Examining the Influence of AI-Supporting HR Practices Towards Recruitment Efficiency with the Moderating Effect of Anthropomorphism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Perceived Interactivity, Perceived Intelligence, and Personalization
2.2. Accuracy, Automation, and Real-Time Experience
2.3. Anthropomorphism
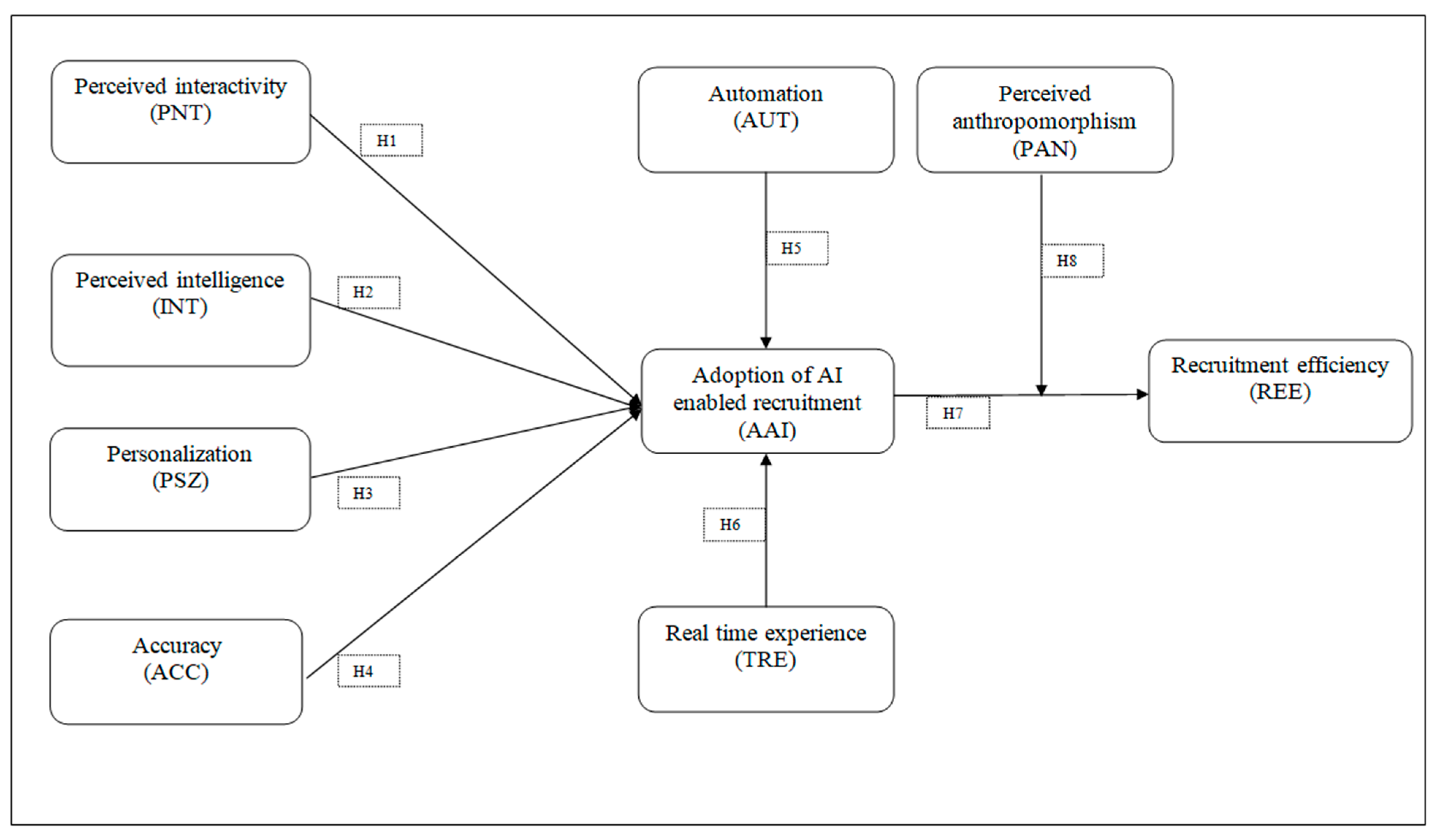
3. Methodology
3.1. Methods and Instrument Development
3.2. Sample Size and Data Collection
4. Data Analysis
4.1. Common Method Bias
4.2. Structural Equation Modeling
4.3. Hypothesis Analysis
4.4. Importance Performance Analysis
4.5. Effect Size Analysis
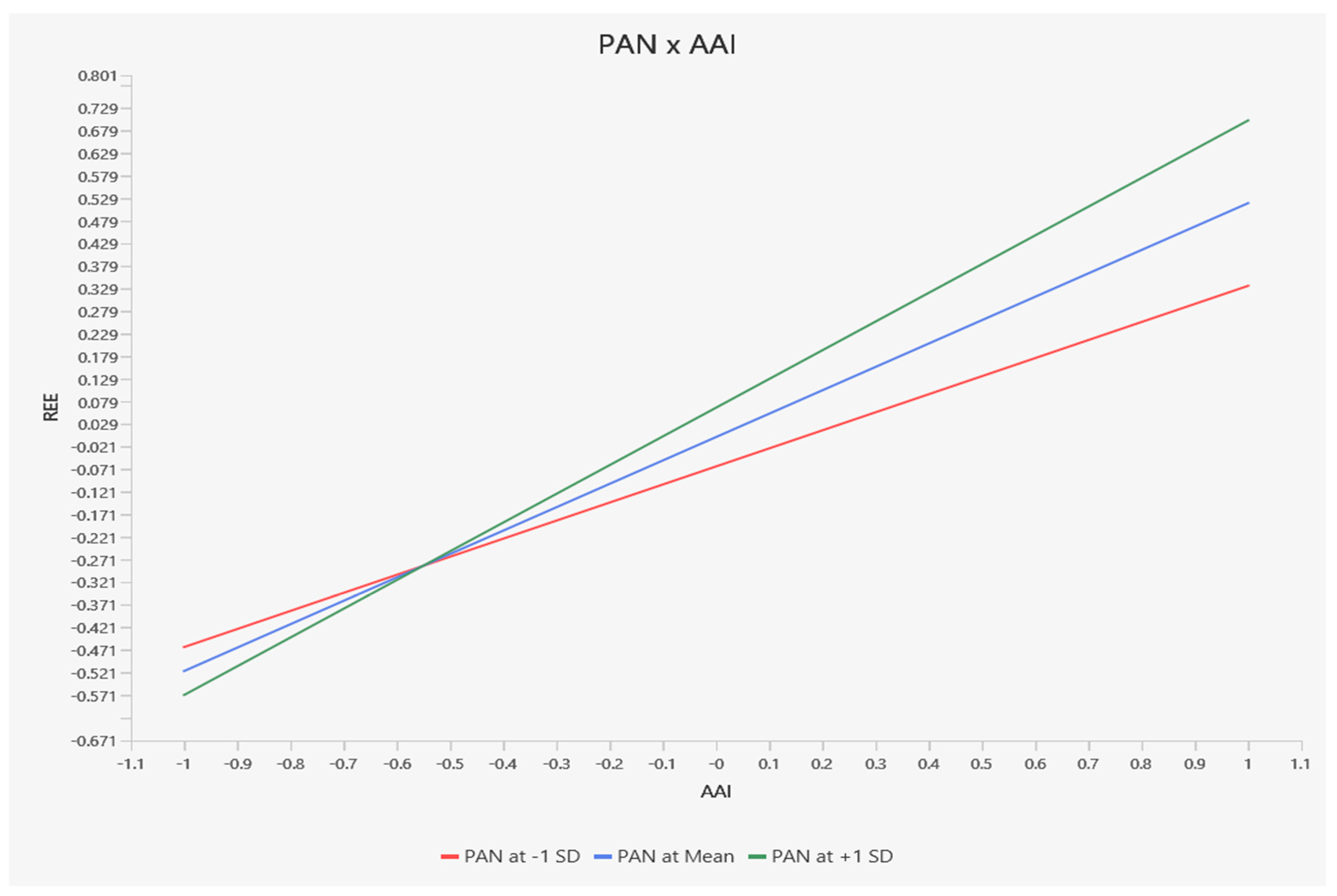
4.6. Moderating Analysis
5. Discussion
5.1. Theoretical Contributions
5.2. Practical Contributions
6. Conclusions
Research Limitations and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Horodyski, P. Recruiter’s perception of artificial intelligence (AI)-based tools in recruitment. Comput. Hum. Behav. Rep. 2023, 10, 100298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.; Sinha, S.; Kar, A.K.; Mani, M. A review of machine learning applications in human resource management. Int. J. Product. Perform. Manag. 2022, 71, 1590–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varsha, P. How can we manage biases in artificial intelligence systems—A systematic literature review. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Data Insights 2023, 3, 100165. [Google Scholar]
- Black, J.S.; van Esch, P. AI-enabled recruiting: What is it and how should a manager use it? Bus. Horiz. 2020, 63, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jatobá, M.N.; Ferreira, J.J.; Fernandes, P.O.; Teixeira, J.P. Intelligent human resources for the adoption of artificial intelligence: A systematic literature review. J. Organ. Change Manag. 