Abstract
Rural tourism, traditionally a niche sector, has gained significance due to changes in societal conditions, emerging as one of the most resilient forms of tourism. This article uses bibliometric analysis to explore the development and current trends in rural tourism research. Data were sourced from the Web of Science, yielding 1675 articles published between 1967 and 2023. Results reveal an average annual significant growth between 2008 and 2015, when 54.4% of all articles were published. Notable peaks include 142 publications in 2014 and a record 1230 citations in 2023, averaging 20.42 citations per article. Key contributions include identifying highly cited works, prolific authors, and leading institutions. Influential researchers such as Hall C. Michael, with 602 publications and an h-index of 67, and Carvalho Celia, a prominent European author, have shaped the field. The Universidad de Extremadura and the Chinese Academy of Sciences are among the top institutions, while journals like Sustainability and Tourism Management stand out for their influence. Six core research themes emerged: (a) the impact of rural tourism on agriculture and the environment, (b) the role of nature conservation and ecotourism in sustainable development, (c) ecological and sustainable approaches in biodiversity conservation, (d) biotechnological innovations in rural tourism, (e) demographic and social factors shaping outdoor recreation, and (f) the impact of rural tourism on sustainable development and community life. The study highlights the need for ongoing innovation to support sustainability goals and emphasizes the importance of understanding historical development and long-term trends in rural tourism research while offering insights into future research directions and practical applications.
1. Introduction
Rural tourism is an increasingly important field of research, recognized for its growing significance as a driver of economic development in less developed regions that lack industrial infrastructure or major tourist attractions. In the face of global environmental challenges–such as climate change, biodiversity loss, and natural resource degradation–rural tourism is seen as a valuable tool for promoting conservation and sustainable development in rural areas [1,2,3].
One of the first widely recognized definitions of rural tourism characterizes it as tourism that takes place in rural areas or countryside settings, often involving activities that are characteristic of rural life, such as agriculture, nature exploration, cultural traditions, and community engagement. According to Lane [4], rural tourism encompasses tourism activities that are located in rural areas, are rural in scale, and functionally depend on the countryside’s natural, cultural, and human resources.
According to the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) [5], rural tourism encompasses a range of activities and experiences tied to nature-based pursuits, agricultural practices, rural lifestyles, fishing, and sightseeing. These activities take place in non-urban regions characterized by low population density, landscapes dominated by agriculture and forestry, and traditional social structures and lifestyles. Rural tourism offers unique perspectives, serving as a distinct form of tourism set in rural environments. It provides opportunities for recreation while fostering entrepreneurship in local communities, contributing to household incomes and regional economies. Additionally, rural tourism promotes sustainable development by leveraging natural, cultural, and historical resources, preserving cultural heritage, and encouraging environmental stewardship. Through these facets, rural tourism plays a multifaceted role in supporting sustainability goals [6].
The concept of rural tourism encompasses four fundamental aspects: its location in non-urban areas, its emphasis on sustainable development, its community-oriented nature, and the unique experiences it offers to visitors [7]. According to Aytuğ and Mikaeili [8], rural tourism can be classified into four main categories based on prior research: urban–suburban tourism, scenic ecotourism, agritourism, and cultural heritage tourism.
As a sustainable alternative to mass tourism, rural tourism not only encourages responsible use of natural resources but also supports the preservation of cultural heritage [9,10,11]. It further fosters economic growth within local communities [12,13], positioning it as a key contributor to global sustainable development [14,15,16,17]. By integrating ecological, social, and economic dimensions, rural tourism enhances its long-term viability and impact. However, while the connection between rural tourism and sustainable development is evident, further exploration is needed to illustrate how its various positive effects can directly contribute to global sustainability.
The uniqueness of rural tourism lies in its ability to engage local communities in the conservation and management of natural resources. Briedenhann and Wickens [9] emphasize that residents involved in the tourism sector are often motivated to protect their natural and cultural heritage, as their economic well-being is directly tied to these assets.
Similarly, scholars such as Sims [1] and Batista et al. [18] underscore the importance of integrating local traditions and practices into tourist experiences, positing that this integration enhances both cultural identity and environmental sustainability. These approaches contribute to reducing the ecological footprint of tourism and promoting responsible resource use. Consequently, a sustainable approach to rural tourism benefits not only tourists but also local communities [19,20] and the environment.
Sustainable rural tourism emphasizes the need to balance tourist demands with environmental protection. As highlighted by Garrod et al. [21], sustainable tourism practices play a vital role in conserving natural resources and minimizing negative impacts on local ecosystems. These practices also help establish a positive destination image, attracting environmentally conscious tourists who prioritize responsible travel. Additionally, educating tourists about ecological issues and resource conservation enhances awareness of environmental protection, motivating them to become active stewards of nature. Integrating ecological elements into health and wellness tourism can further enrich the visitor experience. Implementing sustainable practices in tourist facilities can instill a sense of contribution to environmental conservation among visitors. Furthermore, linking ecological initiatives with diverse tourism forms offers significant opportunities for fostering sustainable and responsible travel. By integrating these elements, the industry can create engaging and meaningful tourist experiences that benefit not only travelers but also local communities and the environment. This approach promotes long-term sustainability, enhancing the environmental, cultural, and economic vitality of regions. As highlighted by Cetin [22], Perdue [23], and Castanho et al. [24], rural tourism will remain a key player in the global tourism industry, with its success hinging on effective management and the ability to adapt to evolving conditions.
Moreover, the rise of digitalization and technological advancement is transforming the operations of rural tourism. The internet and social media platforms empower rural destinations to market themselves on a global scale, attracting tourists from across the globe. Innovations such as booking systems, apps tailored for digital nomads, virtual tours, and interactive guiding services enhance the comfort and accessibility for travelers. These developments strengthen the connection between tourists and local businesses, even in remote rural regions.
The COVID-19 pandemic has introduced new challenges to global tourism, significantly affecting traveler preferences. Rural destinations have gained appeal by providing safer environments with fewer crowds and opportunities for outdoor activities away from congested urban areas. This trend is expected to shape future travel behavior as more individuals seek healthier, eco-friendly, and less commercialized destinations. Lane [25] analyzed the pandemic’s impact on tourism, noting that rural destinations have gained popularity as safer alternatives to crowded cities. This shift in demand has reinforced a long-term trend toward ecological and sustainable tourism. While this phenomenon presents new opportunities for the sustainable development of rural areas, it also brings challenges in management and marketing, as discussed by Couto et al. [26], Hall and Richards [27], and other scholars. Carvalho [28] and Jeong [29] explore management and marketing strategies that could bolster the competitiveness of rural regions in the global tourism market, focusing on digital transformation and innovation.
Effective management and the protection of natural resources are vital for long-term sustainability or rural tourism. Technological advancements and evolving tourist preferences create new possibilities for this sector while highlighting the necessity of sound management practices and the conservation of natural and cultural heritage.
In light of the increasing interest in rural tourism, our study aims to explore the evolution of literature in this field, providing an overview of the current landscape, identifying key research groups, and highlighting future research directions. This work contributes to the literature of sustainable science by addressing the dynamic relationship between tourism and sustainability, particularly through its focus on integrating ecological, social, and economic dimensions. By analyzing publication patterns and citation trends in articles related to rural tourism up to 2023, this research offers valuable insights for academics, industry professionals, and policymakers looking to understand the evolution and potential of this vital sustainability approach.
A notable gap in the literature exists, as no prior study has undertaken a comprehensive review spanning the entire period from the initial intention to define rural tourism to the present, covering articles published from 1967 to 2023. By addressing this gap, our study provides a foundational understanding of how rural tourism has evolved and its contributions to the broader framework of sustainable development.
In our pursuit to gain a comprehensive understanding of the academic landscape surrounding rural tourism, we aimed to identify its fundamental building blocks. By analyzing publication trajectories, the impact of individual works, and the contributions from authors, institutions, countries, and journals, we sought to develop a holistic perspective on the field’s evolution and its core research components. Consequently, our research questions (RQs) are centered on the following areas:
- RQ1:
- What are the current trends in publishing and citation within the realm of rural tourism?
- RQ2:
- Which publications have garnered the most citations?
- RQ3:
- Which authors are the most prolific contributors to the field?
- RQ4:
- Which institutions demonstrate the highest levels of productivity?
- RQ5:
- Which countries are most active in publishing research on rural tourism?
- RQ6:
- Which journals are the most prolific in this area?
Building on our foundational insights, we explored the depth of collaboration within the field of rural tourism research. Recognizing the importance of collective scientific endeavors, we aimed to map the existing collaboration network. To achieve a comprehensive understanding of this area, we also focused on identifying the conceptual and intellectual frameworks that form the basis of the extensive literature on rural tourism. Consequently, we have formulated the following three research questions:
- RQ7:
- What is the current state of collaboration in rural tourism research?
- RQ8:
- What is the composition of the conceptual framework related to rural tourism?
- RQ9:
- Who are the key contributors to the intellectual structure surrounding rural tourism?
Recognizing the dynamic nature of rural tourism, we have sought to identify potential directions for future research. These emerging themes have significant potential to shape the future trajectory of studies within this field. Thus, our final research question addresses the following:
- RQ10:
- What future perspectives can be anticipated in the research of rural tourism?
This study marks a significant advancement in rural tourism research by presenting the first comprehensive bibliometric analysis that explores the field’s development, status, and future directions in depth. Our work systematically examines publication trajectories, assesses the impact of key works, and analyses contributions across various academic disciplines, providing a broad overview of progress in rural tourism. A distinguishing feature of our research is the intricate mapping of collaboration networks and the identification of the conceptual and intellectual frameworks within the literature on rural tourism. This dual analysis of collaboration and intellectual discourse offers a unique contribution that enhances the understanding of how various research directions interrelate. Additionally, our study identifies and delineates emerging research themes, paving the way for future investigations into rural tourism.
The structure of this paper is as follows: Section 2 presents our research methodology, offering a detailed explanation of the bibliometric approach applied to analyze and map rural tourism. Section 3 provides a performance analysis, examining key aspects of rural tourism research, including articles, authors, institutions, countries, and journals. Section 4 investigates the relationships and collaboration dynamics in rural tourism by mapping co-authorship networks at both author and country levels. Section 5 focuses on keyword co-occurrence analysis to identify the conceptual network within rural tourism. This section carefully maps thematic structures, emphasizing the interconnectedness of keywords and their significance in shaping the field’s core topics. Section 6 uses bibliometric coupling to analyze the intellectual structure of rural tourism, clustering articles based on shared references to highlight intellectual connections and key themes. Section 7 introduces emerging research themes, providing insights into their unique characteristics, historical context, and alignment with specific applications in rural tourism. Section 8 explores future research directions, identifying under-researched areas and current challenges. Finally, Section 9 concludes the study by synthesizing key findings from bibliometric analysis and discussing broader implications for scholars, policymakers, and industry professionals. This section also highlights the research’s contributions to potential future avenues for investigation and acknowledges its limitations.
2. Materials and Methods
In this study, we adopted a bibliometric analysis to explore the theoretical foundations and processes within rural tourism research. By conducting this analysis and reviewing the literature on rural tourism, our objective was to trace its evolution and suggest future research directions, providing a solid basis for the continued development of this field. The quantification of key topics was guided by the Green Certificate [30] as a reference source. Our approach began by analyzing the role of rural tourism as a critical element of sustainable tourism planning. We then identified and grouped key insights into specific themes (topic extraction), followed by mapping the relationships between these themes. In some cases, discrepancies arose, such as whether there was a direct relationship between tourism and sustainability. Additionally, our research incorporates elements of phenomenological analysis, as it is solely focused on understanding the dynamics of rural tourism.
2.1. Data Collection (Data Sources and Data Preprocessing)
The data for mapping the rural tourism landscape were obtained from the Web of Science citation database, which offers more extensive coverage than other citation databases and full-text repositories. This database was chosen for its broad scope and comprehensive record count. Data were specifically collected online to ensure a wider impact on the scientific and professional communities, as opposed to relying on “gray literature” from educational institutions. English was selected as the primary language for the study, as the mapping was performed using VOSviewer [31], a tool optimized for English-language analyses.
Data collection occurred between November 2023 and February 2024, with the evaluation and validation process extending through April 2024. We refined our focus on rural tourism by concentrating on three key terms: sustainability, rural tourism, and planning. The term “rural tourism” was deemed too general, covering a wide range of aspects such as location, environment, visitor motivations, activities, and sustainability. Our focus on sustainability stems from its importance across various forms of rural tourism, including rural health tourism, culinary tourism, nature tourism, active rural tourism (e.g., hunting, fishing, cycling), agritourism, cultural and heritage tourism, and rural lifestyle tourism.
