Waste-Derived Porous Geopolymers for Pb(II) Removal: Kinetics, Thermodynamics, and Regeneration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of the Porous Geopolymers
2.3. Characterization of the Materials
2.4. Batch Adsorption Experiments
2.5. Reusability Studies
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Effect of H2O2 Dosage
3.2. Characterization Results
3.2.1. Mineralogic and Microstructural Analysis
3.2.2. Surface and Pore Properties
3.3. The Effects of Operational Parameters
3.3.1. Adsorbent Dosage and Initial Lead Concentration
3.3.2. Initial pH and Temperature
3.4. Isotherm Studies
3.5. Kinetic Studies
3.6. Thermodynamic Investigations
3.7. Desorption and Reuse Efficiencies
3.8. Comparative Evaluation of PGEO with Other Geopolymer-Based Adsorbents
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aigbe, U.O.; Ukhurebor, K.E.; Onyancha, R.B.; Osibote, O.A.; Darmokoesoemo, H.; Kusuma, H.S. Fly Ash-Based Adsorbent for Adsorption of Heavy Metals and Dyes from Aqueous Solution: A Review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 2751–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balali-Mood, M.; Naseri, K.; Tahergorabi, Z.; Khazdair, M.R.; Sadeghi, M. Toxic Mechanisms of Five Heavy Metals: Mercury, Lead, Chromium, Cadmium, and Arsenic. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 643972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arokiasamy, P.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Abd Rahim, S.Z.; Sadique, M.; Ming, L.Y.; Mohd Salleh, M.A.A.; Mohd Arif Zainol, M.R.R.; Ghazali, C.M.R. Diverse Material Based Geopolymer towards Heavy Metals Removal: A Review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 22, 126–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.B.; Nagpal, G.; Agrawal, S.; Rachna. Water Purification by Using Adsorbents: A Review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2018, 11, 187–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Açışlı, Ö.; Acar, İ.; Khataee, A. Preparation of a Surface Modified Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer for Removal of an Anionic Dye: Parameters and Adsorption Mechanism. