Assessing Groundwater Sustainability in Siwa Oasis, Egypt: Evaluating Physico-Chemical and Hydrochemical Suitability for Human and Agricultural Use
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Sampling Program and Water Sampling
2.3. Chemical Analysis
2.4. Water Quality and Irrigation Indices
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physico-Chemical Properties
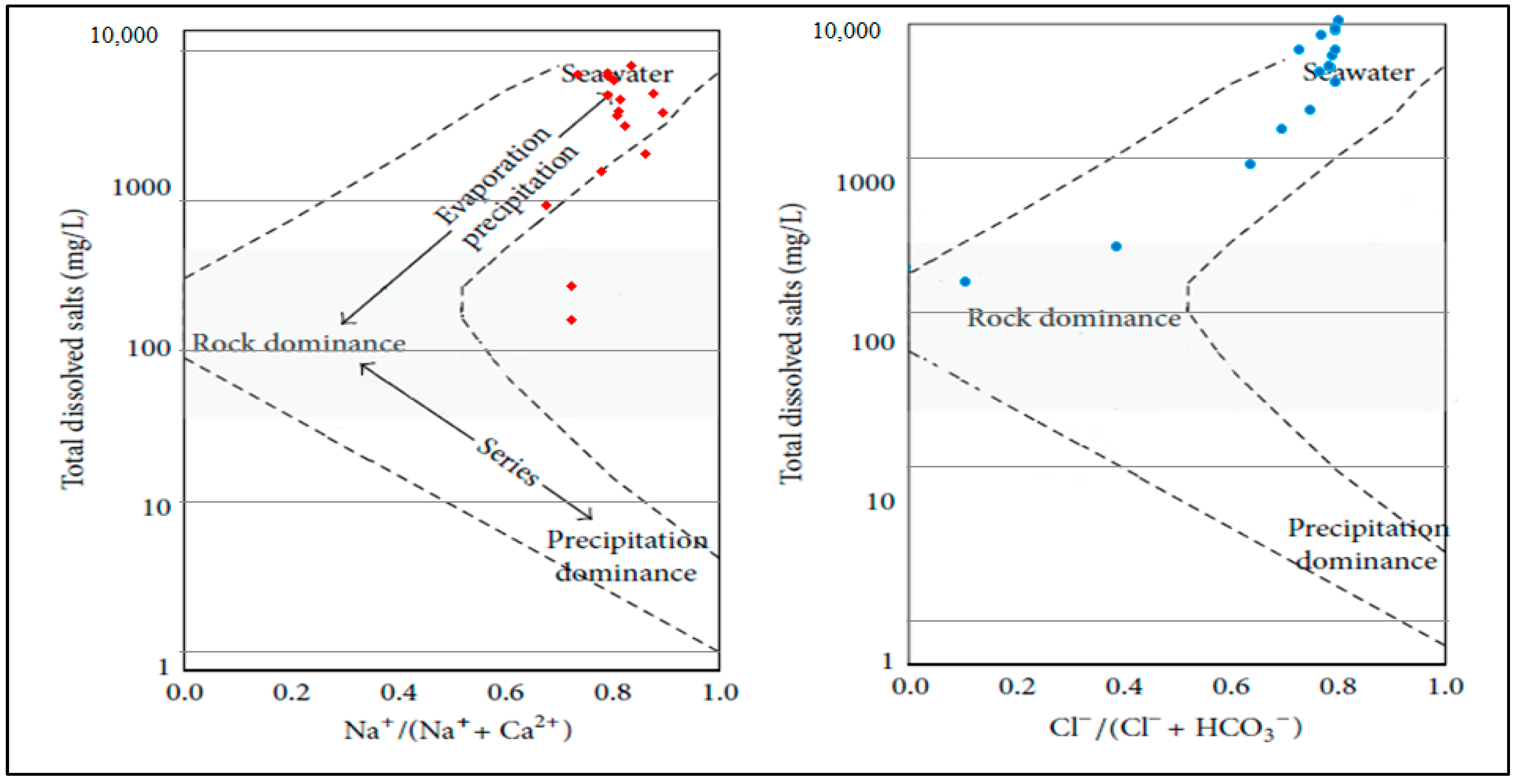
3.2. Hydrogeochemical Criteria of Groundwater
3.3. Water Quality Assessment for Drinking Water
3.4. Hydrogeochemical Types and Evaluation of Groundwater
3.5. Water Quality Assessment for Irrigation Uses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davraz, A.; Batur, B. Hydrogeochemistry characteristics of groundwater and health risk assessment in Yalvaç–Gelendost basin (Turkey). Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemer, H.; Wald, S.; Semiat, R. Challenges and solutions for global water scarcity. Membranes 2023, 13, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Xu, X.; Su, Q.; Wang, S.; Qu, W.; Xing, T. Hydrogeochemical processes and suitability assessment of groundwater in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, R.; Li, Z.; Guo, S. Health risks of shallow groundwater in the five basins of Shanxi, China, Geographical, geological and human activity roles. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 316, 120524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, A.; Gad, A.; Ahmed, A.; Arman, H.; Farhat, H.I. Groundwater Hydrochemical Characteristics and Water Quality in Egypt’s Central Eastern Desert. Water 2023, 15, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahir, M.; Ouazar, D.; Ouhamdouch, S.; Zouari, K. Assessment of groundwater mineralization of alluvial coastal aquifer of essaouira basin (Morocco) using the hydrochemical facies evolution diagram (HFE-Diagram). Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 11, 100487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, A.; Bi, J.; Liu, Y. Source and Enrichment Mechanism of Fluoride in Groundwater of the Hotan Oasis within the Tarim Basin, Northwestern China. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 300, 118962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyika, J.; Magnone, D.; Gould, I. Groundwater salinization challenges in agriculturally valuable low-lying North Sea region: A review. Clean. Water 2024, 2, 100052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Mwiathi, N.F.; Li, C.; Luo, W.; Zhang, X.; An, Y.; Zhang, M.; Gong, P.; Liu, J.; Gao, X. Assessment of shallow aquifer vulnerability to fluoride contamination using modified AHP-DRASTICH model as a tool for effective groundwater management, a case study in Yuncheng Basin, China. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Hao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Yin, S.; Qin, L.; Li, X. Investigating sources, driving forces and potential health risks of nitrate and fluoride in groundwater of a typical alluvial fan plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 802, 149909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, N.; Tyagi, S.; Rawtani, D.; Tharmavaram, M.; Kamboj, R.D. Analysis and assessment of ground water quality in Satlasana Taluka, Mehsana district, Gujarat, India through application of water quality indices. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 10, 100321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Liu, Q.; Peng, W.; Liu, X. Source apportionment and natural background levels of major ions in shallow groundwater using multivariate statistical method, a case study in Huaibei Plain, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 301, 113806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Kang, W.; Li, Y.; Li, Z. Fluoride and nitrate contamination of groundwater in the Loess Plateau, China, sources and related human health risks. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 286, 117287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, Q.; Ma, H.; Liang, J. Chemical compositions evolution of groundwater and its pollution characterization due to agricultural activities in Yinchuan Plain, northwest China. Environ. Res. 2021, 200, 111449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinklebe, J.; Antoniadis, V.; Shaheen, S.M.; Rosche, O.; Altermann, M. Health risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in soils along the Central Elbe River, Germany. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnazer, A.A.; Salman, S.A.; Mohamed, Y.M.; Stafford, J.; Davies, P.; El Nazer, H.A. Siwa Oasis groundwater quality, factors controlling spatial and temporal changes. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salman, S.A.; Abu El Ella, E.M.; Seleem, E.M.; Elnazer, A.A. Groundwater quality and environmental investigations in Siwa Oasis, Egypt. Int. J. Recent Adv. Multidiscip. Res. 2018, 5, 3951–3958. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelkarim, M.S.; Ali, M.H.; Othman, A.A.; Gaber, K.M.; Mahmoud, A.M.; Belal, D. Evaluation of microbiological criteria, planktonic communities and trophic state of groundwater resources in Siwa Oasis, Western Desert, Egypt. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 31090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandan, A.; John, M.; Potdar, V. Achieving UN SDGs in food supply chain using blockchain technology. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoud, A.; Koike, K. Tectonic architecture through Landsat-7 ETM+/SRTM DEM-derived lineaments and relationship to the hydrogeologic setting in Siwa region, NW Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2006, 45, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Gawad, A.M.; El Abd, E.A.; Gedamy, Y.R. Geological characteristics of shallow groundwater aquifer and its relation to hydrochemical features and bacteriological pollutants in Siwa Oasis Egypt. Int. J. Environ. 2020, 9, 17–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.A. Studies On Groundwater Possibilities in the Northern Part of the Western Desert-Egypt. Ph.D. Thesis, Cairo University, Cairo, Egypt, 1991; p. 292. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulaziz, M.A.; Faid, A.M. Evaluation of the groundwater resources potential of Siwa Oasis using three-dimensional multilayer groundwater flow model, Mersa Matruh Governorate, Egypt. Arab. J. Geosci. 2013, 8, 659–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheikh, A.E.; Mohallel, S.A.; Ezzeldin, H.A.; El Ammawy, M.A.; Lateif, R.M.A. Hydrogeological and hydrogeochemical insights on the salinization of the shallow groundwater aquifer in Siwa Oasis–Western Desert–Egypt. Sci. Afr. 2023, 20, e01742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association (APHA). Standard Methods of the Examination of Water and Waste Water, 23th rd. ed; AWWA: Denver, CO, USA; WPC: College Park, MD, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-0-87553-287-5. [Google Scholar]
