Spatial Effects and Driving Factors of Consumption Upgrades on Municipal Solid Waste Eco-Efficiency, Considering Emission Outputs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. MSW Eco-Efficiency
2.2. Consumption Upgrading
2.3. Hypotheses
3. Methodology
3.1. Calculation of GHGs from MSW Treatment
3.1.1. GHG Emissions from Landfills
3.1.2. GHG Emissions from Incineration
3.1.3. GHG Emissions from Composts
3.2. SSBM-DEA Efficiency Model with Undesirable Output
3.3. Measurement of CU
3.4. Gini Coefficient Decomposition Method
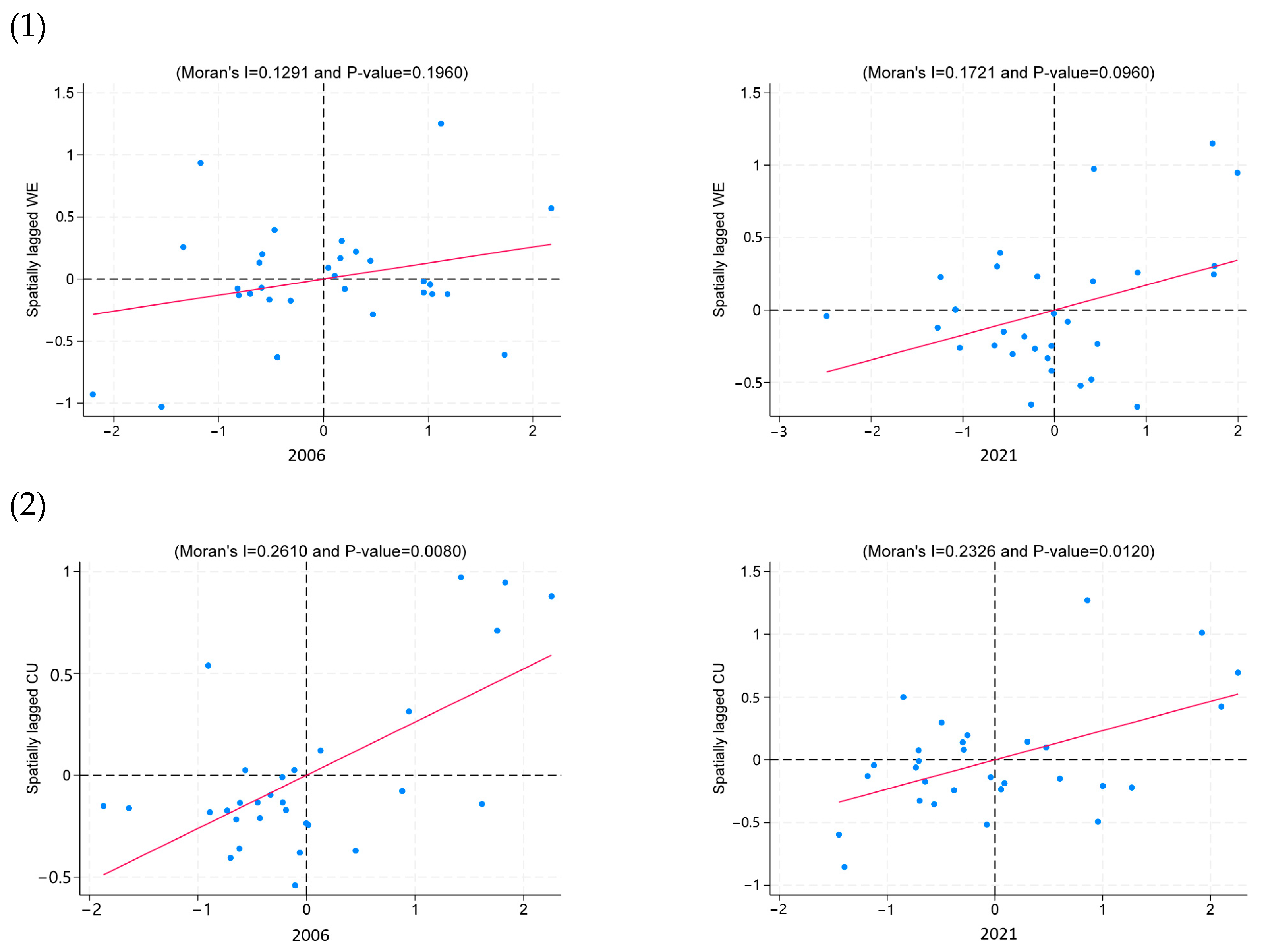
3.5. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
3.6. Spatial Econometric Model
4. Sample Description and Data
4.1. Sample
4.2. Data
4.2.1. Variables for the Super SBM-DEA Model
- (1)
- Input Variables
- Solid Waste Generation: MSW primarily includes residential waste, street cleaning waste, and institutional waste. This study uses the volume of solid waste collected and transported to represent MSW generation. The collection volume includes waste transported via sealed vehicles (or containers), reflecting the current state of waste collection in a region;
- Labor Input: Many scholars, based on the Cobb-Douglas production function, consider labor as a fundamental input indicator. This study uses the number of employees in urban units within the water conservation, environmental, and public facility management sectors as a proxy for labor input;
- Capital Input: Solid waste treatment investment is used as a representative of capital input. Specifically, this study considers investments in urban household waste treatment as a measure of eco-efficiency input proposed by Du et al. [74];
- Harmless Treatment Capacity: The capacity for harmless treatment of solid waste reflects the performance of waste treatment infrastructure [75]. Therefore, this study also includes the harmless treatment capacity of solid waste as an input variable.
- (2)
- Output Variables
- Solid Waste Treatment Volume: The volume of harmlessly treated household waste reflects the current state of harmless treatment. This study uses the harmless treatment volume of MSW to represent the waste treatment situation in different regions.
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: From an environmental perspective, GHGs are an important indicator for evaluating waste treatment efficiency. This study uses the calculated GHGs as the undesirable output to measure the eco-efficiency of MSW [12].