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgarahy, A.M.; Maged, A.; Eloffy, M.G.; Zahran, M.; Kharbish, S.; Elwakeel, K.Z.; Bhatnagar, A. Geopolymers as Sustainable Eco-Friendly Materials: Classification, Synthesis Routes, and Applications in Wastewater Treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 324, 1383–5866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Bai, C.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, K.; Colombo, P. Preparation, Properties and Applications of Fly Ash-Based Porous Geopolymers: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 359, 132043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalheiras, J.; Novais, R.M.; Labrincha, J.A. Metakaolin/Red Mud-Derived Geopolymer Monoliths: Novel Bulk-Type Sorbents for Lead Removal from Wastewaters. Appl. Clay Sci. 2023, 232, 106770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novais, R.M.; Pullar, R.C.; Labrincha, J.A. Geopolymer Foams: An Overview of Recent Advancements. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2020, 109, 100621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Mei, M.; Wang, T.; Li, J. Potentiality of the Porous Geopolymer Sphere in Adsorption of Pb (II) from Aqueous Solutions: Behaviors and Mechanisms. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Zheng, W.; Liu, D. Development of Sulfhydryl Grafted Hierarchical Porous Geopolymer for Highly Effective Removal of Pb (II) from Water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 334, 125954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Guo, L.; Ren, D.; Duan, P. Novel Composites Based on Geopolymer for Removal of Pb(II). Mater. Lett. 2019, 239, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jin, H.; Deng, Y.; Xiao, Y. Comprehensive Utilization Status of Red Mud in China: A Critical Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 289, 125136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Wang, B.; Ai, H.; Qi, Y.; Liu, Z. A Comparative Study on Solidification/Stabilization Characteristics of Coal Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer and Portland Cement on Heavy Metals in MSWI Fly Ash. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 319, 128790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasakthi, M.; Priyadharsini, P. Novel Porous Ambient Temperature Cured Fly Ash Geopolymer for Lead Adsorption from Wastewaters. Energy Sources Part A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. 