Spatiotemporal Characteristic and Driving Factors of Synergy on Carbon Dioxide Emission and Pollutants Reductions in the Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area, China
Abstract
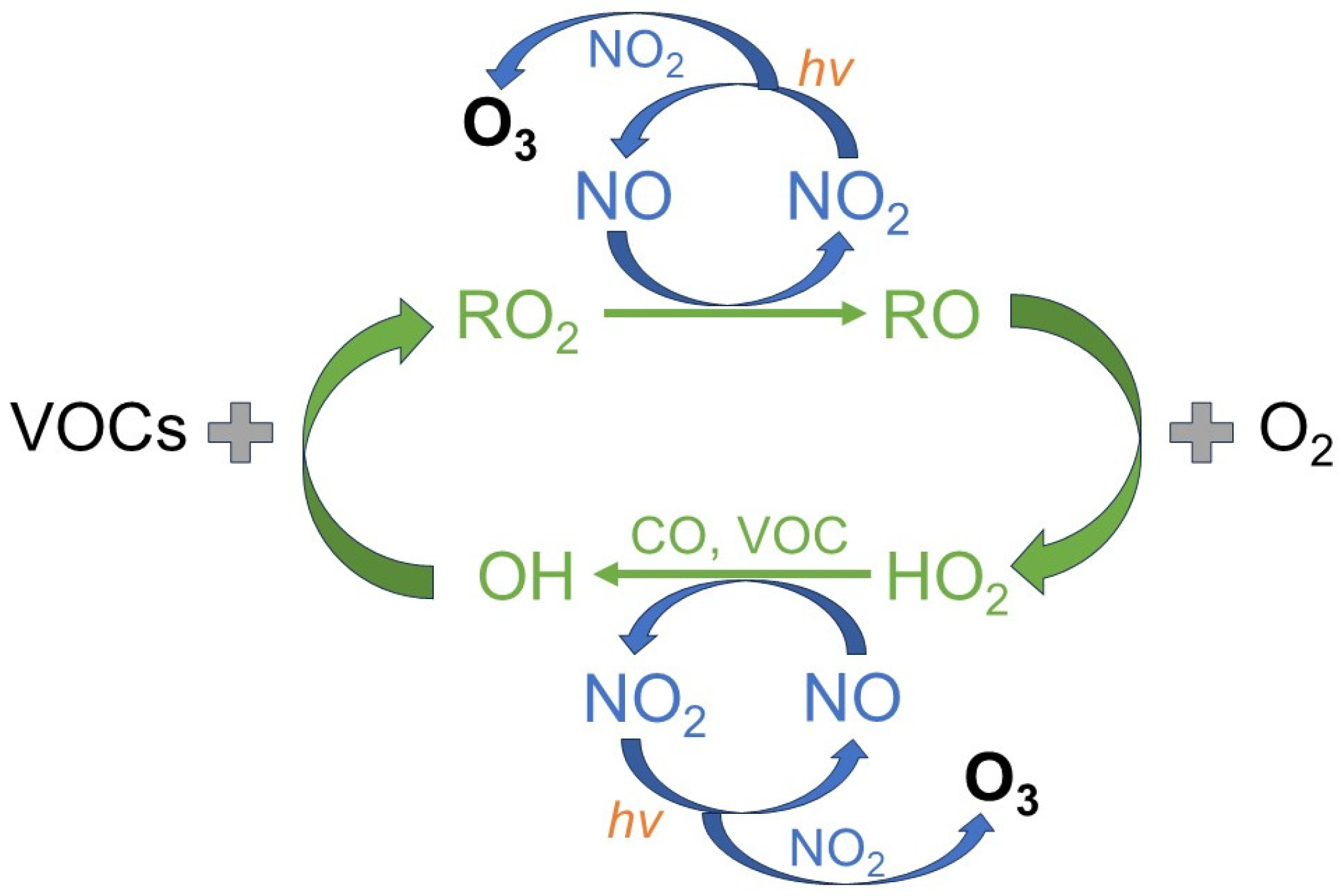
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Data
2.1. Research Methods of Spatiotemporal Evolution Characteristics of CAP
2.1.1. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
2.1.2. Standard Deviation Ellipse (SDE)
