A Study on the Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity and Driving Factors of Mariculture Pollution in the Bohai Rim Region, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
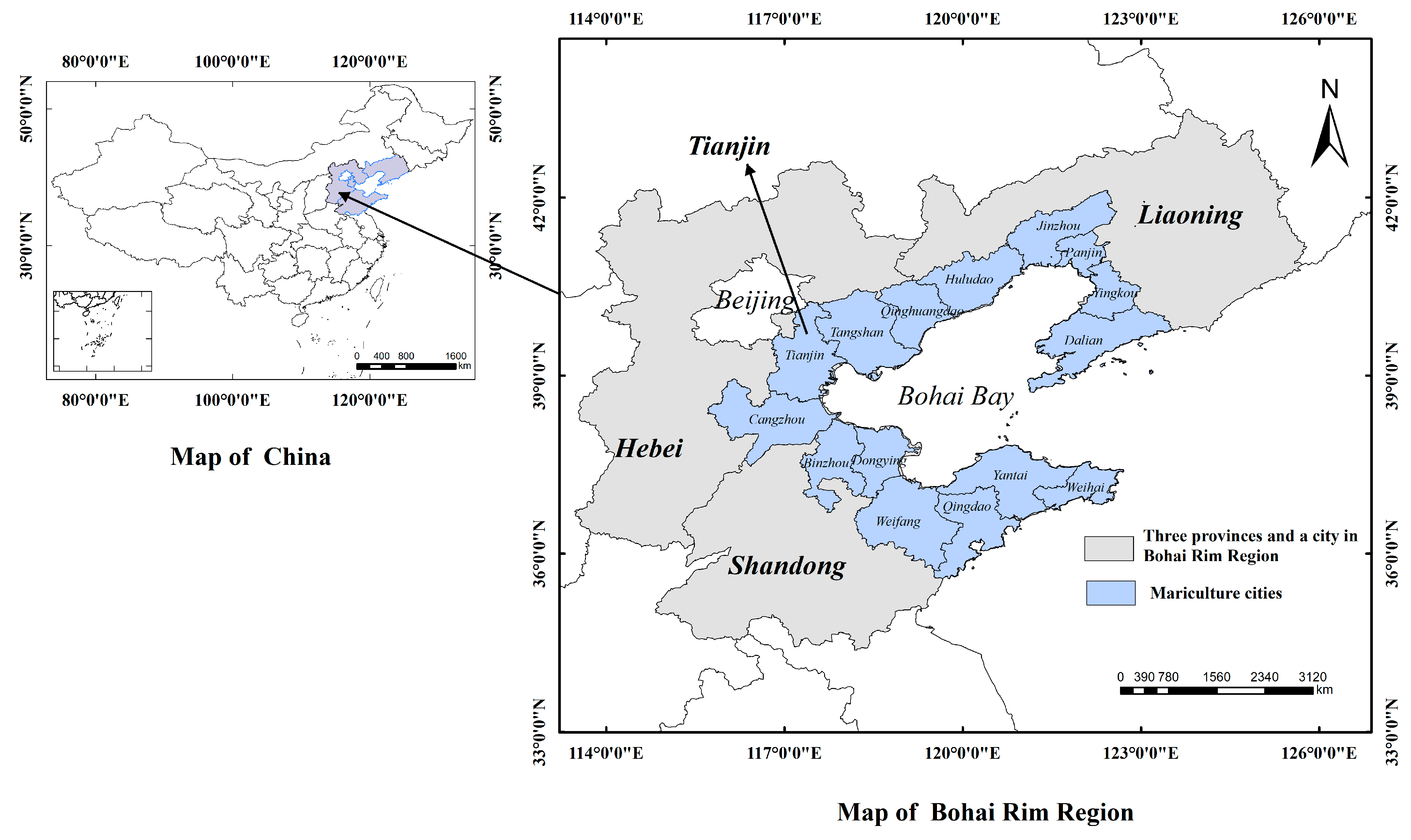
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Resources
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. PCM
2.3.2. Equivalent Pollution Load Method
2.3.3. Logarithmic Mean Divisia Index
2.3.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Overview of Mariculture in the Bohai Rim Region
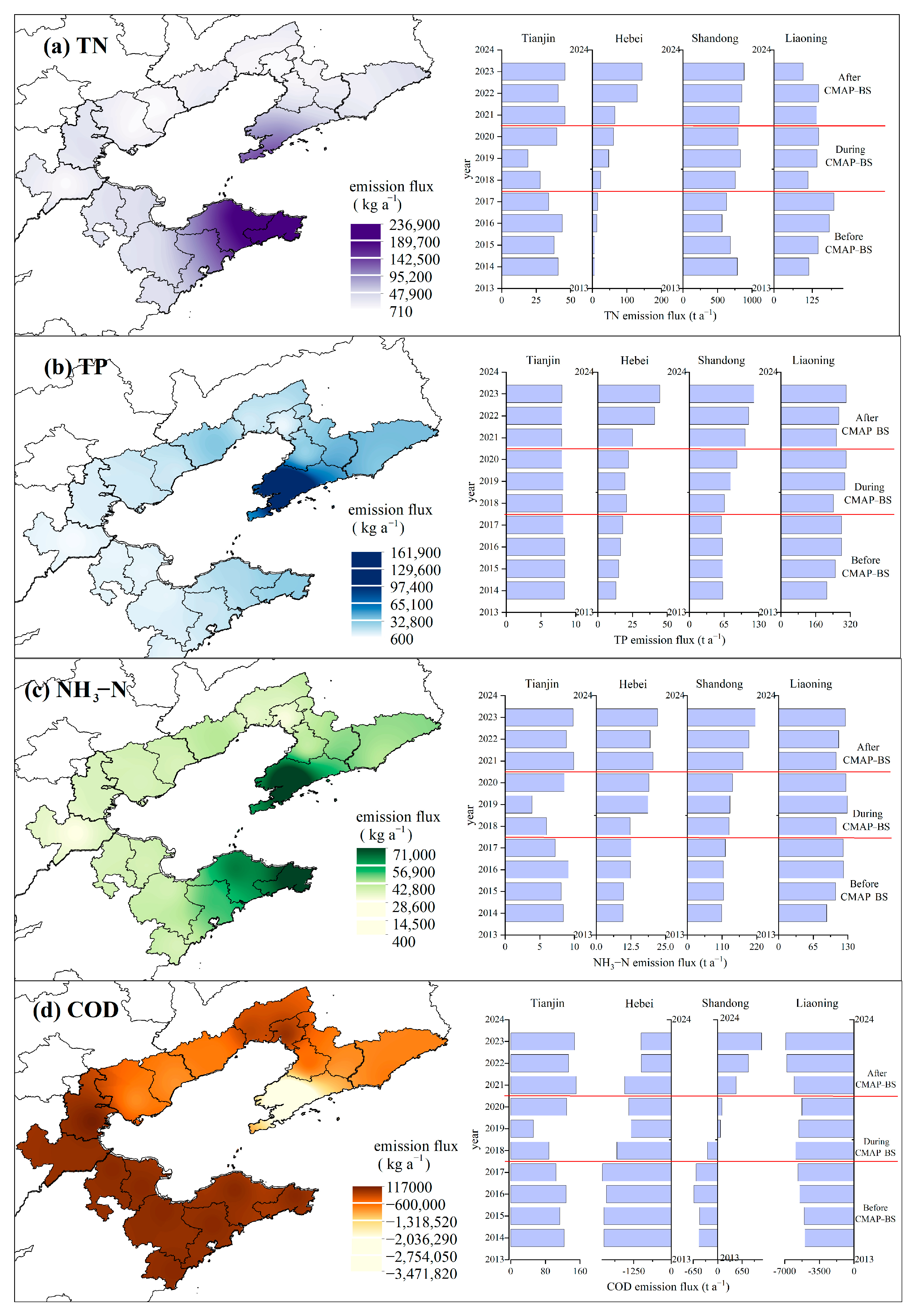
3.2. The Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity of Mariculture Pollution Discharge
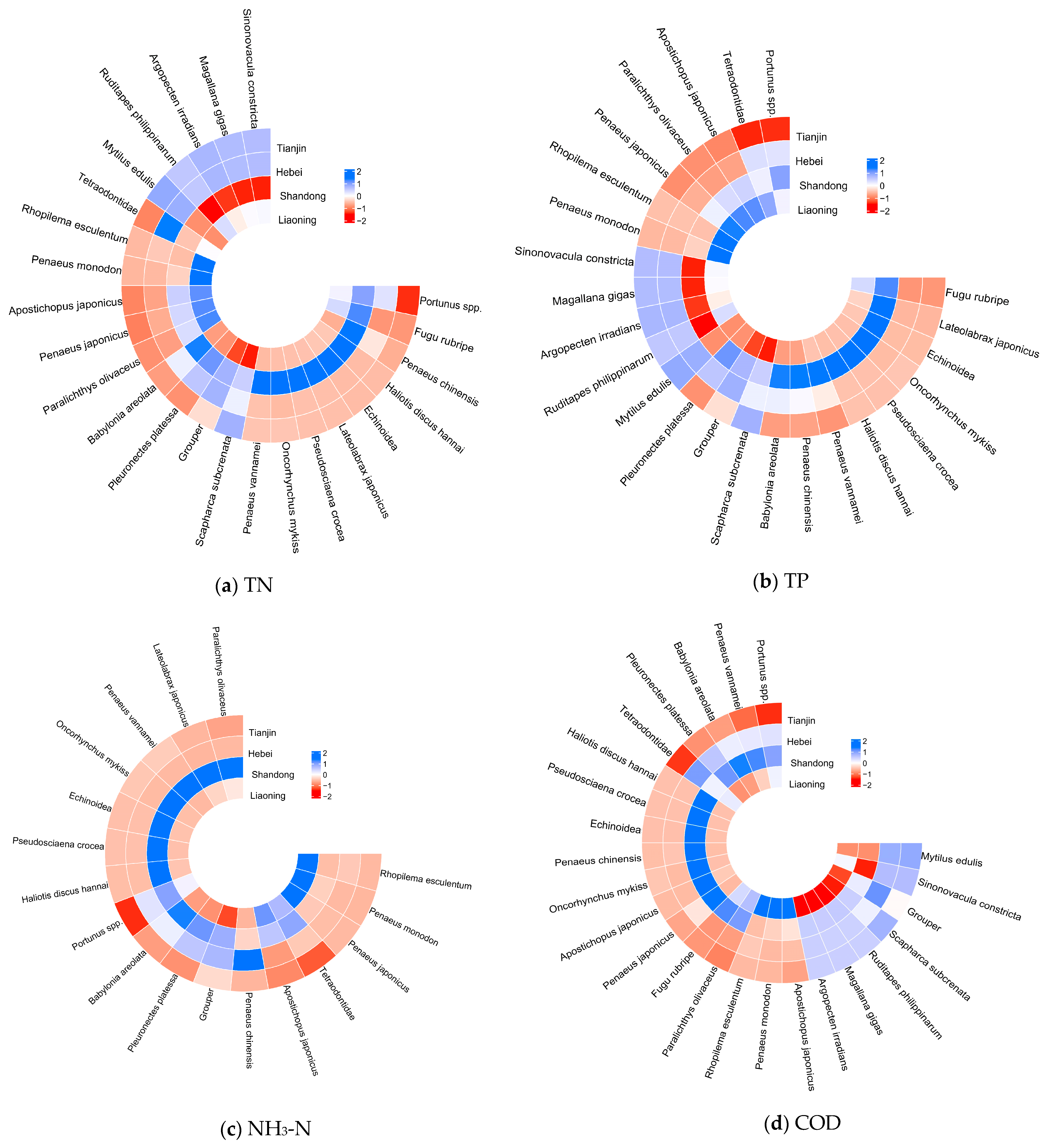
3.3. Impact of Mariculture Taxa on Pollution Emissions
3.4. Decomposition of the Driving Factors of Mariculture Pollution
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, J.-K.; Li, Y.-H. Evolution of marine spatial planning policies for mariculture in China: Overview, experience and prospects. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2020, 196, 105293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Wang, W.; Yang, Y.; Yang, C.; Yuan, Z.; Xiong, S.; Diana, J. Environmental impact of aquaculture and countermeasures to aquaculture pollution in China. Env. Sci. Pollut. R 2007, 14, 452–462. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Cuthbertson, A.; Gualtieri, C.; Shao, D. A Review on Mariculture Effluent: Characterization and Management Tools. Water 2020, 12, 2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwman, L.; Beusen, A.; Glibert, P.M.; Overbeek, C.; Pawlowski, M.; Herrera, J.; Mulsow, S.; Yu, R.; Zhou, M. Mariculture: Significant and expanding cause of coastal nutrient enrichment. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 044026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudouresque, C.-F.; Blanfuné, A.; Pergent, G.; Pergent-Martini, C.; Perret-Boudouresque, M.; Thibaut, T. Impacts of marine and lagoon aquaculture on macrophytes in Mediterranean benthic ecosystems. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honkanen, T.; Helminen, H. Impacts of fish farming on eutrophication: Comparisons among different characteristics of ecosystem. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. A J. Cover. All Asp. Limnol. Mar. Biol. 2000, 85, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Zhu, H.; Shutes, B.; Yan, B.; Zhou, Q.; Yu, X. Historical evolution of mariculture in China during past 40 years and its impacts on eco-environment. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.Y.; Hou, L.C.; Ping, N.X.; Ling, T.D.; Kyo, C.I. Development of mariculture and its impacts in Chinese coastal waters. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2004, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Kuang, C.; Gu, J.; Zou, Q.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Zhu, L. Total maximum allocated load of chemical oxygen demand near Qinhuangdao in Bohai sea: Model and field observations. Water 2020, 12, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jia, C.; Zhao, H.; Teng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P. Investigation on the influence of the Bohai Sea Geological Environment on the submarine stratum stability based on data mining: An intelligent prediction model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 11617–11633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Sun, Y.; Song, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X. Recurrence of the green tide in the Bohai Sea, China: A green tide caused by coastal reclamation projects. J. Sea Res. 2023, 191, 102333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Han, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y. Molecular identification of the macroalgae that cause green tides in the Bohai Sea, China. Aquat. Bot. 2019, 156, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, X.; Yi, Z.; Xiao-Jing, S.; Yun-Ling, Z.; Hai-Peng, Z. The distribution of large floating seagrass (Zostera marina) aggregations in northern temperate zones of Bohai Bay in the Bohai Sea, China. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0201574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Xu, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Xu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Otaki, T.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Y. Seasonal variations in the diversity and benthic community structure of subtidal artificial oyster reefs adjacent to the Luanhe River Estuary, Bohai Sea. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinho-Soriano, E.; Nunes, S.; Carneiro, M.; Pereira, D. Nutrients’ removal from aquaculture wastewater using the macroalgae Gracilaria birdiae. Biomass Bioenergy 2009, 33, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Han, Y. Impact of China’s marine governance policies on the marine ecological environment—A case study of the Bohai rim. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2023, 246, 106913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S. Nitrogen and phosphorus budget in coastal and marine cage aquaculture and impacts of effluent loading on ecosystem: Review and analysis towards model development. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Census, N.P.S. Emission factors Were Derived from the Manual of Emission Coefficient for the Second National Census of Pollution Source; The Second National Census of Pollution Source Office of the Ministry of Ecology and Environment: Beijing, China, 2020. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X. Environmental effects of mariculture in China: An overall study of nitrogen and phosphorus loads. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2022, 41, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, W.; Liao, Y.; Zhao, Z. Estimation and evaluation of aquaculture mass load based on inventory and improved entropy weight: The case of Zhuhai City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 157, 111205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Cui, J.; Wang, S.; Lindley, S. Customizing the coefficients of urban domestic pollutant discharge and their driving mechanisms: Evidence from the Taihu Basin, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 213, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, S.; Wu, S.; Wang, C.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, J. Combining emission inventory and isotope ratio analyses for quantitative source apportionment of heavy metals in agricultural soil. Chemosphere 2018, 204, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Khan, M.A.; Ul Husnain, M.I. Searching appropriate system boundary for accounting India’s emission inventory for the responsibility to reduce carbon emissions. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 295, 112907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Tang, M.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Ma, Y. Analysis of the spatial distribution characteristics of livestock and poultry farming pollution and assessment of the environmental pollution load in Anhui province. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Hao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Su, M. China’s low-carbon industrial transformation assessment based on Logarithmic Mean Divisia Index model. RCR Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2016, 108, 156–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, I.; Khan, S.; Majeed, M.T. Environmental impact of economic activities: Decoupling perspective of Singapore using log mean Divisia index decomposition technique. Geol. J. 2023, 58, 3720–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, J.; Xu, L.; Liang, Y. What drives the growth of China’s mariculture production? An empirical analysis of its coastal regions from 1983 to 2019. Env. Sci. Pollut. R 2023, 30, 111397–111409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Xu, Y.; Dong, B.; Nishino, N. Mariculture carbon sequestration efficiency in China: Its measurement and socio-economic factor analysis. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2023, 40, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Nie, H. Estimation of Mariculture Carbon Sinks in China and Its Influencing Factors. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Lyu, S.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X. Assessing the carbon sink capacity of coastal mariculture shellfish resources in China from 1981–2020. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 981569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, I.; Martínez-Aragón, J.; Tovar, A.; Pérez-Lloréns, J.; Vergara, J. Biofiltering efficiency in removal of dissolved nutrients by three species of estuarine macroalgae cultivated with sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) waste waters 2. Ammonium. J. Appl. Phycol. 2002, 14, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neori, A.; Chopin, T.; Troell, M.; Buschmann, A.H.; Kraemer, G.P.; Halling, C.; Shpigel, M.; Yarish, C. Integrated aquaculture: Rationale, evolution and state of the art emphasizing seaweed biofiltration in modern mariculture. Aquaculture 2004, 231, 361–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ji, J. The decoupling and influencing factors analysis of blue granary Eco-Economy system. J. Agrotech. Econ. 2020, 4, 94–106. [Google Scholar]
- Environment and Ocean [2018] No. 158, Action Plan for Comprehensive Management of the Bohai Sea, Central People’s Government of the People’s Republic of China. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/gongbao/content/2019/content_5377134.htm (accessed on 30 March 2025).
- Uchimura, M. Ecological studies of green tide, Ulva spp. (Chlorophyta) in Hiroshima Bay, the Seto Inland Sea. Jpn. J. Phycol. 2004, 52, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, N.-H.; Zhang, X.-W.; Mao, Y.-Z.; Liang, C.-W.; Xu, D.; Zou, J.; Zhuang, Z.-M.; Wang, Q.-Y. ‘Green tides’ are overwhelming the coastline of our blue planet: Taking the world’s largest example. Ecol. Res. 2011, 26, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Hu, C.; Wang, M.; Shang, S.; Wilson, C. Floating algae blooms in the East China Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 11,501–11,509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, J.K.; Saurel, C.; Nielsen, P.; Timmermann, K. The use of shellfish for eutrophication control. Aquacult. Int. 2016, 24, 857–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.; Bricker, S. Goods and services of extensive aquaculture: Shellfish culture and nutrient trading. Aquacult. Int. 2016, 24, 