An Investigation into the Formation of Tourists’ Pro-Environmental Behavior in Geotourism: Balancing Tourism and Ecosystem Preservation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
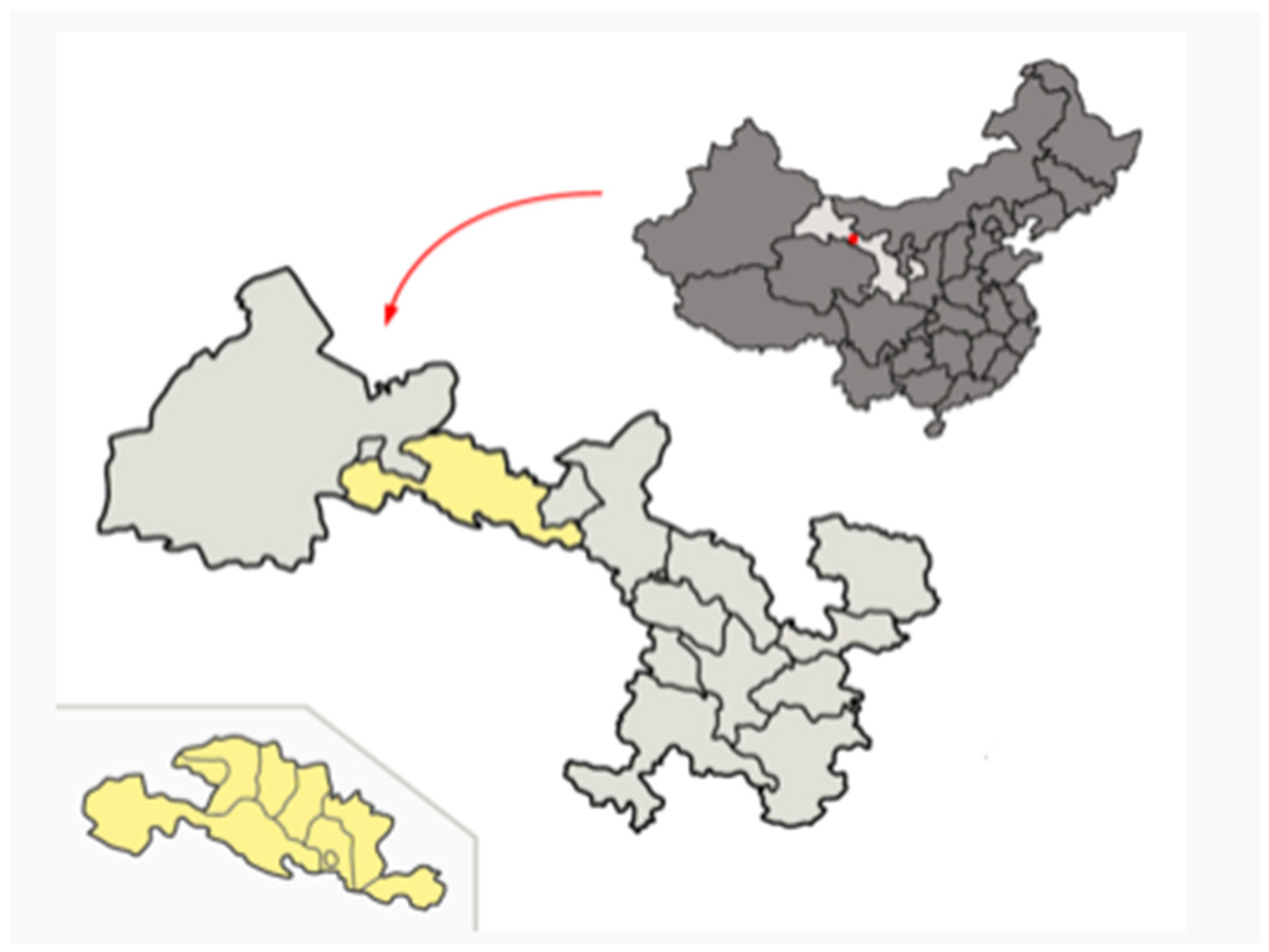
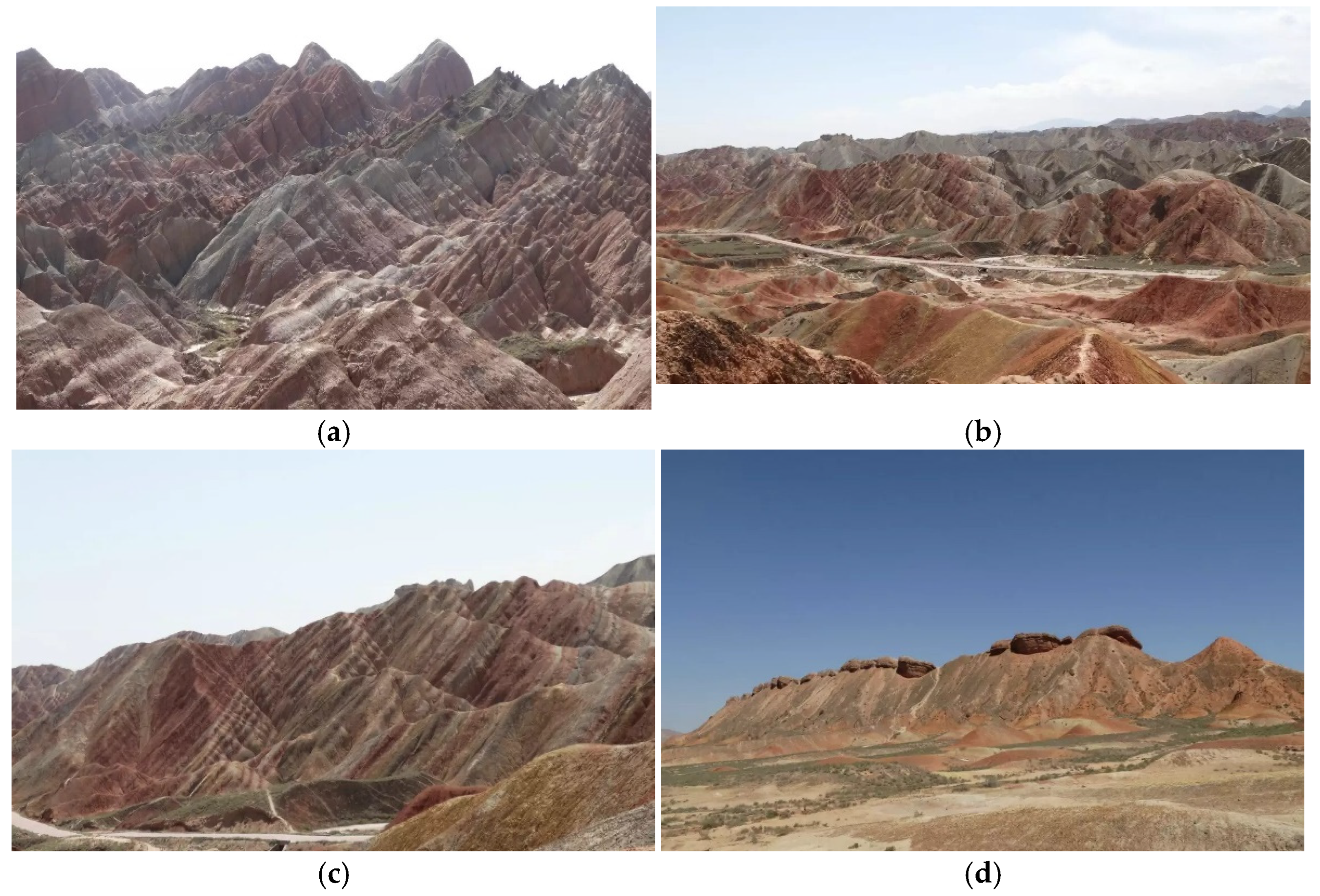
2.1. The Research Case: The Zhangye National Geopark
2.2. Tourist Intention Regarding Pro-Environmental Behaviors
2.3. Norm Activation Model
2.4. Behavioral Reasoning Theory
2.5. Complexity Theory
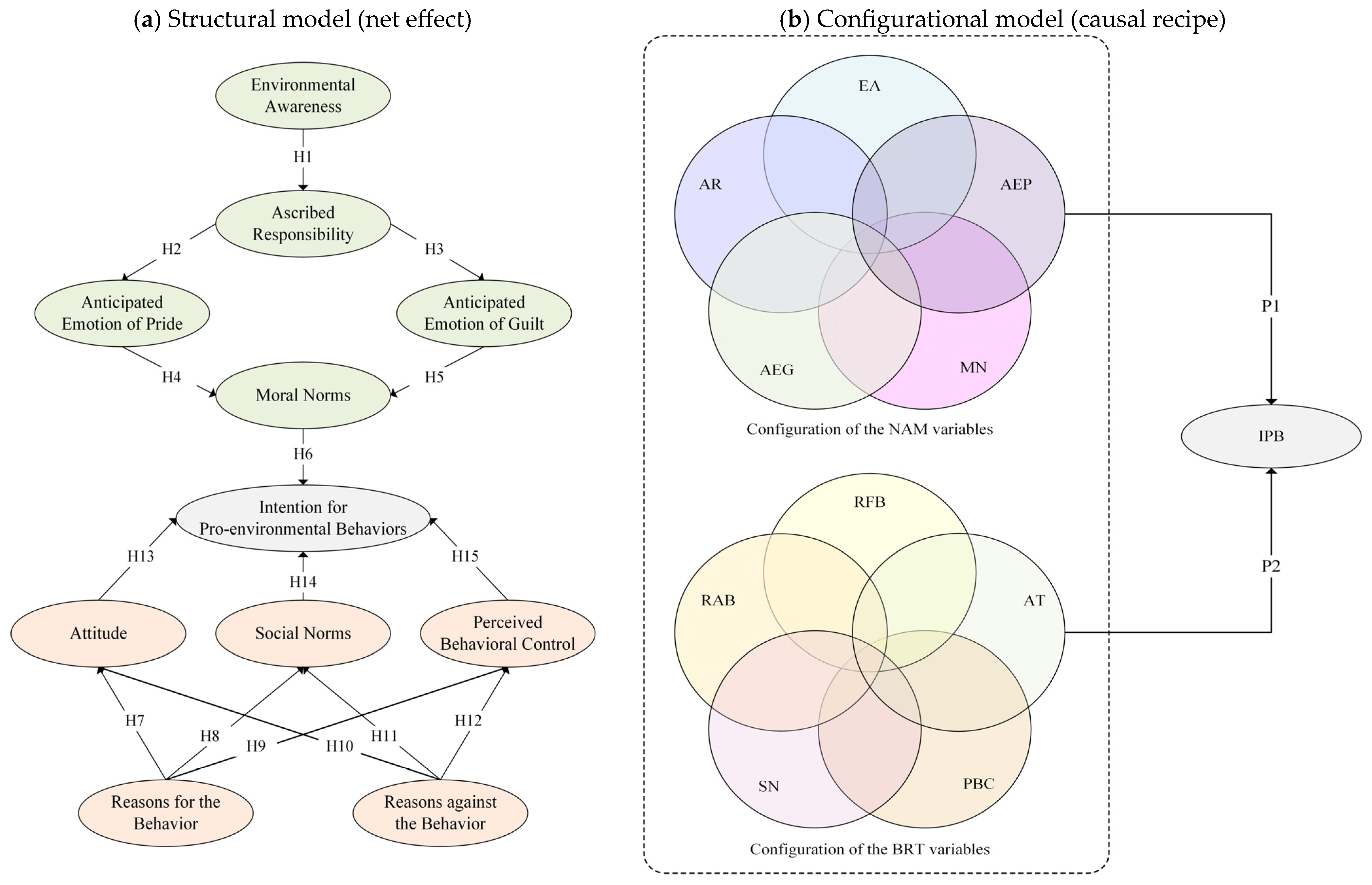
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Measures
3.2. Data Collection
4. Results
4.1. Sample Characteristics and Word Cloud Analysis
4.2. Common Method Variance
4.3. Measurement Model Analysis
4.4. Structural Model Analysis
4.5. Necessary Condition Analysis
4.6. Identification of Causal Factors
5. Discussion
5.1. Theoretical Implications
5.2. Managerial Implications
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TPEB | Tourists’ pro-environmental behavior |
| NAM | Norm activation model |
| BRT | Behavioral reasoning theory |
| PLS-SEM | Partial least squares structural equation modeling |
| fsQCA | Fuzzy set qualitative comparative analysis |
| DMO | Destination management organizations |
| UNESCO | United Nations Education Scientific and Cultural Organization |
| IGGP | International Geoscience and Geoparks Programme |
| IPB | Intention for pro-environmental behaviors |
| PA | Problem awareness |
| EA | Environmental awareness |
| AR | Ascribed responsibility |
| PN | Personal norms |
| MN | Moral norms |
| AEP | Anticipated emotion of pride |
| AEG | Anticipated emotion of guilt |
| AT | Attitudes |
| RFB | Reasons for the behavior |
| RAB | Reasons against the behavior |
| SN | Social norms |
| PBC | Perceived behavioral control |
| TPB | Theory of Planned Behavior |
| λ | Factor loading |
| M | Mean |
| α | Cronbach alpha |
| CR | Composite reliability |
| AVE | Average variance extracted |
| HTMT | Heterotrait–monotrait ratio |
