Quantile Modelling of the Moderating Role of Renewable and Nuclear Energy in the Transportation and Environmental Sustainability Nexus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Theoretical Framework
2.2. Transportation and Environmental Sustainability
2.3. Renewable Energy as a Moderator
2.4. Nuclear Energy, Transportation, and Environmental Sustainability
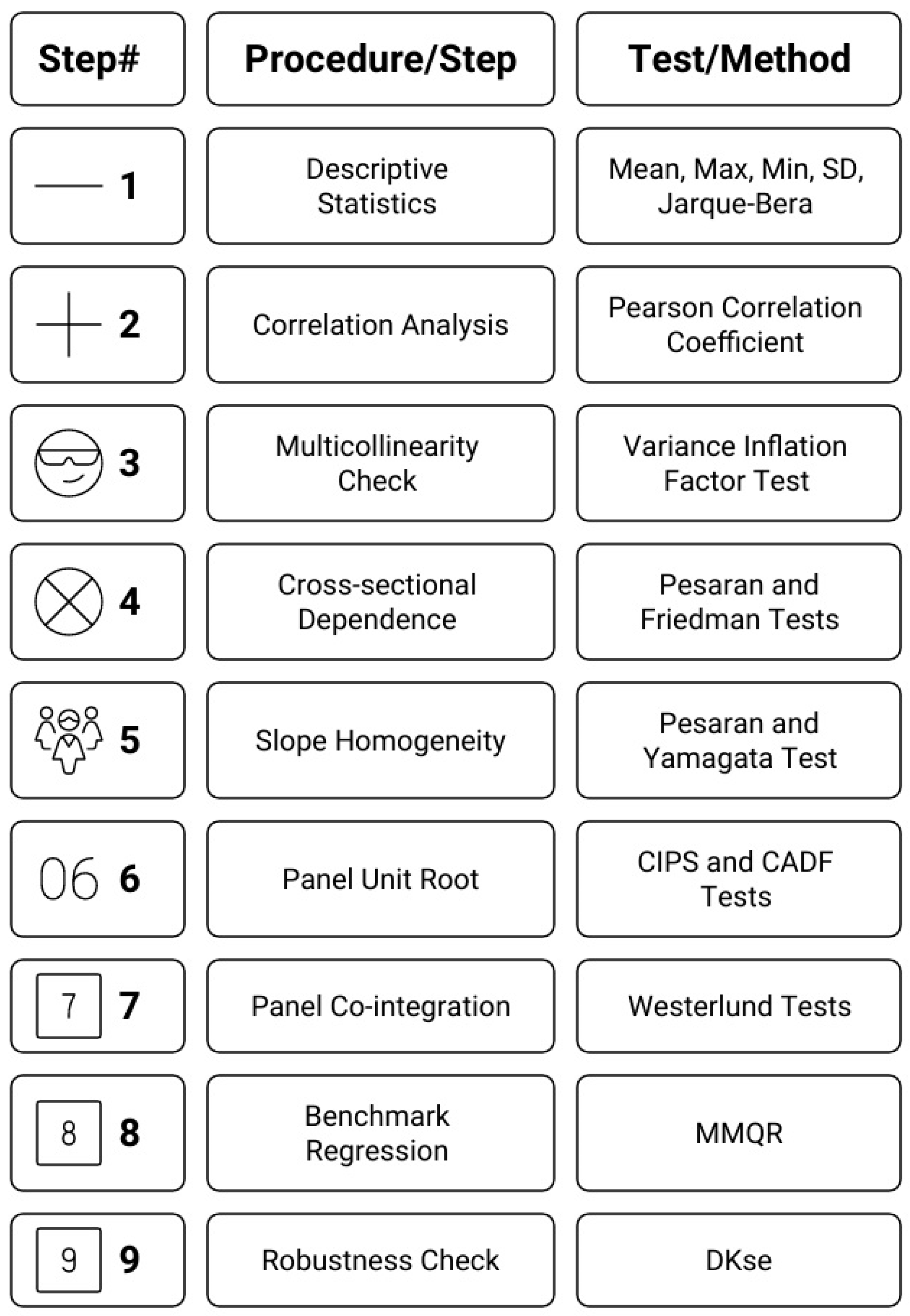
3. Materials and Methods
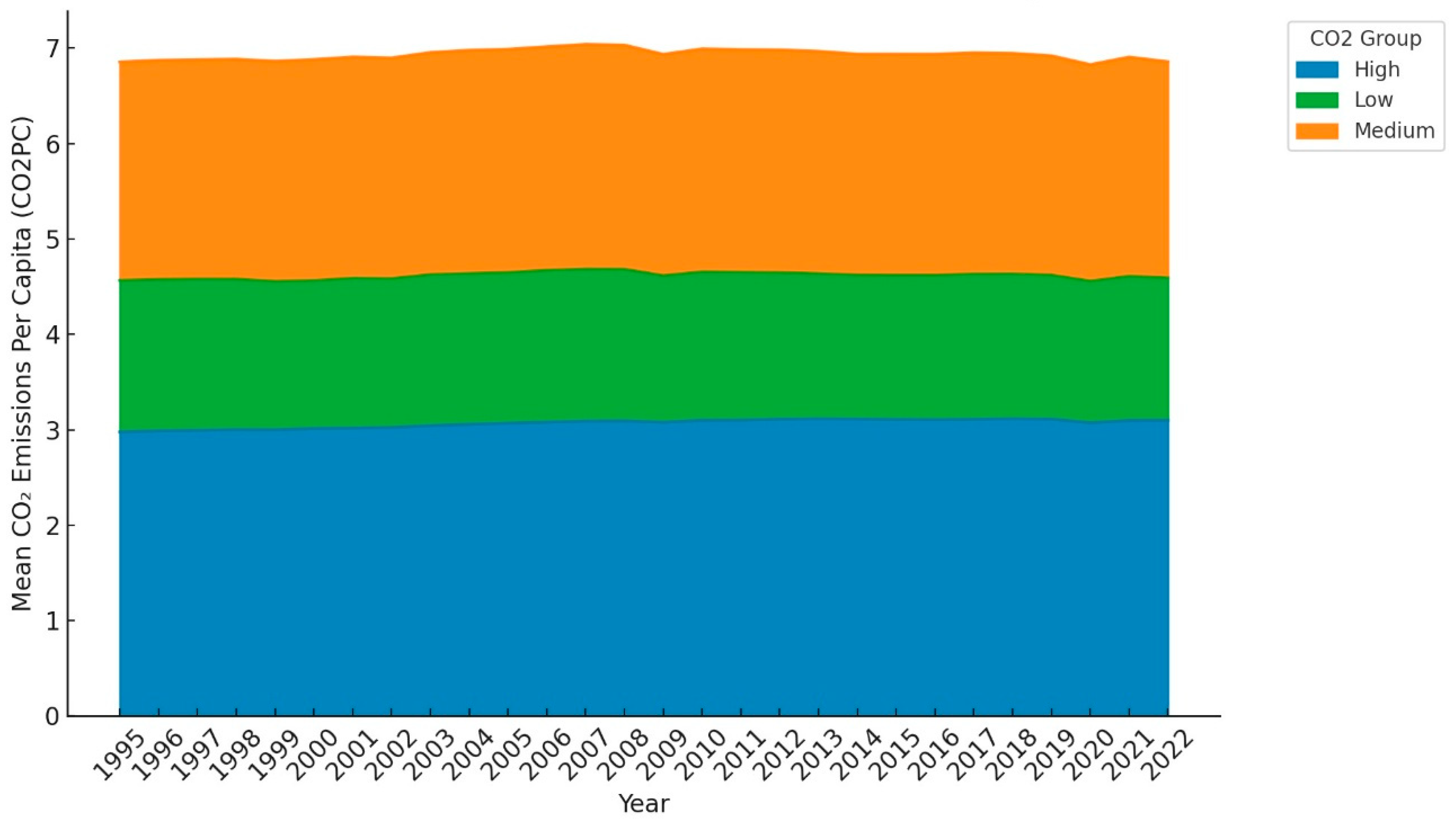
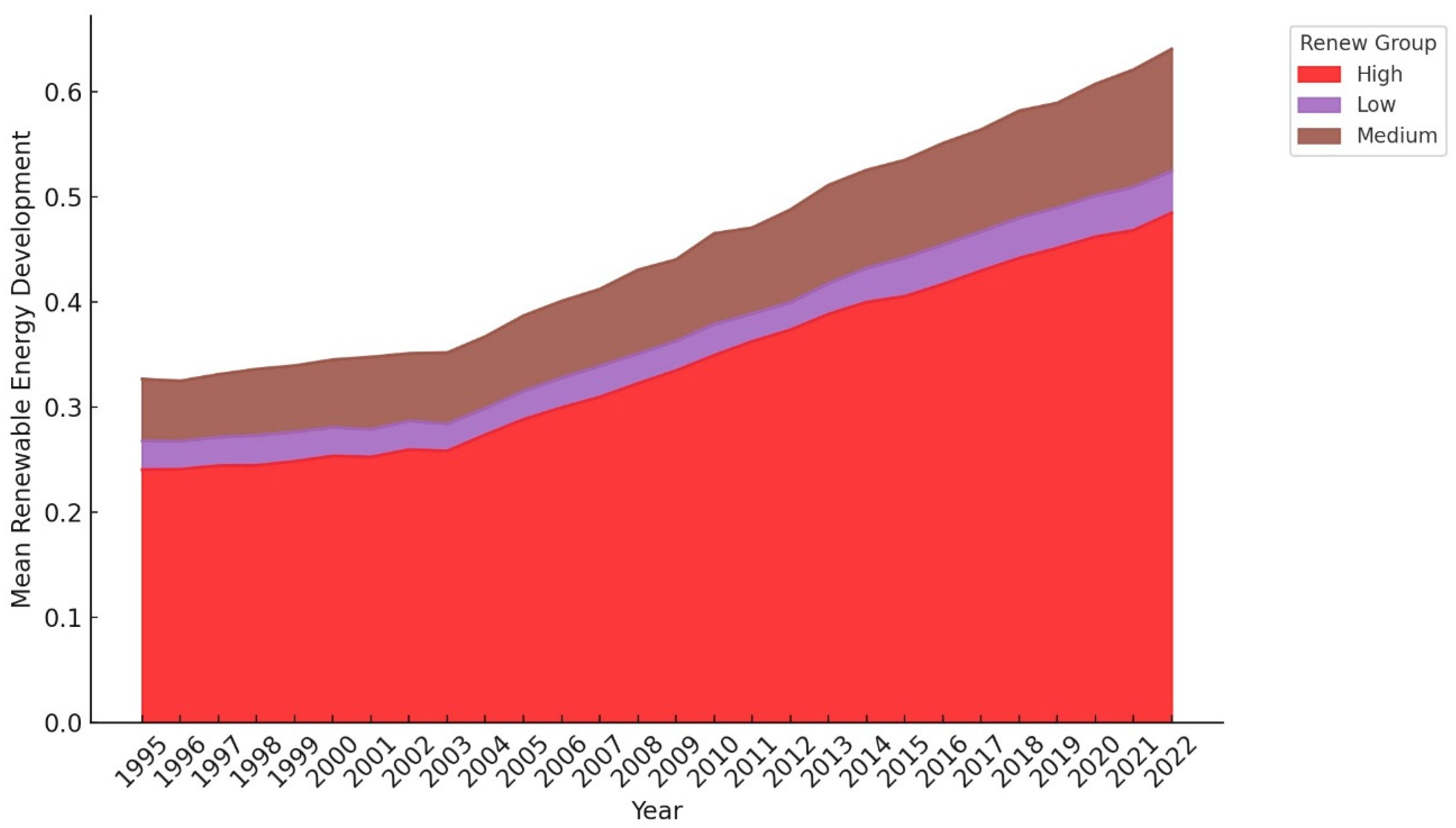
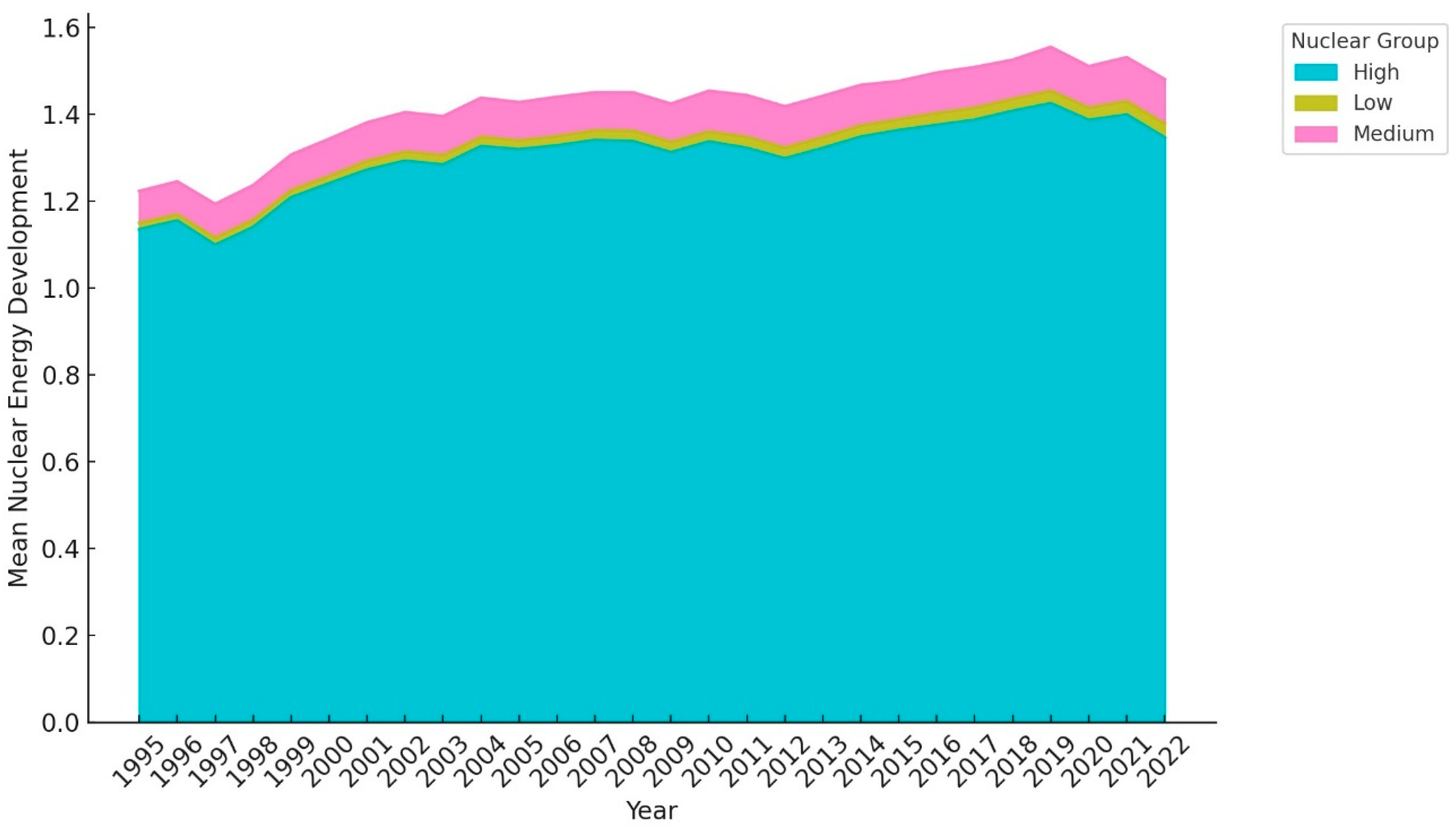
3.1. Data
3.2. Econometric Model
3.3. Empirical Strategy
3.4. Cross-Sectional Dependence (CSD)
3.5. Slope Homogeneity Test
3.6. Panel Unit Root Test
3.7. Panel Cointegration Test
3.8. Estimation Technique MMQR
3.9. Robustness Check
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Results
4.2. Robustness Test
4.3. Discussion
5. Conclusions, Policy Implications, and Limitations
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Prudential Policy Implications
5.3. Limitations and Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adedoyin, F.F.; Bekun, F.V.; Driha, O.M.; Balsalobre-Lorente, D. The effects of air transportation, energy, ICT and FDI on economic growth in the industry 4.0 era: Evidence from the United States. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2020, 160, 120297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Yu, Y.; Jahanger, A.; Balsalobre-Lorente, D. Structural emissions reduction of China’s power and heating industry under the goal of “double carbon”: A perspective from input-output analysis. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 31, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, N.; Mu, H.; Zhang, M.; Pang, J.; Ahmad, M. Study on the long-term and short-term effects of globalization and population aging on ecological footprint in OECD countries. Ecol. Complex. 2021, 47, 100946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, H.; Rosado, P.; Roser, M. Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Our World Data; Global Change Data Lab: Oxford, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.S.; Sasidharan, A.; Bagepally, B.S. Air pollution and cardiovascular disease burden: Changing patterns and implications for public health in India. Heart Lung Circ. 2023, 32, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaewsaeng-on, R.; Mehmood, S. Quantile modeling for environmental risk: SAARC’s journey with green finance, policies, and regulations. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 140234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Fan, Y.; Perry, S.; Klemeš, J.J.; Lee, C.T. A review on air emissions assessment: Transportation. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 194, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gani, A. Fossil fuel energy and environmental performance in an extended STIRPAT model. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffrichter, A.; Miller, A.R.; Hillmansen, S.; Roberts, C. Well-to-wheel analysis for electric, diesel and hydrogen traction for railways. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2012, 17, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, P.; Jain, S. Energy demand and CO2 emissions from urban on-road transport in Delhi: Current and future projections under various policy measures. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 128, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimenc, M. Overview and comparative analysis of emission calculators for inland shipping. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2016, 10, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Wang, T.; Yu, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhu, B. Scenario analysis of CO2 emissions from China’s civil aviation industry through 2030. Appl. Energy 2016, 175, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.S.; Van Wee, B. Toward a better methodology for assessing CO2 emissions for intermodal and truck-only freight systems: A European case study. