Synergistic Remediation of Coastal Wetlands: Identifying Optimal Substrate Amendment and Incorporation Ratio for Enhanced Kandelia obovata Growth and Nutrient Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Experiment of Substrate Amendment Combined with Kandelia obovata Plantation
2.3. Analytical Methods
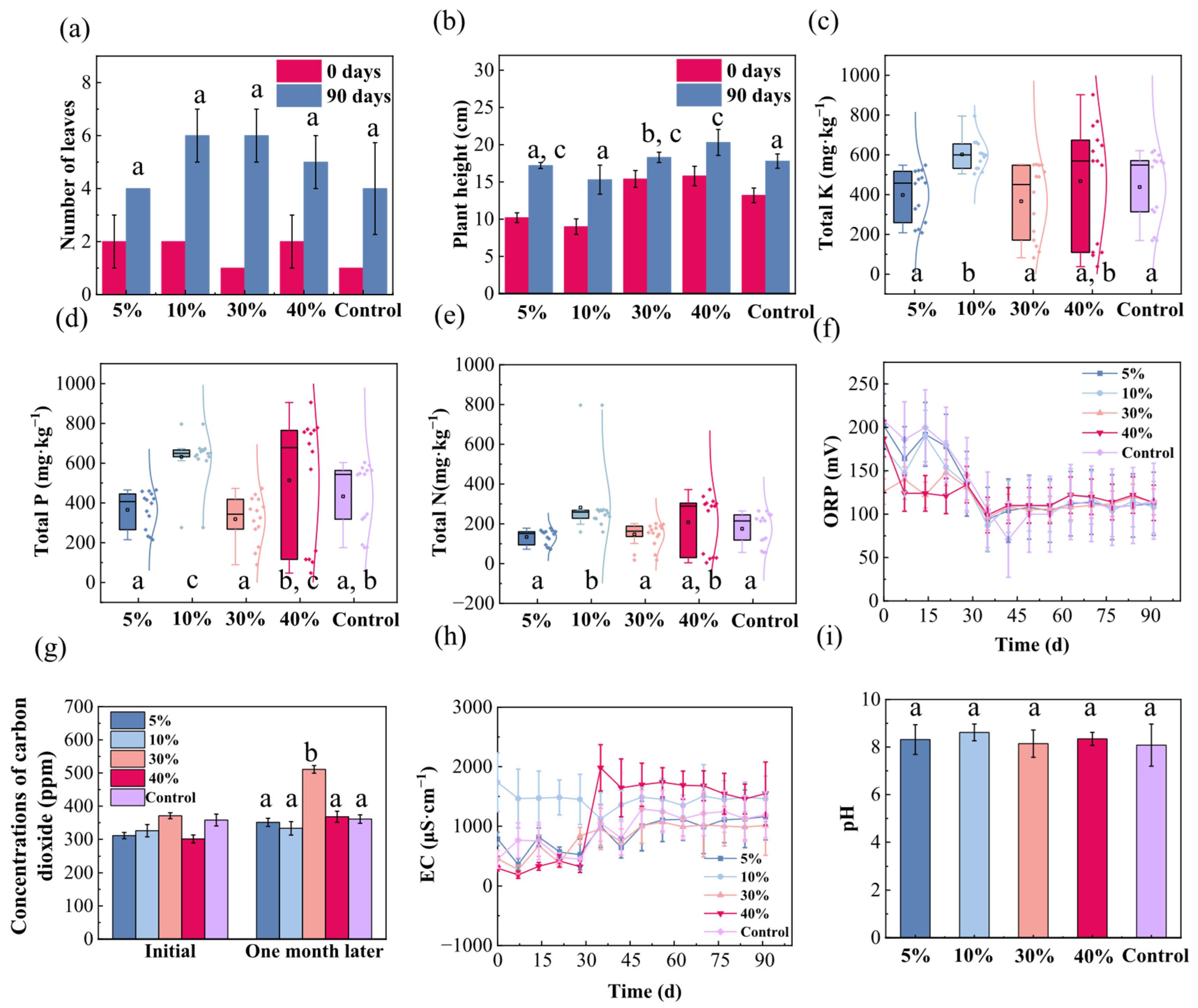
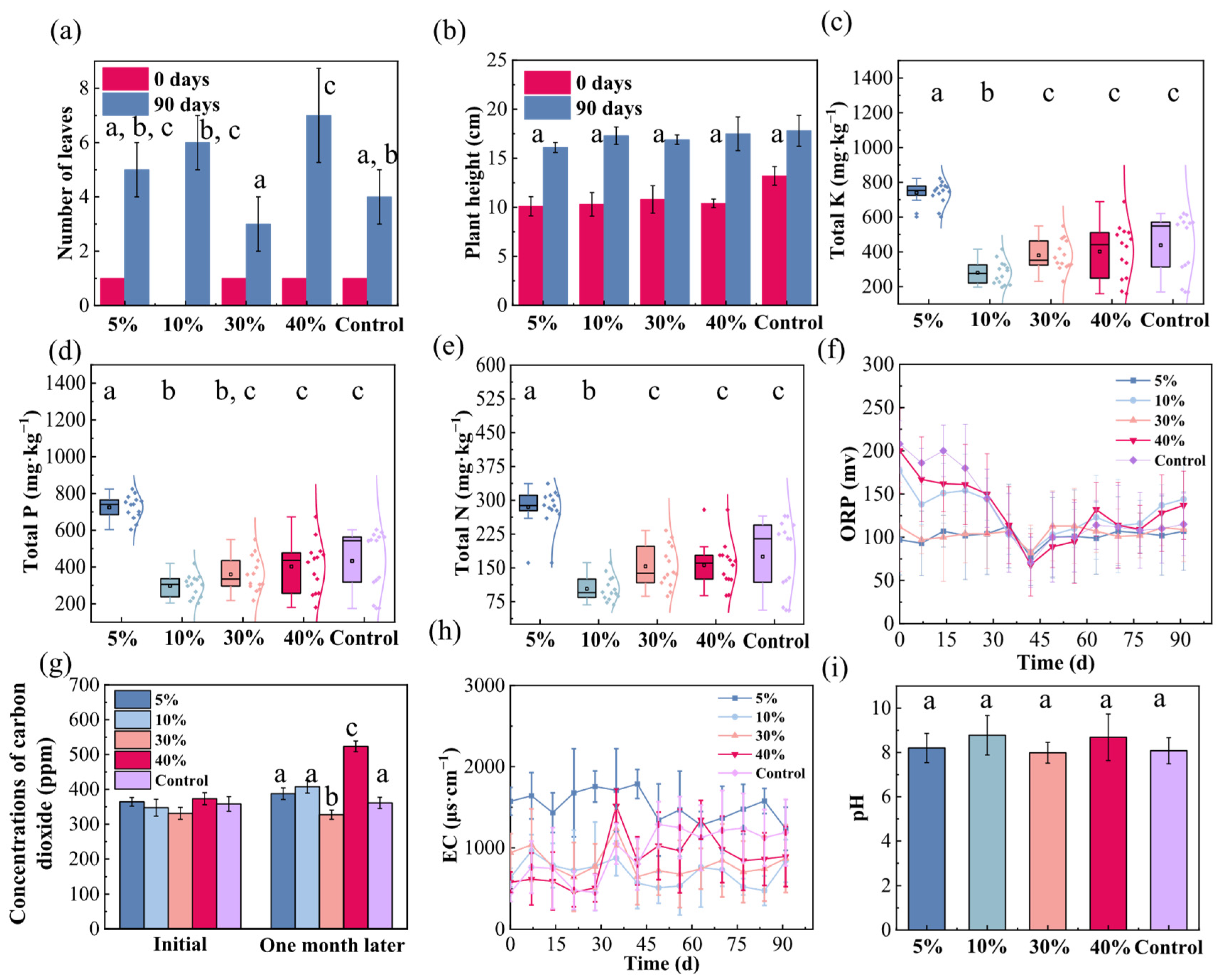
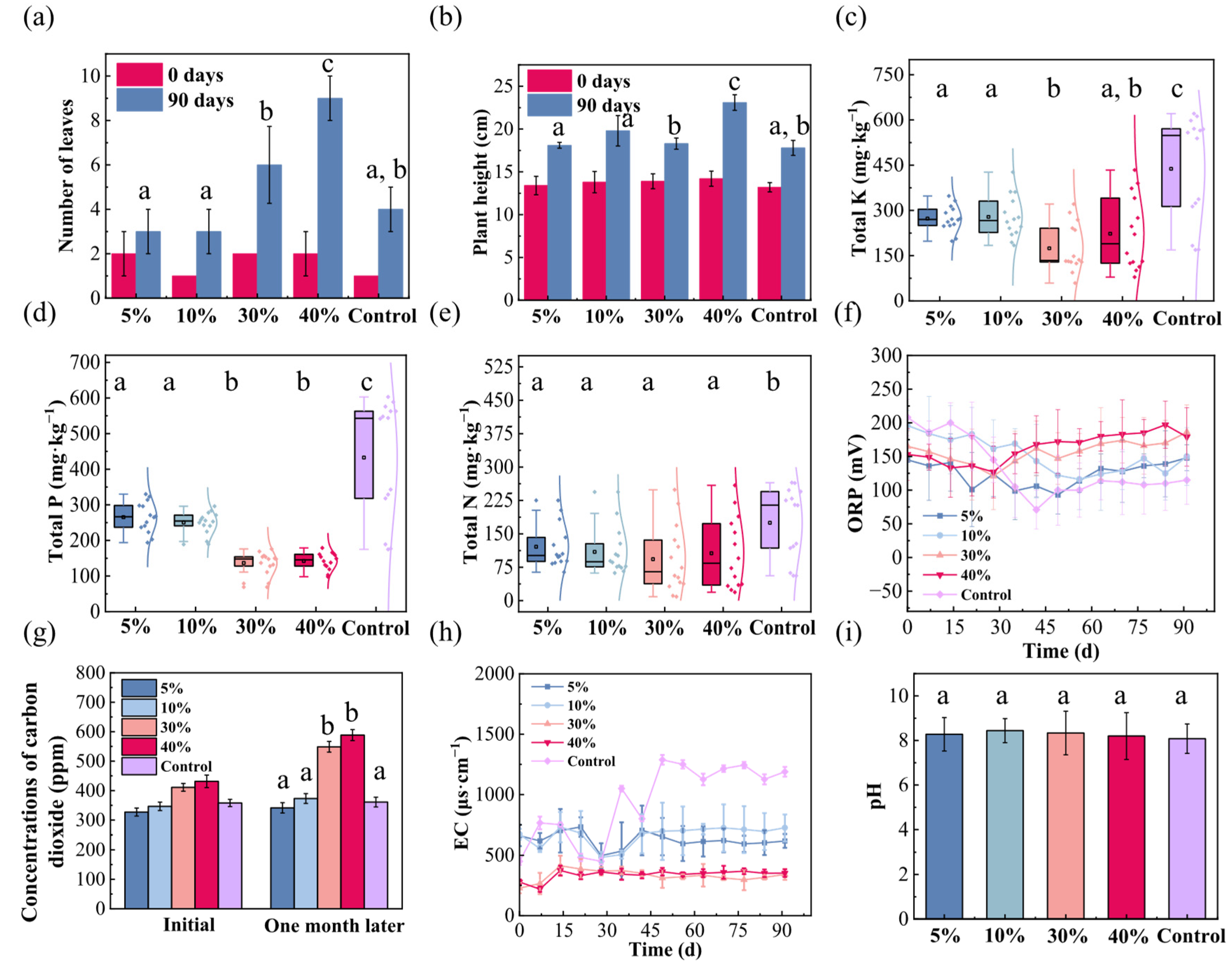
3. Results
3.1. Amendment Effect of Manganese Sand
3.2. Amendment Effect of Maifan Stone
3.3. Amendment Effect of Bentonite
3.4. Amendment Effect of Iron–Carbon
3.5. Amendment Effect of Vermiculite
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, R.; MacDougall, A.S.; Tian, D.; Wang, J.; Niu, S. Wetland restoration is effective but insufficient to compensate for soil organic carbon losses from degradation. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2025, 34, e70063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Qin, L.; Kong, L.; Tian, W.; Zhao, C. Temporal variation of soil phosphorus fractions and nutrient stoichiometry during wetland restoration: Implications for phosphorus management. Environ. Res. 2025, 266, 120486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, Q.; Meng, Q.; Xu, W. Environmental behaviors and ecological risks of trace metals in typical mangrove wetlands in the pearl river delta, south china. Mar. Environ. Res. 2025, 212, 107514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Fan, X.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; He, S.; Lyu, H.; Li, J. Geochemical behavior of iron-sulfur coupling in coastal wetland sediments and its impact on heavy metal speciation and migration. Mar. Environ. Res. 2025, 207, 107065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutillod, C.; Buisson, É.; Mahy, G.; Jaunatre, R.; Bullock, J.M.; Tatin, L.; Dutoit, T. Ecological restoration and rewilding: Two approaches with complementary goals? Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2024, 99, 820–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Liu, G.; Casazza, M.; Dumontet, S.; Yang, Z. Ecosystem restoration programs challenges under climate and land use change. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Ouyang, Y.; Cai, L.; Dai, J.; Wu, Y. Ecological restoration approaches for degraded muddy coasts: Recommendations and practice. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 149, 110182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Tian, C. Soil organic carbon changes following wetland restoration: A global meta-analysis. Geoderma 2019, 353, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Ma, Z. Ecological restoration of coastal wetlands in china: Current status and suggestions. Biol. Conserv. 