2.2. Decomposition of CAP Synergistic Emission Reduction Effect
2.2.1. CAP Emission Reduction Drive Decomposition Based on Kaya–LMDI Model
2.2.2. CAP Synergistic Emission Reduction Effect Model Based on Kaya–LMDI Model
2.3. Decoupling Analysis Method
2.4. Data Sources
2.4.1. CAP Emission Data Sources
2.4.2. Socioeconomic Population Data Sources
3. Result
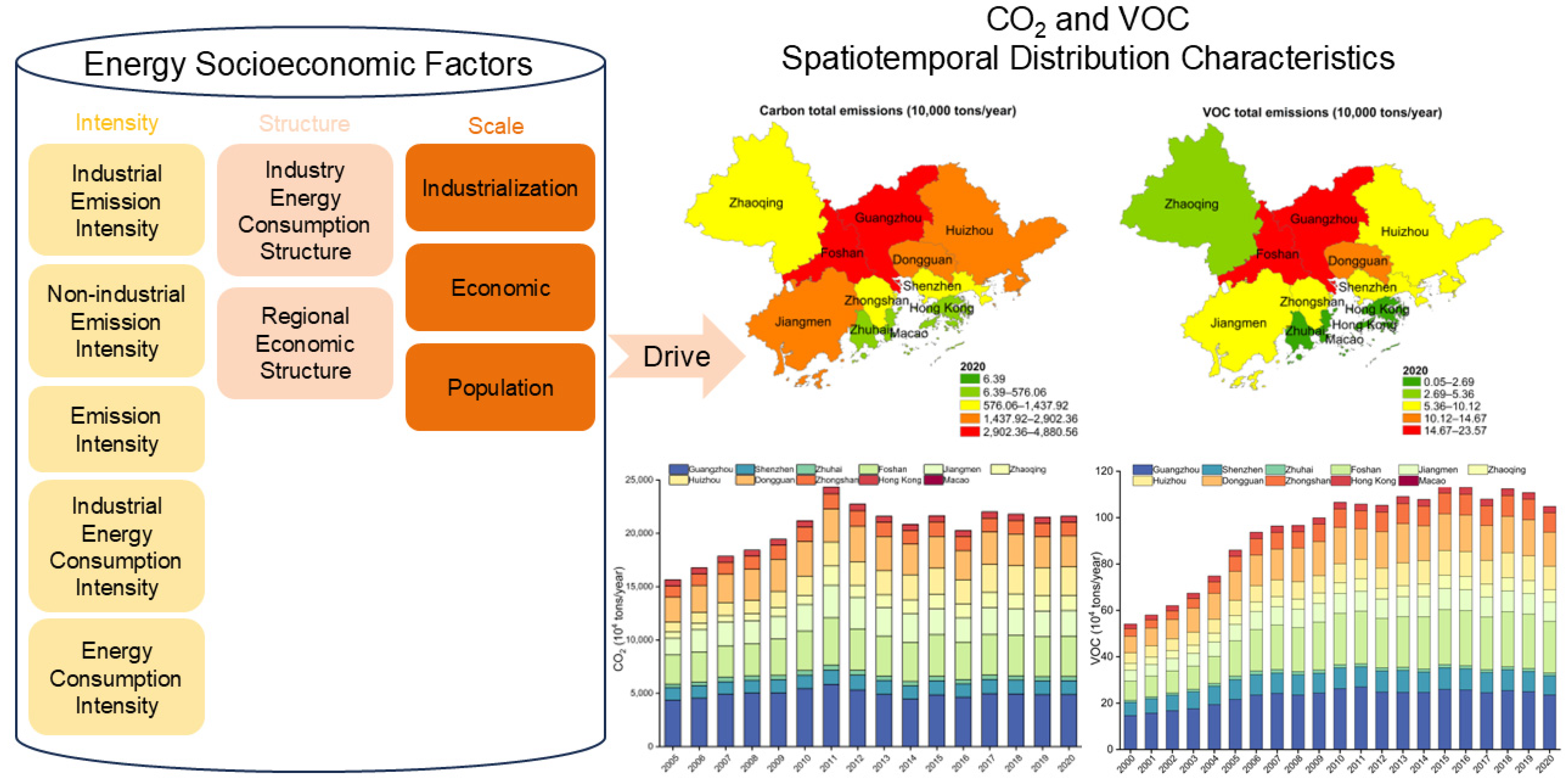
3.1. Analysis of Spatial and Temporal Evolution Characteristics of CAP in the GBA