2023, 45, 11604–11618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagotia, N. Regeneration Strategies for Exhausted Adsorbents Used in Water Treatment—A Critical Review. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 69, 106560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Wang, K.; Yaseen, M.; Tong, Z.; Cui, X. Synthesis of Highly Efficient Porous Inorganic Polymer Microspheres for the Adsorptive Removal of Pb2+ from Wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 193, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korat, L.; Ducman, V. The Influence of the Stabilizing Agent SDS on Porosity Development in Alkali-Activated Fly-Ash Based Foams. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 80, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acisli, O.; Acar, I.; Khataee, A. Preparation of a Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer for Removal of a Cationic Dye: Isothermal, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 83, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, U.; Hussain, S.; Noor-ul-Amin; Imtiaz, M.; Ali Khan, S. Laterite Clay-Based Geopolymer as a Potential Adsorbent for the Heavy Metals Removal from Aqueous Solutions. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2020, 24, 874–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Bai, C.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, X.; Jia, D.; Li, H.; Colombo, P. Porous Geopolymer Composites: A Review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 150, 106629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Yan, C.; Zhou, W.; Ren, D. Development of Fly Ash and Iron Ore Tailing Based Porous Geopolymer for Removal of Cu(II) from Wastewater. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 13507–13518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Song, W.; Li, J.; Li, Q. Improved Simultaneous Adsorption of Cu(II) and Cr(VI) of Organic Modified Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 4811–4823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.M.; Gonçalves, N.P.F.; Gameiro, T.; Alves, Z.; Labrincha, J.A.; Novais, R.M. 3D-Printing Bauxite Residue/Fly Ash-Containing Geopolymers as Promising Metal Sorbents for Water Treatment. Waste Manag. 