| SRMR | Standardized root mean square residual |
| NCA | Necessary condition analysis |
| CSR | Corporate social responsibility |
| ESG | Environmental, social, and governance |
References
- Long, C.; Lu, S.; Zhu, Y. Research on Popular Science Tourism Based on SWOT-AHP Model: A Case Study of Koktokay World Geopark in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Pang, X.; Zhou, C.; He, X. Coupling Coordination Degree between the Socioeconomic and Eco-Environmental Benefits of Koktokay Global Geopark in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2022, 19, 8498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudla, M.; Javorská, M.; Vašková, J.; Čech, V.; Tometzová, D. Inventory and evaluation of geosites: Case studies of the Slovak Karst as a potential geopark in Slovakia. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Chi, X.; Han, H. A Complexity Theory in Geotourism: Traveler Environmentally Sustainable Behaviors in Global Geoparks. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2024, 41, 1021–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandiar, K.; Dowling, R.; Pearce, J.; Goh, E. What a Load of Rubbish! The Efficacy of Theory of Planned Behaviour and Norm Activation Model in Predicting Visitors’ Binning Behaviour in National Parks. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2021, 46, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Huang, L.M.; He, M.; Ye, B.H. Understanding Pro-Environmental Behavior in Tourism: Developing an Experimental Model. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2023, 57, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Huang, L.; Whitmarsh, L. Home and Away: Cross-Contextual Consistency in Tourists’ Pro-Environmental Behavior. J. Sustain. Tour. 2020, 28, 1443–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.F.; Wu, J.C.; Deng, S. The Effect of Destination Social Responsibility on Tourists’ Pro-Environmental Behavior. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2022, 27, 1233–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Cai, X.; Li, G.; Zou, X.; Morrison, A.M. Volunteering and Pro-Environmental Behavior: The Relationships of Meaningfulness and Emotions in Protected Areas. J. Sustain. Tour. 2024, 32, 304–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jia, W.; Chan, J.H.; Sciacca, A. The Awe-Habitual Model: Exploring Tourists’ Pro-Environmental Behaviors in Religious Settings. J. Sustain. Tour. 2024, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Hwang, J.; Lee, M.J.; Kim, J. Word-of-Mouth, Buying, and Sacrifice Intentions for Eco-Cruises: Exploring the Function of Norm Activation and Value-Attitude-Behavior. Tour. Manag. 2019, 70, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, B. Sustainability assessment of geotourism consumption based on energy–water–waste–economic nexus: Evidence from Zhangye Danxia National Geopark. Land 2024, 13, 1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada-Román, A.; Torres-Bernhard, L.; Ruiz-Álvarez, M.A.; Rodríguez-Maradiaga, M.; Velázquez-Espinoza, G.; Espinosa-Vega, C.; Rodríguez-Bolaños, H. Geodiversity, geoconservation, and geotourism in Central America. Land 2021, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubalíková, L.; Bajer, A.; Balková, M.; Kirchner, K.; Machar, I. Geodiversity action plans as a tool for developing sustainable tourism and environmental education. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.E. Travelers’ Pro-Environmental Behaviors in the Hyperloop Context: Integrating Norm Activation and AIDA Models. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2022, 24, 813–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, J.I.; Bondy, K.; Schuitema, G. Listen to others or yourself? The role of personal norms on the effectiveness of social norm interventions to change pro-environmental behavior. J. Environ. Psychol. 