Study on the Coordinated Development of Resources, Environment and Economy on Fuzzy Multi-Objective Programming: A Case Study of Arid and Semi-Arid River Basin in Northern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
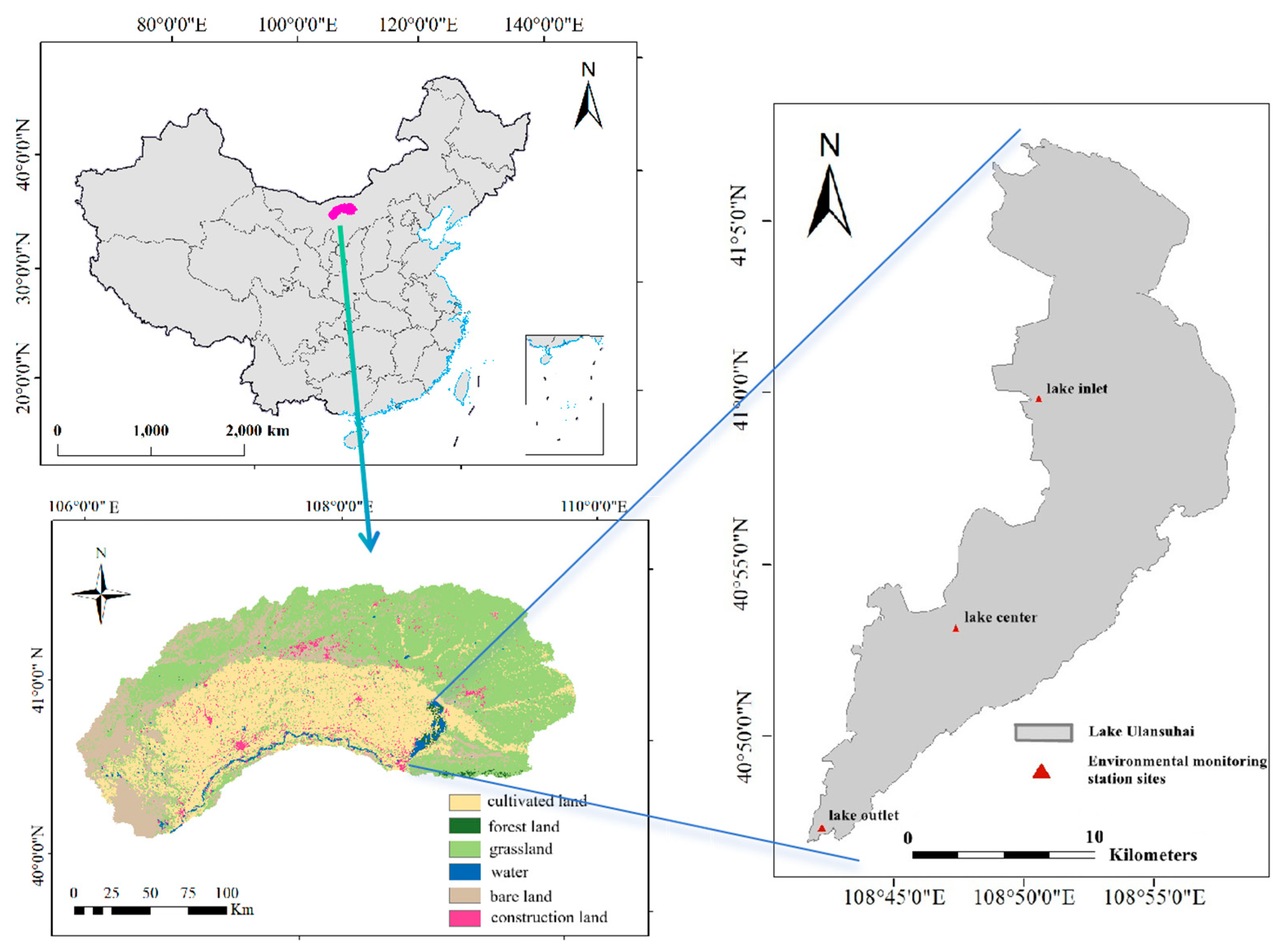
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sets
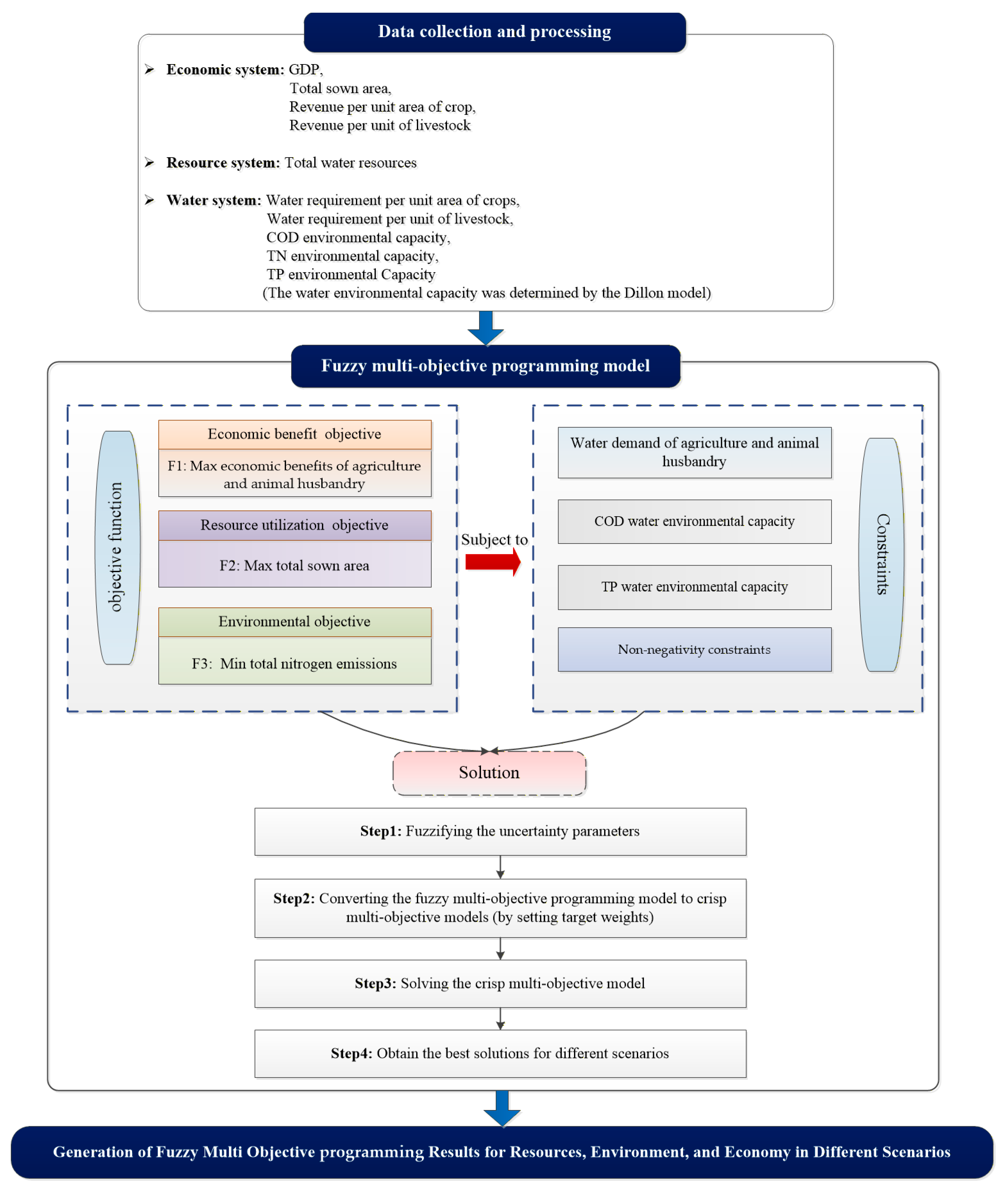
2.3. Establishment of Fuzzy Multi-Objective Programming Model for Ulansuhai Basin
2.3.1. The Objective Function of the Fuzzy Multi-Objective Programming Model
The First Objective Function
The Second Objective Function
The Third Objective Function
2.3.2. Constraints of the Fuzzy Multi-Objective Programming Model
The First Constraint
The Second Constraint
The Third Constraint
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Solution of the Fuzzy Multi-Objective Programming Model for Ulansuhai Basin