We consider sustainability to be the cornerstone of rural tourism, with an enduring influence on how tourism is perceived. The authors of this study have previously examined sustainability in the context of agritourism [32] and have also explored its relationship to nature tourism [33] and renewable energy sources [34]. For this research, we analyzed a dataset comprising 1671 documents.
2.2. Data Analysis (Methods and Application)
Our research was guided by two primary objectives in formulating the research questions:
- to identify information explicitly stated in the text
- to infer information that is not explicitly stated.
We employed a variety of analytical tools depending on the type of data being analyzed, whether numerical or textual. The data collected from the Web of Science database were processed in a structured format, allowing us to extract relevant insights. Our primary interest was the development of rural tourism, from its inception in 1967 as a district form of tourism to the present day. We aim to investigate whether this niche form of tourism has been influenced over the past 56 years by political, social, geopolitical, and ecological changes. Furthermore, we sought to understand how these changes impacted the evolution of rural tourism and its current position while also projecting future research directions in the field. Given the practical implications of our research for society and its potential use within higher education, we selected specific data analysis methods tailored to each research question (RQ).
For RQ1, “What are the current trends in publishing and citation in rural tourism?” we applied statistical methods to process numerical data. We began by segmenting the data based on predefined indicators, which were then quantified. This enabled us to trace the development path and assess the evolving interest in this area over time. This led us to identify the most influential publications in rural tourism, forming the foundation for RQ2: “Which publications are the most frequently cited in rural tourism?” Here, we categorized the data to highlight the key works that have shaped the field.
Next, we explored individual contributions, identifying the most prolific authors who have significantly enriched the discourse and advanced the field (RQ3).
We then analyzed institutional relationships, identifying the leading academic centers that play a prominent role in rural tourism research (RQ4).
Additionally, we mapped the geographical distribution of publications, providing an overview of the most active countries and defining regional research hotspots (RQ5). Finally, we focused on the dissemination of knowledge, identifying the top journals publishing research on rural tourism (RQ6).
To address RQ7, which investigates the current state of collaboration in rural tourism, we utilized scientific mapping methods, specifically creating a co-authorship network at two levels: authors and countries [35,36,37]. This methodology allowed us to visually capture the collaboration landscape and understand the dynamics of partnerships within the field.
For RQ8, which aims to clarify the conceptual structure of rural tourism, we conducted a keyword co-occurrence analysis [37,38,39,40]. Through this analysis, we extracted relevant publications and successfully identified and categorized distinct thematic clusters that characterize the field.
In response to RQ9, focusing on the intellectual structure of rural tourism, we applied the principles of bibliographic coupling [35,40,41]. By organizing articles into thematic groups, we mapped the intellectual landscape of the rural tourism research domain. Our bibliographic connections cover the period from 1967 to 2023, providing a chronological context and a consistent reference framework.
In conclusion, RQ10 focused on identifying future directions in rural tourism research. By defining the main research themes within the rural tourism domain through bibliographic linkages and keyword co-occurrence analysis, we were able to outline potential areas for further investigation. This was accomplished by conducting a content analysis of key contributions. Through this analysis of significant and emerging topics in rural tourism, we identified areas that remain underexplored or show high potential for future research. This methodological approach contributed to our recommendations for future research.
As a result, we gained a clearer understanding of rural tourism development as both a social and cultural phenomenon, as well as a growing sector of societal activity.
2.3. Scientific Method (Methods and Application)
Bibliometric analysis is a widely used method, valued for its ability to (1) manage large volumes of scientific data and (2) produce impactful research. Researchers apply this method for a range of purposes, including identifying current trends in article and journal performance, examining collaboration patterns, analyzing research components, and exploring the intellectual framework within existing literature [42,43].
Often compared to other review methods, like meta-analysis and systematic literature reviews, bibliometric analysis shares a quantitative nature with meta-analysis. Both methods can process extensive literature and provide detailed overviews of a specific field [39]. However, meta-analysis is primarily used to expand theoretical understanding [44], whereas bibliometric analysis focuses on mapping the bibliometric and intellectual landscape of a field by examining relationships among authors, countries, institutions, and research themes. In contrast, systematic literature reviews take a more manual approach, analyzing content and themes by reviewing theories, methods, and domains [45,46].
The bibliometric approach involves the use of quantitative techniques, such as citation analysis, to analyze bibliometric data, including publications and citations [47,48]. To ensure the effective and meaningful application of bibliometric analysis, guidelines, and frameworks have been developed for different variants of this methodology [42] (Figure 1).
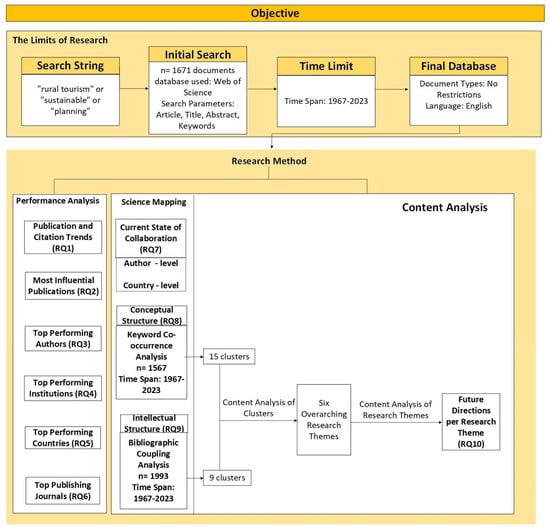
Figure 1.
A preliminary framework for a comprehensive methodology to analyze rural tourism development.
3. Performance Analysis
This section provides a detailed analysis of the main components of rural tourism research, including articles, authors, citations, institutions, countries, and journals. Our analysis is built on various general tools, clearly presented in the corresponding tables, such as citation and bibliometric indicators (e.g., total citations, total publications, and average citation per publication). To gain deeper insight into the unique characteristics of each component, we also introduce specific indicators tailored to individual cases. To assess the impact of each element, we utilize the h-index, with additional metrics like the average number of authors per publication, to further enhance our analysis. Additional metrics, such as the average publication age (APA), which indicates the mean age of individual publications, and the annualized citation rate (ACR), which calculates the average number of citations per year since publication, further enrich our analysis. In the following subsections, we explore each research component in greater detail, providing a comprehensive understanding of rural tourism research.
3.1. Publication and Citation Trends
Table 1 displays the number of publications grouped by Web of Science categories, while Figure 2 shows the growth trends in citations and publications from 1967 to 2023. The first article on rural tourism was published in 1967, and since then, the publishing trend has followed an exponential growth trajectory (R2 = 0.3793) in line with established patterns of growth in scientific publications [49].

Table 1.
Annual publications and citation structure from 1967 to 2023.
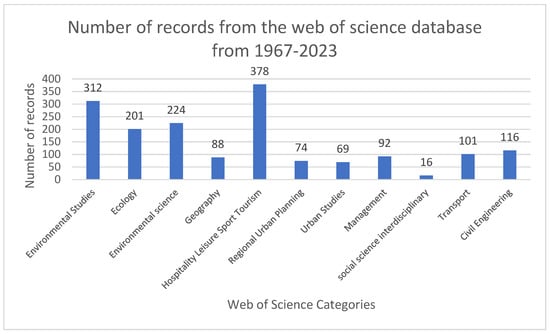
Figure 2.
Number of records from the Web of Science database from 1967–2023.
According to the Web of Science categorization, 22.62% (378) of publications were classified under Hospitality Leisure, Sport & Tourism, followed by 18.7% (312) under Environmental Studies and 13.4% (224) under Environmental Science. In the first third of the analyzed period, the focus was primarily on Environmental Science, particularly in the areas of ecology, agriculture, and anthropology. In the second third, the emphasis shifted toward Hospitality, Leisure, Sport, and Tourism, with Environmental Studies and Environmental Science following. In the final third, the focus returned to Environmental Science and Environmental Studies, with a strong emphasis on green sustainable science and technology.
On average, 29.83 articles were published annually, with the number of publications increasing from 10 in 1993 to 142 in 2014. Notably, 54.4% of all publications (910 out of 1671) were produced between 2008 and 2015. The period before (1967–2007) and after this time frame (2016–2023) saw similar publication volumes, with 22.4% (374 publications) and 23.2% (387 publications) of the total, respectively. In terms of volume, 2014 recorded the highest number of publications with 142 articles, while 2023 was the most impactful year, generating 1230 citations, averaging 20.42 citations per publication. By 2023, the ratio of cumulative total citations to cumulative total publications had reached 29.1. Interestingly, there was a moderate correlation (R2 = 0.6) between the first period (1967–2007) and the third period (2016–2023) due to the early development of regulations, which were later significantly disrupted by the pandemic.
3.2. Most Cited Publications
We identified 29 of the most influential publications in rural tourism research based on their frequency of citation between 1967 and 2023. Citations are a formal representation of scientific communication, typically appearing in academic publications [49]. The selection criterion was set at a minimum of 130 citations in the Web of Science database by the search cut-off date. Notably, four articles exceeded 400 citations, while eight articles surpassed 300 citations. Six articles maintained an average of at least 20 citations per year since their publication. The list includes two publications from the same pair of authors, with the rest authored by different individuals. All selected works are categorized as “articles”.
The article by Sims [1] holds the distinction of being the most cited in rural tourism research, with 719 citations, averaging just under 48 citations per year. Sims focuses on the sustainability of tourism and agriculture, particularly in relation to the development of “alternative” food networks and the renewed interest in food products perceived as traditional and local. Sims argues that “local food” has the potential to enrich the visitor experience by connecting consumers to the region and its cultural heritage.
The second most cited article, by Streimikiene et al. [19], reviews scholarly literature to identify the key factors and strategies that enhance tourism competitiveness through the achievement of economic, social, and environmental goals in tourism destination development. Their systematic literature review reveals several key insights: stakeholders in the tourism industry are eager to adopt recent technologies that benefit both the environment and local communities. However, significant challenges remain in transforming the industry, motivating consumers to embrace sustainable tourism services, and changing consumer behavior toward more sustainable practices. The COVID-19 pandemic, along with the risk of future pandemics, has introduced additional challenges for sustainable tourism development.
Cetin’s article [22] ranks third in citations. This study creates heat maps of environmental perceptions to analyze changes that define bioclimatic comfort zones, which are utilized in urban and rural planning, including for tourism development.
The remaining 29 most influential publications from 56 years of rural tourism research and scientific discourse cover a diverse range of topics. These include the value of natural capital and ecosystem services, the development of rural attractions such as cuisine and food tourism, and the role of tourism as a tool for rural economic growth. Other topics include food tourism’s contribution to maintaining regional identity, diversification in tourism, better food management practices to reduce tourism’s “food carbon footprint”, and the impact of land use/land cover changes on land degradation dynamics. Additionally, they explore the significance of family-owned businesses in rural tourism, public preferences for landscape features, residents’ perspectives on land use, development, and environmental issues in rural communities, and their perceptions of tourism development. Further discussions address the promotion of rural tourism, tourism in boomtowns and its effect on residents’ quality of life, and rural residents’ attitudes toward tourism.
It is also noteworthy that some studies focus on specific regions and their experiences with rural tourism, such as mountainous Mediterranean areas, the western Rocky Mountains, southern Germany, Bursa city, Cornwall (Southwest England), Taiwan’s wetlands, Bigodi village in Uganda, Cyprus, and case studies from Scotland [50].
We should also note that older publications tend to have a higher likelihood of accumulating citations compared to more recent ones. As a result, some highly cited recent articles may not appear in Table 2. To address this, we include two recent articles: the first, by Streimikiene et al. [19], has gathered 203 citations in 2 years and provides a systematic review of sustainable tourism, emphasizing the balance between competitiveness and sustainability. Key challenges addressed include integrating new technologies, supporting local communities, and protecting the environment while highlighting the importance of consumer awareness and behavioral shifts. The second study by Cetin [22] received 194 citations over 4 years and examines how urban planning affects bioclimatic comfort and air quality in Bursa, Turkey. This research offers guidance for aligning urban development with environmental goals to enhance well-being in similar cities.

Table 2.
The most influential articles in rural tourism research.
3.3. Most Prolific Authors
Table 3 presents the most prolific authors in the field of rural tourism, defined by their publication of at least 13 articles and a minimum of 65 citations. Hall C. Michael from the University of Western Australia is the standout author, with an impressive 602 publications between 1974 and 2024. His considerable influence is further demonstrated by an h-index of 67, highlighting his esteemed position within this discipline. In Europe, Carvalho Celia from the University of Azores, Portugal, has similarly excelled, publishing 160 articles. Other notable contributors include Weaver David B. from Auburn University, USA, with 127 articles, and Castanho Rui Alexandre from the University of Extremadura, Spain, who has authored 91 articles on rural tourism.

