The Role of Cheap Chemicals Containing Oxygen Used as Diesel Fuel Additives in Reducing Carbon Footprints
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biodiesel Generation
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Thermodynamic Analysis
- 1.
- The gases entering and exiting the cylinder are assumed to behave as ideal gases;
- 2.
- The temperature of the cylinder walls remains constant during the experiments;
- 3.
- Ambient conditions are maintained at 20 °C and atmospheric pressure (1 atm);
- 4.
- The engine is assumed to operate under continuous, steady-state conditions.
2.4. Energy Analysis
2.5. Exergy Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
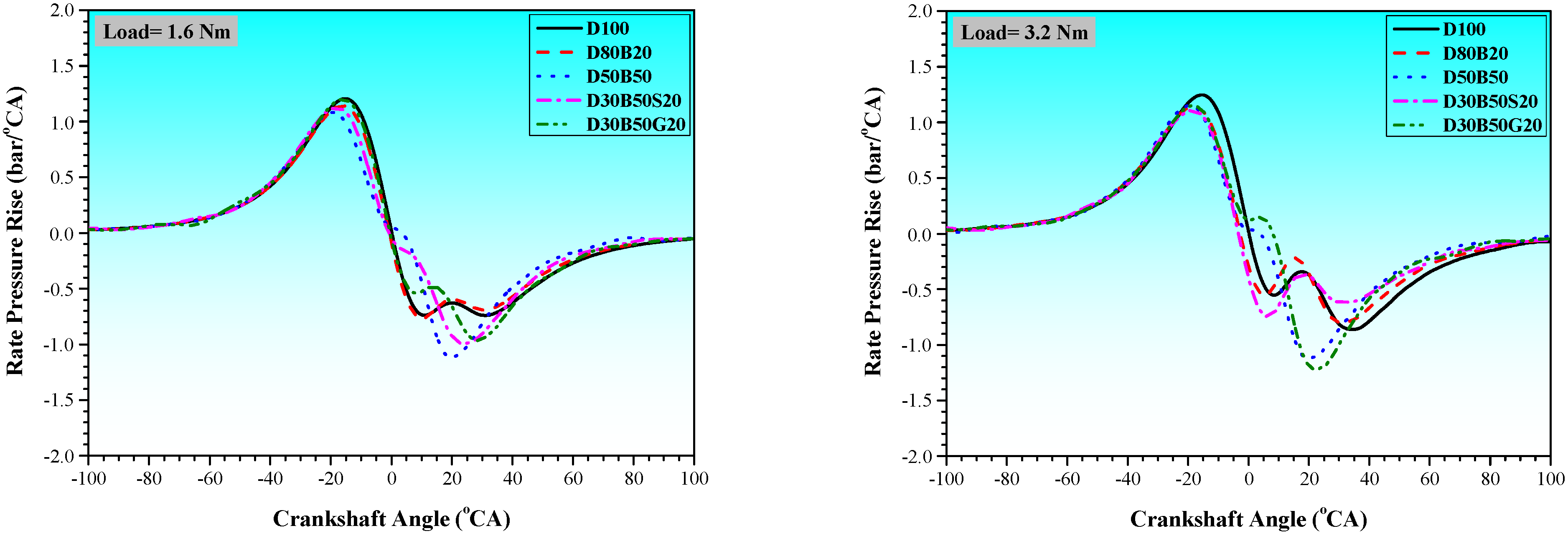
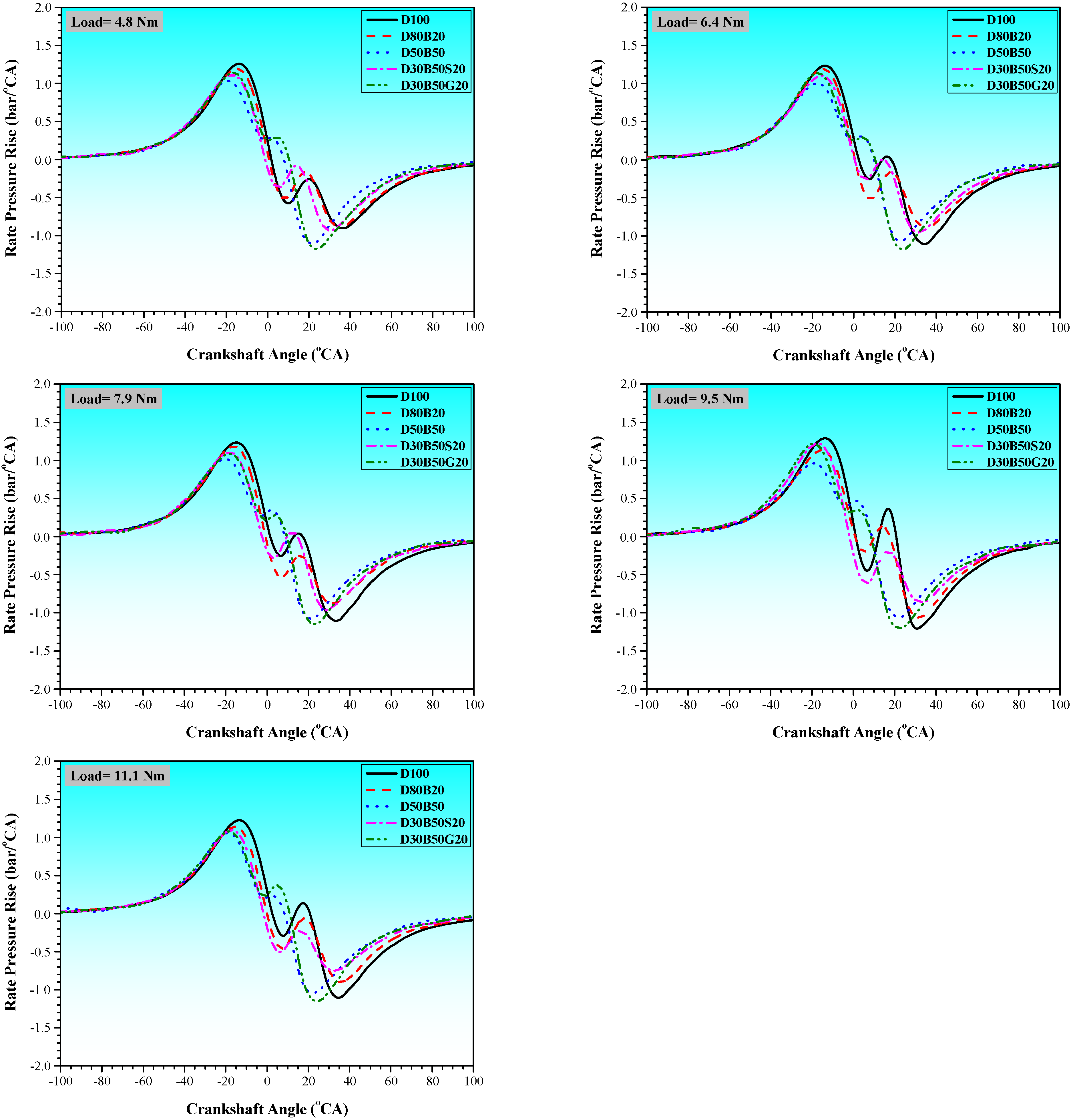
3.1. Combustion Characteristics
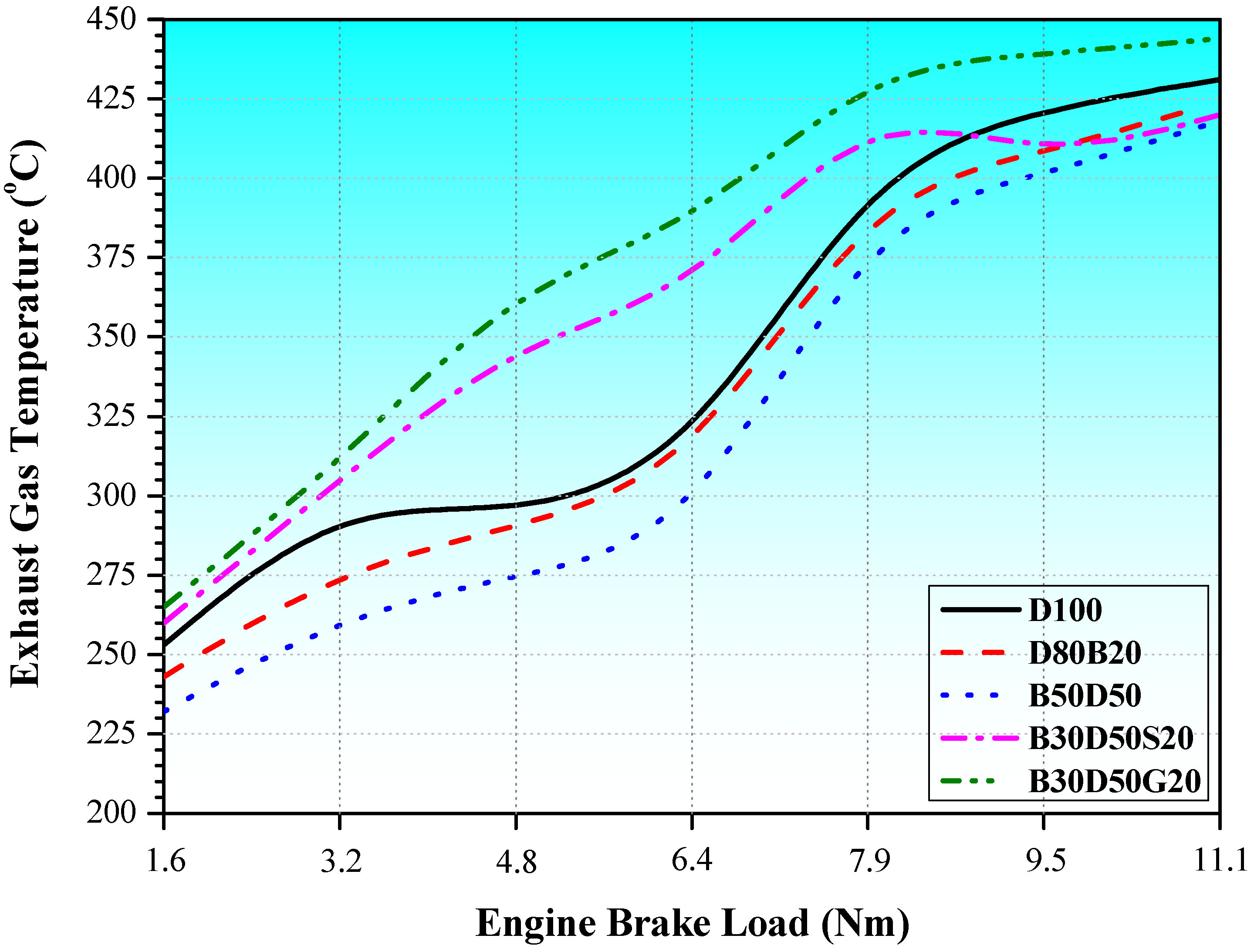
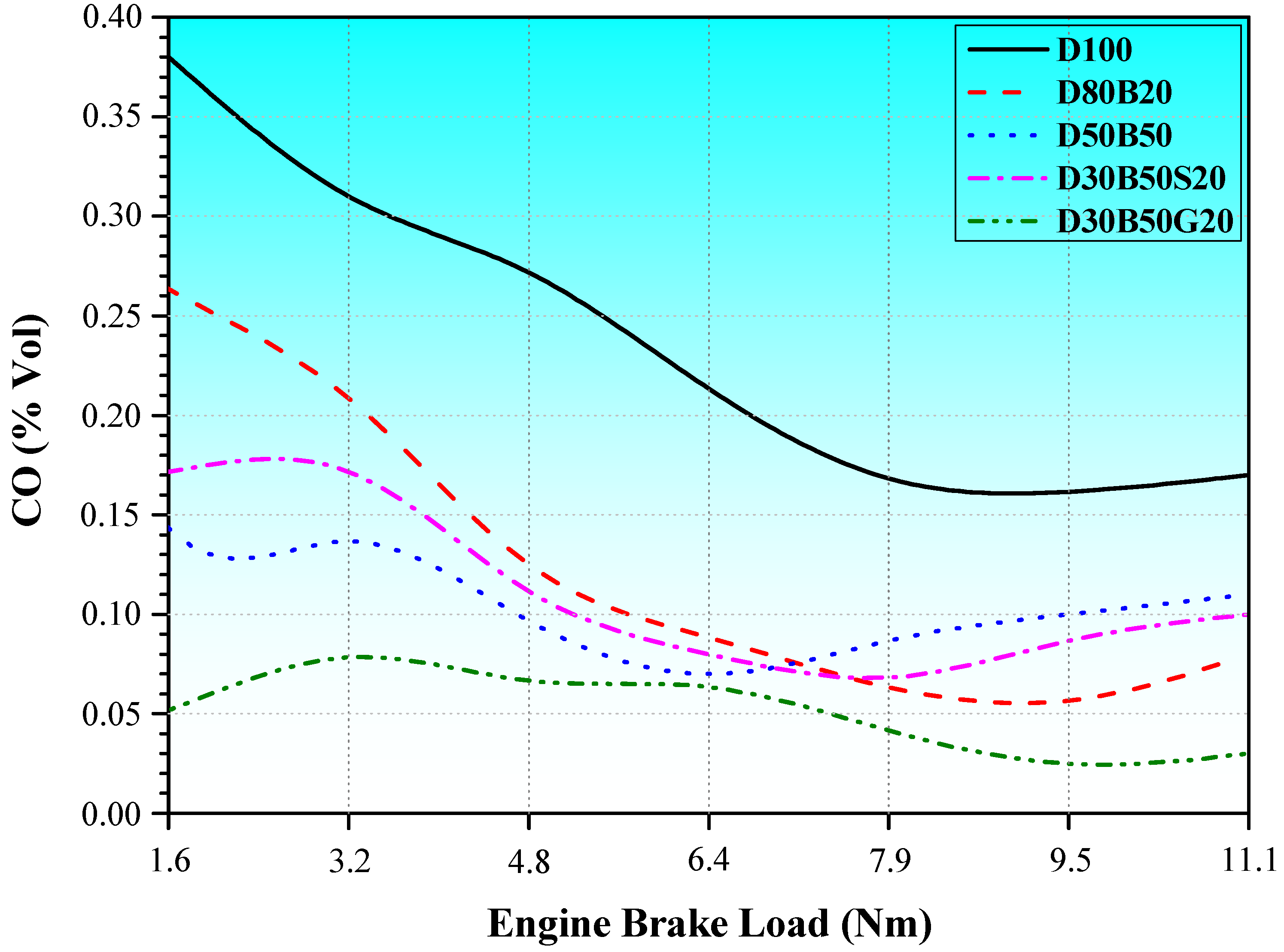
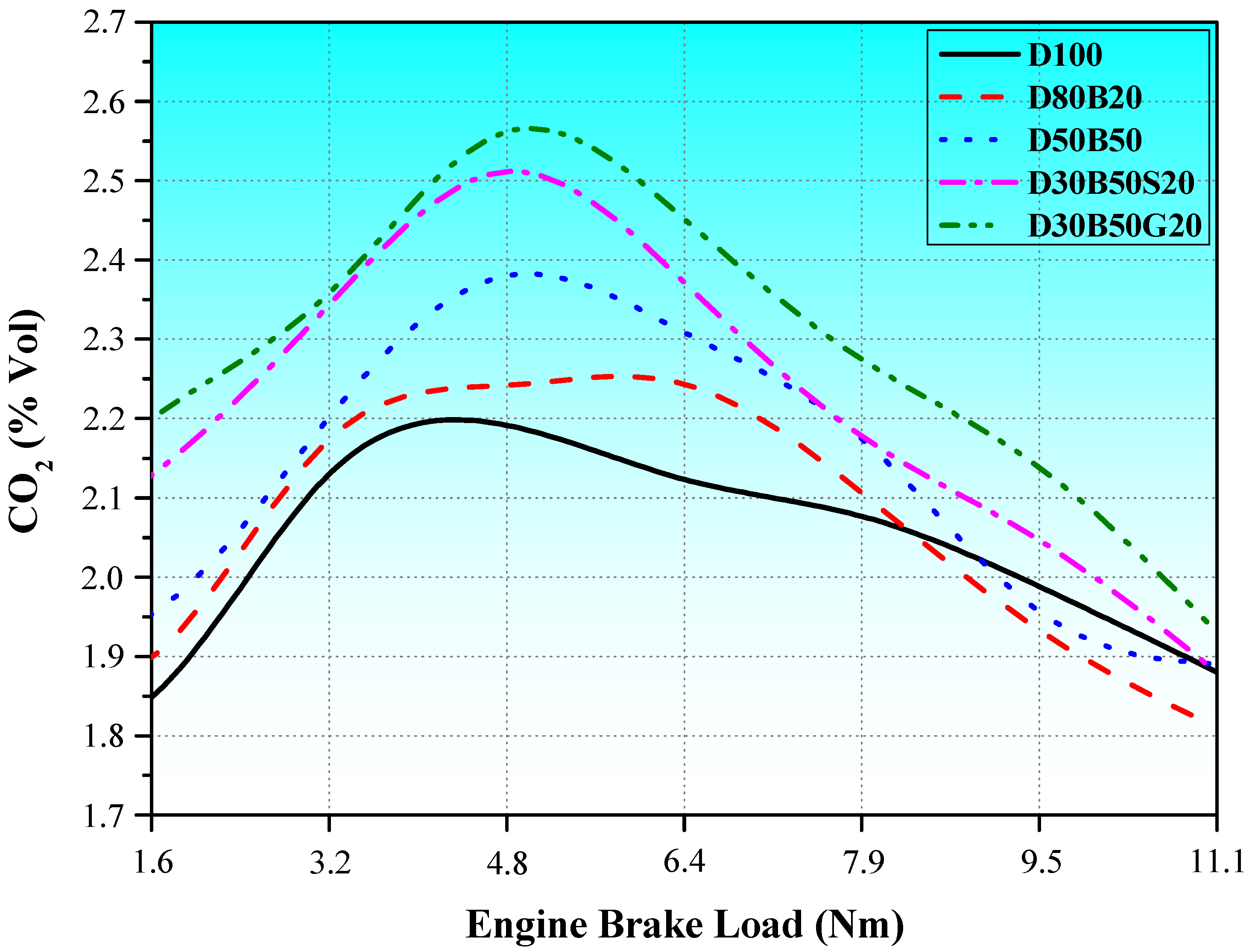
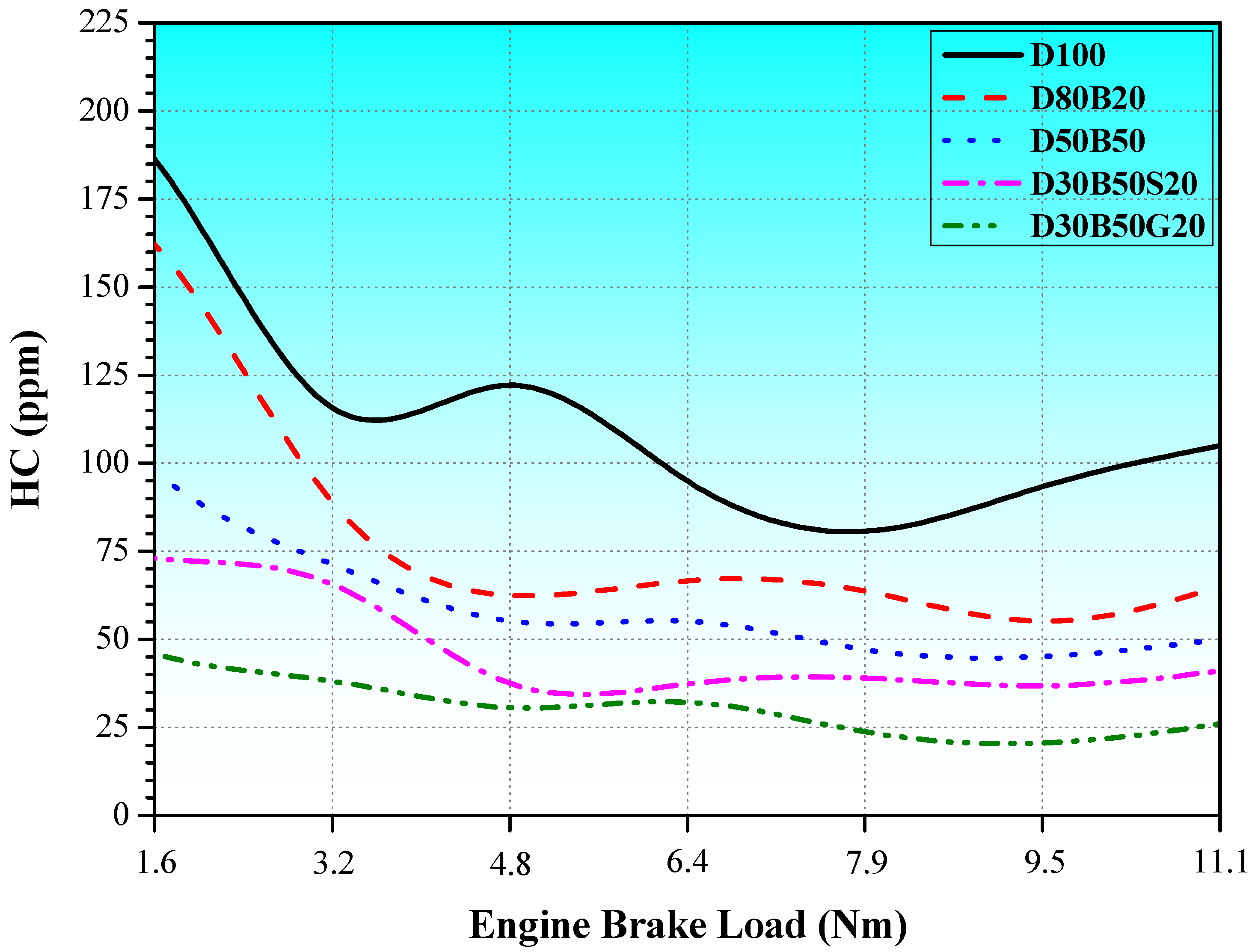
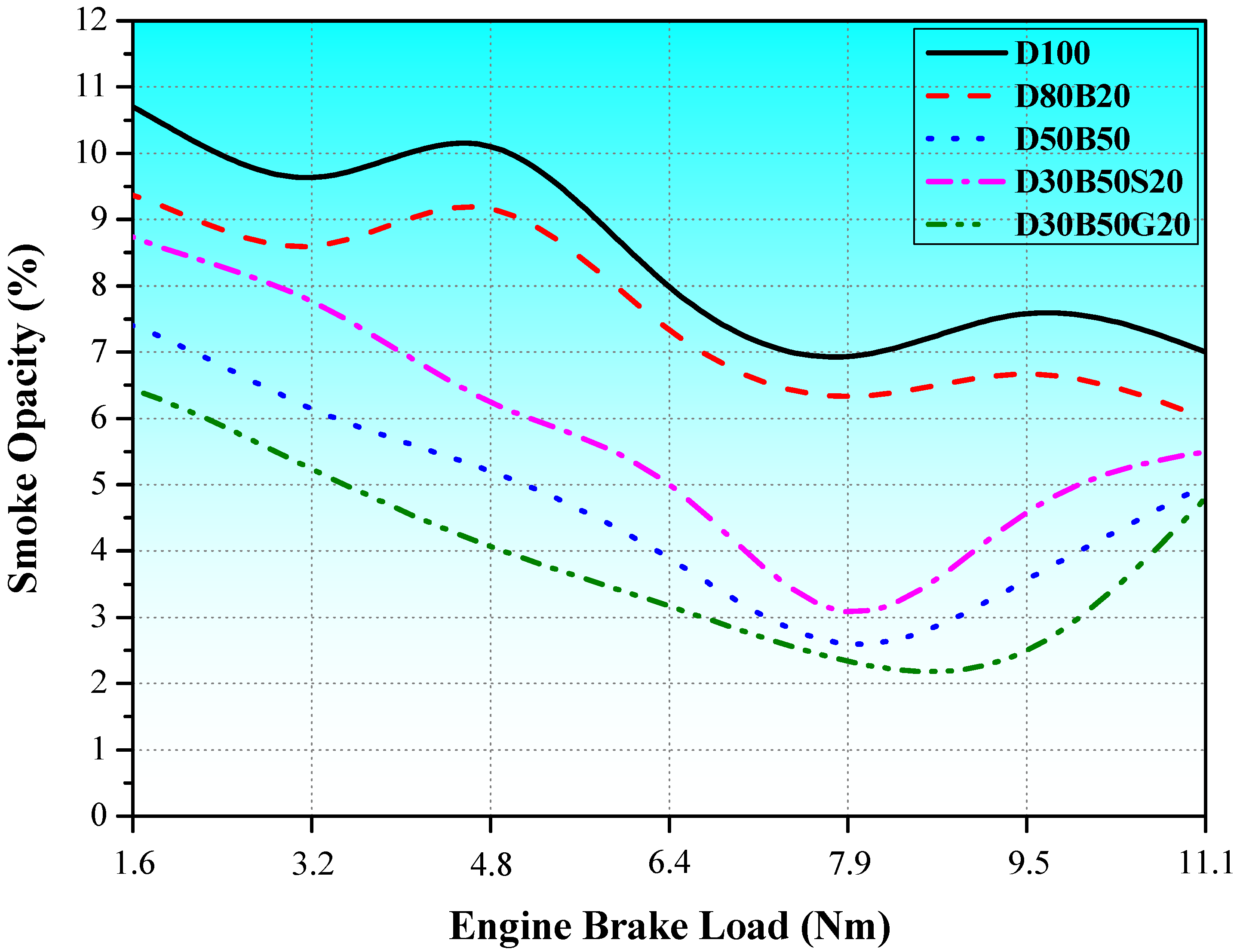
3.2. Exhaust Emissions
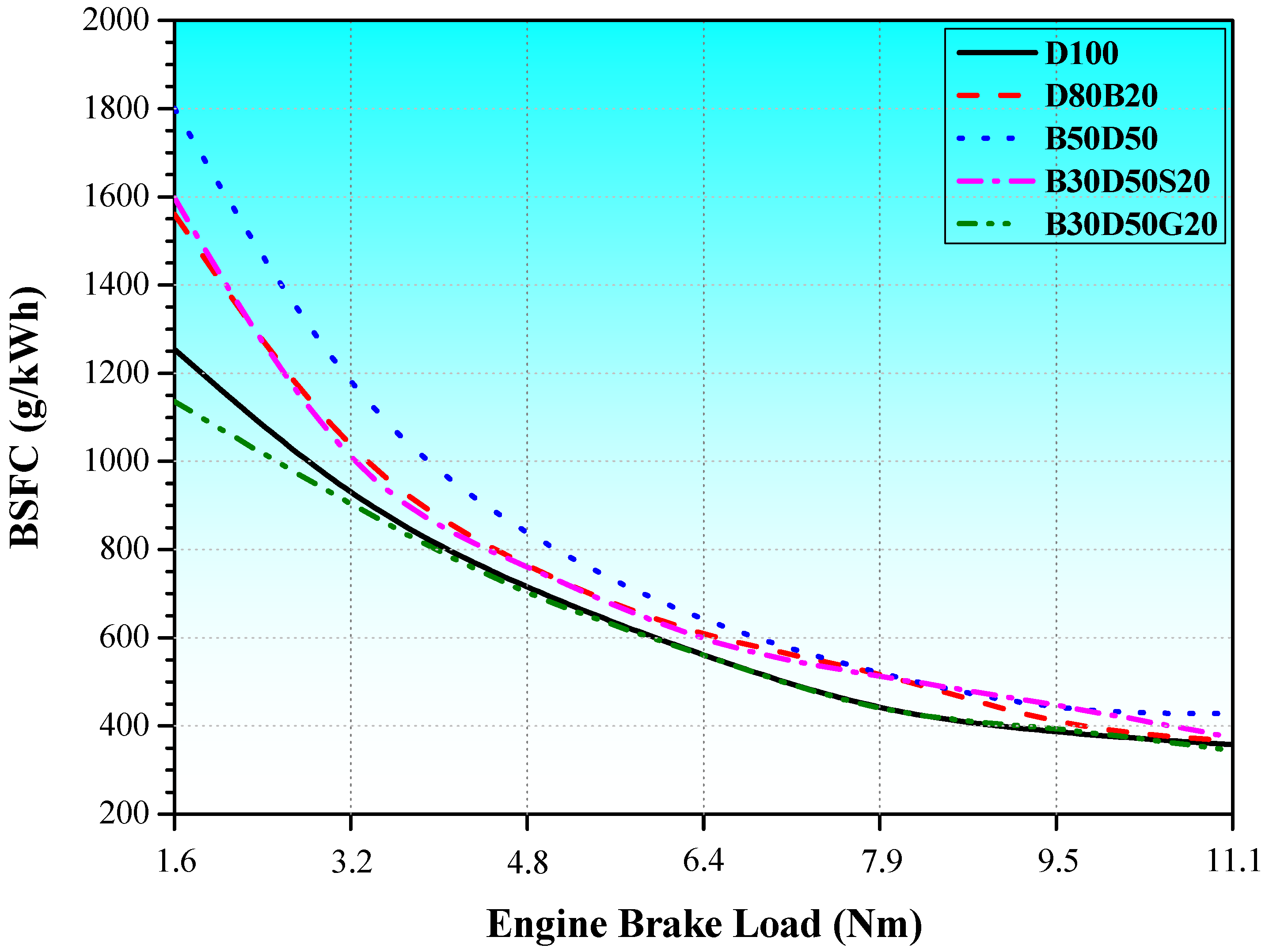
3.3. Energy and Exergy Analyses
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| BSFC | Brake-specific fuel consumption (g/kWh) |
| BTE | brake thermal efficiency |
| C15H25 | diesel |
| CA | crank angle |
| CD | combustion duration (°CA) |
| CHR | cumulative heat release (J) |
| CI | Compression ignition |
| CO | carbon monoxide |
| CO2 | carbon dioxide |
| Cp | in-cylinder pressure (bar) |
| DI | Direct injection |
| D100 | 100% diesel |
| D80B20 | 80% diesel and 20% biodiesel |
| D50B50 | 50% diesel and 50% biodiesel |
| D30B50S20 | 30% diesel, 50% biodiesel, and 20% solketal |
| D30B50G20 | 30% diesel, 50% biodiesel, and 20% butyl diglycol |
| EOC | end of combustion (°CA) |
| HC | hydrocarbon |
| HRR | heat release rate (J/°CA) |
| H2O | water |
| ICE | internal combustion engine |
| ID | Ignition delay |
| NOX | nitrogen oxide |
| O2 | oxygen |
| RoPR | rate of pressure rise (bar/°CA) |
| TDC | top dead center |
References
- Wang, J.; Azam, W. Natural resource scarcity, fossil fuel energy consumption, and total greenhouse gas emissions in top emitting countries. Geosci. Front. 2024, 15, 101757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Abbasi, K.R.; Hussain, K.; Albaker, A.; Alvarado, R. Environmental concerns in the United States: Can renewable energy, fossil fuel energy, and natural resources depletion help? Gondwana Res. 2023, 117, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, K.R.; Shahbaz, M.; Zhang, J.; Irfan, M.; Alvarado, R. Analyze the environmental sustainability factors of China: The role of fossil fuel energy and renewable energy. Renew. Energy 2022, 187, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Haneklaus, N. The role of renewable energy, fossil fuel consumption, urbanization and economic growth on CO2 emissions in China. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 1016–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.H.; Tee, K.; Elnahass, M.; Ahmed, R. Assessing the environmental impacts of renewable energy sources: A case study on air pollution and carbon emissions in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, J.; Yang, C. The performance and emissions characteristics of diesel/biodiesel/alcohol blends in a diesel engine. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 904–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, R.; Rasul, M.G.; Khan, M.M.K.; Salahi, M.M. Experimental and computational analysis of combustion characteristics of a diesel engine fueled with diesel-tomato seed oil biodiesel blends. Fuel 2021, 285, 119243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, E.; Can, Ö.; Usta, N.; Yücesu, H.S. Effects of retarded fuel injection timing on combustion and emissions of a diesel engine fueled with canola biodiesel. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2020, 23, 1466–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyamurthy, R.; Balaji, D.; Gorjian, S.; Muthiya, S.J.; Bharathwaaj, R.; Vasanthaseelan, S.; Essa, F.A. Performance, combustion and emission characteristics of a DI-CI diesel engine fueled with corn oil methyl ester biodiesel blends. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 43, 100981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ou, S.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Z. Preparation of biodiesel from waste cooking oil via two-step catalyzed process. Energy Convers. Manag. 2007, 48, 184–188. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, L.; Bi, L.; Li, Q.; Chen, H.; Xie, Y. Experimental study on spray characteristics, combustion stability, and emission performance of a CRDI diesel engine operated with biodiesel–ethanol blends. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 904–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeşilyurt, M.K.; Arslan, M. Analysis of the fuel injection pressure effects on energy and exergy efficiencies of a diesel engine operating with biodiesel. Biofuels 2019, 10, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Li, C.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, X.; Yao, M. Experimental study on diesel conventional and low-temperature combustion by fueling four isomers of butanol. Fuel 2015, 141, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Dinesha, P.; Ajay, C.M.; Kabbur, P. Combined effect of oxygenated liquid and metal oxide nanoparticle fuel additives on the combustion characteristics of a biodiesel engine operated with higher blend percentages. Energy 2020, 197, 117194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Kumar, S.; Shah, S.; Kumar, S. Study of performance parameters and emissions of four-stroke CI engine using solketal-biodiesel blends. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.C.; Lee, W.J.; Wu, T.S.; Wu, C.Y.; Chen, S.J. Use of water containing acetone–butanol–ethanol for NOx-PM (nitrogen oxide-particulate matter) trade-off in the diesel engine fueled with biodiesel. Energy 2014, 64, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamrozik, A.; Tutak, W.; Grab-Rogaliński, K. Effects of Propanol on the Performance and Emissions of a Dual-Fuel Industrial Diesel Engine. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masera, K.; Hossain, A.K.; Davies, P.A.; Doudin, K. Investigation of 2-butoxyethanol as biodiesel additive on fuel property and combustion characteristics of two neat biodiesels. Renew. Energy 2021, 164, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabi, M.N.; Rasul, M.G. Influence of second-generation biodiesel on engine performance, emissions, energy and exergy parameters. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 169, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Cui, S.; Fang, J.; Zhong, Z.; Li, K.; Ai, X.; Wu, K.; Liang, B.; Wen, J. Exergy analysis-based operating parameter optimization for hydrogen energy hub. Appl. Energy 2025, 38, 5125491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Guo, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, G.; Sun, X.; Sun, H.; Wang, H.; Li, R. A Thermodynamic Perspective on the Efficient Pressure Potential Energy Release in an Ice-Assisted Near-Isothermal Caes System. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=5125925 (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Paul, A.; Panua, R.; Debroy, D. An experimental study of combustion, performance, exergy, and emission characteristics of a CI engine fueled by diesel-ethanol-biodiesel blends. Energy 2017, 141, 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madheshiya, A.K.; Vedrtnam, A. Energy-exergy analysis of biodiesel fuels produced from waste cooking oil and mustard oil. Fuel 2018, 214, 386–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kul, B.S.; Kahraman, A. Energy and exergy analyses of a diesel engine fueled with biodiesel-diesel blends containing 5% bioethanol. Entropy 2016, 18, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseinpour, M.; Sadrnia, H.; Tabasizadeh, M.; Ghobadian, B. Energy and exergy analyses of a diesel engine fueled with diesel, biodiesel-diesel blend, and gasoline fumigation. Energy 2017, 141, 2408–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şanli, B.G.; Uludamar, E. Energy and exergy analysis of a diesel engine fueled with diesel and biodiesel fuels at various engine speeds. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2020, 42, 1299–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoobbakht, G.; Akram, A.; Karimi, M.; Najafi, G. Exergy and energy analysis of combustion of blended levels of biodiesel, ethanol, and diesel fuel in a DI diesel engine. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 99, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarak, M.; Shaija, A.; Suchithra, T.V. Experimental evaluation of Salvinia molesta oil biodiesel/diesel blends fuel on combustion, performance, and emission analysis of diesel engine. Fuel 2021, 287, 119526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, M.S.; Kamel, B.M.; Badruddin, I.A. Improving the diesel engine performance, emissions, and combustion characteristics using biodiesel with carbon nanomaterials. Fuel 2021, 288, 119665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, S.; Molina, F.; Agudelo, J.R. Palm oil biodiesel: An assessment of PAH emissions, oxidative potential, and ecotoxicity of particulate matter. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 101, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alptekin, E. Emission, injection, and combustion characteristics of biodiesel and oxygenated fuel blends in a common rail diesel engine. Energy 2017, 119, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özer, S. Effects of alternative fuel use in a vehicle with TSI (turbocharged direct-injection spark-ignition) engine technology. Int. J. Green Energy 2021, 18, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doğan, B.; Özer, S.; Erol, D. Exergy, exergoeconomic, and exergoenviroeconomic evaluations of the use of diesel/fusel oil blends in compression ignition engines. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 53, 102475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghavifar, H.; Nemati, A.; Walther, J.H. Combustion and exergy analysis of multi-component diesel-DME-methanol blends in HCCI engine. Energy 2019, 187, 115951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özer, S.; Tunçer, E.; Demir, U.; Gülcan, H.E. Thermodynamic, thermoeconomic, and exergoeconomic analysis of a UAV two stroke engine fueled with gasoline-octanol and gasoline-hexanol blends. Energy Convers. Manag. 2025, 327, 119545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, B.; Erol, D.; Yaman, H.; Kodanli, E. The effect of ethanol-gasoline blends on performance and exhaust emissions of a spark ignition engine through exergy analysis. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 120, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ağbulut, Ü. Understanding the role of nanoparticle size on energy, exergy, thermoeconomic, exergoeconomic, and sustainability analyses of an IC engine: A thermodynamic approach. Fuel Process. Technol. 2022, 225, 107060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doğan, B.; Erol, D. The investigation of energy and exergy analyses in compression ignition engines using diesel/biodiesel fuel blends-a review. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2023, 148, 1765–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajpoot, A.S.; Chelladurai, H.; Choudhary, A.K.; Ambade, B.; Choudhary, T. Thermal and environmental assessment of Botryococcus braunii green biodiesel with nanoparticles using energy-exergy-emission-sustainability (3ES) analysis in a diesel engine. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2023, 60, 103473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canakci, M.; Hosoz, M. Energy and exergy analyses of a diesel engine fuelled with various biodiesels. Energy Sources Part B 2006, 1, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, S.; Gharehghani, A. Effect of nano-particles concentrations on the energy and exergy efficiency improvement of indirect-injection diesel engine. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 3273–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.S.; Mohapatra, T. Energy-exergy-emission-economic performance and multi-response optimisation of a VCR CI engine using bio ethanol blended diesel fuel with Al2O3 nanoparticles. Int. J. Exergy 2023, 41, 74–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadidi, B.; Alizade, H.H.A.; Najafi, G. Performance and exergy analysis of a diesel engine run on petrodiesel and biodiesel blends containing mixed CeO2 and MoO3 nanocatalyst. Biofuels 2022, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, H. Energy and exergy analyses of Al2O3-diesel-biodiesel blends in a diesel engine. Int. J. Exergy 2019, 28, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, S.; Natarajan, S.; Eshwar, D.; Alphin, M.S. Energy and exergy analysis and multi-objective optimization of a biodiesel fueled direct ignition engine. Results Chem. 2022, 4, 100284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, M.J.; Shapiro, H.N.; Boettner, D.D.; Bailey, M.B. Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics; John Wiley Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Channapattana, S.V.; Campli, S.; Madhusudhan, A.; Notla, S.; Arkerimath, R.; Tripathi, M.K. Energy analysis of DI-CI engine with nickel oxide nanoparticle added azadirachta indica biofuel at different static injection timing based on exergy. Energy 2023, 267, 126622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jassim, E.I. Exergy analysis of petrol engine accommodated nanoparticle in the lubricant system. Int. J. Exergy 2021, 35, 406–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, M.S.; Aziz, M.M.A.; Kayed, H. Impact of different nano additives on performance, combustion, emissions and exergetic analysis of a diesel engine using waste cooking oil biodiesel. Propuls. Power Res. 2022, 11, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumus, M. A comprehensive experimental investigation of combustion and heat release characteristics of a biodiesel (hazelnut kernel oil methyl ester) fueled direct injection compression ignition engine. Fuel 2010, 89, 2802–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akçay, M.; Yılmaz, İ.T.; Feyzioğlu, A. Effect of hydrogen addition on performance and emission characteristics of a common-rail CI engine fueled with diesel/waste cooking oil biodiesel blends. Energy 2020, 212, 118538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, L.A.; Deepanraj, B.; Rajakumar, S.; Sivasubramanian, V. Experimental investigation on performance, combustion, and emission analysis of a direct injection diesel engine fuelled with rapeseed oil biodiesel. Fuel 2019, 246, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragadeshwaran, A.; Kasianantham, N.; Ballusamy, S.; Tarun, K.R.; Dharmaraj, A.P.; Kaisan, M.U. Experimental study of methyl tert-butyl ether as an oxygenated additive in diesel and Calophyllum inophyllum methyl ester blended fuel in CI engine. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 33573–33590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.; Rana, K.B.; Tripathi, B.; Nayyar, A. Properties and effects of organic additives on performance and emission characteristics of diesel engine: A comprehensive review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 22475–22498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killol, A.; Reddy, N.; Paruvada, S.; Murugan, S. Experimental studies of a diesel engine run on biodiesel n-butanol blends. Renew. Energy 2019, 135, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarabet, L.; Loubar, K.; Lounici, M.S.; Hanchi, S.; Tazerout, M. Eucalyptus biodiesel as an alternative to diesel fuel: Preparation and tests on DI diesel engine. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 235485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Seey, A.I.; He, Z.; Hassan, H.; Balasubramanian, D. Improvement of combustion and emission characteristics of a diesel engine working with diesel/jojoba oil blends and butanol additive. Fuel 2020, 279, 118433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeşilyurt, M.K. A detailed investigation on the performance, combustion, and exhaust emission characteristics of a diesel engine running on the blend of diesel fuel, biodiesel, and 1-heptanol (C7 alcohol) as a next-generation higher alcohol. Fuel 2020, 275, 117893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nour, M.; Attia, A.M.A.; Nada, S.A. Improvement of CI engine combustion and performance running on ternary blends of higher alcohol (Pentanol and Octanol)/hydrous ethanol/diesel. Fuel 2019, 251, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papu, N.H.; Lingfa, P.; Dash, S.K. An experimental investigation on the combustion characteristics of a direct injection diesel engine fueled with an algal biodiesel. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2021, 23, 1769–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, L.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, X.; Lee, C.F. Study on combustion characteristics and particulate emissions of a common-rail diesel engine fueled with n-butanol and waste cooking oil blends. J. Energy Inst. 2019, 92, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadikolaei, M.A.; Wei, L.; Cheung, C.S.; Yung, K.F. Effects of engine load and biodiesel content on performance and regulated and unregulated emissions of a diesel engine using contour-plot map. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 1117–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajak, U.; Nashine, P.; Verma, T.N. Assessment of diesel engine performance using spirulina microalgae biodiesel. Energy 2019, 166, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, A.M.A.; Kulchitskiy, A.R.; Nour, M.; El-Seesy, A.I.; Nada, S.A. The influence of castor biodiesel blending ratio on engine performance including the determined diesel particulate matters composition. Energy 2022, 239, 121951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özer, S. The effect of adding toluene to increase the combustion efficiency of biodiesel. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2020, 46, 9325–9340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagöz, M.; Ağbulut, Ü.; Sarıdemir, S. Waste to energy: Production of waste tire pyrolysis oil and comprehensive analysis of its usability in diesel engines. Fuel 2020, 275, 117844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, P.; Dwivedi, G.; Behura, A.K.; Patel, D.K.; Verma, T.N.; Pugazhendhi, A. Experimental investigation of diesel engine fueled with different alkyl esters of Karanja oil. Fuel 2020, 275, 117920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behçet, R. Performance and emission study of waste anchovy fish biodiesel in a diesel engine. Fuel Process. Technol. 2011, 92, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaichandar, S.; Annamalai, K. Effects of open combustion chamber geometries on the performance of pongamia biodiesel in a DI diesel engine. Fuel 2012, 98, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, P.; Kasimani, R.; Peer, M.S.; Rajamohan, S. Assessment of n-pentanol/Calophyllum inophyllum/diesel blends on the performance, emission, and combustion characteristics of a constant-speed variable compression ratio direct injection diesel engine. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 13731–13744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, N.; Atmanli, A. Experimental assessment of a diesel engine fueled with diesel-biodiesel-1-pentanol blends. Fuel 2017, 191, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, D.; Anand, R. Effect of biodiesel-diesel-n-pentanol and biodiesel-diesel-n-hexanol blends on diesel engine emission and combustion characteristics. Energy 2017, 133, 761–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazrat, M.A.; Rasul, M.G.; Khan, M.M.K.; Ashwath, N.; Rufford, T.E. Emission characteristics of waste tallow and waste cooking oil-based ternary biodiesel fuels. Energy Procedia 2019, 160, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amid, S.; Aghbashlo, M.; Tabatabaei, M.; Hajiahmad, A.; Najafi, B.; Ghaziaskar, H.S.; Rastegari, H.; Hosseinzadeh-Bandbafhaa, H.; Mohammadi, P. Effects of waste-derived ethylene glycol diacetate as a novel oxygenated additive on performance and emission characteristics of a diesel engine fueled with diesel/biodiesel blends. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 203, 112245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Li, G.; Jiang, X.; Huang, Z.; Lee, C.F. Experimental study on the performance of and emissions from a low-speed light-duty diesel engine fueled with n-butanol-diesel and isobutanol–diesel blends. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2013, 227, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabu, A.; Anand, R.B. Effects of oxygenate additive mixture on the performance and emission characteristics of a biodiesel-fueled compression ignition engine. Aust. J. Mech. Eng. 2019, 17, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doğan, O. The influence of n-butanol/diesel fuel blends utilization on a small diesel engine performance and emissions. Fuel 2011, 90, 2467–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskar, P.; Senthilkumar, A. Effects of oxygen-enriched combustion on pollution and performance characteristics of a diesel engine. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2016, 19, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
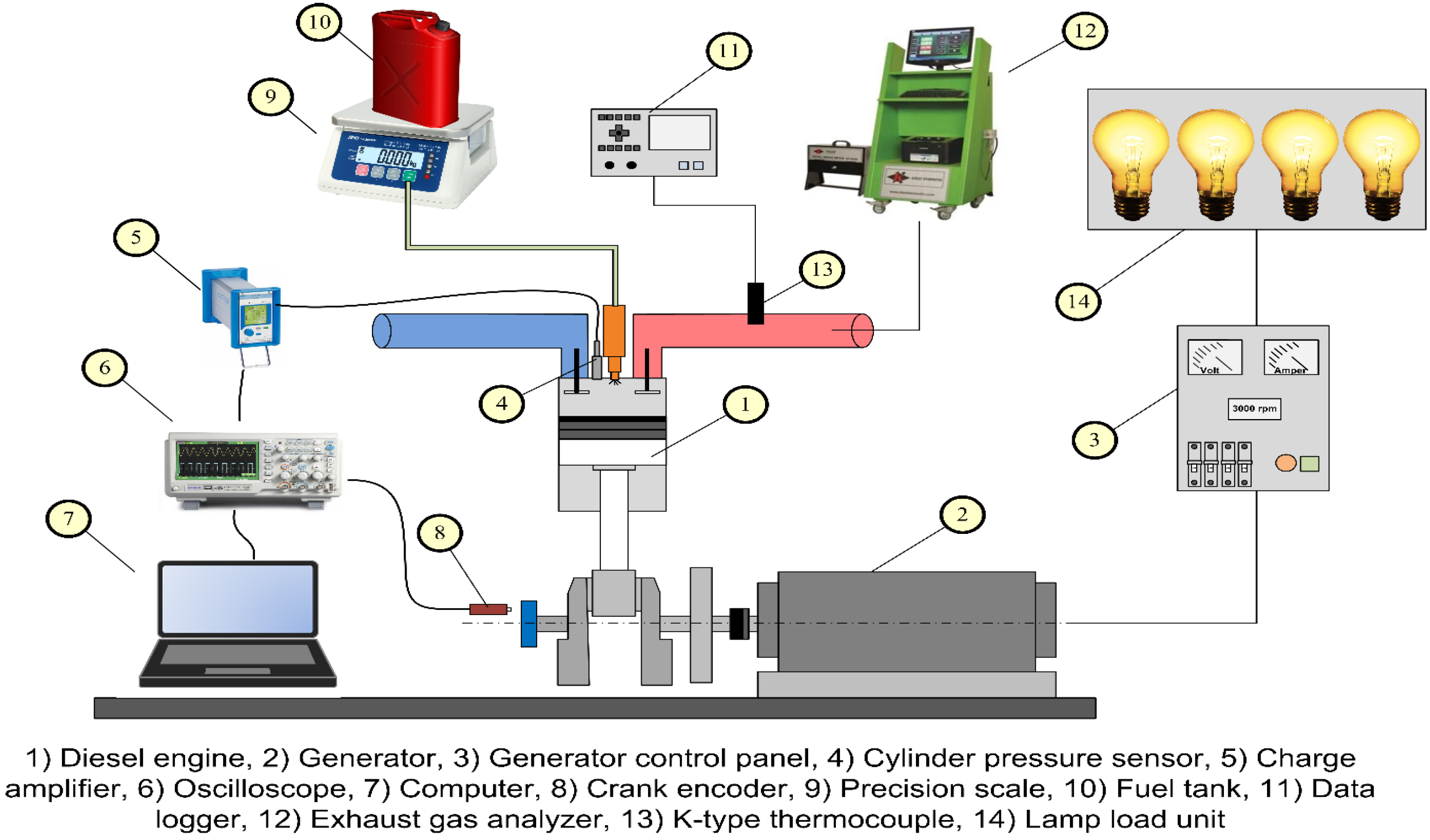
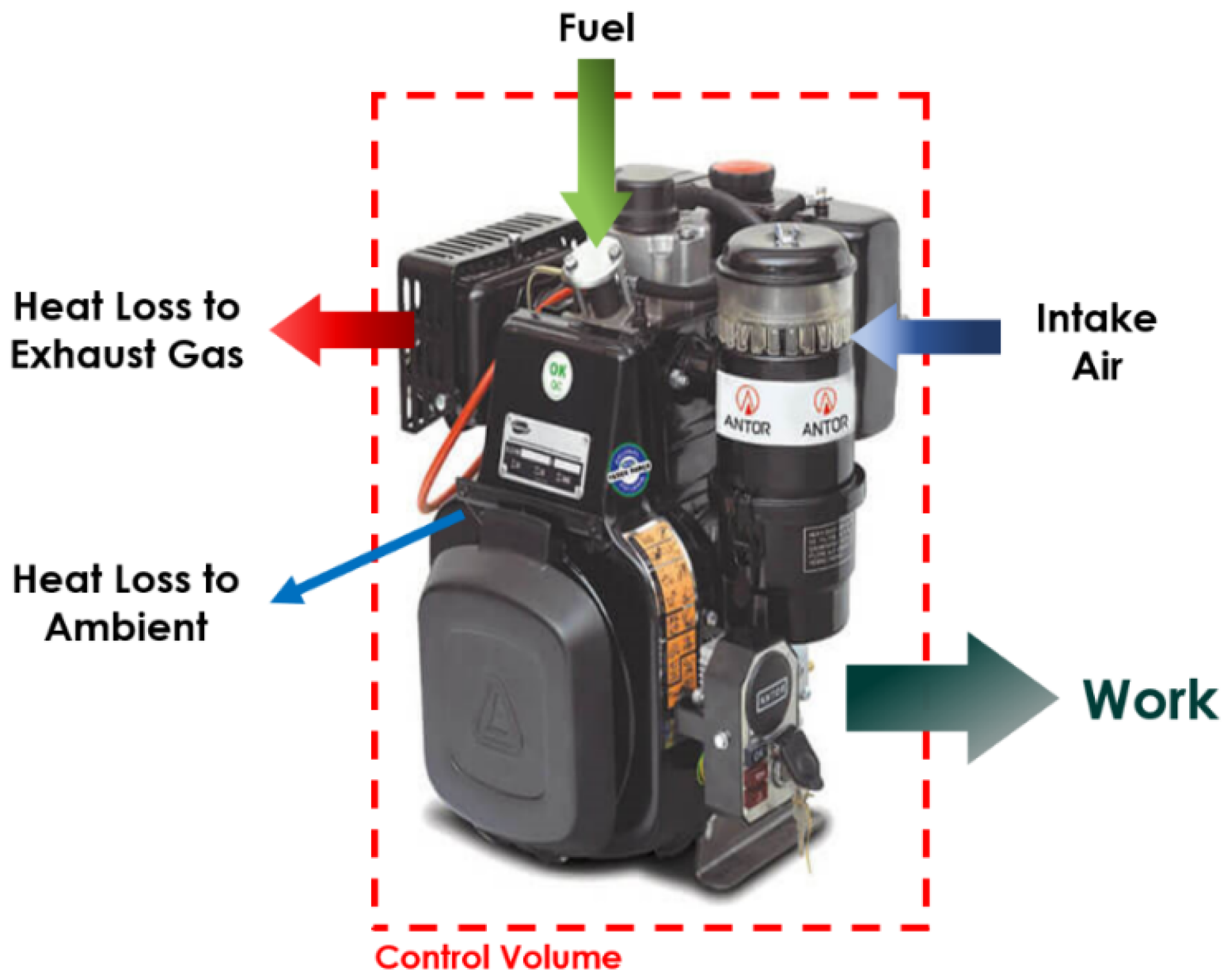
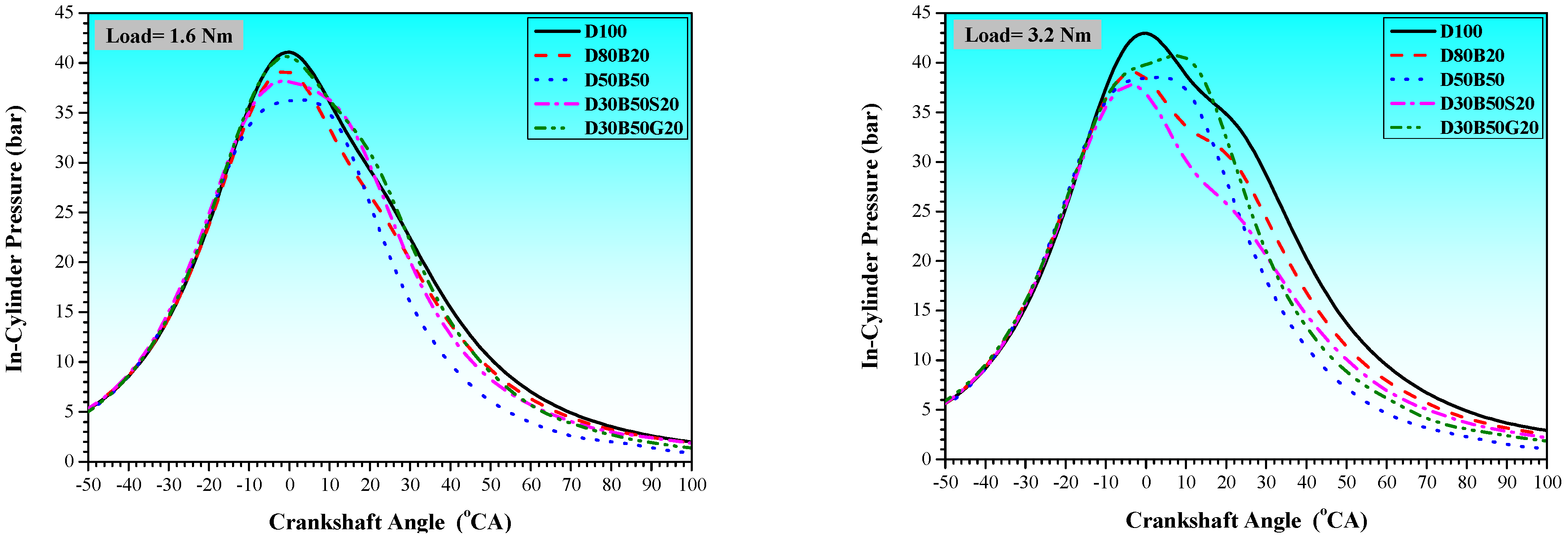
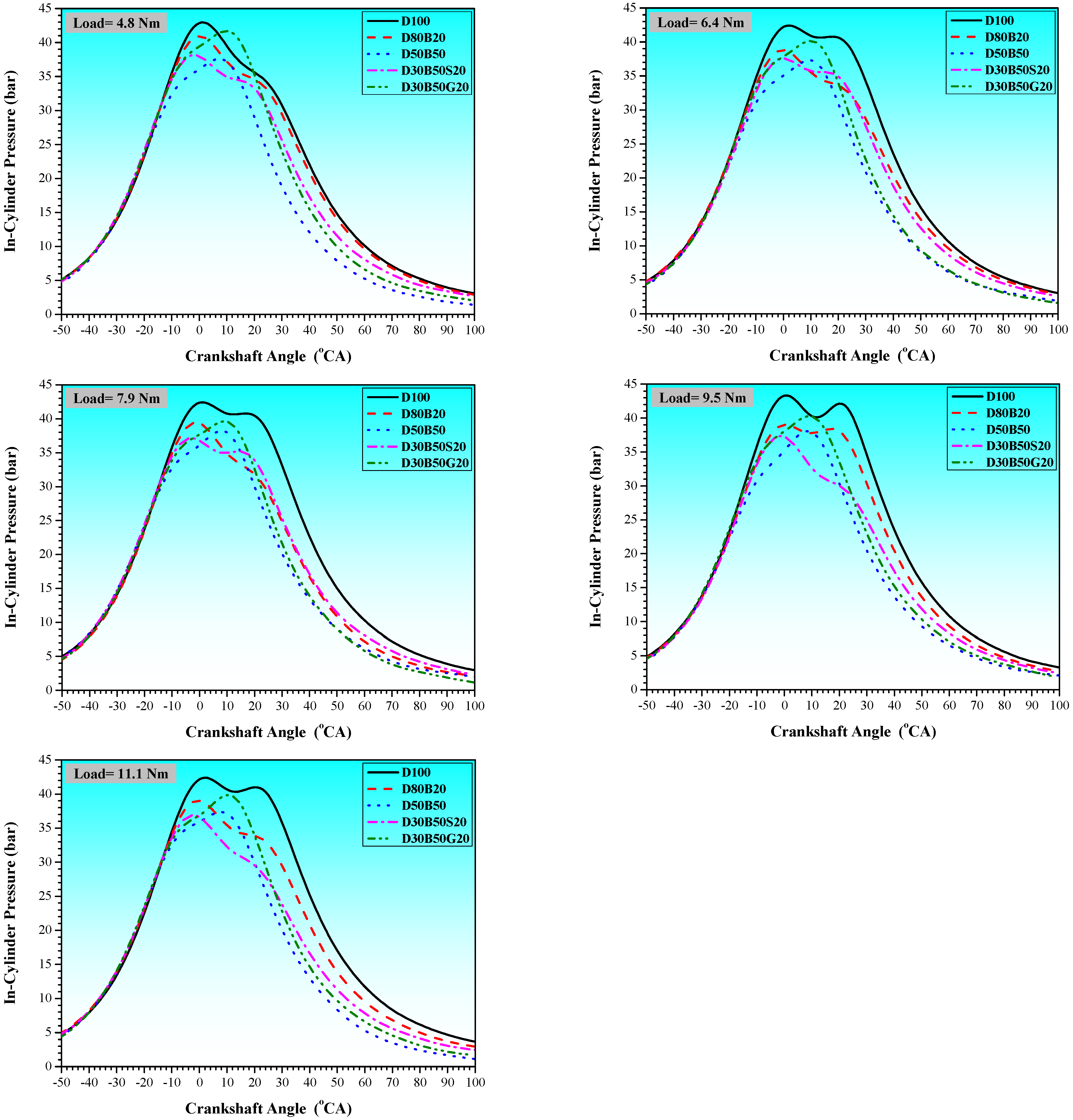
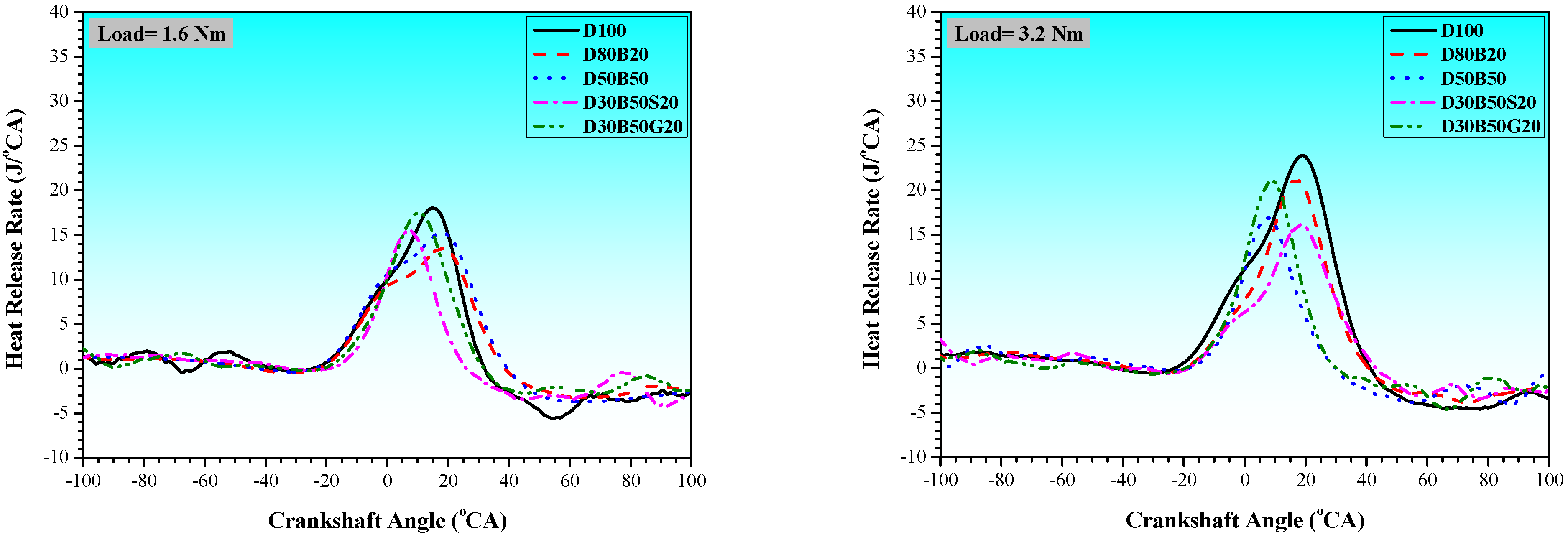
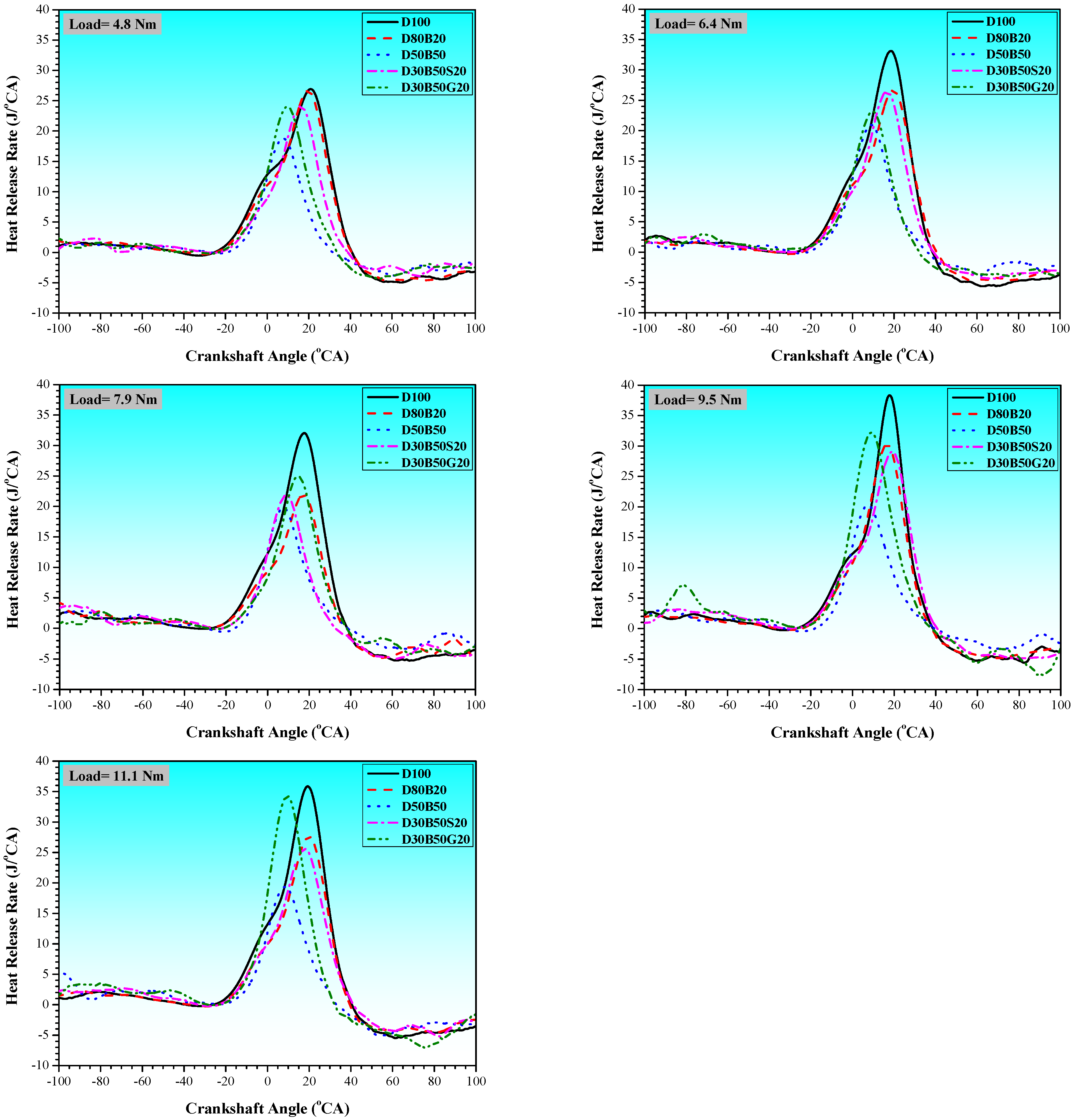
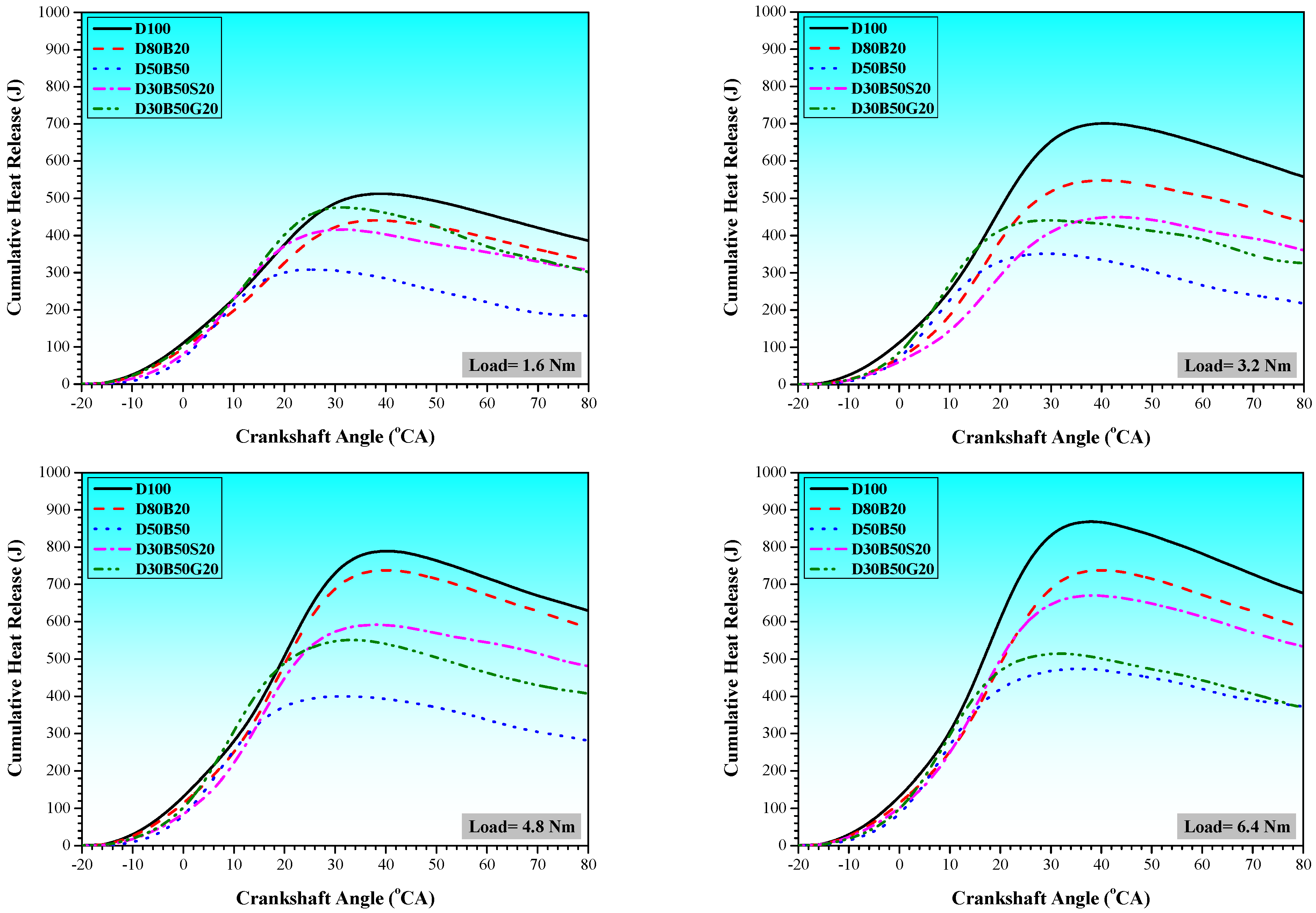
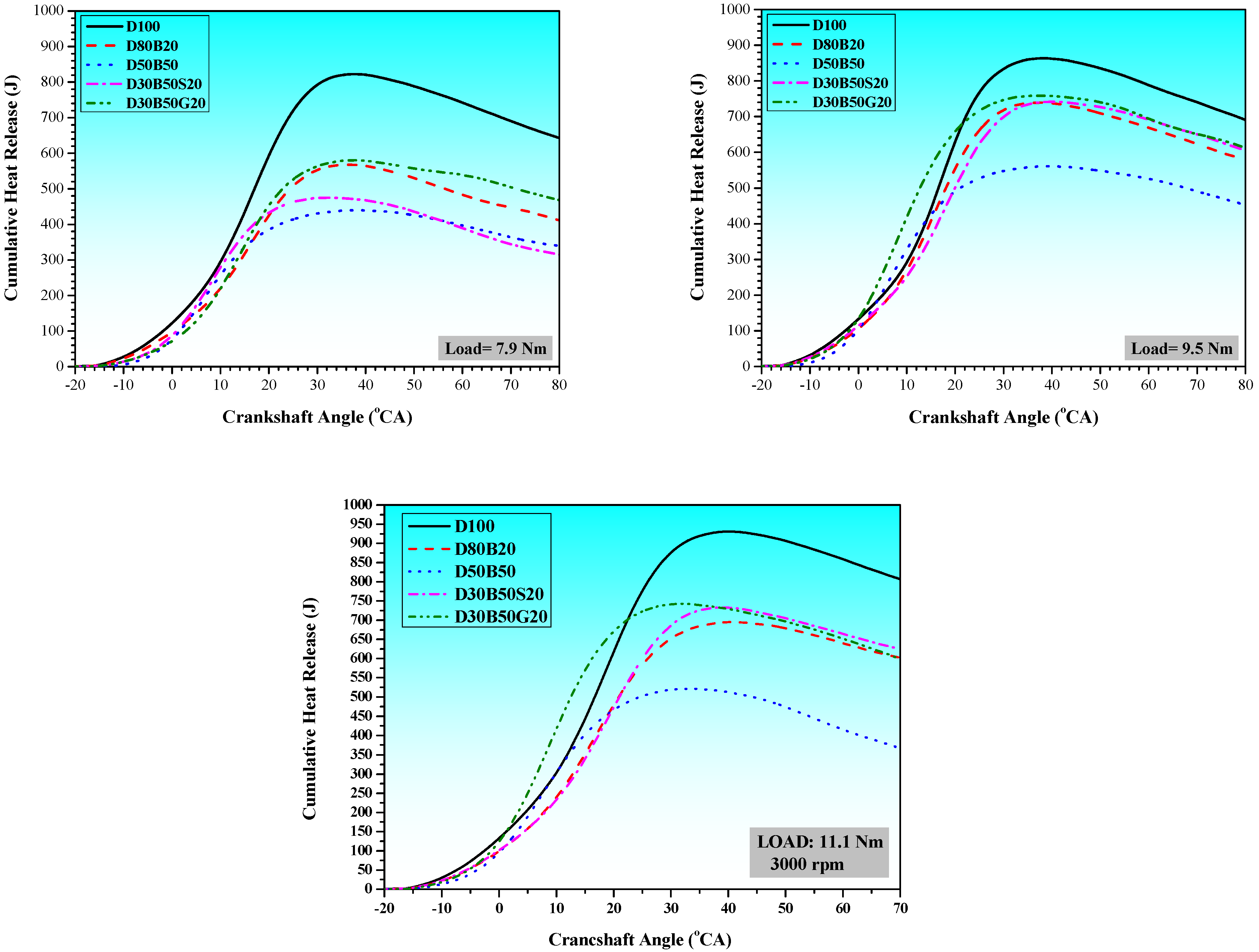
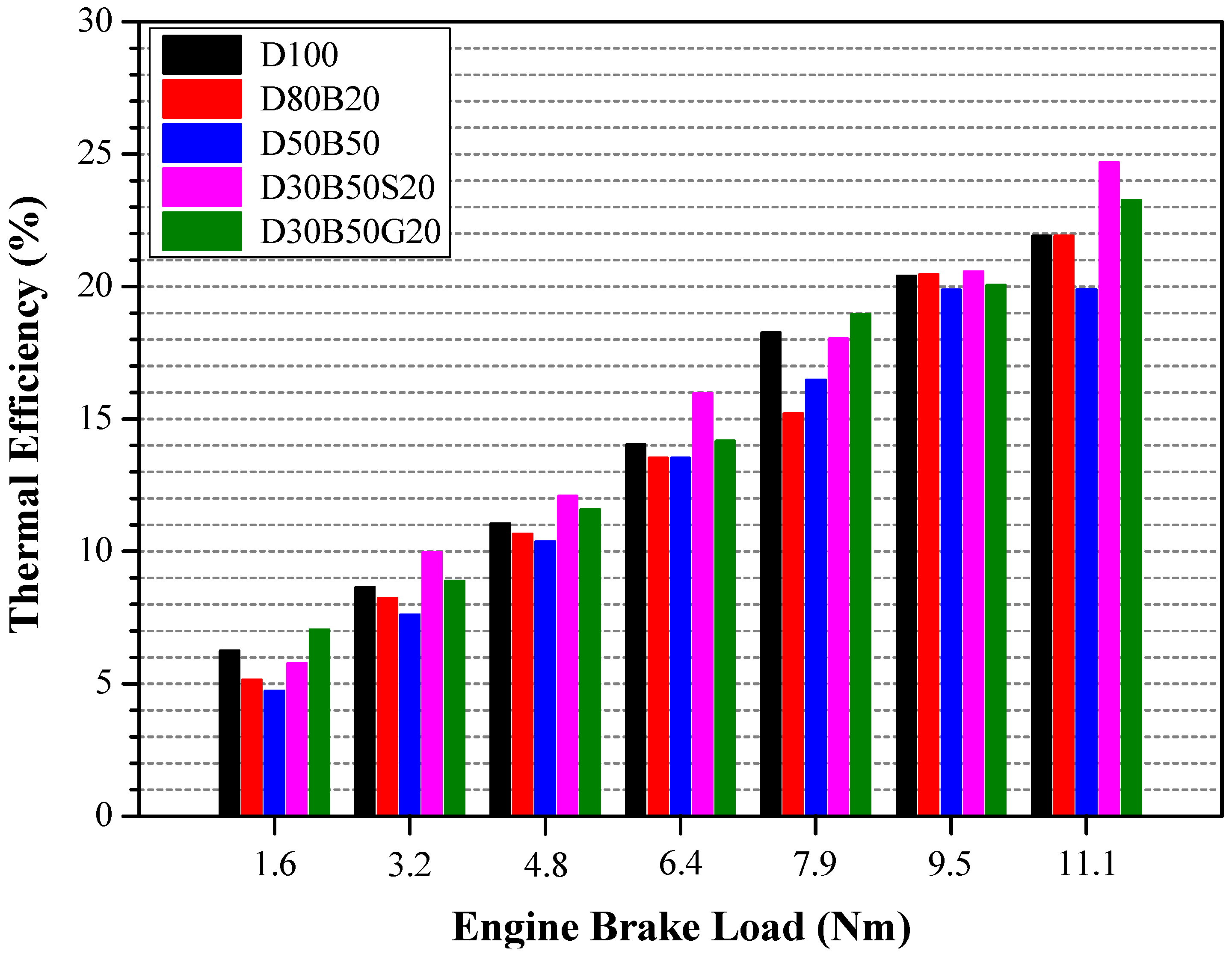
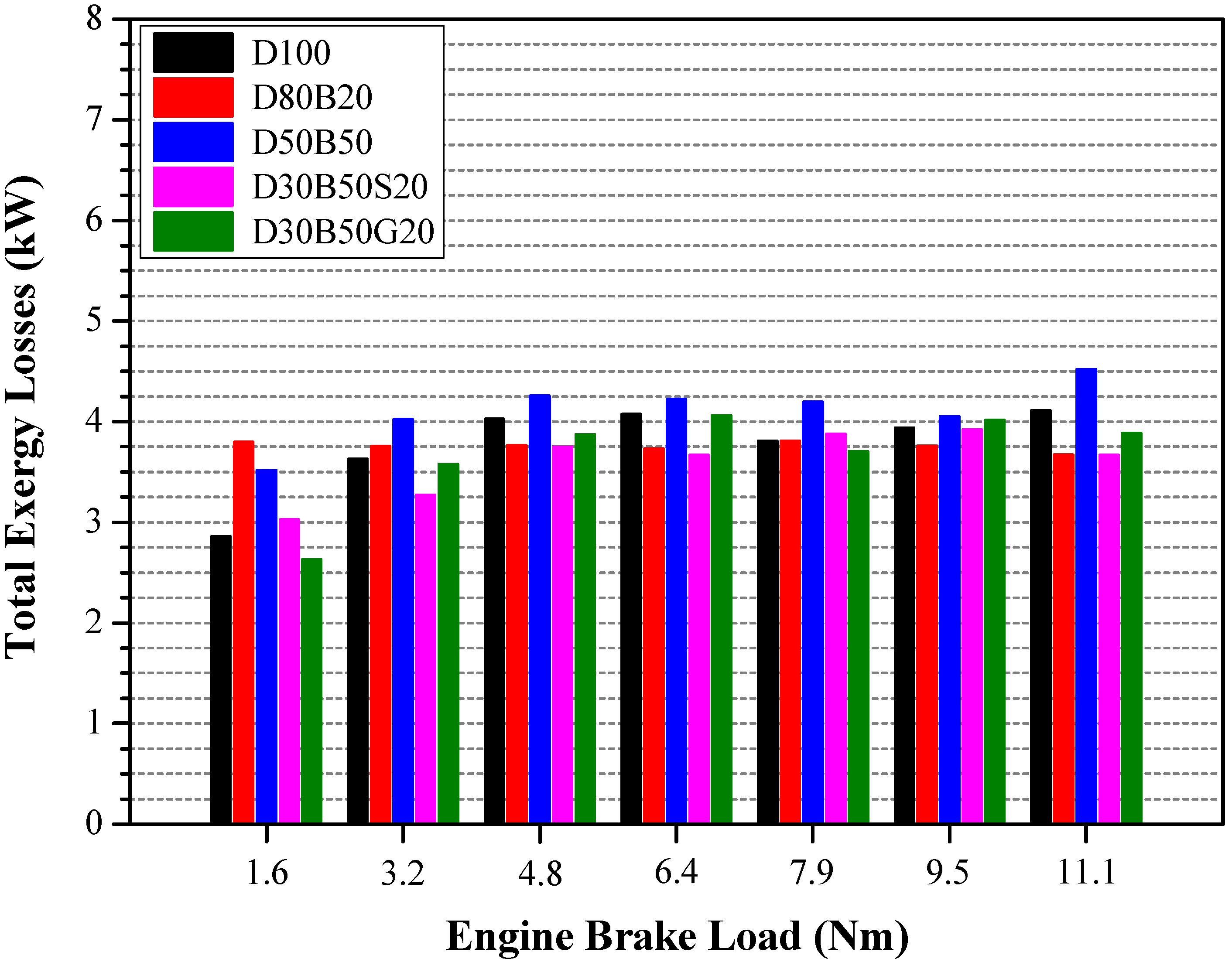
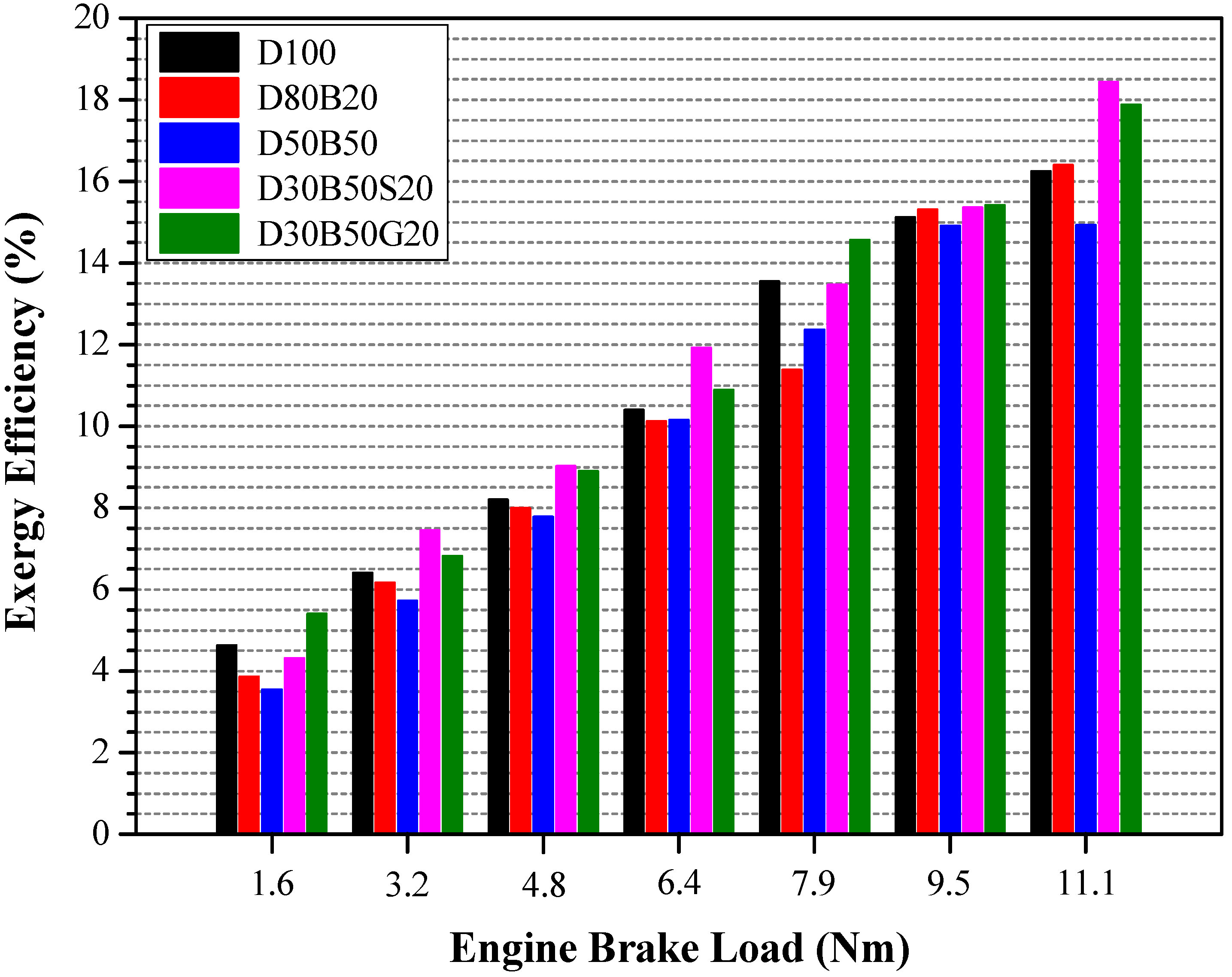
| No | Abbreviation | Diesel | Biodiesel | Solketal | Butyl Diglycol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | D100 | 100% | - | - | - |
| 2 | D80B20 | 80% | 20% | - | - |
| 3 | D50B50 | 50% | 50% | - | - |
| 4 | D30B50S20 | 30% | 50% | 20% | - |
| 5 | D30B50G20 | 30% | 50% | - | 20% |
| Fuels | Density (15 °C, kg/m3) | Viscosity (40 °C, mm2/s) | Thermal Value (MJ/kg) | Flash Point (°C) | Cetane Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test Method | ASTM D4052 | ASTM D445 | ASTM D240 | ASTM D93 | - |
| Diesel | 831.7 | 2.58 | 45.98 | 63 | 56 |
| Biodiesel | 890 | 3.9 | 40.01 | 140 | 58.6 |
| Solketal * | 1071.1 | 5.21 | 25.91 | 84 | - |
| Butyl diglycol ** | 960.6 | 3.654 | 32.0 | 99 | 54 |
| D80B20 | 843.36 | 2.844 | 44.786 | 78.4 | 56.52 |
| D50B50 | 860.85 | 3.24 | 42.995 | 101.5 | 57.3 |
| D30B50S20 | 908.73 | 3.766 | 38.981 | 105.7 | - |
| D30B50G20 | 886.63 | 3.4548 | 40.199 | 108.7 | 56.9 |
| Diesel Engine | |
|---|---|
| Parameters | Specifications |
| Model | 186 FAG |
| Number of cycles | 4 |
| Number of cylinders | 1 |