- CCME Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment. Canadian water quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life, Water Quality Index 1.0, User’s Manual. In Canadian Environmental Quality Guidelines, 1999; Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment: Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ott, W. Environmental Indices, Theory and Practice; Ann Arbor Science Publishers, Inc.: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Matthes, G. The Properties of Groundwater; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Schoeller, H. Qualitative Evaluation of Groundwater Resources (In Methods and Techniques of Groundwater Investigation and Development. Water Resour. Ser. 1967, 33, 44–52. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, L.A. Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkali Soils. In US Dept Agriculture Handbook # 60; Supt. Documents; U. S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox, L.V. The quality of water for irrigation use. US Dep. Agric. Technol. Bull. 1948, 40, 962. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- Abdelkarim, M.S.; Belal, D.M.; Flefil, N.S.; Hegab, M.H.; Mahmoud, A.M.; Al-Afify, A.D.; Aly, W.; Ali, M.H. Ecosystem and Commercializing of Fish in a Rich-Minerals, Low-Salinity Closed Lake. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.M.; Ali, M.H.; Abdelkarim, M.S.; Al-Afify, A.D. Chemical, biochemical, and bioactivity studies on some soda lakes, Wadi El-Natrun, Egypt. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, D.K. Groundwater Hydrology; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Goher, M.E.; Ali, M.H. Monitoring of water quality characteristics and some heavy metals in water, sediment and macrophytes in Main Khors of Lake Nasser Egypt. J. Egypt. Acad. Soc. Environ. Dev. 2009, 10, 109–122. [Google Scholar]
- Krishna Kumar, S.; Bharani, R.; Magesh, N.S.; Godson, P.S.; Chandrasekar, N. Hydrogeochemistry and groundwater quality appraisal of part of south Chennai coastal aquifers, Tamil Nadu, India using WQI and fuzzy logic method. Appl. Water Sci. 2014, 4, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, N.S. Nitrate pollution and its distribution in the groundwater of Srikakulam district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ. Geol. 2006, 51, 631–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, T.; Rajmohan, N.; Elango, L. Groundwater geochemistry and identification of hydrogeochemical processes in a hard rock region, Southern India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 162, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stallard, R.F.; Edmond, J.M. Geochemistry of the Amazon, the influence of geology and weathering environment on the dissolved load. J. Geophys. Res. 1983, 88, 9671–9688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Wu, H.; Qian, H.; Gao, Y.Y. Groundwater chemistry regulated by hydrochemical processes and geological structures, a case study in Tongchuan, China. Water 2018, 10, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelo, C.A.J.; Postma, D. Geochemistry, Groundwater and Pollution; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.H.; Abdelkarim, M.S.; Salem, S.G.; Al-Afify, A.D. Integrated Evaluation of Potential Trace Elements and Pollution Indices in Wadi El-Natrun Saline Lake, Egypt: A Multidimensional Approach to Aquatic Ecosystem Health. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2025, 236, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, S.N.; DeWiest, R.J.M. Hydrogeology; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1966; 463p. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, F. Evaluation of hydrogeochemical parameters of groundwater for suitability of domestic and irrigational purposes, a case study from central Ganga Plain, India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 4121–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H.A.; Ricka, A.; Kuchovsky, T.; El Osta, M.M. Groundwater hydrochemistry and origin in the south-eastern part of Wadi El Natrun, Egypt. Arab. J. Geosci. 2017, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, A.M. A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1944, 256, 914–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Omran, A.M.; Aly, A.A.; Al-Wabel, M.I.; Sallam, A.S.; Al-Shayaa, M.S. Hydrochemical characterization of groundwater under agricultural land in arid environment, a case study of Al-Kharj, Saudi Arabia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wu, X.; Qian, C.; Zhu, G. Hydrogeochemistry and groundwater quality assessment of high fluoride levels in the Yanchi endorheic region, northwest China. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 98, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamma Rao, G.; Gurunadha Rao, V.V.; Srinivasa Rao, Y.; Ramesh, G. Study of hydrogeochemical processes of the groundwater in Ghatprabha river sub-basin, Bagalkot District, Karnataka, India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2013, 6, 2447–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunkari, E.D.; Abu, M.; Zango, M.S. Geochemical evolution and tracing of groundwater salinization using different ionic ratios, multivariate statistical and geochemical modelling approaches in a typical semi-arid basin. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2021, 236, 103742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salifu, M.; Aidoo, F.; Hayford, M.S.; Adomako, D.; Asare, E. Evaluating the suitability of groundwater for irrigational purposes in some selected districts of the Upper West region of Ghana. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Feng, W.; Qian, H.; Zhang, Q. Hydrogeochemical characterization and irrigation quality assessment of shallow groundwater in the Central-Western Guanzhong Basin, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Liu, J.; Feng, J.; Wang, M.; Wu, G. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and the suitability of groundwater in the alluvial-diluvial plain of southwest Shandong Province, China. Water 2019, 11, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, R.S.; Westcott, D.W. Water Quality for Agriculture (No. 29); Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Kawo, N.S.; Karuppannan, S. Groundwater quality assessment using water quality index and GIS technique in Modjo River Basin, central Ethiopia. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2018, 147, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fipps, G. Irrigation Water Quality Standards and Salinity Management Strategies; B-1667, 4-03; Texas Agricultural Extension Service; Texas A&M University System: College Station, TX, USA, 2003; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]







| Feature Category | Specific Formation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| a. Morphological Structure | Siwa Depression | A deep, elongated tectonic depression lying approximately 23 m. below sea level. |
| Boundary | Isolated hills of Eocene–Miocene limestone and Limestone cliffs (e.g., Jabal Al-Mawta and Aghormi ridge). | |
