Seasonal Color Dynamics and Visual Aesthetic Perception in Subtropical Wetland Parks: A Climate-Adaptive Design Framework
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
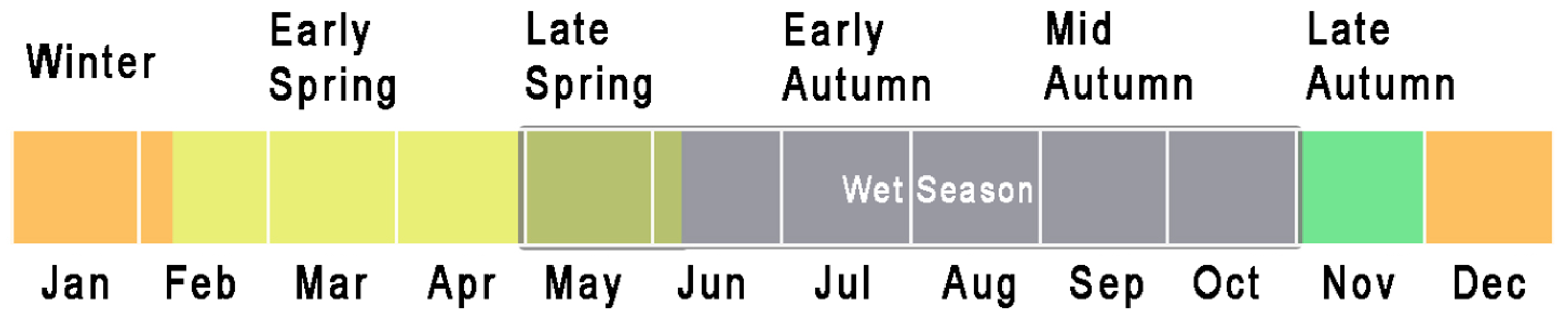
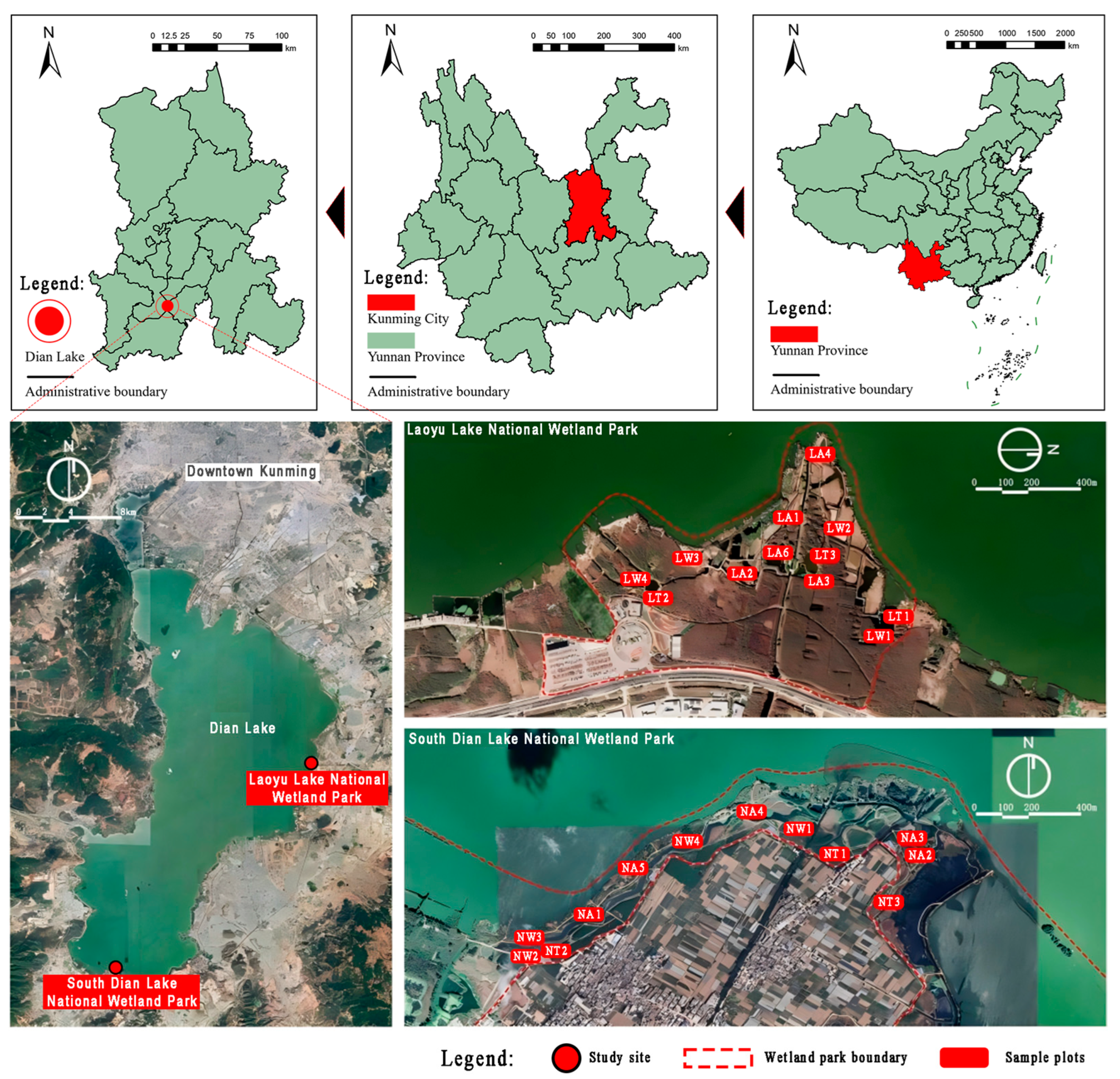
2.1. Study Area and Sample Plot Selection
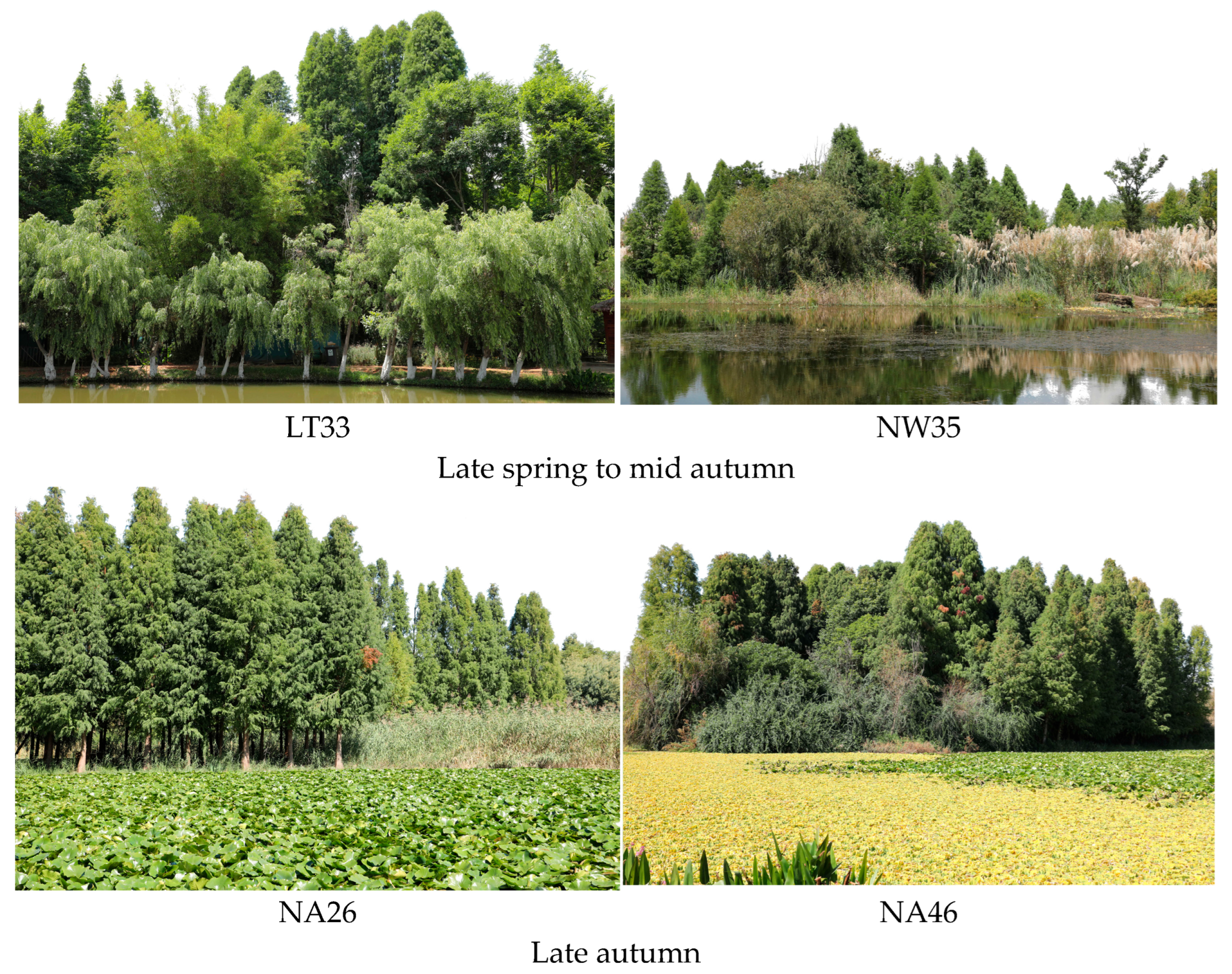
2.2. Photography
2.3. Scenic Beauty Estimation Method
2.4. Color Quantization Based on the HSB Model
3. Results and Analysis
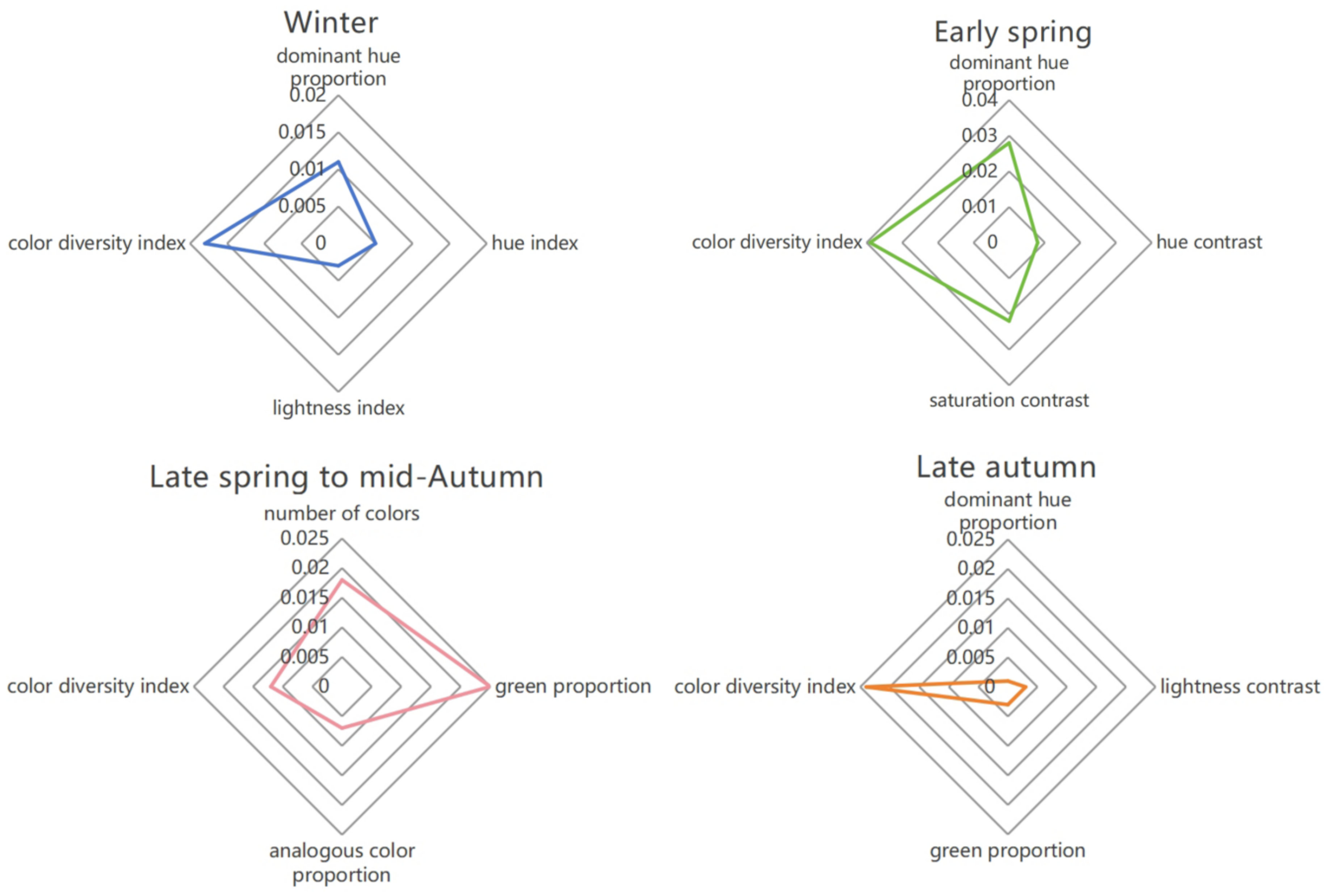
3.1. Quantitative Characteristics of Plant Colors
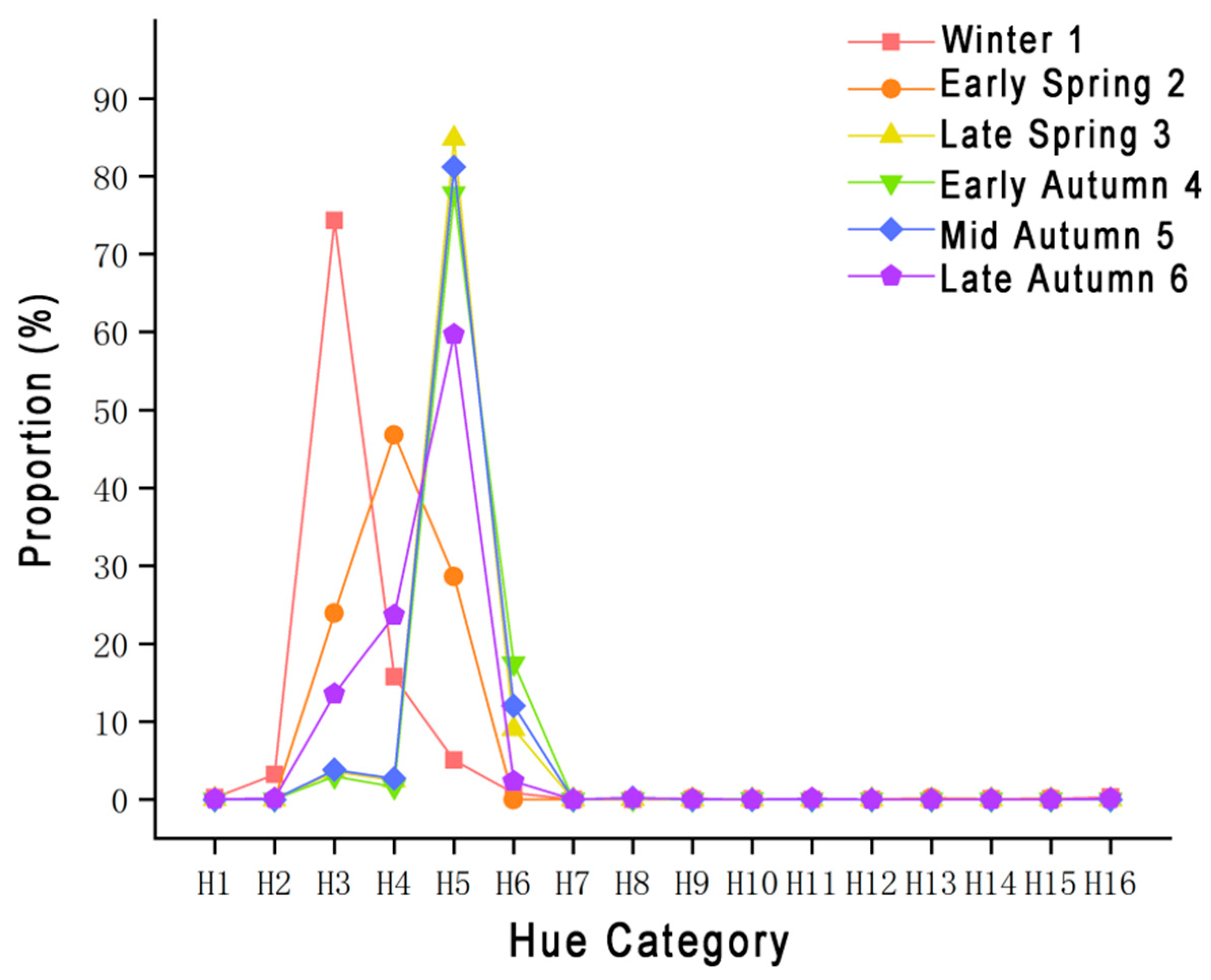
3.1.1. Hue
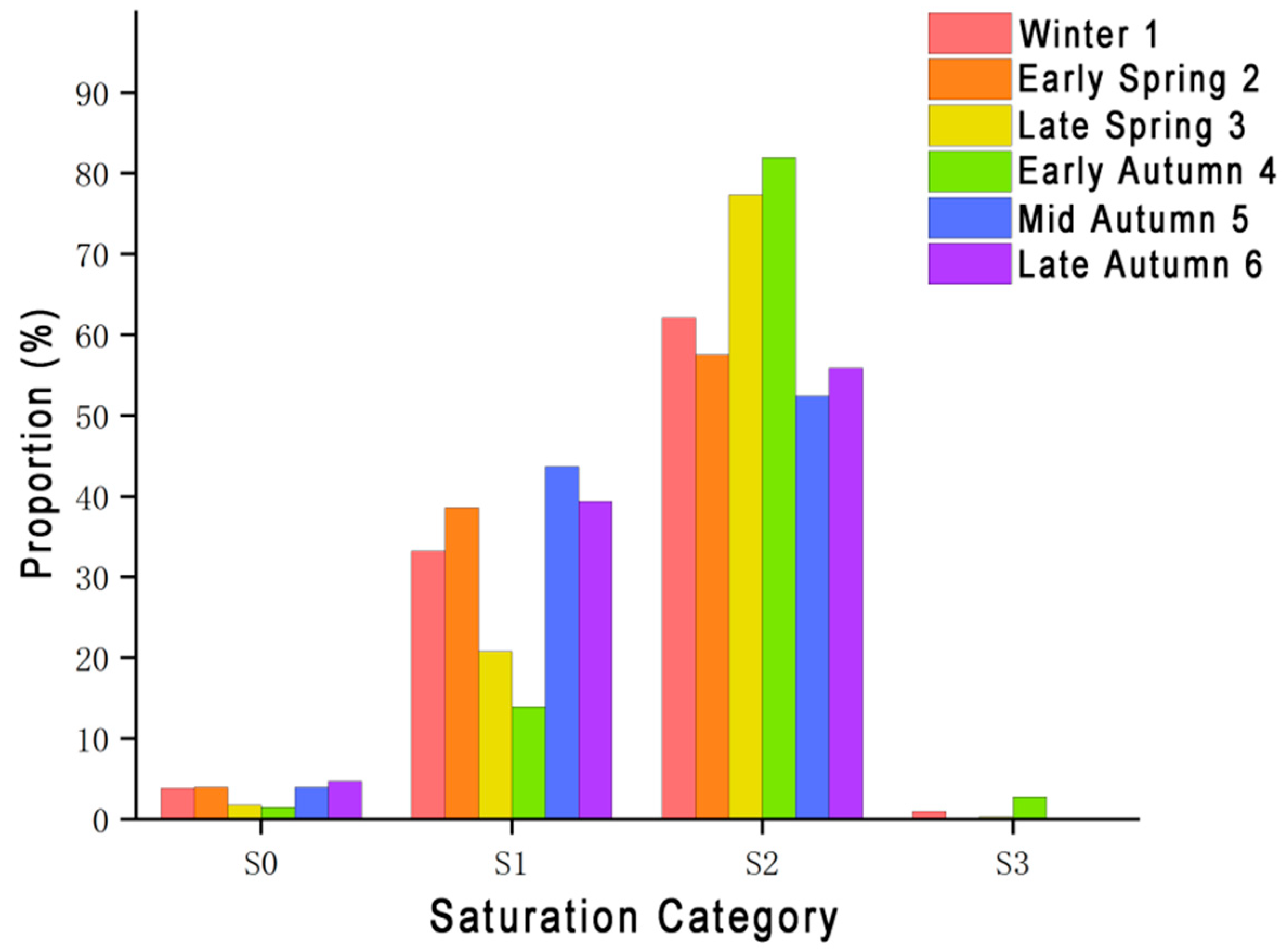
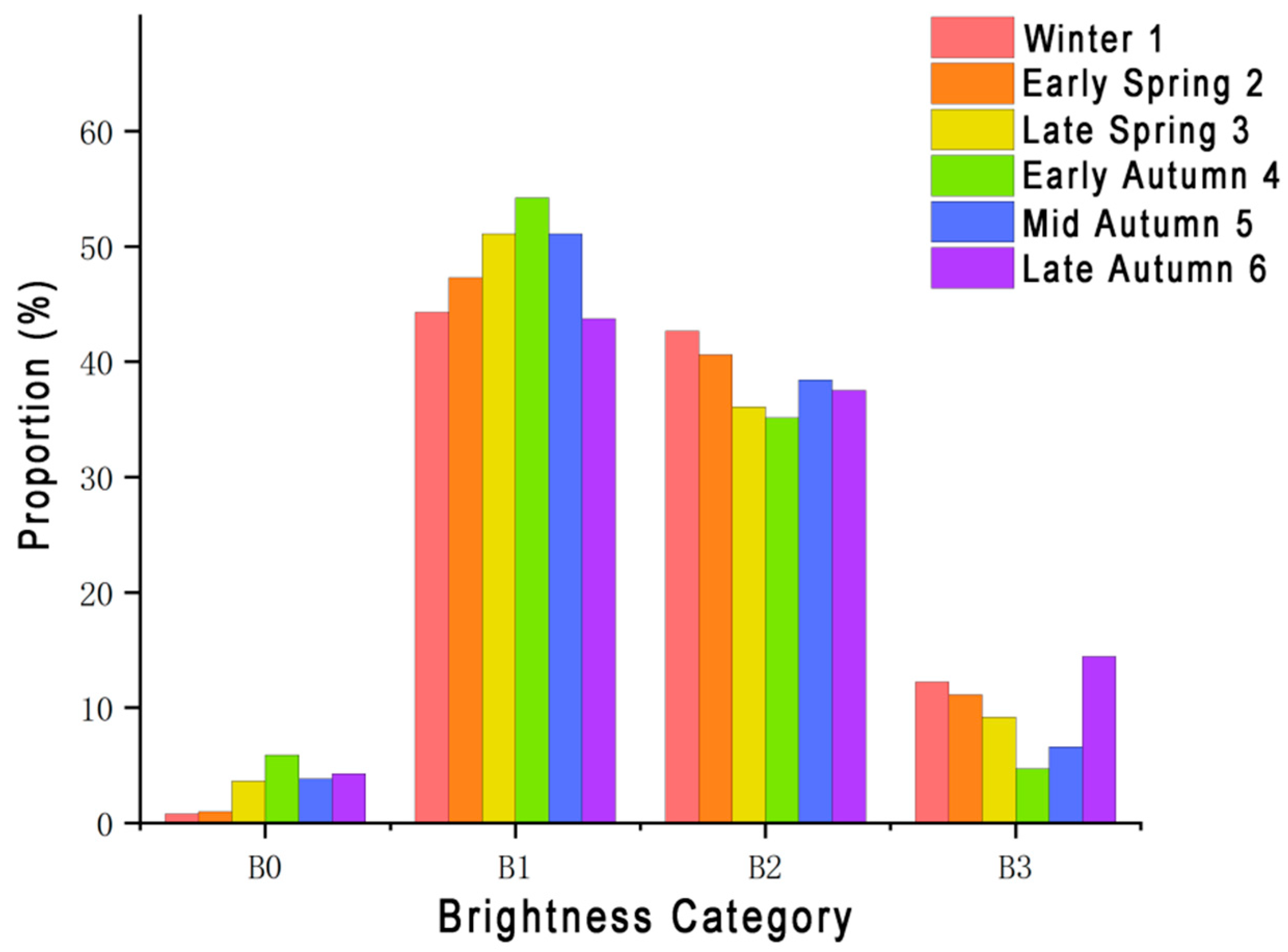
3.1.2. Saturation and Brightness
3.2. Scenic Beauty Estimation Results
3.2.1. Analysis of Questionnaire Results
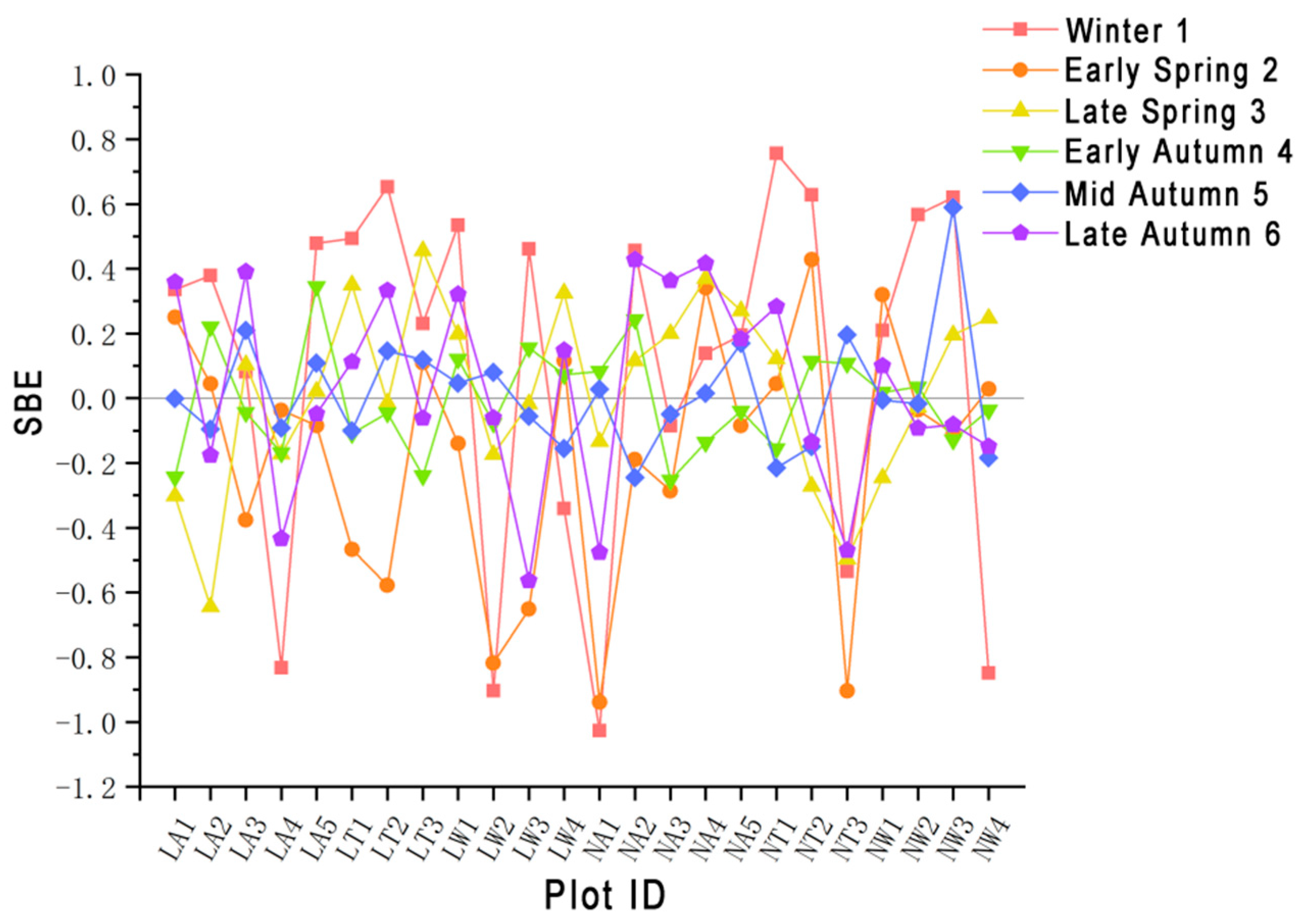
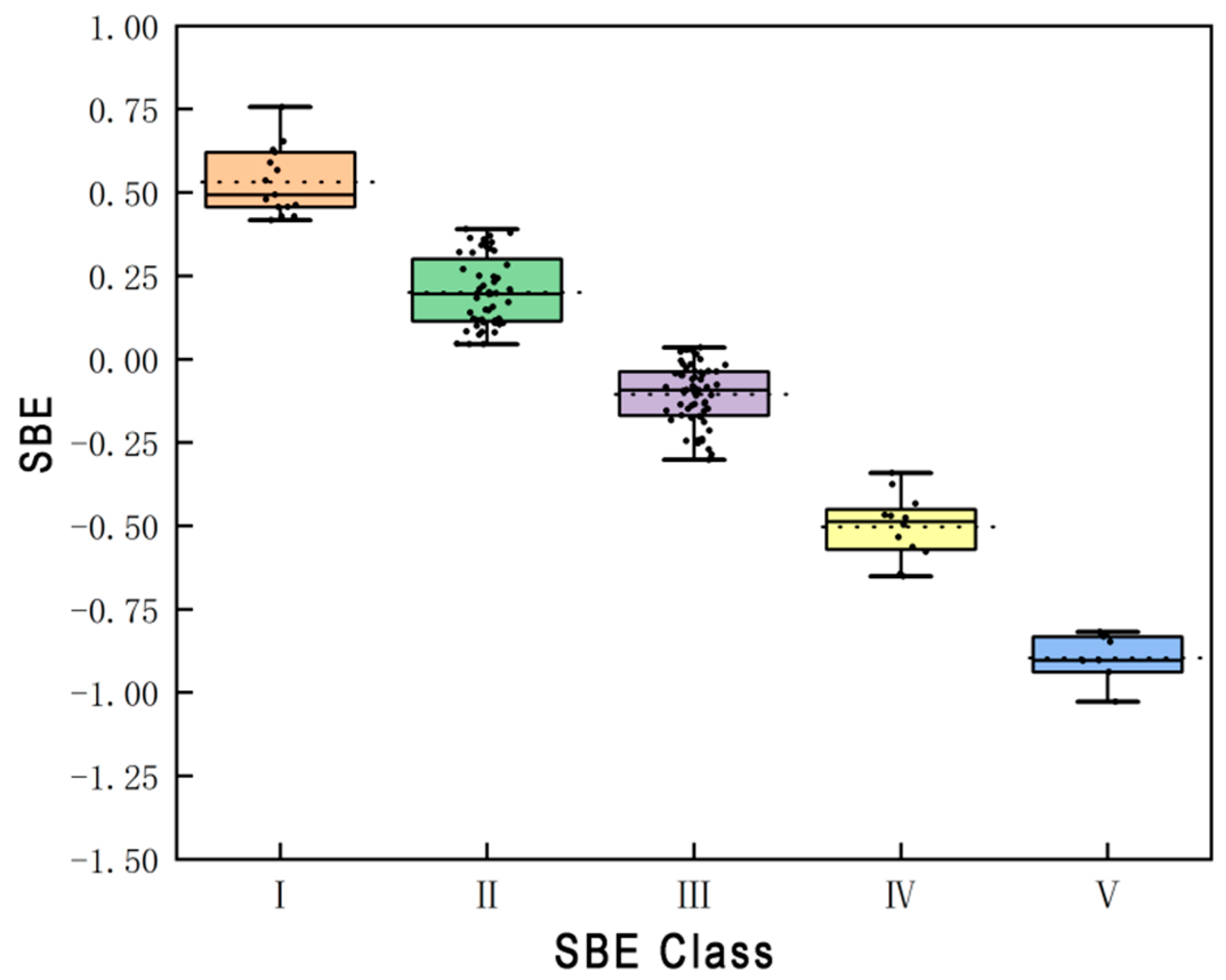
3.2.2. Analysis of SBE
3.3. Correlation Analysis Between Color Factor and Scenic Beauty Estimation
4. Discussion
4.1. Landscape Specificity in Climate Blunt Zones
4.2. Synergy Mechanisms Between Ecology and Aesthetics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, Y.; He, J.; Long, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L.; Tang, Z.; Li, C.; Xiong, X. The relationship between the color landscape characteristics of autumn plant communities and public aesthetics in urban parks in Changsha, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Hauer, R.J.; Xu, C. Effects of design proportion and distribution of color in urban and suburban green space planning to visual aesthetics quality. Forests 2020, 11, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahnema, S.; Sedaghathoor, S.; Allahyari, M.S.; Damalas, C.A.; El Bilali, H. Preferences and emotion perceptions of ornamental plant species for green space designing among urban park users in Iran. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 39, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y. Leaf color attributes of urban colored-leaf plants. Open Geosci. 