Abstract
Architectural heritage structures stand out as important local elements in rural tourism activities carried out in rural areas to observe and experience natural and cultural values, local activities, and rural life culture. The protection and reuse of architectural heritage in rural development promotes environmental sustainability and economic development while raising the living standards of local people. In this context, the protection and use of architectural heritage is an important tool for sustainable rural development in the future. This study is an example of efforts to develop rural areas with tourism using rural architectural heritage values and aims to emphasize the architectural importance of rural architectural heritage and to reveal management studies to be carried out for the use of these heritage values in rural tourism. The rural area of Iznik was selected as the study area due to its natural, historical, and cultural values, rural architectural heritage elements, and rural tourism potential. According to the field studies and interviews with stakeholders, sustainable management approaches and action proposals were created for the integration of rural architectural heritage with rural tourism and rural development.
1. Introduction
Cultural and architectural heritage gives meaning to rural areas as an important value owned by local people [1]. Rural architecture and rural living areas, which are the physical reflection of rural life culture, are shaped according to the natural conditions of the region, its economic activities, traditional life, and production styles. Rural architecture express the authenticity associated with culture and nature [2].
Despite their national and universal values, it is observed that the authentic fabric in rural areas undergoes changes over time, deteriorates, and enters a process of abandonment due to various reasons such as nature-based causes, climate issues, administrative status changes, political, economic, sociocultural reasons, traditional rural architecture’s inability to meet the spatial requirements of contemporary life, physical and functional aging of buildings, and new public/private sector investments [3,4,5,6,7].
The decrease in the human population in rural settlements is the main reason for the disappearance of rural heritage and rural communities and the shrinking of rural local economies [8,9,10]. Tourism activities are one way to economically improve rural populations while maintaining their traditional living cultures [11]. Heritage tourism, a type of tourism activity, contributes to economic development through the income generated from visitors to historical sites and their accompanying expenses in accommodation, food, entrance fees, and shopping [12]. The rural geographical environment and rural culture, which are values unique to their region [11], are important local elements that can contribute to the sustainable development of rural areas through rural tourism activities [13], as well as a basic resource for the development of rural tourism [14].
Rural tourism is a type of tourism that takes place in rural areas bases itself on local natural resources, cultural heritage, and traditional lifestyles. Its aim is to revive the rural economy while preserving the unique cultural and natural resources of the region [14]. It is emphasized that culture, which is generally well preserved in rural areas, is a valuable resource that should be included in tourism [15]. Rural tourism and rural architecture have a close and interdependent relationship [14]. One of the most important elements of rural culture is traditional rural structures. Rural buildings are built using local materials and construction/building techniques of the time they were built. They have economic, sociocultural, and historical characteristics of the time they were built and also have qualities that can increase the importance of rural areas and are effective in preserving the identity of local areas and sustainable development [16].
Although tourism is not the only solution to all rural problems, if managed correctly, it can stimulate low-capital economic growth in local businesses, diversify the work undertaken, and help provide the necessary finance for the preservation of natural and cultural heritage [17]. In this context, the focus of any tourism development in rural areas should be sustainable development that preserves the intrinsic qualities of the rural [18]. Rural tourism approaches have gained significant importance as an alternative development strategy in many countries [19]. Heritage sites and structures are seen as tools for the transmission of historicity and contribute to many contemporary social, political, and economic needs. The aim is not to preserve anything from the past but to use the past in the present [20]. Against economic, social, and environmental challenges, the transformative power of heritage values in rural areas is increasingly recognized as one of the key enablers of sustainable development, and UNESCO advocates culture as an intersecting topic in achieving the 2030 Sustainable Development Agenda [21].
In international studies, the relationship between cultural heritage protection, tourism, and development is addressed in different documents. Supporting the relationship between cultural heritage and sustainable development [22], including cultural heritage in the sustainable development agenda and in the Sustainable Development Goals adopted by the UN in 2015 [23], emphasizing the importance of cultural heritage in development and the roles of local administrators [24], emphasizing that tourism can be an important tool in the development of local people and rural areas and the protection of cultural heritage [25], and the “best tourism villages” movement launched by UNWTO in 2021, with the aim of turning rural tourism into a positive force for sustainable development, transformation, and community well-being [26], have enabled the relationship between cultural heritage protection, tourism, and development to be addressed in different documents.
This article studies the sustainable management of rural architectural heritage through rural tourism. For the purpose of rural development, how rural architectural heritage and rural tourism, which have a complementary relationship in terms of management, should be studied together is investigated in the article. In this context, action proposals have been created for the Iznik rural area, which is the study area. It is thought that the results of this study, conducted on a local scale, will contribute to the literature and practices on this subject.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Relationship Between Rural Architectural Heritage, Rural Tourism, and Rural Development
Rural tourism, which has significant potential to attract tourists seeking new, authentic experiences in areas with undiscovered natural and cultural riches [27], allows people to stay in rural areas to rest and get to know different cultures, as well as to observe and experience activities specific to the region they are in [28]. Rural tourism activities utilize the original values of the natural environment data and cultural heritage sites of rural settlements [27]. For the integration and promotion of cultural heritage values into tourism, it is necessary to create a sense of authenticity, to revive historical and cultural values, to attract interest [29], and to offer experience for the visitor [30]. Architectural structures also have the potential to trigger or support tourism by forming the center of a tourist activity where architecture—and even life—can be experienced in situ, with values of witnessing, representation, monumentality, uniqueness, or being something else [31], encompassing numerous additional historical, artistic, cultural, social, psychological, political, environmental, and educational values [32]. Traditional rural settlements, where the natural and cultural landscape is preserved, historical architectural heritage values exist, and the connection with the authentic way of life is maintained, are important in this context [18].
Traditional architecture, which includes historical rural buildings constructed in rural areas that are repositories of agricultural activities, ancient crafts, and rural lifestyles [33,34,35], can effectively preserve local components and cultural narratives in the context of a sustainable development strategy [36]. There is a close relationship between the preservation and the revitalization of rural heritage. Neither preservation without sustenance nor sustenance without preservation is possible. Rural tourism is seen as a new and effective way of establishing the relationship between humans and the environment in rural areas, and the presence of the local population forms the basis of the preservation of rural architectural heritage. In this context, rural tourism is one of the most important tools in maintaining the vitality of rural heritage [37], and heritage values assume place-specific cultural, social, or economic values beyond just functionality [38]. Rural tourism, which is also addressed within the scope of diversifying the rural economy, can provide various benefits for rural development, such as providing income or additional income for the local population, preventing internal migration, strengthening the relationship between urban and rural people, and preserving rural architectural heritage [28]. Sustainable rural tourism can prevent the depopulation of rural areas and safeguard the natural landscapes [39]. The preservation of the authentic way of life and culture is an important element in the improved rural economy through rural tourism. While the increased number of tourists brings benefits to local communities and national economies, economic improvement and popularity can also pose a potential threat to the natural and cultural integrity and authentic identity of rural areas [40,41,42]. As Nasser (2003) stated in his study, in terms of sustainability of heritage sites, managing tourism can have significant natural potential to support sustainable development and conservation [43]. Income from tourism should feed back to local communities to renovate and reclaim buildings. In this way, economic development is achieved at local, regional, and national levels. In this context, a sustainable management mechanism is required (Figure 1).
