Insights from the Application of Computer-Aided Mapping Technology in Chinese Education for Urban Forestry
Abstract
1. Introduction
- What are the characteristics of scholarly publications on CAM?
- What are the current research hotspots in CAM?
- What are the emerging trends and future directions for CAM research?
- How can CAM technology inform the practical components of urban forestry curricula, and how can its application be optimized to enhance practical skills within the discipline?
2. Materials and Methods
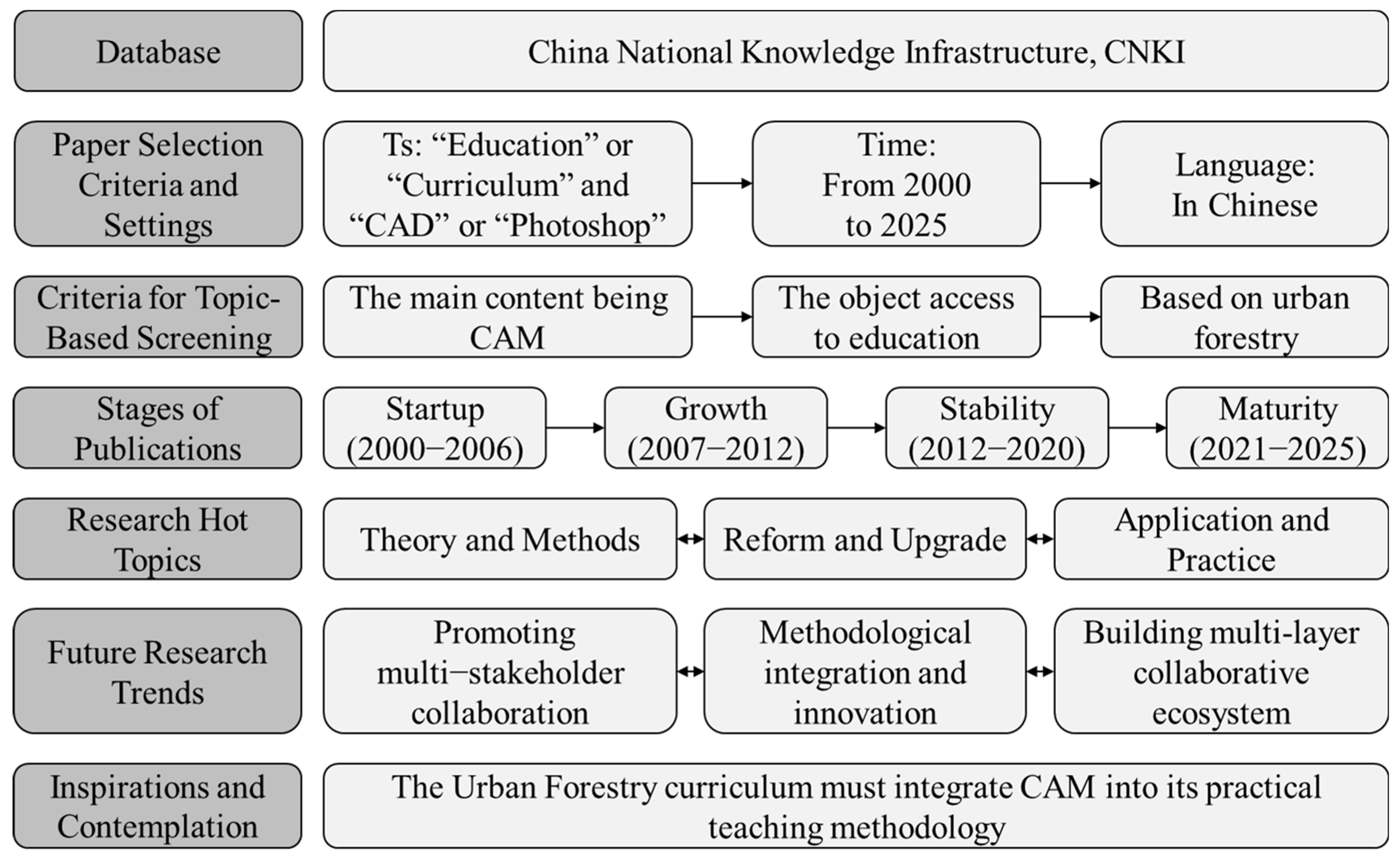
2.1. Data Sources and Screening
