Magnetic Monitoring and Source Traceability of Heavy Metal Pollution in the Urban Topsoil of Xuzhou, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
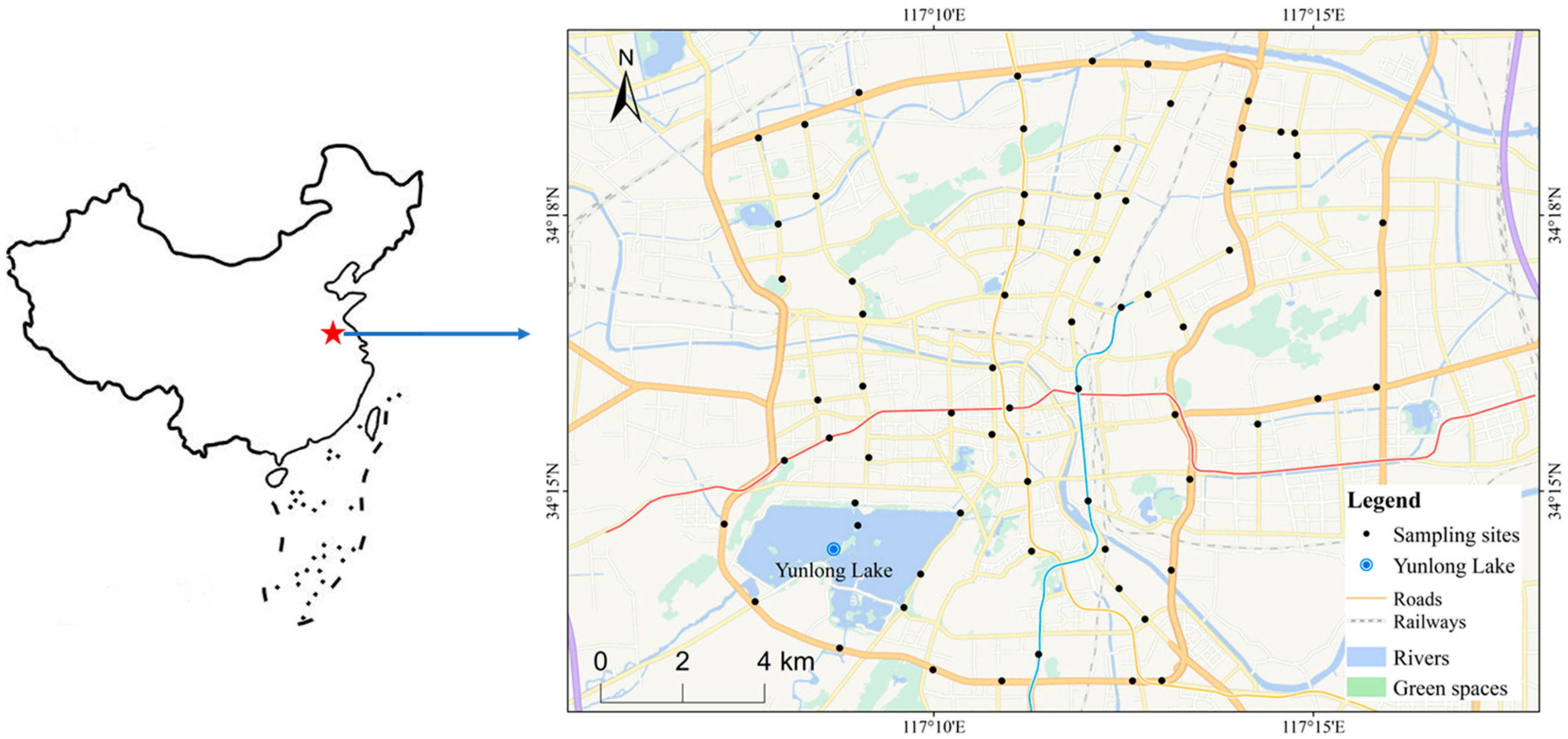
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Pretreatment
2.2. Determination of Heavy Metals
2.3. Determination of Magnetic Parameters
2.4. Evaluation Method
2.4.1. Geo-Accumulation Index (Igeo)
2.4.2. Pollution Load Index (PLI)
2.4.3. Potential Ecological Risk Index (RI)
- Er: Low (<40), Moderate (40–80), Considerable (80–160), High (160–320), Extreme (≥320)
- RI: Low (<150), Moderate (150–300), High (300–600), Extreme (≥600).