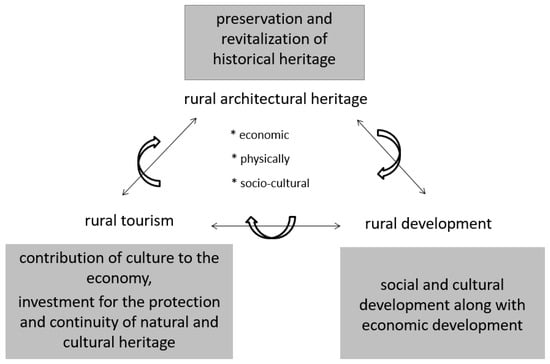
Figure 1.
Relationship between rural architectural heritage, rural tourism, and rural development.
2.2. Rural Tourism and Cultural Heritage Management in the Sustainability of Rural Areas
Cultural heritage management encompasses the effective protection, promotion, and sustainable use of historical and cultural values for current and future generations [44,45]. Key approaches such as supporting development in rural areas, preserving and promoting cultural and natural resources, as well as rural architectural heritage, and respecting the authenticity and intangible vital values of host communities are crucial for the sustainability of rural areas. Heritage tourism, as an economic activity, is based on the use of inherited environmental and sociocultural resources. Sustainability requires effective management to ensure that future generations inherit these resources [46]. In this context, cultural heritage management rises to prominence in the use of approaches addressed in tourism and development without harming rural living culture and rural architectural heritage values [47]. The management of change is crucial to the long-term survival of heritage places [43]. Partnerships between tourism and cultural heritage management are very important for the sustainable development of rural areas [48,49]. The presence of a wide group of stakeholders with different expertise should be taken into account, and a management approach based on common goals should be adopted [47].
Cultural heritage management has become an important focus of academic research in recent years [50]. Zhang et al. (2023) emphasize that cultural heritage management, rural development, and stakeholder studies have received increasing attention in cultural heritage tourism studies [50]. Christina et al. (2005), in their study examining the collaborative approach to heritage management and tourism issues, make recommendations for heritage protection and development [51]. Russo (2002) stated in his study that tourism development in World Heritage cities is no longer sustainable and therefore intervention is necessary [52]. As one of these interventions, he suggests the holistic management of cultural heritage. Dans and Gonzalez (2019), in their study on the World Heritage Site of Altamira, Spain, include holistic approaches that combine the fields of heritage management and sustainable tourism [53]. Ge and Abd Manan (2025) investigate the relationship between rural tourism and traditional architecture, emphasizing their joint roles in cultural heritage preservation and sustainable development [14]. Sardaro et al. (2021) studied a collaborative approach to the conservation of historic rural building types in Apulia, Southern Italy, to identify successful conservation and management strategies [54]. Giliberto and Labadi (2021) investigated the role of cultural heritage in sustainable development and the importance of cultural tourism in rural development in the Southern Moravia region [55]. Rautio (2021) argues that ethnic minority villages in the Dong Autonomous Region of Guizhou Province, which has experienced a significant increase in cultural heritage, have been transformed into sustainable heritage sites through the development of rural development policy and tourism [56]. Ancuta and Jucu’s (2023) study focuses on sustainable rural development, rural cultural heritage and cultural tourism [49]. In their study, which aims to integrate rural and cultural tourism, recommendations were developed specifically for the Brașov County of Romania. Gökarslan and Tuncer Pürselim (2025) presented their study findings, emphasizing the importance of protecting cultural heritage, which constitutes an important component of rural tourism in the example of Sütçüler Beydilli Village in Isparta, Turkey [57]. Although the concepts of heritage, tourism, and local economic development are interrelated, researchers have not necessarily explored all possible connections [58]. This literature review reveals that studies on cultural heritage management, tourism, and development focus on specific issues and that there are gaps in studies on rural areas. The theoretical contribution of this paper is to investigate how sustainable development, heritage-based rural tourism, and heritage management studies should be addressed together by emphasizing their joint roles.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. The Iznik Rural Area
Iznik (historical city of Nikaia/Nicaea), a district of the province of Bursa, is located in the Marmara Region of Turkey in the southeast of the Sea of Marmara in the northeast of the province of Bursa, approximately 90 km away from the provincial center [59] (Figure 2).
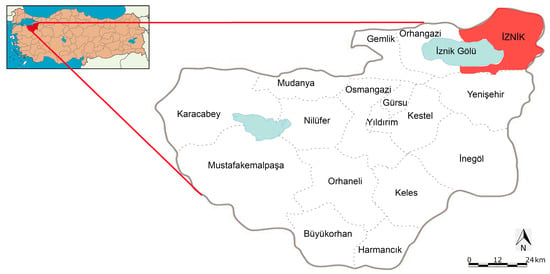
Figure 2.
Location of Iznik district in Türkiye and Bursa. (The image was taken from Bursa Metropolitan Municipality and elaborated by the authors).
The city of Iznik (historical city of Nikaia/Nicea) is a small town established in a rural area. The most important natural asset of rural is Lake Iznik. The olive groves that continue almost uninterruptedly on the southern shores of the lake are an important element of the rural landscape. The countryside of Iznik is quite rich in terms of natural heritage values such as mountains, hills, slopes, plateaus, and canyons. Sansarak and Tacir canyons and the Alıç Plateau are important natural features in the countryside. In the district where the urban and the rural are intertwined, there are 37 villages (rural neighborhoods) and 2 towns with dispersed or clustered settlement characteristics [59]. Some of the rural settlements are close to the center of Iznik (such as Çamdibi, Drazali), some are located on the lake shore (such as Göllüce), while some are mountain villages located further away (such as Elmalı, İhsaniye). According to 2023 population data, 40% of the district’s population lives in rural areas [60]. In the last decade of population changes, the total population of central neighborhoods has increased, but the population of rural neighborhoods has decreased [59]. In the region where a climate similar to the Mediterranean climate prevails, the climate characteristics, landforms, water resources, irrigation possibilities in the lake basin, soil, and vegetation have enabled different agricultural characteristics to emerge, in addition to facilitating agriculture. The primary sector in economic activities in rural areas is agriculture. The northeast of the rural area is the region where mountainous areas are the majority. The main source of income in these areas is forestry and livestock [61].
Tourism activities carried out in rural areas include cultural tours in villages, daily nature walks, canyon tours, harvest events, herb collecting, grazing animals, or camping. Other important tourism activities in the countryside include the Equinox Festival, where you can watch the sunset and activities held on the shores of Lake Iznik and in rural areas in March and September, the Iznik Ultra Marathon race held in the countryside every year, the Iznik Triathlon, the Iznik Canoe Festival, traditional Alıç Plateau wrestling events, and the World Nomad Games held on the shores of the lake in 2022 [62]. UNESCO World Heritage studies in the city of Iznik, where some of the natural and cultural values in the countryside are located (Figure 3), continue today.

Figure 3.
Natural and cultural values in the İznik countryside: (A,B) natural values (Iznik Lake); (C) natural values in the Iznik countryside; (D) olive garden in the Iznik countryside; (E,F) settlements in Iznik rural areas; (G–I) traditional houses in the Iznik rural areas.