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2014, 8, 177–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Pan, S.-Y.; Kim, H.; Linn, J.H.; Chiang, P.-C. Building green supply chains in eco-industrial parks towards a green economy: Barriers and strategies. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 162, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zafar, M.G.R.; Gaudreault, F.; Ben-Salha, O.; Alhebri, A. Stringent environmental policies: How they shape the future of nuclear energy generation. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2025, 57, 103650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Li, J.; Lu, W.; Hafeez, M.; Sohail, M.T.; Akbar, M.W.; Attar, R.W. How does the productivity of renewable energy respond to institutional pressures and higher education? Renew. Energy 2025, 238, 121934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnour, M.; Awan, A.; Hossain, M.E. Towards a green transportation system in Mexico: The role of renewable energy and transport public-private partnership to curb emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 442, 140984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakosta, C.; Pappas, C.; Marinakis, V.; Psarras, J. Renewable energy and nuclear power towards sustainable development: Characteristics and prospects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 22, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, K.K.; Chowdhury, C.R.; Yadav, D.; Verma, R.; Dutta, S.; Jaiswal, K.S.; Karuppasamy, K.S.K. Renewable and sustainable clean energy development and impact on social, economic, and environmental health. Energy Nexus 2022, 7, 100118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.; Altinoz, B.; Dogan, E. Analyzing the determinants of carbon emissions from transportation in European countries: The role of renewable energy and urbanization. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2020, 22, 1725–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirin, M.; Gärtner, S.O.; Pehnt, M.; Reinhardt, G.A. CO2 Mitigation Through Biofuels in the Transport Sector-Status and Perspectives. Main Report; Institute for Energy and Environmental Research: Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Aßmann, D.; Sieber, N. Transport in developing countries: Renewable energy versus energy reduction? Transp. Rev. 2005, 25, 719–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Alvarado, R.; Ali, S.; Ahmed, Z.; Meo, M.S. Transport infrastructure, economic growth, and transport CO2 emissions nexus: Does green energy consumption in the transport sector matter? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 40094–40106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Olivares, A.; Solé, J.; Osychenko, O. Transportation in a 100% renewable energy system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 158, 266–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelides, E.E.; Michaelides, D.N. Impact of nuclear energy on fossil fuel substitution. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2020, 366, 110742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsberg, C.W. Nuclear energy for a low-carbon-dioxide-emission transportation system with liquid fuels. Nucl. Technol. 2008, 164, 348–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, P.; Huang, J. Balancing energy security and marine pollution prevention: Legal challenges of utilizing nuclear power for decarbonizing maritime transportation in the Arctic region. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 40445–40461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.U.; Rehman, Z.U.; Sharif, A.; Anwar, A. Impact of transportation infrastructure and urbanization on environmental pollution: Evidence from novel wavelet quantile correlation approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 3014–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, P.; Ma, S. The impact of different transportation infrastructures on urban carbon emissions: Evidence from China. Energy 2024, 295, 131041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruška, I.; Litavcová, E.; Chovancová, J. Impact of renewable energy sources and nuclear energy on CO2 emissions reductions—The case of the EU countries. Energies 2022, 15, 9563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, S.; Kashif, U.; Rasool, Y.; Akhtar, M. The impact of financial innovation, green energy, and economic growth on transport-based CO2 emissions in India: Insights from QARDL approach. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 28823–28842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Samour, A.; Soomro, S.A.; Khalid, W.; Tursoy, T. A step towards a sustainable environment in top-10 nuclear energy consumer countries: The role of financial globalization and nuclear energy. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2025, 57, 103142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, W.; Islam, M.M.; Vasa, L.; Abbas, S.; Shahzad, U. Impacts of nuclear energy, greener energy, and economic progress on the load capacity factor: What we learn from the leading nuclear power economies? Geosci. Front. 2024, 15, 101739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WorldBank. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/EN.GHG.CO2.PC.CE.AR5 (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- Udeagha, M.C.; Ngepah, N. The drivers of environmental sustainability in BRICS economies: Do green finance and fintech matter? World Dev. Sustain. 2023, 3, 100096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarkson, M.E. A stakeholder framework for analyzing and evaluating corporate social performance. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1995, 20, 92–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Yu, W. Green finance and environmental, social, and governance performance. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2024, 89, 1185–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, R.P.; Arvin, M.B.; Nair, M. Urbanization, transportation infrastructure, ICT, and economic growth: A temporal causal analysis. Cities 2021, 115, 103213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magazzino, C.; Mele, M. On the relationship between transportation infrastructure and economic development in China. Res. Transp. Econ. 2021, 88, 100947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratila, A.; Gavril, I.A.; Nita, S.C.; Hrebenciuc, A. The importance of maritime transport for economic growth in the european union: A panel data analysis. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukinskiy, V.; Pletneva, N. Impact of solutions for goods transportation on business efficiency and traffic safety. Transp. Res. Procedia 2018, 36, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakuriah, P.; Metaxatos, P. Effect of residential location and access to transportation on employment opportunities. Transp. Res. Rec. 2000, 1726, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, A.; Clément, M.-A.; Gélinas, I.; Boucher, N.; Croteau, C.; Morin, D.; Turcotte, M.; Archambault, P.S. The impact of transportation on the employment of people with disabilities: A scoping review. Transp. Rev. 2024, 44, 85–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acheampong, A.O.; Dzator, J.; Dzator, M.; Salim, R. Unveiling the effect of transport infrastructure and technological innovation on economic growth, energy consumption and CO2 emissions. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 182, 121843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.H. An empirical study on the relationship between urbanization, transportation infrastructure, industrialization and environmental degradation in China, India and Indonesia. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanger, A.; Ozturk, I.; Onwe, J.C.; Ogwu, S.O.; Hossain, M.R.; Abdallah, A.A. Do pro-environmental interventions matter in restoring environmental sustainability? Unveiling the role of environmental tax, green innovation and air transport in G-7 nations. Gondwana Res. 2024, 127, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, Z. Liability structure and carbon emissions abatement: Evidence from Chinese manufacturing enterprises. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2022, 83, 481–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, D.; Yang, F.; Hafeez, M. Natural resources and nuclear energy development: Does political stability matter? Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2025, 57, 103328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, K.; Dong, X.; Dong, K. Is smart transportation associated with reduced carbon emissions? The case of China. Energy Econ. 2022, 105, 105715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ağbulut, Ü. Forecasting of transportation-related energy demand and CO2 emissions in Turkey with different machine learning algorithms. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 29, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, J.; Kamb, A.; Nässén, J.; Åkerman, J. Measuring greenhouse gas emissions from international air travel of a country’s residents methodological development and application for Sweden. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2018, 72, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish; Baloch, M.A.; Suad, S. Modeling the impact of transport energy consumption on CO2 emission in Pakistan: Evidence from ARDL approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 9461–9473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avotra, A.A.R.N.; Nawaz, A. Asymmetric impact of transportation on carbon emissions influencing SDGs of climate change. Chemosphere 2023, 324, 138301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyamfi, B.A.; Bekun, F.V.; Balsalobre-Lorente, D.; Onifade, S.T.; Ampomah, A.B. Beyond the environmental Kuznets curve: Do combined impacts of air transport and rail transport matter for environmental sustainability amidst energy use in E7 economies? Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 11852–11870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosqvist, L.S.; Hiselius, L.W. Online shopping habits and the potential for reductions in carbon dioxide emissions from passenger transport. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 131, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Q.-L.; Liu, H.-Z.; Yu, W.-Q.; He, X. The impact of public transportation on carbon emissions—From the perspective of energy consumption. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churchill, S.A.; Inekwe, J.; Ivanovski, K.; Smyth, R. Transport infrastructure and CO2 emissions in the OECD over the long run. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2021, 95, 102857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, R.L.; Ajide, K.B.; Usman, M.; Kousar, R. Heterogeneous effects of renewable energy and structural change on environmental pollution in Africa: Do natural resources and environmental technologies reduce pressure on the environment? Renew. Energy 2022, 200, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-C.; Zhang, J.; Hou, S. The impact of regional renewable energy development on environmental sustainability in China. Resour. Policy 2023, 80, 103245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, F.U.; Islam, M.M.; Miao, Q. Environmental sustainability via green transportation: A case of the top 10 energy transition nations. Transp. Policy 2023, 137, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwilinski, A.; Lyulyov, O.; Pimonenko, T. Reducing transport sector CO2 emissions patterns: Environmental technologies and renewable energy. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2024, 10, 100217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Jiang, J.; Hassan, S.T.; Shah, A.A. Revolution of nuclear energy efficiency, economic complexity, air transportation and industrial improvement on environmental footprint cost: A novel dynamic simulation approach. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2022, 54, 3682–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.T.; Khan, D.; Zhu, B.; Batool, B. Is public service transportation increase environmental contamination in China? The role of nuclear energy consumption and technological change. Energy 2022, 238, 121890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Adebayo, T.S.; Ibrahim, R.L.; Al-Faryan, M.A.S. Does nuclear energy consumption mitigate carbon emissions in leading countries by nuclear power consumption? Evidence from quantile causality approach. Energy Environ. 2023, 34, 2521–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addo, E.K.; Kabo-bah, A.T.; Diawuo, F.A.; Debrah, S.K. The role of nuclear energy in reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and energy security: A systematic review. Int. J. Energy Res. 2023, 2023, 8823507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, Y.; Ali, M.; Mehmood, U.; Abd Rahman, N.R. Decarbonizing Japan: The Role of Nuclear Energy and Environmental Taxation in Mitigating CO2 Emissions. Environ. Chall. 2025, 18, 101097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, M. Nuclear energy for transportation: Paths through electricity, hydrogen and liquid fuels. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2008, 50, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, G.; Flores, J.M. Reducing the CO2 emissions and the energy dependence of a large city area with zero-emission vehicles and nuclear energy. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2015, 78, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B. Does fintech promote the sustainable development of renewable energy enterprises? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 65141–65148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raihan, A.; Voumik, L.C.; Ridwan, M.; Ridzuan, A.R.; Jaaffar, A.H.; Yusoff, N.Y.M. From growth to green: Navigating the complexities of economic development, energy sources, health spending, and carbon emissions in Malaysia. Energy Rep. 2023, 10, 4318–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Yue, G.; Khan, N.U. Uncovering the impact of fintech, natural resources, green finance and green growth on environment sustainability in BRICS: An MMQR analysis. Resour. Policy 2024, 89, 104515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Seo, Y.-J.; Ha, M.-H. The role of maritime, land, and air transportation in economic growth: Panel evidence from OECD and non-OECD countries. Res. Transp. Econ. 2019, 78, 100765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, R.; Toledo, E. Environmental degradation and economic growth: Evidence for a developing country. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2017, 19, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hondroyiannis, G.; Papapetrou, E.; Tsalaporta, P. Environmental degradation and inflation in high-income countries. Econ. Change Restruct. 2025, 58, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhayere, E.; Kartal, M.T.; Adebayo, T.S.; Kavaz, D. Role of energy consumption and trade openness towards environmental sustainability in Turkey. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 21156–21168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, U.; Shafiullah, M. Financial development and governance: A panel data analysis incorporating cross-sectional dependence. Econ. Syst. 2021, 45, 100855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hafeez, M.; Ullah, S.; Yonter, I.U. Cross-sectional dependence in financial openness and its influence on renewable energy consumption in Asia. Energy Environ. 2023, 36, 0958305X231219786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menegaki, A. Ways of treatment of cross-sectional dependence in the energy-growth nexus and the X-variable growth nexus. In A Guide to Econometrics Methods for the Energy-Growth Nexus; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 161–178. [Google Scholar]