2.2. CiteSpace Operation Methodology and Parameter Configuration
3. Results
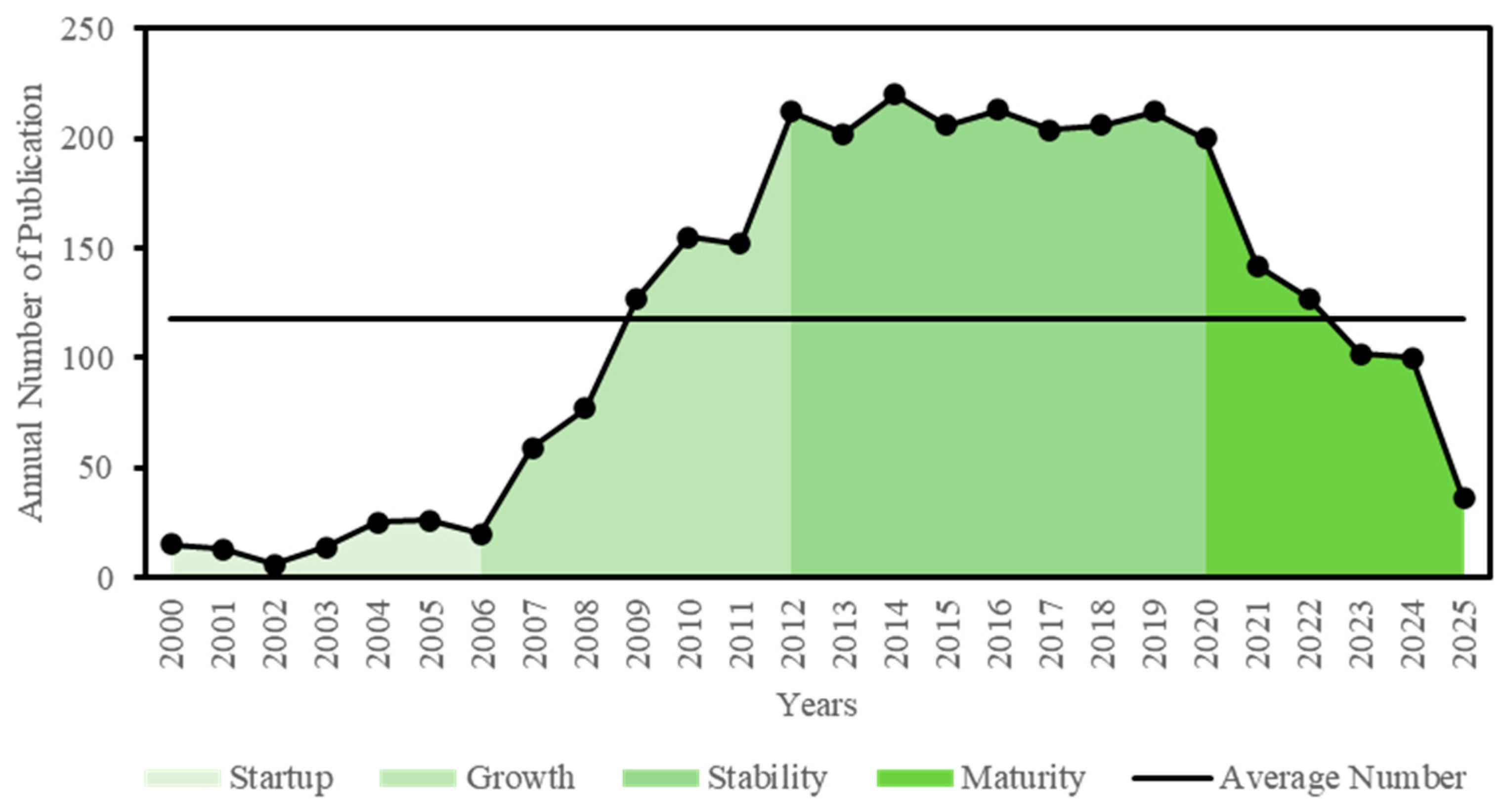
3.1. Publication Characteristics of Computer-Aided Mapping Education Research
3.2. Development and Evolution Characteristics of Computer-Aided Mapping Education Reform in China
3.2.1. Research Progress: Keyword Timeline Mapping
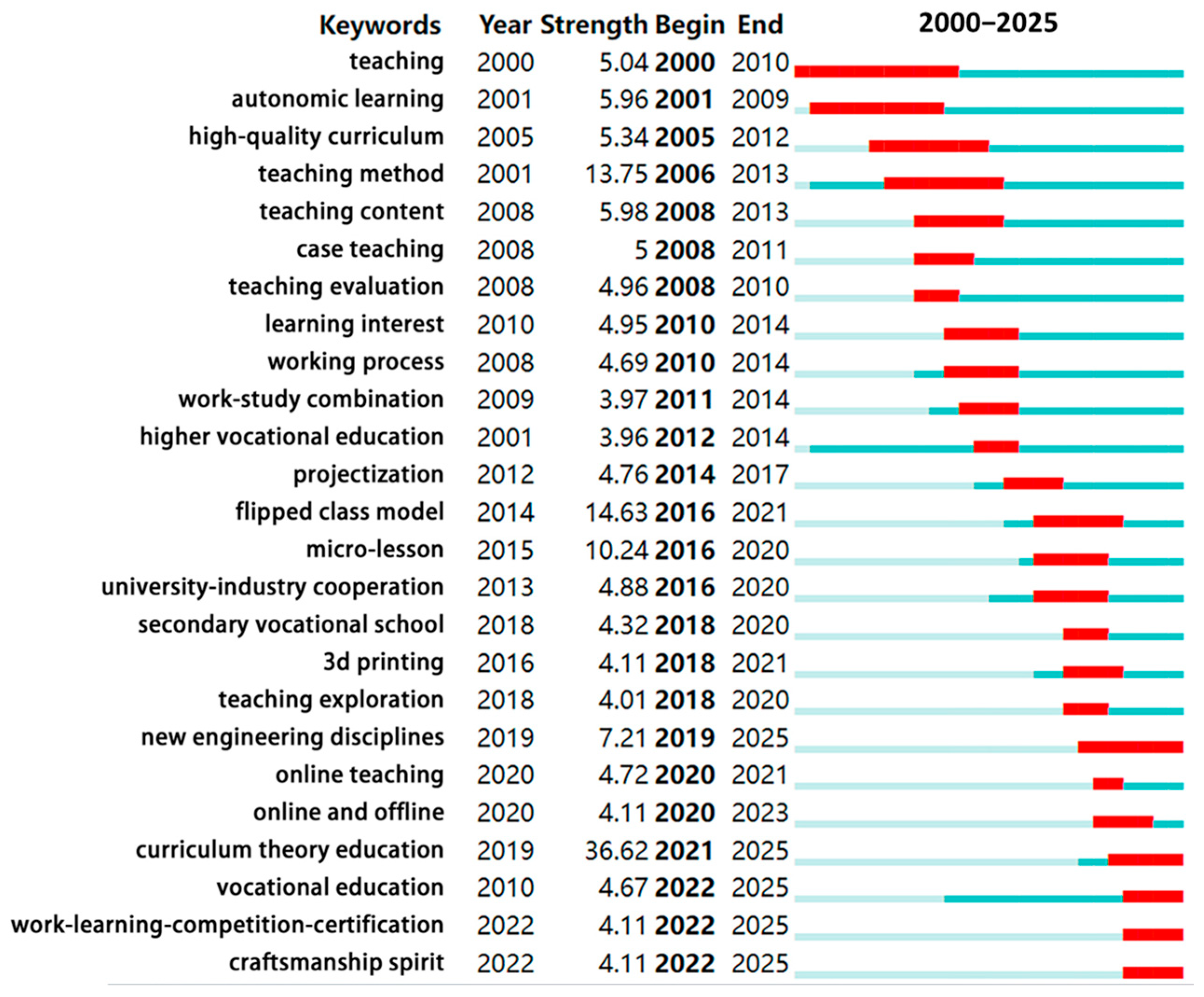
3.2.2. Evolution Trends: Keyword Burst Analysis
3.3. Research Hotspot Themes in Computer-Aided Mapping Education Reform in China
3.3.1. Research Progress: Keyword Timeline Mapping
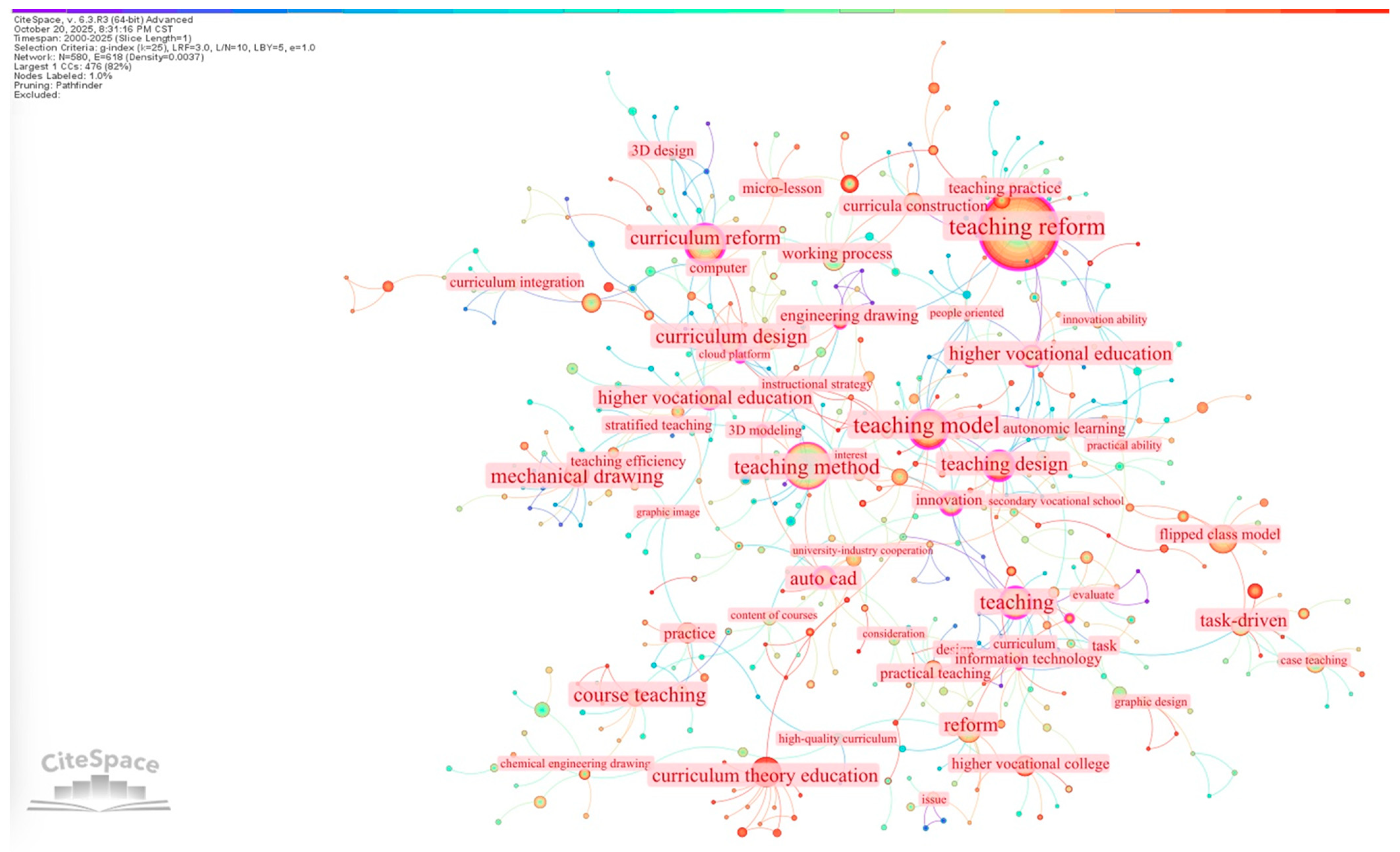
3.3.2. Cluster Analysis
3.4. Different Research Hotspot Themes
3.4.1. Theme of “Theory and Method”
3.4.2. Theme of “Reform and Enhancement”
3.4.3. Theme of “Application and Practice”
4. Discussion
4.1. The Evolution of the CAM Education Paradigm
4.2. The Positive Promoting Role of Multi-Stakeholder Collaboration
4.3. Methodological Integration and Innovation in Future Teaching Models
4.4. Building a Multi-Layer Collaborative Ecosystem for CAM Education in Urban Forestry
4.5. Limitations and Prospects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, L.; Ma, Y.; Shi, J.; Xu, Y.; Chen, C.; Tang, C. Integrated teaching reform of Engineering Drawing and Computer Graphics for mechanical majors under background of emerging engineering education. Agric. Eng. 2025, 15, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, T. Ladder: A Perceptually-Based Language to Simplify Sketch Recognition User Interface Development. Doctoral Dissertation, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland, I. SKETCHPAD: A Man-Machine Graphical Communication System. Doctoral Dissertation, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Autodesk Inc. Available online: https://www.autodesk.com/products/autocad (accessed on 27 October 2025).