3.2. Methodology
This study has the characteristics of a field study, which constitutes an important step in architectural studies. In the field studies, a qualitative research process was followed as it was deemed appropriate for the purpose of the study. In this study, a qualitative research method that includes subjectivity and is based on the in-depth examination of human perceptions and events in social reality and natural environment [63,64,65] was preferred. A qualitative research methodology is widely used in tourism research to analyze different but related stakeholders in villages [66,67,68]. Multiple methods were used to collect data. Data were collected through on-site observation, photographic documentation, note-taking, guided tours, and in-depth interviews to ensure participation. The studies were carried out in two different stages: studies conducted in rural areas and interviews with local stakeholders.
Before the rural area studies, a literature review was conducted on tangible and intangible heritage values in the İznik countryside, and upper-scale studies for the İznik countryside, such as the Bursa, Eskişehir, Bilecik Regional Plan (2024–2028) [61] and the İznik/Nicaea/Nicaea Management Plan study (2022–2027) [59], were examined. The studies carried out in the rural area consist of preliminary studies carried out in 37 villages located in the Iznik countryside in 2020, 2021, and 2023 and on-site observations and guided tours in September, October, and November 2024. The rural architectural heritage values in the villages were documented with photographs, processed on maps in the CAD environment, and transferred to the sheets prepared in the Photoshop CS6 program.
As in the studies of Wang et al. (2019), Özgeriş et al. (2024), and Mirli et al. (2024), stakeholders were analyzed, and interviews were conducted to understand their views on the subject [69,70,71]. In the determination of the stakeholders, a stakeholder analysis was carried out, including the institutions that make decisions and influence the decisions regarding rural development, tourism, and architectural heritage preservation in the rural areas of Iznik. It was observed that some of these stakeholders’ areas of work cover more than one discipline (heritage protection, tourism, development), and there are relevant and intersecting points in the working areas of different actors. After the stakeholder analysis, the semi-structured in-depth interview method, one of the qualitative research methods, was applied in order to understand the roles and perspectives of the stakeholders who are effective in the decision-making, management, and implementation processes. Prior to the interviews, questions were prepared in line with the literature review and research purpose, and new questions were added as needed during the interviews. While creating the questions, information was obtained about the stakeholders’ (i.e., institutions’) general knowledge, opinions, suggestions on the subject, as well as information about the current or planned studies, and we endeavored to determine the types of rural architectural heritage use in rural tourism. The stakeholders interviewed consist of government officials. Before the interviews, ethical approval was obtained from the Bursa Uludag University Faculty of Science and Engineering Research and Publication Ethics Committee in its session dated 22 October 2024 and numbered 2024-09. For the interviews, all participants were informed in advance, their consent was obtained, and the study was carried out between 28 October 2024 and 4 November 2024 in accordance with ethical rules. The participants are identified in Table 1.

Table 1.
Stakeholder institutions interviewed within the scope of the study.
The questions were organized under two headings (Table 2): rural architectural heritage (R.A.H.), in order to understand the importance of architectural heritage values and their usage possibilities in rural tourism for rural development purposes; and integrated management (I.M.), in order to reveal the relationship of rural architectural heritage with other disciplines. In the analysis of the data, the content analysis method, which systematically provides the interpretation and reporting of field notes and interview transcripts [72,73], was applied, and the common, similar, and divergent points in the stakeholders’ responses were identified using the comparison method.

Table 2.
Topics and questions of the interview.
4. Results
The results of this study are presented in two stages: field study conducted in rural areas and interviews with stakeholders. By analyzing the data, the role and significance of architectural heritage in development and tourism were identified, and a method and action proposals were developed to ensure the unity of rural development, rural tourism, and rural architectural heritage protection.
4.1. Field Study Conducted in Rural Areas
The field study has shown that the rural areas of Iznik are rich in natural beauty, with lakes, canyons, mountains, highlands, hiking trails, and scenic viewpoints, as well as possessing original architectural heritage with high potential for rural tourism. Due to their locations, primary sources of livelihood, and the diverse cultural backgrounds of their residents (for example, Inikli as an indigenous settlement; Elmalı as a Georgian village; and İhsaniye as a Yörük village), Iznik’s villages display a wide variety in settlement layout, lifestyles, and local customs. This diversity is most clearly reflected in the architecture. Traditional rural houses, exemplifying authentic vernacular architecture, are generally constructed with an adobe infill within a timber frame, typically as one- or two-story structures in harmony with the natural landscape, forming an organically integrated environment. In particular, Inikli and Ömerli villages are known for traditional Turkish houses that represent unique architectural styles. There are 13 examples of civil architecture in İnikli Village, registered in 1994. In villages with extensive forest cover, such as Elmalı, Hacıosman, Kırıntı, and Kutluca, wood, readily available and easily sourced from the surroundings, serves as the primary building material. By contrast, in mountain villages like Süleymaniye, Osmaniye, and İhsaniye, stone is more commonly used in construction [62,74] (Figure 4).
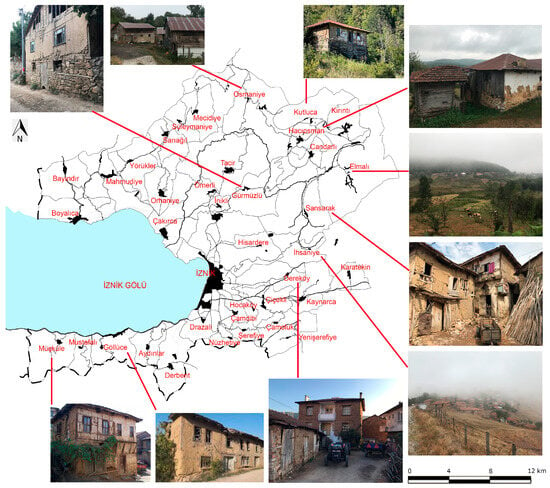
Figure 4.
Settlements in Iznik rural areas. (Images were taken from Bursa Metropolitan Municipality and elaborated by the authors).
One of the most significant features of rural architecture is its adaptation to economic activities. The variations in economic activities are particularly reflected in the extensions of rural houses; indeed, these extensions are key elements that give a dwelling its rural character [74]. In Iznik’s rural areas, various architectural extensions, such as workshops, storage areas, oil mills, mills, barns, haylofts, ovens, garages, and sheds, demonstrate different architectural characteristics and are also regarded as part of the rural industrial architectural heritage (Figure 5). The way these structures and their extensions are arranged and integrated into the landscape in rural settlements creates interesting clusters and patterns. In livestock-oriented areas, barns and haylofts are often placed within a few meters of the residence and arranged adjacently, while in agricultural areas, storage spaces for surplus produce or agricultural equipment are commonly found on the ground floor of homes, as annexes with wooden sheds, or as separate buildings located close to the residence. In addition to these extensions tailored to economic activities, items like tractors parked in village streets or residential gardens, long wooden ladders used during harvest seasons to reach trees, and outdoor ovens attached to homes or placed in gardens contribute to the unique character of rural architecture. Beyond these dwelling and production-related structures, key communal spaces, such as village mosques, coffee houses, and the village headman’s office, typically located in areas that serve as village squares, are essential rural gathering spots used by residents in daily life.

Figure 5.
Different architecturals and architectural extensions in the Iznik countryside: (A) hayloft; (B,D,E,G) examples of storage areas; (C,H) ovens; (F) mill (authors’ archives, 2020, 2023, 2024).
4.2. Stakeholder Interviews
R.A.H.1: What are your thoughts on the role and importance of rural architectural heritage values in the formation of rural culture?
