Effects of Planting Cash Crops on the Diversity of Soil Phosphorus-Functional Microbial Structure in Moso Plantations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Sample Collection
2.2. Determination of Basic Soil Properties
2.3. Soil DNA Extraction and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Differences in Soil Properties Under Different Crop Planting
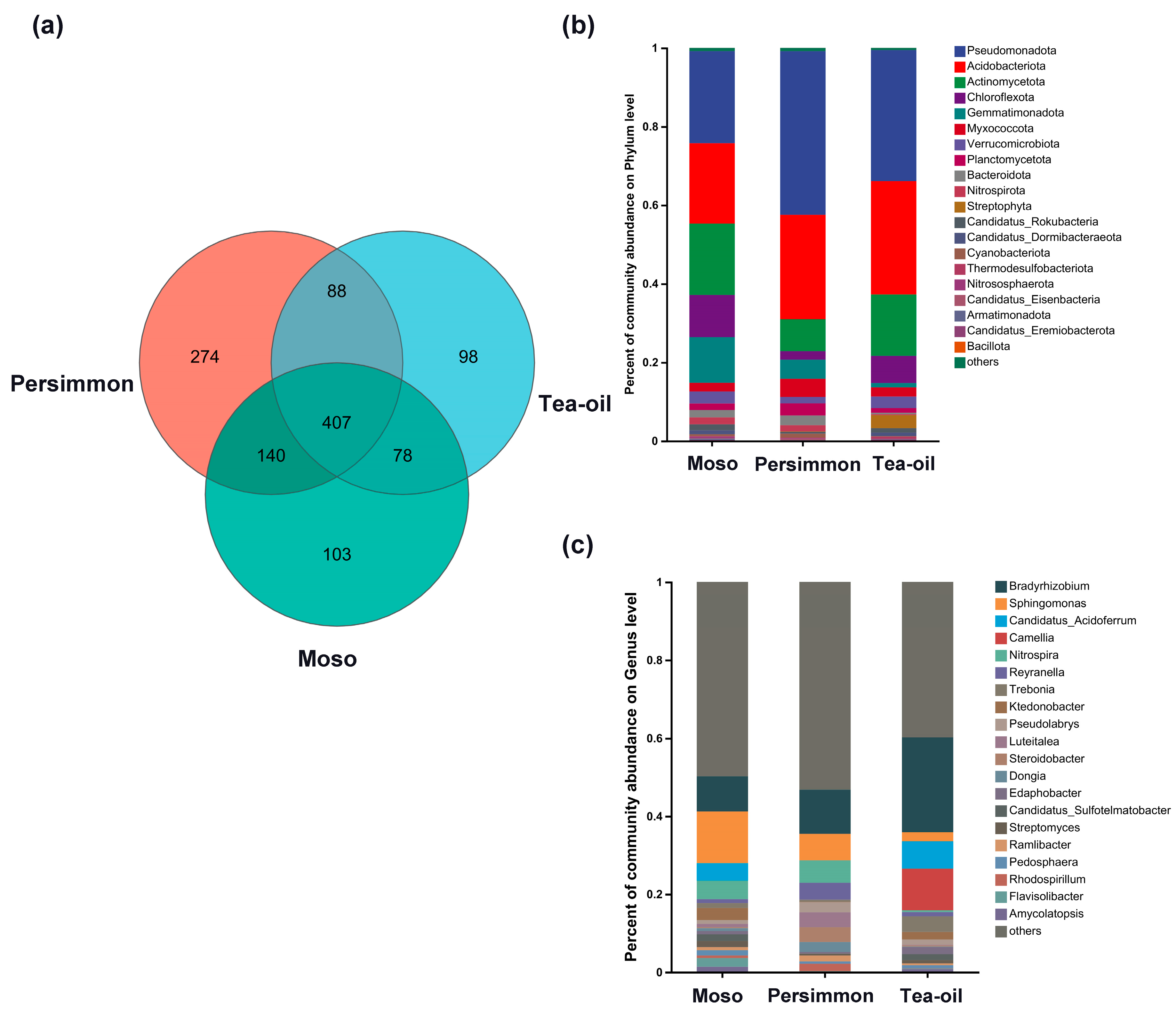
3.2. Soil Phosphorus-Functional Microbial Community Structure Under Different Crop Cultivation
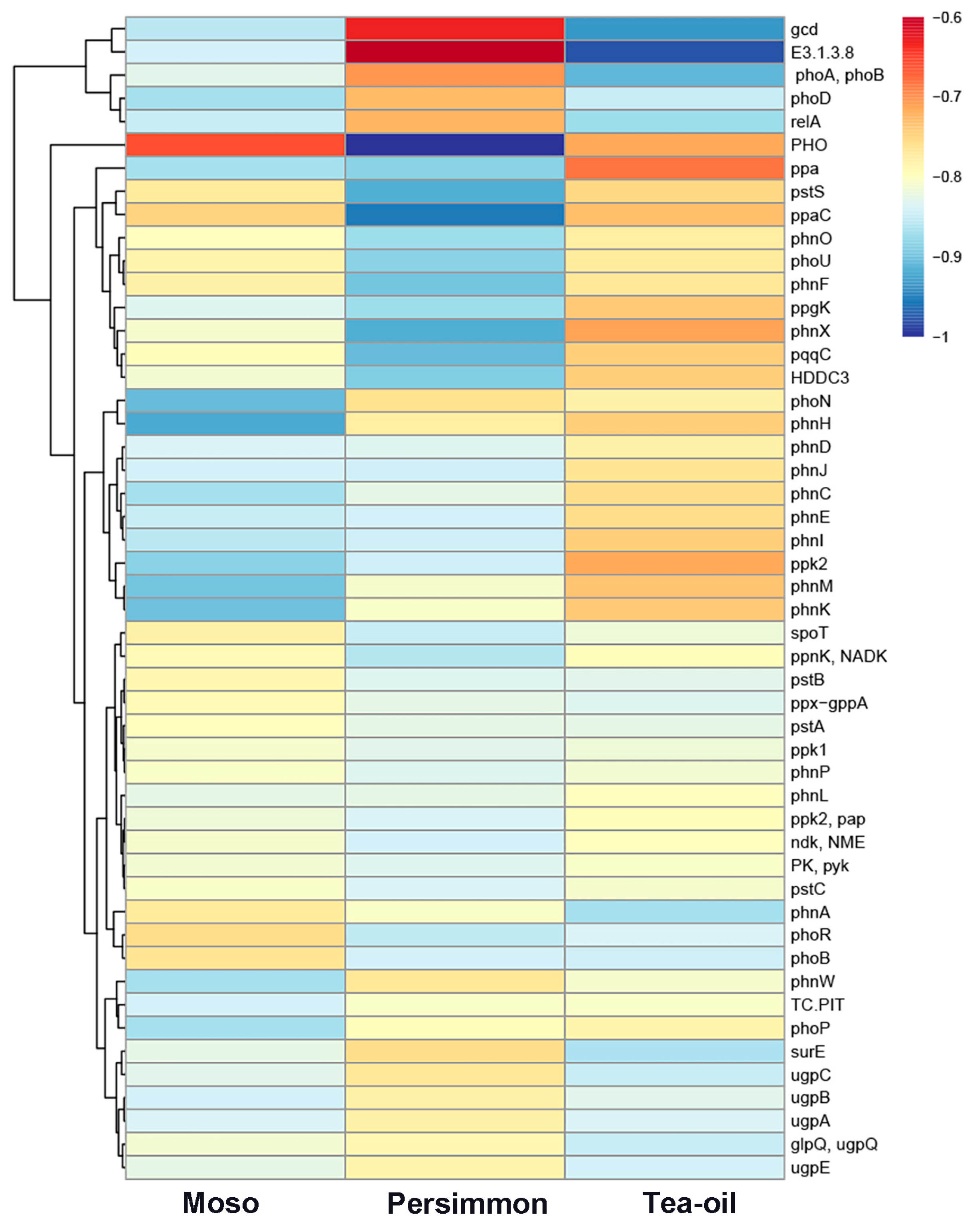
3.3. Changes in the Abundance of Soil Phosphorus-Functional Genes Under Different Crop Cultivation
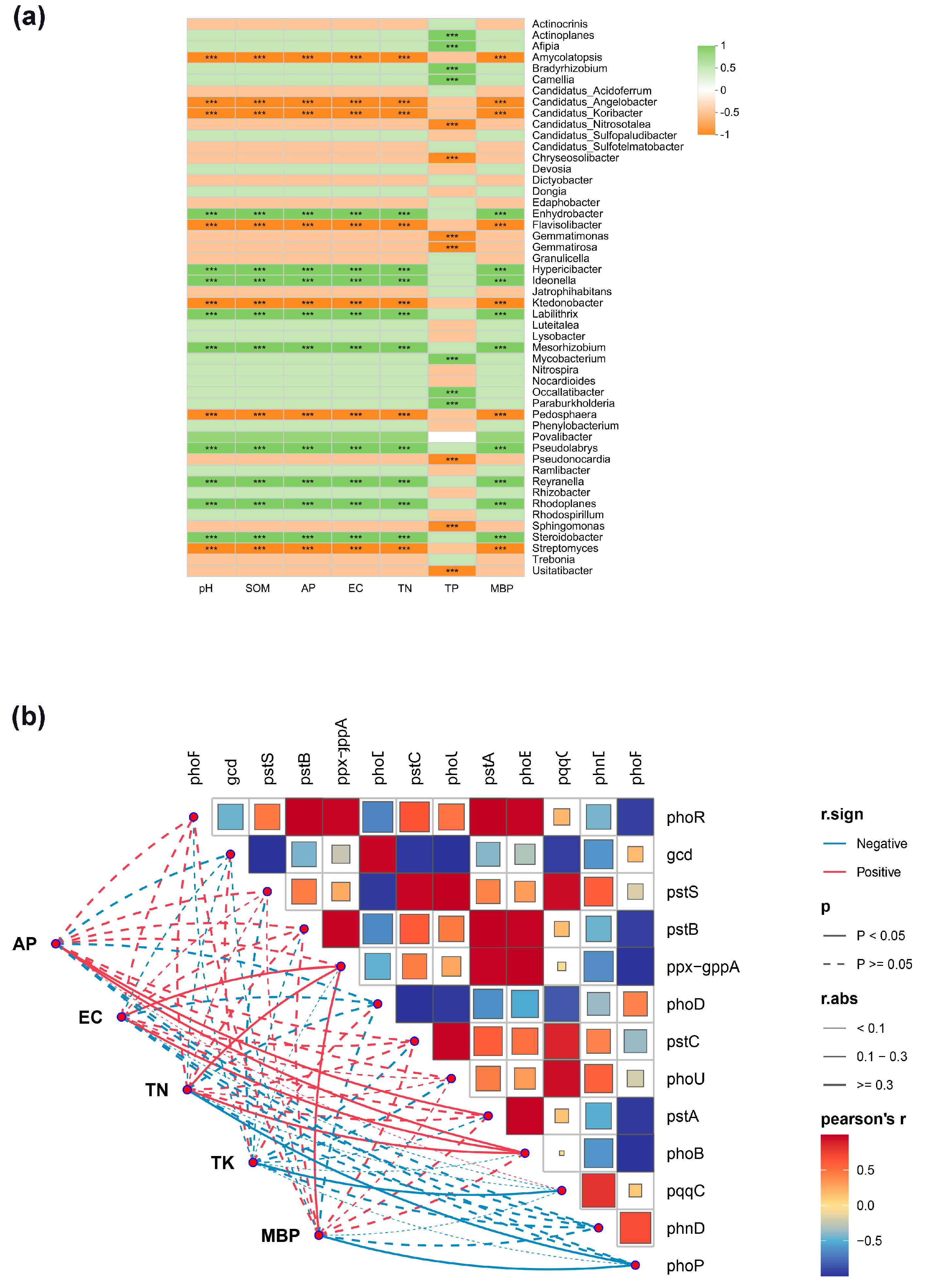
3.4. Correlation Analysis Between Soil Phosphorus-Functional Microorganisms and Basic Soil Properties Under Different Crop Cultivation
4. Discussion
4.1. The Effects of Changing to Cash Crops on Basic Soil Properties in Moso Plantations
4.2. Changes in the Abundance of Phosphate-Functional Flora and Related Genes After the Conversion of Moso Stands to Cash Crops
4.3. Correlation Analysis Between Basic Soil Properties and Phosphorus-Functional Microorganisms After Moso Plantation Was Replanted with Cash Crops
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, C.; Xue, L.; Jiao, R. Soil phosphorus fractions, phosphatase activity, and the abundance of phoC and phoD genes vary with planting density in subtropical Chinese fir plantations. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 209, 104946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Jin, Y.; Liu, C.; Tang, J.; Wang, Q.; Xu, M. Phosphorous fractions in soils of rubber-based agroforestry systems: Influence of season, management and stand age. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 616–617, 1576–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, S.; Chen, J.; Gao, D.; Ai, Y. Distribution patterns and drivers of artificial soil bacterial community on cut-slopes in alpine mountain area of southwest China. CATENA 2020, 194, 104695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, W.; Yang, B.; Liu, Y.; Qi, K.; Yang, T.; Pang, X. Effects of reclamation age on soil microbial communities and enzymatic activities in the sloping citrus orchards of southwestern China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 152, 103566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, F.; Li, Q.; Solanki, M.K.; Wang, Z.; Xing, Y.-X.; Dong, D.