2024, 291, 110513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Liu, Y.; Meadows, M.E. Ecological restoration for sustainable development in china. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2023, 10, nwad033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Lin, B.; Fang, Q.; Jiang, X. Effectiveness assessment of china’s coastal wetland ecological restoration: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 934, 173336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Xu, D.; Xu, Z.; Tang, H.; Jiang, H.; Dong, J.; Liu, Y. Ten key issues for ecological restoration of territorial space. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2024, 11, nwae176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, K.; Yang, L.; Tao, J.; Xu, X.; Zheng, X.; Wu, Y.; Jin, K.; Xiao, D.; Zhao, M.; Han, W. Effect of cipangopaludina chinensis and diversity of plant species with different life forms on greenhouse gas emissions from constructed wetlands. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2024, 15, 102120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Liu, K.; Ning, T.; Huang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Fan, Y.; An, W.; Ji, L.; et al. Environmental remediation promotes the restoration of biodiversity in the shenzhen bay estuary, south china. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2022, 8, 2026250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.K.; Das, S. Potential of plant growth-promoting microbes for improving plant and soil health for biotic and abiotic stress management in mangrove vegetation. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 23, 801–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, S.; Liu, H.; Hu, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Xin, W.; Chen, Q. Physiological and transcriptomic analysis of the mangrove species kandelia obovata in response to flooding stress. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 196, 115598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verâne, J.; Dos Santos, N.C.P.; Da Silva, V.L.; de Almeida, M.; de Oliveira, O.M.C.; Moreira, Í.T.A. Phytoremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in mangrove sediments using rhizophora mangle. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 160, 111687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gan, S.; Yang, P.; Zhou, J.; Huang, X.; Chen, H.; He, H.; Saintilan, N.; Sanders, C.J.; Wang, F. A global assessment of mangrove soil organic carbon sources and implications for blue carbon credit. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ur Rahman, S.; Han, J.; Zhou, Y.; Ahmad, M.