2023, 36, 1099–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ischen, C.; Araujo, T.; van Noort, G.; Voorveld, H.; Smit, E. “I am here to assist you today”: The role of entity, interactivity and experiential perceptions in chatbot persuasion. J. Broadcast. Electron. Media 2020, 64, 615–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussawi, S.; Koufaris, M. Perceived Intelligence and Perceived Anthropomorphism of Personal Intelligent Agents: Scale Development and Validation; University of Hawaii: Honolulu, HI, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pillai, R.; Ghanghorkar, Y.; Sivathanu, B.; Algharabat, R.; Rana, N.P. Adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) based employee experience (EEX) chatbots. Inf. Technol. People 2024, 37, 449–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, R.; Sivathanu, B. Adoption of AI-based chatbots for hospitality and tourism. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2020, 32, 3199–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.; Ko, E.; Joung, H.; Kim, S.J. Chatbot e-service and customer satisfaction regarding luxury brands. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 117, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Laat, M.; Joksimovic, S.; Ifenthaler, D. Artificial intelligence, real-time feedback and workplace learning analytics to support in situ complex problem-solving: A commentary. Int. J. Inf. Learn. Technol. 2020, 37, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemalatha, A.; Kumari, P.B.; Nawaz, N.; Gajenderan, V. Impact of artificial intelligence on recruitment and selection of information technology companies. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Smart Systems (ICAIS), Coimbatore, India, 25–27 March 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Yang, F.; Zheng, J.; Feng, C.; Zhang, L. Personalized human resource management via HR analytics and artificial intelligence: Theory and implications. Asia Pac. Manag. Rev. 2023, 28, 598–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, N.; Arunachalam, H.; Pathi, B.K.; Gajenderan, V. The adoption of artificial intelligence in human resources management practices. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Data Insights 2024, 4, 100208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Kureshi, S.; Suggala, S.; Mendonca, V. HRM 4.0 and the shifting landscape of employer branding. In Human & Technological Resource Management (HTRM): New Insights into Revolution 4.0; Emerald Publishing Limited: Bradford, UK, 2020; pp. 37–51. [Google Scholar]
- Moussawi, S.; Koufaris, M.; Benbunan-Fich, R. How perceptions of intelligence and anthropomorphism affect adoption of personal intelligent agents. Electron. Mark. 2021, 31, 343–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Jiang, S.; Niu, X. Can AI really help? The double-edged sword effect of AI assistant on employees’ innovation behavior. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2024, 150, 107987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blut, M.; Wang, C.; Wünderlich, N.V.; Brock, C. Understanding anthropomorphism in service provision: A meta-analysis of physical robots, chatbots, and other AI. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2021, 49, 632–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Suh, A. Anthropomorphism in AI-enabled technology: A literature review. Electron. Mark. 2022, 32, 2245–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahi, S.; Ghani, M.A.; Al-Okaily, M.; Rashid, A.; Alghizzawi, M.; Shiyyab, F.S. Breaking into the Black Box of Customer Perception Towards Robot Service: Empirical Evidence from Service Sector. Heliyon 2024, 10, e38117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahi, S. Research Design and Methods. CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform. 2018. Available online: https://books.google.com.pk/books?id=FlGktgEACAAJ (accessed on 1 June 2024).