3.1.1. Model Parameter of the Fuzzy Multi-Objective Programming Model for Ulansuhai Basin
3.1.2. Scenario Setting of the Fuzzy Multi-Objective Programming Model for Ulansuhai Basin
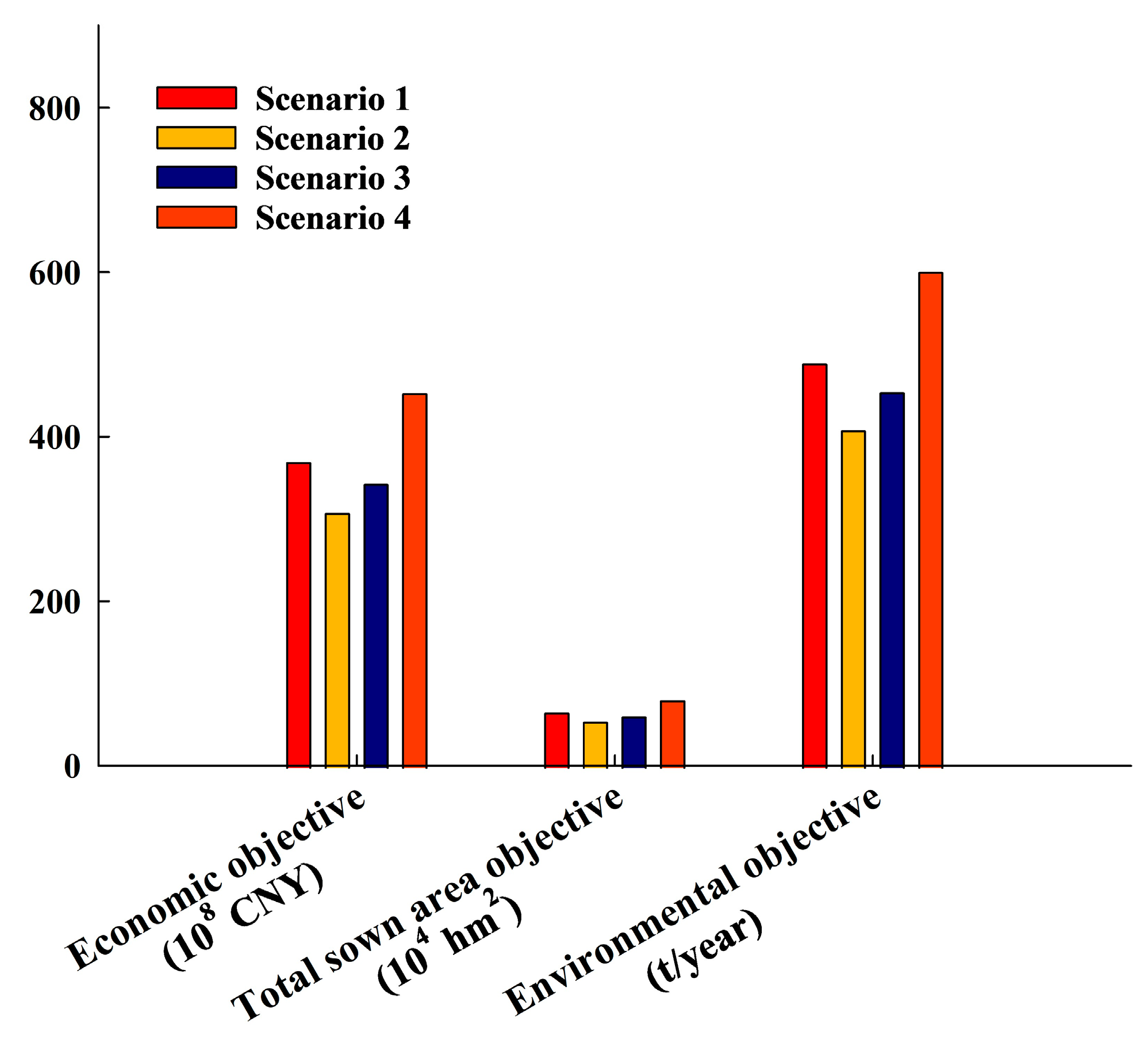
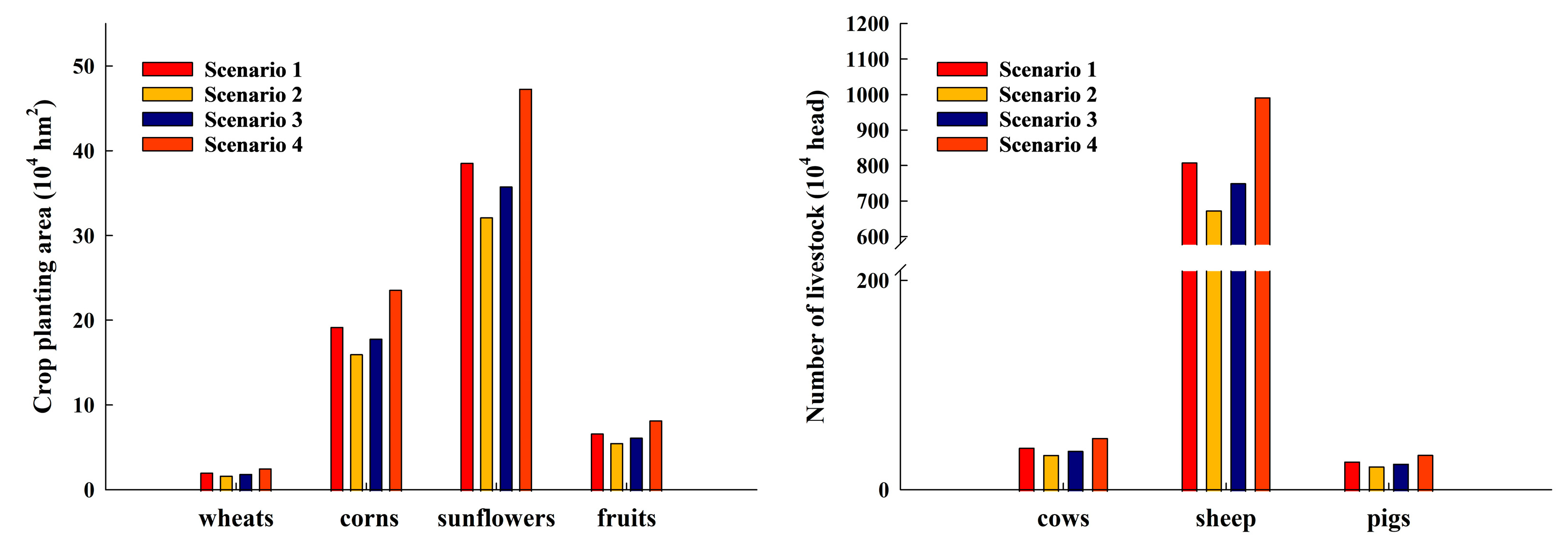
3.2. Analysis of Sustainable Management for the Ulansuhai Basin Based on the Fuzzy Multi-Objective Programming Model for Ulansuhai Basin
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- When the water supply guarantee rate was 90%, the economic objective value was 6.154 billion CNY higher than that at a 75% guarantee rate, the total sown area objective value was 11.11 ten thousand hm2 larger, and the environmental objective value for TN emissions was 81 tons per year higher. In addition, under the Class IV water quality standard, the economic objective value was 11.021 billion CNY lower than that under the Class V standard, the total sown area objective value was 19.87 ten thousand hm2 smaller, and the environmental objective value for TN emissions was 146 tons per year lower.
