Spatiotemporal Changes and Driving Analysis of Ecological Environmental Quality in the Qinghai Lake Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
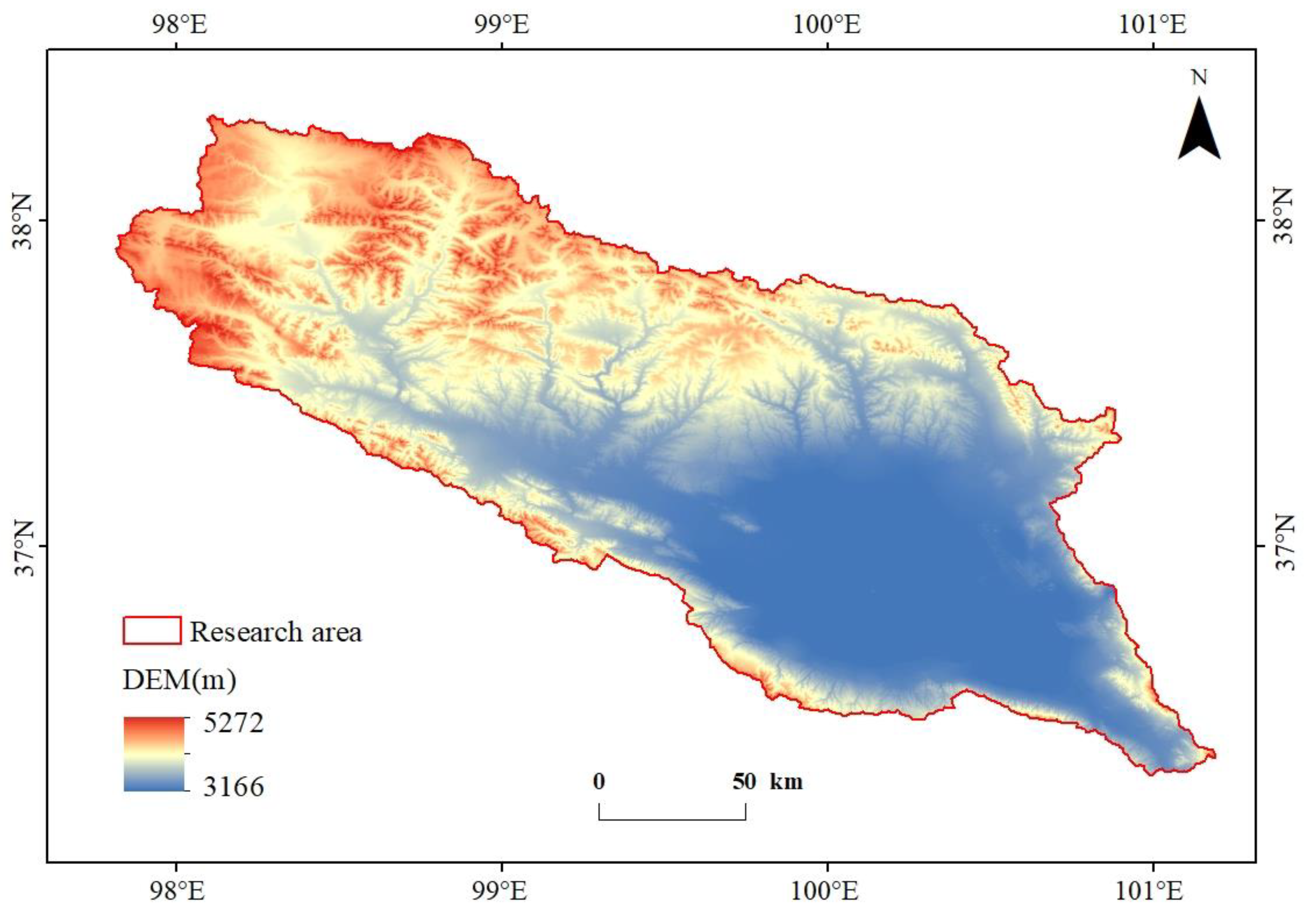
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Pre-Processing
2.3. Remote Sensing Ecological Indices
2.4. Research Methodology
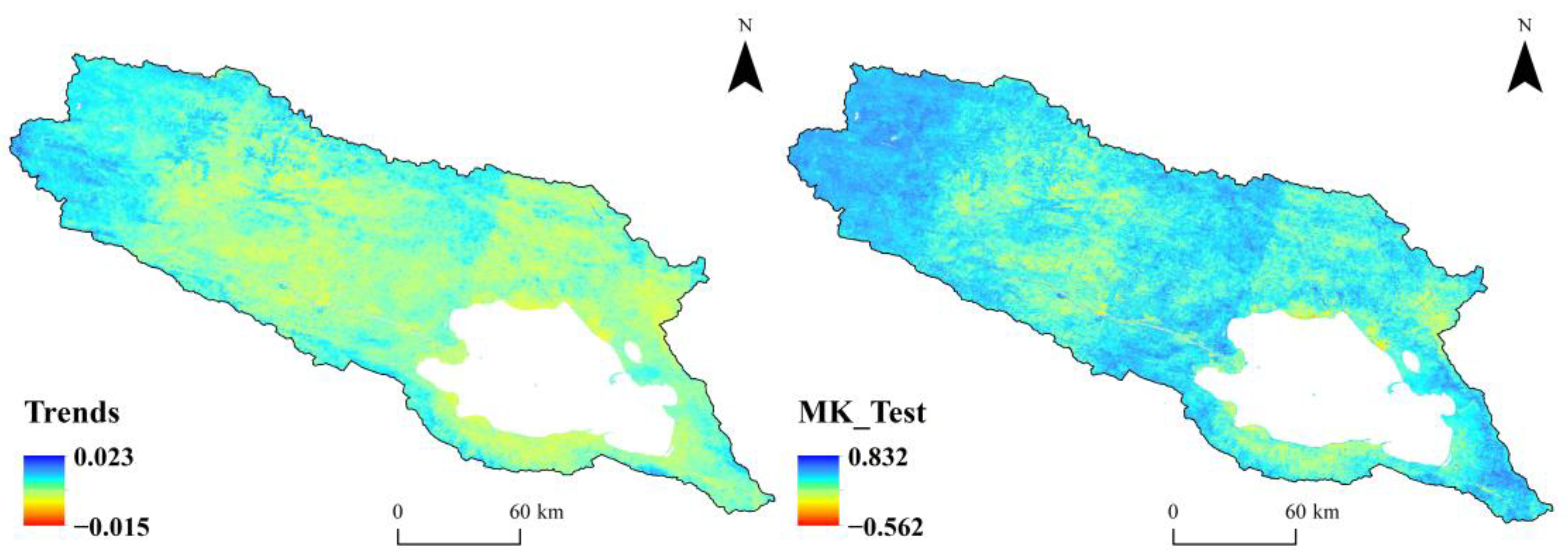
2.4.1. Univariate Linear Trend Analysis and Mann–Kendall Trend Significance Test
2.4.2. Geodetector
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Spatial and Temporal Changes of the RSEI in Qinghai Lake Basin
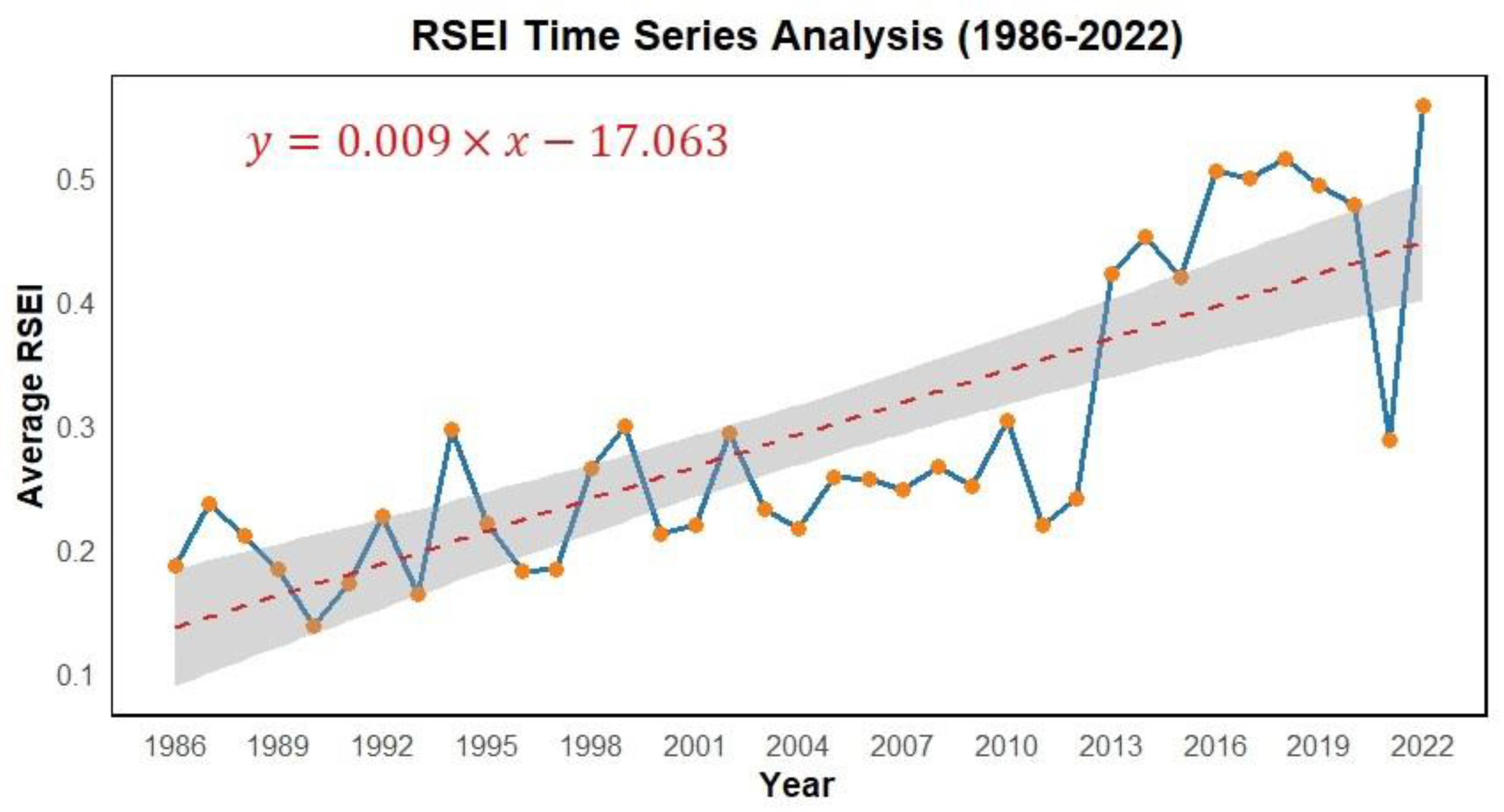
3.1.1. Characteristics of Temporal Changes of the RSEI in Qinghai Lake Basin
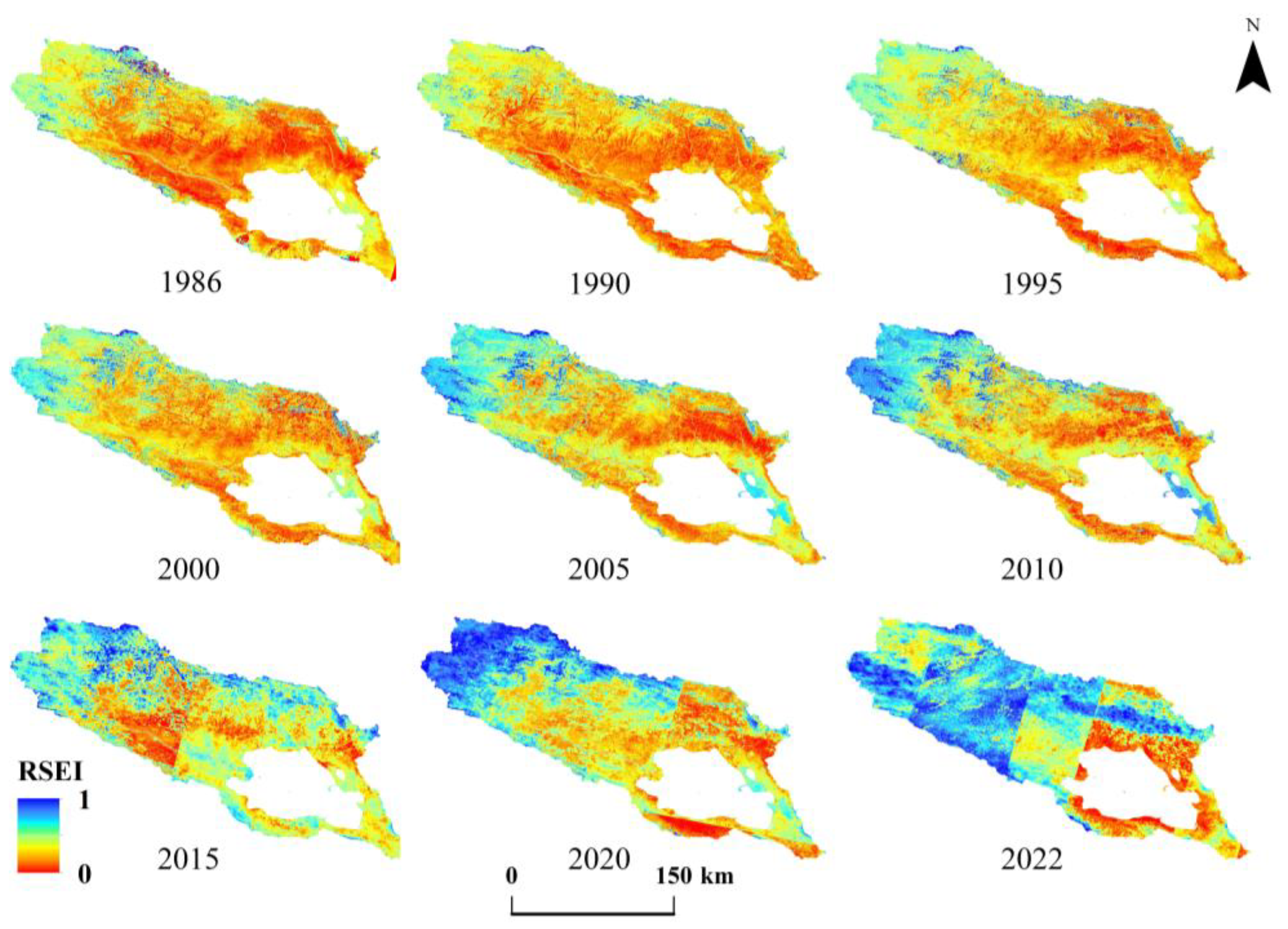
3.1.2. Spatial Distribution Patterns and Variation Characteristics of the RSEI in the Qinghai Lake Basin
3.2. Analysis of Driving Factors for the RSEI in Ecological Environment Quality
3.2.1. Results of Single-Factor Detection
3.2.2. Results of Interaction Detection
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatiotemporal Variation Characteristics and Spatial Distribution Patterns of Ecological Quality in the Qinghai Lake Basin
4.2. Influence of Different Driving Factors on RSEI Changes in Ecological Environment Quality
5. Conclusions
6. Deficiency and Prospect
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RSEI | Remote Sensing Ecological Index |
| GEE | Google Earth Engine |
| NDVI | Normalized Difference Vegetation Index |
| NDBSI | Normalized Difference Bare Soil Index |
| LST | Land Surface Temperature |
References