| b. Geological Framework | Stratigraphy | 1. Moghra Formation (Lower Miocene): Sandstone aquifer. 2. Limestone: Fractured carbonate aquifer. 3. Nubian sandstone: Deep fossil aquifer. 4. Quaternary deposits: Surface sabkha salts, silts, and sands. |
| c. Hydrological System | Aquifers | 1. Carbonate aquifer: Shallow, fractured limestone. 2. Nubian sandstone Aquifer: non-renewable fossil water. 3. Moghra aquifer: Intermediate, mixed fossil/renewable water. 4. Quaternary aquifer: Local, shallow, and saline. |
| Natural Springs | Discharge points along faults from carbonate aquifers. | |
| Salt Lakes | (Al-Markki, Aghormi, Siwa, and Zeitun, Lakes), hypersaline waterbodies. Receive discharge from spring and subsurface flow. | |
| d. Surface Morphology | Sabkhas | Saline plains surrounding lakes. Formed from clay, silt, and evaporites (halite and gypsum). |
| Great Sand Sea | Expanse dune forms, boundary of the depression, effectively isolated the oasis. | |
| Linear Seif Dunes | Periphery dunes, with nabkhas (shrub-coppice dunes) | |
| e. Anthropogenic and Cultivated Land | Cultivation land | Elevated land parcels. Their soil is composed of a mix of ancient Nile silt, organic matter, and sand. |
| Springs | Human-made hillocks from centuries of clearing spring canals. | |
| Irrigation and Drainage Network | Man-made canals distribute spring water; drainage ditches divert saline water to lakes, managing soil salinity. |
| Sample No. | Native Name | Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drains | |||
| D1 | El Qarabeen El Omumy Drain | 29°12′33.8″ | 25°30′16.2″ |
| D2 | Gheet El Khalel Drain | 29°11′37.0″ | 25°34′06.7″ |
| D3 | El-Omumy Drain | 29°10′05.7″ | 25°45′44.9″ |
| Wells | |||
| W01 | Telwa | 29°13′58.7″ | 25°28′41.9″ |
| W02 | Kharafala | 29°14′19.9″ | 25°30′33.8″ |
| W03 | Mohamed Belal | 29°10′58.1″ | 25°29′30.6″ |
| W04 | El-Shaheem | 29°10′51.6″ | 25°29′43.9″ |
| W05 | Tegzerti I | 29°11′14.6″ | 25°29′43.3″ |
| W06 | Tegzerti II | 29°11′14.9″ | 25°29′41.6″ |
| W07 | Fentas | 29°12′01.1″ | 25°30′46.4″ |
| W08 | Cleopatra II | 29°11′42.5″ | 25°32′47.3″ |
| W09 | Telham | 29°11′44.9″ | 25°32′58.6″ |
| W10 | Cleopatra I | 29°11′54.1″ | 25°33′00.2″ |
| W11 | El-Molouk | 29°11′04.9″ | 25°33′15.8″ |
| W12 | Korisht I | 29°12′38.9″ | 25°42′21.2″ |
| W13 | Korisht II | 29°12′24.5″ | 25°42′42.2″ |
| W14 | El-Naqb I | 29°10′35.7″ | 25°45′48.4″ |
| W15 | El-Naqb II | 29°10′43.8″ | 25°46′09.8″ |
| W16 | Hayat | 29°08′39.0″ | 25°43′59.1″ |
| W17 | Zeitoun | 29°09′53.5″ | 25°47′16.8″ |
| Index | Equation | Range | Water classes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water quality index for drinking water | ||||
| CCME-WQI | Equation (1) F1 (scope): The percentage of parameters that exceed the allowable limit F2 (frequency): The percentage of individual tests for each parameter that exceeded the allowable limit F3 (amplitude): The degree to which each failed test exceeds the allowable limit | 91–100 71–90 51–70 26–50 0–25 | Excellent Good Medium Bad Very bad | [26] |
| NSF WQI | Equation (2) Wi = Weight of each assigned parameter i | 91–100 71–90 51–70 26–50 0–25 | Excellent Good Medium Bad Very bad | [27] |
| Water indices for geochemical processes | ||||
| Base-exchange index (r1) | Equation (3) | r1 < 1 r1 > 1 | The water is Na+ − SO42− type The water is Na+ − HCO3− type | [28] |
