Will Participation in Dual Value Chains Promote Manufacturing Upgrades and Green Development?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Theoretical Analysis
2.1. Literature Review
2.1.1. The Measurement of GVCs
2.1.2. NVCs Research
2.1.3. GVCs/NVCs Participation and Industrial Upgrading
2.1.4. GVCs/NVCs Participation and Green Development
2.1.5. A Summary
2.2. Theoretical Analysis
2.2.1. The Interaction Effect of GVCs and NVCs Participation on Manufacturing Upgrading
2.2.2. The Interaction Effect of GVCs and NVCs Participation on Green Development in Manufacturing
3. GVCs and NVCs Participation Measurement
3.1. Measurement Methods
3.2. Data and Measurement Results
4. Empirical Analysis
4.1. Model Setting, Variable Description and Data Sources
4.1.1. Model Setting
4.1.2. Variable Description and Data Sources
4.2. Regression Results and Analysis
4.3. Robustness Test
4.4. Heterogeneity Analysis
4.4.1. Regional Heterogeneity
4.4.2. Sectoral Heterogeneity
4.4.3. Heterogeneity of NVCs Participation Modes
5. Conclusions and Policy Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kano, L.; Tsang, E.W.; Yeung, H.W.-c. Global value chains: A review of the multi-disciplinary literature. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2020, 51, 577–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, W.; Hou, J. Research on the impact of OFDI on the home country’s global value chain upgrading. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2021, 77, 101862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.X.; Zhang, M.; Ramu, S.C. China’s semiconductor industry in global value chains. Asia Pac. Bus. Rev. 2016, 22, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jer, R. What makes export manufacturers pursue functional upgrading in an emerging market? A study of Chinese technology new ventures. Int. Bus. Rev. 2014, 23, 741–749. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Grimes, S. China’s increasing participation in ICT’s global value chain: A firm level analysis. Telecommun. Policy 2016, 40, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, B.R.; Taylor, M.S. North-South trade and the environment. In International Trade and the Environment; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; pp. 205–238. [Google Scholar]
- Grossman, G.M.; Krueger, A.B. Environmental Impacts of a North American Free Trade Agreement; National Bureau of Economic Research: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, M.A.; Elliott, R.J. Determining the trade–environment composition effect: The role of capital, labor and environmental regulations. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2003, 46, 363–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Meng, G.; Liu, J.; Li, Z. Value chain specialization and green economy performance: China’s regional evidence. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 103, 107217. [Google Scholar]