- Pesaran, M.H. General diagnostic tests for cross section dependence in panels. Cambridge Working Papers. Economics 2004, 1240, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, M. The use of ranks to avoid the assumption of normality implicit in the analysis of variance. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1937, 32, 675–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaran, M.H.; Yamagata, T. Testing slope homogeneity in large panels. J. Econom. 2008, 142, 50–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaran, M.H. A simple panel unit root test in the presence of cross-section dependence. J. Appl. Econom. 2007, 22, 265–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerlund, J. Testing for error correction in panel data. Oxf. Bull. Econ. Stat. 2007, 69, 709–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroni, P. Critical values for cointegration tests in heterogeneous panels with multiple regressors. Oxf. Bull. Econ. Stat. 1999, 61, 653–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, C. Spurious regression and residual-based tests for cointegration in panel data. J. Econom. 1999, 90, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerlund, J.; Edgerton, D.L. A simple test for cointegration in dependent panels with structural breaks. Oxf. Bull. Econ. Stat. 2008, 70, 665–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenker, R.; Bassett Jr, G. Regression quantiles. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1978, 46, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, M.; Coad, A. From Average Joe’s happiness to Miserable Jane and Cheerful John: Using quantile regressions to analyze the full subjective well-being distribution. J. Econ. Behav. Organ. 2011, 79, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, J.A.; Silva, J.S. Quantiles via moments. J. Econom. 2019, 213, 145–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoechle, D. Robust standard errors for panel regressions with cross-sectional dependence. Stata J. 2007, 7, 281–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, J.C.; Kraay, A.C. Consistent covariance matrix estimation with spatially dependent panel data. Rev. Econ. Stat. 1998, 80, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| South Africa | Russia | Ukraine | Netherlands | United Kingdom | Belgium |
| Pakistan | Mexico | Romania | France | Spain | Czechia |
| China | Bulgaria | India | Canada | Germany | |
| Armenia | Argentina | Brazil | Hungary | Sweeden | |
| Slovenia | Switzerland | United States | Finland | Slovakia |
| Variables | Codes | Operational Definition | Ref. | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental Sustainability | ENSUS | It represents environmental sustainability measured through CO2 emissions per capita | [71] | WDI |
| Transportation Index | TINDEX | It demonstrates the transportation index calculated using two indicators: air and land transport. The index is calculated through PCA | [72] | WDI |
| Renewable Energy Development | RED | It signifies renewable energy development measured by total energy production from nuclear sources in quad Btu. | [16] | EIA |
| Nuclear Energy Development | NED | It signifies nuclear energy development measured by total energy production from nuclear sources in quad Btu. | [15] | EIA |
| Transportation Index ×Renewable energy development | TINDEX × RED | Interaction term | Author’s Calculation | |
| Transportation Index × Nuclear energy development | TINDEX × NED | Interaction term | Author’s Calculation | |
| Gross Domestic Product | GDP | Gross domestic product constant to 2015 | [73] | WDI |
| Inflation | INFL | It represents the rate of inflation. | [74] | WDI |
| Trade openness | TO | It represents the trade as a percentage of GDP | [75] | WDI |
