Enhanced Stabilization of Lead in Soil Using Novel Biochar Composites Under Simulated Accelerated Aging Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Reagents and Soil Samples
2.2. Preparation of Biochar Materials
2.2.1. Preparation of the AFFA
2.2.2. Preparation of Biochar Composites
2.2.3. Simulation of Natural Aging Processes
2.2.4. Aging Method Establishment
2.3. Characterization and Analysis Methods
2.4. Two-Dimensional FTIR Correlation Spectroscopy (2D-FTIR-COS)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of the Biochar Composites
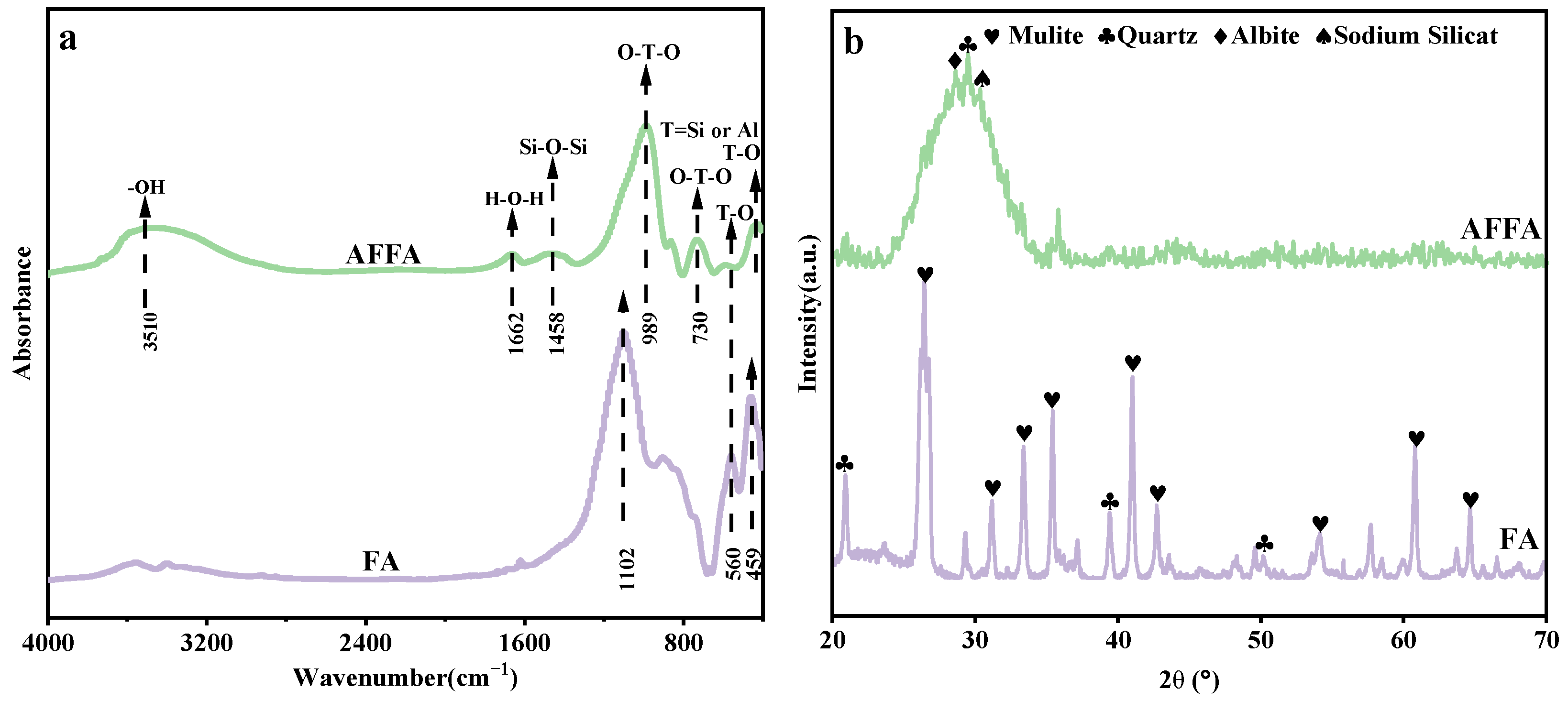
3.1.1. Characteristics of AFFA
3.1.2. Characteristics of AFFA/BC
3.1.3. Reaction Order of Functional Groups in BM with Different AFFA Additions
3.2. Long-Term Stability of Biochar Conditions on Heavy Metals in Soil
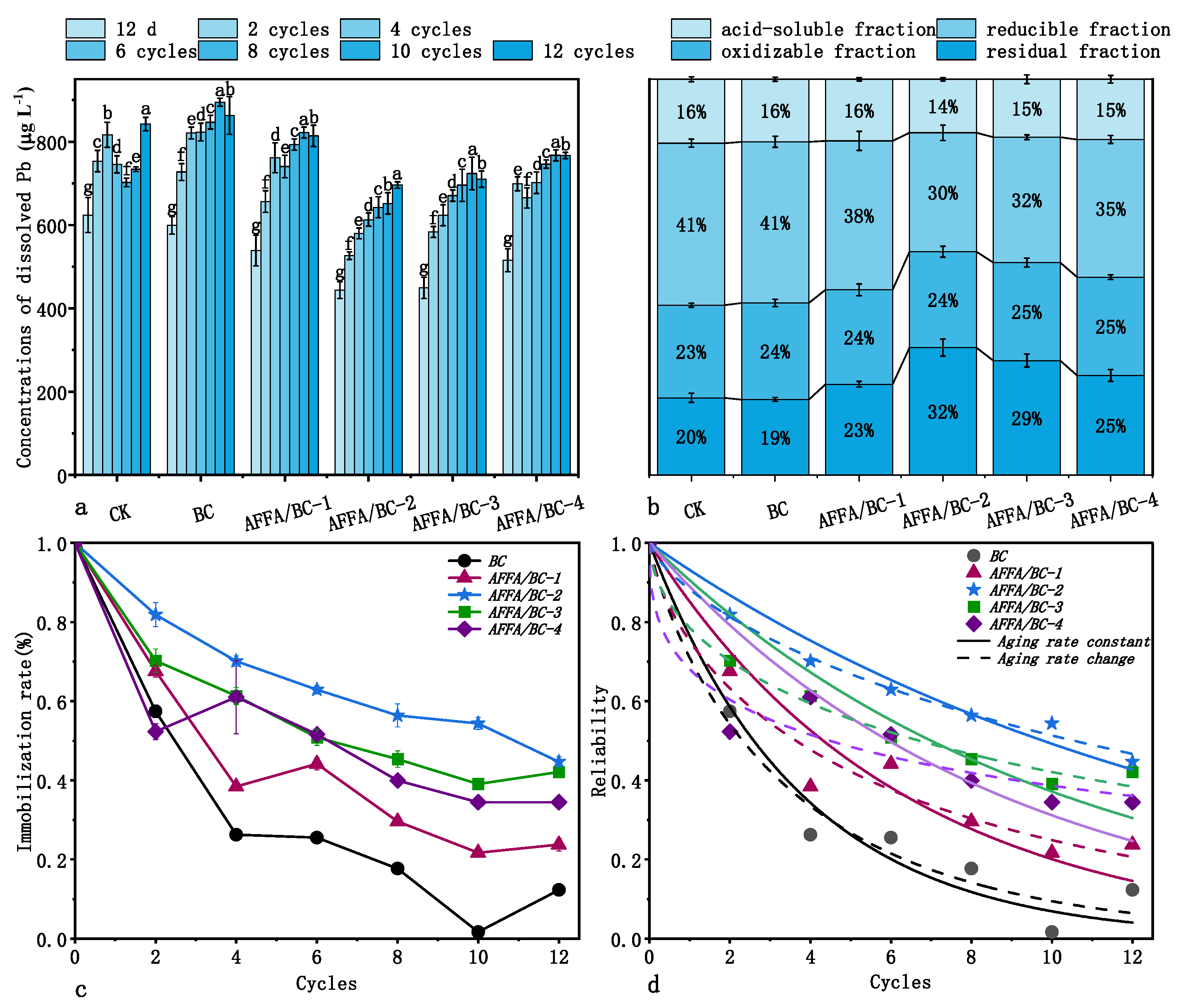
3.2.1. Changes in Soil Physicochemical Properties
3.2.2. The Leaching Concentration of Heavy Metals and the Aging Characteristics of Biochar Materials
3.2.3. Effect of Changes in the Physicochemical Properties of Biochar Induced by Fly Ash on the Long-Term Immobilization Performance of Heavy Metals
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamid, Y.; Tang, L.; Hussain, B.; Usman, M.; Gurajala, H.K.; Rashid, M.S.; He, Z.; Yang, X. Efficiency of lime, biochar, Fe containing biochar and composite amendments for Cd and Pb immobilization in a co-contaminated alluvial soil. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egbosiuba, T.C.; Abdulkareem, A.S.; Tijani, J.O.; Ani, J.I.; Krikstolaityte, V.; Srinivasan, M.; Veksha, A.; Lisak, G. Taguchi optimization design of diameter-controlled synthesis of multi walled carbon nanotubes for the adsorption of Pb(II) and Ni(II) from chemical industry wastewater. Chemosphere 2021, 266, 128937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; Wang, L.; Zhong, L.; Liu, X.; Brookes, P.C.; Xu, J.; Chen, H. Contrasting effects of composting and pyrolysis on bioavailability and speciation of Cu and Zn in pig manure. Chemosphere 2017, 180, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leclercq-Dransart, J.; Demuynck, S.; Bidar, G.; Douay, F.; Grumiaux, F.; Louvel, B.; Pernin, C.; Leprêtre, A. Does adding fly ash to metal-contaminated soils play a role in soil functionality regarding metal availability, litter quality, microbial activity and the community structure of Diptera larvae? Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 138, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.F.; Chi, J.; Ding, Z.; Zhang, F.; Huang, J.J. Removal of lead from two polluted soils by magnetic wheat straw biochars. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 205, 111132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.H.; Che, Y.Y.; Wang, L.Q.; Zhao, Z.J.; Zhang, Y.C.; Wei, L.L.; Xiao, Y. Rice straw biochar and phosphorus inputs have more positive effects on the yield and nutrient uptake of Lolium multiflorum than arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in acidic Cd-contaminated soils. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.H.; Crowley, D.; Wang, K.; Zhang, H.Q.; Li, H.F. Effects of biochar and Arbuscular mycorrhizae on bioavailability of potentially toxic elements in an aged contaminated soil. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 206, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beesley, L.; Moreno-Jiménez, E.; Gomez-Eyles, J.L.; Harris, E.; Robinson, B.; Sizmur, T. A review of biochars’ potential role in the remediation, revegetation and restoration of contaminated soils. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 3269–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.B.; Kim, S.H.; Jeon, E.K.; Kim, D.H.; Tsang, D.; Alessi, D.S.; Kwon, E.E.; Baek, K. Effect of dissolved organic carbon from sludge, Rice straw and spent coffee ground biochar on the mobility of arsenic in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, E.G.; Yang, X.; Chen, H.B.; Shaheen, S.M.; Sarkar, B.; Xu, S.; Song, H.; Liang, Y.; Rinklebe, J.; Hou, D.Y.; et al. Iron-modified biochar and water management regime-induced changes in plant growth, enzyme activities, and phytoavailability of arsenic, cadmium and lead in a paddy soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.H.; Dong, Z.G.; Peng, Q.; Wang, X.; Fan, C.B.; Zhang, X.C. Impacts of coal fly ash on plant growth and accumulation of essential nutrients and trace elements by alfalfa (Medicago sativa) grown in a loessial soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 197, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, S.S.; Kim, K.H. Utilization of coal ash: Is vermitechnology a sustainable avenue? Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 1376–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Shang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Gao, Y.; Guo, J.; Zheng, H.; Xing, B. Co-pyrolysis of alkali-fused fly ash and corn stover to synthesize biochar composites for remediating lead-contaminated soil. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 118938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.R.; Zhao, H.H.; Hu, X.F.; Liu, F.H.; Wang, L.; Zhao, X.; Gao, P.C.; Ji, P.H. Optimization of preparation technology for modified coal fly ash and its adsorption properties for Cd2+. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.F.; Peng, N.; Sun, J.T.; Lu, G.N.; Chen, M.Q.; Deng, F.C.; Dou, R.N.; Nie, L.J.; Zhong, Y.M. Synthesis of silica-composited biochars from alkali-fused fly ash and agricultural wastes for enhanced adsorption of methylene blue. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 139055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Li, J.M.; Wang, C.Y.; An, G.Q. Contrasting microcystin-LR sorption and desorption capability of different farmland soils amended with biochar: Effects of biochar dose and aging time. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 286, 117364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.Z.; Zhong, H.; Liu, G.X.; Dai, Z.M.; Brookes, P.C.; Xu, J. Remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils by biochar: Mechanisms, potential risks and applications in China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Yu, G.; Zhou, X.; Sun, F.; Liu, C. Biogeochemical process governing cadmium availability in sediments of typical coastal wetlands driven by drying-wetting alternation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 