2022, 14, 1591–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, M.; Li, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, W.; Sui, X.; Li, J.; Ma, J.; Li, Y. Evergreen or seasonal? Quantitative research on the color of urban scenic forests based on stress—Attention. Front. For. Glob. Change 2024, 7, 1495806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.Y.; Zhao, H.Y.; Xia, T.; Hong, L. Survey of Plant Landscapes on College Campuses in Cold Regions and Quantitative Analysis of Color. Mod. Hortic. 2023, 46, 22–25. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Gao, Y.; Ren, Q.; Ge, S.; Wang, B.; Du, C.; Liu, Y.; Kong, D. Evaluation of urban green space plant landscape quality in Zhengzhou city using the AHP-SBE method. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0329119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioana-Toroimac, G.; Zaharia, L.; Moroșanu, G.-A.; Grecu, F.; Hachemi, K. Assessment of restoration effects in Riparian wetlands using satellite imagery. Case study on the lower Danube River. Wetlands 2022, 42, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, I.; Zhang, C.; Alonso, L.; Fernández-Marín, B.; García-Plazaola, J.I.; Grebe, S.; Porcar-Castell, A.; Atherton, J. Hyperspectral Imaging Reveals Differential Carotenoid and Chlorophyll Temporal Dynamics and Spatial Patterns in Scots Pine Under Water Stress. Plant Cell Environ. 2025, 48, 1535–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Lin, W.; Diao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Lu, Z.; Guo, W.; Wang, Y.; Hu, C.; Zhao, C. Implementation of the visual aesthetic quality of slope forest autumn color change into the configuration of tree species. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Chen, J.; Li, Q.Y.; Liu, J.C.; Tao, J.P. Color quantification and evaluation of landscape aesthetic quality for autumn landscape forest based on visual characteristics in subalpine region of western Sichuan, China. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 45–54. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Grose, M.J. Green leaf colours in a suburban Australian hotspot: Colour differences exist between exotic trees from far afield compared with local species. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2016, 146, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Yao, Y.; Li, C. Quantitative study on landscape colors of plant communities in urban parks based on natural color system and M-S theory in Nanjing, China. Color Res. Appl. 2022, 47, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, W.J.; Huang, D.; Ma, X.L.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Guan, H.Y. Impact of Urban Waterfront Colorscape on Public Mental Health: A Case Study of the Dasha River Eco-Corridor in Shenzhen. J. Chin. Urban For. 2023, 21, 65–73+113. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Cai, J.G. Research Progress in Quantification of Plant Landscape Color. J. Chin. Urban For. 2022, 20, 134–139. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ye, S.Q.; Zhang, L.; Song, Y.H. Progress in Quantitative Research on Landscape Color. Mod. Hortic. 2024, 47, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, M.M.; Lang, P.J. Measuring emotion: The self-assessment manikin and the semantic differential. J. Behav. Ther. Exp. Psychiatry 1994, 25, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Mei, L.; Meng, Y.; Gao, W. Revealing the Relationship Between Urban Park Landscape Features and Visual Aesthetics by Deep Learning-Driven and Spatial Analysis. Buildings 2025, 15, 2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, G.; Lu, Y. Evaluation of urban wetland landscapes based on a comprehensive model—A comparative study of three urban wetlands in Hangzhou, China. Environ. Res. Commun. 2023, 5, 035004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, Y. The influence of visual and auditory environments in parks on visitors’ landscape preference, emotional state, and perceived restorativeness. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2024, 11, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neale, C.; Griffiths, A.; Pui, L.; Mendu, S.; Boukhechba, M.; Roe, J. Color aesthetics: A transatlantic comparison of psychological and physiological impacts of warm and cool colors in garden landscapes. Wellbeing Space Soc. 2021, 2, 100038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.E.; Yao, Y.; Peng, Q.Y. Study on the Seasonal Variations of the Climate in Low-Latitude Plateaus: A Case Study of Kunming and Dali in Yunnan Province. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2023, 39, 171–182. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Tan, M. The quantitative research of landscape color: A study of Ming Dynasty City Wall in Nanjing. Color Res. Appl. 2018, 43, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, T.C. Measuring Landscape Esthetics: The Scenic Beauty Estimation Method; Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Forest and Range Experiment Station: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1976; Volume 167, pp. 1–66. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, T.C. Whither scenic beauty? Visual landscape quality assessment in the 21st century. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2001, 54, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, B.; Gong, L.; Xu, C. Evaluating the scenic beauty of individual trees: A case study using a nonlinear model for a Pinus tabulaeformis scenic forest in Beijing, China. Forests 2015, 6, 1933–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.H.; Gu, X.; Chen, K.; Dong, F.L.; Zhang, L.G.; Jia, X. The status quo and trend of applying SBE in landscape evaluation. J. West China For. Sci. 2019, 48, 148–156. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Qie, G.; Wang, C.; Jiang, S.; Li, X.; Li, M. Relationship between forest color characteristics and scenic beauty: Case study analyzing pictures of mountainous forests at sloped positions in Jiuzhai Valley, China. Forests 2017, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qian, J.; Cao, J.; Fan, R.; Han, X. Quantitative analysis and evaluation of winter and summer landscape colors in the Yangzhou ancient Canal utilizing deep learning. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.W.; Cai, J.G.; Shu, M.Y. A quantitative study on plant color in the autumn plant community of west lake, Hangzhou. J. Anhui Agric. Univ. 2022, 49, 56–61. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fairchild, M.D. Color Appearance Models; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Z.; Fuzong, L.; Bo, Z. A CBIR method based on color-spatial feature. In Proceedings of the IEEE Region 10 Conference, TENCON 99, ‘Multimedia Technology for Asia-Pacific Information Infrastructure’ (Cat. No.99CH37030), Cheju Island, Republic of Korea, 15–17 September 1999; pp. 166–169. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Huang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Fu, W.; Yao, X.; Huang, J.; Lan, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Dong, J. How vegetation colorization design affects urban Forest aesthetic preference and visual attention: An eye-tracking study. Forests 2023, 14, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Lin, G. Retrieval technique of color image based on color features. J. XiDian Univ. 2002, 29, 43–46. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, B.; Xu, C.; Cui, Y. Effects of color composition in badaling forests on autumn landscape quality. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2018, 33, 258–264. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Xu, B.; Devereux, B. Assessing public aesthetic preferences towards some urban landscape patterns: The case study of two different geographic groups. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasser, E.; Lavdas, A.A.; Schirpke, U. Assessing landscape aesthetic values: Do clouds in photographs influence people’s preferences? PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0288424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zanten, B.T.; Zasada, I.; Koetse, M.J.; Ungaro, F.; Häfner, K.; Verburg, P.H. A comparative approach to assess the contribution of landscape features to aesthetic and recreational values in agricultural landscapes. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 17, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Z. Consensus in visual preferences: The effects of aesthetic quality and landscape types. Urban For. Urban Green. 2016, 20, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirpke, U.; Mölk, F.; Feilhauer, E.; Tappeiner, U.; Tappeiner, G. How suitable are discrete choice experiments based on landscape indicators for estimating landscape preferences? Landsc. Urban Plan. 2023, 237, 104813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieskens, K.F.; Van Zanten, B.T.; Schulp, C.J.; Verburg, P.H. Aesthetic appreciation of the cultural landscape through social media: An analysis of revealed preference in the Dutch river landscape. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2018, 177, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Y. Study on the Landscape Evaluation and Optimization of Urban Mountain Park: A Case Study in Fuzhou Jinjishan Park. Master’s Thesis, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, Fuzhou, China, 2020. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Han, W.; Zhang, C.; Wang, C.; Yin, L. Constructing a forest color palette and the effects of the color patch index on human eye recognition accuracy. Forests 2023, 14, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Luo, P.; Yang, H.; Luo, C.; Li, H.; Wu, S.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Xie, W. Exploring the relationship between forest scenic beauty with color index and ecological integrity: Case study of Jiuzhaigou and Giant Panda National Park in Sichuan, China. Forests 2022, 13, 1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Mu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Diao, X.; Lu, Z.; Guo, W.; Wang, Y.; Xu, B. Research on cognitive evaluation of forest color based on visual behavior experiments and landscape preference. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0276677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spellerberg, I.F.; Fedor, P.J. A tribute to Claude Shannon (1916–2001) and a plea for more rigorous use of species richness, species diversity and the ‘Shannon–Wiener’Index. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2003, 12, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puglielli, G. Beyond the concept of winter-summer leaves of mediterranean seasonal dimorphic species. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.D.; Li, H.M.; Jin, Y.L.; Shi, Y.; Bao, Z.Y. Study on the diversity and community composition of spontaneous vegetation in herb layer in Hangzhou Xixi National Wetland Park. Zhejiang For. Sci. Technol. 2021, 41, 24–31. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, J. Effect of the urbanization of wetlands on microclimate: A case study of Xixi Wetland, Hangzhou, China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Dong, J.; He, Q.; Ye, B. The temporal variation of the microclimate and human thermal comfort in urban wetland parks: A case study of Xixi National Wetland Park, China. Forests 2021, 12, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussotti, F.; Pollastrini, M. Opportunities and threats of Mediterranean evergreen sclerophyllous woody species subjected to extreme drought events. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhu, L.; Xu, Q.; Lundgren, M.R.; Yang, K.; Zhao, P.; Ye, Q. Ecophysiological responses of two closely related Magnoliaceae genera to seasonal changes in subtropical China. J. Plant Ecol. 2018, 11, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemu, J.B.; Richards, D.R.; Gaw, L.Y.-F.; Masoudi, M.; Nathan, Y.; Friess, D.A. Identifying spatial patterns and interactions among multiple ecosystem services in an urban mangrove landscape. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friess, D.A.; Richards, D.R.; Phang, V.X. Mangrove forests store high densities of carbon across the tropical urban landscape of Singapore. Urban Ecosyst. 2016, 19, 795–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dronova, I.; Taddeo, S.; Harris, K. Plant diversity reduces satellite-observed phenological variability in wetlands at a national scale. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabl8214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, T.; Goldstein, J. Amphibious Land Repair: Restoration, Infrastructure and Accumulation in Southeast Asia’s Wetlands. Environ. Soc. 2024, 15, 110–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Mateos, D.; Power, M.E.; Comín, F.A.; Yockteng, R. Structural and functional loss in restored wetland ecosystems. PLoS Biol. 2012, 10, e1001247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, J.T. Wetlands in Europe: Perspectives for restoration of a lost paradise. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 66, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Evaluation Groups | Number of Questionnaires Collected | SBE Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Minimum | Average ± Standard Deviation | ||
| Related Professionals | 251 | 0.847 | −1.125 | 0.000 ± 0.523 |
| Non-professionals | 312 | 0.672 | −0.935 | 0.000 ± 0.491 |
| All Respondents | 563 | 0.756 | −1.027 | 0.000 ± 0.507 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Jiang, L.; Chen, D.; Wei, W.; Lawson, G. Seasonal Color Dynamics and Visual Aesthetic Perception in Subtropical Wetland Parks: A Climate-Adaptive Design Framework. Sustainability 2026, 18, 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/su18010386
Jiang L, Chen D, Wei W, Lawson G. Seasonal Color Dynamics and Visual Aesthetic Perception in Subtropical Wetland Parks: A Climate-Adaptive Design Framework. Sustainability. 2026; 18(1):386. https://doi.org/10.3390/su18010386
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Lanxi, Damei Chen, Wen Wei, and Gillian Lawson. 2026. "Seasonal Color Dynamics and Visual Aesthetic Perception in Subtropical Wetland Parks: A Climate-Adaptive Design Framework" Sustainability 18, no. 1: 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/su18010386
APA StyleJiang, L., Chen, D., Wei, W., & Lawson, G. (2026). Seasonal Color Dynamics and Visual Aesthetic Perception in Subtropical Wetland Parks: A Climate-Adaptive Design Framework. Sustainability, 18(1), 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/su18010386