4.2.2. Variables for the Consumption Upgrade Evaluation System
4.2.3. Control Variables for the SDA Model
5. Results and Discussions
5.1. Regional Differences in CU in China
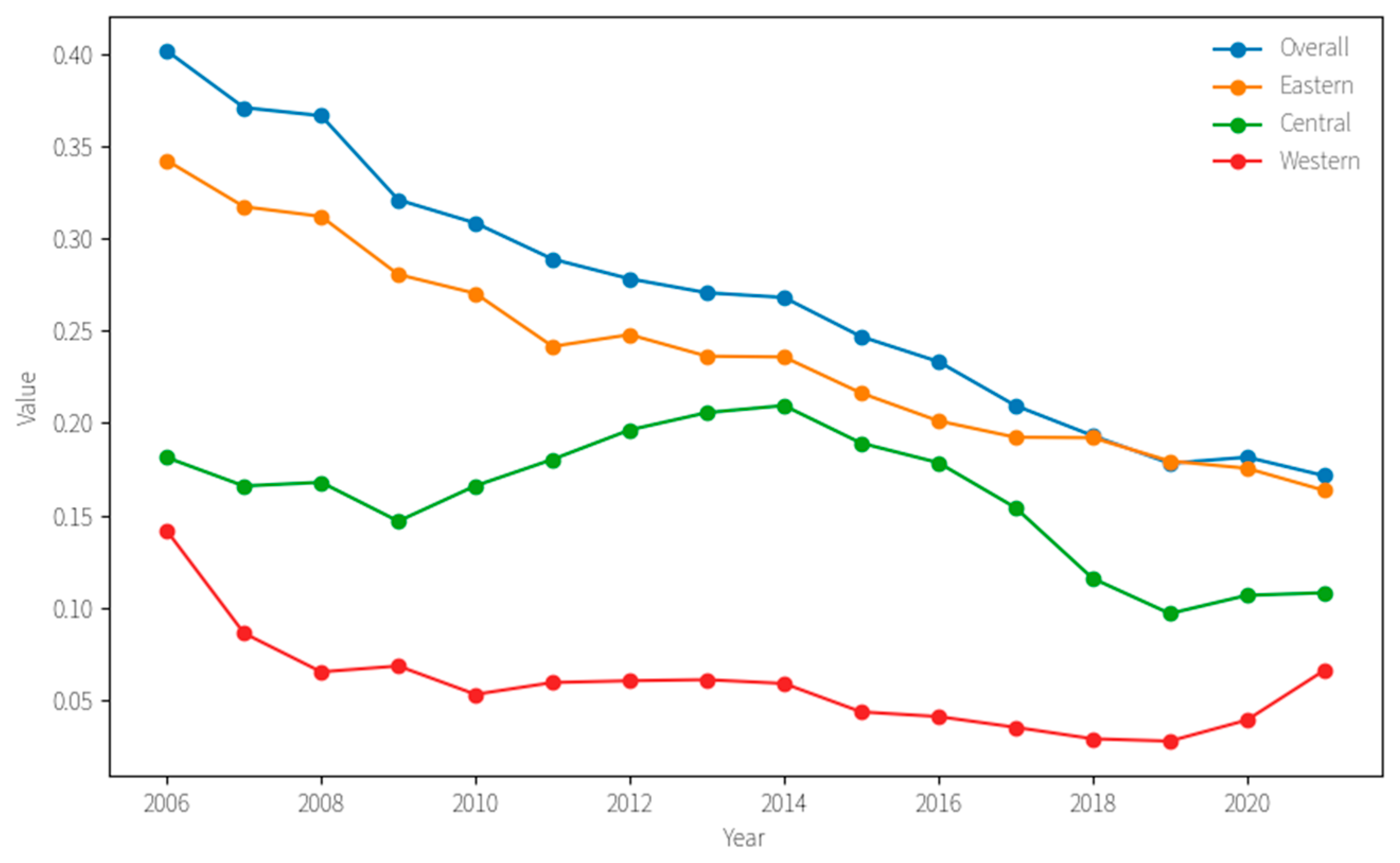
5.2. MSW Eco-Efficiency Spatio-Temporal Pattern
5.3. Analysis of the Impact of CU on MSW Eco-Efficiency
5.4. Robustness Tests
- (1)
- Replacing the Spatial Weight Matrix
- (2)
- Time Lag Effect
5.5. Heterogeneity Tests
5.6. Endogeneity Tests
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Region | Food Waste | Paper | Plastic | Textiles | Wood | Rubber and Leather | Metal | Glass | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northern China | 50.76 | 11.57 | 11.77 | 4.18 | 4.29 | 1.6 | 2.75 | 3.92 | 0.92 |
| Northeast China | 58.87 | 7.24 | 11.14 | 2.69 | 5.94 | 5.5 | 1.08 | 3 | 6.31 |
| Eastern China | 64.5 | 8.65 | 12.45 | 2.3 | 1.77 | 0.8 | 0.65 | 2.92 | 2.02 |
| Central China | 49.42 | 3.12 | 8.61 | 4.04 | 4.75 | 1.5 | 0.76 | 0.81 | 8.3 |
| Southern China | 51.18 | 11.81 | 13.49 | 3.71 | 2.03 | 0.9 | 0.74 | 1.86 | 5.85 |
| Southwest China | 52.22 | 9.98 | 12.61 | 2.81 | 2.5 | 4.1 | 1.16 | 1.62 | 7.11 |
| Northwest China | 51.93 | 6.85 | 9.41 | 2.72 | 1.75 | 1.6 | 1.21 | 2.89 | 4.25 |
| Data Sources | (Bian [12]; Cai [57]; Gu [13]; Lou [56]) | ||||||||
| Emission Factors | Paper | Wood | Textiles | Food Waste | Plastic | Rubber and Leather | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dmi | 0.9 | 0.85 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 1 | 0.84 | 0.9 |
| CFi | 0.46 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.38 | 0.75 | 0.67 | 0.03 |
| FCFi | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.2 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.2 | 1 |
| Data Sources | [56] | ||||||
| Regions | Provinces |
|---|---|
| Northern China | Beijing, Tianjin, Shanxi, Hebei, and Inner Mongolia |
| Northeast China | Heilongjiang, Jilin, and Liaoning |
| Eastern China | Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Anhui, Fujian, Jiangxi and Shandong |
| Central China | Henan, Hubei, and Hunan |
| Southern China | Guangdong, Guangxi, and Hainan |
| Southwest China | Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan, and Chongqing |
| Northwest China | Shaanxi, Gansu, Qinghai, Ningxia, and Xinjiang |
| Variable | Mean | Standard Deviation | Max | Min | Variable | Mean | Standard Deviation | Variable | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Consumer Price Index | 1.90 | 2.66 | 24.81 | 1.00 | Mobile Phone Penetration Rate | 85.89 | 33.18 | 189.50 | 17.40 |
| Innovation Product Supply | 2.79 | 3.28 | 27.18 | 0.17 | Per Capita Postal and Telecommunication Volume | 3297.26 | 3299.39 | 17,583.00 | 581.28 |
| Digital Consumption Environment | 0.36 | 0.27 | 1.07 | 0.02 | Digital Consumption Level | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.80 | 0.01 |
| Logistics Conditions | 0.26 | 0.22 | 2.23 | 0.00 | Proportion of Clean Energy Consumption | 0.15 | 0.06 | 0.79 | 0.07 |
| Per Capita Consumption Level | 66,680.46 | 77,228.04 | 395,894.39 | 4823.25 | Wastewater Emissions | 25.12 | 7.28 | 66.61 | 7.99 |
| Regional Consumption Capacity | 1.82 | 1.21 | 7.26 | 0.19 | Air Emissions | 88.27 | 95.89 | 647.06 | 0.11 |
| Final Consumption Rate | 51.17 | 8.35 | 80.00 | 32.08 | Green Travel | 11.91 | 3.24 | 26.55 | 5.73 |
| Income Scale | 19,904.72 | 12,381.46 | 78,026.60 | 2715.85 | Waste Treatment | 85.05 | 19.38 | 100.00 | 17.80 |
| Unemployment Rate | 3.39 | 0.66 | 5.10 | 1.20 | Green Cover | 38.52 | 4.44 | 55.10 | 23.45 |
| Higher Education Enrollment Rate | 8.39 | 5.19 | 26.86 | 0.36 | Road Sweeping Area | 22,413.82 | 20,476.06 | 132,135.00 | 1367.00 |
| Labor Force Proportion | 0.62 | 0.07 | 0.81 | 0.42 | Per Capita Park Green Area | 12.03 | 3.15 | 21.05 | 5.49 |
| Average Consumption Propensity | 1.02 | 0.25 | 2.52 | 0.60 | Sewage Treatment | 0.84 | 0.16 | 1.00 | 0.20 |
| Clothing Consumption Proportion | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.16 | 0.04 | Environmental Investment | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.00 |
| Housing Consumption Proportion | 0.16 | 0.07 | 0.41 | 0.07 | Industrial Solid Waste Utilization | 6097.56 | 4909.13 | 25,230.00 | 113.00 |
| Education and Culture Consumption Proportion | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.17 | 0.07 | Forest Area | 33.65 | 17.99 | 66.80 | 4.00 |
| Daily Goods and Services Consumption Proportion | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.04 | Financial Situation | 28,550.78 | 29,357.20 | 195,680.62 | 729.83 |
| Transport and Communication Consumption Proportion | 0.13 | 0.02 | 0.21 | 0.09 | Government Support | 0.23 | 0.10 | 0.64 | 0.08 |
| Medical Care Expenditure Proportion | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.04 | Urbanization Level | 56.37 | 13.70 | 89.60 | 27.46 |
| Other Goods and Services Consumption Proportion | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.02 | Social Security Fiscal Expenditure | 0.13 | 0.04 | 0.31 | 0.02 |
| Engel’s Coefficient | 0.58 | 0.03 | 0.67 | 0.49 | Medical Insurance Participation Rate | 0.54 | 0.33 | 1.34 | 0.07 |
| Natural Gas Penetration Rate | 0.92 | 0.09 | 1.14 | 0.57 | Medical Services | 4.79 | 1.51 | 8.34 | 1.60 |
References
- Mahadevan, V.; Subbaiyan, N.; Kannappan Panchamoorthy, G.; Jayaseelan, A.; Palaniappan, S.K.; Siengchin, S. Hydrothermal Liquefaction of Confused Waste to Bio-Oil: A Study on Elemental and Energy Recovery. Energy Convers. Manag. 2025, 325, 119353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MOHURDC (Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of China). Available online: https://www.mohurd.gov.cn/gongkai/fdzdgknr/sjfb/tjxx/index.html (accessed on 11 January 2025).