Table 3.
The most prolific authors in rural tourism research.
Interestingly, while Australia and the USA have their leading prolific authors, Europe has a group of six authors, primarily associated with Castanho Rui Alexandre, who have made substantial contributions to rural tourism research.
In terms of total citations–an essential indicator of scholarly impact–Hall C. Michael leads the field with 20,287 citations. He is followed by Carvalho Celia and Weaver David B., each amassing over 3928 citations. The top five authors are rounded out by Garrod Brian from Swansea University (UK) and RR Perdue from Virginia Polytechnic Institute & State University, with citation totals of 2290 and 1846, respectively. Moreover, Hall C. Michael boasts the highest average citations per article, achieving an exceptional rate of 73.23. He also holds the top position for the highest annualized citation rate (ACR) at 7.68. Notably, among these leading contributors, six authors have published at least one article that has received over 100 citations, while 10 authors have at least one article with more than 50 citations.
3.4. Most Prolific Institutions
Table 4 presents the most prolific institutions in rural tourism research, each of which has published at least five articles in this field. The data indicate a notable geographical concentration, with 75% of the institutions -nine in total- based in Europe, while the remaining three are in China, Iran, and Australia. The Universidad de Extremadura ranks first, having made 12 contributions, followed by the Chinese Academy of Sciences with nine articles. Both the University of Belgrade and WSB University have each contributed eight articles.

Table 4.
The most prolific institutions in rural tourism research.
European institutions play a significant role in rural tourism research, accounting for 75% (65) of all publications in this field. The Chinese Academy of Sciences leads in total citations with 322, averaging over 46 citations per publication. Among European institutions, Universita degli Studi di Bari Aldo Moro (Italy) and Universidad de Extremadura (Spain) have achieved impressive citation rates, with 29.8 and 22.63 citations per publication, respectively. Notably, the 16 most cited publications–each exceeding 150 citations–are attributed to research conducted by European institutions.
3.5. Most Prolific Countries
Of the 1671 publications assessed in this study, 1660 are linked to six continents, while 11 publications do not provide transparent information about their origin. Table 5 outlines the countries that are most productive in rural tourism research, with each contributing a minimum of 11 articles through their researchers and institutions. It is also worth noting that multiple countries have collaborated on single publications, which has emerged as a new trend in academic writing in recent years.

Table 5.
The most prolific countries in rural tourism research.
China leads the global rankings in the total number of publications, with 111, double that of other countries. Italy follows in second place with 65 publications. While Italy’s total is about half of China’s, it exceeds the output of Spain and the USA, which rank third and fourth with 54 and 38 publications, respectively. Notably, several other European countries, including Turkey (65), England (25), Romania (25), and Portugal (24), also demonstrate significant scientific contributions to rural tourism research.
A clear correlation exists between the number of publications and the accumulation of citations. China, with 1043 total citations, is a leader in this regard and maintains a strong presence in highly cited publications (CP = 79). Portugal, Italy, and Spain also serve as key publication hubs, each with over 600 total citations. Meanwhile, the USA surpasses 550 citations.
When analyzing average citations per publication, Europe emerges as a frontrunner. Among the 21 most active contributing countries, Portugal ranks first with an impressive average of 32.62 citations per publication. Taiwan, Malaysia, New Zealand, and Australia follow closely with averages of 29.41, 24.27, 22.07, and 21.19, respectively. Another group of European countries–England, Germany, Sweden, Spain, Romania, and Poland–register averages ranging from 18.64 to 12.33 citations per publication, further solidifying Europe’s academic influence in this area. Additionally, of the 27 publications with more than 150 citations, 20 originate from European nations, with England and Spain leading this subcategory in terms of highly cited works.
The prominence of European countries in rural tourism research is consistent with their pivotal role in developing and implementing forward-thinking strategies to stimulate rural tourism. These countries leverage tourism as a significant driver of economic growth. However, it is important to note the lack of representation from African, South American, and other regions in terms of both research impact and activity in this field. This gap can be attributed to less developed and less supportive frameworks for rural tourism. Addressing these gaps could present an opportunity to boost their contributions to rural tourism research in the future.
3.6. Most Prolific Journals
The analysis covers 1671 publications across 199 different journals and conference proceedings. Table 6 highlights the leading journals in rural tourism research, each of which has contributed at least three articles to the field. Notably, the top 18 journals, representing just 9% of all publications in this area, account for over one-third of the total output on rural tourism (354 out of 986 publications).

Table 6.
The top publishing journals in rural tourism research.
Sustainability leads the list with 73 contributions, followed by Land with 17 articles. However, journals such as Tourism Management, Journal of Rural Studies, and Tourism Geographies stand out for their significant influence, with an average of over 69 citations per article, despite contributing fewer articles. These journals, although limited in quantity, have garnered substantial academic attention. Similarly, Science of the Total Environment (55.33), Tourism Management Perspectives (53.66), and Environmental Management (50.66) also play a pivotal role in shaping rural tourism research, with their high average citations per article. Notably, of the 27 most influential articles on rural tourism (Table 2), 10 were published in Tourism Management, 3 in Sustainability, and 2 in the Journal of Sustainable Tourism.
Several other publications have appeared in various journals, including Land Use Policy (15 articles), Journal of Sustainable Tourism (13 articles), Tourism Management (8 articles), Geoheritage (6 articles), Environment Development and Sustainability (6 articles) and Worldwide Hospitality and Tourism Themes (5 articles).
Together, these eight highly productive journals have an average impact factor of 4.87, suggesting that rural tourism remains a complementary area within the larger tourism industry. A notable entry on this list is the Journal of Cleaner Production, which boasts a significant impact factor of 9.7. Additionally, several other journals, such as Current Issues in Tourism (3 articles), Water (3 articles), and Agriculture Basel (3 articles), have recently seen relatively high citation rates despite contributing fewer articles.
Among publishers, Elsevier ranks first, with its journals securing two of the top five positions. Interestingly, the top two spots are held by MDPI journals.
In the overall list of the most influential publishing journals, only one-third (6 out of 18) are from Elsevier. When considering the total number of publications (TP) across leading publishers, Elsevier contributed 36 out of 176 articles, representing 20.45% of the total. In contrast, MDPI published 96 of the 176 articles, accounting for 54.54%. However, Elsevier’s impact is greater, with 1749 citations out of 4545 overall, representing 38.48% of the total citations.
4. Co-Authorship Networks
The creation of co-authorship networks aims to map out collaborative relationships among authors in rural tourism research. This was achieved by constructing a network of connections between individual authors and a separate network illustrating co-authorship across countries.
4.1. Co-Authorship Networks Among Authors
Using VOSviewer 1.6.20 software [31], a co-authorship network was developed and visualized in Figure 3. To ensure meaningful participation, we applied three key criteria. First, each author must have published at least two articles, ensuring that early career researchers with potential for future contributions were included. Second, a citation threshold of more than 20 citations was applied, filtering out authors with limited impact. Lastly, we focused on authors with a total link strength greater than one–representing the cumulative strength of their collaborative ties–excluding those working in isolation or without significant collaboration.
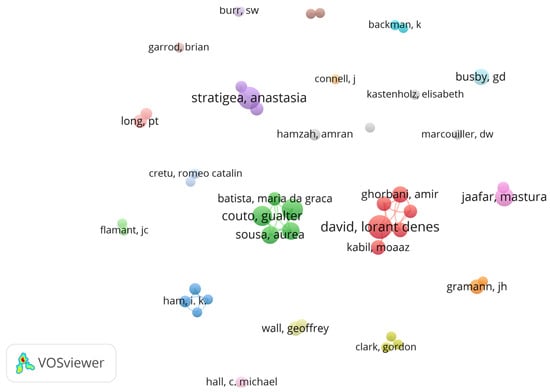
Figure 3.
Co-authorship network by author.
Out of the initial pool of 4565 authors, 290 met these criteria. The size of each node in Figure 3 reflects the total link strength of each author, highlighting those with the most extensive collaborations. Connections between authors indicate the number of co-authored publications they have shared.
Our analysis identified Couto G., Castanho R.A., Pimentel P., and Sousa A. as key figures in collaborative research, with total link strengths of 34, 32, 32, 32, and 32, respectively. The overall co-authorship network consists of three major clusters and two smaller isolated ones, demonstrating minimal to no interaction between them. This confirms the tendency of authors to collaborate within their own teams. The most prominent node includes six authors, led by David Lorant Denes, all concentrated within a single cluster of contributors from the Middle East. Additionally, there are two other isolated groups of primarily European authors, each working with their own clusters. One cluster is centered around Castanho R.A. and Batista Maria da Graca, while the other is led by Ham I.K. and Jo M.H. Notably, no meaningful interactions have developed between these clusters.
4.2. Co-Authorship Network by Country
We utilized the same methodological framework established for the author co-authorship network to develop a co-authorship network by country, resulting in a connection among 73 countries. For clarity, this network is visually represented in Figure 4. Using the same methodological tools initially developed for the author co-authorship network, we extended this approach to map co-authorship connections by country, resulting in a network of 73 interconnected nations. This network is visually represented in Figure 4 for greater clarity. While China leads in the total number of publications (Table 5), its fourth-place ranking in total link strength, at 73, highlights a significant lack of international collaboration compared to EU countries. Chinese researchers primarily collaborate within national borders, a conclusion further supported by our earlier findings in Figure 3.
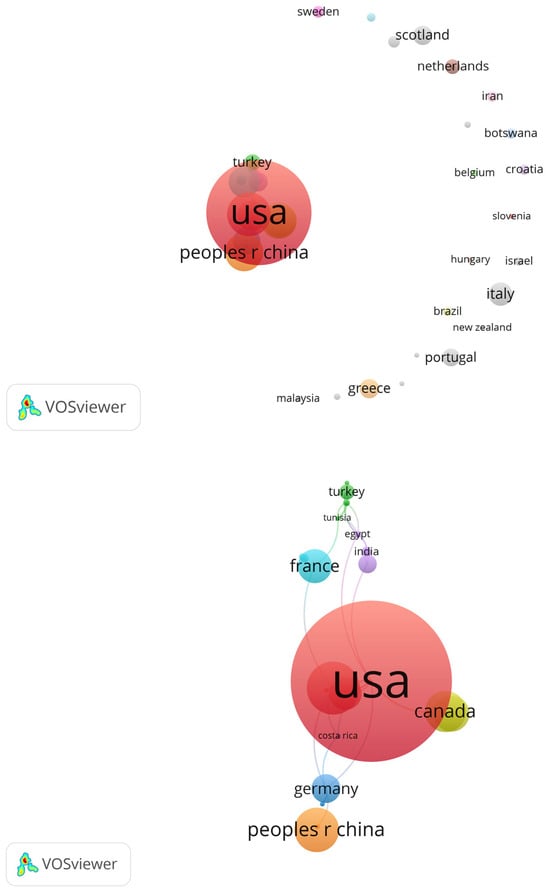
Figure 4.
Co-authorship network by country.
In contrast, the USA emerges as a key hub in the network, with a notable link strength of 50. England and Spain follow closely, with link strengths of 38 and 33, respectively. These four countries serve as central hubs for co-authorship in rural tourism research. The USA shares a cluster with Germany, facilitating collaboration with countries across the EU and Africa (including Spain, England, Kenya, and South Africa), as well as with nations from North Africa and the Middle East (such as Egypt, Turkey, India, and South Korea).
Additionally, we identified two separate clusters led by Canada and France in terms of collaborative networks. It is worth noting the absence of representation from South American nations, as highlighted earlier in Section 3.5. This lack of presence is evident not only in publication volume and influence within the field but also in the limited international collaboration efforts, as shown in the network analysis.
5. Analysis of Conceptual Structure Based on Keyword Co-Occurrence
This chapter focuses on analyzing intellectual capital through keywords to define the conceptual structure of the most frequently used terms in rural tourism research [152]. The analysis is based on the idea that the presence of the same keywords across different documents establishes relationships between core concepts, helping to clarify research directions by revealing associations between these terms [153]. By identifying keyword connections within the literature corpus [154], we can effectively measure the influence of this intellectual capital. These keyword links confirm that the selected terms reliably define the primary themes of the articles [155,156]. This method is a foundational tool for rural tourism research, as it highlights the frequency of key concepts in published works.
As stated earlier, the first step in our keyword co-occurrence analysis was to extract the keywords from the documents in our dataset. We then refined these keywords to minimize redundancy, following the recommendations of Hallinger and Kovačevič [157]. The refinements included converting plural forms to singular, removing duplicates, and expanding abbreviations (e.g., “RT” was clarified as “rural tourism”). These adjustments were made in line with the best practices from previous studies [158,159,160].
