A Study on Bid Decision Factors for Non-Performing Real Estate Project Financing and the Valuation Basis
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Study Background and Objective
1.2. Scope and Method
2. Theoretical Investigation
2.1. Concept and Characteristics of Real Estate PF
2.2. Investigation of Previous Studies
3. Analysis of Bid Decision Factors for Development Sites of Non-Performing Real Estate PF
3.1. Variables
3.2. Descriptive Statistics
3.3. Correlation Analysis
3.4. Model Fitness
3.5. Bid Decision Factor Analysis
4. Valuation Basis in Consideration of Bid Decision Factors
4.1. Hierarchy Setting
4.2. Survey Overview and Details
4.3. Analysis Result
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
6.1. Summary and Implications
6.2. Limitations and Future Issues
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Financial Supervisory Service. Evaluation of Financial Companies’ Business Feasibility and Plans Regarding Their Real Estate PF. Available online: https://www.fss.or.kr/fss/bbs/B0000188/view.do?nttId=137993&menuNo=200218&cl1Cd=&sdate=&edate=&searchCnd=1&searchWrd=&pageIndex=4 (accessed on 21 November 2024).
- Bank of Korea. Global Financial Stability Report; Economic Research Institute: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2024.
- Financial Supervisory Service. The 4th Meeting of Measures for Soft Landing of Real Estate PF. Available online: https://kcg.korea.kr/briefing/pressReleaseView.do?newsId=156647977&pWise=sub&pWiseSub=J2 (accessed on 21 November 2024).
- Maeil Business Newspaper. News Report. Available online: https://www.mk.co.kr/news/economy/11105179 (accessed on 21 November 2024).
- Shim, H.C.; Kim, J.H. Analysis of determinants of successful bidding for insolvent PF projects: With a focus on PF establishments whose construction was suspended by mutual savings banks. Real Estate Acad. Rev. 2017, 71, 93–104. [Google Scholar]
- Korea Asset Management Corporation (KAMCO). Internal Data. 2017. Available online: www.kamco.or.kr (accessed on 21 November 2024).
- Shin, J.C.; Baik, M.S. Research on the Normalization Schemes for Insolvent Development Site on Mutual Savings Banks. J. Korea Acad.-Ind. Coop. Soc. 2015, 16, 195–204. [Google Scholar]
- Jo, K.H.; Lee, C.K.; Kim, S.J. Improving local investment appraisal system for local public investment efficiency. Korea Res. Inst. Local Adm. Basic Res. Proj. 2012, 3, 72–92. [Google Scholar]
- Shim, H.C.; Kim, J.H. A Study on the Application of Weights in the Area of Regional Development for the Examination of Local Financial Investment Project. J. Resid. Environ. Inst. Korea 2020, 18, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.J. Legislative tasks of real estate PF measures to normalize the real estate market. Korea Publ. Land Law 2024, 134, 105–133. [Google Scholar]
- Nevitt, P.K.; Fabozzi, F. Project Financing, 6th ed.; Euromoney Publication: London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.J. An Exploratory Study on Project Financing of Korea Mutual Savings Banks. Corp. Law Res. 2011, 25, 299–328. [Google Scholar]