- Qiu, B.; Chen, G.; Tang, Z.; Lu, D.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C. Assessing the Three-North Shelter Forest Program in China by a Novel Framework for Characterizing Vegetation Changes. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 133, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, K.S. Remote Sensing Change Detection for Ecological Monitoring in United States Protected Areas. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 182, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Xu, W.; Lu, N.; Huang, S.; Wu, C.; Wang, L.; Dai, F.; Kou, W. Assessment of Spatial–Temporal Changes of Ecological Environment Quality Based on RSEI and GEE: A Case Study in Erhai Lake Basin, Yunnan Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. A Remote Sensing Evaluation Index for Regional Ecological Environment Change. China Environ. Sci. 2013, 33, 889–897. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H. Construction and Application of Urban Remote Sensing Ecological Index. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 7853–7862. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, K.; Jia, G.; Yu, X.; Chen, L. Evaluation of Ecological Environment Quality and Analysis of Driving Mechanisms in the Turpan-Hami Region Based on an Improved Remote Sensing Ecological Index. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 3911–3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-Scale Geospatial Analysis for Everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parastatidis, D.; Mitraka, Z.; Chrysoulakis, N.; Abrams, M. Online Global Land Surface Temperature Estimation from Landsat. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, L.; Du, Y. Analysis of Ecological Quality in Lhasa Metropolitan Area during 1990–2017 Based on Remote Sensing and Google Earth Engine Platform. J. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airiken, M.; Li, S. The Dynamic Monitoring and Driving Forces Analysis of Ecological Environment Quality in the Tibetan Plateau Based on the Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Xu, E. Information Entropy and Elasticity Analysis of the Land Use Structure Change Influencing Eco-Environmental Quality in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau from 1990 to 2015. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 18348–18364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, D.; Fan, J. Sustainable Development Problems and Countermeasures: A Case Study of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Geogr. Sustain. 2020, 1, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Guo, Y.; Xu, H.; Ganjurjav, H.; Li, Y.; Wan, Y.; Qin, X.; Ma, X.; Liu, S. Climate Change and Its Impacts on Vegetation Distribution and Net Primary Productivity of the Alpine Ecosystem in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 554–555, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Yuan, R.; Singh, V.P.; Xu, C.-Y.; Fan, K.; Shen, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J. Dynamic Vulnerability of Ecological Systems to Climate Changes across the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 134, 108483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ni, W.; Li, T.; Zhou, B.; Qu, Y.; Yuan, K. Influences of Anthropogenic Factors on Lakes Area in the Golmud Basin, China, from 1980 to 2015. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. An Overview of Ecological Research Conducted on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. JORE 2017, 8, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, F.; Guo, X.; Zhao, J.; Xu, Y.; Liu, X. Assessment of Eco-Environmental Quality Changes and Spatial Heterogeneity in the Yellow River Delta Based on the Remote Sensing Ecological Index and Geo-Detector Model. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 77, 102203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Gong, J. Spatial–Temporal Changes and Driving Mechanisms of Ecological Environmental Quality in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, China. Land 2024, 13, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, H.F.; Yeh, C.F.; Lee, C.H. Mann-Kendall Test and Theil-Sen Estimator for Long-Term Spatial and Temporal Trends of Streamflow in Taiwan. J. Chin. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 47, 73–83. [Google Scholar]
- Sang, Y.-F.; Wang, Z.; Liu, C. Comparison of the MK Test and EMD Method for Trend Identification in Hydrological Time Series. J. Hydrol. 2014, 510, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, L.; Kang, S.; Ao, Y.; Han, L.; Ma, C. Quantitative Analysis of Factors Influencing Spatial Distribution of Soil Erosion Based on Geo-Detector Model under Diverse Geomorphological Types. Land 2021, 10, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Liu, C.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, B.; Fan, F. Habitat Quality Assessment on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau across Vegetation Ecoregions Using InVEST and Geodetector Models. Front. Earth Sci. 2024, 12, 1432434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wu, E.; Wu, S.; Fan, R.; Xu, L.; Ning, K.; Li, Y.; Lu, R.; Xu, X.; Zhang, J.; et al. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Ecological Condition in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Based on Remotely Sensed Ecological Index. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, F.; Hu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y. Spatiotemporal Changes and Driving Analysis of Ecological Environmental Quality along the Qinghai–Tibet Railway Using Google Earth Engine—A Case Study Covering Xining to Jianghe Stations. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Zhang, S.; Huang, L.; Liu, Z.; Yang, L.; Li, R.; Lin, X. Temporal and Spatial Changes of Ecological Environment Quality Based on RSEI: A Case Study in Ulan Mulun River Basin, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Y. Spatial-Temporal Evolution and Motivation of Ecological Vulnerability Based on RSEI and GEE in the Jianghan Plain from 2000 to 2020. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1191532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Zang, F.; Liu, Y.; Chang, Y.; Huang, G.; Fu, G.; Zhao, C.; Liu, X. Remote Sensing-Based Approach for the Assessing of Ecological Environmental Quality Variations Using Google Earth Engine: A Case Study in the Qilian Mountains, Northwest China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Lu, H.; Ji, J.; Yang, Z.; Chen, C. Exploring Evolution Characteristics of Eco-Environment Quality in the Yangtze River Basin Based on Remote Sensing Ecological Index. Heliyon 2023, 9, e23243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Typology | Data Name | Resolution | Unit | Data Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat 5/7/8 | 30 m | — | Google Earth Engine (GEE) | |
| Climate factors | Annual average precipitation | 100 m | mm | China’s Academy of Sciences Resource and Environmental Sciences Data Center (http://www.gscloud.cn (accessed on 1 January 2025)) |