2.5. Data Analysis Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Heavy Metal Concentrations and Spatial Distribution
3.1.1. Statistics of Heavy Metal Concentrations
| 0–2 cm | 3–10 cm | Background Value [29] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Mean | CV/% | Range | Mean | CV/% | ||
| Cr | 11.30–111.83 | 65.57 | 27.61 | 24.60–141.20 | 62.41 | 28.20 | 64.80 |
| Cu | 9.50–246.75 | 47.02 | 75.13 | 15.26–140.80 | 42.12 | 55.59 | 24.30 |
| Fe | 0.42–4.20 | 2.47 | 20.71 | 0.83–4.44 | 2.52 | 20.12 | 3.10 |
| Mn | 72.50–1272.10 | 525.39 | 26.63 | 153.40–975.20 | 515.55 | 22.76 | 633.00 |
| Ni | 10.25–547.30 | 60.00 | 126.95 | 19.07–489.00 | 52.13 | 127.63 | 30.70 |
| Pb | 7.25–82.80 | 27.70 | 53.37 | 4.75–162.80 | 26.19 | 80.14 | 21.30 |
| Zn | 21.00–389.80 | 141.61 | 49.89 | 62.90–413.00 | 126.93 | 49.92 | 74.10 |
3.1.2. Evaluation of Heavy Metal Pollution
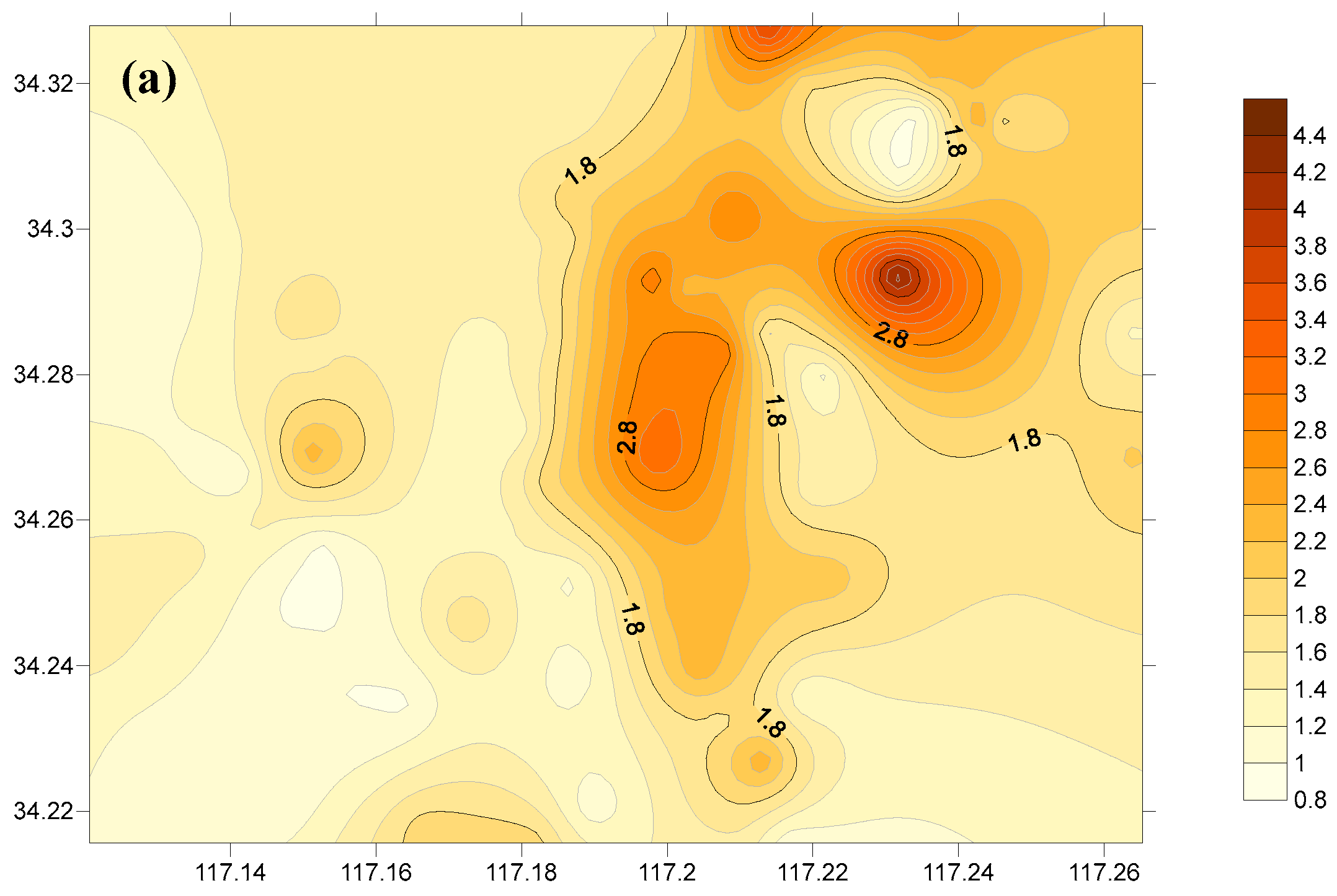
3.1.3. Spatial Distribution of Heavy Metal Pollution
3.2. Magnetic Properties
3.3. Magnetic Response and Traceability of Heavy Metals
3.3.1. Correlation Analysis
3.3.2. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Long, Z.; Zhu, H.; Bing, H.; Tian, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X. Contamination, sources and health risk of heavy metals in soil and dust from different functional areas in an industrial city of Panzhihua City, Southwest China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Han, Q.; Gui, C.; Cao, J.; Liu, Y.; He, X. Differences in the risk assessment of soil heavy metals between newly built and original parks in Jiaozuo, Henan Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 676, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gope, M.; Masto, R.E.; George, J.; Hoque, R.R.; Balachandran, S. Bioavailability and health risk of some potentially toxic elements (Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn) in street dust of Asansol, India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 138, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guney, M.; Zagury, G.J.; Dogan, N.; Onay, T.T. Exposure assessment and risk characterization from trace elements following soil ingestion by children exposed to playgrounds, parks and picnic areas. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 182, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Hu, Y.; Su, B.; Fang, G.; Wang, L.; Xiang, B. A review of heavy metal pollution levels and health risk assessment of urban soils in Chinese cities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 1055–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, Z.; Lu, X.; Duan, Q.; Huang, L.; Bi, J. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: Pollution and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solgi, E.; Oshvandi, Z. Spatial patterns, hotspot, and risk assessment of heavy metals in different land uses of urban soils (case study: Malayer city). Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2018, 24, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo-Gonzalez, J.M.; Torres-Mora, M.A.; Keesstra, S.; Brevik, E.C.; Jimenez-Ballesta, R. Heavy metal accumulation related to population density in road dust samples taken from urban sites under different land uses. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 553, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Wang, L.Q.; Huan, Y.Z.; Wang, R.; Liang, T. Concentrations, spatial distribution, sources and environmental health risks of potentially toxic elements in urban road dust across China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Zheng, N.; Tang, L. Pollution characteristics, sources, and health risk assessment of human exposure to Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb pollution in urban street dust across China between 2009 and 2018. Environ. Int. 2019, 128, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padoan, E.; Romè, C.; Ajmone-Marsan, F. Bioaccessibility and size distribution of metals in road dust and roadside soils along a peri-urban transect. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Men, C.; Liu, R.; Xu, L.; Wang, Q.; Shen, Z. Source-specific ecological risk analysis and critical source identification of heavy metals in road dust in Beijing, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 388, 121763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourliva, A.; Papadopoulou, L.; Aidona, E.; Giouri, K.; Simeonidis, K.; Vourlias, G. Characterization and geochemistry of technogenic magnetic particles (TMPs) in contaminated industrial soils: Assessing health risk via ingestion. Geoderma 2017, 295, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonet, T.; Maher, B.A. Airborne, Vehicle-Derived Fe-Bearing Nanoparticles in the Urban Environment: A Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 9970–9991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourliva, A.; Papadopoulou, L.; Aidona, E.; Giouri, K. Magnetic signature, geochemistry, and oral bioaccessibility of technogenic metals in contaminated industrial soils from Sindos Industrial Area, Northern Greece. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 17041–17055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Lin, H.; Cao, L.; Appel, E.; Hu, S.; Roesler, W. Magnetic response to air pollution recorded by soil and dust-loaded leaves in a changing industrial environment. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 119, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Wu, J.; Shi, T.; Chen, C.; Li, J.; Wang, P.; Song, Y.; Yu, Q.; Zhu, Z. New magnetic proxies to reveal source and bioavailability of heavy metals in contaminated soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 479, 135665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Eshaikh, M.A.; Al-Kahtani, A.A.; El-Shahawi, M.S. Comparison of Different Acid Digestion Methods for the Determination of Heavy Metals in Soil Samples. J. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2013, 5, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- GB 15618-2018; State Administration for Market Regulation. Environmental Quality Standards for Soils—Risk Control Standards for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land (Trial). China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Dinçkal, A.; Carrancho, A.A.; Hernandez, G.C.M.; Mallol, C. Magnetic micro-archaeology: A method for conducting rock magnetic microfacies analysis on archaeological soil micromorphology samples, with a case study from El Salt, Alcoy, Spain. Arch. Anthropol. Sci. 2024, 16, 01946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geol. J. 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.R.; Jeffrey, D.W. Problems in the assessment of heavy metals levels in estuaries and the formation of pollution index. Helgol. Meeresunters. 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control—A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Huang, S.; Wang, M.; Wu, J.; Su, J.; Lin, K.; Chen, X.; He, T.; Li, Y.; Sha, C. Source-oriented health risk assessment and priority control factor analysis of heavy metals in urban soil of Shanghai. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 135859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Xie, M.; Li, G.; Lin, S.; Wang, D.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z. A spatial source-oriented and probability-based risk-assessment framework for heavy metal and PAH contamination of urban soils in Guangzhou, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 482, 136500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojciech, Z.; Małgorzata, T.; Paulina, H.; Małgorzata, B. Impact of traffic and other sources on heavy metal pollution of urban soils (Lublin, Poland). Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2025, 23, 101058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, I.; Grocke, D.R. Determination of the abundance and carbon isotope composition of elemental carbon in sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 1997, 61, 3413–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Li, H.; Lü, L.; Liang, G.; Wu, T.; Zhu, J. Distributions and risk assessment of heavy metals in solid waste in lead-zinc mining areas and across the soil, water body, sediment and agricultural product ecosystem in their surrounding areas. China Geol. 2025, 25, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Environmental Monitoring General Station. Recent Measuring Methods of Elements in Soils; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Oldfield, F.; Richardson, N. Lake sediment magnetism and atmospheric deposition. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1990, 327, 325–330. [Google Scholar]
- Levi, S.; Merrill, R.T. Properties of single-domain, pseudo-single-domain, and multidomain magnetite. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1978, 83, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.P.; Almeida, T.P.; Church, N.S.; Harrison, R.J.; Heslop, D.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Muxworthy, A.R.; Williams, W.; Zhao, X. Resolving the Origin of Pseudo-Single Domain Magnetic Behavior. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2017, 122, 9534–9558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, V.; Knab, M.; Appel, E. Magnetic susceptibility mapping of roadside pollution. J. Geochem. Explor. 1999, 66, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.S. Magnetic properties and heavy metal pollution of soils in the vicinity of a cement plant, Xuzhou (China). J. Appl. Geophys. 2013, 98, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanders, P.J. Collection, measurement, and analysis of airborne magnetic particulates from pollution in the environment. J. Appl. Phys. 1994, 75, 5931–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapička, A.; Jordanova, N.; Petrovsky, E.; Ustjak, S. Magnetic stability of power-plant fly ash in different solutions. Phys. Chem. Earth. 2000, 25, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.S. Black carbon in urban topsoils of Xuzhou (China): Environmental implication and magnetic proxy. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 163, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearing, J.A.; Dann, R.J.L.; Hay, K.; Lees, J.A.; Loveland, P.J.; Maher, B.A.; O’Grady, K. Frequency-dependent susceptibility measurements of environmental materials. Geophys. J. R. Astron. Soc. 1996, 124, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldfield, F. Toward the discrimination of fine-grained ferrimagnets by magnetic measurements in lake and near-shore marine sediments. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1994, 99, 9045–9050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.G.; Bai, S.Q.; Xue, Q.F. Magnetic properties as indicators of heavy metals pollution in urban topsoils: A case study from the city of Luoyang, China. Geophys. J. Int. 2007, 171, 568–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.G.; Bai, S.Q.; Zhu, L. Magnetic properties as indicators of heavy metal pollution in urban topsoil: A case study from Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 435–436, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Liu, Q.S.; Zeng, Q.L.; Chan, L.S. Relationship between magnetic properties