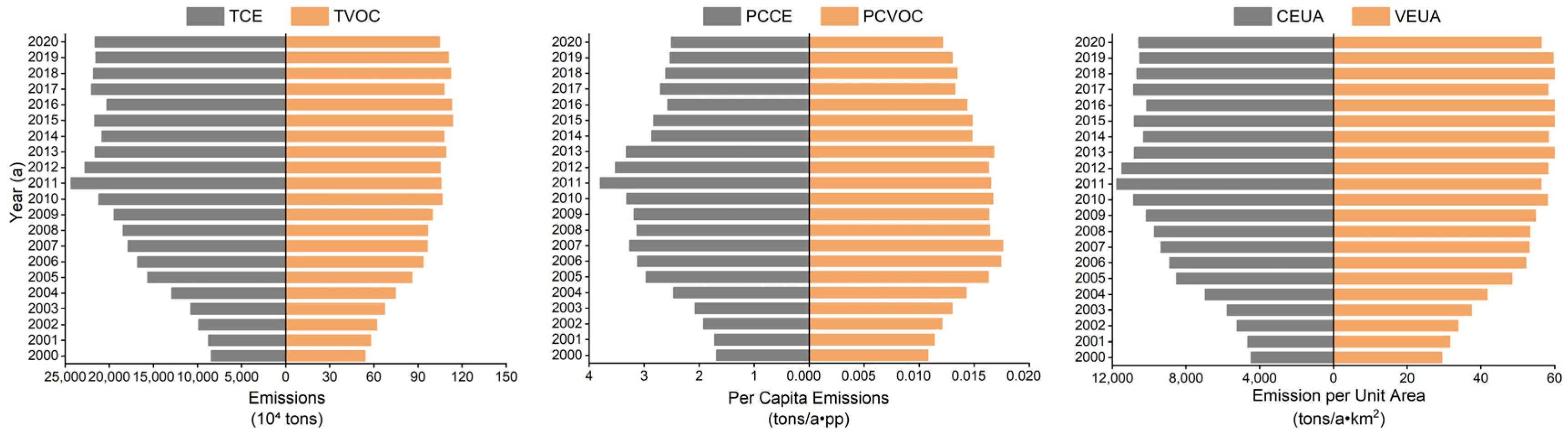
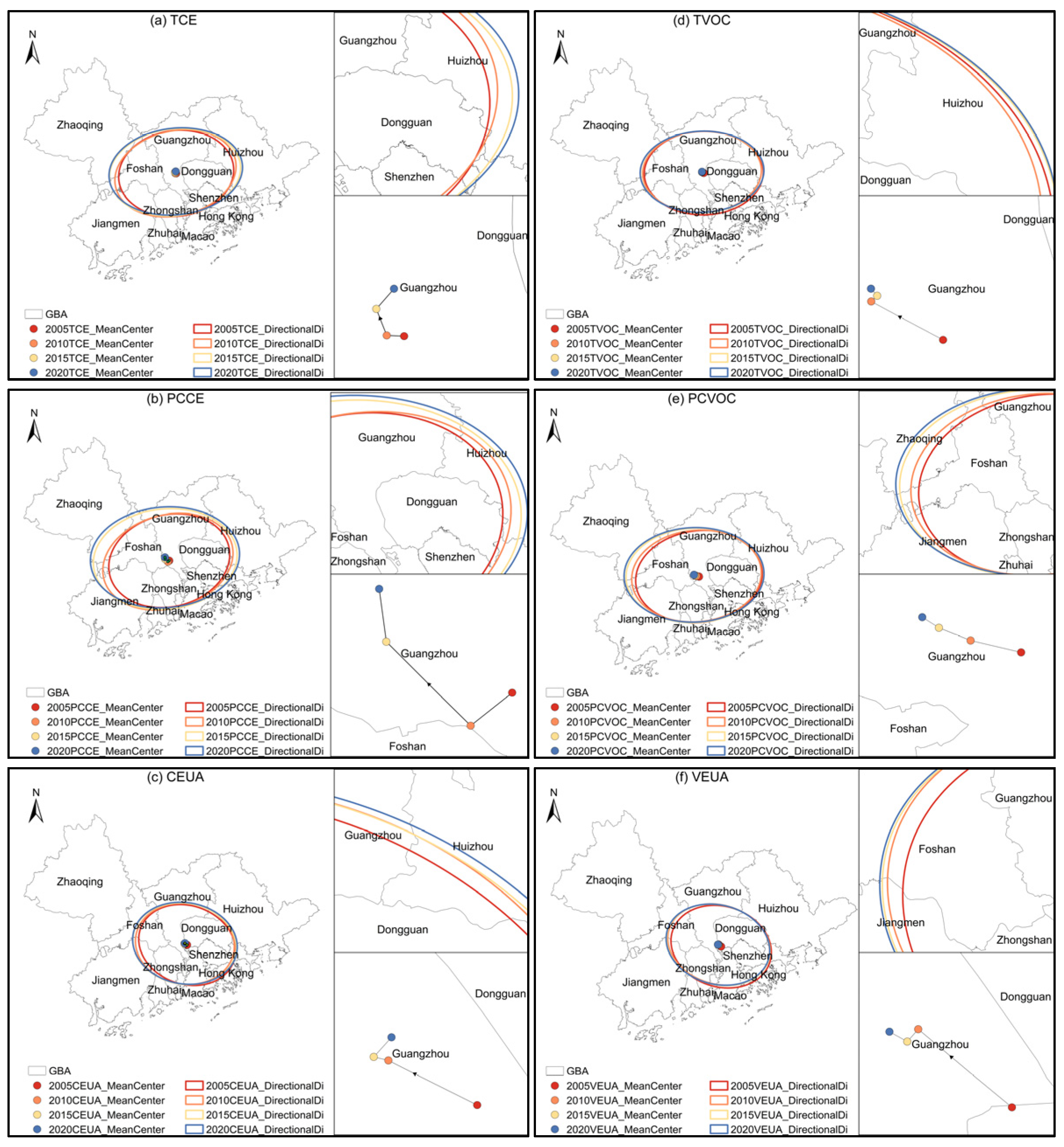
3.1.1. Spatiotemporal Aggregation Trend of CAP Emissions
- (1)
- Urban agglomeration scale
- (2)
- Urban scale
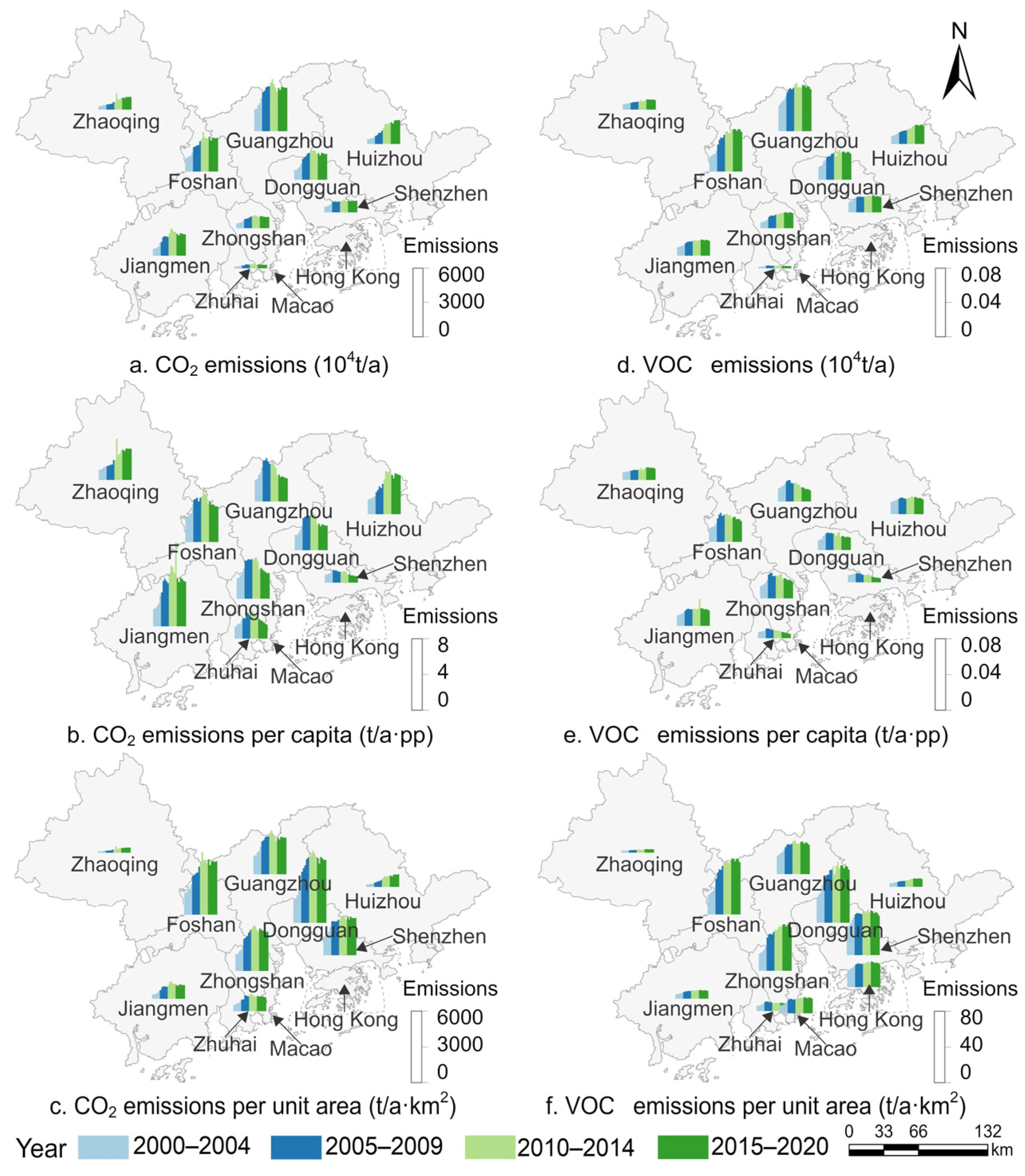
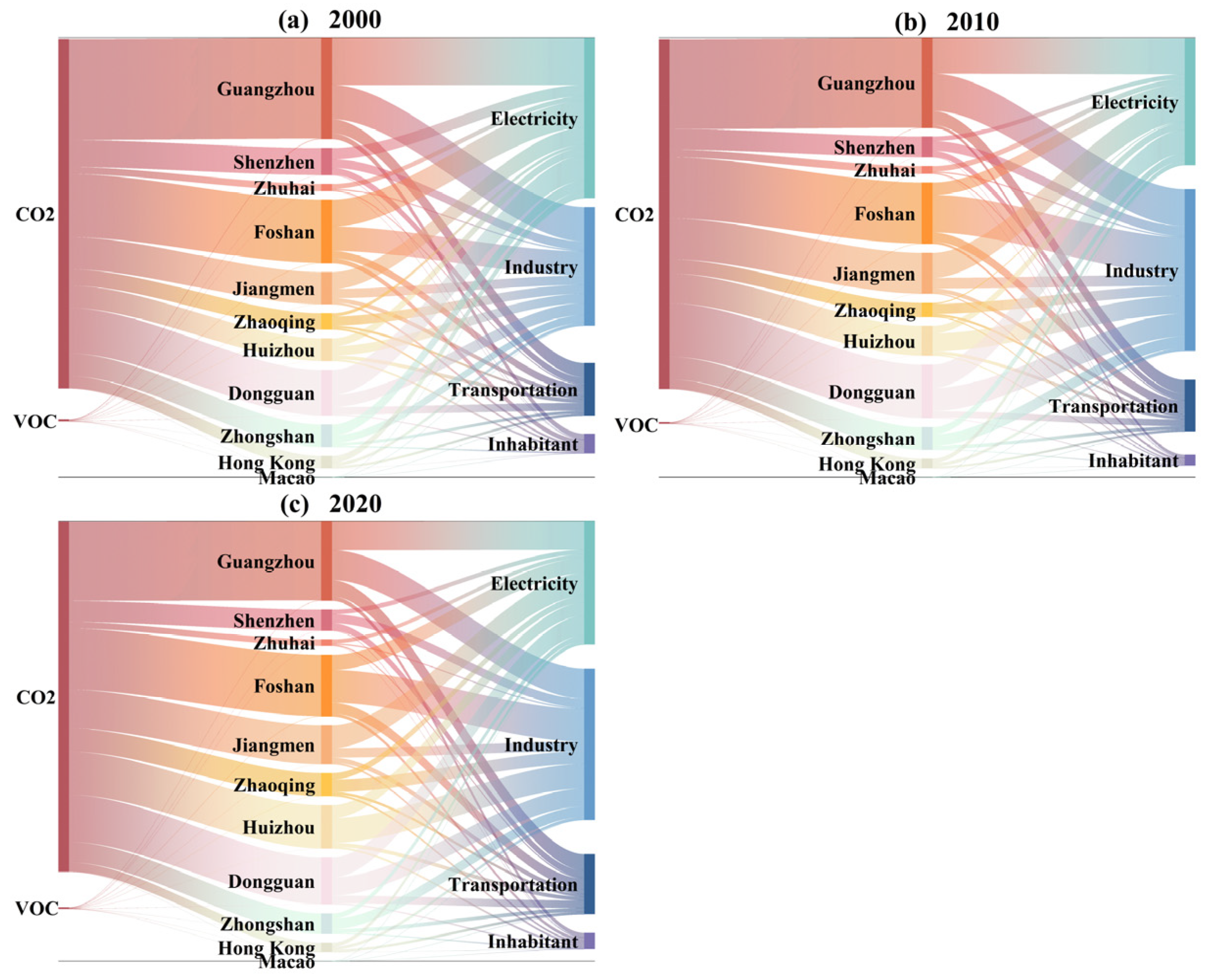
3.1.2. Analysis of CAP Emission Key Cities
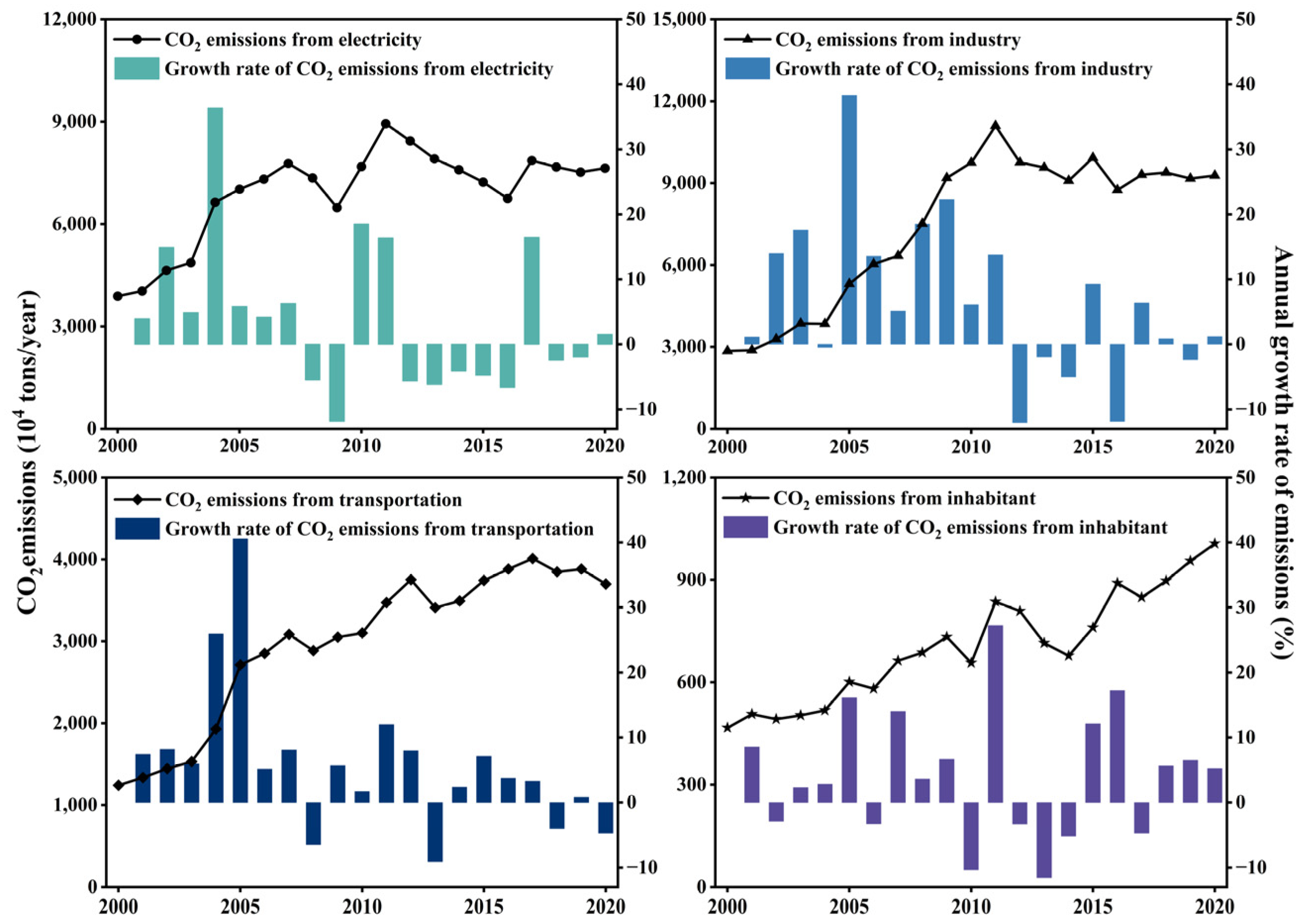
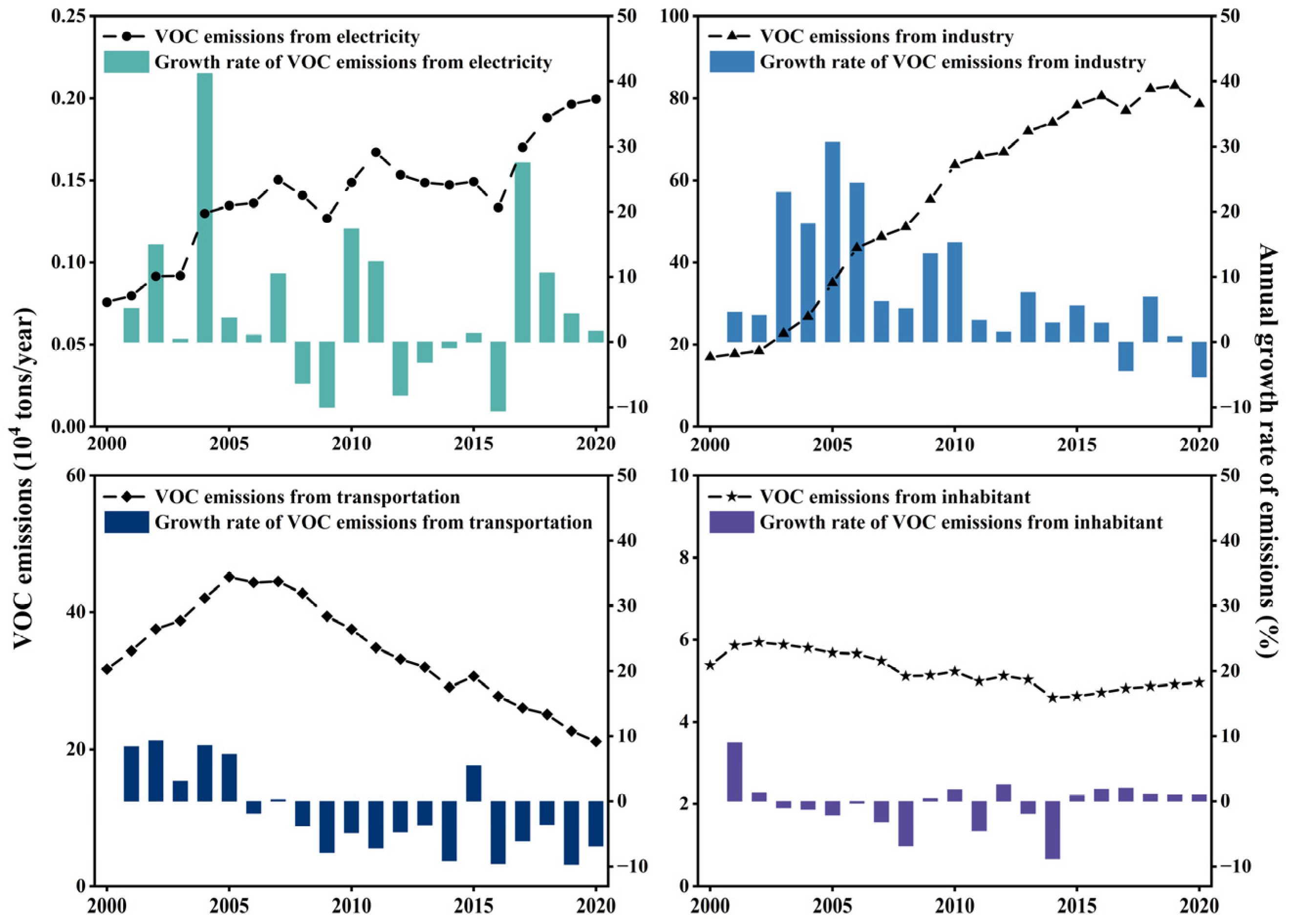
3.1.3. Analysis of CAP Emission Key Sectors