803–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Sen, B.; Shang, J.; He, Y.; Xie, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Johnson, Z.I.; Wang, G. Seasonal influence of scallop culture on nutrient flux, bacterial pathogens and bacterioplankton diversity across estuaries off the Bohai Sea Coast of Northern China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, M.A. Environmental impacts of shellfish aquaculture: Filter feeding to control eutrophication. In Marine Aquaculture and the Environment: A Meeting for Stakeholders in the Northeast; Cape Cod Press: Falmouth, MA, USA, 2001; pp. 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.; Sun, S.; Li, W.; Qiao, Z. Assessment of Carbon Sink Capacity and Economic Value of Maricultured Shellfish and Algae in China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2025, 34, 1311–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA USA. Federal Register: Environmental Protection Agency, 40 CFR Part 745; Lead; Identification of Dangerous Levels of Lead; Final Rule; EPA USA: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Rubino, M.C. Policy considerations for marine aquaculture in the United States. Rev. Fish Sci. Aquac. 2023, 31, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, H. Environmental quality criteria for aquaculture farms in Japanese coastal areas: A new policy and its potential problems. Bull. Natl. Res. Inst. Aquacult. 2000, 29, 123–134. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Strategic Guidelines for a More Sustainable and Competitive EU Aquaculture for the Period 2021 to 2030; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]



| Mariculture Taxa | Mariculture Species | TN | TP | NH3-N | COD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fish | Pseudosciaena crocea | 4.59 | 0.68 | 0.99 | 34.23 |
| Paralichthys spp. | 5.87 | 0.50 | 0.00 | 0.55 | |
| Pleuronectes platessa | 5.87 | 0.50 | 1.18 | 0.55 | |
| Oncorhynchus mykiss | 15.01 | 1.99 | 0.00 | 1.87 | |
| Fugu rubripe | 1.99~48.68 | 0.45~5.63 | 0.09~0.31 | 3.80~13.36 | |
| Lateolabrax japonicus | 0.78~68.03 | 16.27 | 0.95 | 39.64 | |
| Tetraodontidae | 1.99 | 0.45 | 0.31 | 3.80 | |
| Paralichthys olivaceus | 0.47~17.59 | 0.04~1.43 | 0.01~0.77 | 0.46~4.89 | |
| Grouper | 1.70~5.87 | 0.21~0.50 | 0.07 | 0.55~1.75 | |
| Crustacean | Penaeus monodon | 0.27 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 2.62 |
| Penaeus vannamei | 1.39~4.49 | 0.46~0.88 | 0.01~0.97 | 12.88~42.96 | |
| Penaeus japonicus | 0.27 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 2.62 | |
| Penaeus chinensis | 0.27 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 2.62 | |
| Portunus spp. | 1.99~3.60 | 0.38~1.27 | 0~1.44 | 1.55~5.4 | |