- Zhang, X.; Liu, B.; Zhang, N. Forecasting the Mitigation Potential of Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Shenzhen through Municipal Solid Waste Treatment: A Combined Weight Forecasting Model. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhave, P.P.; Jain, V.; Dhawad, C. Life Cycle Assessment Approach to Attain Sustainability in the Waste Management Sector: A Case Study. J. Environ. Eng. 2025, 151, 05024008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldo-Almario, I.; Rueda-Saa, G.; Uribe-Ceballos, J.R. Wasteaware Adaptation to the Context of a Latin American Country: Evaluation of the Municipal Solid Waste Management in Cali, Colombia. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2024, 26, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñiz Sierra, H.; Díaz-Somoano, M.; Šyc, M.; Shtukaturova, A.; González La Fuente, J.M.; Baizán, P.D.; Megido, L. A Comparison of the Comprehensive Municipal Solid Waste Management Systems of the Region of Prague and the Principality of Asturias. the Influence of Collection Systems and Municipality Size on the Waste Collection and the Recycling Rates. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2023, 25, 1672–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertwich, E.G.; Peters, G.P. Carbon Footprint of Nations: A Global, Trade-Linked Analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6414–6420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, X.C.; Nguyen, T.T.H.; La, D.D.; Kumar, G.; Rene, E.R.; Nguyen, D.D.; Chang, S.W.; Chung, W.J.; Nguyen, X.H.; Nguyen, V.K. Development of Machine Learning—Based Models to Forecast Solid Waste Generation in Residential Areas: A Case Study from Vietnam. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 167, 105381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, A.; Alam, P.; Rather, N.A.; Islam, S.U. Characterization and Analysis of Municipal Solid Waste Generated in the Semi-Urban Region of Thanamandi, Jammu and Kashmir (J&K), India: A Basis for Developing a Suitable Waste Management Approach. In Environmental Science and Pollution Research; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massahi, T.; Sharafi, M.; Ahmadi, B.; Parnoon, K.; Hossini, H. Microplastic Pollution in Compost Derived from Mixed Municipal Waste in Kermanshah City: Abundance, Characteristics, and Ecological Risk Evaluation. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2024, 235, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shi, D.; Ma, L.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, J. The Role of Household Energy Consumption Behavior in Environmental Policy Outcomes—The Case of Driving Restriction Policy in Zhengzhou. Energy Policy 2024, 188, 114096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, R.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, F.; Chen, J.; Liang, C.; Li, W.; Sun, Y.; Chai, X.; Fang, X.; Yuan, L. Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Waste Sectors in China During 2006–2019: Implications for Carbon Mitigation. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 161, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W. Research on Strategy Optimization of Sustainable Development towards Green Consumption of Eco-Friendly Materials. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2024, 36, 103190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, M.; Shen, X.; Guo, D. Analysis of Green Transformation and Driving Factors of Household Consumption Patterns in China from the Perspective of Carbon Emissions. Sustainability 2024, 16, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Leng, B.; Xi, J. Assessing the Social Cost of Municipal Solid Waste Management in Beijing: A Systematic Life Cycle Analysis. Waste Manag. 2024, 173, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Deng, S.; Lu, C.; Wang, Y.; Liao, H. Optimization of Green Vehicle Paths Considering the Impact of Carbon Emissions: A Case Study of Municipal Solid Waste Collection and Transportation. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cudjoe, D.; Zhu, B.; Nketiah, E.; Wang, H.; Chen, W.; Qianqian, Y. The Potential Energy and Environmental Benefits of Global Recyclable Resources. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 798, 149258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Wei, Y.-M.; Gomi, K.; Matsuoka, Y. Future Scenarios for Energy Consumption and Carbon Emissions Due to Demographic Transitions in Chinese Households. Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, T.; Hu, Y.-Y. Research on the Impact of Upgrading of Consumption Structure on Energy Intensity under the Background of Urban and Rural Dual Economy. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 793, 012058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutberlet, J.; Baeder, A.M. Informal Recycling and Occupational Health in Santo André, Brazil. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2008, 18, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahar, R.B.; Sahito, A.R.; Yue, D.; Khan, K. Modeling and Simulation of Landfill Gas Production from Pretreated MSW Landfill Simulator. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2016, 10, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Luo, H.; Li, B.; Cheng, J.; Huang, Y. Emission Characteristics and Impact Factors of Air Pollutants from Municipal Solid Waste Incineration in Shanghai, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 310, 114732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istrate, I.-R.; Iribarren, D.; Gálvez-Martos, J.-L.; Dufour, J. Review of Life-Cycle Environmental Consequences of Waste-to-Energy Solutions on the Municipal Solid Waste Management System. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 157, 104778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, F.; Bhandari, R.; Gäth, S. Critical Review on Life Cycle Assessment of Conventional and Innovative Waste-to-Energy Technologies. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 708–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Yu, H.; Liang, S.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Z. Resource Impacts of Municipal Solid Waste Treatment Systems in Chinese Cities Based on Hybrid Life Cycle Assessment. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 130, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jaeger, S.; Eyckmans, J.; Rogge, N.; Van Puyenbroeck, T. Wasteful Waste-Reducing Policies? The Impact of Waste Reduction Policy Instruments on Collection and Processing Costs of Municipal Solid Waste. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 1429–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jaeger, S.; Rogge, N. Waste Pricing Policies and Cost-Efficiency in Municipal Waste Services: The Case of Flanders. Waste Manag. Res. 2013, 31, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llanquileo-Melgarejo, P.; Molinos-Senante, M.; Romano, G.; Carosi, L. Evaluation of the Impact of Separative Collection and Recycling of Municipal Solid Waste on Performance: An Empirical Application for Chile. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Jin, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Song, X. The Evolution of the Spatial-Temporal Differences of Municipal Solid Waste Carbon Emission Efficiency in China. Energies 2022, 15, 3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-C. A Performance Evaluation of MSW Management Practice in Taiwan. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2010, 54, 1353–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- lo Storto, C. Measuring the Eco-Efficiency of Municipal Solid Waste Service: A Fuzzy DEA Model for Handling Missing Data. Util. Policy 2024, 86, 101706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.; Park, Y.-J. Eco-Efficiency Evaluation Considering Environmental Stringency. Sustainability 2017, 9, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Li, W.; Li, G.; Wang, Q. Does Upgrading Household Consumption Affect the Eco-Efficiency of China’s Solid Waste Management as Measured by Emissions? Util. Policy 2024, 89, 101767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ding, H.; Liu, L. Eco-Efficiency Measurement of Industrial Sectors in China: A Hybrid Super-Efficiency DEA Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinos-Senante, M.; Maziotis, A.; Sala-Garrido, R.; Mocholi-Arce, M. The Eco-Efficiency of Municipalities in the Recycling of Solid Waste: A Stochastic Semi-Parametric Envelopment of Data Approach. Waste Manag. Res. 2023, 41, 1036–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Antequera, L.; Gémar, G.; Molinos-Senante, M.; Gómez, T.; Caballero, R.; Sala-Garrido, R. Eco-Efficiency Assessment of Municipal Solid Waste Services: Influence of Exogenous Variables. Waste Manag. 2021, 130, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, G.; Molinos-Senante, M.; Carosi, L.; Llanquileo-Melgarejo, P.; Sala-Garrido, R.; Mocholi-Arce, M. Assessing the Dynamic Eco-Efficiency of Italian Municipalities by Accounting for the Ownership of the Entrusted Waste Utilities. Util. Policy 2021, 73, 101311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Ye, A. Consumption Upgrading and Industrial Structural Change: A General Equilibrium Analysis and Empirical Test with Low-Carbon Green Transition Constraints. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, X.; Shao, X.; Gao, K. The Relationship between Urbanization and Consumption Upgrading of Rural Residents under the Sustainable Development: An Empirical Study Based on Mediation Effect and Threshold Effect. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrescu, I.-E.; Lombardi, M.; Lădaru, G.-R.; Munteanu, R.A.; Istudor, M.; Tărășilă, G.A. Influence of the Total Consumption of Households on Municipal Waste Quantity in Romania. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Li, J.; Zhou, K. From Intention to Behavior: Comprehending Residents’ Waste Sorting Intention and Behavior Formation Process. Waste Manag. 2020, 113, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo-Horna, L.; Kahhat, R.; Vázquez-Rowe, I. Unveiling the Energy Consumption-Food Waste Nexus in Households: A Focus on Key Predictors of Food Waste Generation. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2024, 26, 2099–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Gu, W.; Wang, C. The Impact of Consumption Patterns on the Generation of Municipal Solid Waste in China: Evidences from Provincial Data. IJERPH 2019, 16, 1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, W.; Hu, Y. Internet Development, Consumption Upgrading and Carbon Emissions—An Empirical Study from China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, R.; Geng, W. Mechanisms and Effects of the Upgrading of Consumption Structure on Household Carbon Emissions —Evidence from the Yangtze River Economic Belt. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 374, 124050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q. Income Disparity, Consumption Patterns, and Trends of International Consumption Center City Construction, Based on a Test of China’s Consumer Market. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agriculture | Free Full-Text | Mechanism and Empirical Test of the Impact of Consumption Upgrading on Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity in China. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0472/13/1/151 (accessed on 27 October 2023).