3.2. Analysis of Driving Factors of CAP Emissions
3.2.1. Analysis of Driving Factors of CAP Emission in Urban Agglomeration Scale
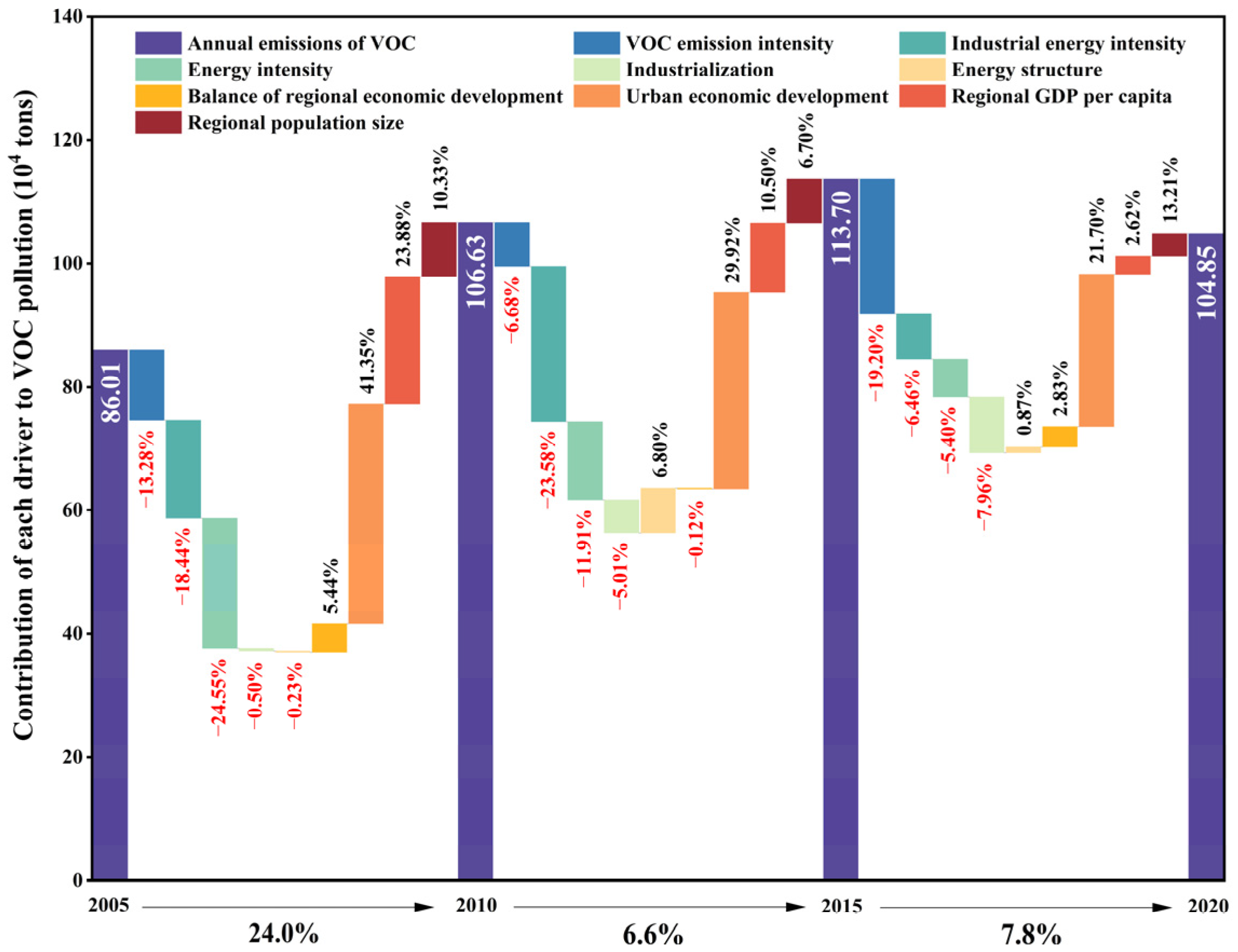
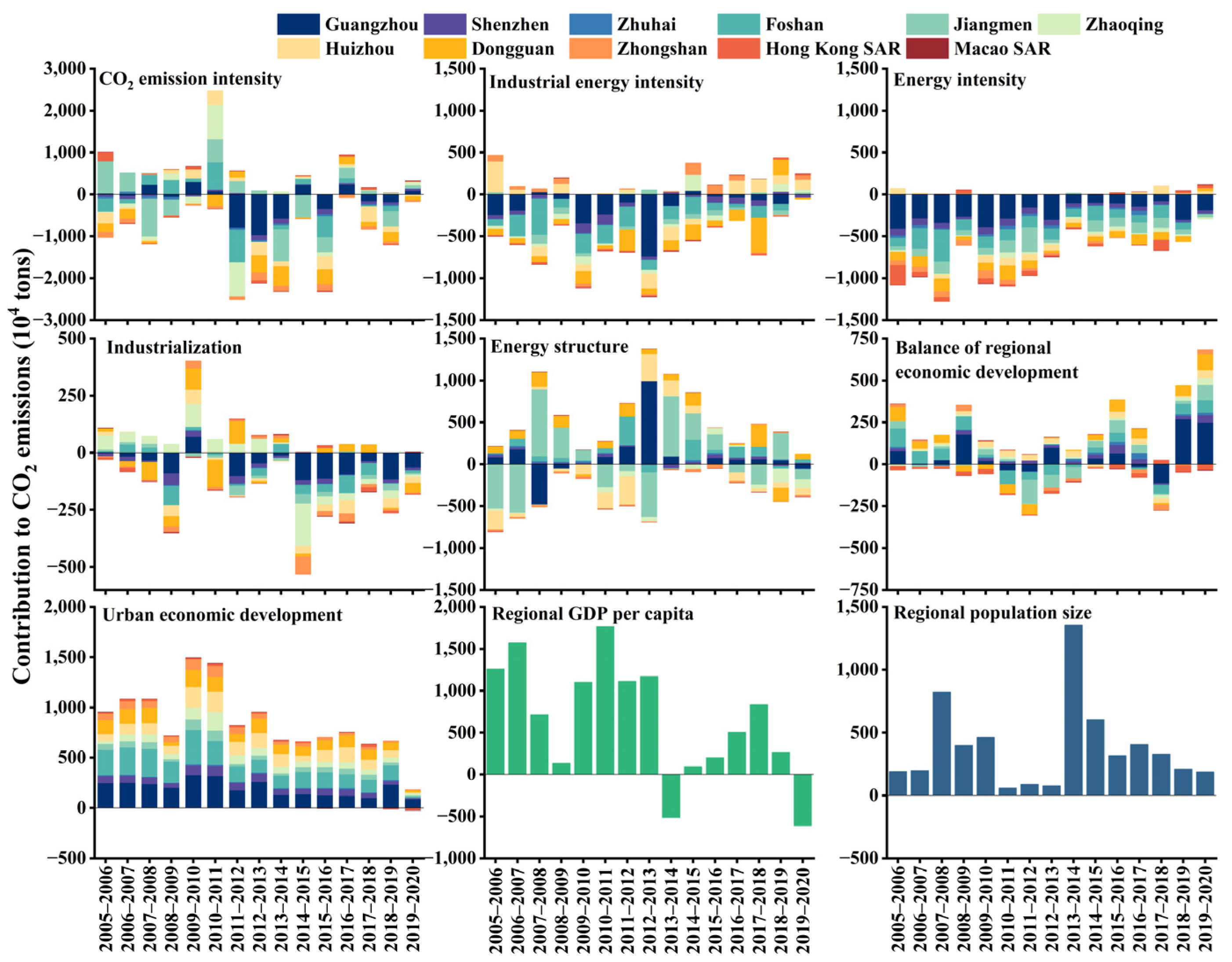
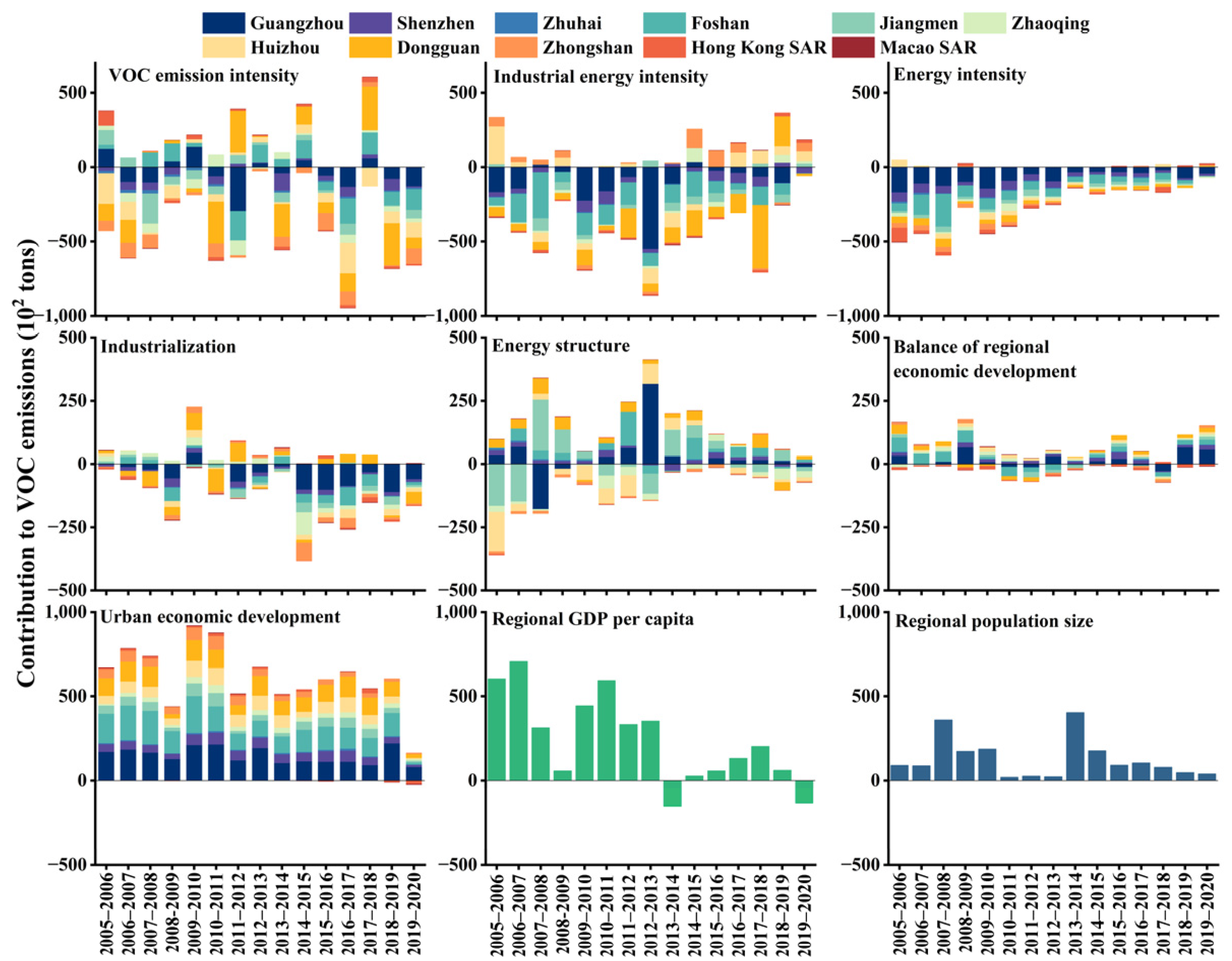
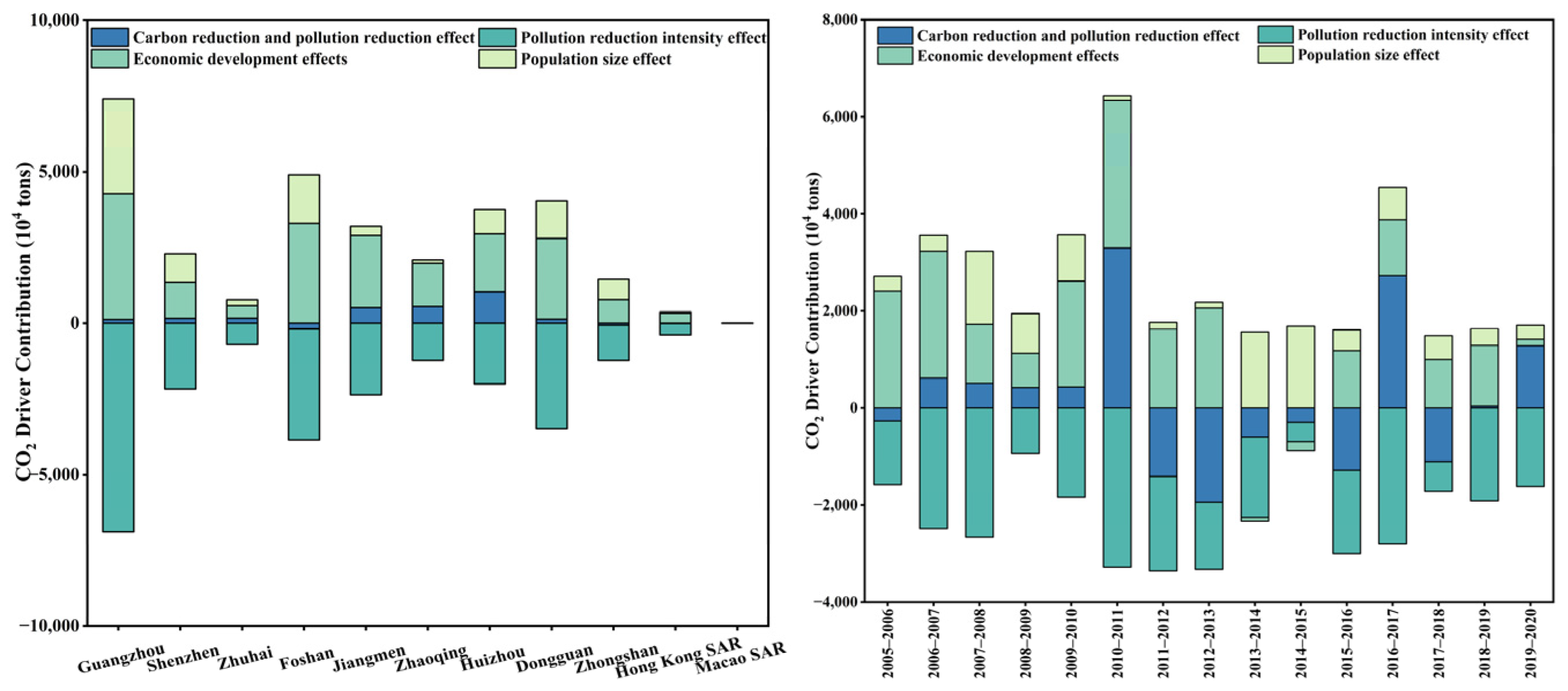
3.2.2. Analysis of the Absolute Contribution of Driving Factors for CO2 and VOC Emission Reduction at Urban Scale
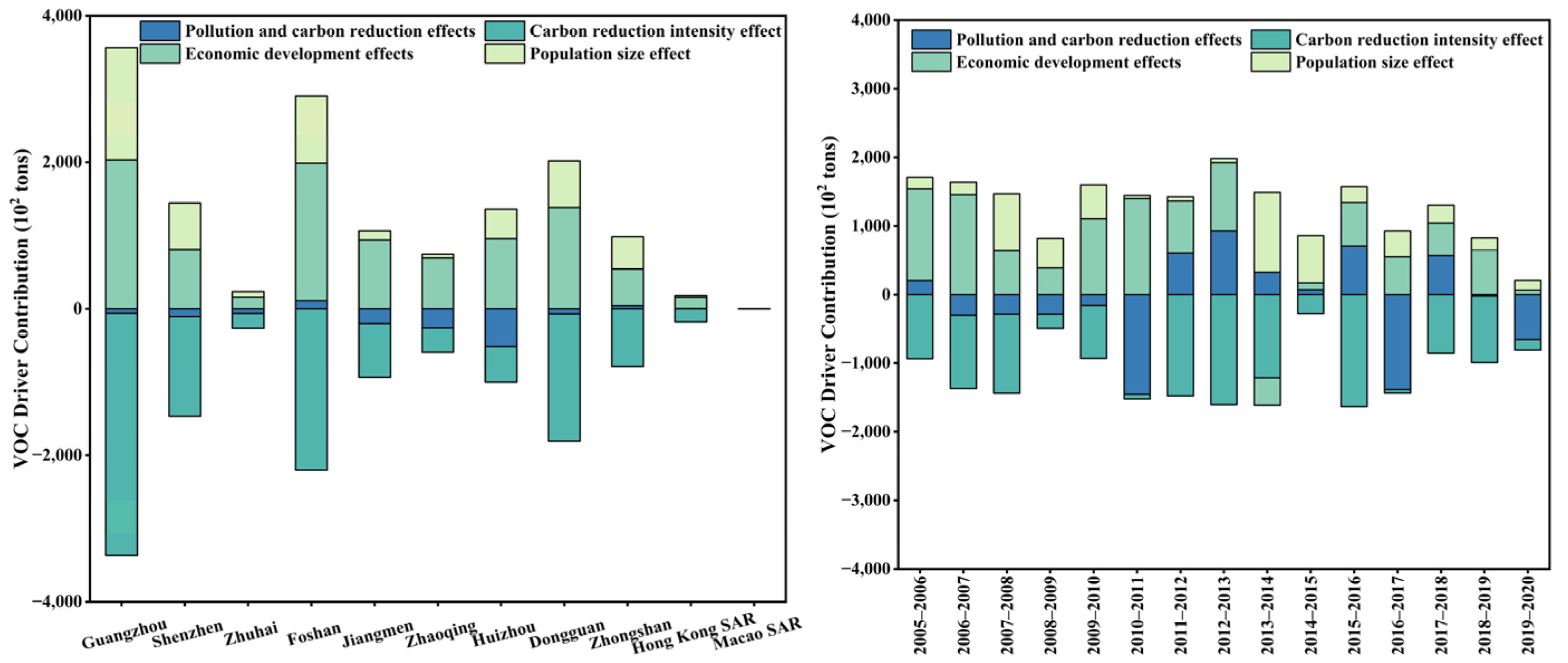