2021, 78, 101688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizin, S.; Van Dael, M.; Van Passel, S. Battery pack recycling: Behaviour change interventions derived from an integrative theory of planned behaviour study. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 122, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, X.; Meng, B.; Lee, H.; Chua, B.L.; Han, H. Pro-Environmental Employees and Sustainable Hospitality and Tourism Businesses: Exploring Strategic Reasons and Global Motives for Green Behaviors. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2023, 32, 4167–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.L.; Abd Aziz, N.; Ngah, A.H. Examining green hotel patronage intention from the perspective of behavioural reasoning theory. Int. J. Bus. Soc. 2021, 22, 901–921. [Google Scholar]
- Sreen, N.; Chatterjee, S.; Bhardwaj, S.; Chitnis, A. Reasons and intuitions: Extending behavioural reasoning theory to determine green purchase behavior. Int. Rev. Public Nonprofit Mark. 2023, 20, 447–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, X.; Cheng, X.; Zhou, H.; Zheng, X.; Cao, J.; Han, H. Investigation on Driving Mechanism of Heritage Tourism Consumption: A Multi-Method Analytical Approach. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2024, 41, 1141–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manosuthi, N.; Lee, J.S.; Han, H. Green Behavior at Work of Hospitality and Tourism Employees: Evidence from IGSCA-SEM and fsQCA. J. Sustain. Tour. 2024, 32, 85–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Qiu, H.; Ren, L. Determinants of Tourists’ Intention to Share Travel Experience on Social Media: An fsQCA Application. Curr. Issues Tour. 2023, 26, 2595–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, P.; Fang, R.; Zhixin, P. A review of Danxia landforms in China. Z. Geomorphol. Suppl. 2015, 59, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhangye Danxia National Geopark. Available online: https://www.zhangyegeopark.cn/en/h-nd-163.html (accessed on 6 November 2024).