- Sun, Y.; Liu, N.; Zhao, M. Factors and Mechanisms Affecting Green Consumption in China: A Multilevel Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Kong, Y.; Zhang, T. The Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Provincial Eco-Efficiency in China Based on SBM Modified Three-Stage Data Envelopment Analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 8557–8569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauscher, M.; Barbier, E.B. Biodiversity and Geography. Resour. Energy Econ. 2010, 32, 241–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahidzadeh, R.; Bertanza, G.; Sbaffoni, S.; Vaccari, M. Regional Industrial Symbiosis: A Review Based on Social Network Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 280, 124054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zou, J.; Zhang, Z. Does China’s Municipal Solid Waste Source Separation Program Work? Evidence from the Spatial-Two-Stage-Least Squares Models. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, D.; Hu, J.; Zhu, X.; Wang, H.; Jeon, C.; Kim, G.-M.; Zeng, Y. Carbon Emission of Municipal Solid Waste Under Different Classification Methods in the Context of Carbon Neutrality: A Case Study of Yunnan Province, China. Fuel 2024, 372, 132167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J. Spatiotemporal Patterns and Drivers of Carbon Emissions from Municipal Solid Waste Treatment in China. Waste Manag. 2023, 168, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Geng, L. Carbon Emissions Calculation from Municipal Solid Waste and the Influencing Factors Analysis in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 104, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Available online: https://www.ipcc-nggip.iges.or.jp/public/2006gl/index.html (accessed on 24 February 2024).
- Cai, B.; Lou, Z.; Wang, J.; Geng, Y.; Sarkis, J.; Liu, J.; Gao, Q. CH4 Mitigation Potentials from China Landfills and Related Environmental Co-Benefits. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar8400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, R.; Chen, J.; Zhang, T.; Gao, C.; Niu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhan, M.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, G. Influence of the Classification of Municipal Solid Wastes on the Reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions: A Case Study of Qingdao City, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 376, 134275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K.; Chang, T.-S.; Wu, C.-H. Handling Negative Data in Slacks-Based Measure Data Envelopment Analysis Models. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2020, 282, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, K.; Wang, Y.; Pei, J.; Tang, S.; Han, Z. Super Efficiency SBM-DEA and Neural Network for Performance Evaluation. Inf. Process. Manag. 2021, 58, 102728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. A Slacks-Based Measure of Super-Efficiency in Data Envelopment Analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 143, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, Q. Sustainability Efficiency Assessment of Listed Companies in China: A Super-Efficiency SBM-DEA Model Considering Undesirable Output. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 47588–47604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G. How Does Agro-Tourism Integration Influence the Rebound Effect of China’s Agricultural Eco-Efficiency? An Economic Development Perspective. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 921103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceriani, L.; Verme, P. The Origins of the Gini Index: Extracts from Variabilità e Mutabilità (1912) by Corrado Gini. J. Econ. Inequal. 2012, 10, 421–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongheng, D.; Shan, X.; Fei, L.; Jinglin, T.; Liyue, G.; Xiaoying, L.; Tingxiao, W.; Hongrui, W. GIS-Based Assessment of Spatial and Temporal Disparities of Urban Health Index in Shenzhen, China. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1429143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harke, F.H.; Merk, M.S.; Otto, P. Estimation of Asymmetric Spatial Autoregressive Dependence on Irregular Lattices. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Yan, T.; Liu, X.; Bao, A. Urban Land Expansion, Fiscal Decentralization and Haze Pollution: Evidence from 281 Prefecture-Level Cities in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 323, 116198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesage, J.P.; Pace, R.K. Introduction to Spatial Econometrics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- China National Statistical Yearbook. Available online: https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/ndsj/ (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- Zhang, C.; Dong, H.; Geng, Y.; Song, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhuang, M. Carbon Neutrality Prediction of Municipal Solid Waste Treatment Sector Under the Shared Socioeconomic Pathways. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 186, 106528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zheng, L. Structure Characteristics and Development Sustainability of Municipal Solid Waste Treatment in China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 152, 110391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Wang, T. Spatial Effects of Urban Expansion on Air Pollution and Eco-Efficiency: Evidence from Multisource Remote Sensing and Statistical Data in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 367, 132973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puertas, R.; Guaita-Martinez, J.M.; Carracedo, P.; Ribeiro-Soriano, D. Analysis of European Environmental Policies: Improving Decision Making through Eco-Efficiency. Technol. Soc. 2022, 70, 102053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Ouyang, X.; Sun, Y. Does International Trade Contribute to Eco-Efficiency Performance Improvement? Evidence from the Emerging and Developing Economies. Energy Effic. 