After this refinement, we identified 1567 unique keywords. To focus exclusively on the concept of rural tourism, we considered only keywords that appeared in at least eight publications.
Figure 5 provides a visual representation of the keyword co-occurrence network, highlighting the most important terms. Each node (circle) on the map represents a keyword, and the connecting lines show how often these keywords appear together in the dataset (across all articles). The size of each node reflects how frequently the keyword appears—the larger the node, the more often the term is used. The distance between two nodes indicates the strength of their relationship: shorter distances represent stronger connections. Likewise, the thickness of the lines between nodes shows the strength of their co-occurrence, with thicker lines indicating a higher frequency of co-occurrence between the two keywords. The overall structure of the network is designed to visually display the shared knowledge in the dataset, making it easier to identify patterns and connections between keywords. Additionally, different thematic clusters within each intellectual domain are color-coded for clarity.
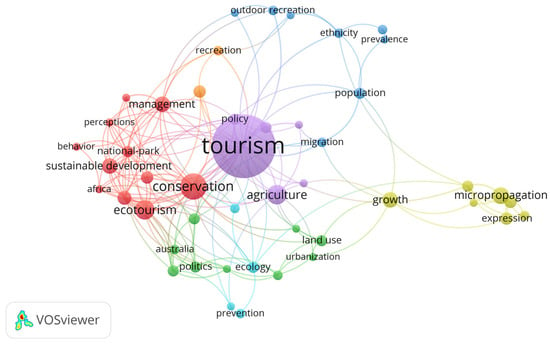
Figure 5.
The keyword co-occurrence network.
The keyword co-occurrence map in Figure 5 reveals eight distinct clusters. After analyzing their content, we initially grouped them into six research themes. Recognizing the inherent subjectivity of this process, we further validated the relative positions of the clusters on the map. The fact that our content-based groupings align with the spatial proximity of the clusters provided additional confirmation of the accuracy of our thematic categorization. Table 7 lists the keywords associated with each cluster and theme, along with their occurrence metrics (keyword frequency) and total link strength (which indicates the keyword’s significance within the field; higher values suggest broader and more frequent connections with other terms). We follow this with a brief discussion of each cluster.

Table 7.
Themes of keyword co-occurrence clusters.
5.1. Research Theme A: The Impact of Rural Tourism on Agriculture and the Environment: Strategies, Consumption, and Quality in the Context of Sustainable Development
This research theme investigates the interconnections among economic, environmental, and social development in rural areas, emphasizing sustainability and a holistic approach to rural tourism.
Cluster 1: This cluster focuses on the relationship between rural tourism and agriculture, a core component of agritourism. It explores how tourism influences local farms and agricultural production, resulting in government policies, legislation, and development plans for rural areas. These initiatives are designed to promote and regulate rural tourism effectively. Successful implementation is evident in consumption patterns that reflect the demand for rural tourism and local products, such as food and handcrafted goods. The primary objective is to deliver not only high-quality experiences within rural tourism but also to enhance the quality of life for residents in these areas. Consequently, environmental considerations play a vital role, encompassing sustainability, nature conservation, and the ecological impacts of tourism on rural landscapes.
5.2. Research Theme B: Nature Conservation and Ecotourism in the Context of Sustainable Development
This research theme investigates the interplay between nature conservation and ecotourism within the framework of sustainable development. It encompasses various elements, including destination management, recreation, rural tourism, and the attitudes and behaviors of visitors in national parks across different geographical regions. The theme integrates aspects of recreation and rural tourism while emphasizing nature conservation and ecotourism.
Cluster 2: This cluster concentrates on nature conservation and the management of protected areas, such as national parks. It explores conservation strategies and the upkeep of these areas in relation to rural tourism. The cluster examines ecotourism and its connection to sustainable development, highlighting practices that promote ecological balance and mitigate the negative environmental impacts of tourism. It underscores the importance of effective management in protected areas and ecotourism, clarifying how management strategies are developed and implemented. Understanding the attitudes, perceptions, and behaviors of visitors and local residents toward protected areas and ecotourism is also essential. This includes investigating how individuals perceive and respond to conservation policies and practices. The research specifically targets a geographical region–China–focusing on particular issues and practices associated with ecotourism and nature conservation in this area.
Cluster 3: This cluster examines issues related to recreational activities taking place in natural and protected areas. The inclusion of recreation suggests that this cluster will explore how natural areas are used for various leisure activities and the implications for management and conservation efforts. In this context, it highlights the relationship between rural tourism and ecotourism, with a specific emphasis on rural areas that encompass protected areas and national parks.
5.3. Research Theme C: Ecological and Sustainable Approaches to Biodiversity Conservation: The Impact of Land Use, Urbanization, and Disease Prevention on Landscapes and Biodiversity in Australia
This research theme explores the policies and management strategies related to biodiversity conservation, specifically examining how land use, urbanization, and disease prevention affect natural landscapes and biodiversity in Australia. It also highlights the crucial role that local communities play in this conservation process.
Cluster 4: This cluster centers on the conservation and management of wildlife and biodiversity, aiming to preserve species and ecosystem diversity through various strategies and approaches. Political factors play a crucial role in this effort, encompassing decision-making, legislation, and government policies that affect environmental conservation. Additionally, the cluster explores the impacts of land use and urbanization on biodiversity and landscapes. It assesses how urban development and land utilization influence the natural environment and its diverse ecosystems. The involvement of local communities is vital in this context, particularly in engaging them in conservation and sustainable development initiatives to foster positive biodiversity outcomes. Finally, the cluster examines landscape-related factors, including landscape diversity and its significance in biodiversity conservation. This analysis is situated within a specific geographical context, focusing on conservation practices and challenges in Australia, which are pertinent to understanding biodiversity and landscape changes in the region.
Cluster 5: This cluster investigates the relationships between living organisms and their environment, with a specific focus on ecological aspects related to biodiversity and nature conservation. It encompasses sustainable practices in nature conservation, land use, and landscape management, all aimed at achieving a long-term balance among environmental, economic, and social factors. Particularly, this cluster centers on a specific disease that has significantly affected agriculture and biodiversity. In this regard, the research may also explore animal health issues and preventive measures, which are crucial for the management of natural and agricultural areas. Furthermore, the cluster examines strategies and actions to mitigate problems such as diseases and other adverse environmental impacts.
5.4. Research Theme D: Biotechnological Approaches in Rural Tourism: Micropropagation, Genetic Transformation, and Plant Sustainability in Agritourism
This research topic seeks to explore the relationship between biotechnological techniques and rural tourism within a comprehensive framework.
Cluster 6: This cluster explores how biotechnological techniques, such as micropropagation and genetic transformation, can advance sustainable agriculture and agritourism. These methods can support the cultivation of specialized crops or plants that enhance tourist attractions. Biotechnology can also improve the quality and yield of local products highlighted to visitors. For instance, improving the quality of local foods or plants can make a region more appealing to tourists. In rural tourism centered on natural and cultural attractions, biotechnological techniques can play a crucial role in conserving and restoring local plants and ecosystems. Micropropagation and regeneration efforts can help revive plant species that are vital to tourism. Additionally, there is a focus on evaluating innovative approaches in rural tourism that integrate biotechnology to create new tourist experiences or products based on plant science and biotechnology.
5.5. Research Topic E: Demographic and Social Factors Shaping Outdoor Recreation: Ethnicity, Migration, and Discrimination in the U.S. Population
This research focuses on key demographic and social factors that influence rural tourism and recreational activities in the United States, with particular attention to ethnicity, migration, and issues of discrimination.
Cluster 7: This cluster focuses on the intersection of ethnicity, migration, and issues of discrimination, particularly within the context of rural tourism. It explores how different ethnic groups migrate and their experiences with discrimination in relation to outdoor recreational activities. The research examines how various population groups access and participate in outdoor leisure opportunities, with particular attention to how migration and ethnicity shape engagement in these activities.
Key topics include the prevalence of discrimination and differences in outdoor participation among ethnic groups. The cluster also analyses the population by segments, categorized by factors such as ethnicity, migration, or involvement in recreational activities. For example, it investigates how different population segments contribute to or engage in rural tourism and outdoor pursuits.
This research is geographically focused, with an emphasis on ethnic and migration dynamics in the U.S. and their influence on outdoor recreation and rural tourism.
5.6. Research Topic F: The Development of Rural Tourism and Its Impacts on Sustainable Development and Community Life
This research topic examines the effects of rural tourism development on key areas such as economic benefits, landscape transformation, and the well-being of local communities. It also focuses on regions where development is less prominent, exploring the reasons behind its lower significance.
Cluster 8: This cluster investigates how rural tourism contributes to sustainable development, with an emphasis on preserving natural and cultural resources in rural areas.
6. Bibliographic Coupling Analysis
As highlighted by Glänzel and Schoepflin in 1999 [161], bibliometric methods are valuable tools for assessing scientific output and making research findings accessible to scholars and other stakeholders. This type of analysis relies on identifying a corpus of literature and using a bibliometric technique based on content or citation analysis to extract and process data [162]. The fundamental concept is that documents citing similar sources are likely to cover related content or themes [163,164]. The intellectual similarity between documents is reflected in their citation patterns, where articles citing the same sources are referred to as bibliographic pairs [165]. The degree of association [166] between two documents increases with the number of shared references, indicating a higher level of thematic similarity [163,167].
Following the principles of bibliographic coupling, we mapped the intellectual structure of rural tourism research by grouping articles into thematic clusters [168]. To ensure meaningful comparisons, it is essential that documents are drawn from the same chronological context, which guarantees that they reference a common body of research [164,169,170,171]. Our analysis focused on a dataset of 1567 articles published between 1967 and 2023. Using VOSviewer software [31], we created a visual representation of the connections between these documents (Figure 6). In this network, each node represents an article. The node’s size reflects its relative frequency of connections with other documents, its color indicates its intellectual cluster, and the thickness of the connecting lines shows the number of shared references. For clarity, we included only articles with more than three shared references, aiming to highlight the most influential and interconnected documents in rural tourism research.
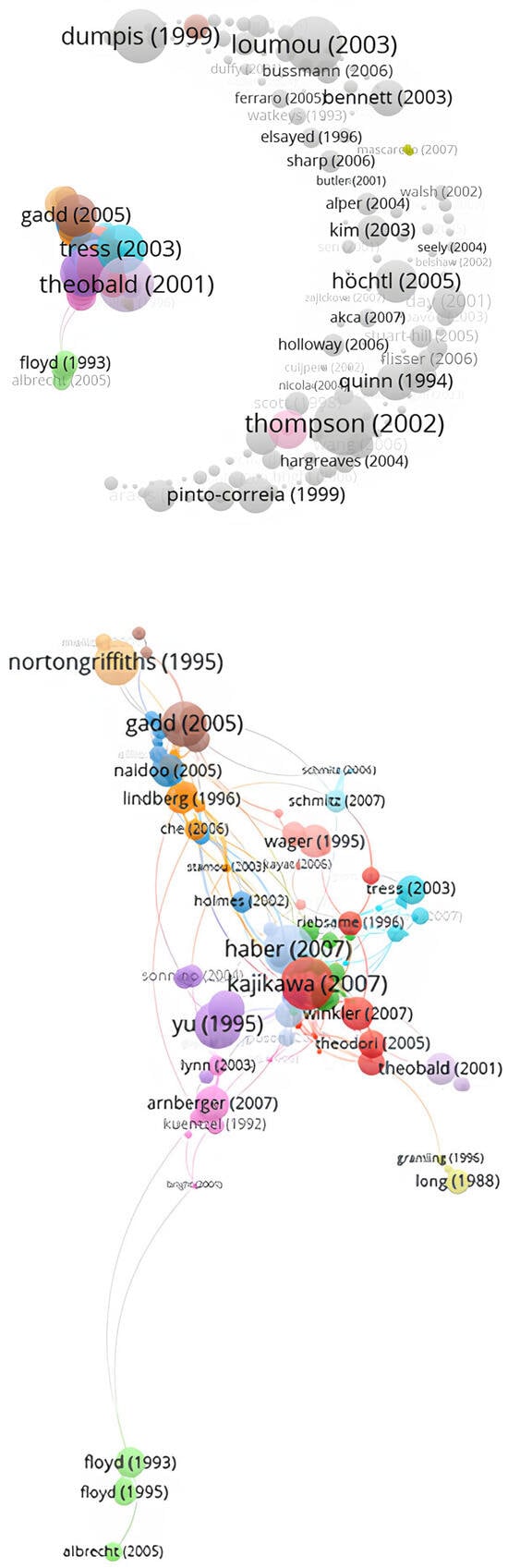
Figure 6.
Bibliographic coupling network.