and heavy metal contamination in industrial city soils: A case study of Wuhan, Central China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 17881–17893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yan, X.; Wang, S.; Yan, R.; Liu, B.; Yu, H. Urban street dust bound 24 potentially toxic metal/metalloids (PTMs) from Xining valley-city, NW China: Spatial occurrences, sources and health risks. Toxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 162, 474–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.S.; Kumar, S.; Nasiruddin, M.; Saha, N. Deciphering the origin of Cu, Pb and Zn contamination in school dust and soil of Dhaka, a megacity in Bangladesh. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 40808–40823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, N.; Keshavarzi, B.; Moore, F.; Tavakol, T.; Lahijanzadeh, A.R.; Jaafarzadeh, N.; Kermani, M. Ecological and human health hazards of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in road dust of Isfahan metropolis. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 712–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Guo, Q.; Wei, R.; Dong, X.; Han, X.; Guo, Z. Atmospheric lead pollution in a typical megacity: Evidence from lead isotopes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 145810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Hassanin, A.; Samak, M.R.; Saleh, E.M.; Abou-Sree, Y.H.; Abdel-Rahman, G.N.E.; Ahmed, M.B.M. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in the different parts of maize cultivated in soils irrigated with different quality of water. Egypt. J. Chem. 2022, 65, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.X.; Zeng, C.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.L.; Scott, C.A.; Yan, X.D. Traffic-related Trace Elements in Soils Along Six Highway Segments on the Tibetan Plateau: Influence Factors and Spatial Variation. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581–582, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Dong, D.; Hua, X.; Dong, S. Investigation of the transport and fate of Pb, Cd, Cr (VI) and As (V) in soil zones derived from moderately contaminated farmland in Northeast, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaha, S.; Appel, S.R. Micro-scale grain-size analysis and magnetic properties coal-fired power plant fly ash and its relevance for environmental magnetic pollution studies. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 8359–8370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, A.; Mandal, H.; Roy, M.; Kusz, J.; Hofmeister, W. Microstructural and magnetic characterization of fly ash from Kolaghat Thermal Power Plant in West Bengal, India. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2011, 323, 3007–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.Y. Elemental Composition and Geochemical Characteristics of Iron-Manganese Nodules in Main Soils of China. Pedosphere 2006, 1, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Guan, D.; Chen, Y.; Dai, J.; Ding, W.; Peart, M.R.; Zhang, C. Distribution and availability of heavy metals in soils near electroplating factories. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 22596–22610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shi, Z.; Yu, D.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, R. Effect of different industrial activities on soil heavy metal pollution, ecological risk, and health risk. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazekašová, D.; Petrovič, F.; Fazekaš, J.; Štofejová, L.; Baláž, I.; Tulis, F.; Tóth, T. Soil Contamination in the Problem Areas of Agrarian Slovakia. Land 2021, 10, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Qian, Y.; Yang, L. Dissolution Potential of Heavy Metal Elements in Coal and Its Influence Factors. J. Earth Sci. Environ. 2023, 45, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Single Potential Ecological Risk Index | Element | Ei Range | Ei Mean | Percentage of Samples with Different Risk Levels/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slight | Moderate | Strong and Above | ||||