Stakeholder 1 (s1): “Rural architectural values are heritage elements that need to be preserved and kept alive. The importance of these values should be known by all segments of the population”.
s2: “Rural architectural heritage is one of the main factors in the formation of rural culture. The importance of cultural values should be known by all of the population”.
s3: “Rural architecture creates original rural identity. Conducting inventory studies for architectural heritage values is important for documenting cultural values. Recording traditional construction techniques, original material usage, local detail solutions, and different architectural elements in the construction of architectural structures is important for identifying cultural values”.
R.A.H.2: What are your practices as an institution regarding the protection and preservation of the natural and cultural heritage in the Iznik countryside? What can be done?
s1: “Under the “Living Iznik Treasures” project of Iznik Municipality Press Publication and Public Relations Directorate, the lives and professions of traditional handicraft masters are being documented. The project, which includes masters living in rural areas, aims to promote local values. By continuing this work for each rural area, local values can be recognized, preserved, and kept alive”.
s2: “In the 1/100,000 Scale Environmental Plan prepared in 2023 by the Spatial Planning and Strategy Office of the Bursa Metropolitan Municipality, Department of Urban Planning and Development, and Urban Planning Branch Directorate, the administrative boundaries of the Iznik and Orhangazi districts are designated as the Northeast Planning Region. Accordingly, the plan focuses on developing culture and faith tourism in relation to protection. This includes enhancing tourism and recreation in rural areas by preserving traditional structures, rural identity, tangible and intangible cultural assets, and sensitive ecosystems; boosting promotional and marketing activities; improving accommodation options for tourism; supporting tourism in villages such as Gürle, Derbent, and Elbeyli; providing training on agricultural practices, especially in rural areas around Lake Iznik; and approaching Iznik’s planning and management with an integrated (protection -revitalization) perspective”.
s4: “The “Digital Iznik Program” was developed under the coordination of the Ministry of Industry and Technology’s General Directorate of Development Agencies by the Bursa Eskişehir Bilecik Development Agency (BEBKA) in collaboration with the Iznik Municipality and the Iznik Chamber of Commerce and Industry (ITSO). Launched in May 2024, this program aims to provide training on branding, digital marketing, e-commerce, and e-export to Iznik’s producers, enabling them to enter national and international digital markets and contribute to the branding of geographically indicated products. This project is intended to support the branding, marketing, and production of products like the geographically certified Müşküle lacework and Derbent weavings, with suggestions for its application to other rural productions as well”.
s4: “The Bursa, Eskişehir, and Bilecik Regional Plan (2024–2028), prepared under BEBKA’s coordination, also includes Iznik and its surrounding rural areas. The plan identifies Iznik as a focal point for agricultural and tourism development. It suggests the implementation of necessary promotional activities and infrastructure investments to develop tourism types such as historical, cultural, and nature tourism”.
s5: “The Bursa Regional Directorate for the Protection of Cultural Heritage (BKVKBK), is responsible for registering and categorizing cultural assets that need preservation, including archaeological, urban, urban archaeological, and historical heritage sites. The board reviews registration applications submitted and makes protection decisions to ensure the preservation of cultural heritage”.
R.A.H.3: How can rural architectural heritage values be used in tourism practices in Iznik rural area?
s6: “In tourism practices, raising awareness among local residents about the value of local cultural assets and rural architectural heritage should be a priority. A training module should be developed in collaboration with the Iznik District Governorship, Iznik Municipality, Bursa Metropolitan Municipality (BBB), Agriculture and Rural Development Support Institution (TKDK), and the Bursa Eskişehir Bilecik Development Agency to guide the local community”.
s7: “Local people can benefit from Instrument for Pre-Accession Assistance Rural Developments (IPARD) rural tourism support and use rural architectural heritage, such as guesthouses and local product sales areas”.
s2: “Abandoned communal structures in rural areas should be restored using original materials and traditional techniques”.
s8: “A selection of traditional rural buildings could be identified and repaired, with some converted into guesthouses reflecting traditional rural life. In these structures and their adjacent areas, local traditional practices could be demonstrated”.
s1: “Traditional production methods (such as basketmaking, woodworking, blacksmithing) carried out in rural workshops such as warehouses and sheds in the rural areas of Iznik can be experienced and observed in these spaces and incorporated into tourism”.
s1: “Tours can be organized for visitors to Iznik and the Iznik countryside, which include visiting olive groves enriched with rural landscape routes, introducing olive culture, participating in the olive harvest depending on the season, explaining olive processing processes, and ending with tasting and olive sales. These tasting and sales events can be held in traditional rural buildings”.
s5: “Sericulture should be reactivated”.
s6: “To facilitate the sale of locally produced goods from specific villages or village clusters, rural cooperatives should be established. These cooperatives would enable business plans to be proposed under their structure. Our institution can support for cooperative education programs”.
s7: “The TKDK, an affiliated institution of the Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry, can offer support through the LEADER project, with priorities including “Development of rural tourism products”, “Enhancement of community cultural and social life” and “Development of value-added products”. This support can be utilized by designing projects in collaboration with the District Governorship and Municipality of Iznik that incorporate values of rural architectural heritage”.
s2: “Technological tools, such as Bursa Metropolitan Municipality’s “GoBursa” smartphone application, can also be further developed to highlight the architectural heritage of Iznik’s rural areas, enhancing information and guidance for visitors”.
R.A.H.4: Does rural tourism have negative effects on the environment, natural beauty and cultural heritage? If yes, what are they and how can they be prevented?
s2: “Tourism can bring about negative effects such as environmental pollution, vandalism targeting architectural heritage, and excessive tourism pressure”.
s3: “Economic improvement and popularity may pose potential threats to the natural and cultural integrity as well as the unique identity of rural areas. Therefore, tourism management plans should be developed, assessing the current conditions and carrying capacities of rural areas, ensuring the preservation of original values, and establishing a balance between protection and usage”.
s8: “Tourism may cause loss of rural values. An integrated approach to development, tourism, and protection as one of the most critical actions for sustaining the values present in rural areas”.
s5: “Definitely. Periodic monitoring reports can be prepared on rural architectural heritage values to track and identify negative impacts”.
S6: “There is no such thing as long as attention is paid”.
R.A.H.5: What kind of tourism plan and strategy should be determined to conserve and preserve rural architectural heritage values?
s8: “Iznik Management Plan Study should be taken as an example in this regard”.
s3: “Visitor management plans should be developed by identifying visitor numbers, visitation periods, and the carrying capacities of the sites”.
s5: “Monitoring indicators should be established to encourage locals who benefit financially from rural tourism to protect and ensure the continuity of heritage values”.
s2: “The tourism plan should also emphasize security in rural areas. Safety, disaster, and emergency response plans should be established for both residents and visitors”.
I.M.1: How can studies that utilize rural architectural heritage in the provision of rural tourism and rural development be handled together?
s8: “In collaborative projects, stakeholders should come together to identify existing or potential projects relevant to their interests, discuss the cross-sectoral impacts of each project, and determine overlapping or redundant topics”.
s1: “Representatives from each group should come together”.
s2: “A management plan similar to the field management should be prepared”.
S6: “Stakeholder meetings should be held at regular intervals and management plans should be prepared”.
I.M.2: Who should make up this collaborative working group?
s8: “Collaborative working group may be a special unit within the İznik Site Management that conducts studies on rural areas. Key participants in this unit could include representatives from local government, local people and relevant NGOs”.
s1: “Collaborative working group may be a special unit within the Iznik Municipality. All stakeholders must be involved”.
s2: “All stakeholders that should be in management models should be included”.