- Autodesk Inc. Available online: https://www.autodesk.com/products/3ds-max (accessed on 27 October 2025).
- Autodesk Inc. Available online: https://www.autodesk.com/products/maya (accessed on 27 October 2025).
- Ligon, S.; Liska, R.; Stampfl, J.; Gurr, M.; Mülhaupt, R. Polymers for 3D printing and customized additive manufacturing. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 10212–10290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teja, S.; Chintalapati, S.; Gupta, V.; Varma, T.; Lee, H.; Sankaranarayanan, A.; Mitra, K. PhotonSplat: 3D scene reconstruction and colorization from SPAD sensors. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Computational Photography (ICCP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 21–23 July 2025; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Kong, F.; Liu, X.; Shi, N. A brief analysis of the history, current situation and future development of CAD technology. Urban Constr. Theory Res. (Electron. Ed.) 2018, 34, 73. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, F.; Pan, R. Construction of forestry professional teaching resource database: Application and practice of constructivist learning theory. Fujian For. 2025, 40, 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R. Construction of dialogue teaching model based on Ausubel. Theor. Pract. Educ. 2016, 36, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Chen, R. From educational process to educational culture: Centennial retrospect of Jerome Seymour Bruner. e-Educ. Res. 2019, 40, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Liang, H.; Li, H.; Fan, W. A network meta-analysis of the teaching effect of 11 teaching methods in internal Medicine. Chongqing Med. J. 2025, in press.
- Döllner, J.; Amicis, R.; Burmeister, J.; Richter, R. Forests in the digital age: Concepts and technologies for designing and deploying forest digital twins. In Proceedings of the 28th International ACM Conference on 3D Web Technology (Web3D ‘23), San Sebastian, Spain, 9–11 October 2023; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tockner, A.; Gollob, C.; Kraßnitzer, R.; Ritter, T.; Nothdurft, A. Automatic tree crown segmentation using dense forest point clouds from Personal Laser Scanning (PLS). Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 114, 103025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingberg, J.; Konarska, J.; Lindberg, K.; Johansson, L.; Thorsson, S. Mapping leaf area of urban greenery using aerial LiDAR and ground-based measurements in Gothenburg, Sweden. Urban For. Urban Gree. 2017, 26, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Park, C. Developing a mapping procedure for urban forests using online map services and Sentinel-2A images. Urban For. Urban Gree. 2023, 89, 128095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Gao, T.; Qiu, L. How do species richness and colour diversity of plants affect public perception, preference and sense of restoration in urban green spaces? Urban For. Urban Gree. 2024, 100, 128487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; He, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ning, Z. Development and application of urban forest management information system (UFMIS) based on CITYgreen mode. Chin. J. Ecol. 2003, 22, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.; Potapov, P.; Moore, R.; Hancher, M.; Turubanova, S.; Tyukavina, A.; Thau, D.; Stehman, S.; Goetz, S.; Loveland, T.; et al. High-resolution global maps of 21st-Century forest cover change. Science 2013, 342, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, H.; Wang, X.; Cai, B.; Niu, X. Teaching research and practice of computer experiment on CAD of engineering drawing course based on the “Internet Plus”. J. Graph. 2017, 38, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P. Teaching reform and innovative practice of mechanical design courses driven by discipline competition and engineering projects. Paperm. Equip. Mater. 2025, 54, 174–176. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Shi, W.; He, B. Reform of task based teaching in Computer Aided Drawing course for material major under the background of new engineering. Adv. Educ. 2024, 14, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Liu, J. Low-Carbon education: Insights and trends for sustainable development through knowledge graphs. Sustainability. 2025, 17, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PRISMA: Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses. Available online: https://www.prismastatement.org (accessed on 18 November 2025).