- Lee, W.; Jeong, C. Effects of Pro-Environmental Destination Image and Leisure Sports Mania on Motivation and Pro-Environmental Behavior of Visitors to Korea’s National Parks. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2018, 10, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Wei, W. Consumers’ Pro-Environmental Behavior and Its Determinants in the Lodging Segment. J. Hosp. Tour. Res. 2016, 40, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Wei, W. Consumers’ Pro-Environmental Behavior and the Underlying Motivations: A Comparison between Household and Hotel Settings. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2013, 32, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhawar, A.; Kumar, P.; Israel, D. Impact of Materialism on Tourists’ Green Purchase Behavior: Extended Norm Activation Model Perspective. J. Vacat. Mark. 2024, 30, 841–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M.; Zakkariya, K.A.; Surira, M.D.; Peethambaran, M. Flipping the script: How awareness of positive consequences outweigh negative in encouraging tourists’ environmentally responsible behavior? J. Sustain. Tour. 2024, 32, 1350–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Hwang, J.; Lee, S. Cognitive, Affective, Normative, and Moral Triggers of Sustainable Intentions among Convention-Goers. J. Environ. Psychol. 2017, 51, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Confente, I.; Scarpi, D. Achieving Environmentally Responsible Behavior for Tourists and Residents: A Norm Activation Theory Perspective. J. Travel Res. 2021, 60, 1196–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arco, M.; Marino, V.; Resciniti, R. Exploring the Pro-Environmental Behavioral Intention of Generation Z in the Tourism Context: The Role of Injunctive Social Norms and Personal Norms. J. Sustain. Tour. 2023, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H. The Norm Activation Model and Theory-Broadening: Individuals’ Decision-Making on Environmentally-Responsible Convention Attendance. J. Environ. Psychol. 2014, 40, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Chi, X.; Kim, C.S.; Ryu, H.B. Activators of Airline Customers’ Sense of Moral Obligation to Engage in Pro-Social Behaviors: Impact of CSR in the Korean Marketplace. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipley, N.J.; van Riper, C.J. Pride and Guilt Predict Pro-Environmental Behavior: A Meta-Analysis of Correlational and Experimental Evidence. J. Environ. Psychol. 2022, 79, 101753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, K.; Lee, J.; Hwang, J. NAM and TPB Approach to Consumers’ Decision-Making Framework in the Context of Indoor Smart Farm Restaurants. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2022, 19, 14604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westaby, J.D. Behavioral Reasoning Theory: Identifying New Linkages Underlying Intentions and Behavior. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 2005, 98, 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.; Casidy, R. The Role of Brand Reputation in Organic Food Consumption: A Behavioral Reasoning Perspective. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2018, 41, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A.K.; Padhy, R.K.; Dhir, A. Envisioning the Future of Behavioral Decision-Making: A Systematic Literature Review of Behavioral Reasoning Theory. Australas. Mark. J. 2020, 28, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Harun, A. Reasons for Tourist Intention to Use E-Bike Sharing Services; An Application Behavioral Reasoning Theory (BRT). Tour. Rev. 2023, 79, 1542–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhir, A.; Koshta, N.; Goyal, R.K.; Sakashita, M.; Almotairi, M. Behavioral Reasoning Theory (BRT) Perspectives on E-Waste Recycling and Management. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 280, 124269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, B.; Chi, X.; Kim, J.J.; Kim, G.; Quan, W.; Han, H. Traveling with Pets and Staying at a Pet-Friendly Hotel: A Combination Effect of the BRT, TPB, and NAM on Consumer Behaviors. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2024, 120, 103771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajzen, I.; Kruglanski, A.W. Reasoned Action in the Service of Goal Pursuit. Psychol. Rev. 2019, 126, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Baah, N.G.; Kim, S.; Chi, X.; Jung, I. Environmentally responsible behaviors in hospitality and tourism service employees: An application of complexity theory. J. Serv. Theory. Pract. 