2022, 15, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xing, L.; Zhou, J.; Wang, K.; Lu, J.; Han, X. Spatial and Temporal Evolution and Driving Factors of County Solid Waste Harmless Disposal Capacity in China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 10, 1056054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, G.V.; Gastaldi, M.; Rapposelli, A.; Romano, G. Assessing Efficiency of Urban Waste Services and the Role of Tariff in a Circular Economy Perspective: An Empirical Application for Italian Municipalities. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 323, 129097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemat, B.; Razzaghi, M.; Bolton, K.; Rousta, K. The Role of Food Packaging Design in Consumer Recycling Behavior—A Literature Review. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Lin, T.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, L.; Ye, Z.; Cui, S. Path Analysis of Factors Influencing Household Solid Waste Generation: A Case Study of Xiamen Island, China. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2016, 18, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gong, E.; Zhao, C. Research on the Relation between Foreign Trade and Green Economic Efficiency in Subdeveloped Region: Based on Data from Central China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Zheng, Y.; Tang, Q.; Ning, M.; Lei, Y. Incorporating VOC Emission Control in China’s Hazardous Waste Regulatory System. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 15569–15571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Jia, L.; Hou, Y.; Wu, X. The Impact of Economic Growth and Tiered Medical Policy on the Medical Waste Generation: An Empirical Analysis Based on the Environmental Kuznets Curve Model. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 824435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Chen, Q.; Na, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, J. Impacts of Industrial Agglomeration on Industrial Pollutant Emissions: Evidence Found in the Lanzhou–Xining Urban Agglomeration in Western China. Front. Public Health 2023, 10, 1109139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, H.; Li, D.; Duan, Y.; Han, Z. Research on the Spatial Correlation and Drivers of Industrial Agglomeration and Pollution Discharge in the Yellow River Basin. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1004343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano-Monserrate, M.A.; Ruano, M.A.; Ormeño-Candelario, V. Determinants of Municipal Solid Waste: A Global Analysis by Countries’ Income Level. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 62421–62430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Liu, Y.; Diao, W. Assessing Regional Differences in Green Innovation Efficiency of Industrial Enterprises in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, R.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, X. Index of Regional Innovation and Entrepreneurship in China (IRIEC). 2021. Available online: https://cer.gsm.pku.edu.cn/info/1037/1059.htm (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Xie, B.-C.; Jiang, J.; Chen, X.-P. Policy, Technical Change, and Environmental Efficiency: Evidence of China’s Power System from Dynamic and Spatial Perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 323, 116232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Liu, S.; Fu, C.; Li, Y. A Joint Optimal Emissions Tax and Solid Waste Tax for Extended Producer Responsibility. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 128007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagawa, S.; Nakamura, S.; Inamura, H.; Yamada, M. Measuring Spatial Repercussion Effects of Regional Waste Management. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2007, 51, 141–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xu, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, C.; Jia, R. Does the Expansion of Highways Contribute to Urban Haze Pollution? Evidence from Chinese Cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 128018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Unit | Mean | Minimum | Maximum | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Garbage Collection (GC) | 10,000 tons | 627.74 | 50.9 | 3347.3 | 486.94 |
| Workforce (WME) | 10,000 people | 7.95 | 0.80 | 21.70 | 3.95 |
| Waste Treatment Investment (INV) | 100 million RMB | 71.18 | 0.01 | 973.04 | 121.49 |
| Solid Waste Treatment Capacity (WTC) | 100 tons per day | 187.35 | 4.00 | 1767.36 | 187.96 |
| Waste Treatment (WT) | 10,000 tons | 592.27 | 59.15 | 3345.77 | 480.74 |
| Greenhouse Gas Emissions (GHGs) | 10,000 tons | 142.54 | 9.72 | 803.26 | 108.78 |
| Waste Eco-efficiency (WE) | / | 0.41 | 0.11 | 1.16 | 0.20 |
| Consumption Updating (CU) | / | −1.54 | −3.53 | −0.08 | 0.68 |
| Educational Year (EY) | / | 2.19 | 1.89 | 2.55 | 0.11 |
| Dependency Ratio (DR) | / | 0.38 | 0.19 | 0.58 | 0.07 |
| Dependence on Foreign Trade (FT) | / | −1.34 | −4.51 | 0.89 | 0.98 |
| Pollution Control (PC) | / | 2.80 | 0.04 | 20.35 | 2.56 |
| ER | 0.21 | 0.08 | 0.54 | 0.10 | |
| Infrastructure Level (INF) | / | 3.57 | 2.12 | 4.46 | 0.41 |
| Economic Level (GDP) | / | 4.54 | 3.76 | 5.26 | 0.28 |
| Population Density (PD) | / | 0.46 | −2.96 | −0.55 | 0.46 |
| Industrial Agglomeration (IA) | / | −2.39 | −4.75 | −1.12 | 0.55 |
| Regional innovation index (RI) | / | 1.44 | 0.82 | 1.53 | 0.09 |