135980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huang, J.; Li, G.; Luo, J.; Bolan, N.S.; Hou, D. Long-term immobilization of soil metalloids under simulated aging: Experimental and modeling approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.X.; Qiao, Y.; Li, T.; Liu, S.; Zhou, J.; Yao, H.; Yang, H.; Xu, M. Improved removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution using zeolite synthesized from coal fly ash via mechano-chemical treatment. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 12, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, B.; Mistry, C.; Shah, A. Seizure modeling of Pb(II) and Cd(II) from aqueous solution by chemically modified sugarcane bagasse fly ash: Isotherms, kinetics, and column study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 2193–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, B.A.; Oluyinka, O.A.; Shah, A.V. Fly Ash Reuse as Mesoporous Ca- and Mg-Zeolitic Composites for the Seclusion of Aniline from Aqueous Solution. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.R.; Zhao, H.H.; Zhang, G.B.; Li, J.T.; Yang, Y.; Ji, P.H. Potential of removing Cd(II) and Pb(II) from contaminated water using a newly modified fly ash. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.L.; Zhang, W.H.; Yang, Y.X.; Huang, X.F.; Wang, S.Z.; Qiu, R.L. Relative distribution of Pb2+ sorption mechanisms by sludge-derived biochar. Water Res. 2012, 46, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchimiya, M.; Bannon, D.I.; Wartelle, L.H. Retention of Heavy Metals by Carboxyl Functional Groups of Biochars in Small Arms Range Soil. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2012, 60, 1798–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.G.; Bai, T.X.; Yan, Y.B.; Ma, K.R. Influence of sodium hydroxide addition on characteristics and environmental risk of heavy metals in biochars derived from swine manure. Waste Manag. 2020, 105, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawal, A.; Joseph, S.D.; Hook, J.M.; Chia, C.H.; Munroe, P.R.; Donne, S.; Lin, Y.; Phelan, D.; Mitchell, D.; Pace, B.; et al. Mineral-Biochar Composites: Molecular Structure and Porosity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 7706–7714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Ahmad, M.; Usman, A.; Al-Faraj, A.S.; Abduljabbar, A.; Ok, Y.S.; Al-Wabel, M.I. Date palm waste-derived biochar composites with silica and zeolite: Synthesis, characterization and implication for carbon stability and recalcitrant potential. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 1687–1704, Erratum in Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yi, B.J.; Yuan, Q.X.; Wu, Y.L.; Wang, M.; Yan, S.P. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by cattle manure-derived low temperature biochar. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 19917–19929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Liu, H.J.; Guo, Y.C.; Liu, Z.G.; Jiao, W.T. Immobilization of heavy metals in contaminated soils by modified hydrochar: Efficiency, risk assessment and potential mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, J.H.; Xu, S.; Wang, M.Z.; Zhang, Y.C.; Xue, X.H. A modified method for enhancing adsorption capability of banana pseudostem biochar towards methylene blue at low temperature. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 282, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.M.; Huang, D.L.; Liu, Y.G.; Zeng, G.M.; Chen, S.; Wang, R.Z.; Xu, P.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, C.; Xue, W.J. Biochar facilitated the phytoremediation of cadmium contaminated sediments: Metal behavior, plant toxicity, and microbial activity. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.Y.; Tan, X.P.; Cheng, J.; Haddix, M.L.; Cotrufo, M.F. Interactions between aged biochar, fresh low molecular weight carbon and soil organic carbon after 3.5 years soil-biochar incubations. Geoderma 2019, 333, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.N.; Guo, Z.H.; Xiao, X.Y.; Wang, S.; Jiang, Z.C.; Zeng, P. Phytostabilisation potential of giant reed for metals contaminated soil modified with complex organic fertiliser and fly ash: A field experiment. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 576, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, B.Q.; Lehmann, J.; Sohi, S.P.; Thies, J.E.; O’Neill, B.; Trujillo, L.; Gaunt, J.; Solomon, D.; Grossman, J.; Neves, E.G.; et al. Black carbon affects the cycling of non-black carbon in soil. Org. Geochem. 2010, 41, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punshon, T.; Adriano, D.C.; Weber, J.T. Restoration of drastically eroded land using coal fly ash and poultry biosolid. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 296, 209–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.Q.; Pan, G.X.; Li, L.Q.; Bian, R.J.; Liu, X.Y.; Yan, J.L.; Quan, G.X.; Ding, C.; Chen, T.M.; Liu, Y.; et al. Continuous immobilization of cadmium and lead in biochar amended contaminated paddy soil: A five-year field experiment. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 93, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Lehmann, J.; Solomon, D.; Kinyangi, J.; Grossman, J.; O’Neill, B.; Skjemstad, J.O.; Thies, J.; Luizão, F.J.; Petersen, J.; et al. Black Carbon Increases Cation Exchange Capacity in Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 1719–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.S.; Xue, Q.; Wang, P.; Li, Z.Z.; Liu, L. Effect of drying-wetting cycles on leaching behavior of cement solidified lead-contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2014, 117, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Wu, Y.G.; Hu, S. Drying-wetting cycles facilitated mobilization and transport of metal-rich colloidal particles from exposed mine tailing into soil in a gold mining region along the Silk Road. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.Q.; Xiao, X.Y.; Guo, Z.H.; Xie, Y.H.; Zhu, H.W.; Peng, C.; Liang, Y.Q. Release of cadmium in contaminated paddy soil amended with NPK fertilizer and lime under water management. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 159, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemingway, J.D.; Rothman, D.H.; Grant, K.E.; Rosengard, S.Z.; Eglinton, T.I.; Derry, L.A.; Galy, V.V. Mineral protection regulates long-term global preservation of natural organic carbon. Nature 2019, 570, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keiluweit, M.; Kleber, M. Molecular-Level Interactions in Soils and Sediments: The Role of Aromatic π-Systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3421–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.Z.; Huang, D.L.; Liu, Y.G.; Zhang, C.; Lai, C.; Zeng, G.M.; Cheng, M.; Gong, X.M.; Wan, J.; Luo, H. Investigating the adsorption behavior and the relative distribution of Cd2+ sorption mechanisms on biochars by different feedstock. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 261, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vithanage, M.; Herath, I.; Almaroai, Y.A.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Huang, L.B.; Sung, J.K.; Lee, S.S.; Ok, Y.S. Effects of carbon nanotube and biochar on bioavailability of Pb, Cu and Sb in multi-metal contaminated soil. Environ. Geochem. Health 2017, 39, 1409–1420, Erratum in Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Soil |
|---|---|
| pH | 7.03 |
| CEC (cmol+ kg−1) | 9.17 |
| moisture content (%) | 7.31 |
| Soil bulk density (g cm−3) | 1.39 |
| SOM (g kg−1) | 2.13 |
| The total of Pb (mg kg−1) | 263 |
| Adsorbents | Yield (%) | pH | SBET (m2 g−1) | Vtotal (cm3 g−1) | Dap (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BC | 22.42 | 10.17 | 25.50 | 0.0156 | 2.432 |
| AFFA/BC-1 | 24.31 | 9.79 | 6.33 | 0.0076 | 4.806 |
| AFFA/BC-2 | 26.89 | 9.76 | 50.60 | 0.0315 | 2.491 |
| AFFA/BC-3 | 34.81 | 9.24 | 42.22 | 0.0384 | 3.635 |
| AFFA/BC-4 | 39.77 | 9.46 | 8.23 | 0.0482 | 23.371 |
| Cycles | Materials | SOM (g kg−1) | CEC (cmol+ kg−1) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry wet cycles | CK | 2.08 | 8.54 | 7.64–8.02 |
| BC | 5.97 | 9.05 | 7.88–8.02 | |
| AFFA/BC-1 | 6.24 | 10.3 | 8.38–8.51 | |
| AFFA/BC-2 | 4.87 | 9.8 | 8.62–8.76 | |
| AFFA/BC-3 | 4.86 | 9.0 | 9.21–9.33 | |
| AFFA/BC-4 | 4.39 | 9.2 | 9.68–9.79 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Zhang, F.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Q.; Ye, R.; Ma, Y.; Liu, X. Enhanced Stabilization of Lead in Soil Using Novel Biochar Composites Under Simulated Accelerated Aging Conditions. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2563. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062563
Li G, Zhang F, Ma Y, Zhang X, Liu Q, Ye R, Ma Y, Liu X. Enhanced Stabilization of Lead in Soil Using Novel Biochar Composites Under Simulated Accelerated Aging Conditions. Sustainability. 2025; 17(6):2563. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062563
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Gang, Fan Zhang, Yue Ma, Xin Zhang, Qingyuan Liu, Rongchuan Ye, Yan Ma, and Xianghui Liu. 2025. "Enhanced Stabilization of Lead in Soil Using Novel Biochar Composites Under Simulated Accelerated Aging Conditions" Sustainability 17, no. 6: 2563. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062563
APA StyleLi, G., Zhang, F., Ma, Y., Zhang, X., Liu, Q., Ye, R., Ma, Y., & Liu, X. (2025). Enhanced Stabilization of Lead in Soil Using Novel Biochar Composites Under Simulated Accelerated Aging Conditions. Sustainability, 17(6), 2563. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062563