I.M.3: What should be the roles and responsibilities of the joint working group?
s1: “Development that sustains local values should be ensured”.
s2: “The sustainability of rural architectural heritage should be ensured through rural tourism”.
s3: “Architectural heritage values should be preserved and preserved and integrated with tourism”.
s5: “For the development of the region, it is necessary to ensure the sustainability of local values and strengthen rural tourism”.
According to the answers in the R.A.H.1 category, rural architectural heritage values play an important role in the formation of rural culture. Despite this, the answers in R.A.H.2 show that the studies carried out/planned for the protection and preservation of the natural and cultural heritage in the İznik countryside are limited to certain villages. In the current situation, as understood from the answers of R.A.H.2 s2 and R.A.H.2 s4, it is understood that there are repetitions in the studies carried out by different stakeholders. The answers in the R.A.H.3 category show the variety of different usage possibilities of rural architectural heritage values in tourism practices in Iznik rural areas. In the answers in R.A.H.4, it is concluded that rural tourism may have negative effects on the environment, natural beauty, and cultural heritage. In R.A.H.5, the answers section includes tourism plans and strategies for the protection and preservation of rural architectural heritage values. The answers in the I.M. category express approaches to the sustainable management of rural architectural heritage through rural tourism by providing rural development. The interview results reveal the importance of holistic approaches based on participation and governance among stakeholders.
4.3. Findings and Recommendations
According to the findings obtained from interviews with stakeholders and field studies, various usage possibilities of rural heritage are possible in the development of rural tourism. In this context, various suggestions have been developed on how we can evaluate the rural heritage in Iznik and how we can apply it in tourism development:
Field studies have shown that new buildings are being constructed with non-original materials in rural settlements, or additions or different new arrangements are being made to existing buildings. It is necessary to identify non-original materials or types of materials and construction that are not suitable for the existing silhouette and prevent these productions. For this purpose, architects working within Iznik Municipality (IB) should take charge.
It is very important to encourage local values and ensure their continuity and revitalization. To be successful in the long term, original livelihoods should not be abandoned, and the authentic position between contemporary life and traditionality should be preserved.
Due to the concentration of tourism accommodations in urban centers, developing alternative accommodations in rural areas, such as guest-houses, caravan and camping areas, and facilities for highland tourism, are recommended in addition to daily visits.
In tourism practices, raising awareness among local residents about the value of local cultural assets and rural architectural heritage should be a priority. Training modules should be developed. Training modules could cover topics such as the importance of architectural heritage and cultural assets for development and tourism, effective communication with visitors, home-based guesthouse management, the importance of local women’s employment, organic farming, utilizing local products, potential partnerships with international organizations such as the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and rural tourism support through programs such as the Instrument for Pre-Accession Assistance for Rural Development (IPARD). The goal of these training courses should be encouraging the local community to take ownership of these initiatives, to consider themselves as key actors, and thus to help ensure the sustainability of development, tourism, and preservation efforts.
Field studies have shown that visitors often tour and take pictures of traditional structures in villages. The architectural heritage structures that are abandoned or at risk of collapse should be identified by Iznik Municipality and surrounded with safety warning signs. The Municipality should also implement necessary safety precautions.
Preserving the region’s identity as a producer, along with its agricultural knowledge and natural and cultural values, can only be achieved by maintaining traditional agricultural and livestock practices. Buildings related to these activities can serve as spaces for visitors to experience village life. For instance, Swiss examples of agricultural tourism, where tourists sleep on hay bales in barns, highlight creative ways to integrate rural facilities into tourism [64]. Similar initiatives should be developed to incorporate rural production structures into tourism.
Activities such as grinding wheat in the old mill in the village of Elmalı or in the his-toric water mill in the village Kırıntı, which still serves its original function, and baking the breads made from these flours in the ovens and offering them as treats can be integrated into rural tourism as snapshots of everyday village life, recalling that the region is a Georgian village.
Crafts such as basketmaking, which has been practiced by the only master in the village of Sansarak for over 60 years; woodworking, such as cane, bread shovel, and rolling pin making in İnikli; and blacksmithing, such as the production of axes, hoes, axes, agricultural tools, grafting knives used in fruit grafting, and pasta boards used in village pasta making in Tacir Village, which have gradually lost their former importance, should be considered as cultural values and rural industrial heritage. These traditional production methods carried out in rural workshops such as warehouses and sheds in the rural areas of Iznik can be experienced and observed in these spaces and incorporated into tourism. These activities, which involve different production processes and human labor and craftsmanship, can provide both a craft and cultural continuity, as well as economic benefits as a side income, by making the production processes visible in the tours to be established in the rural areas of Iznik and by producing and selling these products in smaller sizes [2].
The integration of olive, a cultural element, with tourism is described as a natural process [65], and olive–olive oil tourism/agricultural industry tourism, which includes various activities such as the processing of olives in traditional workshops, olive oil production, and its promotion in museums, fairs, and festivals, is being carried out in countries such as Spain, Italy, Greece, Portugal, France, Morocco, and Tunisia [66]. In 2019, the UNESCO General Conference declared November 26 as “World Olive Tree Day”, emphasizing the cultural importance of olive trees for all of humanity as they represent peace, wisdom, and harmony. In this context, tours can be organized for visitors to Iznik and the rural areas of Iznik, which include experiences such as visiting olive groves enriched with rural landscape routes, being introduced to the olive culture, participating in olive harvesting activities (depending on the season), hearing explanation of the olive processing processes, and tasting, ending with olive sales. The fact that village women sit in front of their houses and make olives during the olive harvest season can also make these tours more striking, being, as they are, integrated with rural life. Carrying out such rural tourism activities in Iznik and the Lake Iznik Basin surrounded by olive trees will provide benefits such as rural development, the continuation of traditional production methods, and the preservation of rural architectural heritage. In this context, rural development projects on themes such as olive farming, olive oil production, tourism, organic agriculture, soil protection, and sustainability, included in the ENRD platform, which includes examples of rural development from around the world, can be taken as examples [67].
From the 17th century until the early 20th century, sericulture and cocoon production served as a primary source of income in the province and rural areas of Bursa, alongside traditional agriculture. The prominence of sericulture as an essential livelihood influenced the region’s architectural styles. However, the shift from traditional to modern production methods in recent times has led to the discontinuation of these activities in rural areas. Many of these structures have been left unused or repurposed entirely for residential purposes, resulting in the gradual loss of their original cultural and architectural value. The settlements, particularly south of Lake Iznik, could play a pivotal role in revitalizing sericulture activities, offering tourists hands-on experiences with these production practices and supporting the sustainable preservation of rural industrial heritage. Reactivating sericulture in these areas would not only create new employment opportunities but could also raise income levels in rural communities [2].
Support for cooperative education programs may be obtained from the Ministry of Trade (TB) or cooperatives associations such as Köy-Koop (Central Union of Village Cooperatives). In addition, unused structures in villages could be repurposed as spaces for the sale and display of products.
Routes linking different points of interest, such as cultural, archaeological, hiking, canyon, and cycling routes, should be created or enhanced to connect diverse areas and heritage assets.