-F. Soil phosphorus transformation and plant uptake driven by phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1383813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Zaidi, A.; Wani, P.A. Role of phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms in sustainable agriculture—A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2007, 27, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Xia, D.; Li, L.; Sun, L.; Yang, K.; Zhang, L. Diversity of Culturable Bacteria Isolated from Root Domains of Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). Microb. Ecol. 2009, 58, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhou, G.; Jiang, H.; Yu, S.; Fu, J.; Li, W.; Wang, W.; Ma, Z.; Peng, C. Carbon sequestration by Chinese bamboo forests and their ecological benefits: Assessment of potential, problems, and future challenges. Environ. Rev. 2011, 19, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amede, E.A.; Hailemariam, E.K.; Hailemariam, L.M.; Nuramo, D.A. Identification of factors on the possibility of bamboo as a scaffolding and a formwork material in Ethiopia. Cogent Eng. 2022, 9, 2051692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamerew, A.N.; Zhu, Z.; Kozak, R.; Shrestha, A.K.; Agdew, S.; Wang, G. Exploring the shift to bamboo alternatives: A Case Study on wood and plastic replacement in Ethiopia. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 486, 144507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, W.; Hu, Q.; Yao, X.; Yang, W.; Wen, S.; Wu, H.; Jin, J.; Shen, L. Conversion of coastal wetlands to paddy fields substantially decreases methane oxidation potential and methanotrophic abundance on the eastern coast of China. Water Res. 2025, 272, 122962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Li, F.; Liu, L.; Yang, K. Changes in soil phosphorus fractions under different land uses in desert grasslands in northwestern China. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2022, 73, e13255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Jiang, M.; Freeman, C.; Zou, Y.; Gao, C.; Tian, W.; Wang, G. Agricultural land use regulates the fate of soil phosphorus fractions following the reclamation of wetlands. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 863, 160891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Gu, C.; Rodrigues, J.L.M.; Li, C.; Bohannan, B.; Nüsslein, K.; Margenot, A.J. Soil phosphorus cycling across a 100-year deforestation chronosequence in the Amazon rainforest. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, Y.; Jaskolowski, A.; Clúa, J. Phosphate acquisition and metabolism in plants. Curr. Biol. 2022, 32, R623–R629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Richardson, A.E.; O’Callaghan, M.; DeAngelis, K.M.; Jones, E.E.; Stewart, A.; Firestone, M.K.; Condron, L.M. Effects of selected root exudate components on soil bacterial communities: Root exudate components and soil microbial communities. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 77, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Ruan, Y.; Sun, W.; Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H.; et al. Metagenomes reveal the effect of crop rotation systems on phosphorus cycling functional genes and soil phosphorus avail–ability. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 364, 108886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gunina, A.; Cheng, H.; Liu, L.; Wang, B.; Dou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liang, C.; An, S.; Chang, S.X. Unlocking Mechanisms for Soil Organic Matter Accumulation: Carbon Use Efficiency and Microbial Necromass as the Keys. Glob.Change Biol. 2025, 31, e70033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloso, F.R.; Marques, D.J.; de Melo, E.I.; Bianchini, H.C.; Maciel, G.M.; de Melo, A.C. Different soil textures can interfere with phosphorus availability and acid phosphatase activity in soybean. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 234, 105842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Liu, W.; Zhu, X.; Chen, C.; Khan, M.N.; Yang, B.; Jiang, X.J. The detrimental effect of rainforest conversion to rubber plantations on soil dissolved organic carbon and C: N stoichiometry, mediated by altered soil biogeochemistry. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, R.; Deng, J.; Xu, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhang, S.; Han, X.; Yang, G.; Ren, C. Altered microbial P cycling genes drive P availability in soil after afforestation. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 328, 116998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Cheng, L.; Xiong, C.; Whalley, W.R.; Miller, A.J.; Rengel, Z.; Zhang, F.; Shen, J. Understanding plant–soil interactions underpins enhanced sustainability of crop production. Trends Plant Sci. 2024, 29, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Koziol, L.; Podzikowski, L.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J. Relationships between soil biodiversity and multifunctionality in croplands depend on salinity and organic matter. Geoderma 2023, 429, 116273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Chen, R.; Xu, C.; Zhang, C.; Dong, L.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X. Apple-marigold intercropping improves soil properties by changing soil metabolomics and bacterial community structures. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1195985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malewski, T.; Borowik, P.; Golińska, P.; Okorski, A.; Olejarski, I.; Oszako, T. Organic Inputs Positively Alter the Bacteriome of Post-Agricultural Soils. Forests 2023, 14, 1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, X.; Yao, S.; Yang, X.; Jiang, X. Correlations between soil metabolomics and bacterial community structures in the pepper rhizosphere under plastic greenhouse cultivation. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 728, 138439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Luo, L.; Tang, B.; Guo, H.; Cao, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Chen, S.; Chen, Z. Dynamic changes of rhizosphere soil bacterial community and nutrients in cadmium polluted soils with soybean-corn intercropping. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, P.; Archana; Uniyal, S.; Srivastava, A.K. Pseudomonas for sustainable agricultural ecosystem. In Microbial Syntrophy-Mediated Eco-Enterprising; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalam, S.; Basu, A.; Ahmad, I.; Sayyed, R.Z.; El-Enshasy, H.A.; Dailin, D.J.; Suriani, N.L. Recent Understanding of Soil Acidobacteria and Their Ecological Significance: A Critical Review. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 580024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, A.A.; Haq, S.; Bhat, R.A. Actinomycetes benefaction role in soil and plant health. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 111, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guo, H.; Wang, J.; He, P.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Ma, M.; Ling, N. Microbial phosphorus-cycling genes in soil under global change. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.; Lee, E.-J. PhoU: A multifaceted regulator in microbial signaling and homeostasis. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2024, 77, 102401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.; Liu, G.; Chen, H.; Chen, C.; Wang, J.; Ai, S.; Wei, D.; Li, D.; Ma, B.; Tang, C.; et al. Long-term nutrient inputs shift soil microbial functional profiles of phosphorus cycling in diverse agroecosystems. ISME J. 2020, 14, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Rensing, C.; Han, D.; Xiao, K.-Q.; Dai, Y.; Tang, Z.; Liesack, W.; Peng, J.