- Stone, D.L.; Lukaszewski, K.M.; Johnson, R.D. Will artificial intelligence radically change human resource management processes? Organ. Dyn. 2024, 53, 101034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijayati, D.T.; Rahman, Z.; Rahman, M.F.W.; Arifah, I.D.C.; Kautsar, A. A study of artificial intelligence on employee performance and work engagement: The moderating role of change leadership. Int. J. Manpow. 2022, 43, 486–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahi, S. Assessing individual behavior towards adoption of telemedicine application during COVID-19 pandemic: Evidence from emerging market. Libr. Hi Tech 2022, 40, 394–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahi, S. Fostering employee work engagement and sustainable employment during COVID-19 crisis through HR practices, employee psychological well-being and psychological empowerment. Ind. Commer. Train. 2023, 55, 324–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahi, S. Structural Equation Modeling Using SmartPLS. CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform. 2017. Available online: https://books.google.com.my/books?id=XwF6tgEACAAJ (accessed on 1 June 2024).
- Fornell, C. A national customer satisfaction barometer: The Swedish experience. J. Mark. 1992, 56, 6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyoubi, B.A.; Yamin, M.A.Y. Investigating the role of diffusion of innovation theory, environmental pressure, and organisational capabilities towards adoption of digital technologies. Int. J. Bus. Inf. Syst. 2024, 46, 32–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamin, M.A.; Almuteri, S.D.; Bogari, K.J.; Ashi, A.K. The Influence of Strategic Human Resource Management and Artificial Intelligence in Determining Supply Chain Agility and Supply Chain Resilience. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Item | Loading | α | AVE | CR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAI1: I predict that I will use artificial intelligence in recruitment. | 0.871 | 0.873 | 0.798 | 0.922 |
| AAI2: I anticipate that I will manage recruitment using artificial intelligence. | 0.904 | |||
| AAI3: I highly intend to adopt artificial-intelligence-driven recruitment. | 0.904 | |||
| ACC1: An artificial-intelligence-driven recruitment process is error-free. | 0.831 | 0.928 | 0.824 | 0.949 |
| ACC2: Use of artificial intelligence in the recruitment process improves its quality. | 0.959 | |||
| ACC3: An artificial-intelligence-driven recruitment process reduces biases in the hiring process. | 0.941 | |||
| ACC4: Artificial-intelligence-driven recruitment enhances the HR team’s preciseness and accuracy. | 0.895 | |||
| AUT1: Artificial-intelligence-driven recruitment is time-saving. | 0.792 | 0.809 | 0.636 | 0.875 |