- Esty, B.C. Modern Project Finance: A Case Book; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, S.H. A Study on Improvement of Project Financing Structure and New Directions in Real Estate Market: Focusing on Financing Structure Founded on Risk Taking of Financial Institutions. Master’s Thesis, Konkuk University Real Estate Graduate School, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, P.R. Project Finance, Subordinated Debt and State Loans; Sweet & Maxwell: London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, Y.S.; Sung, J.H. A Study on the Efficient Risk Management with the Relative Importance of Risk Facts by Stage in the Real Estate Development Project. Korea Real Estate Acad. 2014, 59, 59–73. [Google Scholar]
- Merna, A.; Chu, Y.; Al-Thani, F. Project Finance in Construction: A Structured Guide to Assessment; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Finnerty, J.D. Project Financing: Asset-Based Financial Engineering; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.J. Diagnosis on Project Finance Crisis in Real Estate Market and Policy Response. Constr. Issue Focus 2022, 11, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.J. Diagnosis on Project Finance Crisis in Real Estate Market in Korea and Policy Suggestion. Future Growth Stud. 2023, 9, 101–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, W.H. A Study on Factors of the Financial Distress and the Soundness of the Mutual Savings Banks in Korea. Master’s Thesis, Yonsei University, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.G.; Cha, H.S. An Exploratory Research on Quantitative Risk Assessment Methodology Throughout Success Factor Analysis in Project Financing. Korean J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2013, 14, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, G.J.; Cho, Y.K.; Lee, S.Y. An Analysis on the Investment Determinants for Insolvent Housing Development Projects. Korean J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2014, 15, 112–121. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.S. The Effect of the UEC on the Price of Nearby Lands: Focused on Times Square UEC. Korea Real Estate Acad. Rev. 2014, 58, 60–71. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, U.T.; Lee, H.B. A Research on the Impact of the NPL Related Factors on the Auction Winning Price Rate of Real Estates. Korea Real Estate Acad. Rev. 2016, 67, 116–128. [Google Scholar]
- Ong, S.E.; Lusht, K.; Mak, C.Y. Factors Influencing Auction Outcomes: Bidder Turnout, Auction Houses and Market Conditions. J. Estate Res. 2005, 27, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durdyev, S.; Hosseini, M.R. Causes of delays on construction projects: A comprehensive list. Int. J. Manag. Proj. Bus. 2020, 13, 20–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voronina, N.V.; Steksova, S.Y. Project finance risk management at the stages of the housing projects’ life cycle. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 913, 052002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurmanova, L.R.; Kurmanova, D.A. Financial technologies in project financing of housing construction. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 753, 062024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Ji, K.H. Current Status of Real Estate PF (Project Finance) Loans and Policy Responses. Available online: https://eiec.kdi.re.kr/policy/domesticView.do?ac=0000150505 (accessed on 22 November 2024).
- Lee, B.G.; Lee, C.W. Research on real estate PF crisis response plan. Korean Law Rev. Rehabil. Bankruptcy 2024, 28, 75–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.Y. Actual Status of Real Estate PF Loans and Improvement Measures. Constr. Econ. 2011, 66, 68–79. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, K.H. Study of Analysis of Real Estate Project Financing Issues and Activated through Improvement of a System. Inst. Leg. Stud. 2015, 11, 181–215. [Google Scholar]
- Son, J.J. A Study on Improvement and Problems of PFV System in Korea: Focused on Real Estate Development Business. Master’s Thesis, Kangnam University, Yongin, Republic of Korea, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, J.Y. A Study on the Measure of Securing Stability of the Project Finance. Korea Real Estate Acad. Rev. 2016, 64, 268–280. [Google Scholar]
- You, J.G.; Oh, D.H. Efficient Management Scheme for Insolvent Development Site in Real Estate Project Financing. J. Korea Real Estate Anal. Assoc. 2010, 16, 99–114. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, G.B. A Study on How to Activate Small and Medium-sized Real Estate Development PF. J. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2020, 11, 2205–2216. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, B.K.; You, D.M. Strategies for vitalizing the domestic real estate PF market: Focusing on domestic and foreign precedent research analysis. Korea Real Estate Soc. 2023, 41, 159–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.N.; Kim, J.H. Real Estate Development Project Assessment System: Introduction and Policy Tasks for the Earlier Settlement of Assessment Scheme. J. Korean Hous. Environ. Res. 2013, 11, 209–223. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, T.S. A Study of Influence Factors on Feasibility of Typical Development Projects and Risk Management Method. Master’s Thesis, Hanyang University, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.I.; Gu, B.I. Impact of New Light Transit Line on Apartment Housing Price in the Case of Daegu. J. Real Estate Anal. 2019, 5, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.G. Effects of Multicollinearity in Logit Model. J. Korean Soc. Transp. 2008, 26, 113–126. [Google Scholar]
| Variable Name | Description | Remarks | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent variable | Bidding result | Was set as a dependent variable based on the bidding result of each constructor A successful bidder: 1, A failed bidder: 0 | Subfactor of dummy | |
| Independent variables | ||||