- Hummels, D.; Ishii, J.; Yi, K.-M. The nature and growth of vertical specialization in world trade. J. Int. Econ. 2001, 54, 75–96. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, R.C.; Noguera, G. Accounting for intermediates: Production sharing and trade in value added. J. Int. Econ. 2012, 86, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopman, R.; Wang, Z.; Wei, S.-J. Tracing value-added and double counting in gross exports. Am. Econ. Rev. 2014, 104, 459–494. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wei, S.-J.; Yu, X.; Zhu, K. Measures of Participation in Global Value Chains and Global Business Cycles; National Bureau of Economic Research: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Koopman, R.; Powers, W.; Wang, Z.; Wei, S.-J. Give Credit Where Credit Is Due: Tracing Value Added in Global Production Chains; National Bureau of Economic Research: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Antràs, P.; Chor, D.; Fally, T.; Hillberry, R. Measuring the upstreamness of production and trade flows. Am. Econ. Rev. 2012, 102, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Si, I.; Chen, Z. Does the Belt and Road Initiative promote China and the countries along the route to reconstruct the global value chain? Evidence from value-added trade. Econ. Anal. Policy 2024, 81, 63–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delera, M.; Pietrobelli, C.; Calza, E.; Lavopa, A. Does value chain participation facilitate the adoption of industry 4.0 technologies in developing countries? World Dev. 2022, 152, 105788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostino, M.; Giunta, A.; Ruberto, S.; Scalera, D. Global value chains and energy-related sustainable practices. Evidence from Enterprise Survey data. Energy Econ. 2023, 127, 107068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.; Sasidharan, S.; Chundakkadan, R. Firm automation and global value-chain participation: Cross-country analysis. Appl. Econ. 2024, 57, 317–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschma, R. Global value chains from an evolutionary economic geography perspective: A research agenda. Area Dev. Policy 2022, 7, 123–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostino, M.; Brancati, E.; Giunta, A.; Scalera, D.; Trivieri, F. Firms’ efficiency