| AUT2: Use of artificial intelligence in the recruitment process reduces the workload. | 0.786 | |||
| AUT3: Use of artificial intelligence in the recruitment process is cost-effective. | 0.828 | |||
| AUT4: Artificial-intelligence-driven recruitment assists HR professionals in making the right decisions. | 0.783 | |||
| INT1: Artificial-intelligence-enabled recruitment can find the right candidate. | 0.989 | 0.976 | 0.955 | 0.984 |
| INT2: An artificial-intelligence-enabled recruitment process is sufficiently intelligent to screen potential candidates. | 0.967 | |||
| INT3: I feel that an artificial-intelligence-driven recruitment process is competent in meeting HRs goals. | 0.975 | |||
| PAN1: An artificial-intelligence-driven recruitment application is animated. | 0.807 | 0.781 | 0.696 | 0.873 |
| PAN2: An artificial-intelligence-driven recruitment application has its own mind. | 0.821 | |||
| PAN3: An artificial-intelligence-driven recruitment application can make sense of emotions. | 0.874 | |||
| PNT1: An artificial-intelligence-driven recruitment application provides real-time feedback. | 0.923 | 0.909 | 0.786 | 0.936 |
| PNT2: An artificial-intelligence-driven recruitment application is problem-solving. | 0.864 | |||
| PNT3: An artificial-intelligence-driven recruitment application provides comparative solutions to my issues. | 0.876 | |||
| PNT4: An artificial-intelligence-driven recruitment application can engage the right candidate for a competitive position. | 0.883 | |||
| PSZ1: I can use an artificial-intelligence-enabled recruitment application as per my job requirements. | 0.876 | 0.900 | 0.834 | 0.938 |
| PSZ2: Using an artificial-intelligence-enabled recruitment application makes me feel like I am special. | 0.938 | |||
| PSZ3: An artificial-intelligence-enabled recruitment application provides suitable solutions to my problems. | 0.925 | |||
| REE1: An artificial-intelligence-enabled recruitment application meets organizational expectations. | 0.950 | 0.903 | 0.838 | 0.939 |
| REE2: Use of artificial intelligence in recruitment aids employees in completing tasks on time. | 0.894 | |||
| REE3: The use of artificial intelligence speeds up the recruitment process. | 0.900 | |||
| TRE1: An artificial-intelligence-enabled recruitment application can solve complex problems. | 0.848 | 0.814 | 0.640 | 0.877 |
| TRE2: An artificial-intelligence-enabled recruitment application assists HR professionals in the decision-making process. | 0.757 | |||
| TRE3: Artificial-intelligence-driven recruitment applications can analyze large datasets. | 0.800 | |||
| TRE4: An artificial-intelligence-enabled recruitment application offers real-time solutions. | 0.793 |
| Factors | AAI | ACC | AUT | INT | PAN | PNT | PSZ | REE | TRE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAI | 0.893 | ||||||||
