Extreme Hydrological Shifts Trigger Water Quality Variations in Shallow Lake Ecosystems: Insights from Hydroclimatic Behaviors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
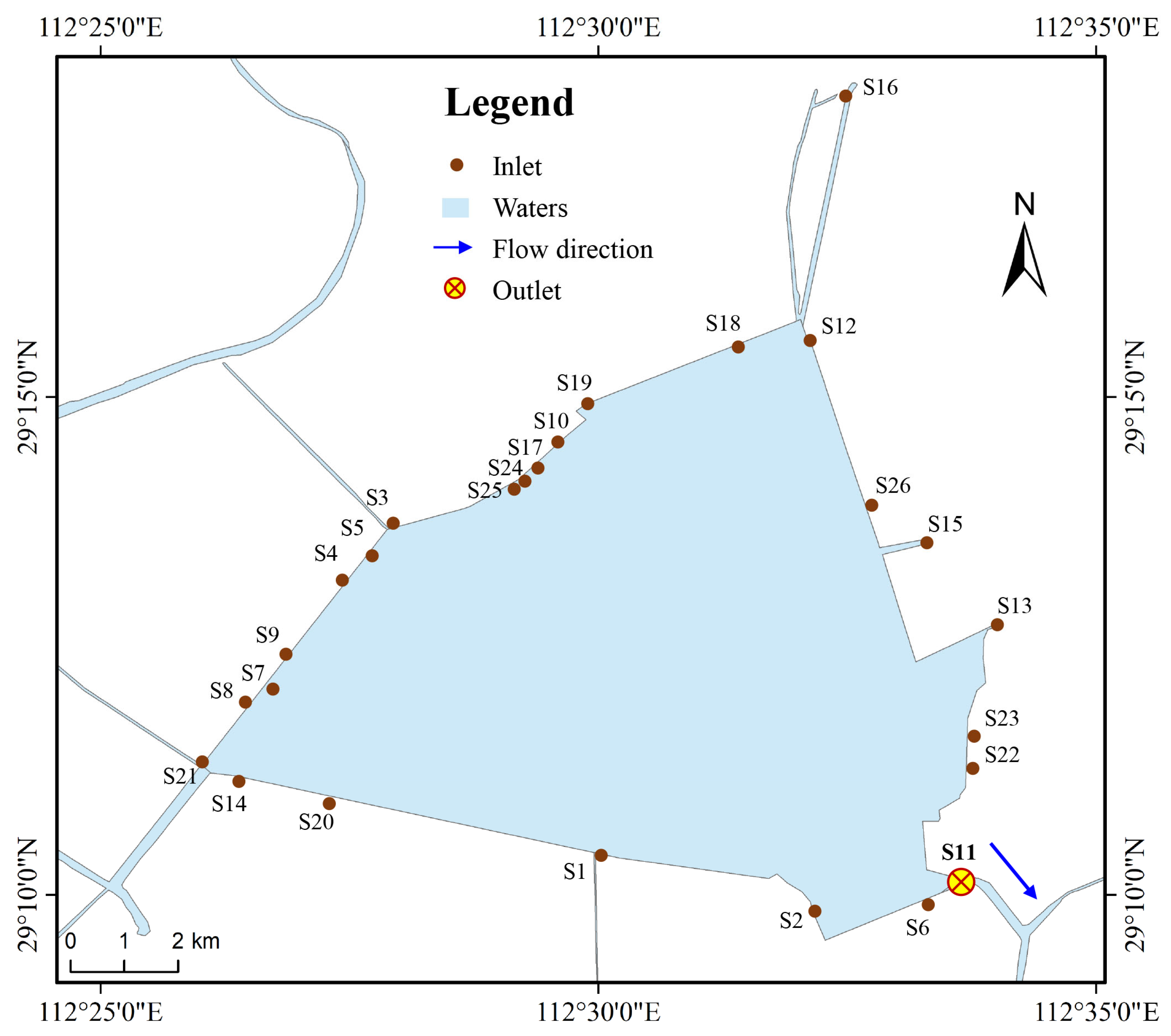
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Hydroclimatic and Water Quality Variability
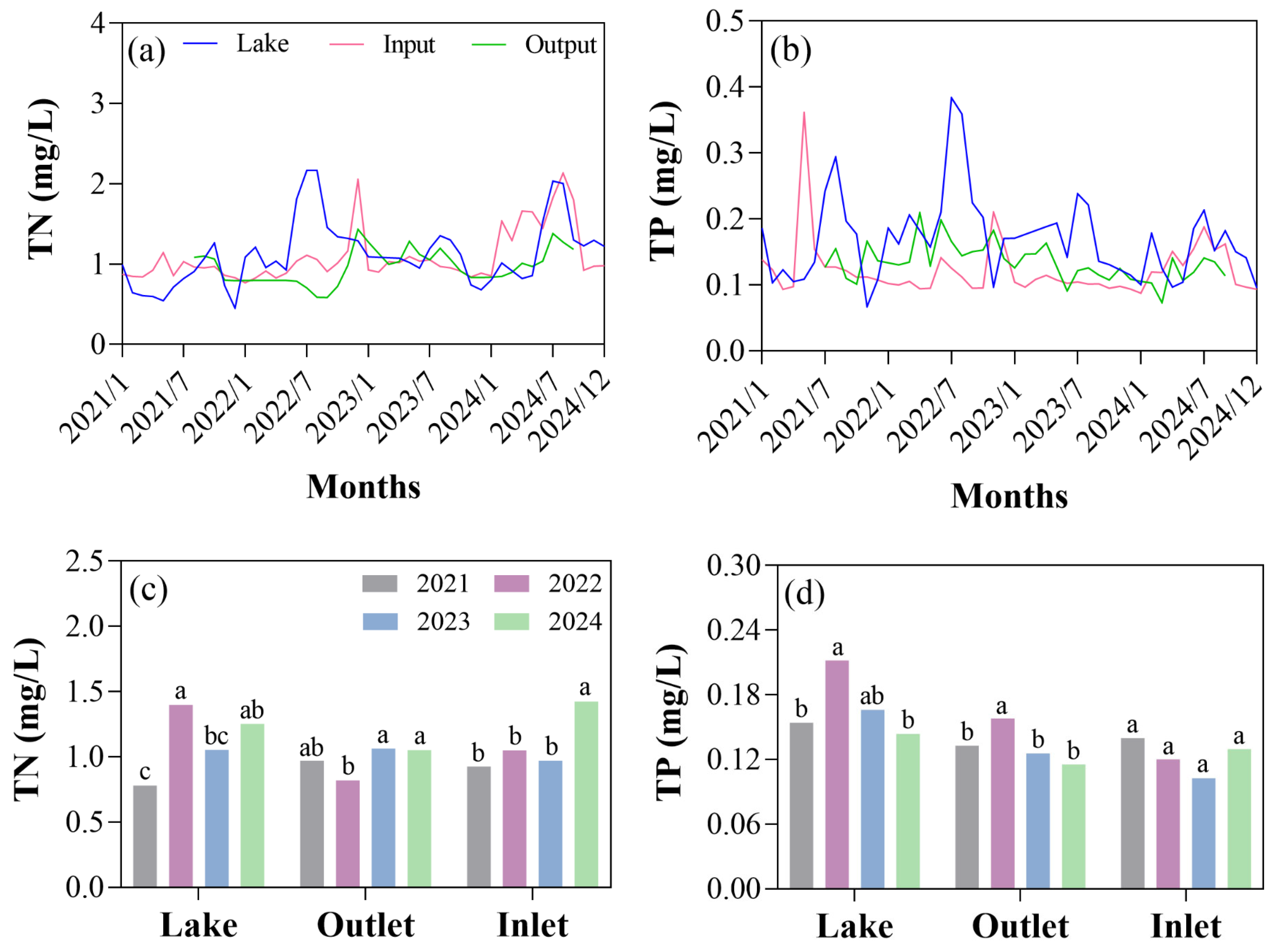
3.1.1. Hydrometeorology
3.1.2. Water Quality
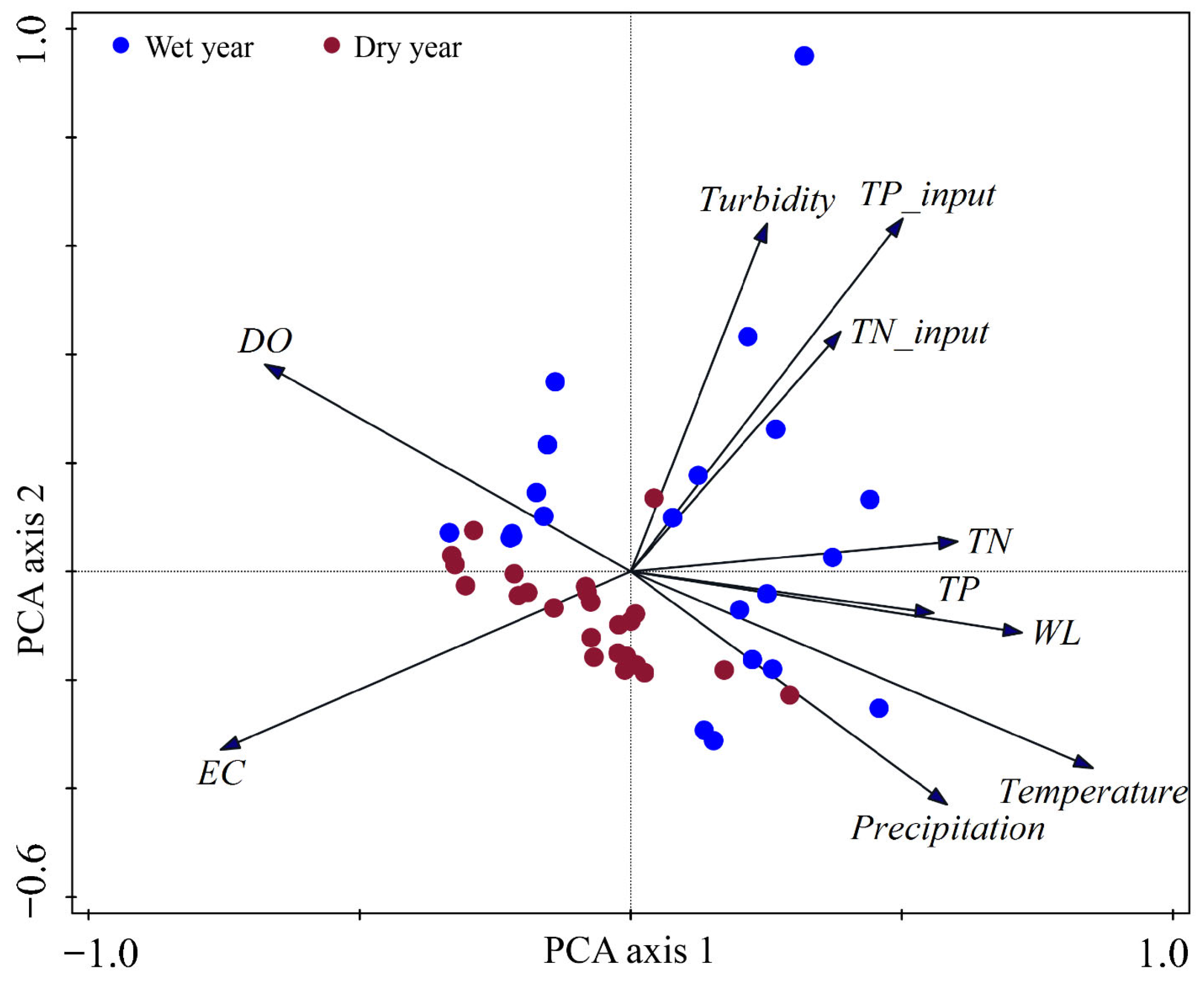
3.2. Comparison of Hydroclimatic Conditions and Water Quality in Extreme Hydrological Years
3.3. Dynamic Response of Lake Water Quality to Extreme Hydrological Years
4. Discussion
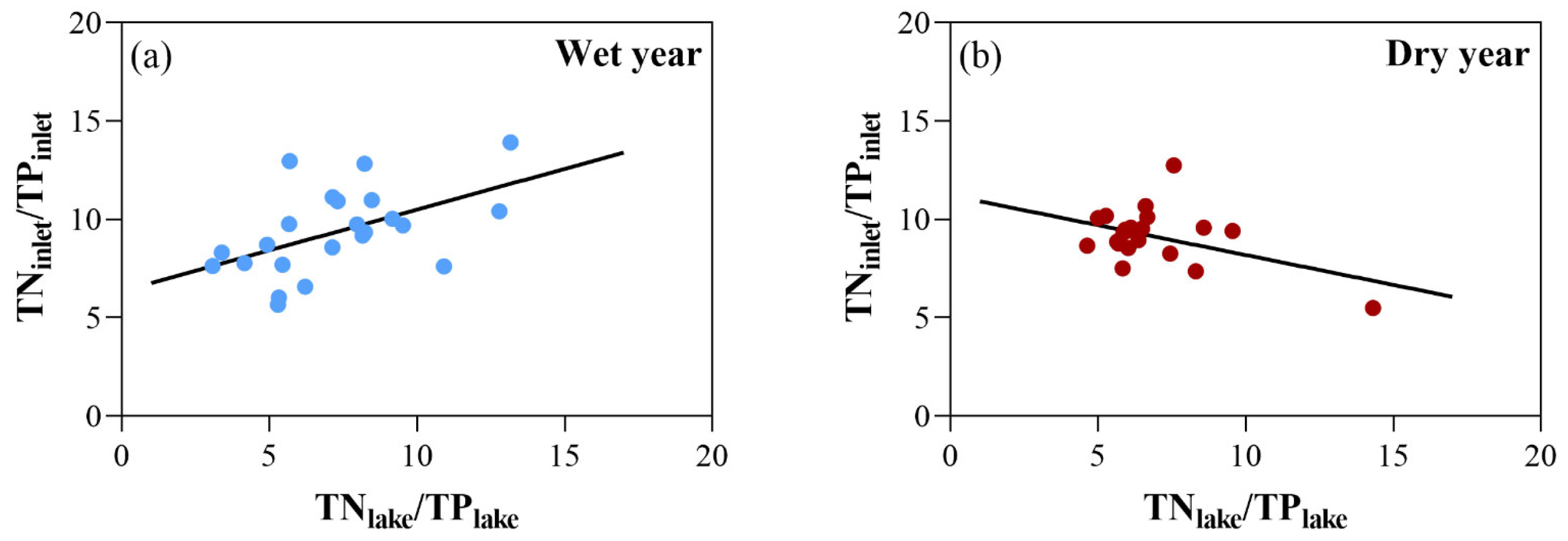
4.1. Trends in Water Quality and Identification of Primary Nutrient Sources
4.2. Drivers of Water Quality Responses During Different Hydrological Extremes
4.3. Implications for Water Quality Improvement in Shallow Lakes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davidson, T.A.; Sayer, C.D.; Jeppesen, E.; Søndergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Johansson, L.S.; Baker, A.; Graeber, D. Bimodality and alternative equilibria do not help explain long-term patterns in shallow lake chlorophyll-a. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Vliet, M.T.H. Complex interplay of water quality and water use affects water scarcity under droughts and heatwaves. Nat. Water 2023, 1, 902–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolway, R.I.; Merchant, C.J. Worldwide alteration of lake mixing regimes in response to climate change. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, X.; Luo, Q.; Feng, L.; Xu, Y.; Tang, J.; Liang, X.; Ma, E.; Cheng, R.; Fensholt, R.; Brandt, M.; et al. Mapping global lake dynamics reveals the emerging roles of small lakes. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewen, C.J.G. Lakes as model systems for understanding global change. Nat. Clim. Change 2023, 13, 304–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2023: Synthesis Report; Lee, H., Romero, J., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 35–115. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Lin, Q.; He, C.; Huang, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, B.; Ge, F.; et al. The changing characteristics of phytoplankton community and biomass in subtropical shallow lakes: Coupling effects of land use patterns and lake morphology. Water Res. 2021, 200, 117235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayley, S.E.; Prather, C.M. Do wetland