 0.449 | 0.318 | 0.045 | 0.066 | 0.027 | 0.589 | 0.318 | 0 | 0 | 0.100 | 0.549 | 0.248 | 0.103 |
| G | 0.019 | 0.039 | 0.243 | 0.564 | 0.135 | 0.029 | 0.043 | 0.349 | 0.519 | 0.060 | 0 | 0 | 0.258 | 0.494 | 0.248 |
| E | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.007 | 0.212 | 0.775 | 0.014 | 0.039 | 0.060 | 0.112 | 0.775 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.323 | 0.677 |
| NW | 0.255 | 0.306 | 0.155 | 0.187 | 0.096 | 0.209 | 0.291 | 0.195 | 0.199 | 0.106 | 0.027 | 0.251 | 0.254 | 0.285 | 0.182 |
| Quantity | Total Area/km2 | Area Within the Nature Reserve/km2 | Proportion/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Methods | 20 | 9939.34 | 2334.44 | 23.49 |
| Core | 2 | 3876.90 | 864.86 | 22.31 |
| Secondary | 4 | 3393.28 | 1256.81 | 37.04 |
| Tertiary | 14 | 2669.16 | 212.77 | 7.97 |
| RSEI-ESP-PLUS | 33 | 7237.05 | 2124 | 29.35 |
| Core | 4 | 2804.29 | 1656.72 | 59.08 |
| Secondary | 6 | 2061.85 | 286.49 | 13.89 |
| Tertiary | 23 | 2370.9 | 180.79 | 7.63 |
| Type | Crucial | Important | General | Potential | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quality | Length/km | Quality | Length/km | Quality | Length/km | Quality | Length/km | |
| NDS | 8 | 608.92 | 34 | 5096.06 | 16 | 1237.84 | 2 | 1379.86 |
| EDS | 5 | 860.23 | 23 | 4314.30 | 2 | 59.92 | 1 | 1123.75 |
| ECS | 8 | 598.19 | 35 | 5176.95 | 20 | 1723.52 | 3 | 1475.13 |
| Type | Ecological Barriers | Ecological Pinch Points | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quality | Area/km2 | Quality | Area/km2 | |
| Nature Development Scenario | 18 | 21.11 | 29 | 17.09 |
| Economic Development Scenario | 12 | 24.85 | 19 | 27.63 |
| Ecological Conservation Scenario | 24 | 19.07 | 22 | 22.85 |
| Metric | Economic Development | Nature Development | Ecological Conservation |
|---|---|---|---|
| α | 0.018 | 0.158 | 0.242 |
| β | 1 | 1.277 | 1.435 |
| γ | 0.356 | 0.444 | 0.500 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Huang, L.; Peng, J. Constructing Ecological Security Patterns Using Remote Sensing Ecological Index Multi-Scenario Simulation and Circuit Theory: A Case Study of Xishuangbanna, a Border City. Sustainability 2026, 18, 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/su18020894
Yang J, Huang L, Peng J. Constructing Ecological Security Patterns Using Remote Sensing Ecological Index Multi-Scenario Simulation and Circuit Theory: A Case Study of Xishuangbanna, a Border City. Sustainability. 2026; 18(2):894. https://doi.org/10.3390/su18020894
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jiaqi, Linyun Huang, and Jiansong Peng. 2026. "Constructing Ecological Security Patterns Using Remote Sensing Ecological Index Multi-Scenario Simulation and Circuit Theory: A Case Study of Xishuangbanna, a Border City" Sustainability 18, no. 2: 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/su18020894
APA StyleYang, J., Huang, L., & Peng, J. (2026). Constructing Ecological Security Patterns Using Remote Sensing Ecological Index Multi-Scenario Simulation and Circuit Theory: A Case Study of Xishuangbanna, a Border City. Sustainability, 18(2), 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/su18020894