| ACC | 0.537 | 0.908 | |||||||
| AUT | 0.488 | 0.236 | 0.798 | ||||||
| INT | 0.839 | 0.447 | 0.422 | 0.977 | |||||
| PAN | 0.047 | −0.049 | −0.015 | 0.006 | 0.834 | ||||
| PNT | 0.898 | 0.463 | 0.415 | 0.796 | 0.107 | 0.887 | |||
| PSZ | 0.612 | 0.204 | 0.307 | 0.460 | 0.028 | 0.500 | 0.913 | ||
| REE | 0.523 | 0.295 | 0.333 | 0.375 | 0.110 | 0.497 | 0.306 | 0.915 | |
| TRE | 0.082 | 0.064 | 0.033 | −0.011 | 0.007 | 0.061 | −0.005 | 0.100 | 0.800 |
| Factor | AAI | ACC | AUT | INT | PAN | PNT | PSZ | REE | TRE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAI1 | 0.871 | 0.458 | 0.429 | 0.974 | 0.021 | 0.831 | 0.460 | 0.363 | 0.010 |
| AAI2 | 0.904 | 0.545 | 0.438 | 0.630 | 0.057 | 0.775 | 0.551 | 0.566 | 0.123 |
| AAI3 | 0.904 | 0.433 | 0.440 | 0.646 | 0.046 | 0.800 | 0.631 | 0.469 | 0.085 |
| ACC1 | 0.491 | 0.831 | 0.233 | 0.535 | −0.047 | 0.448 | 0.196 | 0.181 | 0.035 |
| ACC2 | 0.523 | 0.959 | 0.232 | 0.374 | −0.066 | 0.427 | 0.192 | 0.315 | 0.065 |
| ACC3 | 0.507 | 0.941 | 0.203 | 0.397 | −0.010 | 0.428 | 0.179 | 0.309 | 0.067 |
| ACC4 | 0.413 | 0.895 | 0.184 | 0.305 | −0.054 | 0.372 | 0.172 | 0.258 | 0.065 |
| AUT1 | 0.387 | 0.216 | 0.792 | 0.353 | 0.001 | 0.340 | 0.221 | 0.354 | −0.009 |
| AUT2 | 0.380 | 0.210 | 0.786 | 0.358 | 0.005 | 0.341 | 0.206 | 0.289 | 0.010 |
| AUT3 | 0.394 | 0.167 | 0.828 | 0.362 | −0.055 | 0.326 | 0.274 | 0.253 | 0.032 |
| AUT4 | 0.394 | 0.161 | 0.783 | 0.275 | 0.002 | 0.318 | 0.278 | 0.169 | 0.071 |
| INT1 | 0.853 | 0.456 | 0.418 | 0.989 | 0.011 | 0.812 | 0.447 | 0.375 | 0.007 |
| INT2 | 0.797 | 0.421 | 0.425 | 0.967 | −0.017 | 0.755 | 0.440 | 0.370 | -0.039 |
| INT3 | 0.808 | 0.432 | 0.395 | 0.975 | 0.024 | 0.764 | 0.463 | 0.353 | −0.002 |
| PAN1 | 0.014 | −0.048 | −0.031 | −0.016 | 0.807 | 0.087 | −0.039 | 0.094 | 0.026 |
| PAN2 | 0.082 | −0.035 | 0.022 | 0.055 | 0.821 | 0.102 | 0.054 | 0.088 | 0.042 |
| PAN3 | 0.023 | −0.039 | −0.026 | −0.020 | 0.874 | 0.080 | 0.056 | 0.095 | −0.047 |
| PNT1 | 0.800 | 0.396 | 0.364 | 0.883 | 0.060 | 0.923 | 0.408 | 0.371 | 0.024 |
| PNT2 | 0.826 | 0.475 | 0.389 | 0.562 | 0.131 | 0.864 | 0.465 | 0.567 | 0.113 |
| PNT3 | 0.827 | 0.378 | 0.394 | 0.595 | 0.098 | 0.876 | 0.546 | 0.492 | 0.068 |
| PNT4 | 0.720 | 0.390 | 0.318 | 0.798 | 0.089 | 0.883 | 0.338 | 0.312 | 0.002 |
| PSZ1 | 0.581 | 0.183 | 0.291 | 0.475 | 0.035 | 0.465 | 0.876 | 0.313 | −0.052 |
| PSZ2 | 0.559 | 0.203 | 0.291 | 0.410 | 0.019 | 0.465 | 0.938 | 0.255 | −0.010 |
| PSZ3 | 0.534 | 0.172 | 0.258 | 0.371 | 0.021 | 0.437 | 0.925 | 0.267 | 0.051 |
| REE1 | 0.455 | 0.214 | 0.317 | 0.340 | 0.098 | 0.441 | 0.290 | 0.950 | 0.073 |
| REE2 | 0.540 | 0.375 | 0.319 | 0.371 | 0.080 | 0.511 | 0.283 | 0.894 | 0.103 |
| REE3 | 0.424 | 0.197 | 0.273 | 0.309 | 0.130 | 0.397 | 0.266 | 0.900 | 0.096 |
| TRE1 | 0.074 | 0.069 | 0.010 | −0.022 | 0.079 | 0.046 | −0.007 | 0.116 | 0.848 |