- Huang, X.; Cao, Y. Multimodal learning theory and its application in experimental teaching of computer Graphics. Exp. Technol. Manag. 2012, 29, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Recent research progress on computer graphics in China. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2016, 34, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. Construction of experimental teaching platform for computer graphics course. Res. Explor. Lab. 2019, 38, 147–151+229. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, C. Reform and practice on computer mapping practice for Geographic Information Science major. Eng. Surv. Map. 2018, 27, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Liu, B.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Z.; Lei, K. Semiautomatic Structural BIM-Model Generation Methodology Using CAD Construction Drawings. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2020, 34, 04020006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, M.; Costantino, D. Techniques, tools, platforms and algorithms in close range photogrammetry in building 3D model and 2D representation of objects and complex architectures. Comput.-Aided Des. Appl. 2021, 18, 42–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Huang, S.; Tang, B. Employment-oriented teaching reform practice in “Food Engineering AutoCAD”. Food Ind. 2025, 46, 284–287. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. Exploration and practice of the teaching reform of curriculum ideological and political education in “Engineering Drawing and CAD” Course. Educ. Teach. Forum. 2021, 9, 103–106. [Google Scholar]
- Computer-aided Design. Chinese University MOOC. Available online: https://www.icourse163.org/course/BFU-1003377002 (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- Sun, X. Is the current reform of basic education intended to replace the curriculum system centered on subject knowledge?—A discussion with a curriculum perspective. Educ. Res. Exp. 1998, 2, 4–8+71. [Google Scholar]
- Stacks, D.W.; Salwen, M.B. An Integrated Approach to Communication Theory and Research; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jonassen, D.H. Toward a design theory of problem solving. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2000, 48, 63–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, M. Does active learning work? A review of the research. J. Eng. Edu. 2004, 93, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, S.; Eddy, S.L.; McDonough, M.; Smith, M.K.; Okoroafor, N.; Jordt, H.; Wenderoth, M.P. Active learning increases student performance in Science, Engineering, and Mathematics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 8410–8415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahern, J. From fail-safe to safe-to-fail: Sustainability and resilience in the new urban world. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 100, 341–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, R.S. View through a window may influence recovery from surgery. Science 1984, 224, 420–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartig, T.; Mitchell, R.; De Vries, S.; Frumkin, H. Nature and Health. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2014, 35, 207–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowler, D.E.; Buyung-Ali, L.; Knight, T.M.; Pullin, A.S. Urban greening to cool towns and cities: A systematic review of the empirical evidence. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2010, 97, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.E.; Handley, J.F.; Ennos, A.R.; Pauleit, S. Adapting cities for climate change: The role of the green infrastructure. Built Environ. 