| Meteoric-genesis index (r2) | Equation (4) | r2 < 1 r2 > 1 | Deeper percolation of meteoric water and, hence, longer residence time indicate that meteoric water percolation was up to shallow levels | [28] |
| Chloro-alkaline index (CAI-I) | Equation (5) | CAI > 0 CAI < 0 | Na+ or K+ is replaced by Ca2+ from water to sediment Ca2+ is replaced by Na+ or K+ from water to sediment | [29] |
| Chloro-alkaline index (CAI-II) | Equation (6) | CAI > 0 CAI < 0 | Na+ or K+ is replaced by Ca2+ from water to sediment Ca2+ is replaced by Na+ or K+ from water to sediment | [29] |
| Water quality indices for irrigation | ||||
| Sodium adsorption ratio (SAR) | Equation (7) | <10 10–18 18–26 L >26 | Excellent Good Doubtful Unsuitable | [30] |
| Soluble sodium percentage (Na%) | Equation (8) | <20 20–40 40–60 60–80 >80 | Excellent Good Permissible Doubtful Unsuitable | [31] |
| pH | Temp. (°C) | EC mS/cm | Sal (‰) | Turb. (NTU) | TDS (g/L) | DO mg/L | BOD mg/L | COD mg/L | NO2− µg/L | NO3− µg/L | NH4+ µg/L | PO43− µg/L | TP µg/L | SiO2 mg/L | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agricultural Drains | |||||||||||||||
| D1 | 7.81 ± 0.41 | 19.03 ± 1 | 14.44 ± 0.76 | 8.73 ± 0.46 | 4.56 ± 0.24 | 9.55 ± 0.5 | 2.49 ± 0.13 | 1.87 ± 0.1 | 12.44 ± 0.65 | 17.52 ± 0.92 | 216.3 ± 11.35 | 233.6 ± 12.2 | 249.3 ± 13.0 | 1246.8 ± 65.4 | 6.7 ± 0.36 |
| D2 | 8.03 ± 0.42 | 18.56 ± 0.97 | 16.94 ± 0.89 | 9.98 ± 0.52 | 1.24 ± 0.07 | 10.62 ± 0.56 | 4.15 ± 0.22 | 1.87 ± 0.1 | 5.18 ± 0.27 | 4.67 ± 0.24 | 502.1 ± 26.35 | 29.9 ± 1.57 | 213.7 ± 11.2 | 1068.3 ± 56.0 | 8.6 ± 0.47 |
| D3 | 8.09 ± 0.42 | 18.46 ± 0.97 | 11.73 ± 0.62 | 6.59 ± 0.35 | 1.24 ± 0.07 | 7.02 ± 0.37 | 6.22 ± 0.33 | 2.07 ± 0.11 | 2.7 ± 0.14 | 6.32 ± 0.33 | 904.7 ± 47.48 | 57 ± 2.99 | 227.6 ± 11.9 | 1137.9 ± 59.7 | 7.5 ± 0.41 |
| Groundwater Wells | |||||||||||||||
| W01 | 7.93 ± 0.42 | 24.47 ± 1.28 | 8.56 ± 0.45 | 4.76 ± 0.25 | 0.31 ± 0.02 | 4.91 ± 0.26 | 2.9 ± 0.15 | 1.66 ± 0.09 | 16.79 ± 0.88 | 2.9 ± 0.15 | 201.2 ± 10.56 | 152.5 ± 8 | 124.1 ± 6.51 | 620.4 ± 32.56 | 1.1 ± 0.06 |
| W02 | 8.00 ± 0.42 | 26.76 ± 1.4 | 6.94 ± 0.36 | 3.73 ± 0.2 | 4.56 ± 0.24 | 4.05 ± 0.21 | 4.56 ± 0.24 | 1.45 ± 0.08 | 9.33 ± 0.49 | 3.63 ± 0.19 | 260.2 ± 13.66 | 67.1 ± 3.52 | 90.9 ± 4.77 | 454.6 ± 23.86 | 2 ± 0.11 |
| W03 | 8.24 ± 0.43 | 27.75 ± 1.46 | 1.77 ± 0.09 | 0.89 ± 0.05 | 1.04 ± 0.05 | 0.96 ± 0.05 | 4.15 ± 0.22 | 2.28 ± 0.12 | 4.77 ± 0.25 | 7.15 ± 0.38 | 315.7 ± 16.57 | 47 ± 2.46 | 26 ± 1.37 | 129.9 ± 6.82 | 2.6 ± 0.14 |
| W04 | 8.11 ± 0.42 | 19.02 ± 1 | 8.78 ± 0.46 | 4.91 ± 0.26 | 2.9 ± 0.15 | 5.31 ± 0.28 | 3.32 ± 0.17 | 1.45 ± 0.08 | 4.77 ± 0.25 | 5.08 ± 0.27 | 245.5 ± 12.88 | 117.5 ± 6.16 | 115.1 ± 6.04 | 575.4 ± 30.2 | 1 ± 0.05 |
| W05 | 7.98 ± 0.42 | 18.4 ± 0.97 | 7.14 ± 0.37 | 3.52 ± 0.18 | 5.39 ± 0.28 | 3.87 ± 0.2 | 3.73 ± 0.2 | 1.66 ± 0.09 | 7.46 ± 0.39 | 7.26 ± 0.38 | 294.4 ± 15.45 | 48.3 ± 2.54 | 120.6 ± 6.33 | 603 ± 31.64 | 3.2 ± 0.17 |
| W06 | 8.03 ± 0.42 | 17.13 ± 0.9 | 10.74 ± 0.56 | 6.01 ± 0.32 | 4.77 ± 0.25 | 6.56 ± 0.34 | 3.73 ± 0.2 | 1.24 ± 0.07 | 12.23 ± 0.64 | 4.87 ± 0.26 | 219.3 ± 11.51 | 48.7 ± 2.56 | 193 ± 10.13 | 965.1 ± 50.65 | 4.2 ± 0.23 |
| W07 | 7.06 ± 0.37 | 24.53 ± 1.29 | 6.81 ± 0.36 | 3.73 ± 0.2 | 2.38 ± 0.13 | 4.14 ± 0.22 | 3.32 ± 0.17 | 1.66 ± 0.09 | 18.87 ± 0.99 | 3.94 ± 0.21 | 240.4 ± 12.62 | 285.3 ± 14.9 | 111.2 ± 5.84 | 556.1 ± 29.18 | 2.7 ± 0.15 |
| W08 | 8.08 ± 0.42 | 16.6 ± 0.87 | 8.75 ± 0.46 | 4.9 ± 0.26 | 1.04 ± 0.05 | 5.35 ± 0.28 | 3.73 ± 0.2 | 1.04 ± 0.05 | 8.92 ± 0.47 | 2.28 ± 0.12 | 1104.5 ± 57.9 | 25.2 ± 1.32 | 186.3 ± 9.78 | 931.6 ± 48.89 | 7 ± 0.38 |