| Feasibility assessment | Building characteristics | Floor area ratio | Land area to total ground area ratio | % |
| Feasibility assessment | Building characteristics | Building-to-land ratio | Land area to building area ratio | % |
| Feasibility assessment | Building characteristics | Scale | No. of households in the building | Unit |
| Feasibility assessment | Profitability analysis | Profitability | Financial feasibility analysis result | % |
| Target site basic evaluation | Legal risk review | Legal suitability | No. of legal disputes | Case |
| Target site basic evaluation | Administrative review | License acquisition | License acquisition | Subfactor of dummy |
| Target site basic evaluation | Transportation means | Subway in a radius of 5 km | No. of subway stations in a radius of 5 km | Unit |
| Target site basic evaluation | Cultural and convenience facility | Adjacent movie theaters | Distance from the building to the nearest movie theater | km |
| Adjacent large outlets | Distance from the building to the nearest outlet | km | ||
| Outlet in a radius of 5 km | No. of outlets in a radius of 5 km | Unit | ||
| Target site basic evaluation | Educational facilities | Elementary/middle/high school/university in a radius of 5 km | No. of schools in a radius of 5 km | Unit |
| Business performance evaluation | Business step | Business site buying rate | The percentage of business sites where the purchase is completed among business sites required in the project plan | % |
| Business performance evaluation | Business step | Period of business suspension | Total period during which the construction is suspended in the project schedule | No. of months |
| Investor protection plan | Debt info. | Total amount of bonds | Total amount of bonds for the building | ×1 million won |
| Investor protection plan | Debt info. | Amount of obtained bonds | Amount of obtained bonds | ×1 million won |
| N | Ave | Std | Min | Max | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bidding result (Subfactor of dummy) | 32.0 | 0.4688 | 0.4998 | 0.0 | 1 |
| Floor area ratio (%) | 32.0 | 3.2681 | 2.4196 | 1.53 | 10.56 |
| Building-to-land ratio (%) | 32.0 | 0.2616 | 0.1527 | 0.13 | 0.66 |
| Scale (Unit) | 32.0 | 515.9688 | 465.4663 | 38.0 | 2059 |
| Profitability (%) | 32.0 | 1.2428 | 0.1698 | 1.05 | 1.72 |
| Legal suitability (Case) | 32.0 | 0.375 | 0.6004 | 0.0 | 2 |
| License acquisition (Subfactor of dummy) | 32.0 | 0.7188 | 0.4503 | 0.0 | 1 |
| Subway in a radius of 5 km (Unit) | 32.0 | 6.75 | 11.5044 | 0.0 | 54 |
| Adjacent movie theaters (km) | 32.0 | 2.47 | 3.4084 | 0.27 | 14.68 |
| Adjacent large outlets (km) | 32.0 | 2.684 | 3.1352 | 0.22 | 11.63 |
| Outlet in a radius of 5 km (Unit) | 32.0 | 4.5 | 3.7891 | 0.0 | 14 |
| Elementary/ middle/high school/ university in a radius of 5 km (Unit) | 32.0 | 5.154 | 6.0948 | 0.596 | 26.31 |
| Business site buying rate (%) | 32.0 | 0.9125 | 0.142 | 0.53 | 1 |
| Period of business suspension (No. of months) | 32.0 | 41.5625 | 30.3913 | 0.0 | 111 |