2024, 190, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellatief, M.; Elsafi, M.; Murali, G.; ElNemr, A. Comparative Evaluation of Hybrid Machine Learning Models for Predicting the Strength of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer Concrete Enhanced with Gaussian Noise Augmentation. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 111, 113302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Meng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Cheng, K.; Liang, Y.; Yang, Z. Red Mud Accommodated Mesoporous Black TiO2 Framework with Enhanced Organic Pollutant Photodegradation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 8689–8702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beleuk à Moungam, L.M.; Tchieda, K.V.; Mohamed, H.; Pecheu, N.C.; Kaze, R.C.; Kamseu, E.; Mvondo-Ze, A.D.; Tonle, I.K. Efficiency of Volcanic Ash-Based Porous Geopolymers for the Removal of Pb2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ from Aqueous Solution. Clean. Mater. 2022, 5, 100106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zboon, K.; Al-Harahsheh, M.S.; Hani, F.B. Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer for Pb Removal from Aqueous Solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 188, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, F.; Derun, E.M. Modelling and Optimization of Gold Mine Tailings Based Geopolymer by Using Response Surface Method and Its Application in Pb2+ Removal. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 117766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Xu, D.; Li, Y.; Ou, Z.; Howard, A. Synthesis of a New Porous Geopolymer from Foundry Dust to Remove Pb2+ and Ni2+ from Aqueous Solutions. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 349, 131488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Meng, Y.; Qiu, X.; Zhou, F.; Wang, H.; Zhou, S.; Yan, C. Novel Porous Phosphoric Acid-Based Geopolymer Foams for Adsorption of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Ni(II) Mixtures: Behavior and Mechanism. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 7030–7039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matalkah, F.; Khraisat, H.; Al-Momani, I. The Efficiency of Volcanic Tuff-Based Foamed Geopolymer for Heavy Metals Removal: A Parametric Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2022, 16, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, I.; Tunc, D.; Sayin, F.; Akar, S.T. Study on the Performance of Metakaolin Based Geopolymer for Mn(II) and Co(II) Removal. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 161, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harahsheh, M.S.; Al Zboon, K.; Al-Makhadmeh, L.; Hararah, M.; Mahasneh, M. Fly Ash Based Geopolymer for Heavy Metal Removal: A Case Study on Copper Removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 1669–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atiba, J.O.; Fayomi, O.S.I.; Ogbuozobe, G.O. Evaluation of Vernonia Amygdalina Extract as a Green Inhibitor for Copper Corrosion in Acidic Media: Adsorption Mechanisms, Electrochemical Behaviour, and Thermodynamic Analysis. Prog. Eng. Sci. 2025, 2, 100106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, B.S.; Kumar, P.S. Application of Adsorption Process for Effective Removal of Emerging Contaminants from Water and Wastewater. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 116995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Li, J.B.; Liu, W.W.; Miao, M.; Cheng, B.J.; Zhu, S.W. Novel Synthesis of a Versatile Magnetic Adsorbent Derived from Corncob for Dye Removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 190, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Alouani, M.; Saufi, H.; Moutaoukil, G.; Alehyen, S.; Nematollahi, B.; Belmaghraoui, W.; Taibi, M. Application of Geopolymers for Treatment of Water Contaminated with Organic and Inorganic Pollutants: State-of-the-Art Review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taki, K.; Mukherjee, S.; Patel, A.K.; Kumar, M. Reappraisal Review on Geopolymer: A New Era of Aluminosilicate Binder for Metal Immobilization. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 14, 100345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Ahmad Zaidi, F.H.; Wan Ibrahim, W.M.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Ahmad, R.; Noorlin, F.F.; Azahar, R.H. Investigating the Efficacy of Metakaolin Based Alkali Activated Materials for Efficient Removal of Nickel and Lead Ions. Mater. Res. Express 2025, 12, 036501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Ge, Y.; Wang, K.; He, Y.; Cui, X. Preparation and Characterization of Porous Metakaolin-Based Inorganic Polymer Spheres as an Adsorbent. Mater. Des. 2015, 88, 1244–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novais, R.M.; Buruberri, L.H.; Seabra, M.P.; Labrincha, J.A. Novel Porous Fly-Ash Containing Geopolymer Monoliths for Lead Adsorption from Wastewaters. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 318, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