| W09 | 8.11 ± 0.43 | 25.42 ± 1.33 | 3.32 ± 0.17 | 1.73 ± 0.09 | 0.52 ± 0.03 | 2.16 ± 0.11 | 2.49 ± 0.13 | 1.24 ± 0.07 | 11.2 ± 0.59 | 1.87 ± 0.1 | 230.6 ± 12.1 | 84.1 ± 4.41 | 91.5 ± 4.8 | 457.9 ± 24.03 | 2.5 ± 0.14 |
| W10 | 8.53 ± 0.45 | 19.26 ± 1.01 | 5.34 ± 0.28 | 2.89 ± 0.15 | 1.04 ± 0.05 | 3.27 ± 0.17 | 4.15 ± 0.22 | 0.83 ± 0.04 | 7.88 ± 0.41 | 3.84 ± 0.2 | 175.5 ± 9.21 | 43 ± 2.26 | 92.6 ± 4.86 | 463 ± 24.3 | 3 ± 0.16 |
| W11 | 8.21 ± 0.43 | 25.83 ± 1.36 | 2.79 ± 0.15 | 1.44 ± 0.08 | 2.8 ± 0.15 | 1.64 ± 0.09 | 2.9 ± 0.15 | 1.24 ± 0.07 | 10.99 ± 0.58 | 2.49 ± 0.13 | 466.4 ± 24.48 | 72.9 ± 3.82 | 73.6 ± 3.86 | 368 ± 19.31 | 2.7 ± 0.15 |
| W12 | 8.75 ± 0.48 | 19.34 ± 1.02 | 0.52 ± 0.03 | 0.25 ± 0.01 | 13.58 ± 0.71 | 0.28 ± 0.01 | 3.32 ± 0.17 | 1.24 ± 0.07 | 5.6 ± 0.29 | 6.01 ± 0.32 | 390 ± 20.47 | 66.8 ± 3.5 | 9.3 ± 0.49 | 46.4 ± 2.44 | 3.8 ± 0.21 |
| W13 | 7.71 ± 0.4 | 27.1 ± 1.42 | 13.45 ± 0.71 | 7.73 ± 0.41 | 0.31 ± 0.02 | 8.21 ± 0.43 | 2.49 ± 0.13 | 1.45 ± 0.08 | 6.01 ± 0.32 | 1.87 ± 0.1 | 188.5 ± 9.89 | 50.7 ± 2.66 | 202.2 ± 10.6 | 1011 ± 53.06 | 2.9 ± 0.16 |
| W14 | 7.76 ± 0.41 | 24.79 ± 1.3 | 12.18 ± 0.64 | 6.95 ± 0.36 | 0.62 ± 0.03 | 7.44 ± 0.39 | 1.66 ± 0.09 | 1.24 ± 0.07 | 0.62 ± 0.03 | 5.6 ± 0.29 | 857.8 ± 45.02 | 53.8 ± 2.82 | 204.8 ± 10.7 | 1023.6 ± 53.7 | 1.8 ± 0.1 |
| W15 | 7.98 ± 0.42 | 23.11 ± 1.21 | 11.91 ± 0.63 | 6.59 ± 0.35 | 1.14 ± 0.06 | 7.13 ± 0.37 | 2.49 ± 0.13 | 1.24 ± 0.07 | 10.57 ± 0.55 | 7.98 ± 0.42 | 597.4 ± 31.35 | 68 ± 3.57 | 202.9 ± 10.6 | 1014.5 ± 53.2 | 6.2 ± 0.34 |
| W16 | 7.89 ± 0.41 | 44.26 ± 2.32 | 0.32 ± 0.02 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 2.8 ± 0.15 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 1.24 ± 0.07 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | 10.99 ± 0.58 | 2.8 ± 0.15 | 298.6 ± 15.67 | 40.6 ± 2.13 | 11.1 ± 0.58 | 55.6 ± 2.92 | 1.8 ± 0.1 |
| W17 | 7.55 ± 0.4 | 25.15 ± 1.32 | 11.94 ± 0.63 | 6.6 ± 0.35 | 1.45 ± 0.08 | 7.28 ± 0.38 | 2.49 ± 0.13 | 1.24 ± 0.07 | 0.62 ± 0.03 | 4.87 ± 0.26 | 1620.2 ± 85.03 | 45.4 ± 2.38 | 193 ± 10.13 | 965.1 ± 50.65 | 2.2 ± 0.12 |
| WHO standard * | 6.5–8.5 | 35 | 500 | - | - | 1000 | 5 | 30 | 15 | 10,000 | 5000 | 15 | 30 | - | |
| No. | Major Anions (meq/L) | Major Cations (meq/L) | Ion-Balance Error (%) * | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO32− meq/L | HCO3− meq/L | SO42− meq/L | Cl−1 meq/L | Total Anions (meq/L) | Ca+2 meq/L | Mg2+ meq/L | Na+ meq/L | K+ meq/L | Total Cations (meq/L) | ||
| Agricultural Drains | |||||||||||
| D1 | 0.00 | 3.44 | 22.97 | 122.00 | 148.41 | 18.10 | 46.95 | 73.078 | 7.71 | 145.83 | −0.88 |
| D2 | 0.00 | 3.36 | 20.78 | 86.36 | 110.50 | 10.40 | 31.16 | 58.435 | 5.52 | 105.51 | −2.31 |
| D3 | 0.00 | 4.92 | 21.47 | 141.54 | 167.92 | 12.90 | 49.31 | 87.565 | 8.70 | 158.47 | −2.90 |
| Groundwater Wells | |||||||||||
| W01 | 0.00 | 2.30 | 10.38 | 65.54 | 78.22 | 6.80 | 11.05 | 52.957 | 3.78 | 74.60 | −2.37 |
| W02 | 0.00 | 1.97 | 9.14 | 50.47 | 61.57 | 2.99 | 10.62 | 44.852 | 2.98 | 61.45 | −0.10 |
| W03 | 0.00 | 1.64 | 2.40 | 8.95 | 12.99 | 2.00 | 2.88 | 7.426 | 1.64 | 13.95 | 3.56 |
| W04 | 0.00 | 2.05 | 15.73 | 64.36 | 82.14 | 7.00 | 17.09 | 46.609 | 4.72 | 75.42 | −4.26 |
| W05 | 0.05 | 2.46 | 12.12 | 44.00 | 58.62 | 5.00 | 13.83 | 37.252 | 2.82 | 58.90 | 0.24 |
| W06 | 0.00 | 3.77 | 23.56 | 71.90 | 99.23 | 7.90 | 25.16 | 56.435 | 5.08 | 94.57 | −2.40 |
| W07 | 0.00 | 2.05 | 11.18 | 51.54 | 64.76 | 5.60 | 10.57 | 42.696 | 3.48 | 62.35 | −1.90 |
| W08 | 0.00 | 5.33 | 14.55 | 60.00 | 79.88 | 4.01 | 20.94 | 50.174 | 4.04 | 79.16 | −0.46 |