3.3. Analysis of CAP Collaborative Driving Factors
3.3.1. Analysis of the Contribution Level of CR to PR
3.3.2. Analysis of the Contribution Level of PR to CR
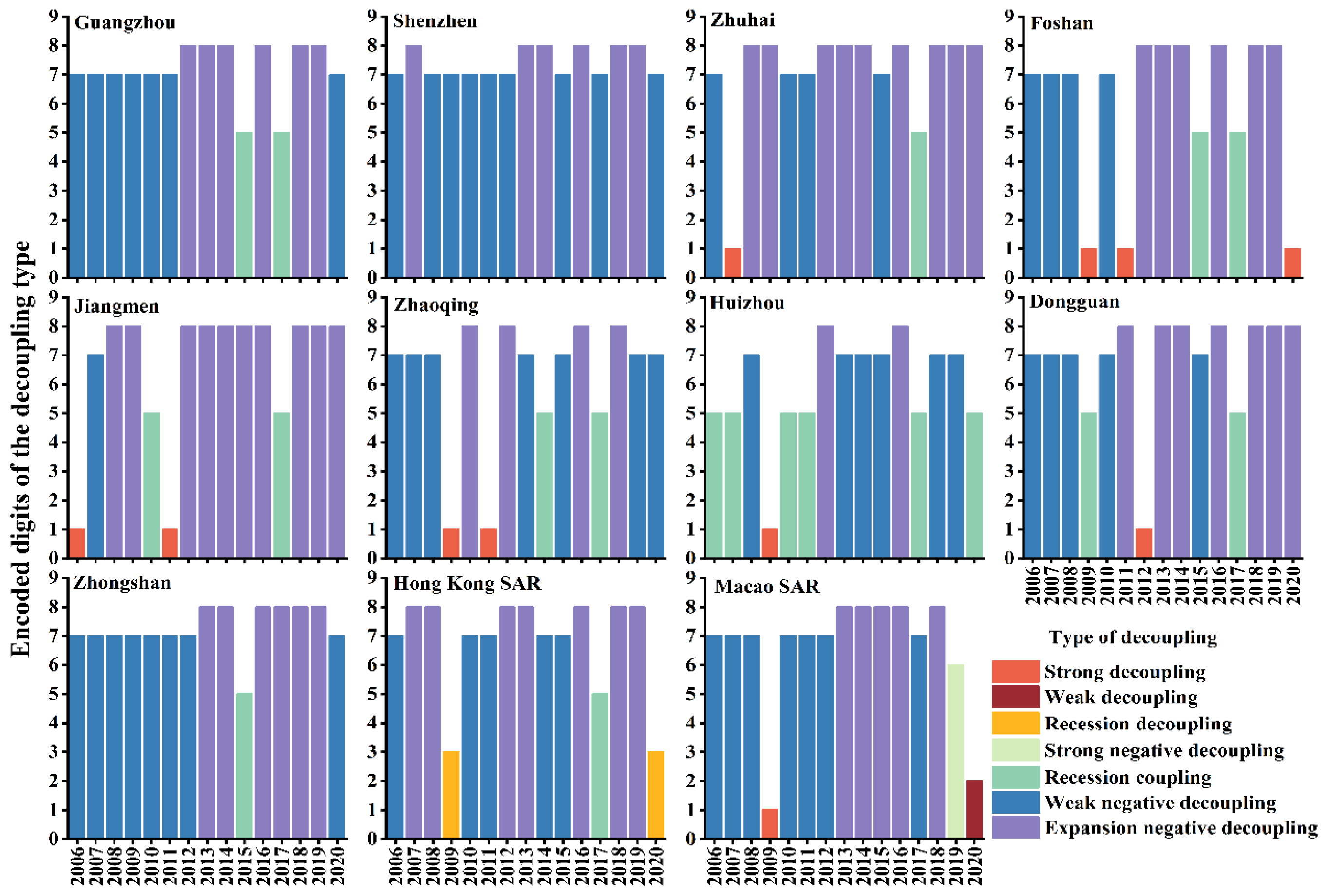
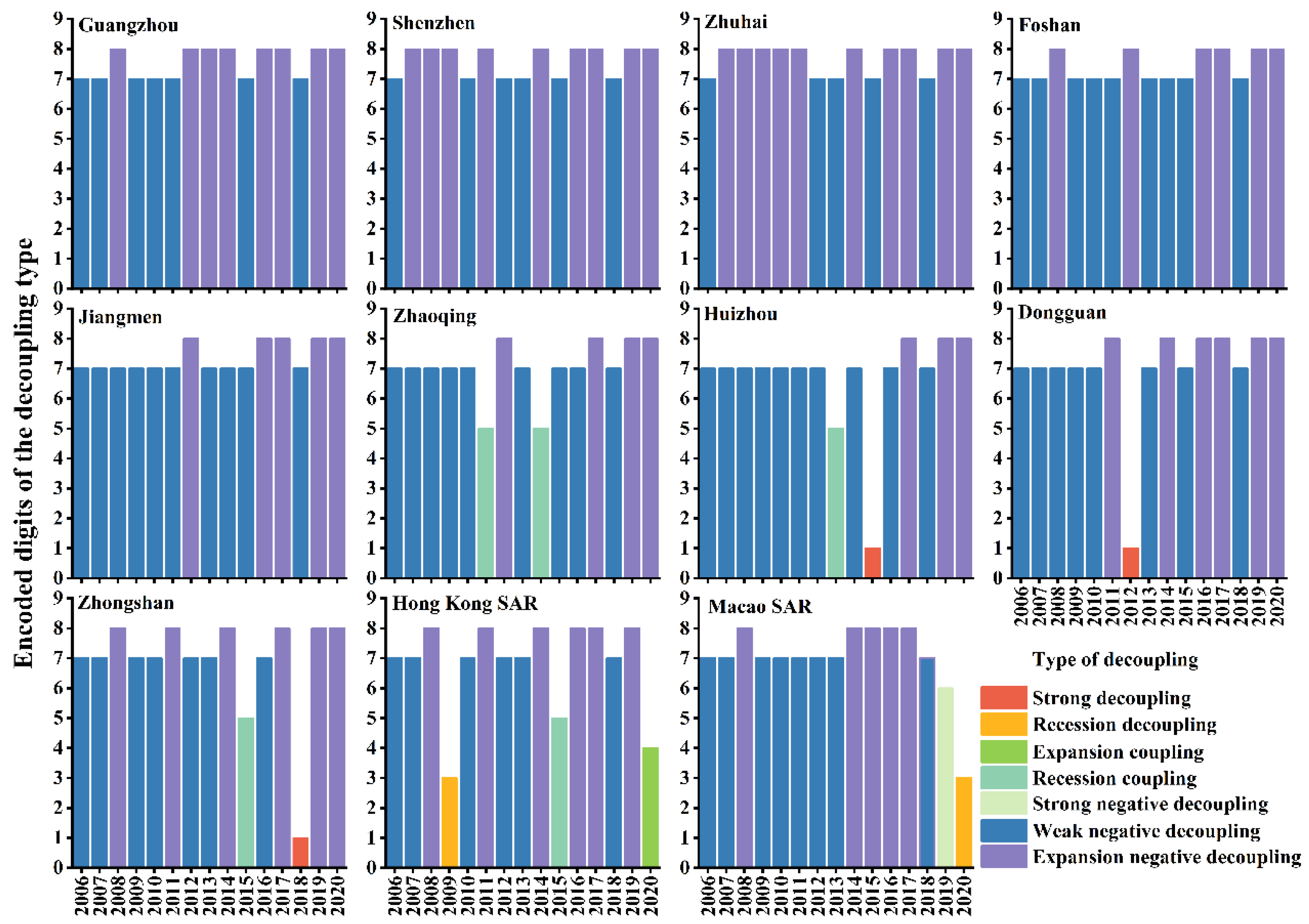
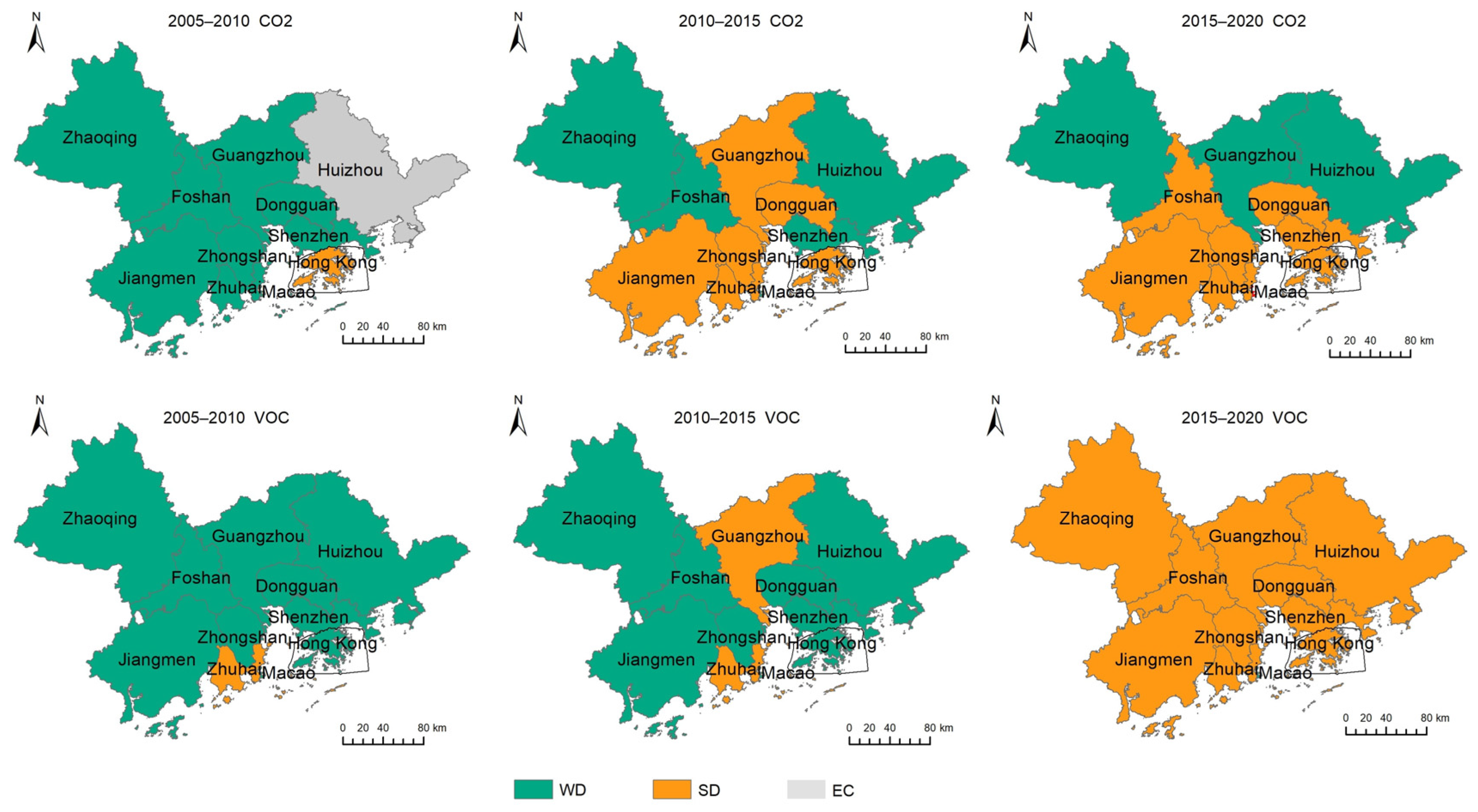
3.4. Decoupling Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. The Spatiotemporal Characteristics of CAP in the GBA
4.2. Sectoral Emission Variance of CAP in the GBA
4.3. Synergistic Driving Factors and Decoupling Status of CAP in the GBA
4.4. Limitation
5. Conclusions and Policy Proposal
- (1)
- Address the negative driving effects of economic development and population size on emissions by promoting decoupling between economic growth and CO2/VOC emissions. Specific measures include optimizing industrial structure, developing green industries, promoting low-carbon technologies, and strengthening end-management measures.