| Variable | Obs | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max | JB-Stats | Prob. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENSUS | 728 | 2.300 | 0.729 | 0.414 | 4.101 | 3.356 | 0.187 |
| TINDEX | 728 | −4.43 × 10−9 | 1.000 | −2.366 | 2.151 | 43.49 | 0.000 |
| RED | 728 | 0.140 | 0.189 | 0 | 1.044 | 2719 | 0.000 |
| NED | 728 | −1.028 | 0.701 | −3.622 | 0.927 | 53.27 | 0.000 |
| GDP | 728 | 11.588 | 0.769 | 9.167 | 13.415 | 9.369 | 0.000 |
| INFL | 728 | 0.877 | 0.311 | 0 | 2.962 | 1266 | 0.000 |
| TO | 728 | 1.846 | 0.230 | 1.296 | 2.309 | 15.28 | 0.000 |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | VIF | 1/VIF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) ENSUS | 1.000 | ||||||||
| (2) TINDEX | 0.893 | 1.000 | 3.90 | 0.256 | |||||
| (3) RED | 0.693 | 0.695 | 1.000 | 2.67 | 0.375 | ||||
| (4) NED | 0.642 | 0.682 | 0.658 | 1.000 | 2.90 | 0.344 | |||
| (5) GDP | 0.824 | 0.684 | 0.694 | 0.708 | 1.000 | 3.76 | 0.266 | ||
| (6) INFL | 0.026 | 0.062 | −0.159 | −0.217 | −0.304 | 1.000 | 1.56 | 0.641 | |
| (7) TO | −0.578 | −0.444 | −0.468 | −0.238 | −0.415 | −0.168 | 1.000 | 1.70 | 0.587 |
| Mean VIF | 2.68 | ||||||||
| Variables | Pesaran | Friedman | ||
| CD-Stats | Prob. | CD-Stats | Prob. | |
| ENSUS | 11.685 *** | 0.000 | 94.112 *** | 0.000 |
| TINDEX | 11.935 *** | 0.000 | 108.561 *** | 0.000 |
| RED | 62.332 *** | 0.000 | 459.259 *** | 0.000 |
| NED | 9.419 *** | 0.000 | 82.719 *** | 0.000 |
| GDP | 88.464 *** | 0.000 | 621.667 *** | 0.000 |
| INFL | 24.779 *** | 0.000 | 190.580 *** | 0.000 |
| TO | 37.793 *** | 0.000 | 288.294 *** | 0.000 |
| Slope homogeneity test | ||||
| Statistics | Prob. | |||
| Delta | 19.873 *** | 0.000 | ||
| Deltaadj | 23.515 *** | 0.000 | ||
| Variables | Panel Unit Root Test | |||||
| CIPS | CADF | Decision | ||||
| I(0) | I(1) | I(0) | I(1) | CIPS | CADF | |
| ENSUS | −0.809 | −4.869 *** | −0.573 | −2.642 *** | I(1) | I(1) |
| TINDEX | −2.150 * | −1.960 | −3.194 *** | I(0) | I(1) | |
| RED | −2.537 ** | −1.925 | −2.891 *** | I(0) | I(1) | |
| NED | −2.452 ** | −1.673 | −3.108 *** | I(0) | I(1) | |
| GDP | −2.699 *** | −2.482 ** | I(0) | I(0) | ||
| INFL | −3.304 *** | −2.585 *** | I(0) | I(0) | ||
| TO | −1.885 | −4.179 *** | −1.990 | −2.293 ** | I(1) | I(1) |
| Panel cointegration test, Westerlund (2007) [83] | ||||||
| Statistics | Gt | Ga | Pt | Pa | Cointegration exist | |
| Value | −3.495 *** | −17.178 *** | −11.336 | −10.584 *** | ||
| Z-value | −7.233 | −4.047 | −0.656 | −1.392 | ||
| Prob. | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.256 | 0.000 | ||
| Panel cointegration test, Westerlund & Edgerton (2008) [86] | ||||||
| Statistics | Gt | Ga | Pt | Pa | Cointegration exist | |
| Value | −1.774 | −7.031 *** | −7.290 *** | −5.314 *** | ||
| Z-value | 3.720 | 3.734 | 3.980 | 3.009 | ||
| Prob. | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.009 | ||
| Robust Prob. | 0.940 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
| Method of Movements Quantile Regression (MMQR) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Location | Scale | Quantiles | ||||||||
| 10th | 20th | 30th | 40th | 50th | 60th | 70th | 80th | 90th | |||
| DV: ENSUS | Lower Quantiles | Middle Quantiles | Upper Quantiles | ||||||||
| Direct effect model | |||||||||||
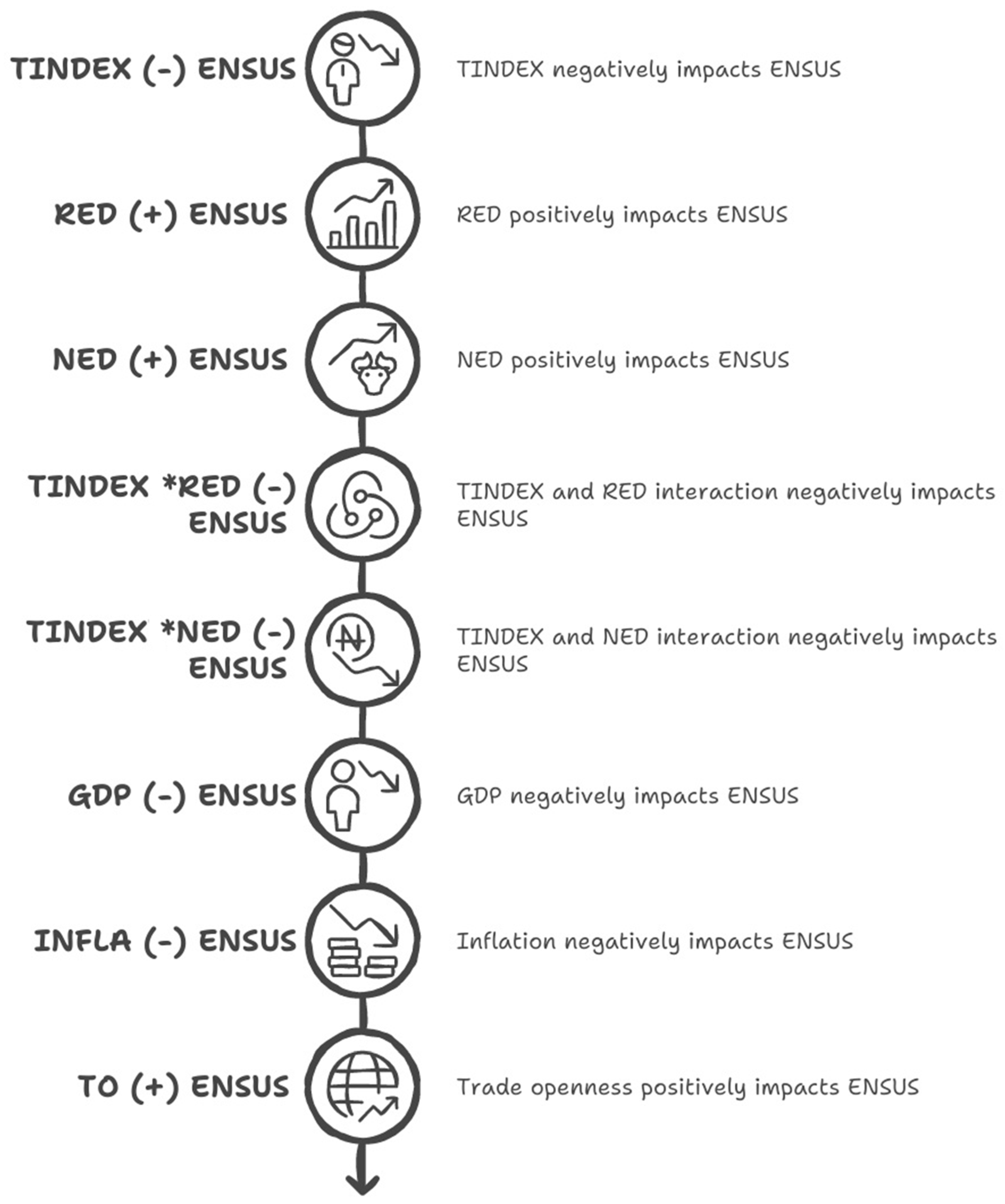
| TINDEX | 0.381 *** | −0.017 *** | 0.410 *** | 0.400 *** | 0.392 *** | 0.386 *** | 0.381 *** | 0.376 *** | 0.369 *** | 0.363 *** | 0.355 *** |
| GDP | 0.413 *** | 0.025 ** | 0.372 *** | 0.386 *** | 0.397 *** | 0.406 *** | 0.413 *** | 0.421 *** | 0.430 *** | 0.439 *** | 0.451 *** |
| INFL | 0.238 *** | −0.046 *** | 0.314 *** | 0.288 *** | 0.267 *** | 0.251 *** | 0.238 *** | 0.223 *** | 0.206 *** | 0.188 *** | 0.167 *** |
| TO | −0.469 *** | 0.068 *** | −0.581 *** | −0.543 *** | −0.511 *** | −0.488 *** | −0.468 *** | −0.446 *** | −0.422 *** | −0.396 *** | −0.365 *** |
| Combine effect Model | |||||||||||
| TINDEX | 0.423 *** | −0.029 *** | 0.473 *** | 0.453 *** | 0.440 *** | 0.432 *** | 0.423 *** | 0.416 *** | 0.404 *** | 0.392 *** | 0.375 *** |