and global value chains: An empirical investigation on Italian industry. World Econ. 2020, 43, 1000–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkovskis, K.; Masso, J.; Tkacevs, O.; Vahter, P.; Yashiro, N. Export and productivity in global value chains: Comparative evidence from Latvia and Estonia. Rev. World Econ. 2020, 156, 557–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Prete, D.; Giovannetti, G.; Marvasi, E. Global value chains participation and productivity gains for North African firms. Rev. World Econ. 2017, 153, 675–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hioki, S.; Hewings, G.J.; Okamoto, N. Identifying the structural changes of China’s spatial production linkages using a qualitative input-output analysis. J. Econom. Study Northeast Asia 2009, 6, 25–55. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, B.; Fang, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y. Measuring China’s domestic production networks through Trade in Value-added perspectives. Econ. Syst. Res. 2017, 29, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seung, C.K. Spatial distribution of the value added from seafood exports: A domestic value chain analysis for Korea. Fish. Res. 2022, 247, 106181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Gao, Y.; Pei, J.; de Vries, G.; Wang, F. China’s domestic production networks. China Econ. Rev. 2022, 72, 101767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xiao, S.; Yan, J.; Zhang, P. Regional and sectoral structures of the Chinese economy: A network perspective from multi-regional input–output tables. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2021, 581, 126196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Huo, W.; Yu, J. Tracing the regional dual value chains: Measurement on the production position and evidence from China. J. Asian Econ. 2023, 85, 101591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Kou, Y. The effect of multiple shocks on domestic production network: Evidence from China’s manufacturing industries. Appl. Econ. 2023, 56, 4315–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keijser, C.; Belderbos, R.; Goedhuys, M. Governance and learning in global, regional, and local value chains: The IT enabled services industry in South Africa. World Dev. 2021, 141, 105398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedyunina, A.A.; Gorodnyi, N.A.; Simachev, Y.V. How the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies is related to participation in global and domestic value chains: Evidence from Russia. Int. J. Innov. Stud. 2024, 8, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Xiao, H.; Jia, Z.; Tang, B. Estimating the effects of regional value chains of the RCEP in a GVC-CGE model. J. Asian Econ. 2023, 88, 101647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.Q.; Pham, H.C.; McClelland, R. Participating and upgrading in global value chains: The case of small and medium enterprises in Vietnam. In The Economy and Business Environment of Vietnam; Palgrave Macmillan: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 75–92. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlan, J.M.; Samat, O.; Othman, A.A. Upgrading in global value chain of Malaysian aviation industry. Procedia Econ. Financ. 2015, 31, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Qu, D.; Mao, Z. Global value chains, industrial policy, and industrial upgrading: Automotive sectors in Malaysia, Thailand, and China in comparison with Korea. Eur. J. Dev. Res. 2021, 33, 275–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Los, B.; Timmer, M.P.; De Vries, G.J. How global are global value chains? A new approach to measure international fragmentation. J. Reg. Sci. 2015, 55, 66–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q. The Impact of Digitalization on the Upgrading of China’s Manufacturing Sector’s Global Value Chains. J. Knowl. Econ. 2024, 15, 15577–15600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, R. The research on influence factors of the servitization of the equipment manufacturing industry under the global value chain (GVC) perspective. Int. J. Secur. Its Appl. 2015, 9, 289–296. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hao, J.; Huang, Q. The impact of green technology innovation on global value chain upgrading in China’s equipment manufacturing industry. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1044583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, H.; Li, S. Future social change of manufacturing and service industries: Service-oriented manufacturing under the integration of innovation-flows drive. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2023, 196, 122808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturgeon, T.J. Upgrading strategies for the digital economy. Glob. Strategy J. 2021, 11, 34–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Zhang, R.; Di, D.; Li, G. Does digital transformation promote global value chain upgrading? Evidence from Chinese manufacturing firms. Econ. Model. 2024, 139, 106810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, Q.; Chen, M.; Su, Y.; Zhu, J. Global Value Chains, Digital Economy, and Upgrading of China’s Manufacturing Industry. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antràs, P. Conceptual aspects of global value chains. World Bank Econ. Rev. 2020, 34, 551–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artuc, E.; Bastos, P.; Rijkers, B. Robots, tasks, and trade. J. Int. Econ. 2023, 145, 103828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acemoglu, D.; Restrepo, P. The wrong kind of AI? Artificial intelligence and the future of labour demand. Camb. J. Reg. Econ. Soc. 2020, 13, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebdioui, A. The political economy of moving up in global value chains: How Malaysia added value to its natural resources through industrial policy. Rev. Int. Political Econ. 2022, 29, 870–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rand, J.; Rodriguez, P.C.; Tarp, F.; Trifkovic, N. Economic and environmental upgrading after a policy reform: The case of timber value chain in Myanmar. J. Rural Stud. 2023, 99, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissi, E.A.; Herzig, C. The implications of governance factors for economic and social upgrading in Ghana’s cocoa value chain. Agric. Food Econ. 2024, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Long, W. An empirical analysis of CO2 emission in Pakistan using EKC hypothesis. J. Int. Trade Law Policy 2013, 12, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, L.-S.; Choong, C.-K.; Eng, Y.-K. Investigation of the environmental Kuznets curve for carbon emissions in Malaysia: Do foreign direct investment and trade matter? Energy Policy 2014, 68, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, Q.; Zheng, L.; Wang, S.; Zhu, J. Global value chains participation and CO2 emissions in RCEP countries. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 332, 130070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Digitalization, positioning in global value chain and carbon emissions embodied in exports: Evidence from global manufacturing production-based emissions. Ecol. Econ. 2023, 205, 107674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Ni, J.; Wen, D. Has GVC participation exacerbated inequality of the embodied carbon in fossil energy industry export trade? Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 11, 1293462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhang, N.; Li, A.; Chen, Y. The path to global climate justice: From the perspective of regional discrepancy in embodied carbon emissions. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 105, 107410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, E.; Bataka, H.; Wonyra, K.O.; Awade, N.E.; Braly, N.N. Global value chains participation and environmental pollution in developing countries: Does digitalization matter? J. Int. Dev. 2024, 36, 451–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, R.; Pan, A. Global value chain and export-embodied carbon emissions: New evidence from foreign-invested enterprises. Econ. Model. 2023, 127, 106449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Gracia, A.; Almazán-Gómez, M.Á.; Jiménez, S. CO2 emissions and global value chains indicators: New evidence for 1995–2018. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 343, 118239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upward, R.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, J. Weighing China’s export basket: The domestic content and technology intensity of Chinese exports. J. Comp. Econ. 2013, 41, 527–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, N.; Li, C.; Cui, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Impact of digital input on enterprise green productivity: Micro evidence from the Chinese manufacturing industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 414, 137272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. The impact of digital inputs on pollution reduction in Chinese manufacturing enterprises. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 428, 139393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Xu, C. Does environmental decentralization aggravate pollution emissions? Microscopic evidence from Chinese industrial enterprises. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Jahanger, A.; Hossain, M.R. How effective has the low-carbon city pilot policy been as an environmental intervention in curbing pollution? Evidence from Chinese industrial enterprises. Energy Econ. 2023, 118, 106523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, L.; Van Biesebroeck, J.; Zhang, Y. Creative accounting or creative destruction? Firm-level productivity growth in Chinese manufacturing. J. Dev. Econ. 2012, 97, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, K.E.; Estrin, S.; Bhaumik, S.K.; Peng, M.W. Institutions, resources, and entry strategies in emerging economies. Strateg. Manag. J. 2009, 30, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
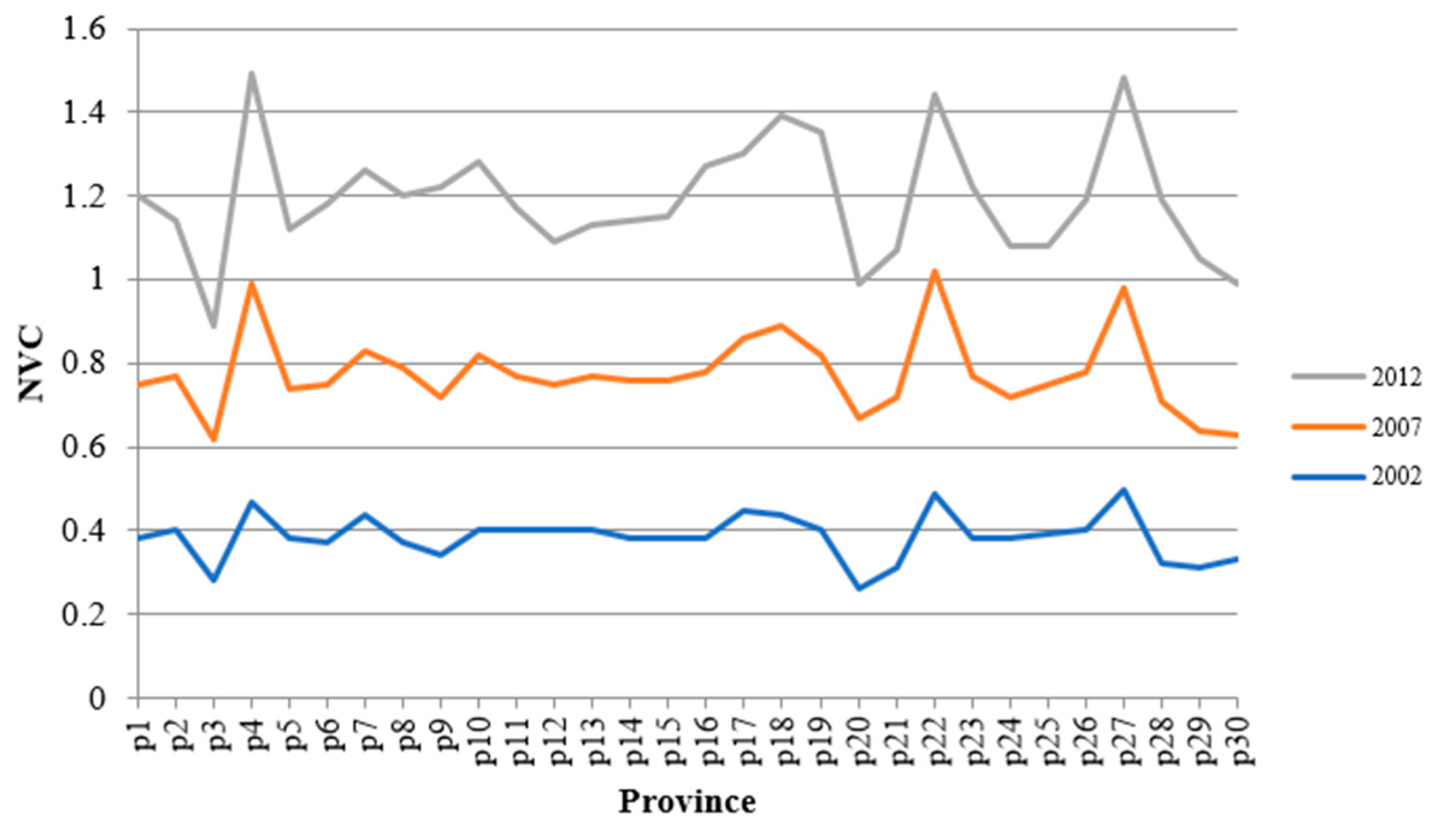
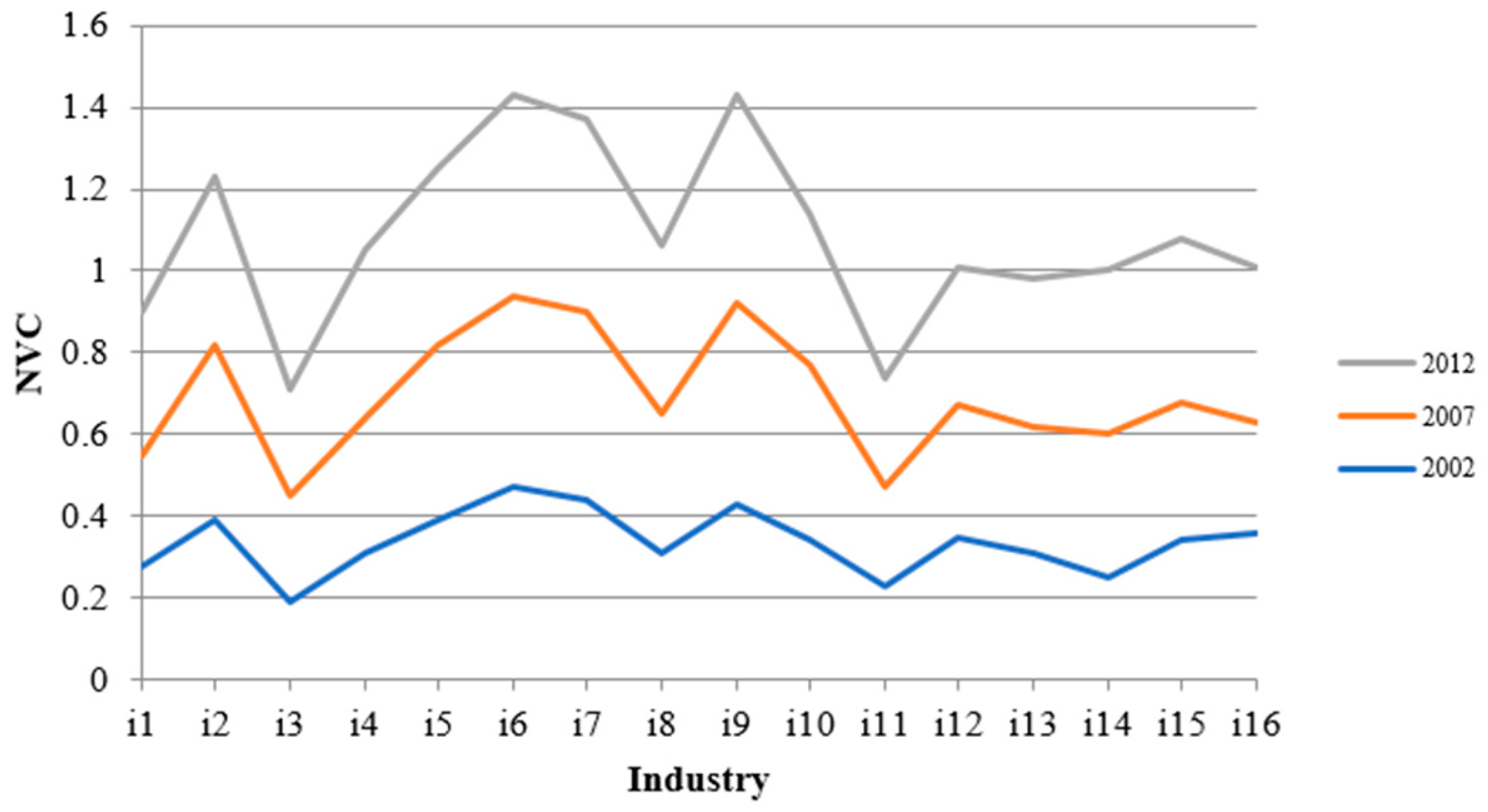
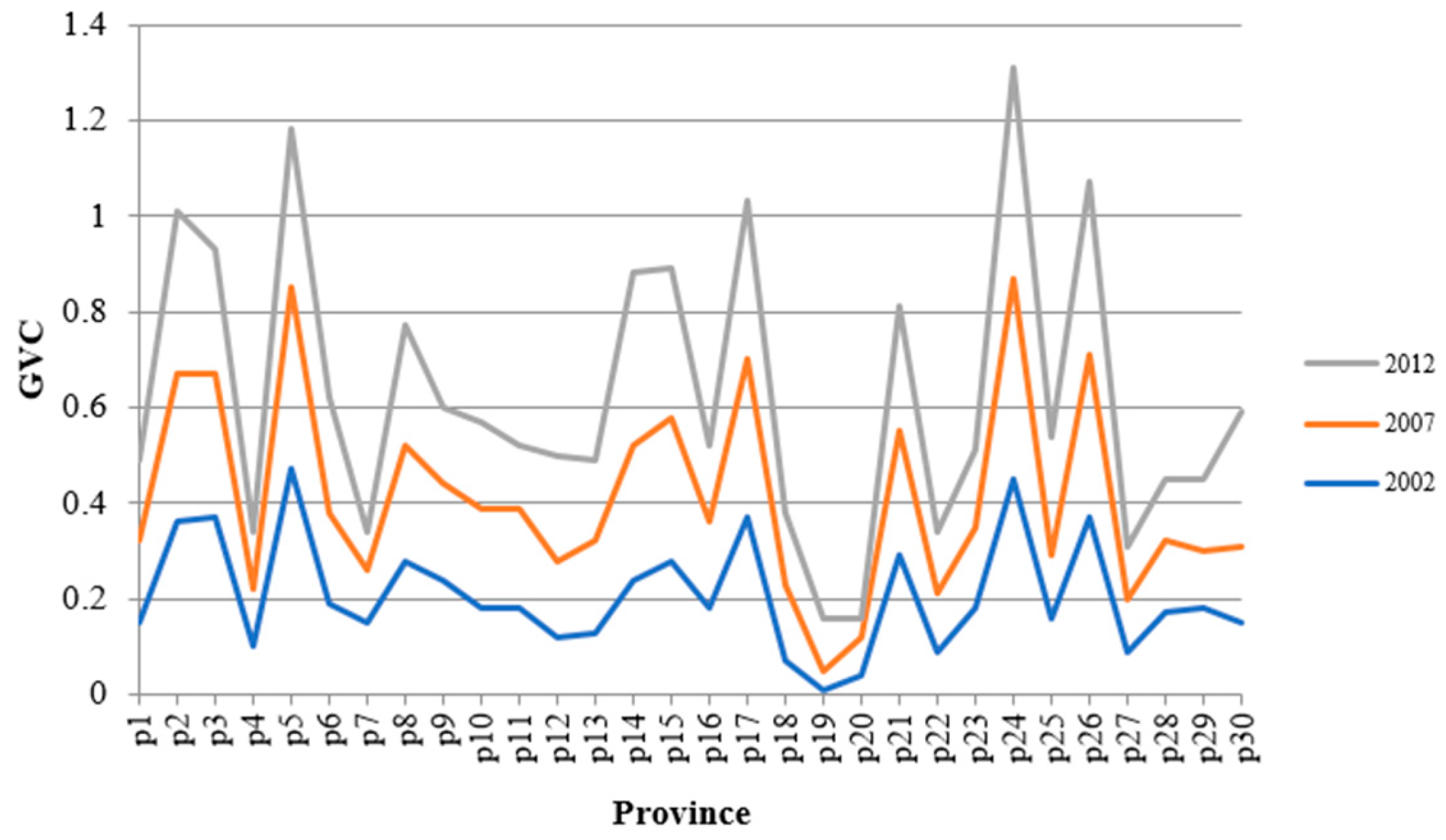


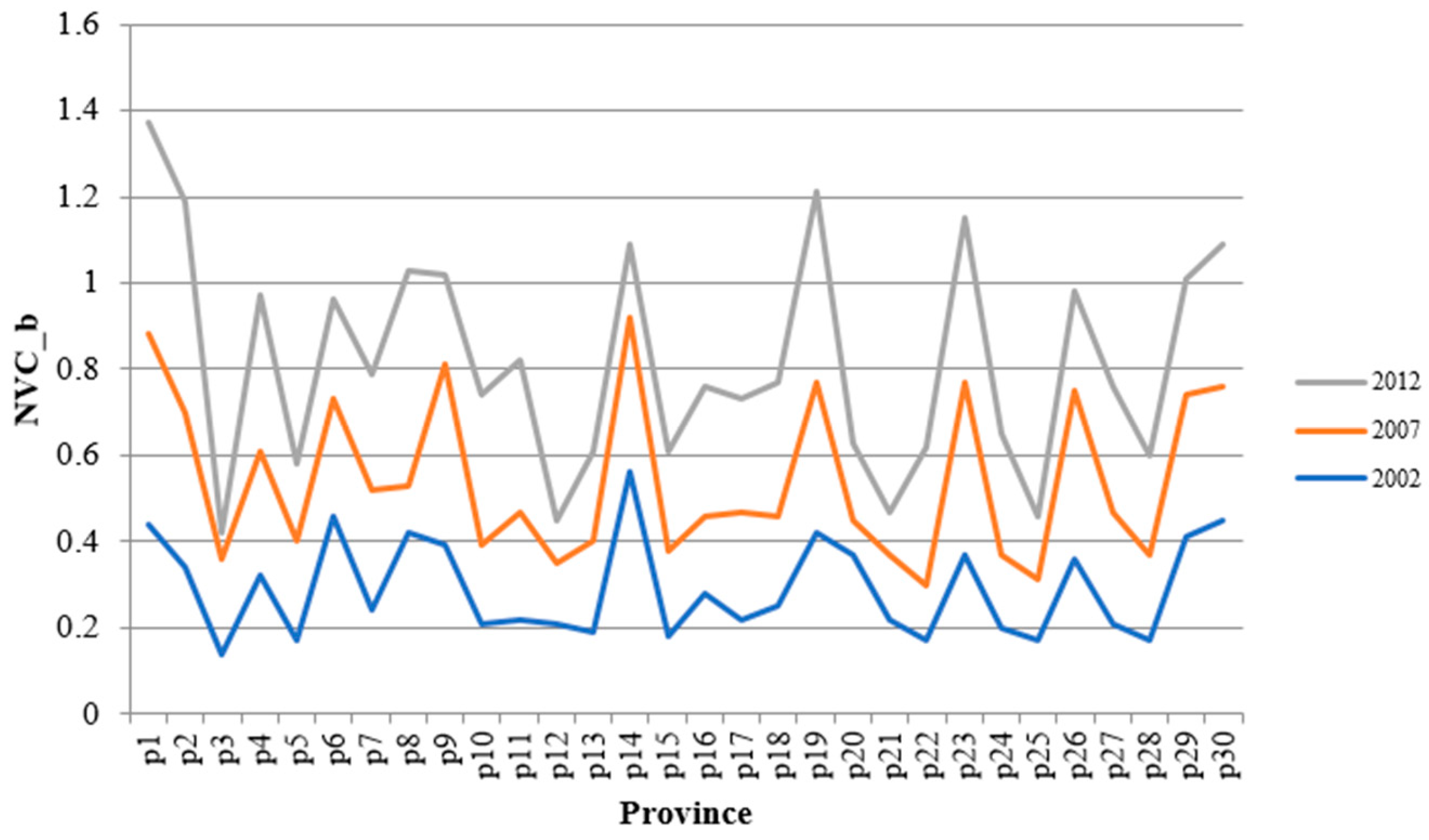
| Variable | INDU | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
| 0.08 ** (0.04) | 0.08 *** (0.01) | 0.05 ** (0.02) | 0.07 *** (0.02) | |||
| 0.07 ** (0.03) | 0.07 * (0.04) | 0.06 ** (0.03) | 0.06 ** (0.03) | |||