Maps promoting year-round tourism in the region (highlighting activities like sunset viewings, harvest events, festivals, etc.) should be prepared to distribute tourism more evenly across rural areas and throughout the year.
For a comprehensive, interdisciplinary approach, an integrated management plan should be developed, focusing, initially, on how tourism can be incorporated into rural development and, subsequently, on how architectural heritage values can be utilized in tourism activities. This plan should identify responsible stakeholders, funding sources, goal timelines, and monitoring indicators. It is recommended that a dedicated unit focused on rural areas be established within the Iznik Site Management, as part of a collaborative working group. Key participants in this unit could include representatives from the Iznik District Governorship and Iznik Municipality, local village leaders and village council members from the relevant villages, local tourism professionals, and experts in protection and development. Additionally, a representative group from higher-level organizations, such as the Bursa Metropolitan Municipality, Bursa Regional Directorate of Cultural Heritage Preservation, TKDK, BEBKA, and relevant NGOs, should be involved to support broader initiatives and provide resources. The primary duties and responsibilities of the collaborative working group are as follows: to ensure the sustainability of local values for the development of the region, to leverage rural tourism, to guide efforts that integrate and preserve architectural heritage values within tourism, and to oversee and enhance the impact of these integrated initiatives. Figure 6 presents a model for the integrated management of rural architectural heritage, rural tourism, and rural development.
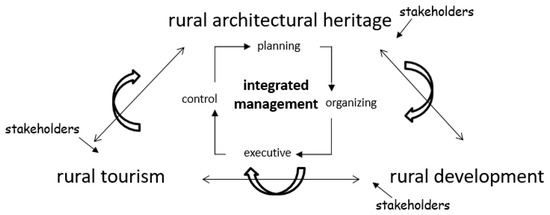
Figure 6.
A model example for the integrated management of rural architectural heritage, rural tourism, and rural development.
Action proposals created to make the sustainability of rural architectural heritage through rural tourism more concrete are organized according to different objectives for each question group in the R.A.H. category. The goals determined according to the interview results are as follows (Figure 7).

Figure 7.
Goals determined according to interview results.
Action proposals for preserving rural architectural heritage and utilizing it for tourism-driven development, along with responsible organizations and goal timelines, are outlined in Table 3. Following stakeholder meetings, it was found that various disciplines and stakeholders are responsible for specific actions; thus, based on the I.M. responses, a proposed action table has been created that identifies stakeholders’ areas of collaboration and distinct initiatives. Goal timelines have also been set, creating a sample action table for the management plan.

Table 3.
Proposed actions, responsible organizations, and goal deadlines.
5. Discussion
The diversity, complexity, and number of initiatives related to rural architectural heritage in the areas of protection, tourism, and development increase the importance of sustainable collaborations [75]. The results of this study show that there are decision-making mechanisms and approaches that concern different disciplines. According to the interview results, stakeholders agree that the studies should be carried out jointly and that there should be holistic approaches. As stated by Wang et al. (2019), all stakeholders, such as local/central government, experts, and local people, should have a say in the management processes and contribute to the sustainability of the heritage [69]. Collaborative governance approaches involving diverse stakeholders at the local level are important [76]. Partnerships between local governments and communities in fostering rural tourism hold inclusive potential, creating opportunities for employment and income [75]. Nocca (2017) emphasizes that tourism, with effective management plans, contributes positively to local economies while protecting cultural and natural resources [77]. According to the results of her study, an effective model should be determined for the sustainable management of cultural heritage. Similarly, according to Özgeriş et al. (2024), tangible heritage elements of tourism should be integrated with natural, cultural and socio-economic values [70]. According to Nasser (2003), the management of cultural heritage values should include the use of heritage values and their integration with the sociocultural needs of the local community [43]. It is clear that a framework of regulations is needed at international, national, regional, and local levels to implement responsibilities and achieve targeted actions. In this context, it is crucial for local and regional authorities to manage and sustain the process through a specialized guide, such as a management plan [38]. The integrated approaches included in this study agree with the results of these studies.
Today, cultural heritage is recognized as playing a strategic role in achieving sustainable development goals by the United Nations, UNESCO, ICOMOS, UNWTO, and numerous national and regional institutions [78,79]. This article, which addresses the sustainable management of rural architectural heritage through rural tourism, is an example of the development effort of rural areas through tourism. This study is significant in terms of identifying the existing and potential tourism potentials in the Iznik’s rural area, diversifying the tourism activities within Iznik, and identifying opportunities for localized rural development, thereby contributing to and benefiting from the UNESCO World Heritage process. In this context, this study agrees with the studies on cultural heritage sites conducted by UNESCO and ICOMOS.
6. Conclusions
This research examines the importance of rural architectural heritage from an architectural perspective and presents management studies for the use of these heritage values in rural tourism. In management studies, there should be no redundancy or gaps, common ground should be found, and continuity of actions should be ensured by determining the authority, boundaries, and responsibilities of the relevant institutions and organizations.
This study, which was conducted on the basis of field work specific to the Iznik countryside and in-depth interviews with relevant stakeholders, shows that the countryside is rich in terms of tourism potential and has unique local values in terms of rural life culture and architectural heritage. In field studies, the architectural heritage values in the rural area of Iznik were identified as traditional historical buildings, architectural extensions, production buildings, and buildings constructed according to old production methods. This research integrates these heritage values and rural tourism activities in the created management model. Interviews with stakeholders show that development, tourism, and heritage management activities in Iznik rural area are inadequate or repetitive. In order to make the studies more comprehensive, to prevent duplication, and to integrate rural architectural heritage with tourism and development, action proposals were developed that included sustainable management approaches, responsible institutions, and goal periods.