2007, 33, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodchild, M.F. Twenty years of progress: GIScience in 2010. J. Spat. Int. Sci. 2010, 1, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzoulas, K.; Korpela, K.; Venn, S.; Yli-Pelkonen, V.; Kaźmierczak, A.; Niemela, J.; James, P. Promoting ecosystem and human health in urban areas using green infrastructure: A literature review. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2007, 81, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, V.; Gaither, C. Approaching environmental health disparities and green spaces: An ecosystem services perspective. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 1952–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, B.A.; Coutts, A.M.; Livesley, S.J.; Harris, R.J.; Hunter, A.M.; Williams, N.S.G. Planning for cooler cities: A framework to priorities green infrastructure to mitigate high temperatures in urban landscapes. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 134, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, D.J.; Dwyer, J.F. Understanding the benefits and costs of urban forest ecosystems. In Urban and Community Forestry in the Northeast; Kuser, J.E., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 25–46. [Google Scholar]
- McPherson, G.; Simpson, J.R.; Peper, P.J.; Maco, S.E.; Xiao, Q. Municipal forest benefits and costs in five US cities. J. Forest. 2005, 103, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, S.R.J. Landscape visualisation and climate change: The potential for influencing perceptions and behaviour. Environ. Sci. Policy 2005, 8, 637–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, J.; Verleger, M. The flipped classroom: A survey of the research. In Proceedings of the 2013 ASEE Annual Conference & Exposition Proceedings, Atlanta, GA, USA, 23–26 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, F.E.; Sullivan, W.C. Environment and crime in the inner city: Does vegetation reduce crime? Environ. Behav. 2001, 33, 343–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, P.; Beatley, T.; Boyer, H. Resilient cities: Responding to peak oil and climate change. Aust. Plan. 2009, 46, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovett, A.; Appleton, K.; Warren-Kretzschmar, B.; Von Haaren, C. Using 3D visualization methods in landscape planning: An evaluation of options and practical issues. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 142, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grêt-Regamey, A.; Fagerholm, N. Key factors to enhance efficacy of 3D digital environments for transformative landscape and urban planning. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2024, 244, 104978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Flaherty, J.; Phillips, C. The use of flipped classrooms in higher education: A scoping review. Internet High. Educ. 2015, 25, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauskis, G. Development of methods and practices of Virtual Reality as a tool for participatory urban planning: A case study of Vilnius City as an example for improving environmental, social and energy sustainability. Energ. Sustain. Soc. 2014, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepańska, A.; Kaźmierczak, R.; Myszkowska, M. Virtual Reality as a tool for public consultations in spatial planning and management. Energies 2021, 14, 6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zeng, W.; Liu, L. UrbanVR: An immersive analytics system for context-aware urban design. Comput. Graph. 2021, 99, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, D.; Frantzeskaki, N.; Elmqvist, T. Ecosystem services in urban landscapes: Practical applications and governance implications. AMBIO 2014, 43, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, P.; Moazzam, M.; Ashraf, A.; Khan, M.N. The interdisciplinary curriculum alignment to enhance graduates’ employability and universities’ sustainability. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 2024, 22, 101037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepper-Kittredge, C. We are all in this together: Building a network of makerspaces in California community colleges. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Academic Makerspaces, Cleveland, OH, USA, 24–27 September 2017; p. 115. [Google Scholar]