| Total amount of bonds (×1 million won) | 32.0 | 41,324.6562 | 34,623.9782 | 3000.0 | 196,614 |
| Amount of obtained bonds (×1 million won) | 32.0 | 32,282.8125 | 17,520.8063 | 3000.0 | 68,327 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Bidding result (Subfactor of dummy) | 1.0000 *** | |||||||||||||||
| 2.1 Floor area ratio (%) | −0.1027 * | 1.0000 *** | ||||||||||||||
| 2.2 Building-to-land ratio (%) | −0.0384 | 0.8938 *** | 1.0000 *** | |||||||||||||
| 2.3 Scale (Unit) | −0.3728 *** | −0.1394 ** | −0.2184 *** | 1.0000 *** | ||||||||||||
| 2.4 Profitability (%) | −0.1559 *** | −0.1441 *** | −0.1599 *** | −0.0190 | 1.0000 *** | |||||||||||
| 3.1 Legal suitability (Case) | −0.1697 *** | −0.1011 * | −0.1124 ** | 0.1192 ** | −0.0380 | 1.0000 *** | ||||||||||
| 3.2 License acquisition (Subfactor of dummy) | −0.1088 * | −0.0983 * | −0.1806 *** | 0.0800 | 0.0063 | −0.4203 *** | 1.0000 *** | |||||||||
| 3.3 Subway in a radius of 5 km (Unit) | −0.2303 *** | 0.0601 | 0.0183 | −0.0432 | −0.0601 | 0.4175 *** | −0.4553 *** | 1.0000 *** | ||||||||
| 3.4 Adjacent movie theaters (km) | 0.0906 | −0.2130 *** | −0.0229 | −0.0064 | −0.1597 *** | −0.1638 *** | 0.0511 | −0.1568 *** | 1.0000 *** | |||||||
| 3.5 Adjacent large outlets (km) | 0.2198 *** | −0.2127 *** | −0.0174 | −0.1234 ** | 0.2384 *** | −0.2224 *** | 0.0569 | −0.2763 *** | 0.7347 *** | 1.0000 *** | ||||||
| 3.6 Outlet in a radius of 5 km (Unit) | −0.1407 ** | 0.0917 | 0.0079 | −0.0681 | −0.0962 * | 0.1929 *** | −0.2480 *** | 0.7134 *** | −0.3792 *** | −0.5549 *** | 1.0000 *** | |||||
| 3.7 Elementary/middle/high school/university in a radius of 5 km (Unit) | 0.1637 *** | −0.2285 *** | −0.0218 | −0.0671 | 0.0333 | −0.2060 *** | 0.0579 | −0.2298 *** | 0.9371 *** | 0.9252 *** | −0.4975 *** | 1.0000 *** | ||||
| 4.1 Business site buying rate (%) | 0.0762 | 0.2524 *** | 0.2199 *** | −0.2735 *** | 0.1443 *** | 0.1802 *** | −0.2733 *** | 0.2880 *** | −0.6328 *** | −0.3780 *** | 0.3088 *** | −0.5483 *** | 1.0000 *** | |||
| 4.2 Period of business suspension (No. of months) | −0.3538 *** | −0.1126 ** | −0.1367 ** | −0.0667 | 0.2183 *** | −0.0717 | 0.3414 *** | −0.1150 ** | −0.0419 | 0.0391 | −0.1840 *** | −0.0033 | 0.0804 | 1.0000 *** | ||
| 5.1 Total amount of bonds (×1 million won) | −0.0183 | 0.0056 | 0.0227 | 0.6137 *** | −0.0214 | 0.1192 ** | 0.0771 | −0.0528 | −0.0279 | −0.0291 | −0.1649 *** | −0.0306 | −0.2229 *** | −0.0761 | 1.0000 *** | |
| 5.2 Amount of obtained bonds (×1 million won) | 0.1335 ** | 0.1584 *** | 0.1850 *** | 0.2931 *** | −0.0014 | 0.0351 | 0.0113 | −0.0017 | 0.0208 | −0.0267 | −0.1334 ** | −0.0021 | −0.0257 | −0.0816 | 0.8051 *** | 1.0000 *** |
| Classification | B | S.E. | Wald | Degree of Freedom | Significant Probability | Exp(B) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | Building coverage ratio (%) | −31.3215 | 6.8623 | 20.833 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Scale (Unit) | −0.0684 | 0.0175 | 15.2359 | 1.0 | 0.0001 | 0.9339 | |
| Profitability (%) | −28.5572 | 6.9241 | 17.0098 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| Legal suitability (Case) | −2.404 | 1.8507 | 1.6872 | 1.0 | 0.194 | 0.0904 | |