Alignment of Clusters of Bibliographic Links with Themes of Co-Occurring Keywords
Our content analysis of clusters of bibliographic links has identified strong connections between groups of keywords that frequently co-occur in the network, as detailed in Section 5. Below, we elaborate on each cluster by discussing the core ideas, the interrelationships of the articles within them, and their alignment with corresponding research themes.
- Group 1:
- Rural Development, Agriculture, and Cultural Connections in Tourism
This group comprises seven articles that embody a multidisciplinary approach to rural development. They explore various dimensions of tourism, including economic diversification, cultural and social aspects, and environmental management. The focus is on the comprehensive and sustainable development of rural areas achieved through the strategic integration of agriculture, tourism, and community engagement.
The authors in this group emphasize a holistic perspective on rural development, highlighting the interconnectedness of agricultural practices, tourism, environmental management, and social factors. llbery [67] examines rural development, agricultural diversification, and the linkages between agriculture and rural tourism. Gibson [68] and Allen and Dillman [73] analyze the impacts of tourism on local communities and economies, also addressing the cultural dimensions of rural tourism. Similarly, Waitt [69] investigates the social and environmental consequences of tourism, including community involvement and sustainability in rural contexts. In contrast, Law [70] explores urban and regional development, focusing on tourism infrastructure, which may inform rural development strategies. Farmer et al. [71] discuss agricultural policy and its effects on rural communities and tourism. Finally, Gramling and Freudenburg [72] address environmental and social issues associated with land use, particularly concerning the conservation of rural areas.
This focus aligns with Research Theme A, which takes a multidisciplinary approach to analyze the effects of rural tourism on both agriculture and the environment.
- Group 2:
- Economic, Social, and Environmental Aspects of Rural Tourism and Its Impact on Sustainable Regional Development
This group features 12 authors who investigate the comprehensive development of rural areas by analyzing the economic, social, cultural, and environmental dimensions of rural tourism while assessing its influence on sustainability and regional development.
Authors examine a diverse array of aspects related to rural tourism [72], focusing on its economic [78], social [75,77], cultural [79], and environmental dimensions [84]. Their research emphasizes the assessment of tourism’s impact on the sustainable development of rural areas [85], including analyses of regional policies [74,80], participatory planning [81,82], and innovations in tourism practices [83]. They explore various approaches to tourism planning and evaluation, as well as the associated benefits and challenges for local communities and the natural environment.
The group also aligns with Research Theme A, emphasizing the interplay between rural tourism, agriculture, and environmental considerations within the framework of sustainable development.
- Group 3:
- Analysis and Evaluation of the Impacts of Rural Tourism on Communities and the Environment
This group comprises 15 authors who investigate multiple aspects of rural tourism, including its economic [76,92,93,97,98,99,100,101], cultural [94], and environmental impacts [95,96,102]. Their work encompasses an analysis of the impacts on local communities, landscape and ecological characteristics, policy and regulations, and evaluations of sustainable development practices and tourism [103,104,106].
Group 3 concentrates on nature conservation and ecotourism. It offers valuable insights into the management of protected areas, the role of ecotourism, and the interplay between conservation efforts and recreational activities. This aligns with Research Task B, which similarly explores nature conservation and ecotourism within the framework of sustainable development.
- Group 4:
- Sustainable Development and the Impacts of Rural Tourism on Ecosystems and Communities
This group consists of 10 authors who focus on comprehensive analyses of rural tourism and its effects on ecosystems and communities. Their studies cover economic aspects [105,108,112,115], environmental issues [107,110,111,116], and social dimensions [109,113]. They also explore practices and planning [114] associated with sustainable development.
These studies reflect the objectives of Research Theme B, emphasizing sustainable approaches in ecotourism and nature protection.
- Group 5:
- Integrated Approaches to Evaluating and Planning Rural Tourism
This group includes seven authors who investigate the social and cultural impacts of rural tourism on local communities, cultural practices, and social dynamics [117,118]. Their analyses focus on changes in community life [120,122] and the effects of tourism activities on traditional values and practices. Some contributions address demographic factors and the economic impacts of tourism [123] on local economies. This research evaluates how various social and economic factors influence rural tourism participants and the economic benefits of tourism for regions. Perry et al. [121] discuss planning and policy aspects of rural tourism, assessing different approaches and models for the effective management of tourist destinations and the protection of natural and cultural heritage. Another author examines the effects of tourism activities on the natural environment and evaluates the effectiveness of policies and practices aimed at sustainable development of conservation [119].
- Group 6:
- Holistic Approaches to Rural Tourism: Sustainability, Cultural Impacts, and Planning
This group comprises nine authors who explore various dimensions of rural tourism, with a particular emphasis on sustainability and environmental issues. They examine the impact of rural tourism on the natural environment [124,125,129], evaluating policies and practices for nature conservation and sustainable development. Their research assesses the effectiveness of environmental strategies and approaches. Beaumont [172], Holmes and Marra [130], and Elliott [132] analyze the effects of tourism on local communities and cultural practices, focusing on changes in social structures and cultural integrity. Their work investigates the interactions between tourists and residents and their implications for cultural values. Additionally, Wolf [173] and Naidoo and Adamowicz [131] concentrate on the planning and strategic management of rural tourism, exploring various approaches for developing tourist destinations and implementing sustainable practices. Wells and Joseph [126] share a similar focus, assessing the economic benefits and challenges associated with rural tourism and examining how tourism influences local economies and practices in tourism regions.
Groups 5 and 6 emphasize ecological and sustainable approaches to biodiversity conservation, along with the impacts of land use and urbanization. Their discussions cover a range of topics from biotechnological methods and ecological strategies to political and community factors influencing biodiversity conservation. This focus is directly aligned with the objectives of Research Task C, which also prioritizes ecology and biodiversity protection.
- Group 7:
- Social, Economic, and Environmental Aspects of Rural Tourism
This group consists of 6 authors conducting a comprehensive analysis of rural tourism, addressing its social, economic, and environmental impacts as well as the practices and policies aimed at effective planning and sustainable development. Specifically, Ree et al. [136] and Cloke [139] investigate how rural tourism affects local communities and cultural practices, including shifts in social dynamics and traditional values. O’Rourke [137] evaluates the economic benefits and challenges of rural tourism, focusing on its impact on local economies and rural development. Smutny and Takahashi [138] examine the effects of tourism on the natural environment, proposing strategies for its conservation and sustainable development. Notably, Olesen et al. [140] and Jurkovich [141] are recognized for their work on various approaches and policies for planning and managing rural tourism, concentrating on the creation and implementation of strategies for effective and sustainable development.
Group 7 provides insights into how ethnicity, migration, and discrimination influence access to recreational activities and rural tourism. Correspondingly, Research Task E investigates demographic and social factors affecting outdoor recreation.
- Group 8:
- Interactions and Development in Rural Tourism: Social, Economic, and Environmental Aspects
This group comprises six authors who investigate the complex effects of rural tourism on local communities, regional development, and the natural environment. The studies of Stamou and Paraskevopoulos [86] and Garrod and Pickering [91] focus on the social and cultural impacts of tourism, including its influence on the daily lives and cultural practices of residents. Klak [89] discusses the economic benefits and challenges associated with tourism activities, while Naughton-Treves et al. [87] and Chen et al. [90] examine planning processes. Cruz et al. [88] evaluate the environmental impacts of tourism and assess various strategies for sustainable development and nature conservation.
Group 8 aligns similarly to Groups 1 and 2 to Research Theme A.
- Group 9:
- Multidimensional Studies of Rural Tourism: Social Integration, Economic Benefits, and Environmental Challenges
This group consists of 12 researchers conducting a thorough examination of rural tourism from multiple perspectives. The work of Johnson et al. [144], Huppert et al. [146], Beaumont [128], and Theodori [150] addresses the social and cultural impacts of tourism on local communities. Ashton and Green [142] analyze the economic benefits and challenges associated with tourism activities, while Winkler et al. [143] and Nicholls et al. [148] focus on environmental impacts and conservation efforts. Additionally, this group explores the planning and management of tourist destinations, evaluating the effectiveness of various approaches and strategies for sustainable development [127,145,147,149,151].
Group 9 addresses various aspects of tourism’s impact on rural areas, including economic, social, and environmental dimensions. Similarly, Research Task F explores the implications of rural tourism development for sustainable development and community life.
- Group 10:
- Development and Impacts of Rural Tourism: Economic, Historical, and Environmental Perspectives
This group comprises three authors. Jacobson and Robles [134] explore the historical development of rural tourism, highlighting the factors that have shaped its present form. Haber and Reichel [135] investigate the environmental aspects of tourism, evaluating the impact of tourist activities on the natural environment and proposing strategies for sustainable development. Pulina et al. [133] assess the influence of rural tourism on local economies and social structures by analyzing the benefits and challenges that tourism brings to the development of rural areas.
Group 10 specifically examines biotechnological approaches in the context of rural tourism. It seeks to leverage biotechnology to enhance sustainability and quality in agritourism, directly correlating with Research Task D, which emphasizes the relationship between biotechnological innovations and rural tourism.
While the groupings may initially appear subjective, their positions on the map provide strong evidence for their accuracy. For example, the proximity of clusters 1 (purple), 2 (red), and 8 (pink) aligns with Research Task A. Similarly, clusters 3 (green) and 4 (pea green) correspond to Research Task B. Clusters 5 (brown) and 6 (light blue) reflect the themes of Research Task C, while cluster 10 (gray) relates to Research Task D. Finally, clusters 7 and 9 are closely tied to Research Tasks E and F respectively. A detailed overview of these groups, organized by research tasks, is presented in Table 8, which lists all references from each group, ranked by citation count. The table also indicates the overall strength of the links for each article.

Table 8.
Bibliographic linkages aligned with research tasks on rural tourism.
7. Emerging Themes in Rural Tourism Research
This chapter highlights the unique attributes and historical development of each research task associated with rural tourism. It also explains how these tasks align with specific aspects of rural tourism, such as the connection between rural tourism and agritourism, sustainable tourism with biodiversity conservation, and the demographic and social factors influencing recreation.
- Research Task A:
- The Impact of Rural Tourism on Agriculture and the Environment
This task adopts a multidisciplinary approach to rural tourism, recognizing its complexity. As demonstrated by Group 1, integrating agriculture, tourism, and cultural activities can be highly effective in promoting sustainable rural development. Authors like Ilbery [67] and Waitt [69] focus on agricultural diversification and its links to tourism, identifying that these approaches can offer economic stability and cultural enrichment for rural areas. However, tensions often exist between traditional agricultural practices and tourist activities, which may negatively impact local communities and the natural environment.
Gibson [68] and Law [70] emphasize the importance of cultural connections and regional development, stressing the need to balance agricultural and tourism interests. Exploring community involvement and cultural aspects is crucial to ensuring that tourism benefits not only the economy but also the social and cultural fabric of rural areas.
- Research Task B:
- Economic, Social, and Environmental Aspects
Group 2 provides an in-depth look at the various dimensions of rural tourism, including its economic benefits and environmental challenges. Mordue [74] and Riebsame et al. [75] highlight that while tourism can bring economic advantages, it can also place pressure on local resources and infrastructure. Economic gains may be significant, but their uneven distribution can lead to social tensions and adverse impacts on local communities.
Midmore [77] and Perkins and Salomon [78] stress the need for planning and regulation to ensure that economic benefits are distributed and that environmental impacts are minimized. This includes evaluating modern trends and innovative approaches, as suggested by Pena [76] and Wulff [80], which can help mitigate some of tourism’s negative effects.
- Research Task C:
- Impacts on Communities and the Environment
Group 3 focuses on assessing the effects of rural tourism on communities and ecosystems. Authors such as Hunt and Lambe [92] and Floyd and Wooldridge [94] demonstrate that tourism can impact local communities, including changes in social structures and cultural practices. Understanding these effects is essential for comprehending how tourism influences residents’ daily lives and relationships with nature.
Arnberger and Brandenburg [96] and Mbaiwa [97] address environmental challenges, emphasizing the need to implement environmental strategies to protect natural resources. Effective tourism destination management must consider these environmental factors and ensure that tourism activities do not jeopardize the long-term sustainability of natural and cultural resources.
- Research Task D:
- Sustainable Approaches and Future Challenges
Groups 4 and 5 offer valuable insights into sustainable development and integrated approaches to planning rural tourism. Gadd [107] and Lepp and Holland [108] suggest that sustainable rural tourism development requires comprehensive approaches integrating environmental, social, and economic aspects. This includes implementing policies that promote long-term sustainability and prevent negative impacts on natural and cultural resources.