| Year | Overall | Intra-Regional Difference | Inter-Regional Difference | Contribution Rate | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eastern | Central | Western | Eastern and Central | Eastern and Western | Central and Western | Intra-Regional | Inter-Regional | Super-Variation Density | ||
| 2006 | 0.40 | 0.34 | 0.18 | 0.14 | 0.47 | 0.56 | 0.22 | 26.70 | 69.05 | 4.25 |
| 2007 | 0.37 | 0.32 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 0.46 | 0.51 | 0.16 | 25.95 | 70.45 | 3.60 |
| 2008 | 0.37 | 0.31 | 0.17 | 0.07 | 0.47 | 0.50 | 0.15 | 25.61 | 70.66 | 3.73 |
| 2009 | 0.32 | 0.28 | 0.15 | 0.07 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.13 | 25.57 | 70.53 | 3.90 |
| 2010 | 0.31 | 0.27 | 0.17 | 0.05 | 0.40 | 0.42 | 0.13 | 25.59 | 69.33 | 5.08 |
| 2011 | 0.29 | 0.24 | 0.18 | 0.06 | 0.37 | 0.40 | 0.14 | 24.97 | 68.00 | 7.03 |
| 2012 | 0.28 | 0.25 | 0.20 | 0.06 | 0.34 | 0.38 | 0.16 | 26.50 | 64.52 | 8.98 |
| 2013 | 0.27 | 0.24 | 0.21 | 0.06 | 0.33 | 0.36 | 0.16 | 26.36 | 63.57 | 10.07 |
| 2014 | 0.27 | 0.24 | 0.21 | 0.06 | 0.32 | 0.36 | 0.17 | 26.57 | 62.76 | 10.67 |
| 2015 | 0.25 | 0.22 | 0.19 | 0.04 | 0.30 | 0.34 | 0.15 | 25.90 | 63.89 | 10.21 |
| 2016 | 0.23 | 0.20 | 0.18 | 0.04 | 0.28 | 0.32 | 0.15 | 25.43 | 64.47 | 10.09 |
| 2017 | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.04 | 0.26 | 0.28 | 0.12 | 25.98 | 64.32 | 9.70 |
| 2018 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.24 | 0.27 | 0.10 | 26.25 | 66.60 | 7.15 |
| 2019 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 0.22 | 0.26 | 0.08 | 25.89 | 67.91 | 6.20 |
| 2020 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.11 | 0.04 | 0.22 | 0.26 | 0.10 | 25.81 | 66.20 | 7.99 |
| 2021 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.11 | 0.07 | 0.17 | 0.25 | 0.14 | 26.71 | 64.65 | 8.64 |
| Year | WE | CU | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | p | I | p | |
| 2006 | 0.13 | 0.03 | 0.62 | 0.00 |
| 2007 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.30 | 0.00 |
| 2008 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.31 | 0.00 |
| 2009 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.30 | 0.00 |
| 2010 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.31 | 0.00 |
| 2011 | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.29 | 0.00 |
| 2012 | 0.18 | 0.04 | 0.27 | 0.00 |
| 2013 | 0.17 | 0.05 | 0.25 | 0.00 |
| 2014 | −0.05 | 0.85 | 0.22 | 0.01 |
| 2015 | −0.05 | 0.91 | 0.23 | 0.01 |
| 2016 | 0.16 | 0.04 | 0.22 | 0.01 |
| 2017 | 0.17 | 0.06 | 0.23 | 0.01 |
| 2018 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.24 | 0.00 |
| 2019 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.27 | 0.00 |
| 2020 | 0.28 | 0.00 | 0.23 | 0.01 |
| 2021 | 0.28 | 0.00 | 0.23 | 0.01 |
| Test | WE | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| LM test | LM-error | 7.09 | 0.01 |
| Robust LM-error | 14.73 | 0.00 | |
| LM-lag | 1.94 | 0.16 | |
| Robust LM-lag | 9.57 | 0.00 | |
| LR test | LR-SDM/SAR | 37.22 | 0.00 |
| LR-SDM/SEM | 42.28 | 0.00 | |
| Wald test | Wald-SDM/SAR | 38.17 | 0.00 |
| Wald-SDM/SEM | 43.07 | 0.00 | |
| Spatial-temporal fixed effects test | Lrtest-id-both | 67.82 | 0.00 |
| Lrtest-time-both | 739.13 | 0.00 | |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ind | Time | Both | Wx-Ind | Wx-Time | Wx-Both | |
| CU | 0.359 *** | 0.321 *** | 0.332 *** | −0.118 | 0.429 *** | 0.349 ** |
| (−6.490) | (−6.850) | (−6.360) | (−1.11) | (−3.310) | (−2.650) | |
| EY | −0.114 | 2.101 *** | 0.134 | 0.268 | 1.092 | 0.145 |
| (−0.30) | (−8.210) | (−0.360) | (−0.480) | (−1.580) | (−0.170) | |
| FT | −0.0728 * | −0.122 *** | −0.0637 * | −0.078 | 0.100 | −0.224 ** |
| (−2.29) | (−4.77) | (−2.14) | (−1.250) | −1.300 | (−2.820) | |
| ER | 0.017 | 0.022 | 0.004 | 0.0512 * | −0.069 | −0.032 |
| (−1.200) | (−1.250) | (−0.320) | (−2.160) | (−1.62) | (−0.99) | |
| DR | −0.208 | 0.266 * | −0.184 | 0.041 | 0.435 | 0.806 * |
| (−1.55) | (−2.230) | (−1.42) | (−0.210) | (−1.440) | (−2.390) | |
| INF | 0.073 | −0.996 *** | 0.175 * | 1.209 *** | 0.122 | −0.217 |
| (−0.970) | (−21.000) | (−2.370) | (−6.530) | (−0.760) | (−0.940) | |
| GDP | 0.413 | 0.139 | −0.677 | 1.093 * | −1.327 ** | 3.954 *** |
| (−1.120) | (−0.910) | (−1.780) | (−2.540) | (−3.280) | (−4.580) | |
| PD | 0.020 | −0.155 ** | 0.033 | 0.333 * | −0.032 | 0.629 *** |
| (−0.390) | (−2.79) | (−0.670) | (−2.360) | (−0.21) | (−4.400) | |
| IA | 0.055 | 0.019 | −0.027 | −0.312 ** | −0.315 * | −0.871 *** |
| (−1.180) | (−0.420) | (−0.60) | (−2.61) | (−2.04) | (−5.41) | |
| RI | 0.048 | −0.144 | 0.027 | 0.141 | 0.245 | 0.046 |
| (−0.390) | (−0.790) | (−0.230) | (−0.580) | (−0.580) | (−0.170) | |
| rho | 0.406 *** | 0.101 | 0.0664 * | |||
| (−6.840) | (−1.310) | (−0.910) | ||||
| sigma2 | 0.0250 *** | 0.0557 *** | 0.0215 *** | |||
| (−15.320) | (−15.480) | (−15.480) | ||||
| Individual fixed | Yes | No | Yes | |||
| Time fixed | No | Yes | Yes | |||
| R2 | 0.118 | 0.506 | 0.064 | |||
| N | 480 | 480 | 480 |
| Direct | Indirect | Total | Direct | Indirect | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CU | 0.336 *** | 0.395 ** | 0.730 *** | INF | 0.173 * | −0.217 | −0.044 |
| −0.052 | −0.145 | −0.132 | −0.069 | −0.244 | −0.254 | ||
| EY | 0.096 | 0.119 | 0.215 | GDP | −0.710 * | −4.159 *** | −4.869 *** |
| −0.323 | −1.044 | −1.133 | −0.349 | −0.875 | −0.955 | ||
| FT | −0.0637 * | −0.250 *** | −0.313 *** | PD | 0.031 | 0.678 *** | 0.709 *** |
| −0.031 | −0.074 | −0.072 | −0.044 | −0.136 | −0.147 | ||
| ER | 0.005 | −0.027 | −0.022 | IA | −0.032 | −0.961 *** | −0.993 *** |
| −0.015 | −0.033 | −0.038 | −0.035 | −0.156 | −0.164 | ||
| DR | −0.206 | 0.843 * | 0.636 | RI | 0.025 | 0.054 | 0.079 |
| −0.149 | −0.375 | −0.410 | −0.121 | −0.313 | −0.261 | ||
| rho | 0.0664 * | sigma2 | 0.0215 *** | ||||
| −0.073 | −0.001 | ||||||
