Temporal–Spatial Variations in Physicochemical Factors and Assessing Water Quality Condition in River–Lake System of Chaohu Lake Basin, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
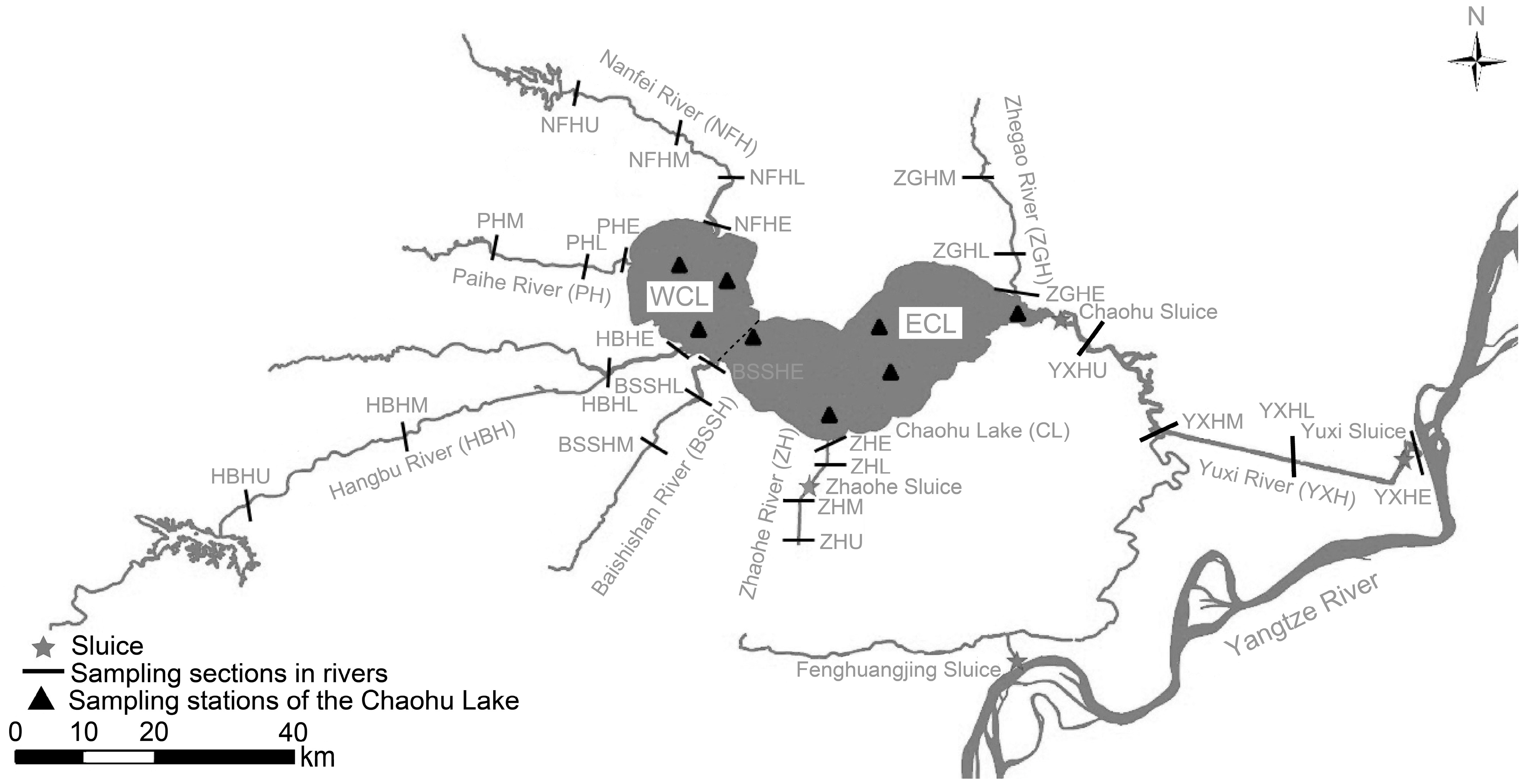
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
2.2. Laboratory Analyses of Water Physicochemical Parameters
2.3. Evaluation Method of Nutritional Status of Rivers and Lakes
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Spatiotemporal Distribution Pattern of Water Quality Parameters
3.2. Water Quality Patterns Based on Water Parameters
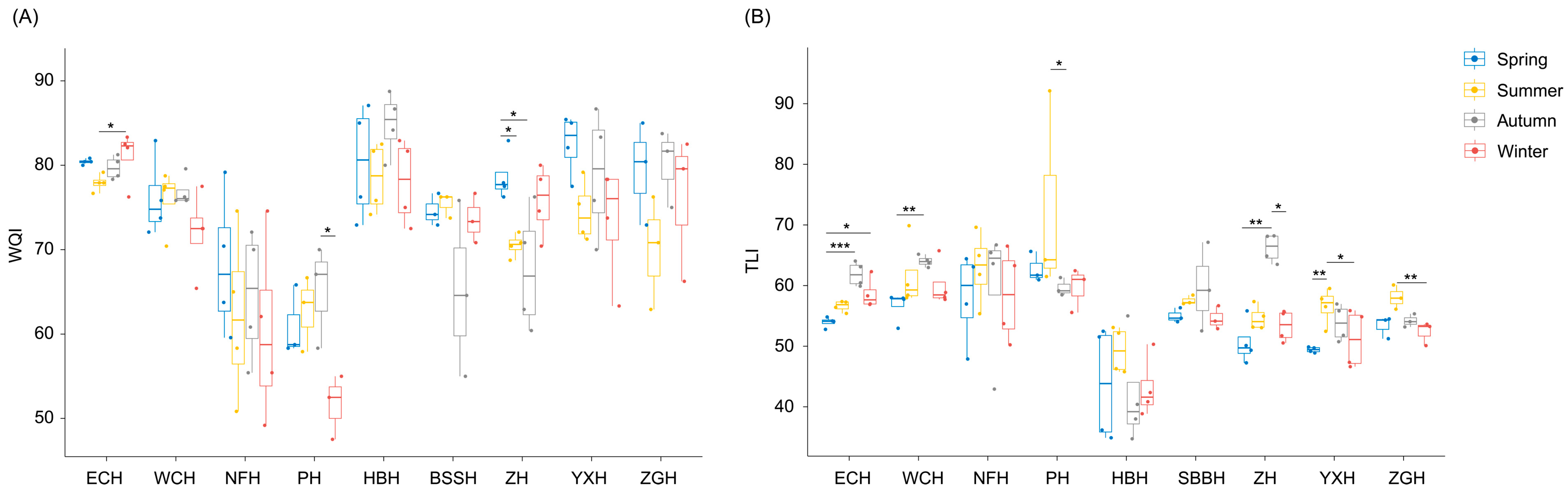
3.3. TLI and WQI of the Chaohu Lake and River Water
4. Discussion
4.1. Water Qualities and Patterns Based on Water Parameters
4.2. Water Quality Assessment Based on the WQI and TLI
4.3. Comparison of TLI and WQI
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huisman, J.; Codd, G.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Ibelings, B.W.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Visser, P.M. Cyanobacterial blooms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payen, S.; Cosme, N.; Elliott, A.H. Freshwater eutrophication: Spatially explicit fate factors for nitrogen and phosphorus emissions at the global scale. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2021, 26, 388–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, J.J.; DelSontro, T.; Downing, J.A. Eutrophication will increase methane emissions from lakes and impoundments during the 21st century. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paerl, H.W.; Hall, N.S.; Hounshell, A.G.; Luettich, R.A., Jr.; Rossignol, K.L.; Osburn, C.L.; Bales, J. Recent increase in catastrophic tropical cyclone flooding in coastal North Carolina, USA: Long-term observations suggest a regime shift. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; McIntyre, P.B.; Gessner, M.O.; Dudgeon, D.; Prusevich, A.; Green, P.; Glidden, S.; Bunn, S.E.; Sullivan, C.A.; Liermann, C.R.; et al. Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity. Nature 2010, 467, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernauer, T.; Böhmelt, T. International conflict and cooperation over freshwater resources. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Qin, B.; Shi, K.; Deng, J.Z.Y. Aquatic vegetation in response to increased eutrophication and degraded light climate in Eastern Lake Taihu: Implications for lake ecological restoration. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Li, K.; Zhang, L.; Cai, Y.; Wang, X.; Heino, J. Nutrient enrichment homogenizes taxonomic and functional diversity of benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages in shallow lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2019, 64, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, S.C.; Housley, L.; Back, J.A.; King, R.S. Freshwater eutrophication drives sharp reductions in temporal beta diversity. Ecology 2018, 99, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behmel, S.; Damour, M.; Ludwig, R.; Rodriguez, M.J. Water quality monitoring strategies—A review and future perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 1312–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Bing, H.; Peng, J.; Dong, F.; Gao, J.; Arhonditsis, G.B. Characterizing the river water quality in China: Recent progress and on-going challenges. Water Res. 2021, 201, 117309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, D.V.; Bradley, C.; Gettel, G.M.; Hatvani, I.G.; Hein, T.; Kovács, J.; Liska, I.; Oliver, D.M.; Tanos, P.; Trásy, B.; et al. Developments in water quality monitoring and management in large river catchments using the Danube River as an example. Environ. Sci. Policy 2016, 64, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zy Harifidy, R.; Zy Misa Harivelo, R.; Hiroshi, I.; Jun, M.; Kazuyoshi, S. A systematic review of water resources assessment at a large river basin scale: Case of the major river basins in Madagascar. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Lai, X.; Li, K. Water quality assessment of rivers in Lake Chaohu Basin (China) using water quality index. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhu, S.; Hu, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, X.; Peng, Z. Assessment of impacts of water transfer on lake flow and water quality in Lake Chaohu using a three-dimensional hydrodynamic-ecological model. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 46, 101333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Guo, Y.; Qi, P.; Wan, N.; Lai, X. Analysis of accuracy of GPM IMERGE precipitation data in Chaohu Basin. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 27, 188–193. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Shen, M.; Duan, H. Temporal and spatial distribution of algal blooms in Lake Chaohu, 2000–2015. J. Lake Sci. 2017, 29, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kong, X.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, G.; Hu, W.; Zhou, X. Retention of nitrogen and phosphorus in Lake Chaohu, China: Implications for eutrophication management. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 41488–41502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jiang, X.; Jin, X. Classification and pollution characteristic analysis for inflow rivers of Chaohu Lake. Environ. Sci. 2011, 32, 2834–2839. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Jiang, X.; Jin, X. Spatial-temporal variations of aquatic environmental factors and their influences to algal blooming in Lake Chaohu. J. Lake Sci. 2011, 23, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Liu, G.; Jiang, M.; Wang, R.; Zheng, L. Partition characteristics and correlation of heavy metal between sediment and surface water from Lake Chaohu. J. Univ. Sci. Technol. China 2011, 41, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Wu, X.; Liu, B.; Yan, D.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, Y. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of dissolved organic matter and influencing factors in Lake Chaohu. Environ. Sci. 2015, 36, 3186–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, S.; Zhou, C.; Liu, G.; Wu, L.; Wang, P. Spatial and temporal distributions of nitrogen and phosphate in the Chaohu Lake. Environ. Sci. 2016, 37, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Yin, H.; Deng, J.; Gao, F.; Hu, W.; Gao, J. Spring community structure of phytoplankton of Lake Chaohu and its relationship to environmental factors. J. Lake Sci. 2010, 22, 950–956. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, Y.; Gao, F.; Deng, J.; Hu, W.; Gao, J.; Zhao, Z. Biological assessment of water quality in Chaohu Lake watershed: A case study of benthic macroinvertebrate. Chin. J. Ecol. 2012, 31, 916–922. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Zhou, M.; Shen, Z.; Geng, M.; Feng, W. Characteristics of zooplankton community and water quality Assessment in Chaohu Lake and its tributaries. Chin. J. Zool. 2017, 52, 792–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Yu, Y.; Yi, Y. Analysis of future nitrogen and phosphorus loading in watershed and the risk of lake blooms under the influence of complex factors: Implications for management. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, R.K. An index number system for rating water quality. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1965, 37, 300–306. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, R.M.; McClelland, N.I.; Deininger, R.A.; Tozer, R.G. A water quality index-Do we dare? Water Sew. Works 1970, 117, 339–343. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, M.G.; Nash, S.; Olbert, A.I. A review of water quality index models and their use for assessing surface water quality. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Ji, L.; Chen, X.; Ni, J.; Zhang, Y.; Geng, M. Distribution of zooplankton functional groups in the Chaohu Lake Basin, China. Water 2022, 14, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesce, S.; Wunderlin, D.A. Use of water quality indices to verify the impact of Córdoba City (Argentina) on Suquía River. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2915–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohebbi, M.R.; Saeedi, R.; Montazeri, A.; Azam Vaghefi, K.; Labbafi, S.; Oktaie, S.; Abtahi, M.; Mohagheghian, A. Assessment of water quality in groundwater resources of Iran using a modified drinking water quality index (DWQI). Ecol. Indic. 2013, 30, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, X.; Shao, D.; Zhong, H.; Liang, J. Evaluation of water quality in the South-to-North Water Diversion Project of China using the water quality index (WQI) method. Water Res. 2020, 178, 115781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, T.; Sadiq, R.; Mazumder, A. Adaptation and evaluation of the Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment Water Quality Index (CCME WQI) for use as an effective tool to characterize drinking source water quality. Water Res. 2012, 46, 3544–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Xia, W.; Lu, Y.; Gang, D.-D.; Lin, L.-S. A holistic assessment of water quality condition and spatiotemporal patterns in impounded lakes along the Eastern Route of China’s South-to-North Water Diversion Project. Water Res. 2020, 185, 116275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Yang, W.; Yao, R.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Lin, A. Evaluating surface water quality using water quality index in Beiyun River, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 35449–35458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Zhu, G.; Cai, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhu, M.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B. The limitations of comprehensive trophic level index (TLI) in the eutrophication assessment of lakes along the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River during summer season and recommendation for its improvement. J. Lake Sci. 2020, 32, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhao, J.; Peng, W.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Q.; Fu, Y.; Duan, M. Stochastic trophic level index model: A new method for evaluating eutrophication state. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 280, 111826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, D.; Zhu, J.; Zou, B.; Ma, Z.; Xu, J.; Li, L. Identify the seasonal differences in water quality and pollution sources between river-connected and gate-controlled lakes in the Yangtze River Basin. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 206, 116760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Cai, Y.; Deng, J. Assessing river water quality using water quality index in Lake Taihu Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajloon, F.H.; Dong, X.; Ayejoto, D.A.; Ayeni, E.A.; Sabo, M.Y. Seasonal assessment of water quality and water quality index (WQI) variations, in Jiangsu Kunshan Tianfu National Wetland Park, China. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2024, 104, 5444–5463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cao, X.; Huo, S.; Ma, C.