| Shellfish | Haliotis discus hannai | 0.74~2.51 | −0.08~0.96 | 0.02~0.07 | −0.01~8.12 |
| Sinonovacula constricta | −0.10 | −0.01 | 0.00 | −1.64 | |
| Ruditapes philippinarum | −0.10 | −0.01 | 0.00 | −1.64 | |
| Scapharca subcrenata | −0.10 | −0.01 | 0.00 | −1.64 | |
| Babylonia areolata | 0.76 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 2.22 | |
| Magallana gigas | −0.17 | −0.01 | 0.00 | −7.24~0.02 | |
| Argopecten irradians | −0.17~0.74 | −0.01~0.16 | 0~0.07 | −7.24~2.18 | |
| Mytilus edulis | −0.17 | −0.01 | 0.00 | −7.24~0.02 | |
| Others | Apostichopus japonicus | 0.74~10.94 | 0.05~1.74 | 0.01~0.34 | 3.09~15.76 |
| Echinoidea | 1.30~10.94 | 0.2~1.74 | 0.01~0.34 | 8.78 | |
| Rhopilema esculentum | 1.95 | 0.24 | 1.53 | 14.46 | |
| Others | 3.53~23.04 | 0.76~4.68 | 0.00~3.41 | 0.02~20.40 |
| Name | TN | TP | NH3–N ① | COD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tianjin | 8.0 (10.0) ② | 0.8(1.0) ② | 2.0 | 20 |
| Hebei | 8.0 | 1.0 | — | 20 |
| Shandong | 6.0 | 1.0 | — | 20 |
| Liaoning | 8.0 | 1.0 | — | 20 |
| Name | TN | TP | NH3-N | COD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tianjin | 0.490 | 0.059 | 0.490 | 0.4902 |
| Hebei | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.007 | 0.0099 |
| Shandong | 0.219 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.0025 |
| Liaoning | 0.697 | 0.219 | 0.219 | 0.3576 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, H.; Zhai, H.; Li, Y.; Han, S.; Tian, Y.; Liu, J. A Study on the Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity and Driving Factors of Mariculture Pollution in the Bohai Rim Region, China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4063. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094063
Yuan H, Zhai H, Li Y, Han S, Tian Y, Liu J. A Study on the Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity and Driving Factors of Mariculture Pollution in the Bohai Rim Region, China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(9):4063. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094063
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Hui, Haojie Zhai, Yongren Li, Shaoqiang Han, Ye Tian, and Jiahong Liu. 2025. "A Study on the Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity and Driving Factors of Mariculture Pollution in the Bohai Rim Region, China" Sustainability 17, no. 9: 4063. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094063
APA StyleYuan, H., Zhai, H., Li, Y., Han, S., Tian, Y., & Liu, J. (2025). A Study on the Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity and Driving Factors of Mariculture Pollution in the Bohai Rim Region, China. Sustainability, 17(9), 4063. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094063