| Fixed effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | R2 | 0.064 | R2 | 0.064 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CU | 0.410 *** | 0.365 *** | 0.421 *** | 0.048 | −0.161 | −0.030 |
| −0.054 | −0.059 | −0.060 | −0.103 | −0.129 | −0.120 | |
| EY | 0.100 | −0.461 | −0.258 | −0.291 | 0.740 | 1.055 |
| −0.388 | −0.396 | −0.393 | −0.855 | −0.928 | −0.846 | |
| FT | −0.0996 *** | −0.122 *** | −0.123 *** | 0.029 | 0.152 * | 0.155 * |
| −0.030 | −0.031 | −0.030 | −0.053 | −0.076 | −0.071 | |
| ER | −0.001 | 0.001 | −0.003 | −0.037 | −0.051 | −0.0782 * |
| −0.014 | −0.014 | −0.014 | −0.029 | −0.034 | −0.032 | |
| DR | 0.022 | 0.089 | 0.092 | −0.269 | 0.828 ** | 0.911 *** |
| −0.136 | −0.137 | −0.137 | −0.259 | −0.311 | −0.275 | |
| INF | 0.017 | −0.017 | −0.017 | −0.430 * | 0.299 | −0.116 |
| −0.079 | −0.079 | −0.077 | −0.203 | −0.226 | −0.218 | |
| GDP | −0.409 | −1.292 *** | −1.204 ** | −2.361 ** | 1.074 | −1.477 |
| −0.395 | −0.385 | −0.381 | −0.760 | −0.999 | −0.846 | |
| PD | 0.090 | 0.147 ** | 0.119 * | 0.341 ** | −0.244 ** | −0.156 * |
| −0.049 | −0.051 | −0.050 | −0.122 | −0.078 | −0.077 | |
| IA | −0.018 | −0.113 * | −0.078 | −0.013 | −0.119 | −0.176 * |
| −0.045 | −0.052 | −0.049 | −0.119 | −0.076 | −0.074 | |
| RI | −0.038 | 0.029 | 0.003 | 0.238 | 0.304 | 0.205 |
| −0.108 | −0.098 | −0.096 | −0.182 | −0.207 | −0.195 | |
| rho | 0.277 *** | 0.076 | 0.129 * | |||
| −0.057 | −0.069 | −0.066 | ||||
| sigma2 | 0.0227 *** | 0.0242 *** | 0.0239 *** | |||
| −0.001 | −0.002 | −0.002 | ||||
| Fixed effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||
| N | 480 | 480 | 480 | |||
| R2 | 0.043 | 0.089 | 0.023 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lagged One Period | Lagged One Period | Lagged Two Period | Lagged Two Period | |
| WE_1 | 0.677 *** | 0.671 *** | 0.624 *** | 0.613 *** |
| −0.040 | −0.028 | −0.072 | −0.046 | |
| WE_2 | 0.061 | 0.061 | ||
| −0.061 | −0.042 | |||
| CU | 0.055 | 0.040 | ||
| −0.050 | −0.051 | |||
| Control variables | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Individual Fixed | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Time Fixed | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| rho | 0.155 *** | 0.016 *** | 0.161 *** | 0.024 *** |
| −0.034 | −0.064 | −0.034 | −0.064 | |
| sigma2 | 0.012 *** | 0.011 *** | 0.012 *** | 0.011 *** |
| −0.002 | −0.001 | −0.002 | −0.001 |
| WE | Eastern Region | Central Region | Western Region | Delete Municipalities |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CU | −0.135 | 0.289 *** | 0.214 ** | 0.428 *** |
| (−1.48) | (3.77) | (2.59) | (8.51) | |
| CVs | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| WX | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| rho | −0.337 *** | 0.252 ** | −0.237 * | 0.375 *** |
| (0.78) | (3.11) | (−2.22) | (5.86) | |
| sigma2 | 0.0134 *** | 0.0059 *** | 0.0191 *** | 0.0174 *** |
| (9.71) | (8.44) | (8.42) | (14.42) | |
| Fixed effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 192 | 144 | 144 | 416 |
| R2 | 0.0273 | 0.317 | 0.512 | 0.0255 |
| Ind | Time | Both | Wx-Ind | Wx-Time | Wx-Both | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CU_lag1 | 0.234 *** | 0.244 *** | 0.220 *** | −0.0190 | 0.536 *** | 0.406 ** |
| (4.50) | (5.25) | (4.40) | (−0.19) | (4.07) | (3.23) | |
| EY_lag1 | −0.570 | 2.113 *** | −0.376 | 1.392 ** | 0.806 | 1.138 |
| (−1.61) | (8.33) | (−1.05) | (2.63) | (1.17) | (1.37) | |
| FT_lag1 | −0.0539 | −0.103 *** | −0.0420 | −0.142 * | 0.106 | −0.213 ** |
| (−1.78) | (−4.01) | (−1.45) | (−2.33) | (1.37) | (−2.77) | |
| ER_lag1 | 0.0167 | 0.0404 * | 0.00677 | 0.0555 * | −0.0638 | −0.0146 |
| (1.25) | (2.35) | (0.52) | (2.30) | (−1.51) | (−0.49) | |
| DR_lag1 | −0.370 ** | 0.157 | −0.388 ** | 0.0784 | 0.183 | 0.407 |
| (−2.95) | (1.33) | (−3.17) | (0.42) | (0.61) | (1.28) | |
| INF_lag1 | 0.0986 | −1.010 *** | 0.164 * | −0.979 *** | 0.326 * | −0.321 |
| (1.36) | (−21.63) | (2.30) | (−5.57) | (2.06) | (−1.45) | |
| GDP_lag1 | 0.765 * | 0.136 | −0.164 | 0.101 | −1.760 *** | −3.922 *** |
| (2.24) | (0.88) | (−0.45) | (0.25) | (−4.24) | (−4.77) | |
| PD_lag1 | −0.0410 | −0.156 ** | −0.0165 | 0.646 *** | 0.0572 | 0.883 *** |
| (−0.87) | (−2.86) | (−0.36) | (4.91) | (0.38) | (6.43) | |
| IA_lag1 | 0.0860 * | 0.0311 | 0.0234 | −0.434 *** | −0.274 | −0.820 *** |
| (1.99) | (0.72) | (0.55) | (−3.63) | (−1.78) | (−5.36) | |
| RI_lag1 | 0.0347 | −0.246 | −0.0143 | 0.0969 | 0.850 | 0.222 |
| (0.30) | (−1.36) | (−0.13) | (0.42) | (1.91) | (0.81) | |
| rho | 0.479 *** | 0.207 ** | 0.247 *** | |||
| (8.13) | (2.68) | (3.50) | ||||
| R2 | 0.0622 | 0.533 | 0.0486 | |||
| Log_L | 228.1229 | 228.6259 | 261.8842 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, B.; Li, W. Spatial Effects and Driving Factors of Consumption Upgrades on Municipal Solid Waste Eco-Efficiency, Considering Emission Outputs. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2356. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062356
Jin B, Li W. Spatial Effects and Driving Factors of Consumption Upgrades on Municipal Solid Waste Eco-Efficiency, Considering Emission Outputs. Sustainability. 2025; 17(6):2356. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062356
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Baihui, and Wei Li. 2025. "Spatial Effects and Driving Factors of Consumption Upgrades on Municipal Solid Waste Eco-Efficiency, Considering Emission Outputs" Sustainability 17, no. 6: 2356. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062356
APA StyleJin, B., & Li, W. (2025). Spatial Effects and Driving Factors of Consumption Upgrades on Municipal Solid Waste Eco-Efficiency, Considering Emission Outputs. Sustainability, 17(6), 2356. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062356