| W09 | 0.00 | 1.89 | 3.16 | 27.18 | 32.22 | 1.85 | 7.76 | 20.226 | 2.22 | 32.05 | −0.27 |
| W10 | 0.01 | 1.23 | 7.22 | 40.00 | 48.46 | 4.00 | 7.21 | 32.870 | 3.02 | 47.10 | −1.42 |
| W11 | 0.00 | 2.05 | 5.31 | 17.18 | 24.54 | 2.20 | 6.97 | 13.843 | 1.47 | 24.48 | −0.12 |
| W12 | 0.01 | 1.23 | 0.52 | 1.82 | 3.57 | 0.40 | 1.35 | 1.852 | 0.39 | 3.99 | 5.52 |
| W13 | 0.00 | 2.54 | 26.57 | 93.79 | 122.90 | 8.80 | 33.22 | 79.304 | 5.98 | 127.30 | 1.76 |
| W14 | 0.00 | 2.87 | 20.57 | 88.72 | 112.16 | 9.00 | 39.12 | 60.191 | 4.41 | 112.72 | 0.25 |
| W15 | 0.00 | 2.62 | 20.39 | 85.90 | 108.91 | 9.00 | 32.98 | 60.348 | 4.68 | 107.01 | −0.88 |
| W16 | 0.00 | 1.48 | 0.18 | 0.37 | 2.02 | 0.19 | 0.76 | 0.870 | 0.23 | 2.04 | 0.54 |
| W17 | 0.00 | 2.62 | 19.39 | 85.90 | 107.91 | 11.90 | 32.50 | 58.313 | 4.34 | 107.05 | −0.40 |
| Sample No. | Water Indices for Geochemical Processes | Water Quality Indices for Irrigation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r1 | r2 | CAI I | CAI II | SAR meq/L | Na% | |
| Agricultural Drains | ||||||
| D1 | −2.13 | −1.79 | 0.338 | 1.560 | 12.81 | 54.2% |
| D2 | −1.34 | −1.08 | 0.259 | 1.715 | 12.82 | 59.8% |
| D3 | −2.51 | −2.11 | 0.320 | 0.928 | 15.70 | 60.8% |
| Groundwater Wells | ||||||
| W01 | −1.21 | −0.85 | 0.134 | 0.694 | 17.72 | 73.3% |
| W02 | −0.61 | −0.29 | 0.052 | 0.237 | 17.19 | 77.4% |
| W03 | 0.63 | 0.05 | −0.013 | −0.029 | 4.75 | 62.9% |
| W04 | −1.13 | −0.83 | 0.202 | 0.733 | 13.43 | 66.7% |
| W05 | −0.56 | −0.32 | 0.089 | 0.269 | 12.14 | 66.8% |
| W06 | −0.66 | −0.44 | 0.144 | 0.380 | 13.88 | 64.4% |
| W07 | −0.79 | −0.48 | 0.104 | 0.405 | 15.01 | 71.8% |
| W08 | −0.68 | −0.40 | 0.096 | 0.291 | 14.21 | 69.2% |
| W09 | −2.20 | −1.50 | 0.174 | 0.938 | 9.23 | 70.5% |
| W10 | −0.99 | −0.57 | 0.103 | 0.486 | 13.88 | 74.1% |
| W11 | −0.63 | −0.35 | 0.109 | 0.253 | 6.47 | 62.1% |
| W12 | 0.06 | 0.82 | −0.232 | −0.240 | 1.98 | 57.2% |
| W13 | −0.55 | −0.32 | 0.091 | 0.292 | 17.30 | 66.7% |
| W14 | −1.39 | −1.17 | 0.272 | 1.028 | 12.27 | 57.5% |
| W15 | −1.25 | −1.02 | 0.243 | 0.906 | 13.17 | 60.4% |
| W16 | 2.81 | 4.09 | −2.001 | −0.442 | 1.27 | 56.0% |
| W17 | −1.42 | −1.20 | 0.271 | 1.055 | 12.38 | 57.1% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Ali, M.H.H.; Abdelkarim, M.S.; Attwa, K.M.; Al-Afify, A.D.G. Assessing Groundwater Sustainability in Siwa Oasis, Egypt: Evaluating Physico-Chemical and Hydrochemical Suitability for Human and Agricultural Use. Sustainability 2026, 18, 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/su18010357
Ali MHH, Abdelkarim MS, Attwa KM, Al-Afify ADG. Assessing Groundwater Sustainability in Siwa Oasis, Egypt: Evaluating Physico-Chemical and Hydrochemical Suitability for Human and Agricultural Use. Sustainability. 2026; 18(1):357. https://doi.org/10.3390/su18010357
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Mohamed H. H., Mohamad S. Abdelkarim, Khadija M. Attwa, and Afify D. G. Al-Afify. 2026. "Assessing Groundwater Sustainability in Siwa Oasis, Egypt: Evaluating Physico-Chemical and Hydrochemical Suitability for Human and Agricultural Use" Sustainability 18, no. 1: 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/su18010357
APA StyleAli, M. H. H., Abdelkarim, M. S., Attwa, K. M., & Al-Afify, A. D. G. (2026). Assessing Groundwater Sustainability in Siwa Oasis, Egypt: Evaluating Physico-Chemical and Hydrochemical Suitability for Human and Agricultural Use. Sustainability, 18(1), 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/su18010357