lakes exhibit alternative stable states? Submersed aquatic vegetation and chlorophyll in western boreal shallow lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 2335–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, T.K.; Nielsen, A.; Jeppesen, E.; Hu, F.N.; Bolding, K.; Liu, Z.W.; Sondergaard, M.; Johansson, L.S.; Trolle, D. Predicting ecosystem state changes in shallow lakes using an aquatic ecosystem model: Lake Hinge, Denmark, an example. Ecol. Appl. 2020, 30, e02160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Wu, H.; Chen, M. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus on phytoplankton composition and biomass in 15 subtropical, urban shallow lakes in Wuhan, China. Limnologica 2011, 41, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recknagel, F.; Talib, A.; van der Molen, D. Phytoplankton community dynamics of two adjacent Dutch lakes in response to seasons and eutrophication control unravelled by non-supervised artificial neural networks. Ecol. Inform. 2006, 1, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Woolway, R.I.; Timmermann, A.; Lee, S.-S.; Rodgers, K.B.; Yamaguchi, R. Emergence of lake conditions that exceed natural temperature variability. Nat. Geosci. 2024, 17, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jane, S.F.; Hansen, G.J.A.; Kraemer, B.M.; Leavitt, P.R.; Mincer, J.L.; North, R.L.; Pilla, R.M.; Stetler, J.T.; Williamson, C.E.; Woolway, R.I.; et al. Widespread deoxygenation of temperate lakes. Nature 2021, 594, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Q.; Wang, Y.M.; Liang, R.F.; Feng, J.J.; Li, Y.; An, R.D.; Li, K.F. Field observations of the lethality characteristics of endangered and endemic fish under the stress of total dissolved gas supersaturation. River Res. Appl. 2021, 37, 1156–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Jin, Z.; Guo, J.; Yang, H.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, Y. Simultaneous removal of phosphate and ammonium nitrogen from agricultural runoff by amending soil in lakeside zone of Karst area, Southern China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 289, 106745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, A.; James, D.E.; Hannoun, I.A. Effects of lake water level fluctuation due to drought and extreme winter precipitation on mixing and water quality of an alpine lake, Case Study: Lake Arrowhead, California. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Bush, R.T.; Mao, R.; Xiong, L.; Ye, C. Extreme drought causes distinct water acidification and eutrophication in the Lower Lakes (Lakes Alexandrina and Albert), Australia. J. Hydrol. 2017, 544, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Wei, W.; Ye, C.; Li, C.; Zheng, Y.; Shi, X.; Chang, M.; Chen, H. Determining the Optimal Biomass of Macrophytes during the Ecological Restoration Process of Eutrophic Shallow Lakes. Water 2021, 13, 3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Li, C.-h.; Ye, C.; Chen, H.-s.; Xu, J.; Dong, X.-h.; Liu, X.-s.; Li, D. Effects of aquaculture on the shallow lake aquatic ecological environment of Lake Datong, China. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2022, 34, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.; Dong, L.; Yu, W.; Huang, R.; Qin, X.; Xie, Y.; Li, F. Competitive Outcomes Between Floating-Leaved and Submerged Plants Under Eutrophication Depend on Growth Form. Freshw. Biol. 2025, 70, e70050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xing, B.; Zuo, Z.; Lv, T.; Chao, C.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Yu, D. Drivers of organic carbon stocks in eutrophic lake sediments after reestablishment of submerged aquatic vegetation. Plant Soil 2024, 499, 639–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.D.; Huang, J.L.; Zeng, X.F.; Gao, C.; Jiang, T. Impacts of climate change on streamflow in the upper Yangtze River basin. Clim. Change 2017, 141, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Yuan, X.; Liu, X.Y. Intensification of drought propagation over the Yangtze River basin under climate warming. Int. J. Climatol. 2023, 43, 5640–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Kong, F.; Fang, J.Y.; Zhao, L. Observed changes in hydrological extremes and flood disaster in Yangtze River Basin: Spatial-temporal variability and climate change impacts. Nat. Hazards 2018, 93, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, T.; Xiao, T.; Yu, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, K.; Liu, A.; Li, Z. Phytoplankton’ s community structure and its relationships with environmental factors in an aquaculture lake, Datong Lake of China. Chinses J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 23, 2107–2113. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.; Lv, T.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Han, C.; Yu, W.; Yan, Z.; Ma, X.; Zhao, H.; Zuo, Z.; et al. The spatiotemporal characteristics of water quality and phytoplankton community in a shallow eutrophic lake: Implications for submerged vegetation restoration. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 821, 153460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.H.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, D.; Ye, X.C. Lake flooding sensitivity to the relative timing of peak flows between upstream and downstream waterways: A case study of Poyang Lake, China. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 4217–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanidis, K.; Varlas, G.; Vourka, A.; Papadopoulos, A.; Dimitriou, E. Delineating the relative contribution of climate related variables to chlorophyll-a and phytoplankton biomass in lakes using the ERA5-Land climate reanalysis data. Water Res. 2021, 196, 117053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.; Tan, Z.; Yao, J. The role of a seasonal lake groups in the complex Poyang Lake-floodplain system (China): Insights into hydrological behaviors. J. Hydrol. 2019, 578, 124055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yu, S.; Xing, B.; Xu, X.; Yu, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Liu, C.; Yu, D. Vigilance against climate change-induced regime shifts for phosphorus restoration in shallow lake ecosystems. Water Res. 2025, 278, 123397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Bi, S.; Bashir, B.; Ge, Z.; Wu, K.; Alsalman, A.; Ayugi, B.O.; Alsafadi, K. Historical Trends and Characteristics of Meteorological Drought Based on Standardized Precipitation Index and Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index over the Past 70 Years in China (1951–2020). Sustainability 2023, 15, 10875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isia, I.; Hadibarata, T.; Jusoh, M.N.H.; Bhattacharjya, R.K.; Shahedan, N.F.; Bouaissi, A.; Fitriyani, N.L.; Syafrudin, M. Drought Analysis Based on Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index and Standardized Precipitation Index in Sarawak, Malaysia. Sustainability 2023, 15, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zuo, Z.; Yan, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Liu, C.; Yu, D. In situ remediation mechanism of internal nitrogen and phosphorus regeneration and release in shallow eutrophic lakes by combining multiple remediation techniques. Water Res. 2023, 229, 119394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Wu, L.; Lv, T.; Tong, C.; Gao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xing, B.; Chao, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Response of spatio-temporal changes in sediment phosphorus fractions to vegetation restoration in the degraded river-lake ecotone. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 308, 119650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakoc, G.; Erkoc, F.U.; Katiricoglu, H. Water quality and impacts of pollution sources for Eymir and Mogan Lakes (Turkey). Environ. Int. 2003, 29, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Xiao, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Characteristics and Factors of Water Level Variations in the Dongting Lake during the Recent 50 Years. South-to-North Water Transf. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 10, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.; Lv, T.; Liu, Y.; Xing, B.; Chao, C.; Li, Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Yu, D. Responses of soil phosphorus cycling and bioavailability to plant invasion in river–lake ecotones. Ecol. Appl. 2023, 33, e2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, T.; Setiawan, F.; Subehi, L.; Jiang, D.L.; Matsushita, B. Water temperature and some water quality in Lake Toba, a tropical volcanic lake. Limnology 2023, 24, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Xu, H.; McCarthy, M.J.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B.; Li, Y.; Gardner, W.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China): The need for a dual nutrient (N & P) management strategy. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1973–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferencz, B.; Toporowska, M.; Dawidek, J. Role of Hydrology in Cyanobacterial Blooms in the Floodplain Lakes. Water 2023, 15, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paule-Mercado, M.C.; Rabaneda-Bueno, R.; Porcal, P.; Kopacek, M.; Huneau, F.; Vystavna, Y. Climate and land use shape the water balance and water quality in selected European lakes. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callbeck, C.M.; Ehrenfels, B.; Baumann, K.B.L.; Wehrli, B.; Schubert, C.J. Anoxic chlorophyll maximum enhances local organic matter remineralization and nitrogen loss in Lake Tanganyika. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camarero, L.; Catalan, J. Atmospheric phosphorus deposition may cause lakes to revert from phosphorus limitation back to nitrogen limitation. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Søndergaard, M.; Jensen, J.P.; Jeppesen, E. Role of sediment and internal loading of phosphorus in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 2003, 506, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Zhu, G.