- (2)
- Among these four scenarios, Scenario 4 (i.e., environmental capacity meeting the Class V water quality standard, with other objectives maintaining upper limits) exhibited the largest economic and total sown area objective values, and its environmental target was more consistent with the expected value. To attain this state, it is necessary to coordinate the proportion of agricultural and animal husbandry sectors and the efficiency of resource utilization, as well as to enhance the monitoring and early warning capabilities for the ecological environment by integrating the water environmental capacity under different water diversion scenarios of the Yellow River.
- (3)
- Based on the decision variable results derived from fuzzy multi-objective programming, prioritizing the cultivation of sunflowers and corn maintained the optimal model results. In the livestock sector, maintaining a cattle-to-pig breeding ratio of 1.5:1 and a sheep-to-cattle ratio of approximately 20:1 ensured optimal model results. When the ratio of cultivation area to livestock quantity was 13.16:1 (head:hm2), the Basin’s economic and environmental development was most coordinated, and all objective functions were consistent with the expected values. Currently, the ratio of the planting structure to the livestock structure in the Ulansuhai Basin stands at approximately 9.93:1 (head:hm2). However, there remains a certain gap between this ratio and the sustainable development target of 13.16:1 (head:hm2) established in this study. This finding provides a solid data foundation for relevant departments to further optimize and rationalize the adjustment of the agricultural and animal husbandry structure ratio.