- (2)
- Leverage successful pollution and carbon reduction experiences from Guangzhou, Foshan, Dongguan, and Jiangmen for replication in other cities. Enhance regional collaborative governance to achieve holistic improvements in environmental quality.
- (3)
- Expand clean energy adoption, optimize industrial structures, and improve energy efficiency to realize win-win outcomes between economic growth and environmental quality improvement.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, J.T.; Nielsen, C.P.; Zhao, Y.; Lei, Y.; Liu, Y.; Mcelroy, M.B. Recent Changes in Particulate Air Pollution over China Observed from Space and the Ground: Effectiveness of Emission Control. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7771–7776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.B.; Liu, Z.; Geng, Y.; Lindner, S.; Hubacek, K. The gigatonne gap in China’s carbon dioxide inventories. Nat. Clim. Change 2012, 2, 672–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Yu, B.Y.; Chen, J.M.; Wei, Y.M. Green transition pathways for cement industry in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 166, 105355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jacob, D.J.; Liao, H.; Shen, L.; Zhang, Q.; Bates, K.H. Anthropogenic drivers of 2013-2017 trends in summer surface ozone in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SCC (State Council of China). Action Plan for Sustained Improvement of Air Quality (State Council of China). 2023. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/202312/content_6919000.htm (accessed on 7 December 2023).
- Wang, T.; Xue, L.; Brimblecombe, P.; Lam, Y.F.; Li, L.; Zhang, L. Ozone pollution in China: A review of concentrations, meteorological influences, chemical precursors, and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1582–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.R.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, R. Per-capita carbon emissions in 147 countries: The effect of economic, energy, social, and trade structural changes. Sustain. Prod. Consump. 2021, 27, 1149–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.Y.; Yuan, Z.L. Effect evaluation and expansion mechanism analysis of synergistic emission reduction in China’s power industry. China Ind. Econ. 2017, 2, 17. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Cheng, R.K.; Li, X.R.; Zhao, M.M. On the driving factors of China’s provincial carbon emission from the view of periods and groups. Environ. Sci. Pollut. 2021, 28, 51971–51988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.X.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.X.; Su, B.; Chen, Z.L.; Lin, W.C. China’s environmental policy intensity for 1978–2019. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Tan, Z.X.; Mu, S.Y.; Wang, J.Y.; Chen, Y.Y.; He, X.W. Synergy level of pollution and carbon reduction in the Yangtze River Economic Belt: Spatial-temporal evolution characteristics and driving factors. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 98, 104859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.H.; He, L.Y. Study on the synergistic effect of air pollution prevention and carbon emission reduction in the context of “dual carbon”: Evidence from China’s transport sector. Energy Policy 2023, 173, 113370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.Z.; Sun, W. Synergistic impacts of clean energy demonstration policy on air pollution and carbon reduction. Sustainability 2014, 16, 9928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.L.; Li, H.M.; Deng, X.H. Measuring the Synergistic Effect of Pollution and Carbon Reduction in China’s Industrial Sector. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.P.; Wei, Y.J.; Wang, T.Y.; Shen, J.L.; Zhao, T.; Dong, L. Spatial correlation network on synergy between carbon reduction and pollution control in key areas for air pollution prevent and control. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 491, 144777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, Y.L.; Zhu, X.D. Investigation of a coupling model of coordination between urbanization and the environment. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 98, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.N.; Liao, M.J.; Hu, M.Y.; Xu, C.B.; Tao, Y.; Zhou, J.L. Effectiveness assessment of air pollution prevention and control under collaborative supervision in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region based on combination weights and grey fuzzy synthetic evaluation analysis. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 64, 102543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Rong, B.; Kang, L.; Zhang, N.N.; Chu, C.J. Heterogeneity and typology of the city-level synergy between CO2 emission, PM2.5, and ozone pollution in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 405, 136871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.B.; Lei, Y.; Liu, X.; Shi, X.R.; Liu, Z.Y.; Xu, Y.L.; Chen, X.J.; Song, X.H.; Zheng, Y.X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Synergistic assessment of air pollution and carbon emissions from the economic perspective in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, R.P.; Li, L.P. Research on construction and application of evaluation index system of synergistic degree of urban pollution reduction and carbon reduction. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2024, 20, 242–252. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yi, H.R.; Zhao, L.J.; Qian, Y.; Zhou, L.X.; Yang, P.L. How to achieve synergy between carbon dioxide mitigation and air pollution control? Evidence from China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 78, 103609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.Y.; Li, J.M.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhou, A.Q.; Li, M.H. County carbon emissions in the Yangtze River Delta region: Spatial layout, dynamic evolution and spatial spillover effects. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 977198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.Z.; Zhang, K.R.; Li, D.Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Liu, W.Y. Analysis of the spatial-temporal evolution and driving factors of carbon emission efficiency in the Yangtze River economic Belt. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 165, 112092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.C.; Sun, H.; Yang, Z.D.; Zhu, S.S. Evaluation on evolution of spatial relationship between carbon emissions and economic growth in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Environ. Sci. Pollut. 2024, 31, 8453–8466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Z.M.; Wu, T.; Wu, S.Y.; Yin, T.W. The decoupling analysis of CO2 emissions from power generation in Chinese provincial power sector. Energy 2022, 255, 124488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.J.; Lyu, W.; Zang, X.H.; Zheng, F.; Zhao, W.C.; Xu, Q.; Lu, J.Y. Exploring the factors effecting on carbon emissions in each province in China: A comprehensive study based on symbolic regression, LMDI and Tapio models. Environ. Sci. Pollut. 2023, 30, 87071–87086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Sun, S. Air pollution driving factors analysis: Evidence from economically developed area in China. Environ. Prog. Sustain. 2016, 35, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.R.; Ji, Q.; Fan, Y. Spatial linkage analysis of the impact of regional economic activities on PM2.5 pollution in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 139, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Liu, W.; Khan, I.; Zhang, J.F. The nexus between natural resources, renewable energy consumption, economic growth, and carbon dioxide emission in BRI countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. 2023, 30, 36692–36709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.Q.; Agyeman, S.D. Assessing Sub-Saharan Africa’s low carbon development through the dynamics of energy-related carbon dioxide emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 274, 122676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.Z.; Matsumoto, K. Drivers of the change in carbon dioxide emissions under the progress of urbanization in 30 provinces in China: A decomposition analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 322, 129000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.C.; Zhu, W.J.; Wang, S.G.; Chen, B. Drivers of global carbon emissions 1990–2014. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 371, 133371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, M.; Fan, M.; Xie, P. Synergistic relationship and interact driving factors of pollution and carbon reduction in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. 2023, 30, 118677–118692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.R.; Song, Y.; Zhou, A.N.; Liu, J.; Pang, J.R.; Zhang, M. Study on the pollution emission efficiency of China’s provincial regions: The perspective of Environmental Kuznets curve. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.J.; Huang, Q.X.; Yue, H.B.; He, C.Y.; Wang, C.B.; Zhang, H. Reexamining the relationship between urbanization and pollutant emissions in China based on the STIRPAT model. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 273, 111134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Miao, Y.M.; Li, Y.F.; Li, Y.W.; Ma, X.X.; Xu, S.C.; Wang, S.X. Decomposition Analysis of Factors that Drive the Changes of Major Air Pollutant Emissions in China at a Multi-Regional Level. Sustainability 2020, 11, 7713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Zhao, T.; Wang, J. Analyzing driving forces of China’s carbon emissions from 1997 to 2040 and the potential emission reduction path: Through decomposition and scenario analysis. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2022, 24, 1219–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Liu, G.L.; Liu, S.X. Driving factors of NOx emission reduction in China’s power industry: Based on LMDI decomposition model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. 2023, 30, 51042–51060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.Y.; Jiang, W.; Gao, W.D.; Lu, C. Unveiling the Spatial-Temporal Characteristics and Driving Factors of Greenhouse Gases and Atmospheric Pollutants Emissions of Energy Consumption in Shandong Province, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.Y.; Hochman, G.; Timilsina, G.R. Do drivers of CO2 emission growth alter overtime and by the stage of economic development? Energy Policy 2020, 140, 111420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.M.; Wang, Y.; Peng, J.T.; Li, F.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, H.H.; Shi, R. Can China achieve its 2030 and 2060 CO2 commitments? Scenario analysis based on the integration of LEAP model with LMDI decomposition. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 888, 164151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, B.; Lopez, N.S.A.; Biona, J.B.M.; Chiu, A.S.F.; Blesl, M. Driving forces of Iran’s CO2 emissions from energy consumption: An LMDI decomposition approach. Appl. Energy 2017, 206, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, T.; Ang, B.W.; Su, B.; Wang, H. Drivers of stagnating global carbon intensity of electricity and the way forward. Energy Policy 2018, 113, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.J.; Lv, D.H. Analysis of Agricultural CO2 Emissions in Henan Province, China, Based on EKC and Decoupling. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.G.; Yan, F.Q.; Su, F.Z. Impacts of urbanization on the ecosystem services in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao greater bay area, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Pan, M.X.; Wu, X.L. Sustainable development in the export trade from a symbiotic perspective on carbon emissions, exemplified by the case of Guangdong, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, K.J.; Liang, S.; Zeng, X.L.; Cai, Y.P.; Meng, J.; Shan, Y.L.; Guan, D.B.; Yang, Z.F. Trends, Drivers, and Mitigation of CO2 Emissions in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. Engineering 2023, 23, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guangdong Provincial Eco-Environmental Monitoring Center. Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Pearl River Delta Regional Air Monitoring Network 2022 Monitoring Results Report [R/OL]. Available online: https://gdee.gd.gov.cn/attachment/0/528/528233/4199318.pdf (accessed on 7 April 2023).