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Gu, Z. Estimation of the algal-available phosphorus pool in sediments of a large, shallow eutrophic lake (Taihu, China) using profiled SMT fractional analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 173, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Zhu, G.; Zhu, M.; Xu, H.; Zou, W.; Xiao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B. Bloom-induced internal release controlling phosphorus dynamics in large shallow eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ao, H.; Chen, K.; Wu, C. Nitrogen-phosphorus stoichiometry and Cladophora growth affected by grass-sourced dissolved organic matter in the littoral zone of the Qinghai Lake, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 495, 138847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Tang, N.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, R.; Gao, X.; Yan, M.; Hu, T.; Ma, H.; Li, G.; Li, W.; et al. Unraveling the interaction of dissolved organic matter and microorganisms with internal phosphorus cycling in the floodplain lake ecosystem. Environ. Res. 2025, 270, 120966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Gong, J.; Song, B.; Li, J.; Cao, W.; Zhao, J. Co-influence of biochar-supported effective microorganisms and seasonal changes on dissolved organic matter and microbial activity in eutrophic lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 923, 171476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Li, Z.; Zeng, S.; Zou, L.; She, D.; Cheng, D. Perspectives on eco-water security and sustainable development in the Yangtze River Basin. Geosci. Lett. 2021, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, P.C.; Hicks, A.L. Human shoreline development and the nutrient stoichiometry of aquatic plant communities in Canadian Shield lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 69, 1642–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.S.; Xenopoulos, M.A.; Hogsden, K.; Metcalfe, R.A.; Dillon, P.J. Natural lake level fluctuation and associated concordance with water quality and aquatic communities within small lakes of the Laurentian Great Lakes region. Hydrobiologia 2008, 613, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Indicators | N | Mean | SE | Median | Mode | Min. | Max. | 95% C.I. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitation (mm) | 1445 | 2.57 | 0.21 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | (2.17, 2.97) |