| Maximum engine power | 7 kW (3600 rpm) |
| Type of fuel | Diesel fuel |
| Type of ignition | Compression ignition |
| Type of fuel injection | Direct injection |
| Intake system | Naturally aspirated |
| Engine speed | 3000 rpm |
| Swept volume | 418 cm3 |
| Stroke | 70 mm |
| Bore | 86 mm |
| Cooling system | Air-cooled |
| Injector nozzle number | 4 |
| Pressure of injection | 19.6 ± 0.49 Mpa |
| Fuel delivery advance angle | 22 ± 1 (°CA) BTDC |
| Compression ratio | 18:1 |
| Measurement | Measuring Range | Resolution | Precision |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO (% vol) | 0–10 | 0.01 | ±1% |
| CO2 (% vol) | 0–20 | 0.01 | ±0.5% |
| HC (ppm) | 0–20,000 | 1 | ±12 |
| NOX (ppm) | 0–5000 | 1 | ±10 |
| O2 (% vol) | 0–21 | 0.01 | ±0.5% |
| Smoke opacity (%) | 0–20 | 0.01 | ±2 |
| Engine Brake Load (Nm) | Energy Flow (kW) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D100 | D80B20 | D50B50 | D30B50S20 | D30B50G20 | |
| 1.6 | 8.010 | 9.704 | 10.577 | 8.649 | 7.117 |
| 3.2 | 11.567 | 12.154 | 13.131 | 10.034 | 11.275 |
| 4.8 | 13.559 | 14.066 | 14.485 | 12.414 | 12.952 |
| 6.4 | 14.257 | 14.791 | 14.783 | 12.530 | 14.114 |
| 7.9 | 13.689 | 16.441 | 15.176 | 13.867 | 13.186 |
| 9.5 | 14.704 | 14.665 | 15.100 | 14.589 | 14.954 |
| 11.1 | 15.974 | 15.972 | 17.601 | 14.175 | 15.046 |
| Engine Brake Load (Nm) | Exergy Flow (kW) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D100 | D80B20 | D50B50 | D30B50S20 | D30B50G20 | |
| 1.6 | 10.803 | 12.964 | 14.090 | 11.583 | 9.263 |
| 3.2 | 15.600 | 16.236 | 17.492 | 13.437 | 14.675 |
| 4.8 | 18.287 | 18.791 | 19.295 | 16.625 | 16.858 |
| 6.4 | 19.228 | 19.759 | 19.693 | 16.780 | 18.370 |
| 7.9 | 18.461 | 21.964 | 20.216 | 18.571 | 17.163 |
| 9.5 | 19.831 | 19.591 | 20.115 | 19.537 | 19.464 |
| 11.1 | 21.544 | 21.338 | 23.446 | 18.983 | 19.583 |
| Engine Brake Load (Nm) | Entropy Generation (kW/K) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D100 | D80B20 | D50B50 | D30B50S20 | D30B50G20 | |
| 1.6 | 0.025 | 0.031 | 0.034 | 0.027 | 0.021 |
| 3.2 | 0.037 | 0.038 | 0.042 | 0.031 | 0.034 |
| 4.8 | 0.043 | 0.044 | 0.045 | 0.038 | 0.039 |
| 6.4 | 0.044 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.037 | 0.041 |
| 7.9 | 0.041 | 0.050 | 0.045 | 0.041 | 0.037 |
| 9.5 | 0.043 | 0.042 | 0.044 | 0.042 | 0.042 |
| 11.1 | 0.047 | 0.046 | 0.052 | 0.040 | 0.041 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Özer, S. The Role of Cheap Chemicals Containing Oxygen Used as Diesel Fuel Additives in Reducing Carbon Footprints. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3146. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073146
Özer S. The Role of Cheap Chemicals Containing Oxygen Used as Diesel Fuel Additives in Reducing Carbon Footprints. Sustainability. 2025; 17(7):3146. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073146
Chicago/Turabian StyleÖzer, Salih. 2025. "The Role of Cheap Chemicals Containing Oxygen Used as Diesel Fuel Additives in Reducing Carbon Footprints" Sustainability 17, no. 7: 3146. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073146
APA StyleÖzer, S. (2025). The Role of Cheap Chemicals Containing Oxygen Used as Diesel Fuel Additives in Reducing Carbon Footprints. Sustainability, 17(7), 3146. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073146