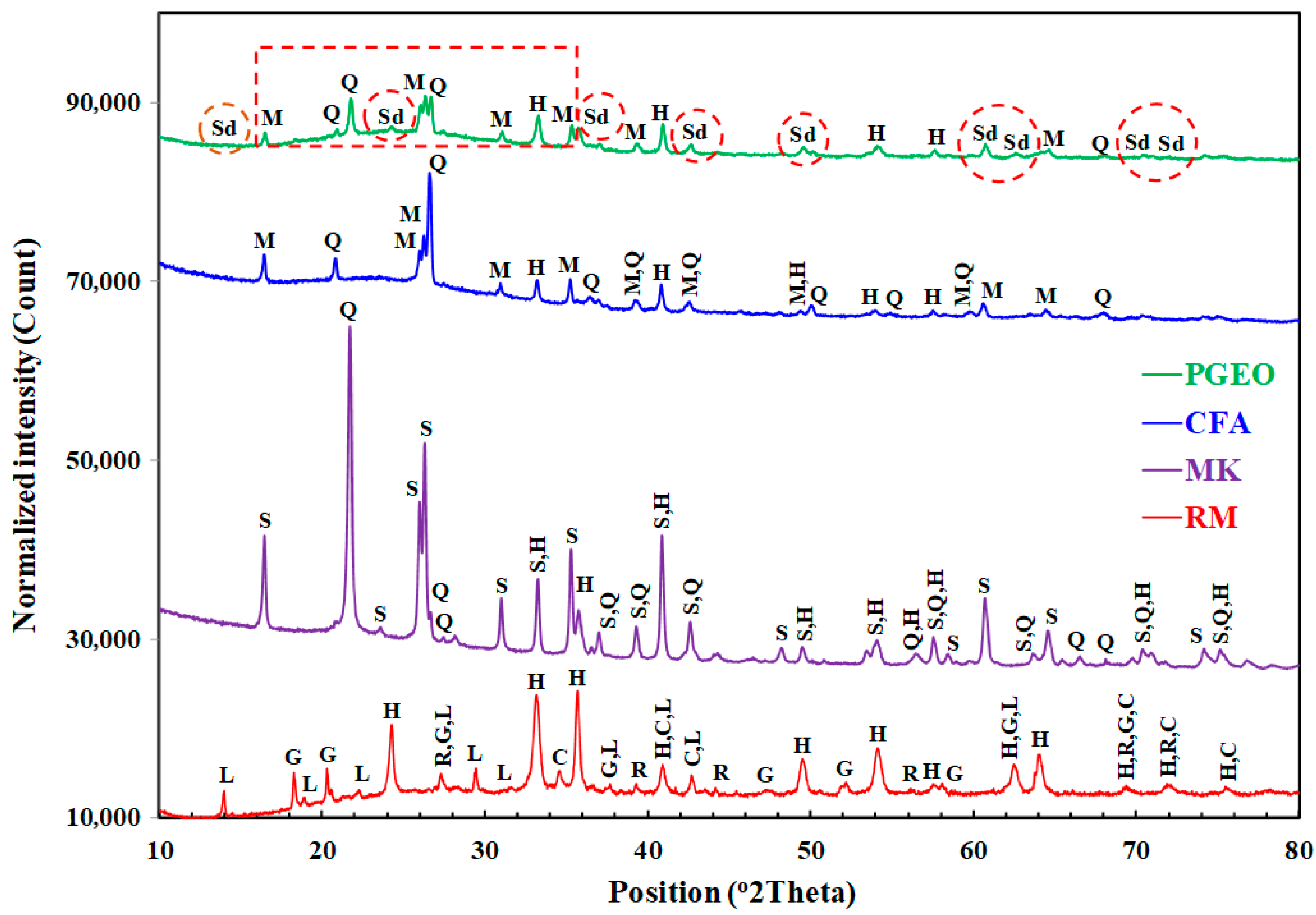
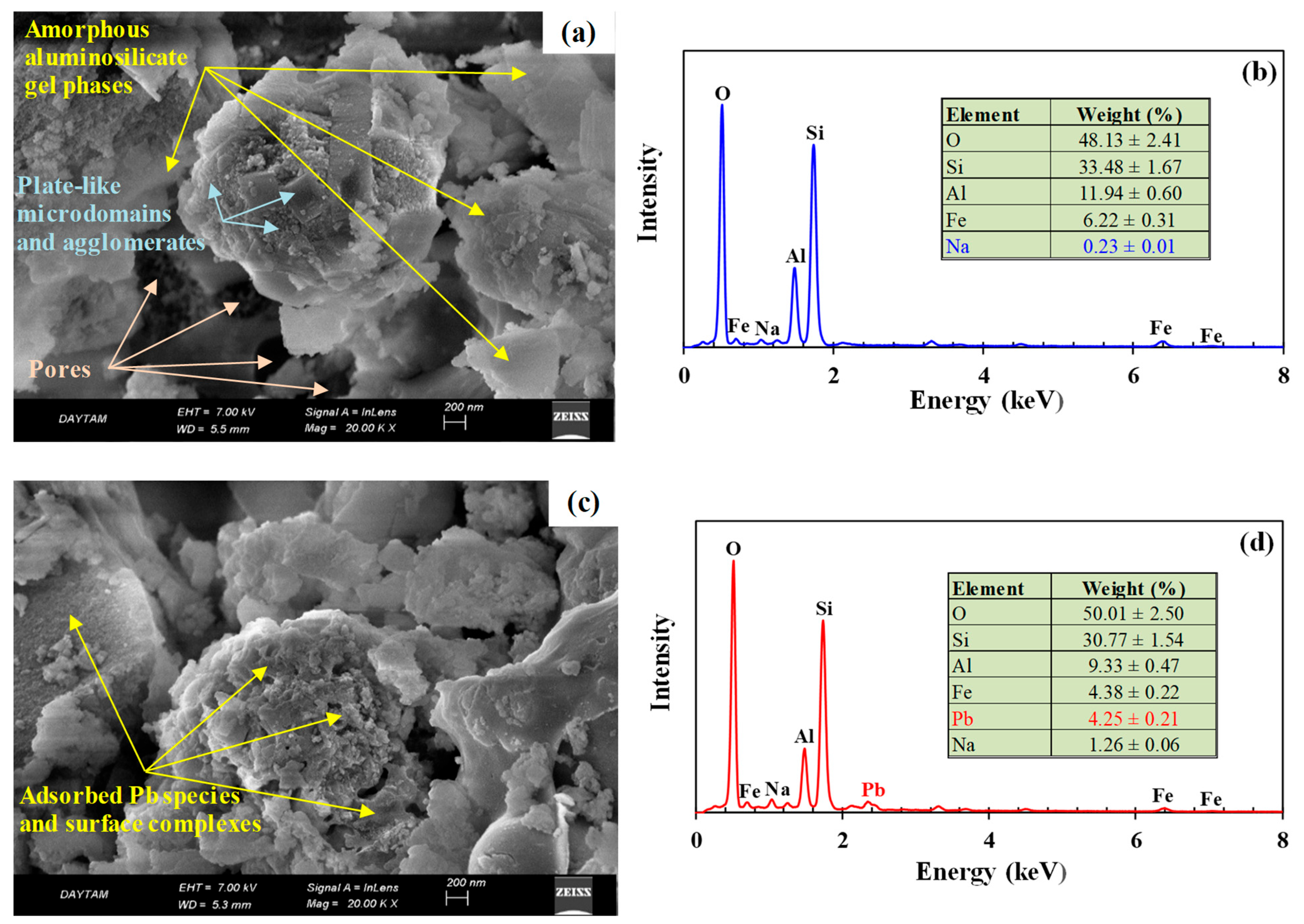


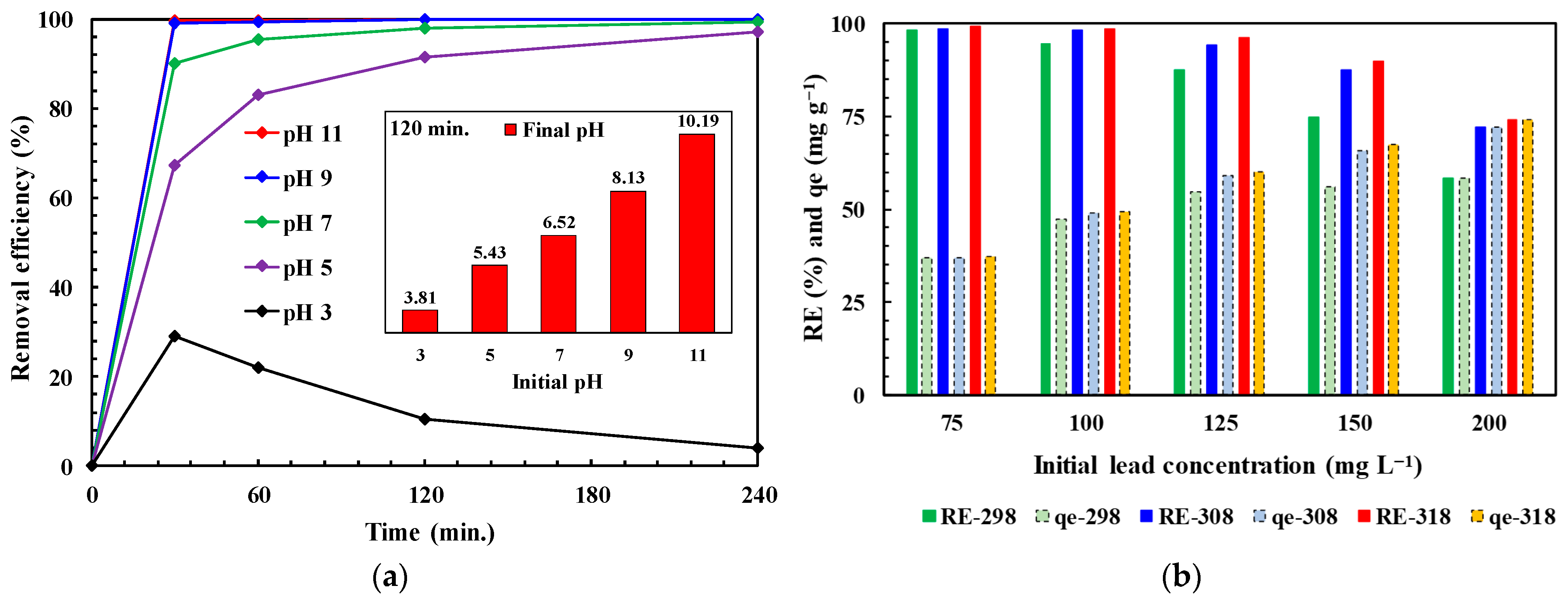
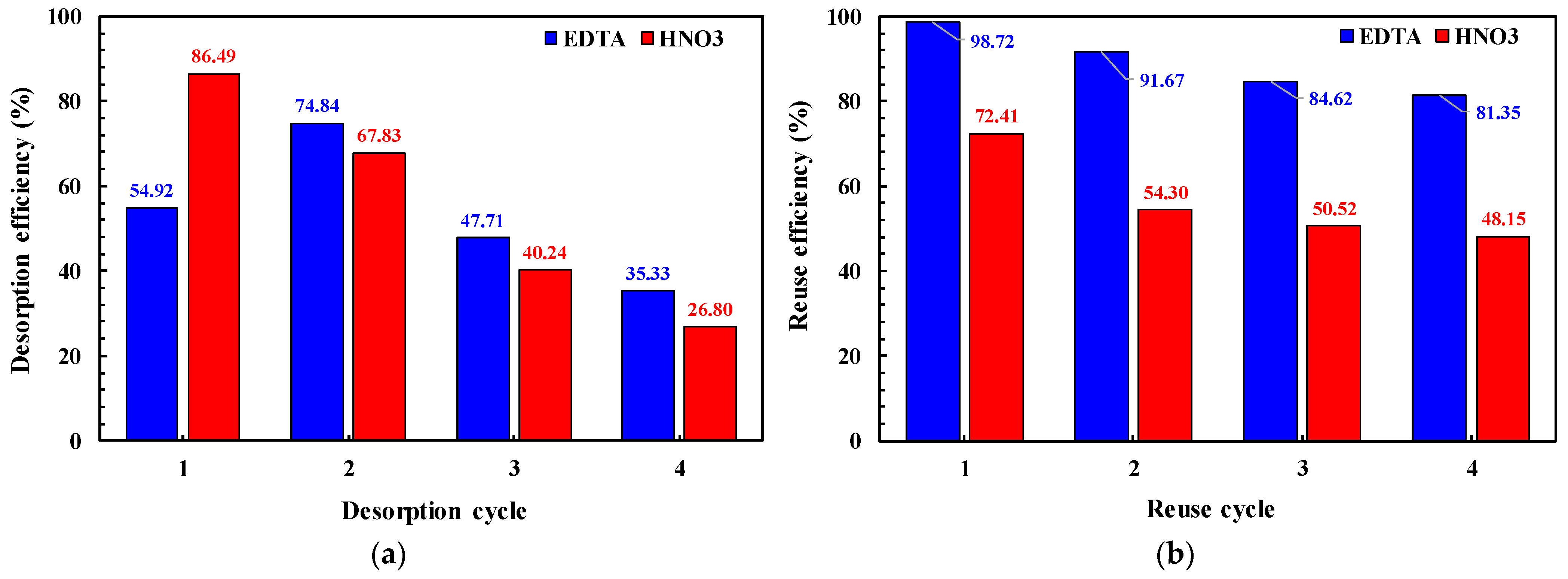
| Chemical Constituents (%) | CFA | MK | RM |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 53.4 ± 2.67 | 50.7 ± 2.54 | 15.2 ± 0.76 |
| Al2O3 | 27.2 ± 1.36 | 44.5 ± 2.23 | 22.1 ± 1.10 |
| Fe2O3 | 7.8 ± 0.39 | 2.1 ± 0.11 | 33.3 ± 1.67 |
| CaO | 1.4 ± 0.07 | 0.4 ± 0.02 | 3.6 ± 0.18 |
| MgO | 2.2 ± 0.11 | 0.2 ± 0.01 | 0.4 ± 0.02 |
| Na2O | 0.4 ± 0.02 | 0.1 ± 0.01 | 9.4 ± 0.47 |
| K2O | 4.6 ± 0.23 | 0.2 ± 0.01 | 0.7 ± 0.03 |
| TiO2 | 1.2 ± 0.06 | 1.4 ± 0.07 | 5.1 ± 0.25 |
| Loss on ignition (LOI, %) | 1.8 | 0.3 | 10.3 |
| Physical Properties | |||
| Average particle size (µm) | 34.50 | 6.51 | 0.97 |
| Specific gravity | 2.19 | 2.49 | 2.94 |
| BET surface area (m2 g−1) | 1.48 | 1.08 | 47.06 |
| Isotherm | Equation | Parameter | 298 K | 308 K | 318 K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | qe,exp (mg g−1) | 58.53 a | 71.95 a | 74.26 a | |
| qm (mg g−1) | 59.17 b | 73.53 b | 75.19 b | ||
| KL (L mg−1) | 0.7647 | 0.7273 | 0.9852 | ||
| R2 | 0.9998 | 0.9995 | 0.9995 | ||
| C0 (mg L−1) | RL | ||||
| 75 | 0.0171 | 0.0180 | 0.0134 | ||
| 100 | 0.0129 | 0.0136 | 0.0100 | ||
| 125 | 0.0104 | 0.0109 | 0.0081 | ||
| 150 | 0.0086 | 0.0091 | 0.0067 | ||
| 200 | 0.0065 | 0.0068 | 0.0050 | ||
| Freundlich | KF | 37.59 | 41.23 | 44.37 | |
| n | 8.97 | 6.56 | 6.84 | ||
| R2 | 0.9202 | 0.8941 | 0.9056 | ||
| Temkin | KT = RT/b | 5.27 | 8.20 | 8.02 | |
| aT | 1168.26 | 147.52 | 269.05 | ||
| R2 | 0.9430 | 0.9451 | 0.9552 | ||
| Kinetic Model | Equation | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order model | qe,cal (mg g−1) | 20.68 | |
| k1 (g mg−1 min−1) | 0.0264 | ||
| R2 | 0.8902 | ||
| Pseudo-second-order model | qe,exp (mg g−1) | 48.49 | |
| qe,cal (mg g−1) | 49.26 | ||
| k2 (g mg−1 min−1) | 0.0043 | ||
| h (mg g−1 min−1) | 10.36 | ||
| R2 | 0.9993 | ||
| Intraparticle diffusion model | kid (mg g−1 min−0.5) | 1.0734 | |
| C | 34.912 | ||
| R2 | 0.8037 |