- Tobler, W. On the first law of geography: A reply. Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2004, 94, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. Local indicators of spatial association-LISA. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Zhou, W.S.Q.; Yuan, S.; Huo, L. Spatiotemporal Characterization of the Three-Dimensional Morphology of Urban Buildings Based on Moran’s I. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefever, D.W. Measuring geographic concentration by means of the standard deviational ellipse. Am. J. Sociol. 1926, 32, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.W.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Zhang, P. A new method for identifying industrial clustering using the standard deviational ellipse. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.D.; Wang, P.; Cui, L.B.; Huang, S.; Song, M.L. Decomposition and decoupling analysis of CO2 emissions in OECD. Appl. Energy 2018, 231, 937–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, Y. Impact of Carbon Dioxide Emission Control on GNP Growth: Interpretation of Proposed Scenarios; IPCC Energy and Industry Subgroup: Paris, France, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- To, W.M.; Lai, T.M.; Lo, W.C.; Lam, K.H.; Chung, W.L. The growth pattern and fuel life cycle analysis of the electricity consumption of Hong Kong. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 165, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Liang, H.W. Spatial analysis on China’s regional air pollutants and CO2 emissions: Emission pattern and regional disparity. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 92, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hou, L.P.; Wang, L.; Tang, L.N. Decoupling Analysis between Economic Growth and Air Pollution in Key Regions of Air Pollution Control in China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.R.; Li, L.J.; Wang, Q. The impact of energy efficiency on carbon emissions: Evidence from the transportation sector in Chinese 30 provinces. Sustain. Cities. Soc. 2022, 82, 103880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, Z.; Mao, X.Q.; Cai, B.F.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Chen, Y.P.; Gao, Y.B.; Guo, Z. Exploring the spatiotemporal pattern evolution of carbon emissions and air pollution in Chinese cities. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Lv, J.H. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Tapio Decoupling Analysis of Energy-Related Carbon Emissions Using Nighttime Light Data: A Quantitative Case Study at the City Scale in Northeast China. Energies 2024, 17, 4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Zha, X.X.; Ma, J.Y.; Li, B.Y.; Wang, X.P. Dynamic Optimal Control Strategy of CCUS Technology Innovation in Coal Power Stations Under Environmental Protection Tax. Systems 2025, 13, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Tam, V.W.Y.; Shuai, C.Y.; Shen, L.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, S.J. Decoupling China’s economic growth from carbon emissions: Empirical studies from 30 Chinese provinces (2001–2015). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 656, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, M.H.; Zhou, M. A comparative study on decoupling relationship and influence factors between China’s regional economic development and industrial energy-related carbon emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 783–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.H.; Zhang, C. A dynamic analysis of a green closed-loop supply chain with different on-line platform smart recycling and selling models. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2025, 200, 110748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Tong, D.; Li, M.; Liu, F.; Hong, C.P.; Geng, G.N.; Li, H.Y.; Li, X.; Peng, L.Q.; Qi, J.; et al. Trends in China’s anthropogenic emissions since 2010 as the consequence of clean air actions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 14095–14111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Pan, J.H.; Wang, W.D.; Liu, Z.X.; Kan, H.D.; Qiu, Y.; Meng, X.; Wang, W.B. Association of particulate matter pollution and case fatality rate of COVID-19 in 49 Chinese cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.S.; Liu, F.; Wang, H.B.; Yang, R.F.; Chen, D.B.; Wang, X.X.; Lu, F.M.; Rao, H.Y.; Chen, H.S. Prevention and control measures significantly curbed the SARS-CoV-2 and influenza epidemics in China. J. Virus. Erad. 2021, 7, 100040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Uno, I.; Yumimoto, K.; Itahashi, S.; Chen, X.S.; Yang, W.Y.; Wang, Z.F. Impacts of COVID-19 lockdown, Spring Festival and meteorology on the NO2 variations in early 2020 over China based on in-situ observations, satellite retrievals and model simulations. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 244, 117972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Mei, Y.R.; Zhang, T.; Xie, Y.B. Paths to carbon neutrality in China’s chemical industry. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 999152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Z. Research on synergistic mechanism of carbon reduction and pollution prevention. Energy Conserv. 2022, 6, 84–86. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Wang, W.L.; Yao, X. Study on the impact of coal power emission reduction on air pollutant emission control in China. Electr. Power 2019, 52, 110–117. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.D.; Wang, B.; Huang, S.; Song, M.L. The influence of increased population density in China on air pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Symbols | Meanings | Symbols | Meanings |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO2/VOC total emissions | CO2/VOC emission intensity of the j sector in City i | ||
| CO2/VOC emissions of the j sector in City i | Energy consumption intensity of industrial sectors | ||
| Energy consumption | Level of industrialization of City i | ||
| Output value of the j sector in City i | Energy consumption structure of the j sector in City i | ||
| Economic output of City i | Energy intensity of City i | ||
| Gross regional product (GDP) | Proportion of the economic output of City i | ||
| Number of permanent residents | Per capita GDP |
| Variables | Unit | Mean | Standard Deviation | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total energy consumption | Tons of standard coal | 19,972.07 | 3322.73 | 14,287.75 | 24,933.67 |
| Industrial added value | Hundred million yuan | 25,350.29 | 9016.09 | 10,622.19 | 38,031.49 |
| Gross regional product | Hundred million yuan | 79,592.97 | 29,957.67 | 32,711.41 | 124,690.17 |
| Gross domestic product per capita | Ten thousand yuan/person | 11.14 | 2.65 | 6.20 | 14.66 |
| Population | Ten thousand person | 7025.69 | 1093.08 | 5279.35 | 8634.52 |
| Symbols | Meanings | Symbols | Meanings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total VOC emissions | Cooperative emission reduction coefficient of CO2 and VOCs | ||
| Total CO2 emissions | CO2 emission reduction intensity of City i | ||
| CO2/VOC emissions of the j sector in City i | VOC emission reduction intensity of City i | ||
| Economic output of City i | Per capita GDP | ||
| Number of permanent residents |
| Decoupling State | Decoupling Type | Environmental Pressure Growth Rate () | Economy Driven Growth Rate () | Decoupling Index, |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decoupling | Strong decoupling (SD) | (− 0) | (0, ) | |
| Weak decoupling (WD) | (0, ) | (0, ) | ||
| Recession decoupling (RD) | (−, 0) | (−, 0) | ||
| Coupling | Expansion coupling (EC) | (0, ) | (0, ) | |
| Recession coupling (RC) | (−, 0) | (−, 0) | ||
| Negative decoupling | Strong negative decoupling (SND) | (0, ) | (−, 0) | |
| Weak negative decoupling (WND) | (−, 0) | (−, 0) | ||
| Expansion negative decoupling (END) | (0, ) | (0, ) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, S.; Jia, Y.; Lv, Q.; Shi, L.; Gao, L. Spatiotemporal Characteristic and Driving Factors of Synergy on Carbon Dioxide Emission and Pollutants Reductions in the Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area, China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4066. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094066
He S, Jia Y, Lv Q, Shi L, Gao L. Spatiotemporal Characteristic and Driving Factors of Synergy on Carbon Dioxide Emission and Pollutants Reductions in the Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area, China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(9):4066. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094066
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Sinan, Yanwen Jia, Qiuli Lv, Longyu Shi, and Lijie Gao. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Characteristic and Driving Factors of Synergy on Carbon Dioxide Emission and Pollutants Reductions in the Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area, China" Sustainability 17, no. 9: 4066. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094066
APA StyleHe, S., Jia, Y., Lv, Q., Shi, L., & Gao, L. (2025). Spatiotemporal Characteristic and Driving Factors of Synergy on Carbon Dioxide Emission and Pollutants Reductions in the Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area, China. Sustainability, 17(9), 4066. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094066