| Water level (m) | 1423 | 27.16 | 0.01 | 27.1 | 27.13 | 26.29 | 28.71 | (27.14, 27.18) |
| Temperature (°C) | 1352 | 20.29 | 0.24 | 20.80 | 29.50 | 0.60 | 35.10 | (19.82, 20.76) |
| pH | 1352 | 8.19 | 0.02 | 8.00 | 8.00 | 5.00 | 10.00 | (8.16, 8.22) |
| DO (mg/L) | 1352 | 9.10 | 0.07 | 8.90 | 10.00 | 5.10 | 19.50 | (8.96, 9.23) |
| EC (μS/cm) | 1352 | 338.13 | 1.94 | 346.75 | 377.70 | 10.10 | 636.50 | (334.33, 341.93) |
| Turbidity (NTUs) | 1350 | 107.41 | 4.06 | 70.40 | 60.90 | 1.70 | 1100.90 | (99.45, 115.37) |
| CODMn (mg/L) | 1293 | 4.76 | 0.05 | 4.40 | 4.40 | 0.90 | 13.00 | (4.65, 4.86) |
| NH3-N (mg/L) | 1332 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 2.50 | (0.05, 0.06) |
| TP (mg/L) | 1341 | 0.17 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.62 | (0.17, 0.18) |
| TN (mg/L) | 1340 | 1.13 | 0.01 | 1.07 | 1.12 | 0.17 | 5.83 | (1.11, 1.16) |
| Algal density (105 cells/L) | 1345 | 172.75 | 5.61 | 86.16 | 75.50 | 8.22 | 1560.00 | (161.74, 183.76) |
| Variables | PC1 | PC2 |
|---|---|---|
| Precipitation | 0.58 | −0.42 |
| WL | 0.71 | −0.17 |
| Temperature | 0.85 | −0.37 |
| DO | −0.72 | 0.38 |
| EC | −0.78 | −0.36 |
| Turbidity | 0.22 | 0.61 |
| TN | 0.60 | 0.08 |
| TP | 0.52 | −0.09 |
| TN_input | 0.37 | 0.41 |
| TP_input | 0.46 | 0.62 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Geng, M.; Xie, Y. Extreme Hydrological Shifts Trigger Water Quality Variations in Shallow Lake Ecosystems: Insights from Hydroclimatic Behaviors. Sustainability 2025, 17, 11110. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172411110
Li D, Geng M, Xie Y. Extreme Hydrological Shifts Trigger Water Quality Variations in Shallow Lake Ecosystems: Insights from Hydroclimatic Behaviors. Sustainability. 2025; 17(24):11110. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172411110
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Dan, Mingming Geng, and Yonghong Xie. 2025. "Extreme Hydrological Shifts Trigger Water Quality Variations in Shallow Lake Ecosystems: Insights from Hydroclimatic Behaviors" Sustainability 17, no. 24: 11110. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172411110
APA StyleLi, D., Geng, M., & Xie, Y. (2025). Extreme Hydrological Shifts Trigger Water Quality Variations in Shallow Lake Ecosystems: Insights from Hydroclimatic Behaviors. Sustainability, 17(24), 11110. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172411110