| K | 0.17 * (0.10) | 0.57 *** (0.04) | 0.47 *** (0.01) | |||
| L | 0.42 * (0.22) | 0.38 ** (0.19) | 0.26 * (0.15) | |||
| Tec | 0.49 *** (0.06) | 0.10 ** (0.04) | 0.21 *** (0.02) | |||
| Scale | −0.17 *** (0.05) | −0.14 *** (0.02) | −0.11 *** (0.00) | |||
| OS | −0.02 (0.07) | −0.03 (0.09) | −0.02 (0.07) | |||
| EP | 2.17 *** (0.21) | 2.01 *** (0.32) | 2.78 *** (0.16) | |||
| TI | −3.81 *** (0.62) | −9.23 *** (0.57) | −1.39 ** (0.64) | |||
| FDI | 2.31 *** | 1.77 * | 3.15 ** | |||
| (0.82) | (0.91) | (1.39) | ||||
| Constant | 1.56 ** (0.70) | 0.76 * (0.42) | 1.88 *** (0.52) | 0.93 *** (0.26) | 2.13 ** (0.98) | 1.15 ** (0.56) |
| Sector Fixed Effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Province Fixed Effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year Fixed Effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Variable | Green | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
| −0.46 * (0.27) | −0.53 * (0.31) | −0.31 ** (0.14) | −0.35 ** (0.15) | |||
| −0.55 ** (0.26) | −0.57 ** (0.27) | −0.13 ** (0.06) | −0.14 ** (0.07) | |||
| ES | 3.35 *** (0.08) | 3.66 *** (0.03) | 3.79 *** (0.05) | |||
| EE | −0.11 * (0.06) | −0.15 * (0.08) | −0.16 * (0.09) | |||
| OS | 0.13 (0.12) | −0.28 (0.29) | −0.53 (0.33) | |||
| FDI | 2.98 *** (0.02) | 2.55 *** (0.01) | 3.06 *** (0.03) | |||
| Constant | 7.33 *** (0.01) | 7.91 ** (0.01) | 6.89 *** (0.02) | 6.13 *** (0.02) | 5.03 *** (0.02) | 5.11 *** (0.03) |
| Sector, Province and Year Fixed Effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Variable | INDU | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | |
| 0.07 *** (0.02) | 0.15 *** (0.02) | |
| 0.21 *** (0.03) | 0.16 *** (0.01) | |
| 0.03 * (0.16) | 0.02 * (0.01) | |
| Control Variable | No | Yes |
| Sector, Province and Year Fixed Effect | Yes | Yes |
| Variable | Green | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | |
| −0.03 ** (0.01) | −0.08 ** (0.04) | |
| −0.36 *** (0.05) | −0.55 *** (0.01) | |
| −0.77 *** (0.01) | −0.56 *** (0.02) | |
| Control Variable | No | Yes |
| Sector, Province and Year Fixed Effect | Yes | Yes |
| Variable | INDU | INDU Panel Tobit Model |
|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | |
| 0.02 * (0.01) | ||
| 0.11 *** (0.03) | ||
| 0.03 *** (0.01) | 0.37 * (0.22) | |
| 0.07 ** (0.03) | ||
| 0.03 ** (0.01) | ||
| Control Variable | Yes | Yes |
| Sector, Province and Year Fixed Effect | Yes | Yes |
| Variable | Green | Green Panel Tobit Model | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | |
| −0.91 * (0.48) | |||
| −0.13 ** (0.06) | 0.43 ** (0.21) | ||