Serving as an example for rural areas at risk of abandonment and loss of heritage values, this study is expected to guide the integration of protection, tourism, and development efforts. More studies that reveal and strengthen relationships among relevant disciplines are needed to understand and advance the strategic role of rural architectural heritage in sustainable rural development. Similar studies can be applied and expanded for other rural areas. Due to the complexity of the stakeholders, future research should still be conducted in depth and local people should be involved in the management processes. Despite these limitations, this paper suggests useful implications for governments in ensuring the sustainability of architectural heritage through rural tourism in rural development. This study can complement the policies, goals, and actions outlined in the development plans prepared by the Turkish Presidency of Strategy and Budget, as well as in the tourism strategic plans of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism. While this study takes an architectural perspective, it could also be diversified by incorporating viewpoints from other disciplines.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.S.E., M.T. and N.T.; methodology, B.S.E., M.T. and N.T.; validation, M.T. and N.T.; formal analysis, B.S.E., M.T. and N.T.; investigation, B.S.E., M.T. and N.T.; resources, B.S.E., M.T. and N.T.; data curation, B.S.E., M.T. and N.T.; writing—original draft preparation, B.S.E.; writing—review and editing, B.S.E., M.T. and N.T.; visualization, B.S.E.; supervision, M.T. and N.T.; project administration, M.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All subjects provided their informed consent for inclusion. before they participated in this study. This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and the protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Bursa Uludag University Research and Publication (22 October 2024, 2024-09).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
Thanks are given to all participants, both the public and NGO employees, whose names I cannot write due to the research method, for taking the time to share their sincere opinions and thoughts and for their hospitality and assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Quintana, D.C.; Díaz-Puente, J.M.; Gallego-Moreno, F. Architectural and cultural heritage as a driver of social change in rural areas: 10 years (2009–2019) of management and recovery in Huete, a town of Cuenca, Spain. Land Use Policy 2022, 115, 106017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, M.J.; Lima, J.; Silva, A.L. Landscape and the rural tourism experience: Identifying key elements, addressing potential, and implications for the future. J. Sustain. Tour. 2015, 23, 1217–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soykök Ede, B.; Taş, M.; Taş, N. UNESCO Dünya Miras Süreci üzerinden İznik kırsal endüstri mimari mirasının sürdürülebilir korunması, yaşatılması ve canlandırılması. In Disiplinlerarası Yaklaşımlarla Kırsal Endüstri Mirası; Baykal, F., Karadağ, A., Eds.; Ege Üniversitesi Yayınları: İzmir, Türkiye, 2023; pp. 75–95. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/380632354_UNESCO_DUNYA_MIRAS_SURECI_UZERINDEN_IZNIK_KIRSAL_ENDUSTRI_MIMARI_MIRASININ_SURDURULEBILIR_KORUNMASI_YASATILMASI_VE_CANLANDIRILMASI (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- Harbiankova, A.; Scherbina, E.; Budzevich, M. Exploring the Significance of Heritage Preservationin Enhancing the Settlement System Resilience. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, D.; Crabtree, J.R.; Wiesinger, G.; Dax, T.; Stamou, N.; Fleury, P.; Gutierrez Lazpita, J.; Gibon, A. Agricultural abandonment in mountain areas of Europe: Environmental consequences and policy response. J. Environ. Manag. 2000, 59, 47–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güler, K.; Kahya, Y. Developing an approach for conservation of abandoned rural settlements in Turkey. ITU A|Z 2019, 16, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, M.L.; Pereira, M.H. Rewilding abandoned land-scapes in Europe. Ecosystems 2012, 15, 900–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muilu, T.; Rusanen, J. Rural young people in regional development the case of Finland in 1970–2000. J. Rural. Stud. 2003, 19, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amcoff, T.; Westholm, E. Understanding rural change-demography as a key to the future. Futures 2007, 39, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Westlund, H.; Liu, Y. Why some rural areas decline while some others not: An overview of rural evolution in the World. J. Rural. Stud. 2019, 68, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soykan, F. Kırsal turizm ve Türkiye turizmi için önemi. Ege Coğrafya Derg. 2003, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Timothy, D.J.; Boyd, S.W. Heritage Tourism; Prentice Hall: Harlow, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Barrientos, F.; Martin, J.; De Luca, C.; Tondelli, S.; Gómez-García-Bermejo, J.; Zalama Casanova, E. Computational methods and rural cultural & natural heritage: A review. J. Cult. Herit. 2021, 49, 250–259. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, W.; Abd Manan, M.S.b. A Review of and Prospect of Village Architecture Research from the Perspective of Rural Tourism. World 2025, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, R.; Jolliffe, L. Cultural rural tourism: Evidence from Canada. Ann. Tour. Res. 2003, 30, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlato, M.C.M.; Valenti, F.; Porto, S.M.C. Sustainable Promotion of Traditional Rural Buildings as Built Heritage Attractions: A Heritage Interpretation Methodology Applied in South Italy. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, P.; Lane, B. Rural Tourism Development. In Trends in Outdoor Recreation, Leisure and Tourism; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2000; pp. 299–308. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Ingrid-Schneider-3/publication/292016815_Recreation_conflict_management/links/60e31ae1a6fdccb74507b58a/Recreation-conflict-management.pdf#page=321 (accessed on 13 January 2025)ISBN 978-0-85199-403-1.
- Lane, B. What is rural tourism? J. Sustain. Tour. 1994, 2, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briedenhann, J.; Wickens, E. Tourism routes as a tool for the economic development of rural areas—Vibrant hope or impossible dream? Tour. Manag. 2004, 25, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, G.J. Preservation, Conservation and Heritage: Approaches to the Past in the Present through the Built Environment. Asian Anthropol. 2012, 10, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Encouraging Sustainable Cultural Heritage Management. 2023. Available online: https://www.unesco.org/en/fieldoffice/bangkok/clt/sustainable-cultural-heritage-management (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Available online: https://whc.unesco.org/en/sustainabledevelopment/ (accessed on 9 December 2023).
- ICOMOS. Action Plan: Cultural Heritage and Localizing the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). 2017. Available online: https://www.icomos.org/images/DOCUMENTS/Secretariat/2017/ICOMOS_Action_Plan_Cult_Heritage_and_Localizing_SDGs_20170721.pdf (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- ICOMOS. Heritage and The Sustainable Development Goals: Policy Guidance for Heritage and Development Actors. 2021. Available online: https://www.icomos.org.tr/Dosyalar/ICOMOSTR_en0542142001619167638.pdf (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- World Tourism Organization and United Nations Development Programme. Tourism and the Sustainable Development Goals—Journey to 2030; UNWTO: Madrid, Spain, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://www.unwto.org/news/unwto-announces-list-of-best-tourism-villages-2021 (accessed on 9 December 2023).
- Su, Y.W.; Lin, H.L. Analysis of international tourist arrivals worldwide: The role of world heritage sites. Tour. Manag. 2014, 40, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soykan, F. Doğal çevre ve kırsal kültürle bütünleşen bir turizm türü: Kırsal turizm. Anatolia Tur. Araştırmaları Derg. 1999, 10, 67–75. Available online: https://scholar.google.com.tr/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=tr&user=yJo_3BQAAAAJ&citation_for_view=yJo_3BQAAAAJ:ZeXyd9-uunAC (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- McKercher, B.; Ho, P.; du Crus, H. Relationship between tourism and cultural heritage management: Evidence from Hong Kong. Tour. Manag. 2005, 26, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonincontri, P.; Morvillo, A.; Okumus, F.; van Niekerk, M. Managing the experience co-creation process in tourism destinations: Empirical findings from Naples. Tour. Manag. 2017, 62, 264–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkal, N. Gösteri olarak mimarlık: Turizmin güncel mimarlığa etkileri üzerine. Mimarlık 2017, 336, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Taş, M.; Taş, N.; Çahantimur, A. A participatory governance model for the sustainable development of Cumalikizik, a heritage site in Turkey. Environ. Urban. 2009, 21, 161–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, J.M. Methodological bases for documenting and reusing vernacular farm architecture. J. Cult. Herit. 2010, 11, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amit-Cohen, I.; Sofer, M. Cultural heritage and its economic potential in rural society: The case of the kibbutzim in Israel. Land Use Policy 2016, 57, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benni, S.; Carfagna, E.; Torreggiani, D.; Maino, E.; Bovo, M.; Tassinari, P. Multidimensional measurement of the level of consistency of farm buildings with rural heritage: A methodology tested on an Italian case study. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, W.; Bahauddin, A. Heritage and rehabilitation strategies for confucian courtyard architecture: A case study in Liaocheng, China. Buildings 2023, 13, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Shi, D. Rural heritage: Value, conservation and revitalisation-from the perspective of the human–land relationship. Built Herit. 2019, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council of Europe. European Rural Heritage Observation Guide—CEMAT. In Proceedings of the 13th Session of the Council of Europe’s European Conference of Ministers responsible for Regional Planning, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 16–17 September 2003; p. 62. [Google Scholar]
- Lupi, C.; Giaccio, V.; Mastronardi, L.; Giannelli, A.; Scardera, A. Exploring the features of agritourism and its contribution to rural development in Italy. Land Use Policy 2017, 64, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charters, T.; Saxon, E. Tourism and mountains. In A Practical Guide to Managing the Environmental and Social Impacts of Mountain Tours; UNEP United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2007; p. 53. [Google Scholar]
- Rio, D.; Nunes, L.M. Monitoring and evaluation tool for tourism destinations. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2012, 4, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conaghan, A.; Hanrahan, J.; Mcloughlin, E. The sustainable management of a tourism destination in Ireland: A focus on county clare. Adv. Hosp. Tour. Res. 2015, 3, 62–87. [Google Scholar]
- Nasser, N. Planning for Urban Heritage Places: Reconciling Conservation, Tourism, and Sustainable Development. J. Plan. Lit. 2003, 17, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. World Heritage Tourism Programme. 2012. Available online: https://whc.unesco.org/archive/2012/whc12-36com-5E-en.pdf (accessed on 19 March 2024).