| Equations Used | T (K) | ΔG° (kJ mol−1) | R2 | ΔH° (kJ mol−1) | ΔS° (kJ mol−1 K−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | −4.84 | ||||
| 308 | −7.22 | 0.9734 | 51.81 | 0.191 | |
| 318 | −8.63 |
| Geopolymer Properties | Operating Conditions | Eq. Uptake, qe (mg g−1) | k2 (g mg−1 min−1) | qt-2h (mg g−1) | Reference | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precursors/ Shape | Surface Area (m2 g−1) | Dosage (g L−1) | C0 (mg L−1) | pH | T (K) | Eq. Time (h) | ||||
| CFA, MK, and RM/ Ground | 42.05 | 2.0 | 200 | 7 | 318 | 2 | 74.26 | 0.00427 | 72.36 | This study |
| MK/Ground | NI a | NI a | 100 | 6 | RT b | 1 | 68.60 | NI a | ND c (≈69) | [40] |
| (MK, and SF) G–S composite/Crushed | 154.27 | 1.0 | 300 | 6.3 | 298 | 6 | 386.3 | 0.00022 | 352.03 | [11] |
| MK, and RM/ Parallelepiped | 28.8 | NI a | 600 | 5 | RT b | 6 | 30.70 | NI a | ND c (<30.70) | [8] |
| MK/Cube | 7.25 | 4.0 | 50 | 7 | 298 | 24 | 11.99 d | NI a | ND c (<11.99) | [31] |
| CGFA, SS, and MK/ Sphere | 9.73 | 1.5 | 90 | 5–6 | 308 | 24 | 59.31 | 0.00037 | 42.82 | [10] |
| (MK) G–A–C composite/Sphere | 230 | NI a | 300 | 5 | 298 | NI a | 142.67 | 0.0215 | 142.28 | [12] |
| MK, and BFA/ Cylindrical disk | NI a | NI a | 50 | 5 | RT b | 24 | 6.34 | NI a | ND c (<6.34) | [42] |
| MK/Sphere | 53.95 | 1.5 | 100 | 5 | NI a | 60 | 45.60 | 0.00004 | 7.85 | [41] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Acar, İ.; Aykul, S. Waste-Derived Porous Geopolymers for Pb(II) Removal: Kinetics, Thermodynamics, and Regeneration. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9940. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17229940
Acar İ, Aykul S. Waste-Derived Porous Geopolymers for Pb(II) Removal: Kinetics, Thermodynamics, and Regeneration. Sustainability. 2025; 17(22):9940. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17229940
Chicago/Turabian StyleAcar, İlker, and Serkant Aykul. 2025. "Waste-Derived Porous Geopolymers for Pb(II) Removal: Kinetics, Thermodynamics, and Regeneration" Sustainability 17, no. 22: 9940. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17229940
APA StyleAcar, İ., & Aykul, S. (2025). Waste-Derived Porous Geopolymers for Pb(II) Removal: Kinetics, Thermodynamics, and Regeneration. Sustainability, 17(22), 9940. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17229940