| RED | −0.186 *** | 0.058 | −0.286 *** | −0.246 *** | −0.220 *** | −0.203 *** | −0.186 *** | −0.171 *** | −0.147 ** | −0.123 * | −0.089 |
| NED | −0.084 *** | 0.012 | −0.104 *** | −0.096 *** | −0.091 *** | −0.087 *** | −0.084 *** | −0.081 *** | −0.076 *** | −0.072 *** | −0.065 *** |
| GDP | 0.458 *** | 0.016 | 0.430 *** | 0.441 *** | 0.448 *** | 0.453 *** | 0.458 *** | 0.462 *** | 0.469 *** | 0.476 *** | 0.485 *** |
| INFL | 0.205 *** | −0.020 | 0.240 *** | 0.226 *** | 0.217 *** | 0.211 *** | 0.205 *** | 0.200 *** | 0.191 *** | 0.183 *** | 0.171 *** |
| TO | −0.466 *** | 0.103 *** | −0.643 *** | −0.572 *** | −0.526 *** | −0.495 *** | −0.466 *** | −0.440 *** | −0.397 *** | −0.354 *** | −0.294 *** |
| Moderation effect model | |||||||||||
| TINDEX | 0.271 *** | 0.012 | 0.251 *** | 0.259 *** | 0.263 *** | 0.266 *** | 0.270 *** | 0.276 *** | 0.280 *** | 0.284 *** | 0.289 *** |
| RED | −1.624 *** | 0.372 *** | −2.226 *** | −1.997 *** | −1.958 *** | −1.768 *** | −1.645 *** | −1.469 *** | −1.347 *** | −1.232 *** | −1.074 *** |
| NED | −0.080 *** | 0.012 | −1.100 *** | −0.093 *** | −0.088 *** | −0.085 *** | −0.081 *** | −0.075 *** | −0.071 *** | −0.067 *** | −0.062 ** |
| TINDEX × RED | −0.853 *** | −0.245 *** | −1.249 *** | −1.098 *** | −1.007 *** | −0.947 *** | −0.866 *** | −0.750 *** | −0.670 *** | −0.594 *** | −0.490 *** |
| TINDEX × NED | −0.069 *** | 0.024 *** | −0.108 *** | −0.094 *** | −0.085 *** | −0.079 *** | −0.071 *** | −0.059 *** | −0.051 *** | −0.044 *** | −0.034 *** |
| GDP | 0.515 *** | 0.020 | 0.482 *** | 0.494 *** | 0.502 *** | 0.507 *** | 0.513 *** | 0.523 *** | 0.530 *** | 0.536 *** | 0.545 *** |
| INFL | 0.214 *** | −0.010 | 0.229 *** | 0.223 *** | 0.220 *** | 0.217 *** | 0.214 *** | 0.210 *** | 0.206 *** | 0.203 *** | 0.199 *** |
| TO | −0.522 *** | 0.074 *** | −0.641 *** | −0.596 *** | −0.568 *** | −0.550 *** | −0.526 *** | −0.491 *** | −0.467 *** | −0.444 *** | −0.413 *** |
| DV: ENSUS | DKse | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Effect Model | Combine Effect Model | Moderation Effect Model | |
| Variables | Coef. Std. Err. | Coef. Std. Err. | Coef. Std. Err. |
| TINDEX | 0.381 *** (0.016) | 0.423 *** (0.018) | 0.271 *** (0.043) |
| RED | −0.186 * (0.096) | −1.624 *** (0.152) | |
| NED | −0.084 *** (0.023) | −0.080 *** (0.016) | |
| TINDEX × RED | −0.852 *** (0.071) | ||
| TINDEX × NED | −0.069 *** (0.020) | ||
| GDP | 0.413 *** (0.028) | 0.458 *** (0.029) | 0.515 *** (0.032) |
| INFL | 0.238 *** (0.036) | 0.205 *** (0.035) | 0.214 *** (0.033) |
| TO | −0.469 *** (0.055) | −0.466 *** (0.059) | −0.522 *** (0.068) |
| _Cons | −1.824 *** (0.416) | −2.385 *** (0.465) | −2.822 *** (0.455) |
| No of Groups. | 728 | 728 | 728 |
| No of Obs. | 26 | 26 | 26 |
| R2 | 0.9153 | 0.9195 | 0.9295 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Asif, H.M.; Gao, Y.; Zafar, M.G.R. Quantile Modelling of the Moderating Role of Renewable and Nuclear Energy in the Transportation and Environmental Sustainability Nexus. Sustainability 2025, 17, 10541. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310541
Asif HM, Gao Y, Zafar MGR. Quantile Modelling of the Moderating Role of Renewable and Nuclear Energy in the Transportation and Environmental Sustainability Nexus. Sustainability. 2025; 17(23):10541. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310541
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsif, Hafiz Muhammad, Yunfeng Gao, and Mian Gohar Rahman Zafar. 2025. "Quantile Modelling of the Moderating Role of Renewable and Nuclear Energy in the Transportation and Environmental Sustainability Nexus" Sustainability 17, no. 23: 10541. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310541
APA StyleAsif, H. M., Gao, Y., & Zafar, M. G. R. (2025). Quantile Modelling of the Moderating Role of Renewable and Nuclear Energy in the Transportation and Environmental Sustainability Nexus. Sustainability, 17(23), 10541. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310541