- IUCN. Management planning for natural world heritage properties. In A Resource guide for Practitioners; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2008; Available online: https://portals.iucn.org/library/sites/library/files/Documents/2008-077.pdf (accessed on 19 March 2024).
- Fyall, A.; Garrod, B. Heritage tourism: At what price? Manag. Leis. 1998, 3, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO; ICCROM; ICOMOS; IUCN. Managing Cultural World Heritage; United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization: Paris, France, 2013; p. 152. [Google Scholar]
- McKercher, B.; Du Cros, H. Cultural Tourism: The Partnership Between Tourism and Cultural Heritage Management; Routledge: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ancuta, C.; Jucu, I.S. Sustainable Rural Development through Local Cultural Heritage Capitalization—Analyzing the Cultural Tourism Potential in Rural Romanian Areas: A Case Study of Hărman Commune of Brașov Region in Romania. Land 2023, 12, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liang, J.; Su, X.; Chen, Y.; We, Q. Research on global cultural heritage tourism based on bibliometric analysis. Herit. Sci. 2023, 11, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christina, A.; Ladkin, A.; Fletcher, J. Stakeholder collaboration and heritage management. Ann. Tour. Res. 2005, 32, 28–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.P. The “vicious circle” of tourism development in heritage cities. Ann Tour. Res. 2002, 29, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dans, E.P.; Gonzalez, P.A. Sustainable tourism and social value at World Heritage Sites: Towards a conservation plan for Altamira, Spain. Ann. Tour. Res. 2019, 74, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardaro, R.; La Sala, P.; De Pascale, G.; Faccilongo, N. The conservation of cultural heritage in rural areas: Stakeholder preferences regarding historical rural buildings in Apulia, southern Italy. Land Use Policy 2021, 109, 105662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giliberto, F.; Labadi, S. Harnessing cultural heritage for sustainable development: An analysis of three internationally funded projects in MENA Countries. Int. J. Herit. Stud. 2021, 28, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautio, S. Material compromises in the planning of a ‘traditional village’ in Southwest China. Soc. Anal. 2021, 65, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökarslan, A.B.; Tuncer Pürselim, H. The Role of Cultural Heritage in Ecotourism Planning in Rural Areas: The Case of Isparta Sütçüler Beydilli Village. Sustainability 2025, 17, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, M.; Shipley, R. An analysis of the literature at the nexus of heritage, tourism, and local economic development. J. Herit. Tour. 2012, 7, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KULELI Mimarlık Müşavirlik. İznik/Nikaia/Nicaea Yönetim Planı Çalışması (2022–2027); Bursa Metropolitan Municipality: Bursa, Turkey, 2024; 311p. [Google Scholar]
- TÜİK. 2023. Available online: https://www.tuik.gov.tr/media/announcements/Favori_Tablolar.xlsx (accessed on 29 March 2024).
- Raporu, A.S. Bursa, Eskişehir, Bilecik Kalkınma Ajansı (BEBKA). In İznik İlçe Raporu; BEBKA: Bursa, Turkey, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Soykök, B.; Taş, M. İznik Kırsalındaki Kırsal Turizm Potansiyellerinin Incelenmesi; Mimarlık ve Kent Araştırmaları Konferansı: İstanbul, Türkiye, 2021; pp. 84–90. [Google Scholar]
- Baltacı, A. Nitel Araştırma Süreci: Nitel Bir Araştırma Nasıl Yapılır? AEÜSBED 2019, 5, 368–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatch, J.A. Doing Qualitative Research in Education Settings; State University of New York Press: Albany, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Merriam, S.B.; Grenier, R.S. Qualitative Research in Practice: Examples for Discussion and Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ghaderi, Z.; Henderson, J.C. Sustainable rural tourism in Iran: A perspective from Hawraman Village. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2012, 2–3, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanagustín Fons, M.; Fierro, J.A.M. Rural tourism: A sustainable alternative. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polukhina, A.; Sheresheva, M.; Efremova, M.; Suranova, O.; Agalakova, O.; Antonov-Ovseenko, A. The concept of sustainable rural tourism development in the face of COVID-19 crisis: Evidence from Russia. J. Risk Financ. Manag. 2021, 14, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Liu, G.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J. Identifying the critical stakeholders for the sustainable development of architectural heritage of tourism: From the perspective of China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgeriş, M.; Demircan, N.; Karahan, A.; Gökçe, O.; Karahan, F.; Sezen, I.; Akpınar Külekçi, E. Cultural heritage management in the context of sustainable tourism: The case of Öskvank Monastery (Uzundere, Erzurum). Sustainability 2024, 16, 9964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirli, A.; Bakas, T.; Latinopoulos, D.; Kagalou, I.; Spiliotis, M. Participatory management of a Mediterranean Lagoon Complex social-ecological system using ıntuitionistic fuzzy TOPSIS. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altunışık, R.; Coşkun, R.; Bayraktaroğlu, S.; Yıldırım, E. Sosyal Bilimlerde Araştırma Yöntemleri; Sakarya Yayıncılık: Sakarya, Turkey, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yurdakul Kabakçı, I. Nitel Veri Analizinin Temelleri: Nitel Veri Analizinde Adım Adım NVivo Kullanımı; Yurdakul Kabakçı, I., Ed.; Anı Yayıncılık: Ankara, Turkey, 2016; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Akbulak, C. İznik gölü havzasında arazi kullanımının seçilmiş köyler üzerinde incelenmesi. Coğrafya Derg. 2007, 15, 24–43. Available online: https://dergipark.org.tr/tr/pub/iucografya/issue/25064/264598 (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- OECD. A New Rural Development Paradigm for the 21st Century: A Toolkit for Developing Countries, Development Centre Studies; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrwajfah, M.M.; Almeida-García, F.; Cortés-Macías, R. The satisfaction of local communities in World Heritage Site destinations. The case of the Petra region, Jordan. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2021, 39, 100841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocca, F. The role of cultural heritage in sustainable development: Multidimensional ındicators as decision-making tool. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gražulevičiūtė, I. Cultural heritage in the context of sustainable development. Environ. Res. Eng. Manag. 2006, 3, 74–79. [Google Scholar]
- Cucco, P.; Maselli, G.; Nesticò, A.; Ribera, F. An evaluation model for adaptive reuse of cultural heritage in accordance with 2030 SDGs and European Quality Principles. J. Cult. Herit. 2023, 59, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).