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, F. Genome-Resolved Metagenomics Reveals Distinct Phosphorus Acquisition Strategies between Soil Microbiomes. mSystems 2022, 7, e0110721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Le, Y.; Sardans, J.; Yan, R.; Zhong, Y.; Sun, D.; Tong, C.; Peñuelas, J. Moderate salinity improves the availability of soil P by regulating P-cycling microbial communities in coastal wetlands. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Xiong, X.; Zhu, H.; Xu, H.; Leng, P.; Li, J.; Tang, C.; Xu, J. Association of biochar properties with changes in soil bacterial, fungal and fauna communities and nutrient cycling processes. Biochar 2021, 3, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, G.; Wei, Y.; Dong, Y.; Hou, L.; Jiao, R. Isolation and screening of multifunctional phosphate solubilizing bacteria and its growth-promoting effect on Chinese fir seedlings. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Duan, Y.; Huo, W.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, D.; Xu, M.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, B.; Kuzyakov, Y.; et al. C:P stoichiometric imbalance between soil and microorganisms drives microbial phosphorus turnover in the rhizosphere. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2022, 58, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwalb, S.A.; Hemkemeyer, M.; Christensen, B.T.; Heinze, S.; Oliva, R.L.; Joergensen, R.G.; Wichern, F. Disentangling the effects of mineral fertiliser N, P and K on microbial biomass, necromass and ionome in soil from the Askov long-term field experiment. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 195, 109449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirriam, A.; Mugwe, J.; Nasar, J.; Kisaka, O.; Ranjan, S.; Gitari, H. Role of Phosphorus and Inoculation with Bradyrhizobium in Enhancing Soybean Production. Adv. Agric. 2023, 2023, 3231623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisil, O.V.; Efimenko, T.A.; Efremenkova, O.V. Looking Back to Amycolatopsis: History of the Antibiotic Discovery and Future Prospects. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargali, S.S.; Padalia, K.; Bargali, K. Effects of tree fostering on soil health and microbial biomass under different land use systems in the Central Himalayas. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 1984–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padalia, K.; Bargali, S.S.; Bargali, K.; Manral, V. Soil microbial biomass phosphorus under different land use systems of Central Himalaya. Trop. Ecol. 2022, 63, 30–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, V.R.; Zago, L.M.S.; Ramalho, W.P.; Caramori, S.S. What Physical Aspects Influence