2025, 35, 114–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olya, H.G.; Al-Ansi, A. Risk Assessment of Halal Products and Services: Implication for Tourism Industry. Tour. Manag. 2018, 65, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ismail, H.N.; Yee, T.P.; Li, F. Exploring the Effect of Destination Social Responsibility on Responsible Tourist Behavior: Symmetric and Asymmetric Analysis. Asia. Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2024, 29, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Sahoo, S.; Ali, F.; Cobanoglu, C. Rise of fsQCA in Tourism and Hospitality Research: A Systematic Literature Review. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2024, 36, 2165–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehran, J.; Olya, H.G. Canal Boat Tourism: Application of Complexity Theory. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2020, 53, 101954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Wang, Y. The Formation of Tourists’ Pro-Environmental Behavior in Natural History Museum Scene: A Configuration Analysis Based on Motivation–Opportunity–Ability Theory. J. Vacat. Mark. 2024, 13567667241247073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olya, H.; Kim, N.; Kim, M.J. Climate change and pro-sustainable behaviors: Application of nudge theory. J. Sustain. Tour. 2024, 32, 1077–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manosuthi, N.; Meeprom, S.; Leruksa, C. Exploring multifaceted pathways: Understanding behavioral formation in green tourism selection through fsQCA. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2024, 41, 640–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacharach, S.B. Organizational theories: Some criteria for evaluation. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1989, 14, 496–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, M. Being There: How Sensory Impressions Influence Tourists’ Pro-Environmental Behaviors. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2024, 59, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harman, H.H. Modern Factor Analysis; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, W.W. Commentary: Issues and opinion on structural equation modeling. MIS Q. 1998, 22, vii–xvi. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F.; Black, W.C.; Babin, B.J.; Anderson, R.E. Multivariate Data Analysis, 7th ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Nunally, J.C.; Bernstein, I.H. Psychology Theory; McGrew-Hil: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Henseler, J.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J. Aca. Mark. Sci. 2015, 43, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Risher, J.J.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M. When to use and how to report the results of PLS-SEM. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2019, 31, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henseler, J.; Hubona, G.; Ray, P.A. Using PLS path modeling in new technology research: Updated guidelines. Indus. Manag. Data. Sys. 2016, 116, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, Z.; Thiesbrummel, C.; Henneberg, S.C.; Naudé, P. Understanding configurations of relational attractiveness of the customer firm using fuzzy set QCA. J. Bus. Res. 2015, 68, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragin, C.C. What is Qualitative Comparative Analysis? Sage Publications: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Pong, V.; Tam, K.P. Relationship between Global Identity and Pro-Environmental Behavior and Environmental Concern: A Systematic Review. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1033564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savari, M.; Damaneh, H.E.; Cotton, M. Integrating the Norm Activation Model and Theory of Planned Behaviour to Investigate Farmer Pro-Environmental Behavioural Intention. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Wu, W. Geoparks and Geotourism in China: A Sustainable Approach to Geoheritage Conservation and Local Development—A Review. Land. 2022, 11, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parashar, S.; Singh, S.; Sood, G. Examining the Role of Health Consciousness, Environmental Awareness and Intention on Purchase of Organic Food: A Moderated Model of Attitude. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 386, 135553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, X.; Kim, S.; Chiriko, A.Y.; Han, H.; Cheng, X.; Meng, B.; Kim, J.J. Tourists’ Ethically Responsible Participation in Animal-Based Tourism: A Configurational Impact Assessment. J. Vacat. Mark. 2024, 13567667241268650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olya, H.G.; Gavilyan, Y. Configurational Models to Predict Residents’ Support for Tourism Development. J. Travel Res. 2017, 56, 893–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Chi, X. Investigation on Festival Consumption Promotion Mechanism in the Post-Pandemic Period: The Case of the Qingdao International Beer Festival. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, M.; Azarkamand, S.; Wooldridge, C.; Selén, V.; Darbra, R.M. Insights on the Environmental Management System of the European Port Sector. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzali, S.; Qingyao, H.; Tianhui, S.; Xinyi, L.; Qifeng, J. Ecotourism Industry in Constrained Environments: Bhutan as a Case Study. In Tropical Constrained Environments and Sustainable Adaptations; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 95–114. [Google Scholar]
- Matshusa, K.; Leonard, L.; Thomas, P. Challenges of Geotourism in South Africa: A Case Study of the Kruger National Park. Resources 2021, 10, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-López, L.; Del Barrio-García, S.; Prados-Peña, M.B. How Do Ecotourists Co-Create Value on Digital Platforms? The Moderating Role of Ecotourist Typology. Span. J. Mark.-ESIC. 2023, 27, 324–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Chi, X.; Han, H. Perceived Authenticity and the Heritage Tourism Experience: The Case of Emperor Qinshihuang’s Mausoleum Site Museum. Asia Pac. J. Tourism Res. 2023, 28, 503–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sihombing, I.H.H.; Suastini, N.M.; Puja, I.B.P. Sustainable Cultural Tourism in The Era of Sustainable Development. Int. J. Sustain. Compet. Tour. 2024, 3, 100–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Anand, S.; Wei, D.; Wang, G.; Tripathi, S.C. Exploring Applied Sustainable Strategies through Geoheritage and Geotourism: A Systematic Literature Review. Int. J. Geoheritage Parks 2024, 12, 660–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahantigh Mand, S. Geotourism Protection Strategies and Geological Heritage (Case Study: Lorestan Province). Tour. Manag. Stud. 2024, 19, 135–182. [Google Scholar]
- Tormey, D. New Approaches to Communication and Education through Geoheritage. Int. J. Geoheritage Parks 2019, 7, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Wu, F.; Watanabe, M.; Han, J. Characteristics of Geoparks in China and Japan: Similarities and Differences. Geoheritage 2021, 13, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | N (502) | % | Variables | N (502) | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Occupation | ||||
| Female | 240 | 47.8% | Institutional organization/Civil servant | 33 | 6.6% |
| Male | 262 | 52.2% | Company staff | 195 | 38.8% |
| Age | Full-time self-employed | 117 | 23.3% | ||
| 18–25 | 127 | 25.3% | Part-time employment | 48 | 9.6% |
| 26–30 | 187 | 37.2% | Unemployed | 12 | 2.4% |
| 31–40 | 151 | 30.1% | Student | 83 | 16.5% |
| 41–50 | 28 | 5.6% | Other | 14 | 2.8% |
| Over 50 | 9 | 1.8% | Education | ||
| Income | High school or below | 29 | 5.8% | ||
| Less than RMB 3000 | 125 | 24.9% | Three-year high school or college | 151 | 30.1% |
| RMB 3001~6000 | 178 | 35.5% | Bachelor’s degree | 238 | 47.4% |
| RMB 6001~15,000 | 143 | 28.5% | Master’s degree | 69 | 13.7% |
| Over RMB 15,000 | 56 | 11.2% | Doctorate or above | 15 | 3.0% |
| Construct and Items | λ | M | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental Awareness (EA) | α = 0.853, CR = 0.854, AVE = 0.773 | ||
| 0.894 | 4.37 | |
| 0.879 | 4.45 | |
| 0.865 | 4.37 | |
| Ascribed Responsibility (AR) | α = 0.882, CR = 0.885, AVE = 0.809 | ||
| 0.904 | 4.69 | |
| 0.909 | 4.64 | |
| 0.885 | 4.77 | |
| Anticipated Emotion of Pride (AEP) | α = 0.840, CR = 0.842, AVE = 0.758 | ||
| 0.879 | 4.47 | |
| 0.863 | 4.39 | |
| 0.870 | 4.33 | |
| Anticipated Emotion of Guilt (AEG) | α = 0.780, CR = 0.784, AVE = 0.694 | ||
| 0.843 | 4.27 | |
| 0.820 | 4.33 | |
| 0.837 | 4.32 | |
| Moral Norms (MN) | α = 0.895, CR = 0.895, AVE = 0.826 | ||
| 0.919 | 4.70 | |
| 0.903 | 4.87 | |
| 0.906 | 4.79 | |
| Intention for Pro-environmental Behaviors (IPB) | α = 0.908, CR = 0.914, AVE = 0.731 | ||
| 0.874 | 4.59 | |
| 0.860 | 4.73 | |
| 0.862 | 4.72 | |
| 0.844 | 4.66 | |
| 0.835 | 4.66 | |
| Attitude (AT) | α = 0.858, CR = 0.860, AVE = 0.779 | ||
| 0.886 | 4.57 | |
| 0.892 | 4.57 | |
| 0.869 | 4.55 | |
| Social Norms (SN) | α = 0.883, CR = 0.883, AVE = 0.810 | ||
| 0.895 | 4.86 | |
| 0.906 | 4.80 | |
| 0.898 | 4.87 | |
| Perceived Behavioral Control (PBC) | α = 0.831, CR = 0.834, AVE = 0.747 | ||
| 0.877 | 4.47 | |
| 0.875 | 4.59 | |
| 0.841 | 4.35 | |