| Annual average temperature | 100 m | °C | China’s Academy of Sciences Resource and Environmental Sciences Data Center (http://www.gscloud.cn (accessed on 1 January 2025)) | |
| Topographic factors | Slope | 30 m | ° | China’s Academy of Sciences Resource and Environmental Sciences Data Center (http://www.gscloud.cn (accessed on 1 January 2025)) |
| Aspect | 30 m | ° | China’s Academy of Sciences Resource and Environmental Sciences Data Center (http://www.gscloud.cn (accessed on 1 January 2025)) | |
| Elevation | 30 m | m | China’s Academy of Sciences Resource and Environmental Sciences Data Center (http://www.gscloud.cn (accessed on 1 January 2025)) | |
| Human factors | Land use | 30 m | — | China’s Academy of Sciences Resource and Environmental Sciences Data Center (http://www.gscloud.cn (accessed on 1 January 2025)) |
| Population density | 100 m | people/km2 | National Earth System Science Data Center (http://www.geodata.cn (accessed on 1 January 2025)) |
| Indicator | Method of Calculation |
|---|---|
| NDVI | |
| WET | |
| NDBSI | |
| LST |
| Type of Interaction | Comparison of q-Values |
|---|---|
| Nonlinear attenuation | q(X1∩X2) < Min[q(X1), q(X2)] |
| One-factor nonlinear attenuation | Min[q(X1), q(X2)] < q(X1∩X2) < Max[q(X1), q(X2)] |
| Two-factor enhancement | q(X1∩X2) > Max[q(X1), q(X2)] |
| Independent | q(X1∩X2) = q(X1) + q(X2) |
| Nonlinear enhancement | q(X1∩X2) > q(X1) + q(X2) |
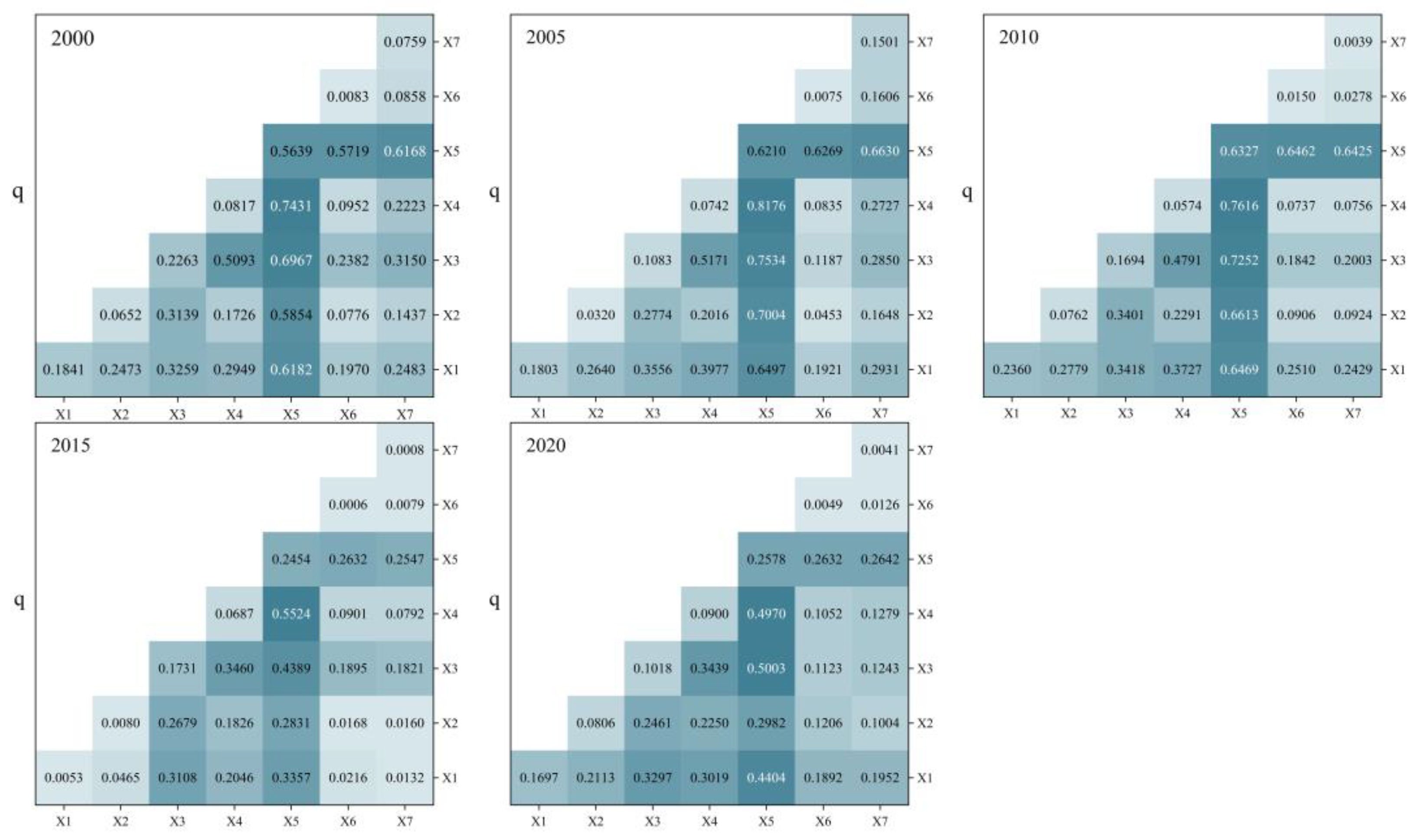
| Driving Factor | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | Average 2000–2020 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| q | Ranking | q | Ranking | q | Ranking | q | Ranking | q | Ranking | q | Ranking | |
| Annual average precipitation | 0.1841 | 3 | 0.1803 | 2 | 0.2360 | 2 | 0.0053 | 5 | 0.1697 | 2 | 0.1551 | 3 |