| License acquisition (Subfactor of dummy) | −26.7496 | 7.2176 | 13.7355 | 1.0 | 0.0002 | 0.0 | |
| Subway in a radius of 5 km (Unit) | −3.0774 | 0.8723 | 12.4458 | 1.0 | 0.0004 | 0.0461 | |
| Outlet in a radius of 5 km (Unit) | 2.1577 | 0.6487 | 11.0628 | 1.0 | 0.0009 | 8.651 | |
| Elementary/Middle school/High school/University within a 5 km radius (Unit) | −0.0285 | 0.0365 | 0.61 | 1.0 | 0.4348 | 0.9719 | |
| Business site buying rate (%) | −26.9258 | 7.5165 | 12.8322 | 1.0 | 0.0003 | 0.0 | |
| Period of business suspension (No. of months) | −0.3643 | 0.0998 | 13.3163 | 1.0 | 0.0003 | 0.6947 | |
| Total amount of bonds (×1 million won) | 0.0005 | 0.0001 | 15.3272 | 1.0 | 0.0001 | 1.0005 | |
| Constant term | 21.3263 | 3.3149 | 16.0176 | 1.0 | 0.0001 | 0.9128 | |
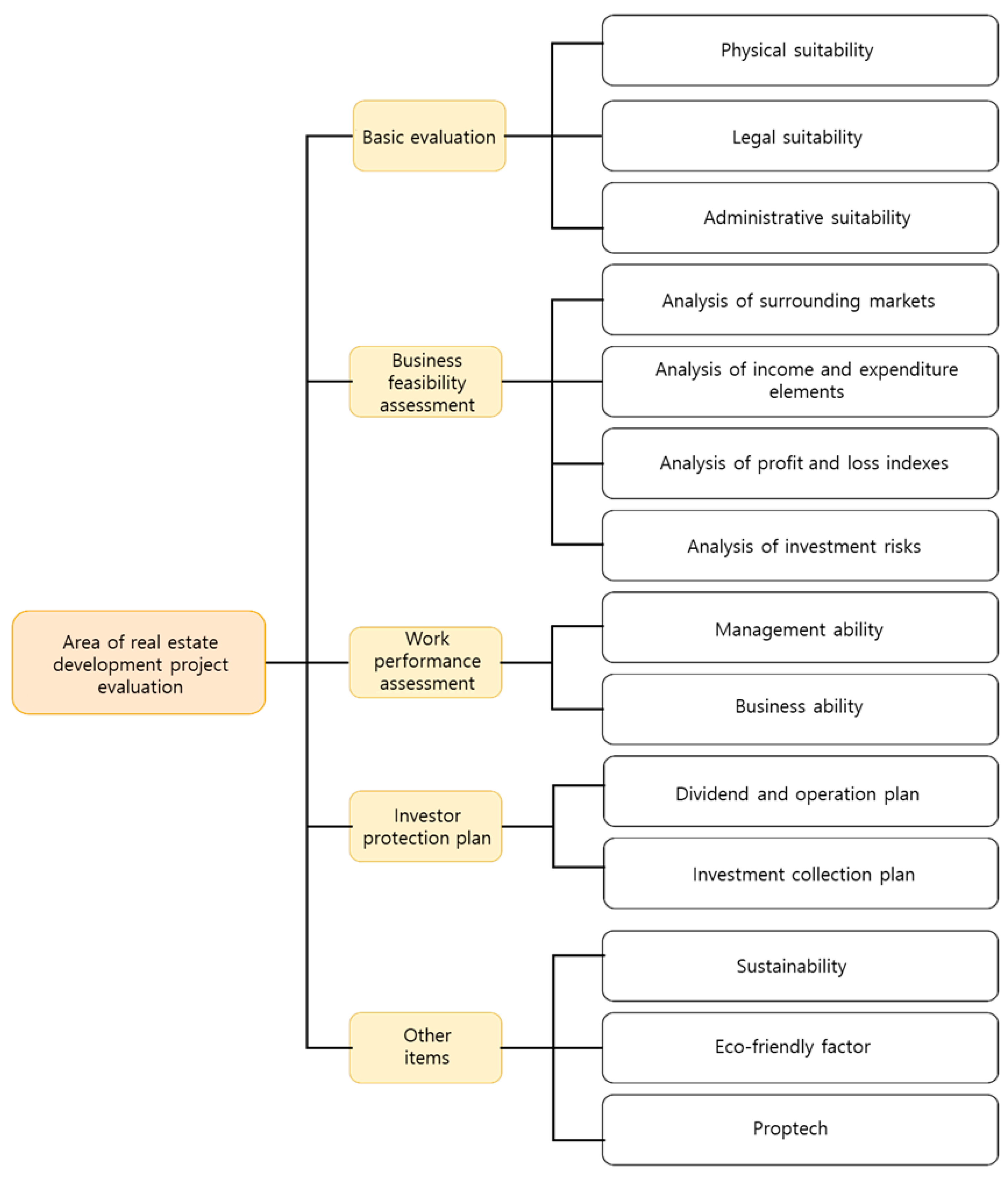
| Class 1 | Class 2 | Significance/Weight of Criterion | Class 3 | Significance/Weight of Criterion | Final Correction Value | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area of real estate development project valuation | Basic evaluation | 0.188 | Physical suitability | 0.215 | 0.0404 | 14 |
| Legal suitability | 0.422 | 0.0793 | 6 | |||
| Administrative suitability | 0.363 | 0.0682 | 7 | |||
| Feasibility assessment | 0.311 | Analysis of surrounding markets | 0.168 | 0.0522 | 12 | |
| Analysis of income and expenditure elements | 0.328 | 0.1020 | 1 | |||
| Analysis of profit and loss indexes | 0.299 | 0.0930 | 4 | |||
| Analysis of investment risks | 0.205 | 0.0638 | 8 | |||
| Business performance valuation | 0.184 | Management ability | 0.452 | 0.0832 | 5 | |
| Business ability | 0.548 | 0.1008 | 2 | |||
| Investor protection plan | 0.162 | Dividend and operation plan | 0.622 | 0.1007 | 3 | |
| Investment collection plan | 0.378 | 0.0612 | 9 | |||
| Other items | 0.155 | Sustainability | 0.387 | 0.0600 | 10 | |
| Eco-friendly factor | 0.271 | 0.0420 | 13 | |||
| Proptech | 0.342 | 0.0530 | 11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, T.; Shim, H.; Kim, S. A Study on Bid Decision Factors for Non-Performing Real Estate Project Financing and the Valuation Basis. Sustainability 2025, 17, 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17030915
Kim T, Shim H, Kim S. A Study on Bid Decision Factors for Non-Performing Real Estate Project Financing and the Valuation Basis. Sustainability. 2025; 17(3):915. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17030915
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Taegeun, Heecheol Shim, and Sungrok Kim. 2025. "A Study on Bid Decision Factors for Non-Performing Real Estate Project Financing and the Valuation Basis" Sustainability 17, no. 3: 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17030915
APA StyleKim, T., Shim, H., & Kim, S. (2025). A Study on Bid Decision Factors for Non-Performing Real Estate Project Financing and the Valuation Basis. Sustainability, 17(3), 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17030915