- (4)
- The multi-objective programming model developed in this study was specifically tailored to arid and semi-arid watersheds characterized by water resource scarcity. Furthermore, by adjusting the weights of the objective function in alignment with the practical conditions of other research regions, the model’s application in the field of ecological environment management can be effectively facilitated.
- (5)
- In future research related to fuzzy multi-objective programming models, efforts to advance theoretical innovation and algorithmic optimization in this field should be further strengthened. Specifically, such endeavors may focus on addressing existing limitations in theoretical frameworks and optimizing algorithmic efficiency, such as reducing computational complexity while improving solution accuracy for large-scale multi-objective optimization problems.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Toprak, Z. Brundtland Report; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; de Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1998, 25, 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Zhou, C.; Xiao, T.; Xu, Q. Coordinated Development of the Digital Economy and Urban–Rural Integration in the Yangtze River Delta and Its Spatial Correlation Structure. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Tang, X.; Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Liu, L. Assessment of coordinated development between tourism development and resource environment carrying capacity: A case study of Yangtze River economic Belt in China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y. China’s water security: Current status, emerging challenges and future prospects. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 54, 106–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, Z. Industrial water pollution, water environment treatment, and health risks in China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, D.W.; Baek, J.H.; Hwang, S.Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, W.S.; Choi, J.Y. Analysis of the Pollution Load Contribution Rate of Inflowing Tributaries for the Sustainable Management of the Seomjin River (Seombon D). Sustainability 2025, 17, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.J.; Wang, R.S. The social-economic-natural complex ecosystem. Acta Ecol. Sin. 1984, 4, 56–63. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, S.Y.; Liu, G.Q.; Mei, Y.D. Water resources-ecological economic complex system and its sustainable development. Eng. J. Wuhan Univ. 1995, 28, 624–629. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, L.J.; Fang, G.H.; Guo, Y.H. Researches on the relationship among water resources, social economy and ecological environment. J. Econ. Water Resour. 2007, 25, 4–7+81. [Google Scholar]
- Radmehr, R.; Brorsen, B.W.; Shayanmehr, S. Adapting to climate change in arid agricultural systems: An optimization model for water-energy-food nexus sustainability. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 303, 109052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Q.; Zhu, S.; Yue, W.; Su, M.; Cai, Y. Predictive simulation and optimal allocation of surface water resources in reservoir basins under climate change. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2024, 12, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Lev, B. An interval two-stage robust stochastic programming under a bi-level multi-objective framework toward river basin water resources allocation. Comput. Oper. Res. 2025, 180, 107045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.M. System Coupling model and evaluation of water resources environment and urban eco-economy. Water Resour. Power 2018, 36, 55–58+27. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.; Liu, X.; Ding, W.; Zhang, S. Cloud model-based multi-stage multi-attribute decision-making method under probabilistic interval-valued hesitant fuzzy environment. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 255, 124595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Ding, W.; Zhang, S.; Xu, H. Large group decision-making with a rough integrated asymmetric cloud model under multi-granularity linguistic environment. Inf. Sci. 2024, 678, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.H.; Xia, C.; Jin, F.J.; M, L.; Wen, Z.; Fu, B.J. Implementation effectiveness and promotion strategies of ecological protection and high-quality development strategy in the Yellow River Basin. J. Nat. Resour. 2025, 40, 569–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Shi, X.; Kang, R.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Huotari, J. Seasonal freeze-thaw CO2 sink ‘midday rest’ phenomenon in lakes: A case study of the largest freshwater lake in the Yellow River Basin. J. Hydrol. 2025, 658, 133208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khezri, R.; Mahmoudi, A. Review on the state-of-the-art multi-objective optimisation of hybrid standalone/grid- connected energy systems. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2020, 14, 4285–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, W.; Jiao, Y.; Ma, X.; Qi, W. Quantitative analysis of dissolved carbon sources in the farmland artificial ditch drainage-Lake UlanSuhai continuum in the Hetao Irrigation District’s, Inner Mongolia. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 55, 101910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Cui, J.; Wang, D.; Li, G.; Lu, H.; Tian, Z.; Zhao, C.; Li, M.; Zhang, L. Prediction of aquatic vegetation growth under ecological recharge based on machine learning and remote sensing. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 452, 142054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Qu, S.; Li, M.; Duan, L.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, X.; Yang, X.; Dong, S.; Yu, R. Spatio-temporal variability of lacustrine groundwater discharge and related pollutant fluxes in an agricultural drainage lake: Coupled influence of meteorological factors and vegetation coverage dynamics. J. Hydrol. 2025, 662, 134061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Deng, Y.; Liang, D.; Li, Y.; Gu, Q. Applying water environment capacity to assess the non-point source pollution risks in watersheds. Water Res. 2023, 240, 120092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ongley, E.D.; Xiaolan, Z.; Tao, Y. Current status of agricultural and rural non-point source Pollution assessment in China. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.H.; Liu, H.M.; Jing, J.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Cao, X.; Ma, L.; Zhuo, Y.; Wen, L.; Wang, L. How the land use/cover changes and environmental factors at different scales affect lake water quality in arid and semi-arid regions. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1188927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ge, Z.; Xia, R.; He, S.; Zhan, S. Hydrogeochemistry and stable isotopes of water: Characteristics, influencing factors and sources in a semi-arid irrigated basin, Hetao Plain. J. Arid. Environ. 2025, 227, 105313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, S.; Luo, M.; Zhao, X.; Lin, X.; Zhang, Q.; Fang, K.; Lv, S. Impacts of land use and crop structure change on the value of ecosystem services in Hetao Irrigation District of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 480, 144113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.C.; Zhou, H.; Li, H.H.; Wang, Y.H.; Cui, Z.M.; Shan, C.H.; Wang, F.C.; Shi, H.B. Soil water and salt dynamics under various irrigation and drainage methods in the Hetao irrigation district: A SahysMod-based analysis. Agric. Res. Arid Areas 2025, 43, 245–259. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S. Impacts of Temperature and Nutrient Dynamics on Phytoplankton in a Lake: A Case Study of Wuliangsuhai Lake, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 11195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.B.; Ma, S.H.; Cao, H.B.; Zhang, Y. Analysis and Countermeasures of Pollution in Wuliangsuhai Basin. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2011, 39, 10402–10405+10408. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Shang, S. Integrated assessment of crop planting suitability: A case study in the Hetao Irrigation District of China using HJ-1A/1B satellite data. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 301, 18939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Duan, J.J.; Wang, T.; Bi, Y.; Gao, F. Prediction of water-saving potential in Inner Mongolia Loop using distributed water cycle model and machine learning. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2023, 39, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Q.W.; Zhai, J.Q.; Zhao, Y.; He, G.H.; Zhang, Y. Effects of the Planting Structure Adjustment on Water Budget of Field System in Hetao Irrigation Area. J. Irrig. Drain. 2017, 36, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, P.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, F. Optimization and Evaluation of Multi-objective Planting Structure in Hetao Irrigation District Based on Water Footprint. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2021, 52, 346–357. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Wang, Q.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, W. Exploring the impact of rural labor transfer on the production and ecological sustainability of crop planting structure in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 22668–22685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Qiao, R.; Ji, S.; Bai, X.; Wang, L.; Chang, X. Changes and driving factors of crops planting structure in Hetao Irrigation Region in Inner Mongolia. J. Desert Res. 2021, 41, 110–117. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, F.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yan, J. Balancing water saving, market attractiveness, and pollution control in crop spatial planting structure planning of arid regions. Agric. Water Manag. 2025, 309, 109348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.Q.; Long, K.S. The Impact of non-grain production on fa rmers’ income: From a macro-comparative perspective. Res. Agric. Mod. 2023, 44, 244–253. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Q.W.; Cui, H.Z. Exploration and enlightenment on improving the quality of agricultural and animal husbandry products in Bayannaoer City, Inner Mongolia. China Dev. Obs. 2020, 232, 113–116. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.G.; Shi, H.B.; Li, X.Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, H. Effects of irrigation-fertilization-tillage on nutrient loading and crop yield in Ulansuhai watershed based on improved SWAT Model. J. Lake Sci. 2022, 34, 1505–1523. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Awada, T.; Shi, Y.; Jin, V.L.; Kaiser, M. Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Agriculture: Pathways to Sustainable Reductions. Glob. Change Biol. 2025, 31, e70015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Cai, Y.; Yu, C.; Yue, W. Identification of optimal strategies for agricultural nonpoint source management in Ulansuhai Nur watershed of Inner Mongolia, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2016, 30, 137–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.L.; Yang, G.Q.; Wang, C.Z.; Huo, Z. Linking agricultural water-food-environment nexus with crop area planning: A fuzzy credibility-based multi-objective linear fractional programming approach. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 277, 108135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, C.; Richetti, L. Environmental impacts of unregulated livestock production on river basin phosphorus cycles (1980–2017). Nat. Food 2020, 1, 320–328. [Google Scholar]
| System Type | Indicators | Unit | Data Source | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Economic system | GDP | 104 CNY | Statistical Yearbook of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region | [4] |
| Total sown area | hectare | [11] | ||
| Revenue per unit area of crop | CNY/(hm2·year) | China Rural Statistical Yearbook | [27] | |
| Revenue per unit of livestock | CNY/head | |||
| Resource system | Total water resources | 108 m3 | Water Resources Bulletin of Bayannur City | [11,12] |
| Water system | Water requirement per unit area of crops | m3/(hm2·year) | [28] | |
| Water requirement per unit of livestock | m3/(head·year) | |||
| COD environmental capacity | t/year | Water quality sampling and monitoring data | [7,13] | |
| TN environmental capacity | t/year | |||
| TP environmental capacity | t/year |
| The Obligatory Targets | Lower Limit | Upper Limit |
|---|---|---|
| total water resources (108 m3) | 42 | 48 |
| COD environmental capacity (t/year) | 15,875.40 | 21,167.20 |
| TN environmental capacity (t/year) | 960.37 | 1280.49 |
| TP environment capacity (t/year) | 42.77 | 85.53 |
| Crop | Revenue per Unit Area of Crop CNY/(hm2·Year) | Water Requirement per Unit Area of Crops m3/(hm2·Year) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Limit | Upper Limit | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |
| wheat | 1150 | 1800 | 500 | 550 |
| corn | 850 | 1100 | 447 | 491 |
| sunflower | 1600 | 2000 | 207 | 269 |
| fruit | 8000 | 10,000 | 125.3 | 165.6 |
| Livestock | Revenue per Unit of Livestock CNY/Head | Water Requirement per Unit of Livestock m3/(Head·Year) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Limit | Upper Limit | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |
| cow | 7895 | 11,843 | 1.83 | 2.19 |
| sheep | 1644 | 2467 | 7.2 | 9 |
| pig | 822.7 | 1234.3 | 1.44 | 1.8 |
| Solution Scenarios | Scenario Description |
|---|---|
| Scenario 1 | The watershed water supply guarantee rate was 90%, and other targets were maintained at the upper limit |
| Scenario 2 | The watershed water supply guarantee rate was 75%, and other targets were maintained at the upper limit |
| Scenario 3 | The environmental capacity reaches the Class IV water quality standard, and other targets were maintained at the upper limit |
| Scenario 4 | The environmental capacity reaches the Class V water quality standard, and other targets were maintained at the upper limit |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Jiang, S.; Liu, H.; Wen, Y.; Gao, F.; Wang, L. Study on the Coordinated Development of Resources, Environment and Economy on Fuzzy Multi-Objective Programming: A Case Study of Arid and Semi-Arid River Basin in Northern China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 10757. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310757
Liu X, Jiang S, Liu H, Wen Y, Gao F, Wang L. Study on the Coordinated Development of Resources, Environment and Economy on Fuzzy Multi-Objective Programming: A Case Study of Arid and Semi-Arid River Basin in Northern China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(23):10757. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310757
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xuhua, Shan Jiang, Huamin Liu, Yunhao Wen, Feng Gao, and Lixin Wang. 2025. "Study on the Coordinated Development of Resources, Environment and Economy on Fuzzy Multi-Objective Programming: A Case Study of Arid and Semi-Arid River Basin in Northern China" Sustainability 17, no. 23: 10757. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310757
APA StyleLiu, X., Jiang, S., Liu, H., Wen, Y., Gao, F., & Wang, L. (2025). Study on the Coordinated Development of Resources, Environment and Economy on Fuzzy Multi-Objective Programming: A Case Study of Arid and Semi-Arid River Basin in Northern China. Sustainability, 17(23), 10757. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310757