Kuentzel and Heberlein [104] and Ruddell and Gramann [105] emphasize the importance of participatory planning and evaluation of tourism projects, stressing the need to involve local communities in the decision-making process. This ensures that tourism activities align with residents’ needs and contribute to their well-being.
8. Discussion
This study utilized a comprehensive bibliometric analysis to explore scholarly sources on rural tourism, guided by ten research questions covering a broad spectrum of topics. These ranged from publication patterns and key influential works to collaboration networks and intellectual structures. The literary sources were gathered from the Web of Science database, yielding 1671 publications after review.
Our analysis revealed several important insights into the evolution and current landscape of rural tourism research. The publication trends show a steady rise from the first paper in 1967, peaking significantly by 2015, followed by a slight decline through 2023. As of 2023, 1671 papers were published, with 55% appearing between 2008 and 2015. The most influential works focused on the link between tourism and local food products, which are key to enhancing visitors’ experiences. Another highly cited paper was a systematic review of the literature on rural tourism. China emerged as the leading contributor in terms of publication volume, while Europe, particularly Spain, had a notable academic impact. The journals Sustainability and Land stood out as key platforms for disseminating research on rural tourism.
The co-authorship network analysis showed diverse collaboration patterns at the author and country levels. Key researchers such as Castanho, Couto, Pimentel, and Sousa [24] were highlighted. However, the network also revealed a tendency toward isolated clusters with minimal interaction, suggesting a preference for consistent team collaborations. On the country level, China ranked highest in total publications but showed limited international cooperation. In contrast, the USA, Germany, and England emerged as significant hubs promoting global research partnerships.
A co-occurrence keyword analysis was conducted to map the conceptual framework of rural tourism research, identifying 1671 keywords. The most frequent terms were “tourism”, “conservation”, “ecotourism”, and “agriculture”. The resulting network identified eight distinct clusters, which were further categorized into six key research areas: “The Impact of Rural Tourism on Agriculture and the Environment”, “Nature Conservation and Ecotourism in the Context of Sustainable Development”, “Ecological and Sustainable Approaches in Biodiversity Conservation”, “Biotechnological Approaches in Rural Tourism”, “Demographic and Social Factors Influencing Outdoor Recreation”, and “The Development of Rural Tourism and Its Effects on Sustainable Development and Community Life”.
To map the intellectual structure of rural tourism research, we used bibliographic coupling analysis, focusing on publications between 1967 and 2023. This led to identifying ten distinct author groups, whose content was analyzed, categorized, and organized into themes. These themes validated the six research areas identified earlier, supporting their robustness and relevance in the broader context of rural tourism research.
This study offers several conclusions that may impact both academics and other stakeholders. Academically, the bibliometric analysis we conducted enhances the understanding of rural tourism, identifies gaps in the existing literature, and serves as a valuable foundation for future research. Our findings reveal distinct differences in the perception of rural tourism across Europe [174,175,176], North America [177,178,179], and China [180,181,182]. The state of rural tourism closely mirrors the economic context of a country, highlighting differences between developing [183,184,185] and developed [186,187,188] nations. In developed countries, rural tourism is viewed as a tool for promoting sustainability, preserving cultural heritage, and boosting the economic well-being of rural communities. In contrast, in developing countries, rural tourism is primarily aimed at poverty reduction and the economic revitalization of rural areas. The image of rural tourism is deeply rooted in the cultural context of each country, whether it is based on traditional heritage [189,190] or modern approaches [191,192]. Additionally, the nature of rural tourism is influenced by the social dynamics of both residents and tourists [193,194,195]. Across all these concepts, sustainability stands as the central pillar [196,197,198], explicitly or implicitly acknowledged by scholars throughout the field.
9. Conclusions
The study underscores the need for rural tourism to evolve as a multidimensional sector, adapting to new tourist behaviors and embracing innovations. From a policy and management standpoint, the research highlights rural tourism’s role in advancing sustainability, fostering the transition toward carbon neutrality, and supporting a broader shift toward a greener future.
Our bibliometric analysis provides a comprehensive understanding of the field, offering valuable insights into the trajectory of rural tourism, collaboration dynamics, and research priorities. Furthermore, the paper provides a significant theoretical contribution by systematically mapping the evolution of rural tourism research through bibliometric analysis of 1675 articles published between 1967 and 2023, identifying six core research themes, and analyzing collaboration networks and intellectual structures in the field. This holistic perspective emphasizes sustainability and innovation as critical for the continued growth and impact of rural tourism.
This work contributes to the literature of sustainable science by offering a comprehensive framework for understanding the intersections of rural tourism, sustainability, and innovation, thus providing critical insights for advancing sustainable development goals in the tourism sector.
Despite its contributions, the study has several limitations that warrant attention. One limitation is its reliance on a single Web of Science database, which may exclude significant works from other databases or platforms. To address this, future research should integrate data from multiple databases, such as Scopus, Google Scholar, and regional repositories, to ensure broader coverage. Another limitation is the inherent subjectivity of bibliometric methods, such as keyword clustering and network visualization through software like VOSviewer. Incorporating alternative software tools and triangulating results with manual content analysis could help mitigate potential biases. Furthermore, the clustering methods employed face challenges with overlapping themes and group assignments. Future studies could apply hybrid approaches that combine bibliometric techniques with qualitative thematic analysis to enhance research themes’ multidimensional relevance and clarity. Additionally, this study does not delve deeper into the characteristics of academic contributions or the differences in research directions within rural tourism studies. However, future research could explore these aspects in greater detail and provide a more comprehensive understanding of the field.
The findings of this study offer significant theoretical and practical contributions. First, identifying six core research areas provides a robust framework for understanding rural tourism. These themes highlight the field’s dynamic and interdisciplinary nature, emphasizing the need for integrated approaches to research and policy-making. Second, the systematic mapping of collaboration networks and intellectual structures uncovers key nodes and interactions within the academic community, offering a foundation for fostering more targeted and inclusive research partnerships. The study offers the most extensive overview of rural tourism research to date.
To address future challenges, researchers should explore the intersection of rural tourism with emerging global priorities, such as climate resilience, digital transformation, and inclusive economic development. Methodologically, advancing predictive analytics and machine learning tools for bibliometric studies could refine future trend identification and enhance the accuracy of research forecasts. Practical implications include encouraging rural tourism stakeholders to adopt innovative technologies and sustainable practices, supported by evidence-based policies informed by collaborative research.
Looking ahead, rural tourism research must prioritize not only understanding the current state of the field but also shaping its future trajectory. By overcoming methodological limitations and embracing interdisciplinary, cross-sectoral, and international collaborations, the field can contribute more effectively to sustainable development goals. This study provides a foundation for these efforts, offering a clear roadmap for both researchers and practitioners to advance rural tourism as a catalyst for sustainable, inclusive, and innovative growth.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.S.-B., J.R., and A.S.; methodology, L.S.-B., J.R., and R.R.; software, J.R. and R.R.; validation, L.S.-B., J.R., D.T., and R.R.; formal analysis, D.T. and A.S.; investigation, L.S.-B. and J.R.; resources, J.R. and A.S.; data curation, D.T. and A.S.; writing—original draft preparation, L.S.-B. and J.R.; writing—review and editing, L.S.-B. and D.T.; visualization, L.S.-B., J.R., and R.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sims, R. Food, place, and authenticity: Local food and the sustainable tourism experience. J. Sustain. Tour. 2009, 17, 321–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, C. Sustainable tourism as an adaptive paradigm. Ann. Tour. Res. 1997, 24, 850–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, R. Rural tourism and the challenge of tourism diversification: The case of Cyprus. Tour. Manag. 2002, 23, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, B. What is rural tourism? J. Sustain. Tour. 1994, 2, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNWTO. Available online: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/RegData/etudes/BRIE/2023/751464/EPRS_BRI(2023)751464_EN.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2024).
- Onoyko, Y. Rural tourism: The content, features and types. Hum. Geogr. J. 2017, 23, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosalina, P.D.; Dupré, K.; Wang, Y. Rural tourism: A systematic literature review on definitions and challenges. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2021, 47, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aytuğ, H.K.; Mikaeili, M. Evaluation of Hopa’s rural tourism potential in the context of European Union tourism policy. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2017, 37, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briedenhann, J.; Wickens, E. Tourism routes as a tool for the economic development of rural areas: Vibrant hope or impossible dream? Tour. Manag. 2004, 25, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, S.; Aitchison, C. The role of food tourism in sustaining regional identity: A case study of Cornwall, South West England. J. Sustain. Tour. 2008, 16, 150–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayadi, S. Touristic values of rural areas in Iran: A case study of the Khorasan province. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2009, 11, 529–540. [Google Scholar]
- Raymond, C.M.; Bryan, B.A.; MacDonald, D.H.; Cast, A.; Strathearn, S.; Grandgirard, A.; Kalivas, T. Mapping community values for natural capital and ecosystem services. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68, 1301–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, B. Rural tourism: An overview. In Rural Tourism and Sustainable Development; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, T.H.; Hsieh, H. Indicators of sustainable tourism: A case study from a Taiwan’s wetland. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 67, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepp, A. Residents’ attitudes towards tourism in Bigodi village, Uganda. Tour. Manag. 2007, 28, 876–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frochot, I. A benefit segmentation of tourists in rural areas: A Scottish perspective. Tour. Manag. 2005, 26, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getz, D. Explore the nature and scope of rural tourism: A potential model for rural tourism development. Tour. Manag. 2000, 21, 297–309. [Google Scholar]
- Castanho, R.A.; Couto, G.; Pimentel, P.; Carvalho, C.; Sousa, Á.; da Graça Batista, M. Analysing the Public Administration and Decision-Makers Perceptions Regarding the Potential of Rural Tourism Development in the Azores Region. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. Plan. 2021, 16, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streimikiene, D.; Svagzdiene, B.; Jasinskas, E.; Simanavicius, A. Sustain. tourism develop. and competitiveness: The systematic literature review. Sustainability 2020, 29, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidali, K.L.; Kastenholz, E.; Bianchi, R. Food tourism, niche markets and products in rural tourism: Combining the intimacy model and the experience economy as a rural development strategy. In Rural Tourism: New Concepts, New Research, New Practice; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Garrod, B.; Wornell, R.; Youell, R. Re-conceptualising rural resources as countryside capital: The case of rural tourism. J. Rural Stud. 2006, 22, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, M. The effect of urban planning on urban formations determining bioclimatic comfort area’s effect using satellitia imagines on air quality: A case study of Bursa city. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 6119–6136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdue, S. The role of agriculture in rural tourism: Issues and challenges. J. Travel Res. 2006, 45, 169–178. [Google Scholar]
- Castanho, R.A.; Couto, G.; Sousa, Á.; Pimentel, P.; Batista, M.G.; Carvalho, C. The rural and nature tourism development potential in islands. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, B. Rural tourism: Development, management and sustainability in rural establishments. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1555. [Google Scholar]
- Couto, G.; Pimentel, P.; Batista, M.; Sousa, A.; Carvalho, C.; Castanho, R.A. The Potential of Rural Tourism Development in the Azores Islands from the Perspective of Public Administration and Decision-Makers. WSEAS Trans. Environ. Dev. 2021, 17, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.; Richards, G. (Eds.) Tourism and Sustainable Community Development; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, C. Rural tourism as a promoter of sustainable development: An analysis of rural tourism experiences in Portugal. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2433. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, J.S. The impact of rural tourism on sustainable development in South Korea. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1418. [Google Scholar]
- Stamatios, A.; Georgakellos, D.A. Green certificates research: Bibliometric assessment of current state and future directions. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VoSwiever. Available online: https://www.vosviewer.com/ (accessed on 10 October 2024).