| Number | Frequency | Centrality | Keywords |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 514 | 0.24 | Teaching Reform |
| 2 | 228 | 0.14 | Teaching Method |
| 3 | 155 | 0.37 | Teaching Model |
| 4 | 153 | 0.21 | Curriculum Reform |
| 5 | 115 | 0.28 | Teaching |
| 6 | 101 | 0.10 | Mechanical Drawing |
| 7 | 95 | 0.21 | Teaching Design |
| 8 | 86 | 0.14 | Vocational Education |
| 9 | 85 | 0.09 | Reform |
| 10 | 83 | 0.04 | Flipped Classroom |
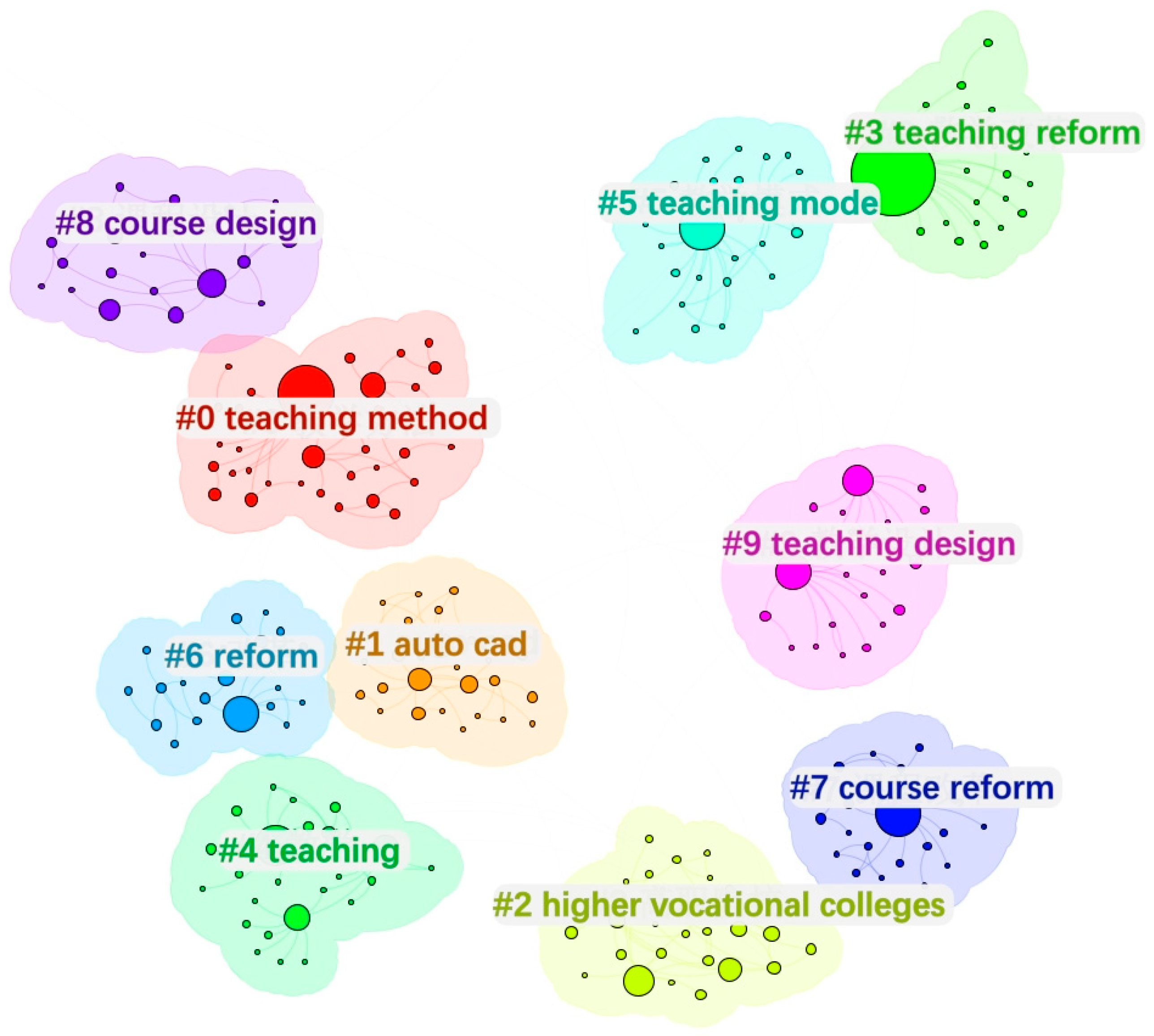
| Topic Name | Cluster Number | Size | Contour Value | Marker Word | Log-Likelihood Label Value Top Five Keywords |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Theory and Methods | #0 | 35 | 0.966 | Teaching Methods | Teaching Methods (120.17); Secondary Vocational (32.43); Innovation (30.72); Teaching Reform (28.57); Art Design (26.77) |
| #1 | 27 | 0.969 | AutoCAD | AutoCAD (55.63); Engineering Drawing (54.41); 3D Modeling (41.64); Industry-Education Integration (27.1); School-Enterprise Cooperation (19.6) | |
| #5 | 24 | 0.992 | Teaching Model | Teaching Model (151.34); Teaching Practice (39.06); People-Oriented (11.53); Diversification (10.82); Innovation and Entrepreneurship (7.83) | |
| Reform and Upgrading | #3 | 26 | 0.999 | Teaching Reform | Teaching Reform (295.89); Teaching (17.18); Curriculum reform (17.18); Photoshop (13.55); Flipped Classroom (13.52) |
| #6 | 23 | 0.999 | Reform | Reform (61.96); Issues (28.8); Chemical Engineering Drawing (27.99); Premium Courses (22.96); Construction (19.95) | |
| #7 | 23 | 0.994 | Curriculum Reform | Curriculum Reform (146.79); 3D Design (24.48); Online Learning (12.21); Mechanical Engineering (12.21); Reducer (12.21) | |
| Applications and Practice | #2 | 27 | 0.902 | Vocational Colleges | Vocational Colleges (43.92); Image Processing (42.24); Information Technology (28.74); Tasks (18.72); Secondary Vocational Education (15.74) |
| #4 | 26 | 0.989 | Teaching | Teaching (98.52); Courses (65.75); Practical Teaching (45.04); Teaching Reform (11.88); Theoretical Teaching (10.97) | |
| #8 | 22 | 0.993 | Course Design | Course Design (65.64); Informatization (30.14); Case Studies (24.09); Teaching Strategies (24.09); Mechanical Design (24.09) | |
| #9 | 22 | 0.924 | Instructional Design | Instructional Design (91.6); Higher Vocational Education (65.78); Architectural Drafting (13.65); Constructivism (12.02); Teaching Implementation (8.3) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, B.; Liang, T.; Li, J.; Hu, Z. Insights from the Application of Computer-Aided Mapping Technology in Chinese Education for Urban Forestry. Sustainability 2025, 17, 10701. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310701
Ma B, Liang T, Li J, Hu Z. Insights from the Application of Computer-Aided Mapping Technology in Chinese Education for Urban Forestry. Sustainability. 2025; 17(23):10701. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310701
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Bingqian, Te Liang, Jiheng Li, and Zuoyou Hu. 2025. "Insights from the Application of Computer-Aided Mapping Technology in Chinese Education for Urban Forestry" Sustainability 17, no. 23: 10701. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310701
APA StyleMa, B., Liang, T., Li, J., & Hu, Z. (2025). Insights from the Application of Computer-Aided Mapping Technology in Chinese Education for Urban Forestry. Sustainability, 17(23), 10701. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310701