| −0.05 ** (0.02) | −0.86 ** (0.41) | 0.17 *** (0.01) | |
| −0.33 *** (0.03) | |||
| −1.09 ** (0.52) | 0.11 ** (0.05) | ||
| Control Variable | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Sector, Province and Year Fixed Effect | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Variable | INDU | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) EAST | (2) CENTRAL | (3) WEST |
(4) HIGH |
(5) MEDIUM |
(6) LOW |
(7) |
(8) | |
| 0.04 *** (0.01) | 0.03 * (0.02) | 0.04 (0.03) | 0.08 ** (0.03) | 0.09 ** (0.04) | 0.16 (0.15) | 0.04 ** (0.02) | 0.06 ** (0.03) | |
| 0.12 *** (0.04) | 0.20 *** (0.07) | 0.15 (0.19) | 0.11 ** (0.05) | 0.28 ** (0.11) | 0.35 (0.24) | 0.29 *** (0.06) | 0.17 * (0.09) | |
| 0.39 *** (0.05) | 0.04 * (0.02) | 0.21 (0.19) | 0.27 ** (0.13) | 0.15 * (0.09) | 0.32 (0.44) | 0.59 ** (0.28) | 0.08 * (0.05) | |
| Control Variable | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Sector, Province and Year Fixed Effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Variable | Green | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
(1) EAST |
(2) CENTRAL |
(3) WEST |
(4) HIGH |
(5) MEDIUM |
(6) LOW |
(7) |
(8) | |
| −0.11 *** (0.03) | −0.01 ** (0.01) | −0.09 (0.24) | −0.19 *** (0.07) | −0.51 *** (0.02) | −0.04 (0.03) | −0.04 ** (0.02) | −0.03 ** (0.02) | |
| −0.88 ** (0.38) | −0.07 *** (0.02) | −0.04 (0.06) | −0.33 *** (0.05) | −0.70 *** (0.01) | −0.82 (0.60) | −0.69 *** (0.02) | −0.41 ** (0.16) | |
| −0.90 ** (0.42) | −0.17 * (0.10) | −0.49 (0.40) | −0.08 *** (0.01) | −0.09 *** (0.01) | −0.66 (0.81) | −0.72 *** (0.01) | −0.01 * (0.01) | |
| Control Variable | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Sector, Province and Year Fixed Effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Wang, S. Will Participation in Dual Value Chains Promote Manufacturing Upgrades and Green Development? Sustainability 2025, 17, 4234. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094234
Wang S, Wang S. Will Participation in Dual Value Chains Promote Manufacturing Upgrades and Green Development? Sustainability. 2025; 17(9):4234. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094234
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shi, and Shanshan Wang. 2025. "Will Participation in Dual Value Chains Promote Manufacturing Upgrades and Green Development?" Sustainability 17, no. 9: 4234. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094234
APA StyleWang, S., & Wang, S. (2025). Will Participation in Dual Value Chains Promote Manufacturing Upgrades and Green Development? Sustainability, 17(9), 4234. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094234