| Reasons for the Behavior (RFB) | α = 0.850, CR = 0.854, AVE = 0.691 | ||
| 0.814 | 4.42 | |
| 0.858 | 4.34 | |
| 0.868 | 4.46 | |
| 0.782 | 4.36 | |
| Reasons against the Behavior (RAB) | α = 0.886, CR = 0.888, AVE = 0.746 | ||
| 0.887 | 3.04 | |
| 0.864 | 3.33 | |
| 0.885 | 3.36 | |
| 0.816 | 3.39 | |
| AEG | AEP | AR | AT | EA | IPB | MN | PBC | RAB | RFB | SN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AEG | |||||||||||
| AEP | 0.546 | ||||||||||
| AR | 0.557 | 0.587 | |||||||||
| AT | 0.571 | 0.571 | 0.583 | ||||||||
| EA | 0.589 | 0.553 | 0.562 | 0.597 | |||||||
| IPB | 0.498 | 0.390 | 0.433 | 0.731 | 0.570 | ||||||
| MN | 0.522 | 0.484 | 0.457 | 0.648 | 0.613 | 0.787 | |||||
| PBC | 0.558 | 0.538 | 0.507 | 0.762 | 0.598 | 0.709 | 0.668 | ||||
| RAB | 0.411 | 0.419 | 0.343 | 0.525 | 0.375 | 0.333 | 0.275 | 0.377 | |||
| RFB | 0.522 | 0.531 | 0.460 | 0.583 | 0.486 | 0.460 | 0.432 | 0.507 | 0.466 | ||
| SN | 0.426 | 0.433 | 0.463 | 0.691 | 0.565 | 0.719 | 0.769 | 0.676 | 0.314 | 0.483 |
| Hypotheses | Paths | Coefficient | t-Value | p-Value | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | EA→AR | 0.489 | 13.164 | 0.000 | Supported |
| H2 | AR→AEP | 0.507 | 14.113 | 0.000 | Supported |
| H3 | AR→AEG | 0.464 | 12.150 | 0.000 | Supported |
| H4 | AEP→MN | 0.282 | 6.481 | 0.000 | Supported |
| H5 | AEG→MN | 0.314 | 7.398 | 0.000 | Supported |
| H6 | MN→IPB | 0.381 | 9.250 | 0.000 | Supported |
| H7 | RFB→AT | 0.377 | 9.180 | 0.000 | Supported |
| H8 | RFB→SN | 0.368 | 8.187 | 0.000 | Supported |
| H9 | RFB→PBC | 0.355 | 7.955 | 0.000 | Supported |
| H10 | RAB→AT | −0.306 | 7.297 | 0.000 | Supported |
| H11 | RAB→SN | −0.129 | 2.919 | 0.004 | Supported |
| H12 | RAB→PBC | −0.182 | 4.167 | 0.000 | Supported |
| H13 | AT→IPB | 0.241 | 5.556 | 0.000 | Supported |
| H14 | SN→IPB | 0.153 | 3.561 | 0.000 | Supported |
| H15 | PBC→IPB | 0.158 | 4.083 | 0.000 | Supported |
| Outcome (IPB) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Antecedent conditions in the NAM | Consistency | Coverage |
| EA | 0.733 | 0.777 |
| ~EA | 0.533 | 0.541 |
| AR | 0.712 | 0.729 |
| ~AR | 0.520 | 0.546 |
| AEP | 0.684 | 0.734 |
| ~AEP | 0.579 | 0.581 |
| AEG | 0.718 | 0.730 |
| ~AEG | 0.544 | 0.575 |
| MN | 0.799 | 0.820 |
| ~MN | 0.468 | 0.490 |
| Antecedent conditions in theBRT | Consistency | Coverage |
| RFB | 0.712 | 0.736 |
| ~RFB | 0.539 | 0.551 |
| RAB | 0.545 | 0.571 |
| ~RFB | 0.698 | 0.716 |
| AT | 0.807 | 0.790 |
| ~AT | 0.452 | 0.498 |
| SN | 0.781 | 0.804 |
| ~SN | 0.488 | 0.5 |
| PBC | 0.778 | 0.787 |
| ~PBC | 0.491 | 0.522 |
| Antecedent conditions in the NAM | Solution 1 | Solution 2 | Solution 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| EA | ● | ● | ● |
| AR | ● | ⊗ | |
| AEP | ● | ⊗ | |
| AEG | ● | ● | ⊗ |
| MN | ● | ● | ● |
| Consistency | 0.893 | 0.896 | 0.942 |
| Raw coverage | 0.488 | 0.472 | 0.250 |
| Unique coverage | 0.036 | 0.022 | 0.053 |
| Overall solution consistency | 0.891 | ||
| Overall solution coverage | 0.577 | ||
| Antecedent conditions in the BRT | Solution 1 | Solution 2 | Solution 3 |
| RFB | ● | ● | |
| RAB | ⊗ | ⊗ | |
| AT | ● | ● | ● |
| SN | ● | ● | |
| PBC | ● | ● | |
| Consistency | 0.892 | 0.914 | 0.908 |
| Raw coverage | 0.600 | 0.479 | 0.485 |
| Unique coverage | 0.169 | 0.039 | 0.045 |
| Overall solution consistency | 0.877 | ||
| Overall solution coverage | 0.684 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, X.; Lin, Y.; Cheng, X.; Ahn, Y.-j.; Chi, X. An Investigation into the Formation of Tourists’ Pro-Environmental Behavior in Geotourism: Balancing Tourism and Ecosystem Preservation. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1422. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17041422
Zheng X, Lin Y, Cheng X, Ahn Y-j, Chi X. An Investigation into the Formation of Tourists’ Pro-Environmental Behavior in Geotourism: Balancing Tourism and Ecosystem Preservation. Sustainability. 2025; 17(4):1422. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17041422
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Xinjie, Yuhao Lin, Xin Cheng, Young-joo Ahn, and Xiaoting Chi. 2025. "An Investigation into the Formation of Tourists’ Pro-Environmental Behavior in Geotourism: Balancing Tourism and Ecosystem Preservation" Sustainability 17, no. 4: 1422. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17041422
APA StyleZheng, X., Lin, Y., Cheng, X., Ahn, Y.-j., & Chi, X. (2025). An Investigation into the Formation of Tourists’ Pro-Environmental Behavior in Geotourism: Balancing Tourism and Ecosystem Preservation. Sustainability, 17(4), 1422. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17041422