- Rybárová, J.; Rybár, R.; Tometzová, D.; Wittenberger, G. The Use of Cultural Landscape Fragmentation for Rural Tourism Development in the Zemplín Geopark, Slovakia. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molokáč, M.; Kornecká, E.; Tometzová, D. Proposal for Effective Management of Geoparks as a Tool for Sustainable Tourism in the Conditions of the Slovak Republic. Land 2024, 13, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, M.; Rybár, R.; Kaľavský, M. Renewable energy sources as an attractive element of industrial tourism. Curr. Issues Tour. 2018, 21, 2139–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donthu, N.; Kumar, S.; Pattnaik, D. Forty-Five Years of Journal of Business Research: A Bibliometric Analysis. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 109, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, H.K.; Pandey, N.; Kumar, S.; Haldar, A. A Bibliometric Analysis of Board Diversity: Current Status, Development, and Future Research Directions. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 108, 232–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-López, F.J.; Merigó, J.M.; Valenzuela-Fernández, L.; Nicolás, C. Fifty Years of the European Journal of Marketing: A Bibliometric Analysis. Eur. J. Mark. 2018, 52, 439–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, N. Mapping the Expatriate Literature: A Bibliometric Review of the Field from 1998 to 2017 and Identification of Current Research Fronts. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2021, 32, 4687–4724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustak, M.; Salminen, J.; Plé, L.; Wirtz, J. Artificial Intelligence in Marketing: Topic Modeling, Scientometric Analysis, and Research Agenda. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 124, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, K.; Kumar, S. Financial Literacy: A Systematic Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Int. J. Consum. Stud. 2021, 45, 80–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzi, S.; Caputo, A.; Corvino, A.; Venturelli, A. Management Research and the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): A Bibliometric Investigation and Systematic Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donthu, N.; Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, D.; Pandey, N.; Lim, W.M. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 133, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Gustafsson, A. Investigating the emerging COVID-19 research trends in the field of business and management: A bibliometric analysis. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 118, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguinis, H.; Pierce, C.A.; Bosco, F.A.; Dalton, D.R.; Dalton, C.M. Debunking myths and urban legends about meta-analysis. Organ. Res. Methods 2011, 14, 306–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combs, J.G.; Ketchen, D.J.; Crook, T.R.; Roth, P.L. Assessing cumulative evidence within ‘macro’ research: Why meta-analysis should be preferred over vote counting. J. Manag. Stud. 2011, 48, 178–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiri, S.; Dutta, S.; Huang, H. Analyzing research trends in the field of family business: A bibliometric approach. J. Fam. Bus. Strategy 2021, 12, 100331. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, W.M.; Lee, M.S.; Kwon, Y.J. The role of marketing and communication in green product consumption: A bibliometric analysis. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 132, 896–905. [Google Scholar]
- Broadus, R.N. Toward a definition of “bibliometrics”. Scientometrics 1987, 12, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, A. Statistical bibliography or bibliometrics? J. Doc. 1969, 25, 348–349. [Google Scholar]
- Price, D.J.D.S. Little Science, Big Science; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Bessière, J. Local development and heritage: Traditional food and cuisine as tourist attractions in rural areas. Sociol. Rural. 1998, 38, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, B.; Kastenholz, E. Rural tourism: The evolution of practice and research approaches—Towards a new agenda. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2020, 35, 100–108. [Google Scholar]
- Gössling, S. Food management in tourism: Reducing tourism’s carbon footprint. J. Sustain. Tour. 2011, 19, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajocco, S.; Chiarucci, A.; De Angelis, A. The impact of land use/land cover changes on ecosystem services in rural areas: A case study of the Italian Apennines. Ecosyst. Serv. 2012, 2, 56–67. [Google Scholar]
- Bruwer, J. South African wine routes: Some perspectives on the wine tourism industry. Tour. Manag. 2003, 24, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawley, M. Integrated rural tourism: Concepts and practice. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2008, 10, 153–164. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, P. Residents’ attitudes to proposed tourism development. Tour. Manag. 2000, 21, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getz, D. Characteristics and goals of family and owner-operated businesses in the tourism industry. Tour. Manag. 2000, 21, 622–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayadi, S. Public preferences for landscape features: The case of agricultural landscapes in mountainous Mediterranean areas. Tour. Manag. 2009, 30, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.D.; Krannich, R.S. “Culture Clash’’ Revisited: Newcomer and Longer-Term Residents’ Attitudes Toward Land Use, Development, and Environmental Issues in Rural Communities in the Rocky Mountain West. Rural Sociol. 2000, 65, 396–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.D.; Snepenger, D.J.; Akis, S. Residents’ perceptions of tourism development. Ann. Tour. Res. 1994, 21, 629–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischer, A.; Felsenstein, D. Support for rural tourism: Does it make a difference? Ann. Tour. Res. 2000, 27, 1007–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdue, R.R.; Long, P.T.; Kang, Y.S. Boomtown tourism and resident quality of life: The marketing of gaming to host community residents. J. Bus. Res. 1999, 44, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrigal, R. A tale of tourism in two cities. Ann. Tour. Res. 1993, 20, 336–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppermann, M. Rural tourism in southern Germany. Ann. Tour. Res. 1996, 23, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdue, R.R.; Long, P.T.; Allen, L. Rural resident tourism perceptions and attitudes. Ann. Tour. Res. 1987, 14, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilbery, B.W. The Geography of Rural Change; Longman: Harlow, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, C. Rural transformation and cultural industries: Popular music on the New South Wales Far North Coast. Aust. Geogr. 2004, 35, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waitt, G. Researching tourism as a social force. In The Critical Turn in Tourism Studies: Innovative Research Methodologies; Ateljevic, I., Pritchard, A., Morgan, N., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 139–154. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, B.H.; Ye, H.; Law, R. Systematic review of smart tourism research. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, F.L.; Ilvento, T.W.; Luloff, A.E. Rural-community poverty: A LISREL measurement model. Rural Sociol. 1989, 54, 491–508. [Google Scholar]
- Gramling, R.; Freudenburg, W.R. Environmental sociology: Toward a paradigm for the 21st century. Sociol. Spectr. 1996, 16, 347–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.C.; Dillman, D.A. Rural areas and their political economy. In Investing in People: The Human Capital Needs of Rural America; Beaulieu, L.J., Mulkey, D., Eds.; Westview Press: Boulder, CO, USA, 1991; pp. 95–114. [Google Scholar]
- Mordue, T. Heartbeat Country: Conflicting values, coinciding visions. Environ. Plan. A 1999, 31, 629–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riebsame, W.E.; Gosnell, H.; Theobald, D.M. Land use and landscape change in the Colorado Mountains I. Theory, scale, and pattern. Mt. Res. Dev. 1996, 16, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, E.D. Lost in translation: Methodological considerations in cross-cultural research. Child Dev. 2007, 78, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midmore, P. Towards a postmodern agricultural economics. J. Agric. Econ. 1996, 47, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, D.N.; Salomon, G. Are cognitive skills context-bound? Educ. Res. 1989, 18, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, D.G. Marriage, Celibacy, and Heresy in Ancient Christianity: The Jovinianist Controversy; OUP Oxford: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wulff, H. Dancing at the Crossroads: Memory and Mobility in Ireland; Berghahn Books: New York, NY, USA, 2007; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Baxter, M.; Kouparitsas, M.A. Determinants of business cycle comovement: A robust analysis. J. Monet. Econ. 2005, 52, 113–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notar, B.E. Displacing Desire: Travel and Popular Culture in China; University of Hawaii Press: Hawaii, HI, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Tress, B.; Tress, G.; Fry, G. Integrative studies on rural landscapes: Policy expectations and research practice. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2005, 70, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.R.; Collins, C. US socioeconomic and racial differences in health: Patterns and explanations. Annu. Rev. Sociol. 1995, 21, 349–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joss, A.; Zabczynski, S.; Göbel, A.; Hoffmann, B.; Löffler, D.; McArdell, C.S.; Ternes, T.A.; Thomsen, A.; Siegrist, H. Biological degradation of pharmaceuticals in municipal wastewater treatment: Proposing a classification scheme. Water Res. 2006, 40, 1686–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamou, A.G.; Paraskevopoulos, S. Ecotourism experiences in visitors’ books of a Greek reserve: A critical discourse analysis perspective. Sociol. Rural. 2003, 43, 34–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naughton-Treves, L.I.S.A.; Grossberg, R.; Treves, A. Paying for tolerance: Rural citizens’ attitudes toward wolf depredation and compensation. Conserv. Biol. 2003, 17, 1500–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, F.W., Jr.; Burns, S.J.; Karmann, I.; Sharp, W.D.; Vuille, M.; Cardoso, A.O.; Ferrari, J.A.; Silva Dias, P.L.; Viana, O., Jr. Insolation-driven changes in atmospheric circulation over the past 116,000 years in subtropical Brazil. Nature 2005, 434, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klak, T. Sustainable ecotourism development in Central America and the Caribbean: Review of debates and conceptual reformulation. Geogr. Compass 2007, 1, 1037–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Liu, W.L.; Liaw, S.L.; Yu, C.H. Development of a dynamic strategy planning theory and system for sustainable river basin land use management. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 346, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrod, S.; Pickering, M.J. Alignment in dialogue. In The Oxford Handbook of Psycholinguistics; Oxford University Press: Oxford, MI, USA, 2007; pp. 443–451. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, S.D.; Lambe, C.J. Marketing’s contribution to business strategy: Market orientation, relationship marketing and resource-advantage theory. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2000, 2, 17–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentice, R.C.; Witt, S.F.; Hamer, C. Tourism as experience: The case of heritage parks. Ann. Tour. Res. 1998, 25, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floyd, S.W.; Wooldridge, B. Middle management’s strategic influence and organizational performance. J. Manag. Stud. 1997, 34, 465–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, N.A.; Brown, R.D. Effects of recreational use impacts on hiking experiences in natural areas. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2003, 64, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnberger, A.; Brandenburg, C. Past on-site experience, crowding perceptions, and use displacement of visitor groups to a peri-urban national park. Environ. Manag. 2007, 40, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbaiwa, J.E. The problems and prospects of sustainable tourism development in the Okavango Delta, Botswana. J. Sustain. Tour. 2005, 13, 203–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennell, M.J. Low self-esteem: A cognitive perspective. Behav. Cogn. Psychother. 1997, 25, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kgathi, D.L.; Kniveton, D.; Ringrose, S.; Turton, A.R.; Vanderpost, C.H.; Lundqvist, J.; Seely, M. The Okavango; a river supporting its people, environment and economic development. J. Hydrol. 2006, 331, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Li, Y.; Tang, Z.; Yu, D.; Ni, L.; Liu, H.; Xie, P.; Da, L.; et al. Biodiversity changes in the lakes of the Central Yangtze. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2006, 4, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, R.J.; Klein, R.J. Climate change and coastal management on Europe’s coast. In Managing European Coasts: Past, Present and Future; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 199–226. [Google Scholar]
- Guyer, J. Endowments and Assets: The Anthropology of Wealth and the Economics of Intrahousehold Allocation. Intrahousehold Re-source Allocation in Developing Countries: Methods, Models, and Policy. 1997. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/243660577_Endowments_and_assets_The_anthropology_of_wealth_and_the_economics_of_intrahousehold_allocation (accessed on 10 November 2024).