| TRE2 | 0.048 | 0.094 | 0.059 | −0.029 | 0.065 | 0.029 | 0.031 | 0.137 | 0.757 |
| TRE3 | 0.064 | 0.061 | 0.020 | 0.003 | −0.066 | 0.045 | −0.037 | 0.059 | 0.800 |
| TRE4 | 0.070 | −0.006 | 0.028 | 0.006 | −0.045 | 0.069 | 0.005 | 0.024 | 0.793 |
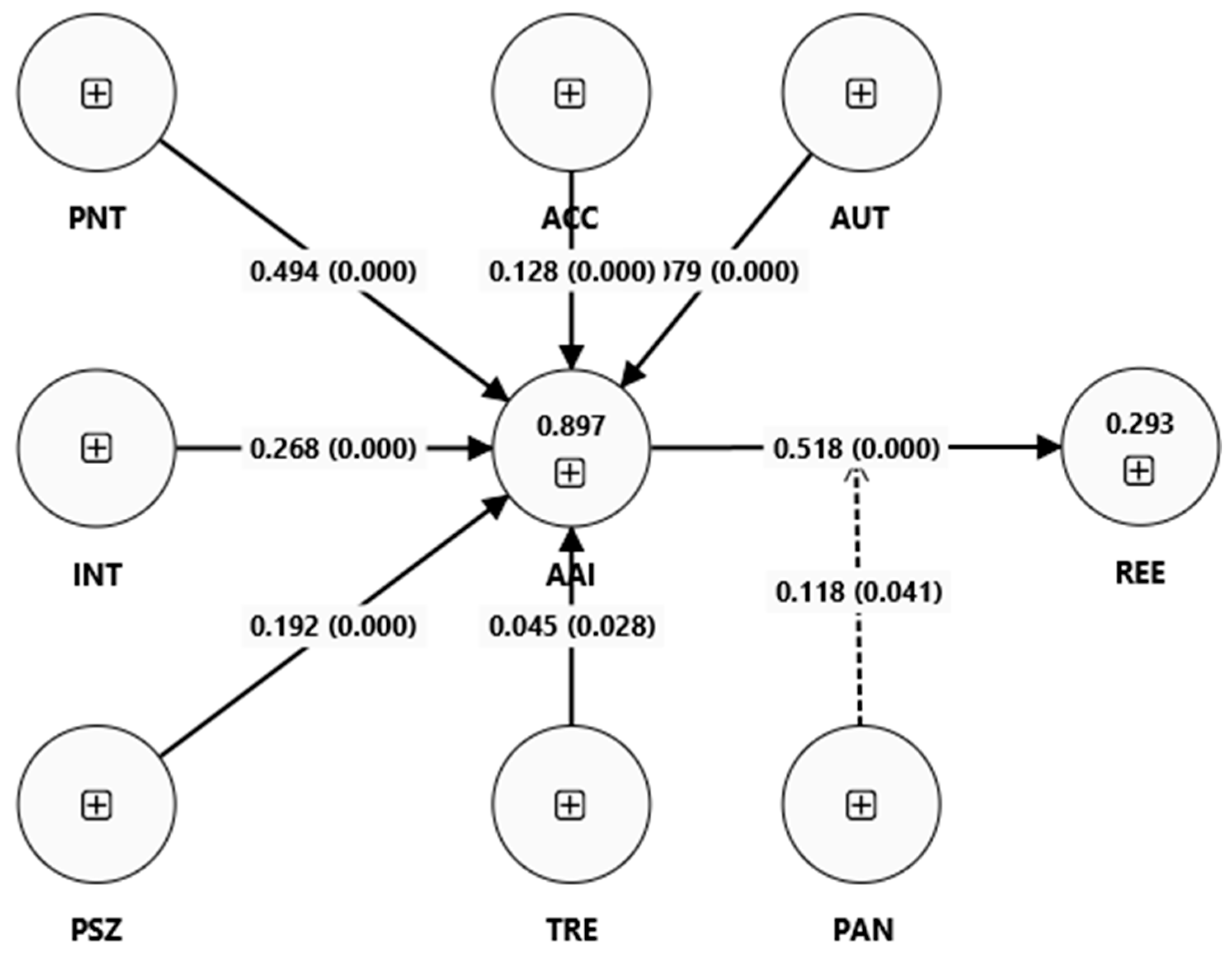
| Hypothesis | Path | β | STDEV | t-Statistic | Significance | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | PNT -> AAI | 0.494 | 0.098 | 5.032 | 0.000 | Supported |
| H2 | INT -> AAI | 0.268 | 0.077 | 3.491 | 0.000 | Supported |
| H3 | PSZ -> AAI | 0.192 | 0.040 | 4.844 | 0.000 | Supported |
| H4 | ACC -> AAI | 0.128 | 0.029 | 4.368 | 0.000 | Supported |
| H5 | AUT -> AAI | 0.079 | 0.022 | 3.607 | 0.000 | Supported |
| H6 | TRE -> AAI | 0.045 | 0.023 | 1.923 | 0.028 | Supported |
| H7 | AAI -> REE | 0.518 | 0.058 | 8.863 | 0.000 | Supported |
| Recruitment Efficiency | ||
|---|---|---|
| Outlined Factors | Total Effect | Performance Index |
| Adoption of AI-enabled recruitment | 0.518 | 61.879 |
| Accuracy | 0.066 | 61.655 |
| Automation | 0.041 | 71.303 |
| Perceived intelligence | 0.139 | 62.912 |
| Perceived anthropomorphism | 0.065 | 60.416 |
| Perceived interactivity | 0.256 | 60.716 |
| Personalization | 0.100 | 60.826 |
| Real-time experience | 0.023 | 77.713 |
| Factors | Size | |
|---|---|---|
| Adoption of AI-enabled recruitment | ||
| Accuracy | 0.120 | Small |
| Automation | 0.048 | Small |
| Perceived intelligence | 0.237 | Medium |
| Perceived interactivity | 0.761 | Large |
| Personalization | 0.259 | Medium |
| Real-time experience | 0.019 | Small |
| Recruitment efficiency | ||
| Adoption of AI-enabled recruitment | 0.379 | Large |
| Perceived anthropomorphism | 0.006 | Small |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dalain, A.F.; Yamin, M.A. Examining the Influence of AI-Supporting HR Practices Towards Recruitment Efficiency with the Moderating Effect of Anthropomorphism. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062658
Dalain AF, Yamin MA. Examining the Influence of AI-Supporting HR Practices Towards Recruitment Efficiency with the Moderating Effect of Anthropomorphism. Sustainability. 2025; 17(6):2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062658
Chicago/Turabian StyleDalain, Ali Falah, and Mohammad Ali Yamin. 2025. "Examining the Influence of AI-Supporting HR Practices Towards Recruitment Efficiency with the Moderating Effect of Anthropomorphism" Sustainability 17, no. 6: 2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062658
APA StyleDalain, A. F., & Yamin, M. A. (2025). Examining the Influence of AI-Supporting HR Practices Towards Recruitment Efficiency with the Moderating Effect of Anthropomorphism. Sustainability, 17(6), 2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062658