| Annual average temperature | 0.0652 | 6 | 0.0320 | 6 | 0.0762 | 4 | 0.0080 | 4 | 0.0806 | 5 | 0.0524 | 5 |
| Slope | 0.2263 | 2 | 0.1083 | 4 | 0.1694 | 3 | 0.1731 | 2 | 0.1018 | 3 | 0.1558 | 2 |
| Aspect | 0.0817 | 4 | 0.0742 | 5 | 0.0574 | 5 | 0.0687 | 3 | 0.0900 | 4 | 0.0744 | 4 |
| Elevation | 0.5639 | 1 | 0.6210 | 1 | 0.6327 | 1 | 0.2454 | 1 | 0.2578 | 1 | 0.4642 | 1 |
| Land use | 0.0083 | 7 | 0.0075 | 7 | 0.0150 | 6 | 0.0006 | 7 | 0.0049 | 6 | 0.0072 | 7 |
| Population density | 0.0759 | 5 | 0.1501 | 3 | 0.0039 | 7 | 0.0008 | 6 | 0.0041 | 7 | 0.0469 | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, P.; Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Gao, H. Spatiotemporal Changes and Driving Analysis of Ecological Environmental Quality in the Qinghai Lake Basin. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3421. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083421
Yao P, Yu X, Wang Y, Feng Y, Gao H. Spatiotemporal Changes and Driving Analysis of Ecological Environmental Quality in the Qinghai Lake Basin. Sustainability. 2025; 17(8):3421. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083421
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Panpan, Xinxiao Yu, Yukun Wang, Yankai Feng, and Hongyan Gao. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Changes and Driving Analysis of Ecological Environmental Quality in the Qinghai Lake Basin" Sustainability 17, no. 8: 3421. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083421
APA StyleYao, P., Yu, X., Wang, Y., Feng, Y., & Gao, H. (2025). Spatiotemporal Changes and Driving Analysis of Ecological Environmental Quality in the Qinghai Lake Basin. Sustainability, 17(8), 3421. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083421