- Bixter, M.T. Happiness, political orientation, and religiosity. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2015, 72, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuentzel, W.F.; Heberlein, T.A. Cognitive and behavioral adaptations to perceived crowding: A panel study of coping and displacement. J. Leis. Res. 1992, 24, 377–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruddell, E.J.; Gramann, J.H. Goal orientation, norms, and noise-induced conflict among recreation area users. Leis. Sci. 1994, 16, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wager, J. Environmental planning for a world heritage site: Case study of Angkor, Cambodia. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 1995, 38, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadd, M.E. Conservation outside of parks: Attitudes of local people in Laikipia, Kenya. Environ. Conserv. 2005, 32, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepp, A.; Holland, S. A comparison of attitudes toward state-led conservation and community-based conservation in the village of Bigodi, Uganda. Soc. Nat. Resour. 2006, 19, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, A. Immigration, health and social control: Medical aspects of the policy governing Aliyah from Morocco and Tunisia, 1951–1954. J. Isr. Hist. 2003, 22, 32–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jim, C. Planning strategies to overcome constraints on greenspace provision in urban Hong Kong. Town Plan. Rev. 2002, 73, 127–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maikhuri, R.K.; Nautiyal, S.; Rao, K.S.; Saxena, K.G. Conservation policy–people conflicts: A case study from Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve (a world heritage site), India. For. Policy Econ. 2001, 2, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton-Griffiths, M.; Southey, C. The opportunity costs of biodiversity conservation in Kenya. Ecol. Econ. 1995, 12, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, D.; Jara, F.; Moreno, C. Escaped salmon in the inner seas, southern Chile: Facing ecological and social conflicts. Ecol. Appl. 2001, 11, 1750–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.B.; Ye, Y.M. The evolvement of land consolidation in rural China from the perspective of governing tension between construction land expansion and farmland protection. In Land Governance and Gender: The Tenure-Gender Nexus in Land Management and Land Policy; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2021; pp. 115–128. [Google Scholar]
- Munthali, S.M. Transfrontier conservation areas: Integrating biodiversity and poverty alleviation in Southern Africa. In Natural Resources Forum; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2007; Volume 31, pp. 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Melick, D.; Yang, X.; Xu, J. Seeing the wood for the trees: How conservation policies can place greater pressure on village forests in southwest China. Plant Conserv. Biodivers. 2007, 6, 385–397. [Google Scholar]
- Floyd, M.F.; Gramann, J.H. Effects of acculturation and structural assimilation in resource-based recreation: The case of Mexican Americans. J. Leis. Res. 1993, 25, 6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floyd, M.F.; Gramann, J.H. Perceptions of discrimination in a recreation context. J. Leis. Res. 1995, 27, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaull, S.L.; Gramann, J.H. The effect of cultural assimilation on the importance of family-related and nature-related recreation among Hispanic Americans. J. Leis. Res. 1998, 30, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossio, D.A.; Girvan, M.S.; Verchot, L.; Bullimore, J.; Borelli, T.; Albrecht, A.; Scow, K.M.; Ball, A.S.; Pretty, J.N.; Osborn, A.M. Soil microbial community response to land use change in an agricultural landscape of western Kenya. Microb. Ecol. 2005, 49, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, R.W.; Lindell, M.K.; Tierney, K.J. (Eds.) Facing the Unexpected: Disaster Preparedness and Response in the United States; Joseph Henry Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Verchot, L.V.; Van Noordwijk, M.; Kandji, S.; Tomich, T.; Ong, C.; Albrecht, A.; Mackensen, J.; Bantilan, C.; Anupama, K.V.; Palm, C. Climate change: Linking adaptation and mitigation through agroforestry. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Change 2007, 12, 901–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdock, S.H.; Albrecht, D.E.; Hamm, R.R.; Backman, K. Role of sociodemographic characteristics in projections of water use. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 1991, 117, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, O.J. Predator diversity and trophic interactions. Ecology 2007, 88, 2415–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koellner, T.; Schmitz, O.J. Biodiversity, ecosystem function, and investment risk. BioScience 2006, 56, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, A.; Joseph, G.M. Summer of Discontent, Seasons of Upheaval: Elite Politics and Rural Insurgency in Yucatan, 1876–1915; Stanford University Press: Redwood City, CA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, M.; Van Doorn, G.S.; Leimar, O.; Weissing, F.J. Life-history trade-offs favour the evolution of animal personalities. Nature 2007, 447, 581–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaumont, C. Women, citizenship and Catholicism in the Irish free state, 1922–1948. Women’s Hist. Rev. 1997, 6, 563–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, A.E.; Vlek, C.A.; Coeterier, J.F. Group differences in the aesthetic evaluation of nature development plans: A multilevel approach. J. Environ. Psychol. 1998, 18, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, J.; Marra, M. Having a laugh at work: How humour contributes to workplace culture. J. Pragmat. 2002, 34, 1683–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidoo, R.; Adamowicz, W.L. Economic benefits of biodiversity exceed costs of conservation at an African rainforest reserve. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2005, 102, 16712–16716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.R. Referral hiring and ethnically homogeneous jobs: How prevalent is the connection and for whom? Soc. Sci. Res. 2001, 30, 401–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pulina, M.; Dettori, D.G.; Paba, A. Life cycle of agrotouristic firms in Sardinia. Tour. Manag. 2006, 27, 1006–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, S.K.; Robles, R. Ecotourism, sustainable development, and conservation education: Development of a tour guide training program in Tortuguero, Costa Rica. Environ. Manag. 1992, 16, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, S.; Reichel, A. The cumulative nature of the entrepreneurial process: The contribution of human capital, planning and environment resources to small venture performance. J. Bus. Ventur. 2007, 22, 119–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ree, A.H.; Florenes, V.A.; Berg, J.P.; Maelandsmo, G.M.; Nesland, J.M.; Fodstad, O. High levels of messenger RNAs for tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMP-1 and TIMP-2) in primary breast carcinomas are associated with development of distant metastases. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 1997, 3, 1623–1628. [Google Scholar]
- O’Rourke, K.H. Economic integration and convergence: An historical perspective. J. Econ. Integr. 1999, 14, 133–168. [Google Scholar]
- Smutny, G.; Takahashi, L. Economic change and environmental conflict in the Western Mountain states of the USA. Environ. Plan. A 1999, 31, 979–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloke, P. Conceptualizing rurality. Handb. Rural Stud. 2006, 18, 18–28. [Google Scholar]
- Olesen, J.E.; Carter, T.R.; Diaz-Ambrona, C.H.; Fronzek, S.; Heidmann, T.; Hickler, T.; Holt, T.; Minguez, M.I.; Morales, P.; Palutikof, J.P.; et al. Uncertainties in projected impacts of climate change on European agriculture and terrestrial ecosystems based on scenarios from regional climate models. Clim. Change 2007, 81, 123–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurkovich, G.J. Paint the ceiling: Reflections on illness. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 1997, 43, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashton, D.; Green, F. Education, Training and the Global Economy; Edward Elgar: Cheltenham, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Winkler, R.; Field, D.R.; Luloff, A.E.; Krannich, R.S.; Williams, T. Social landscapes of the inter-mountain West: A comparison of ‘old West’ and ‘new West’ communities. Rural Sociol. 2007, 72, 478–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, G.; Melin, L.; Whittington, R. Micro strategy and strategizing: Towards an activity-based view. J. Manag. Stud. 2003, 40, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon-Jones, E.; Mills, J. Cognitive dissonance. In Progress on a Pivotal Theory in Social Psychology; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Huppert, J.D.; Foa, E.B.; Furr, J.M.; Filip, J.C.; Mathews, A. Interpretation bias in social anxiety: A dimensional perspective. Cogn. Ther. Res. 2003, 27, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theobald, D.M. Land-use dynamics beyond the American urban fringe. Geogr. Rev. 2001, 91, 544–564. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls, S.; Vogt, C.; Jun, S.H. Heeding the call for heritage tourism: More visitors want an “experience” in their vacations—Something a historical park can provide. Parks Recreat. 2004, 39, 38–48. [Google Scholar]
- Crone, T.M. An alternative definition of economic regions in the United States based on similarities in state business cycles. Rev. Econ. Stat. 2005, 87, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodori, G.L. Community and community development in resource-based areas: Operational definitions rooted in an interactional perspective. Soc. Nat. Resour. 2005, 18, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connell, J.; Reynolds, P. The implications of technological developments on Tourist Information Centres. Tour. Manag. 1999, 20, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Sanz, J.M.; Penelas-Leguía, A.; Gutiérrez-Rodríguez, P.; Cuesta-Valiño, P. Sustainable development and consumer behavior in rural tourism—The importance of image and loyalty for host communities. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, M.J.; Martínez, M.A.; Gutiérrez, J. Content analysis of bibliometric studies: A bibliometric analysis. Scientometrics 2011, 87, 653–676. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, C.; Li, G.; Kamarthi, S.; Jin, X.; Moghaddam, M. Trends in intelligent manufacturing research: A keyword co-occurrence network based review. J. Intell. Manuf. 2022, 33, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biber, D.; Conrad, S.; Reppen, R. Corpus linguistics: Investigating Language Structure and Use; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- McEnery, T.; Wilson, A. Corpus Linguistics: An introduction; Edinburgh University Press: Edinburgh, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hallinger, P.; Kovačević, J. A Bibliometric Review of Research on Educational Administration: Science Mapping the Literature, 1960 to 2018. Rev. Educ. Res. 2019, 89, 335–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yin, Y.; Liu, W.; Dunford, M. Visualizing the Intellectual Structure and Evolution of Innovation Systems Research: A Bibliometric Analysis. Scientometrics 2015, 103, 135–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, M.M. Bibliographic Coupling between Scientific Papers. Am. Doc. 1963, 14, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, B.H. Bibliographic Coupling: A Review. Inf. Storage Retr. 1974, 10, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glänzel, W.; Schoepflin, U. A bibliometric study of reference literature in the sciences and social sciences. Scientometrics 1999, 44, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallin, J.A. Bibliometric methods: Pitfalls and possibilities. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2005, 97, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennell, D.A. Ecotourism in Theory and Practice; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Prentice, R. Chapter 10. Revisiting ‘Heritage: A Key Sector of the (then) “New” Tourism’—Out With the ‘New’ and Out With ‘Heritage’? In Classic Reviews in Tourism, 1st ed.; Cooper, C., Ed.; Blue Ridge Summit; Channel View Publications: Bristol, UK, 2003; pp. 164–191. [Google Scholar]
- Glänzel, W.A. bibliometric approach to social sciences: National research performances in 6 selected social science areas, 1990–1992. Scientometrics 1996, 35, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderberg, M.R. Cluster Analysis for Applications; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Floyd, M.F.; Gramann, J.H. Experience-based setting management: Implications for market segmentation of hunters. Leis. Sci. 1997, 19, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldenderfer, M.S.; Blashfield, R.K. Cluster Analysis (Sage University Paper Series on Quantitative Applications in the Social Sciences, 07-044); Sage Publications: Beverly Hill, CA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- López-Fernández, M.C.; Serrano-Bedia, A.M.; Pérez-Pérez, M. Entrepreneurship and Family Firm Research: A 1411 Bibliometric Analysis of An Emerging Field. J. Small Bus. Manag. 2016, 54, 622–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Börner, K.; Chen, C.; Boyack, K.W. Visualizing Knowledge Domains. Annu. Rev. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 179–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, N. Scheduling staff using mixed integer programming. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1997, 98, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, M. Bourdieu’s rules of the game: An introspection into methodological questions of translation sociology. Matraga Rio Jan. 2007, 14, 130–145. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, G.; Williams, A.M. Critical Issues in Tourism: A Geographical Perspective; Blackwell Publishers: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, D.; Roberts, L.; Mitchell, M. New Directions in Rural Tourism; Ashgate Publishing: Farnham, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Weaver, D.B. Comprehensive and minimal ecotourism: Accommodation and movement towards a continuum. Tour. Manag. 2005, 26, 422–432. [Google Scholar]
- Long, P.T.; Perdue, R.R.; Allen, L. Rural resident tourism perceptions and attitudes by community level of tourism. J. Travel Res. 1994, 32, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGehee, N.G.; Andereck, K.L. Volunteer tourism and the “voluntoured”: The case of Tijuana, Mexico. J. Sustain. Tour. 2007, 15, 466–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B. Rural tourism in China. Tour. Manag. 2011, 32, 1438–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. Community decision-making: Participation in development. Ann. Tour. Res. 2006, 33, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Ritchie, J.R.B.; Echtner, C.M. Social capital and tourism entrepreneurship. Ann. Tour. Res. 2009, 37, 487–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Chiang, J.T.; Ko, P.F. The benefits of tourism for rural community development. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2023, 10, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, R. Challenges of a globalized tourism: A perspective from rural areas in the Dominican Republic. Ann. Tour. Res. 2003, 30, 347–363. [Google Scholar]
- González, M.A.; León, C. Rural tourism in Latin America: A comparison of community-based tourism and agrotourism. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2014, 16, 422–434. [Google Scholar]
- Kneafsey, M. Local food and rural tourism: The case of North Yorkshire. Tour. Hosp. Res. 2001, 3, 132–143. [Google Scholar]
- McGehee, N.G. For love of the land: The role of agritourism in rural development. Rural Tour. Res. 2002, 1, 18–26. [Google Scholar]
- Bramwell, B. Collaborative Tourism Planning: A Case Study of the Lake District, England. In Tourism and Migration: New Relationships Between Production and Consumption; Hall, D.R., Williams, A.M., Eds.; The Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998; pp. 29–42. [Google Scholar]
- Urry, J. The Tourist Gaze: Leisure and Travel in Contemporary Societies; Sage Publications: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, G. Cultural Tourism in Europe; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Cottam, H. Rural Tourism: A Way Sustain Rural Areas? Int. J. Tour. Res. 2004, 6, 177–186. [Google Scholar]
- Hjalager, A.-M. A review of innovation research in tourism. Tour. Manag. 2002, 23, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelliher, F.; Hjalager, A.-M.; Mura, P. The role of rural tourism in the revitalization of local communities: The case of Wales. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2018, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J. Rural tourism, social stability, and community resilience: Evidence from rural China. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2021, 39, 54–63. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhuang, H. Exploring the social impact of rural tourism on community identity and cohesion. Tour. Geogr. 2021, 23, 387–404. [Google Scholar]
- López-Sanz, J.M.; Penelas-Leguía, A.; Gutiérrez-Rodríguez, P.; Cuesta-Valiño, P. Rural tourism and the sustainable development goals. A study of the variables that most influence the behavior of the tourist. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 722973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Kanthawala, S.; Choi, E.; Kim, Y. Rural and non-rural digital divide persists in older adults: Internet access, usage, and attitudes toward technology. Gerontechnology 2021, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramwell, B. Rural tourism and sustainable rural tourism. J. Sustain. Tour. 1994, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, J.L.; Sousa, B. The basic social process of “re-functionalising” and its implications for housing tourism: A niche tourism perspective. In Advances in Tourism, Technology and Systems; Abreu, A., Liberato, D., González, E.A., Ojeda, J.C.G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).