| Ei | Cr | 0.35–3.50 | 1.96 | 100.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Cu | 1.95–50.77 | 9.13 | 99.30 | 0.70 | 0.00 | |
| Fe | 0.30–1.29 | 0.80 | 100.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Mn | 0.17–1.49 | 0.82 | 100.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Ni | 1.67–47.00 | 8.57 | 97.20 | 2.80 | 0.00 | |
| Pb | 1.12–21.08 | 6.21 | 100.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Zn | 0.28–4.77 | 1.80 | 100.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Total Potential Ecological Risk Index | RI Range | RI Mean | Percentage of Samples with Different Risk Levels/% | |||
| Slight | Moderate | Strong and Above | ||||
| RI | 6.42–91.38 | 29.29 | 100.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Depth | Magnetic Parameters | Mean | Range | CV/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–2 cm | χ/(10−8 m3·kg−1) | 132.3 | 22.4–613.5 | 97.0 |
| χfd/% | 3.5 | 0.3–11.2 | 66.5 | |
| SOFT/(10−5 A·m2·kg−1) | 719.4 | 89.4–2753.9 | 91.0 | |
| SIRM/(10−5 A·m2·kg−1) | 1530.2 | 199.8–6471.3 | 90.1 | |
| χARM/(10−8 m3·kg−1) | 285.0 | 3.3–787.2 | 58.4 | |
| χARM/χ | 2.7 | 0.1–9.5 | 45.0 | |
| χARM/SIRM/(10−3 m·A−1) | 0.2 | 0.01–0.5 | 37.9 | |
| 3–10 cm | χ/(10−8 m3·kg−1) | 99.6 | 11.4–823.5 | 113.4 |
| χfd/% | 4.8 | 0.4–11.7 | 54.5 | |
| SOFT/(10−5 A·m2·kg−1) | 494.4 | 104.4–3208.0 | 91.9 | |
| SIRM/(10−5 A·m2·kg−1) | 1088.3 | 225.6–7049.2 | 87.1 | |
| χARM/(10−8 m3·kg−1) | 169.4 | 5.4–846.9 | 77.0 | |
| χARM/χ | 2.3 | 0.1–5.2 | 112.3 | |
| χARM/SIRM | 0.2 | 0.0–0.4 | 58.1 |
| Variable | PCA1 | PCA2 | PCA3 | PCA4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | 0.599 | 0.502 | 0.062 | 0.239 |
| Cu | 0.427 | 0.004 | 0.740 | 0.286 |
| Fe | 0.601 | 0.693 | −0.144 | −0.180 |
| Mn | 0.245 | 0.842 | −0.197 | −0.286 |
| Ni | 0.180 | 0.140 | 0.830 | −0.372 |
| Pb | 0.861 | 0.075 | −0.069 | 0.228 |
| Zn | 0.900 | 0.136 | 0.059 | 0.075 |
| χ | 0.856 | −0.315 | −0.168 | −0.051 |
| χfd | −0.490 | 0.537 | 0.003 | 0.468 |
| SOFT | 0.912 | −0.247 | −0.120 | −0.008 |
| SIRM | 0.915 | −0.256 | −0.096 | −0.004 |
| χARM | 0.854 | −0.170 | −0.021 | 0.001 |
| Eigenvalue | 5.918 | 2.027 | 1.359 | 0.670 |
| Variance contribution ratio/% | 49.321 | 16.893 | 11.329 | 5.585 |
| Cumulative contribution ratio/% | 49.321 | 66.214 | 77.542 | 83.127 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, M.; Li, N. Magnetic Monitoring and Source Traceability of Heavy Metal Pollution in the Urban Topsoil of Xuzhou, China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2554. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062554
Liu Y, Wang X, Yang M, Li N. Magnetic Monitoring and Source Traceability of Heavy Metal Pollution in the Urban Topsoil of Xuzhou, China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(6):2554. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062554
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yinghong, Xuesong Wang, Menghui Yang, and Na Li. 2025. "Magnetic Monitoring and Source Traceability of Heavy Metal Pollution in the Urban Topsoil of Xuzhou, China" Sustainability 17, no. 6: 2554. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062554
APA StyleLiu, Y., Wang, X., Yang, M., & Li, N. (2025). Magnetic Monitoring and Source Traceability of Heavy Metal Pollution in the Urban Topsoil of Xuzhou, China. Sustainability, 17(6), 2554. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062554