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Tong, Y.; Wu, F. Changes in China’s river water quality since 1980: Management implications from sustainable development. npj Clean Water 2023, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, S.; Li, J.; Zeng, L.; Chen, X. Seasonal and interannual changes (2005–2021) of lake water quality and the implications for sustainable management in a rapidly growing metropolitan region, central China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 36995–37009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Chang, F.; Wen, X.; Duan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, H. Seasonal variation in the water quality and eutrophication of Lake Xingyun in Southwestern China. Water 2022, 14, 3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vliet, M.T.H.; Ludwig, F.; Zwolsman, J.J.G.; Weedon, G.P.; Kabat, P. Global river temperatures and sensitivity to atmospheric warming and changes in river flow. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W02544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Xia, R.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Song, J.; Dou, J. Spatial response of water level and quality shows more significant heterogeneity during dry seasons in large river-connected lakes. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Cui, H.; Liu, X.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, H. Water pollution characteristics and analysis of Chaohu Lake Basin by using different assessment methods. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 18168–18181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Xiao, Q.; Li, X. Urban rivers are hotspots of riverine greenhouse gas (N2O, CH4, CO2) emissions in the mixed-landscape Chaohu Lake Basin. Water Res. 2021, 189, 116624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Tang, X.; Jiang, C.; Ye, R.; Qian, X. Study of the response of water quality to the inflows in the water source region of Chaohu Lake. Environ. Prot. Sci. 2018, 44, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Li, J.X.; Li, G.W.; Li, Y.; Xi, B.D.; Wu, Y.W.; Li, C.L.; Li, W.; Zhang, L.Y. The eutrophication and its regional heterogeneity in typical lakes of China. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2018, 42, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Du, Y.; Yu, S.; Luo, J.; Duan, H. Human activities determine quantity and composition of dissolved organic matter in lakes along the Yangtze River. Water Res. 2020, 168, 115132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koçer, M.A.T.; Sevgili, H. Parameters selection for water quality index in the assessment of the environmental impacts of land-based trout farms. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 36, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shao, S.; Liu, C.; Xu, T.; Fan, C. Forms of nutrients in rivers flowing into Lake Chaohu: A comparison between urban and rural rivers. Water 2015, 7, 4523–4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Deng, H.; Wang, D.; Ye, M.; Tan, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xu, S. Nitrous oxide emissions in the Shanghai River network: Implications for the effects of urban sewage and IPCC methodology. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 2999–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Yuan, X.; Wu, N.; Zhang, Y.; Yue, J.; Zhang, Q.; Diao, Y.; Zhou, L. Effect of watershed urbanization on N2O emissions from the Chongqing Metropolitan River Network, China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 171, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, Y.; Chen, H.; Yuan, X.; Peng, C.; Yue, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, L. CH4 concentrations and fluxes in a subtropical metropolitan river network: Watershed urbanization impacts and environmental controls. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, X.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Li, S.; Han, S. An urban polluted river as a significant hotspot for water–atmosphere exchange of CH4 and N2O. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.M.; Kaushal, S.S.; Beaulieu, J.J.; Pennino, M.J.; Welty, C. Influence of infrastructure on water quality and greenhouse gas dynamics in urban streams. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 2831–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, X.; Yuan, X.; Gong, X.; Hou, C. Spatial-temporal characteristics and driving factors of greenhouse gas Emissions from rivers in a rapidly urbanizing area. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 2827–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şener, Ş.; Davraz, A.; Karagüzel, R. Evaluating the anthropogenic and geologic impacts on water quality of the Eğirdir Lake, Turkey. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 2527–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulsby, C.; Langan, S.J.; Neal, C. Environmental change, land use and water quality in Scotland: Current issues and future prospects. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 265, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharpley, A.N.; McDowell, R.W.; Kleinman, P.J. Phosphorus loss from land to water: Integrating agricultural and environmental management. Plant Soil 2001, 237, 287–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Tian, X.; Wu, S. Analysis of pollution flux in the Nanfeihe River and its treatment. Water Resour. Prot. 2020, 36, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şener, Ş.; Şener, E.; Davraz, A. Evaluation of water quality using water quality index (WQI) method and GIS in Aksu River (SW-Turkey). Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quick, A.M.; Reeder, W.J.; Farrell, T.B.; Tonina, D.; Feris, K.P.; Benner, S.G. Nitrous oxide from streams and rivers: A review of primary biogeochemical pathways and environmental variables. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 191, 224–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amneera, W.A.; Najib, N.W.A.Z.; Yusof, S.N.M.; Ragunathan, S. Water quality index of Perlis River, Malaysia. Int. J. Civ. Environ. Eng. 2013, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Hu, W.; Liu, G.; Zhang, H.; Gao, R. Large lake sluice operations during an extreme rainfall season greatly affect circulation and water quality dynamics of a shallow eutrophic lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Shi, X.; Yang, Z.; Chen, K. The variation of water quality from 2012 to 2018 in Lake Chaohu and the mitigating strategy on cyanobacterial blooms. J. Lake Sci. 2020, 32, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wu, L.; Ma, C.; Guan, H.; Sun, X.; Lu, S.; Shang, G.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xu, J.; et al. Holocene environmental evolution recorded by multi-proxies from Lacustrine sediments of the Hangbu River Valley, Lake Chaohu Basin, East China. J. Lake Sci. 2020, 32, 1869–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xia, S.; Ma, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, X. Temporal and spatial variation of water pollution in Zhegao River of Chao Lake Basin. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2011, 25, 243–248. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Huang, X.; Chen, H.; Godfray, H.C.J.; Wright, J.S.; Hall, J.W.; Gong, P.; Ni, S.; Qiao, S.; Huang, G.; et al. Managing nitrogen to restore water quality in China. Nature 2019, 567, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooney, R.J.; Stanley, E.H.; Rosenthal, W.C.; Esselman, P.C.; Kendall, A.D.; McIntyre, P.B. Outsized nutrient contributions from small tributaries to a Great Lake. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 28175–28182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, J.P.S.; Windsor, F.M.; Wilson, R.W.; Tyler, C.R. Global variation in freshwater physico-chemistry and its influence on chemical toxicity in aquatic wildlife. Biol. Rev. 2021, 96, 1528–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Shi, Z.; Yin, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, X.; Yang, Y.; Pan, L. Excessive use of chemical fertilizers in catchment areas raises the seasonal pH in natural freshwater lakes of the subtropical monsoon climate region. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, J.; Lauerwald, R.; Moosdorf, N. GLORICH—Global river chemistry database [dataset]. PANGAEA 2019, 10, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerin, A.J.; Weise, A.M.; Chu, J.W.F.; Wilcox, M.A.; Greene, E.S.; Therriault, T.W. High-resolution freshwater dissolved calcium and pH data layers for Canada and the United States. Sci. Data. 2024, 11, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Gao, L.; Xi, B.; Su, J.; Huo, S.; Ji, D.; Lü, N.; Zhu, J. Improved TLI index method and its application in nutritional states evaluation in Chaohu Lake. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2013, 7, 2127–2133. [Google Scholar]
- Editorial Committee of Encyclopedia of Rivers and Lakes in China. Encyclopedia of Rivers and Lakes in China. Section of Changjiang River Basin; China Water Power Press: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kannel, P.R.; Lee, S.; Lee, Y.S.; Kanel, S.R.; Khan, S.P. Application of water quality indices and dissolved oxygen as indicators for river water classification and urban impact assessment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 132, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Water Parameter | Season | Station | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | p | F | p | |
| WT (°C) | 2902.85 | <0.001 | 5.909 | <0.001 |
| DO (mg/L) | 20.991 | <0.001 | 4.752 | <0.001 |
| pH | 26.588 | <0.001 | 9.561 | <0.001 |
| Cond (μS/cm) | 17.293 | <0.001 | 20.039 | <0.001 |
| TN (mg/L) | 4.777 | 0.0038 | 34.092 | <0.001 |
| TP (mg/L) | 5.731 | 0.0012 | 9.912 | <0.001 |
| PO42−-P (mg/L) | 4.733 | 0.0040 | 6.806 | <0.001 |
| NH4−-N (mg/L) | 4.361 | 0.0063 | 8.067 | <0.001 |
| NO3−-N (mg/L) | 7.205 | 0.0002 | 26.646 | <0.001 |
| NO2−-N (mg/L) | 4.328 | 0.0066 | 9.223 | <0.001 |
| CODMn (mg/L) | 1.465 | 0.22895 | 3.472 | 0.0015 |
| BOD5 (mg/L) | 0.211 | 0.888286 | 12.714 | <0.001 |
| Chl a (mg/L) | 1.356 | 0.2609 | 7.765 | <0.001 |
| SD (cm) | 4.762 | 0.0039 | 23.979 | <0.001 |
| WQI | 4.055 | 0.009 | 21.569 | <0.001 |
| TLI | 7.514 | 0.000 | 16.477 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, L.; Liu, K.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Sang, R.; Zhu, H.; Wang, X.; Pang, Y.; Tong, J.; Liu, X.; et al. Temporal–Spatial Variations in Physicochemical Factors and Assessing Water Quality Condition in River–Lake System of Chaohu Lake Basin, China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2182. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17052182
Wu L, Liu K, Wang Z, Yang Y, Sang R, Zhu H, Wang X, Pang Y, Tong J, Liu X, et al. Temporal–Spatial Variations in Physicochemical Factors and Assessing Water Quality Condition in River–Lake System of Chaohu Lake Basin, China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(5):2182. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17052182
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Li, Kai Liu, Ziqi Wang, Yujie Yang, Rui Sang, Haoyue Zhu, Xitong Wang, Yuqing Pang, Jiangshan Tong, Xiangting Liu, and et al. 2025. "Temporal–Spatial Variations in Physicochemical Factors and Assessing Water Quality Condition in River–Lake System of Chaohu Lake Basin, China" Sustainability 17, no. 5: 2182. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17052182
APA StyleWu, L., Liu, K., Wang, Z., Yang, Y., Sang, R., Zhu, H., Wang, X., Pang, Y., Tong, J., Liu, X., Ma, M., Wang, Q., Ma, K., & Liu, F. (2025). Temporal–Spatial Variations in Physicochemical Factors and Assessing Water Quality Condition in River–Lake System of Chaohu Lake Basin, China. Sustainability, 17(5), 2182. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17052182