Biochemical Activity in Soil in a Natural Landscape? Front. J. Soc. Technol. Environ. Sci. 2020, 9, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garland, G.; Banerjee, S.; Edlinger, A.; Oliveira, E.M.; Herzog, C.; Wittwer, R.; Philippot, L.; Maestre, F.T.; van der Heijden, M.G.A. A closer look at the functions behind ecosystem multifunctionality: A review. J. Ecol. 2021, 109, 600–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chai, Y.; Xie, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, X.; Hao, S.; Gai, J.; Chen, Y. Responses of soil microbial diversity, network complexity and multifunctionality to three land-use changes. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 859, 160255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | pH | SOM (g·kg−1) | AP (mg·kg−1) | EC (μs·cm−1) | TN (g·kg−1) | TK (g·kg−1) | MBP (mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moso | 6.49 ± 0.02 a | 12.68 ± 0.70 a | 0.13 ± 0.05 b | 16.63 ± 0.40 c | 0.95 ± 0.05 b | 18.41 ± 0.48 b | 0.45 ± 0.11 b |
| Persimmon | 5.13 ± 0.02 c | 18.05 ± 4.87 a | 35.73 ± 0.75 a | 89.64 ± 1.71 a | 3.90 ± 0.12 a | 19.49 ± 0.47 b | 2.43 ± 0.31 a |
| Tea-oil | 5.80 ± 0.06 a | 16.48 ± 0.55 a | 0.16 ± 0.04 b | 24.22 ± 1.54 b | 1.38 ± 0.05 b | 21.15 ± 0.49 a | 0.79 ± 0.08 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, R.; Yang, W.; Zhang, K.; Ding, L.; Ye, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, D. Effects of Planting Cash Crops on the Diversity of Soil Phosphorus-Functional Microbial Structure in Moso Plantations. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2784. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062784
Li R, Yang W, Zhang K, Ding L, Ye Z, Wang X, Liu D. Effects of Planting Cash Crops on the Diversity of Soil Phosphorus-Functional Microbial Structure in Moso Plantations. Sustainability. 2025; 17(6):2784. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062784
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ronghui, Wenyan Yang, Kunyang Zhang, Liqun Ding, Zhengqian Ye, Xudong Wang, and Dan Liu. 2025. "Effects of Planting Cash Crops on the Diversity of Soil Phosphorus-Functional Microbial Structure in Moso Plantations" Sustainability 17, no. 6: 2784. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062784
APA StyleLi, R., Yang, W., Zhang, K., Ding, L., Ye, Z., Wang, X., & Liu, D. (2025). Effects of Planting Cash Crops on the Diversity of Soil Phosphorus-Functional Microbial Structure in Moso Plantations. Sustainability, 17(6), 2784. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062784