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yasin, G.; Ansari, M.J.; Saeed, M.; et al. Adaptation and remediation strategies of mangroves against heavy metal contamination in global coastal ecosystems: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 441, 140868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, S.; Riya, K.K.; Jolly, Y.N.; Akter, S.; Mamun, K.M.; Kabir, J.; Paray, B.A.; Arai, T.; Yu, J.; Ngah, N.; et al. Effectiveness of artificially planted mangroves on remediation of metals released from ship-breaking activities. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 212, 117587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bappy, M.M.M.; Rahman, M.M.; Hossain, M.K.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Yu, J.; Arai, T.; Paray, B.A.; Hossain, M.B. Distribution and retention efficiency of micro- and mesoplastics and heavy metals in mangrove, saltmarsh and cordgrass habitats along a subtropical coast. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 370, 125908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evenson, G.R.; Golden, H.E.; Christensen, J.R.; Lane, C.R.; Kalcic, M.M.; Rajib, A.; Wu, Q.; Mahoney, D.T.; White, E.; D’Amico, E. River basin simulations reveal wide-ranging wetland-mediated nitrate reductions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 9822–9831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Ni, B.; Zou, Y.; Freeman, C.; Peng, X.; Yang, L.; Wang, G.; Jiang, M. Deciphering soil environmental regulation on reassembly of the soil bacterial community during wetland restoration. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Huang, X.; Chen, S.; Xu, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Jia, R.; Zhang, S.; Lin, W.; Jiao, X.; Shi, M.; et al. Bioremediation of heavy metals by mangrove rhizosphere microbes: Extracellular adsorption mechanisms and enhanced performance of immobilized aestuariibaculum sp. JKB11. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 498, 139968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meera, S.P.; Bhattacharyya, M.; Nizam, A.; Kumar, A. A review on microplastic pollution in the mangrove wetlands and microbial strategies for its remediation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 4865–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Xia, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, Z.; Su, Z.; Ren, H. Enhanced sediment microbial diversity in mangrove forests: Indicators of nutrient status in coastal ecosystems. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 211, 117421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lin, X.; An, X.; Liu, S.; Wei, X.; Zhou, T.; Li, Q.; Chen, Q.; Liu, X. Mangrove afforestation as an ecological control of invasive spartina alterniflora affects rhizosphere soil physicochemical properties and bacterial community in a subtropical tidal estuarine wetland. PeerJ 2024, 12, e18291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Dong, J.; Wang, H.; Shang, M.; Xie, H.; Du, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y. Spatiotemporal response of water quality in fragmented mangroves to anthropogenic activities and recommendations for restoration. Environ. Res. 2023, 237, 117075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Z.; Lin, G.; Lin, Y.; Liang, X.; Ling, J.; Wee, A.K.S.; Lin, H.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Coastal urbanization may indirectly positively impact growth of mangrove forests. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhou, J.; Lv, C. Effects of biochar and plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on plant performance and soil environmental stability. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Liu, Q.; Pan, F.; Yao, Y.; Luo, X.; Chen, C.; Liu, T.; Zou, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; et al. Research advances in the impacts of biochar on the physicochemical properties and microbial communities of saline soils. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xie, H.; Liu, X.; Kong, D.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C. A novel green substrate made by sludge digestate and its biochar: Plant growth and greenhouse emission. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 797, 149194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Pan, Y.; Jin, X.; Zhao, S.; Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; Shen, Z.; Chen, C. A novel biochar-PGPB strategy for simultaneous soil remediation and safe vegetable production. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 356, 124254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.; Ilyas, N.; Bibi, F.; Shabir, S.; Jayachandran, K.; Sayyed, R.Z.; Shati, A.A.; Alfaifi, M.Y.; Show, P.L.; Rizvi, Z.F. Development of novel kinetic model based on microbiome and biochar for in-situ remediation of total petroleum hydrocarbons (TPHs) contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2023, 324, 138311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Ye, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Peng, W.; Wang, H.; Tang, D. Evaluation and characterization of biochar on the biogeochemical behavior of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in mangrove wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 864, 161039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, T.; Meng, M.; Wang, N.; Xu, X.; Lu, H.; Yang, Q. Investigation on desorption of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminants by active and passive particle self-rotation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cui, Z.; Li, S.; Song, Z.; He, M.; Huang, D.; Feng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, K.; Wang, X.; et al. Unlocking osmotic energy harvesting potential in challenging real-world hypersaline environments through vermiculite-based hetero-nanochannels. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Duan, X.; Wang, J.; Cheemaa, N.; Nazish, H.T.; Peng, G. Bentonite and its modified derivatives: Application and factors influencing radioactive nuclide adsorption. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2026, 191, 106104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, H.; Ma, C.; Chen, W.; Huangfu, X. Treatment of wastewater containing thallium(i) by long-term operated manganese sand filter: Synergistic action of MnOx and MnOM. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Hu, Y.; Fu, N.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Q. Improving semi-thermophilic anaerobic digestion of kitchen waste by iron-carbon materials regulation: Insights from energy supply and genetic information processing. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2025, 203, 107971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X. Microbial conversion of CO2 to organic compounds. Energy Environ. Sci. 2024, 17, 7017–7034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, M.; Xie, Y.; Shi, R.; Huang, X.; Tuo, Y.; He, X.; Xiang, P. Mn-modified bamboo biochar improves soil quality and immobilizes heavy metals in contaminated soils. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 34, 103630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüggenwirth, L.; Behrens, R.; Schnee, L.S.; Sauheitl, L.; Mikutta, R.; Mikutta, C. Interactions of manganese oxides with natural dissolved organic matter: Implications for soil organic carbon cycling. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2024, 366, 182–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Zheng, X.; Wen, Y.; Yu, C.; Li, D.; Zhang, H. Microbial-induced carbon dioxide (CO2) mineralization: Investigating the bio-mineralization chemistry process and the potential of storage in sandstone reservoir. Appl. Energy 2025, 377, 124268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Qu, F.; Sun, Z.; Shah, S.P.; Li, W. Carbon sequestration, performance optimization and environmental impact assessment of functional materials in cementitious composites. J. CO2 Util. 2024, 90, 102986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Jin, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, G.; Xing, F.; Tang, L. Exploring the carbon capture and sequestration performance of biochar-artificial aggregate using a new method. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, B.; Yuan, Y.; Lei, J.; Qian, C. Interactions between deep microbial biosphere and geo-sequestrated CO2: A review. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2025, 197, 105958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Xu, W.; Wang, H.; Zhao, D.; Ding, H. Nitrogen and phosphorus removal efficiency and denitrification kinetics of different substrates in constructed wetland. Water 2022, 14, 1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Hu, M.; Xu, Y.; Tao, M.; Guan, L.; Kong, Y.; Cao, S.; Jing, Z. Synergistic removal of nitrogen and phosphorus in constructed wetlands enhanced by sponge iron. Water 2024, 16, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Jing, Z.; Shen, Y.; Cao, S.; Li, Y. Nitrogen and phosphorus removal in microbial fuel cell-constructed wetland integrated with layered double hydroxides coated filter for treating low carbon wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 70, 106907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhou, K.; Huang, L. Effects of manganese sand proportion on nitrogen and phosphorus removal performance and microbial community in constructed wetlands. Processes 2025, 13, 3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y.; He, S.; Mochida, K.; Zhao, M.; Zheng, X.; Jin, H. Synergistic Remediation of Coastal Wetlands: Identifying Optimal Substrate Amendment and Incorporation Ratio for Enhanced Kandelia obovata Growth and Nutrient Management. Sustainability 2025, 17, 11142. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172411142
Pan X, Li J, Wang Z, Jiang S, Liu Y, He S, Mochida K, Zhao M, Zheng X, Jin H. Synergistic Remediation of Coastal Wetlands: Identifying Optimal Substrate Amendment and Incorporation Ratio for Enhanced Kandelia obovata Growth and Nutrient Management. Sustainability. 2025; 17(24):11142. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172411142
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Xian, Jianhua Li, Zhiquan Wang, Shunfeng Jiang, Yawei Liu, Shengbing He, Keiichi Mochida, Min Zhao, Xiangyong Zheng, and Huachang Jin. 2025. "Synergistic Remediation of Coastal Wetlands: Identifying Optimal Substrate Amendment and Incorporation Ratio for Enhanced Kandelia obovata Growth and Nutrient Management" Sustainability 17, no. 24: 11142. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172411142
APA StylePan, X., Li, J., Wang, Z., Jiang, S., Liu, Y., He, S., Mochida, K., Zhao, M., Zheng, X., & Jin, H. (2025). Synergistic Remediation of Coastal Wetlands: Identifying Optimal Substrate Amendment and Incorporation Ratio for Enhanced Kandelia obovata Growth and Nutrient Management. Sustainability, 17(24), 11142. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172411142






